Abstract
The primary challenge in Multimodal sentiment analysis (MSA) lies in developing robust joint representations that can effectively learn mutual information from diverse modalities. Previous research in this field tends to rely on feature concatenation to obtain joint representations. However, these approaches fail to fully exploit interactive patterns to ensure consistency and differentiation across different modalities. To address this limitation, we propose a novel framework for multimodal sentiment analysis, named CDML (Consistency and Difference using a Multitask Learning network). Specifically, CDML uses an attention mechanism to assign the attention weights of each modality efficiently. Adversarial training is used to obtain consistent information between modalities. Finally, the difference among the modalities is acquired by the multitask learning framework. Experiments on two benchmark MSA datasets, CMU-MOSI and CMU-MOSEI, showcase that our proposed method outperforms the seven existing approaches by at least 1.3% for Acc-2 and 1.7% for F1.
1. Introduction
With the recent surge in social media platforms, there has been an increasing focus on multimodal learning [1,2]. Multimodal data, consisting of Acoustic (Ac), Visual (Vi), and Language (La) modalities, have become prevalent in various applications. Multimodal sentiment analysis (MSA) [3,4,5,6] is an approach that leverages information from multiple modalities to enhance the prediction accuracy of emotional states. Researchers in MSA have primarily concentrated on studying intricate fusion models [7,8,9], such as tensor-based fusion [10] and attention-based fusion. However, despite the advancements made in previous studies using benchmark datasets, the fusion mechanisms employed in MSA still encounter difficulties in effectively addressing the existing modality gaps between diverse modalities. These modality gaps refer to the variances that exist among the different modalities, posing a challenge in integrating their information seamlessly for accurate sentiment prediction.
In the field of multimodal sentiment analysis, researchers have proposed various approaches to address the challenges associated with heterogeneous modalities. One such approach is the Multimodal Transformer (MulT) provided by Tsai et al. [11]. The model leverages a crossmodal attention mechanism to adapt information between different modalities. However, MulT ignores the interaction between modalities, and MulT can not obtain comprehensive joint representations. Another important aspect emphasized by Lv et al. [12] is the consideration of information exchange among all modalities for effective multimodal fusion. According to their argument, the capture of joint representations is a difficult task because of inherent differences in heterogeneity across modalities. Simply concatenating modality features to create a common representation does not fully explore the interrelationships between different modalities. On the other hand, projecting different modalities into the same representation space can achieve consistency but overlooks complementarity. In conclusion, the main challenges for multimodal sentiment analysis are capturing the joint representation and exploiting effective interactions across modalities. This involves the integration of consistency and complementarity to achieve enhanced accuracy in sentiment analysis.
To address the aforementioned challenges, we propose a novel framework for multimodal sentiment analysis called Consistency and Difference using a Multitask Learning network (CDML). CDML can integrate unimodal diversity and bimodal consistency in a unified framework. For bimodality, we put forward a Joint Representation Translator (JRTran) to integrate joint representations of Vi-La, Ac-La, and Vi-Ac. The JRTran employs cycle translation. Generators and discriminators are designed in the cycle translation for adversarial training, which enables the translated features to better approximate the source features and further improve the performance of sentiment analysis. The process of translating between a source modality and a target modality yields an intermediate representation that acquires consistent information. Additionally, the attention mechanism is introduced to effectively assign the attention weights of each modality. Based on attention weights, the features of each modality can be efficiently fused. In the meantime, the generation of redundant information and interference of nonimportant modalities can be effectively reduced. At the end of CDML, a multitask learning framework is introduced to enhance the classification performance of the model. The model can pay more attention to the differentiated representations of each unimodal itself by jointly training multimodal tasks and unimodal subtasks. Multitask learning acts as a model regularizer with the help of unimodal auxiliary tasks.
To sum up, the main novelties of this paper can be characterized as follows:
- A multimodal sentiment analysis model that operates on joint representations is introduced. This model employs an attention mechanism to effectively allocate attention weights to each modality, thereby enabling the features of each modality to be more effectively integrated.
- Adversarial training is used to ensure the consistency of the distribution between the source and translated modalities, which acquire consistent information between modalities.
- The generalization ability of the model is improved by a multitask learning framework. A single-modal label generation module is adopted to obtain single-modal sentiment labels and thus learn the differences among the modalities.
2. Related Work
2.1. Multimodal Sentiment Analysis
Multimodal fusion networks provide a distinct advantage in various applications, showcasing their superiority over unimodal approaches. They excel in tasks such as sentiment analysis [6,10,13], action recognition [14,15], and semantic segmentation [16,17,18], benefiting from the integration of multiple modalities to achieve improved performance and accuracy. Multimodal fusion is a core problem for multimodal sentiment analysis. According to the different stages in the algorithm model, existing methods can be categorized into early fusion (feature-level fusion) and late fusion (decision-level fusion) [19]. Early fusion methods are the fusion on the feature level by simple concatenation. Williams et al. [8] proposed Early Fusion LSTM (EF-LSTM), which connects feature vectors from different modalities as input and captures the long-range dependencies with LSTM. Zadeh et al. [9] proposed a memory fusion network, which stores the interaction information between modalities through gated memory units. To effectively address the complexities of multimodal relationships, Zadeh et al. [10] introduced a Tensor Fusion Network (TFN), which utilizes tensor fusion to model the intermodal dynamics, while the intramodal dynamics are captured by three modal embedding subnetworks. Furthermore, Liu et al. [20] introduced Low-Rank Multimodal Fusion (LMF), leveraging modality-specific low-rank factors to improve efficiency in the fusion process. Wang et al. [21] presented an advanced framework that utilizes an attention-based model to dynamically adapt word embeddings based on auxiliary nonverbal features such as video and audio features. Sun et al. [22] devised the Interaction Canonical Correlation Network (ICCN), which uses the outer product of feature pairs and canonical correlation to establish associations between language-based video and language-based audio.
Our work is fundamentally different from these available works. We do not use contextual information and neither focus on complex tensor fusion mechanisms. Instead, we emphasize the importance of joint representation and multitask learning.
2.2. Multitask Learning
Multitask learning [23,24,25] endeavors to enhance the performance of each task by integrating multiple tasks into one model. In multitask learning, the model can learn and perform multiple related tasks simultaneously, thus better exploring shared information and complementary features among different tasks. Compared with single-task learning, multitask learning has the following advantages: multitask learning can make full use of the relationships among tasks to obtain more information than a single task, and different and similar tasks added to the model training are similar to a model regularization to improve the robustness of the model. Furthermore, multitask learning can enhance the generalization ability and reduce the risk of model overfitting. Jiang et al. [26] introduced a multitask learning framework that exhibits the ability to dynamically adjust the weight of loss for each subtask. Given the intricate interconnection between sentiment analysis and emotion recognition tasks, Akhtar et al. [27] posited a multitask framework rooted in contextual cues. Zheng et al. [28] posited a discriminative joint multitask framework (DJMF) that concurrently achieves sentiment prediction and emotion recognition. Yu et al. [29] adopted self-supervised learning and introduced adaptive weights to balance the variability between modalities.
While previous work has focused more on adjusting the weights between multitasks, our work is designed to capture joint representations between modalities in a multitasking framework. We jointly learn unimodal and multimodal tasks with the self-supervised strategy. Our method learns similarity information from multimodal tasks and learns differentiated information from unimodal tasks.
3. Proposed Method
In this section, we explain the proposed CDML in detail. The overall architecture of the CDML is shown in Figure 1. In the following subsections, Section 3.1 presents the overall architecture of CDML. Section 3.2 and Section 3.3 describe important components of the CDML. Section 3.4 introduces the loss function.
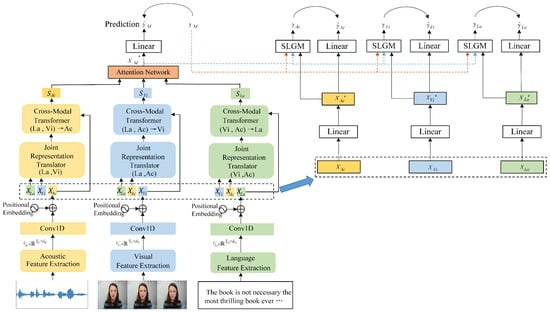
Figure 1.
Overall architecture of CDML.
3.1. Overall Architecture
The input of the CDML contains acoustic, visual, and language modalities. To handle diverse input sources, the architecture is structured into three branches with each branch dedicating to a specific input source. Firstly, after the data processing, we obtain three distinct sequences of processed modality features, which are represented as , . Subsequently, we adopt a Joint Representation Translator (JRTran) to capture joint representations of bimodality. Next, a Cross-Modality Transformer (CMTran) is adopted to investigate the synergistic relationship among modalities. Afterward, the CMTran used to process different branches generates modality reinforcement representations , , and . The attention network distinguishes the weights of different modalities. Finally, we make the prediction with the fusion feature through a fully connected layer. In the model training stage, to focus on the differences across modalities, CDML produces three additional unimodal outputs, denoted as , where . In the model reasoning phase, we solely utilize as the ultimate predictive output. The primary focus of this paper is the setting of word alignment to ensure that . Considering these sequences , , and , the primary task is to predict the sentimental intensity result .
3.2. Data Processing
This section presents the methods for extracting modality features for different modalities of the multimodal sentiment analysis task. For acoustic, we employ COVAREP [30] to extract low-level acoustic features. The dimension of the feature is 74. For visual, we employ Facet [31] to encode each video frame to signify 35 facial action units for representing basic and advanced emotions on a per-frame basis. For language, we employ Glove [32] to transform visual transcripts into language embeddings. The embedding is a 300-dimensional vector. Thus, we obtain the feature sequence , , where represents the length of the sequence, represents the dimension of each modality. Feature sequences , are passed into a one-dimensional convolutional neural network to ensure that they are of the same dimension:
For the modal sequence to incorporate temporal information, we employ positional embedding (PE) to the output of the convolutional layer. As a result, we obtain the processed feature sequences, which are denoted as , :
3.3. Modality Fusion
3.3.1. Joint Representation Translator
To effectively capture the joint representation of different modalities, we adopt a Joint Representation Translator (JRTran). This approach involves sequentially applying cyclic translations on each pairwise modality. By taking this approach, the JRTran enables the modeling of intermodal relationships and enhances the understanding of multimodal data. Figure 2 explains the process of obtaining the joint representation between modality Vi and Ac. The whole process is denoted as Joint Representation Translator (Vi, Ac). Other paired Joint Representation Translators are similar, i.e., Joint Representation Translator (La, Vi) and Joint Representation Translator (La, Ac).
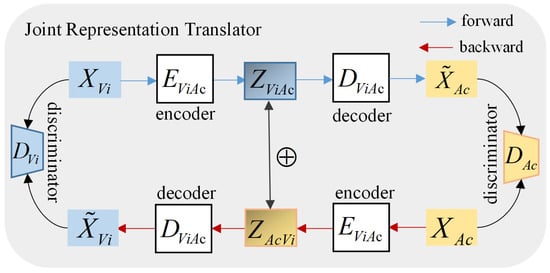
Figure 2.
The overall architecture of the Joint Representation Translator (Vi, Ac).
In the JRTran, the presence of two modalities is denoted by and , where and . We adopt the Seq2Seq model [33], which is implemented to design the encoder-decoder that serves the purpose of the JRTran . During the forward translation process, the encoder E processes the input in modality and generates the joint representation Z. Next, the decoder D translates the joint representation into the target modality :
During the backward translation process, the modality , which has been translated, is fed into the identical encoder E. Subsequently, the decoder takes the translated modality and performs a backward translation to convert it back into modality :
Especially, the encoder E employs the GRU architecture to process modality . The representation of the hidden layer’s output of the encoder can be summarized as
The forward joint representation is derived by amalgamating the previous outputs of the hidden layers. The decoder D utilizes this forward joint representation Z along with the modality as a prior condition to perform the decoding process:
We employ backward translation to ensure that the joint representation is learned to retain the maximum information of all modalities. Backward translation allows the encoder to capture the target modality. The information obtained by backward translation is combined with the source modality information. Thus, we acquire significant joint representation.
To facilitate the handling of acoustic, visual, and language modalities, there are three Joint Representation Translators:
(1) To achieve modality fusion between language and visual, we design a Joint Representation Translator composed of the encoder and the decoder . The forward translation (FT) process is shown in Equation (8) as follows, and the backward translation (BT) process is shown in Equation (9) as follows:
(2) To achieve modality fusion between language and acoustic, we design a Joint Representation Translator composed of the encoder and the decoder , as follows:
(3) To achieve modality fusion between acoustic and visual, we design a Joint Representation Translator composed of the encoder and the decoder , as follows:
Upon fusing and , we project the resultant representation to for further interaction. is utilized as the joint representation of bimodality. Eventually, we obtain three distinct joint representations: , , .
Cycle consistency [34] requires that the translated modality be close to the original modality. Inspired by GAN [35], we design a generator G: Z→X mapping the joint representation to the translated modality , and a discriminator D trying to identify whether the modality is translated or original. The discriminator D is treated as a binary classification network, where the translated modality is set with label 0 while the original modality is set with label 1. For training, the adversarial loss L is defined as
Specifically, we design 3 discriminators, , , , for visual, language, and acoustic modalities, respectively, which encourage the translated modality to be similar to the original modality . As a result, the distribution of the translated modality is indistinguishable from the distribution of the original modality. Combining adversarial loss in each JRT(La, Ac), JRT(Vi, Ac), and JRT(La, Vi), we obtain the overall adversarial loss .
3.3.2. Cross-Modality Transformer
Following the acquisition of the joint representations Z between bimodalities, we employ a Cross-Modality Transformer (CMTran) to exploit interaction among modalities. The CMTran is designed to preserve unimodal information while integrating shared information across different modalities. Additionally, the CMTran leverages joint representations to reinforce a specific modality, further improving its performance.
For the sake of brevity, we denote bimodal information as and unimodal information as . Subsequently, we explain the procedure by which the joint representation Z is transmitted to the language modality, denoted as “Cross-Modality Transformer (Vi-Ac)→La”. The diagram illustrating the architecture of CMTran (Vi-Ac)→La can be observed in Figure 3. The CMTran architecture of other branches is similar.
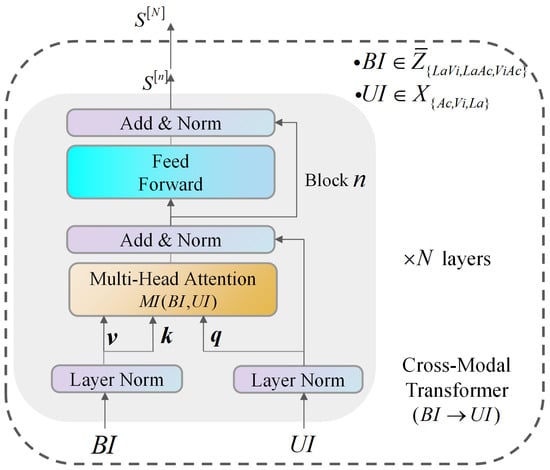
Figure 3.
The architecture of Cross-Modality Transformer (Vi-Ac)→La.
During modality interaction, we employ a multihead attention mechanism [36] with heads to promote interactions. The joint representations are converted to key/value pairs to interact with the unimodality . For the j-th head, we denote query, key, and value as , respectively, where , d represents the hidden dimension. Modality Interaction (MI) from bimodality to unimodality is computed as follows:
where and Concat represents concatenation.
In Figure 3, each CMTran is built with N layers of blocks. Each layer computes in a feed-forward manner, gradually transforming bimodal information into an unimodal representation. The layers use Layer Normalization (LN) and a Position Feedforward (PF) sublayer with a skip connection to enhance the transformation process. Throughout the computation, the output of each layer is denoted as . By stacking N layers together, the final output is represented as . The computation is computed as follows:
where N represents the number of layers in the CMTran.
Eventually, the acquired modality-reinforced representation provides a comprehensive integration of both the unique features from each modality and the common features shared among different modalities. Specifically, we obtain modality-reinforced representations , , and , which are computed as follows:
3.3.3. Attention Network
The features output from the Cross-Modality Transformer are input to the attention network, and the attention network assigns different attention weights according to different modalities. The fusion feature for sentiment task prediction is obtained by the weighted accumulation of each modality feature , which is calculated as shown below.
where is the hidden layer, and and are the weights and biases of the linear transformation matrix, respectively. are the normalized weight vectors. Then, the fused features are used as inputs to a fully connected layer to predict sentiment, which is calculated as follows:
3.3.4. Multitask Learning
The three individual unimodal tasks share modal representations with the multimodal task. To mitigate the dimensional disparity between modalities, we project them into a novel feature space and use linear regression to derive unimodal results, which are computed as follows:
where .
To facilitate the single-modal training process, we adopt a Single-modal Label Generation Module (SLGM) to acquire single-modal labels. The details of the SLGM are elaborated as follows:
The SLGM aims to obtain three single-modal sentiment labels. The SLGM shares the same input with the multimodal task. The SLGM calculates the offset based on the relative distance between modality representations and class centers, as depicted in Figure 4. Each subtask has a corresponding positive sentiment center and negative sentiment center :
where , M denotes the multimodal task; , , denotes the acoustic, visual, and language modality, respectively, N represents the number of samples involved in training, indicates the characteristic function, and refers to the global representation of the sample in the modality k.
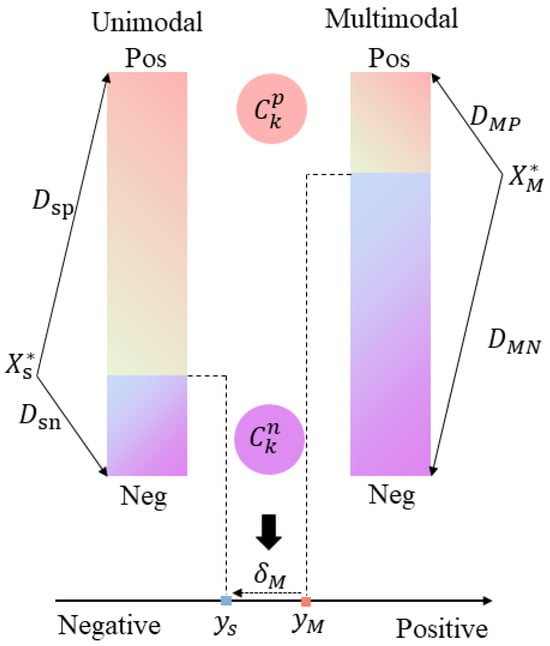
Figure 4.
Example of single-modal label generation. The single-modal label adds a negative offset to the multimodal label .
We use L2 regularization to calculate the distance between the modal representation and the positive and negative class centers:
where is the dimension of the modal representation.
Since the feature representations of different modalities are distributed in their respective feature spaces, the use of absolute distances between modal representations and positive and negative class centers lacks accuracy, so this paper uses relative distances to assess the proximity of the modal representation to the class centers of the positive and negative, which are calculated as shown below:
where is the amount of deviation to prevent the denominator from being zero.
Based on the fact that the ratio of unimodal to multimodal labels is proportional to the ratio of the corresponding unimodal to multimodal predicted values, the following equation can be derived:
We can obtain the sentiment labels of related subtasks:
where indicates the offset of the generated unimodal supervisory value to the multimodal label value.
Eventually, we jointly learn multimodal and unimodal tasks. Notably, these unimodal tasks are solely present during the training stage. Hence, we utilize as the ultimate output. For the unimodal auxiliary task, this paper uses the difference between the single-modal labels and the multimodal sentiment labels as the weight of the loss function. This allows the model to focus more on samples with large differences between multimodal labels and single-modal labels, and the loss function for the unimodal auxiliary task is shown below:
3.4. Loss Function
For the training phase, we employ the Mean Absolute Error (MAE) to measure the disparity between the ground truth and predicted output. Finally, the loss function for task prediction is defined as follows:
where represents the MAE, refers to the prediction output and y represents ground truth. The ultimate loss function is formulated by integrating task prediction loss , adversarial loss , and auxiliary task loss .
where are the trade-off hyperparameters. All parameters are optimized by minimizing . For the hyperparameters, we conduct a grid search to select the model with the optimal loss.
4. Experiment and Analysis
In this section, we assess the effectiveness of the CDML on datasets CMU-MOSI [37] and CMU-MOSEI [38]. We illustrate our experiments based on the subsequent aspects. Firstly, we furnish details regarding the datasets and baselines employed in our experiment. Then, we introduce the basic settings including experimental details and evaluation metrics. Finally, we proceed to present and engage in a comprehensive discourse on our experimental results.
4.1. Dataset
The effectiveness of the proposed model is assessed using CMU-MOSI and CMU-MOSEI datasets, recognized benchmarks in the domain of multimodal sentiment analysis. These two public datasets are also more conducive to comparative analysis with models proposed by other researchers in order to better evaluate the performance of the proposed models. Table 1 presents important statistics about these datasets. Here, we provide a succinct overview of the aforementioned datasets.

Table 1.
Statistics of CMU-MOSI and CMU-MOSEI.
CMU-MOSI: The dataset is a multimodal corpus derived from 93 opinion videos. The videos are segmented into 2199 segments, and each example is endowed with a sentiment intensity rating that ranges from −3 (indicating extremely negative emotions) to 3 (representing extremely positive emotions).
CMU-MOSEI: This dataset is based on the above dataset with improvements, which offers a larger and more diverse collection, consisting of 23,453 annotated video clips. It involves 1000 distinct speakers discussing a wide range of 250 topics. Like its predecessor, the dataset assigns sentiment scores within the range of [−3, +3] to each video clip, enabling in-depth sentiment analysis.
4.2. Baselines
To determine the effectiveness of CDML, a comprehensive comparative study was conducted. This study evaluates the CDML along with several excellent baseline models. These models can be categorized as follows:
(i) Neural Network based methods: RAEVN, MulT, MISA, MoNIG;
(ii) Translation based methods: MCTN, CMJRT;
(iii) Multitask-learning-based methods: Self-MM.
RAVEN [21]: The recurrent attended variation embedding network utilizes information in the nonverbal modality to supplement the semantic information represented by the words.
MCTN [39]: The Multimodal Cyclic Translation Network is based on Seg2seq, which requires only unimodal input data and robust multimodal joint representation learning methods in the testing phase.
MulT [11]: The Multimodal Transformer provides a mechanism for fusing cross-modal information by directly focusing on the lower-order features of other modalities, fusing multimodal information.
MISA [40]: Modality-Invariant and -Specific Representations decompose each modality into modality-invariant and -specific representations and then fuse them to predict affective states.
Self-MM [29]: The Self-Supervised Multitask Multimodal sentiment analysis network generates corresponding modal labels for each modality by self-supervision.
MoNIG [41]: The mixture of Normal-Inverse Gamma distributions algorithm ensures the reliability of the final output by capturing both modality-specific and fused uncertainties.
CMJRT [42]: The Cross-Modal Joint Representation Transformer enables effective information integration and processing across modalities by leveraging hierarchical interactions. Additionally, the passing of joint representations allows for a comprehensive understanding of the interplay between different modalities.
4.3. Basic Settings
To enable a fair comparison, the hyperparameters used in each benchmark are provided in Table 2. The performance of CDML and the compared models is evaluated based on five runs, and the average performance was reported. All experiments were carried out on an RTX-2080Ti GPU.

Table 2.
The hyperparameter settings adopted in each benchmark.
To evaluate the efficacy of the models, a range of metrics including 7-class accuracy (Acc7), binary accuracy (Acc2), F1 score, Mean Absolute Error (MAE), and correlation (Corr) are employed. Higher values for Acc7, Acc2, F1 score, and Corr signify better performance, indicating that the models have achieved more accurate and reliable results. In contrast, for MAE, lower values showcase better performance as they indicate smaller errors in predictions.
4.4. Experimental Results
Firstly, we assess the effectiveness of the CDML on the CMU-MOSI benchmark. Table 3: Perspective analysis results from multimodal data with different models on the CMU-MOSI dataset. By comparison, the CDML model demonstrates notable enhancements across all evaluation metrics when juxtaposed with the baselines. Regarding the 2 classification accuracy, Acc-2, in the sentiment task classification metric, CDML achieved 83.7%, showcasing an enhancement ranging from 1.3% to 5.7% in comparison to the baseline models. Regarding the classification metric F1, CDML improved by 1.5–7.7% compared with the baseline models. CDML reached 39.1% on the 7 classification accuracy Acc-7, an improvement of about 1.2–5.9% compared with the baseline models. Regarding the sentiment task regression metric Pearson’s coefficient Corr, the model improved by about 0.021–0.049. All of the above metrics reached the optimal level in the baseline model.

Table 3.
Comparison with baselines on CMU-MOSI benchmark. ↑ means higher is better and ↓ means lower is better.
Subsequently, we assess the performance of the CDML model on the CMU-MOSEI benchmark. Table 4 showcases the empirical findings of diverse baselines, alongside CDML, within the CMU-MOSEI dataset. Evidently, the CDML model outperforms the alternative baselines notably. The primary reasons for this superiority are as follows: The proposed attention network can focus on filtering the modal information that is more important for the sentiment prediction task, and the generative adversarial constraint is added to the loss function, which helps the features of the translation modality to better approximate the source modality features during the translation process. In addition, the multitask learning strategy is used to collaboratively train the multimodal task and each single-modal auxiliary task, which helps the model pay more attention to the differences between different modalities, and then more comprehensively handle the sentiment prediction task and improve the prediction accuracy of the model.

Table 4.
Comparison with baselines on the CMU-MOSEI benchmark.
4.5. Ablation Study
4.5.1. Modality Ablation Experiment
To show the degree of influence of different modal combinations on the final sentiment task prediction, modality ablation experiments are conducted in this section on the dataset CMU-MOSEI. Table 5 illustrates the outcomes of the experiments with separate combinations of unimodal, bimodal, and trimodal modes. It should be noted that the acoustic, visual, and language unimodality in Table 5 refer to a branch in the left half of Figure 1 (multimodal task) and the corresponding unimodal branch in the right half of Figure 1 (unimodal task). For example, the check mark “Acoustic modal” in the second row of the table means that it contains branch 1 in the left half of Figure 1 and branch 1 in the right half of Figure 1 (acoustic unimodal subtask).

Table 5.
Modality combination comparison experiment on CMU-MOSEI. ✓ means information containing this modal.
From Table 5, it is obtained that when the model contains all the branches (i.e., when acoustic, visual, and language modality tasks are used simultaneously), the model has the closest sentiment prediction performance to the labeled values and the best fusion performance. When fusing bimodal information, the performance of the experimental evaluation metrics is the next best. The performance is worse when the model contains only unimodal branches. It can be concluded that multimodal information fusion helps to capture the consistency and difference information between modalities; providing global feature information helps the accuracy of model sentiment task prediction.
4.5.2. Algorithm Ablation Experiment
Combined with the CDML proposed, this subsection compares the effects of the proposed enhancement algorithms on the model performance. The experiments are conducted in the datasets CMU-MOSI and CMU-MOSEI, respectively. Table 6 and Table 7 show the results of the algorithmic ablation experiments for CMU-MOSI and CMU-MOSEI. Comparing Table 6 and Table 7, it can be concluded that when either enhancement algorithm is missing, all performance evaluation indexes of the model are reduced to some extent. That is, the proposed enhancement algorithm can improve the performance of sentiment prediction within the model and validate the effectiveness of the enhancement algorithm.

Table 6.
Comparison of enhancement algorithm ablation experiments on CMU-MOSI. In each row, the corresponding component is progressively removed from the CDML.

Table 7.
Comparison of enhancement algorithm ablation experiments on CMU-MOSEI. In each row, the corresponding component is progressively removed from the CDML.
The experimental results of the attention-based mechanism, adversarial training, and multitask learning augmentation algorithm show significant improvement compared with CMJRT. Regarding the evaluation metrics Acc-7, Acc-2, and F1, the amalgamation of all augmentation algorithms (CDML) improved by 1.2%, 1.3%, and 1.5%, respectively, over CMJRT on the CMU-MOSI, and by 1.3%, 1.4%, and 1.7%, respectively, on the CMU-MOSEI. The experiments illustrate that the attention mechanism can focus on filtering features that are more important to the effective task. The unimodal subtask in multitask learning shares feature information with the main sentiment prediction task, which makes the model pay more attention to samples with greater variability and helps provide more comprehensive information for the model sentiment prediction task.
4.6. Case Study
The case study is to show the performance of our proposed method on the dataset CMU-MOSI in a visual form. We aim to illustrate in an intuitive way that the single-modal label generation module makes the model more attentive to the differences between unimodal and multimodal labels. In this section, a case study of the unimodal label generation module is performed, and three typical samples from the CMU-MOSI are selected for visualization, and the samples are positive, neutral, and negative. Section 4.4 describes in detail the comparison of our proposed model with the baselines. The case study of the label generation module is shown in Figure 5. The acoustic, visual, and language label values in the figure are the calculated sentiment values from the unimodal label generation module, and the raw labels are the sentiment annotated values from the multimodal dataset.
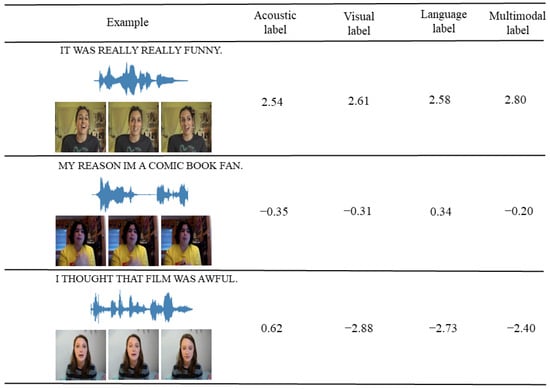
Figure 5.
Case study on CMU-MOSI.
The sentiment state in the first case tends to be consistent with that of the label generation values for each unimodal state. In the third case, the sentiment prediction of the audio modal label generation values is shifted concerning the multimodal labels. The predictions obtained from both the textual and visual modalities are negative, but the differences in the audio modality may give a small adjustment to the overall prediction, which is more comprehensive and accurate. That is, the label generation module can make the model pay more attention to the difference between the unimodal labels and the multimodal labels so that the CDML can obtain not only consistency between the modalities during the learning process but also pay more attention to the difference in the sentiment representations.
5. Conclusions
In this article, we introduced CDML, which is a framework for multimodal sentiment analysis. While current researches focus more on fusion mechanisms, our work aims to capture information about consistency and differentiation among modalities in a multitask framework. It facilitates the transfer of joint representations from bimodality to unimodality by using hierarchical interactions among modalities. First, the attention mechanism is used to efficiently assign the attention weights of each modality. Then, adversarial training is introduced to constrain the training process to optimize the ability to extract consistent information between modalities. Moreover, the difference among the modalities is acquired by the multitask learning framework. Finally, the proposed CDML outperforms the comparison model in metrics and achieves an improvement in overall performance.
In real-world situations, we sometimes encounter the problem of missing modalities, where it is unclear which modalities are missing. In the future, we plan to propose an efficient model that addresses the uncertain missing modality problem to improve robustness.
Author Contributions
Funding acquisition, C.F.; methodology, F.L.; project administration, C.F.; software, F.L.; supervision, C.F.; visualization, F.G.; writing—original draft, F.L.; writing—review and editing, C.F. and T.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Civil Aviation Thermal Hazards Prevention and Emergency Response, Civil Aviation University of China (Grant number: RZH2021-KF-08), and Safety Capacity Building Fund Project of the Civil Aviation Administration of China (Grant number: KJZ49420240071).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available at https://github.com/CMU-MultiComp-Lab/CMU-MultimodalSDK and https://aclanthology.org/P18-1208/ (accessed on 30 May 2023), reference [37] and https://aclanthology.org/P18-1208/ (accessed on 30 June 2023), reference [38].
Conflicts of Interest
The second author, Feifei Liang, is an intelligent driving software engineering developer at FAW (Nanjing) Technology Development Co., Ltd., and she declares no conflicts of interest. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Xu, P.; Zhu, X.; Clifton, D.A. Multimodal learning with transformers: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 12113–12132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahate, A.; Walambe, R.; Ramanna, S.; Kotecha, K. Multimodal co-learning: Challenges, applications with datasets, recent advances and future directions. Inf. Fusion 2022, 81, 203–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qablan, T.A.; Mohd Noor, M.H.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Khader, A.T. A survey on sentiment analysis and its applications. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 21567–21601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, A.; Adhvaryu, K.; Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Hussain, A. Multimodal sentiment analysis: A systematic review of history, datasets, multimodal fusion methods, applications, challenges and future directions. Inf. Fusion 2023, 91, 424–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Li, L.; Yang, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, H.; Qian, J. Multimodal sentiment analysis with image-text interaction network. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 3375–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Kautish, S. Multimodal sentiment analysis: A survey and comparison. In Research Anthology on Implementing Sentiment Analysis Across Multiple Disciplines; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2022; pp. 1846–1870. [Google Scholar]
- Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Howard, N.; Huang, G.B.; Hussain, A. Fusing audio, visual and textual clues for sentiment analysis from multimodal content. Neurocomputing 2016, 174, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, A.; Liang, P.P.; Poria, S.; Vij, P.; Cambria, E.; Morency, L.P. Multi-attention recurrent network for human communication comprehension. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LO, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, A.; Liang, P.P.; Mazumder, N.; Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Morency, L.P. Memory fusion network for multi-view sequential learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LO, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, A.; Chen, M.; Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Morency, L.P. Tensor fusion network for multimodal sentiment analysis. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.07250. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, Y.H.H.; Bai, S.; Liang, P.P.; Kolter, J.Z.; Morency, L.P.; Salakhutdinov, R. Multimodal transformer for unaligned multimodal language sequences. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; Volume 2019, pp. 6558–6569. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, F.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Duan, L.; Lin, G. Progressive modality reinforcement for human multimodal emotion recognition from unaligned multimodal sequences. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 2554–2562. [Google Scholar]
- Soleymani, M.; Garcia, D.; Jou, B.; Schuller, B.; Chang, S.F.; Pantic, M. A survey of multimodal sentiment analysis. Image Vis. Comput. 2017, 65, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ling, Q. Adaptive convolution for object detection. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 21, 3205–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.Y.; Gao, B.B.; Wu, J. Adaptive feeding: Achieving fast and accurate detections by adaptively combining object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3505–3513. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Lin, K.Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, W.; Qian, C.; Li, H.; Zeng, G. Bi-directional cross-modality feature propagation with separation-and-aggregation gate for RGB-D semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 561–577. [Google Scholar]
- Seichter, D.; Köhler, M.; Lewandowski, B.; Wengefeld, T.; Gross, H.M. Efficient rgb-d semantic segmentation for indoor scene analysis. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 13525–13531. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, W.; Sun, F.; Xu, T.; Rong, Y.; Huang, J. Deep multimodal fusion by channel exchanging. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 4835–4845. [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandram, D.; Taylor, G.W. Deep multimodal learning: A survey on recent advances and trends. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2017, 34, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shen, Y.; Lakshminarasimhan, V.B.; Liang, P.P.; Zadeh, A.; Morency, L.P. Efficient low-rank multimodal fusion with modality-specific factors. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.00064. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liang, P.P.; Zadeh, A.; Morency, L.P. Words can shift: Dynamically adjusting word representations using nonverbal behaviors. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 7216–7223. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Sarma, P.; Sethares, W.; Liang, Y. Learning relationships between text, audio, and video via deep canonical correlation for multimodal language analysis. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 8992–8999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q. An overview of multi-task learning. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Shi, X. A multitask co-training framework for improving speech translation by leveraging speech recognition and machine translation tasks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 8641–8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Seok, J. Multi Task Learning: A Survey and Future Directions. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC), Bali, Indonesia, 20–23 February 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 232–235. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Wei, R.; Liu, H.; Wen, J.; Tu, G.; Zheng, L.; Cambria, E. A multitask learning framework for multimodal sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), Virtual, 7–10 December 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Chauhan, D.S.; Ghosal, D.; Poria, S.; Ekbal, A.; Bhattacharyya, P. Multi-task learning for multi-modal emotion recognition and sentiment analysis. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.05812. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Gong, J.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, P. DJMF: A discriminative joint multi-task framework for multimodal sentiment analysis based on intra-and inter-task dynamics. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 242, 122728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Xu, H.; Yuan, Z.; Wu, J. Learning modality-specific representations with self-supervised multi-task learning for multimodal sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtually, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 10790–10797. [Google Scholar]
- Degottex, G.; Kane, J.; Drugman, T.; Raitio, T.; Scherer, S. COVAREP—A collaborative voice analysis repository for speech technologies. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, Italy, 4–9 May 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 960–964. [Google Scholar]
- Baltrušaitis, T.; Robinson, P.; Morency, L.P. Openface: An open source facial behavior analysis toolkit. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Placid, NY, USA, 7–10 March 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C.D. Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1532–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O.; Le, Q.V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 3104–3112. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Shao, L. Cycle-consistent deep generative hashing for cross-modal retrieval. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 1602–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, A.; Zellers, R.; Pincus, E.; Morency, L.P. Multimodal sentiment intensity analysis in videos: Facial gestures and verbal messages. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2016, 31, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, A.B.; Liang, P.P.; Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Morency, L.P. Multimodal language analysis in the wild: Cmu-mosei dataset and interpretable dynamic fusion graph. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Melbourne, Australia, 2018; pp. 2236–2246. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, H.; Liang, P.P.; Manzini, T.; Morency, L.P.; Póczos, B. Found in translation: Learning robust joint representations by cyclic translations between modalities. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 6892–6899. [Google Scholar]
- Hazarika, D.; Zimmermann, R.; Poria, S. Misa: Modality-invariant and-specific representations for multimodal sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 1122–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Han, Z.; Zhang, C.; Fu, H.; Zhou, J.T.; Hu, Q. Trustworthy multimodal regression with mixture of normal-inverse gamma distributions. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 6881–6893. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Liang, F.; Su, X.; Fang, C. CMJRT: Cross-Modal Joint Representation Transformer for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 131671–131679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).