Unsteady Multi-Element Time Series Analysis and Prediction Based on Spatial-Temporal Attention and Error Forecast Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Problem Formulation
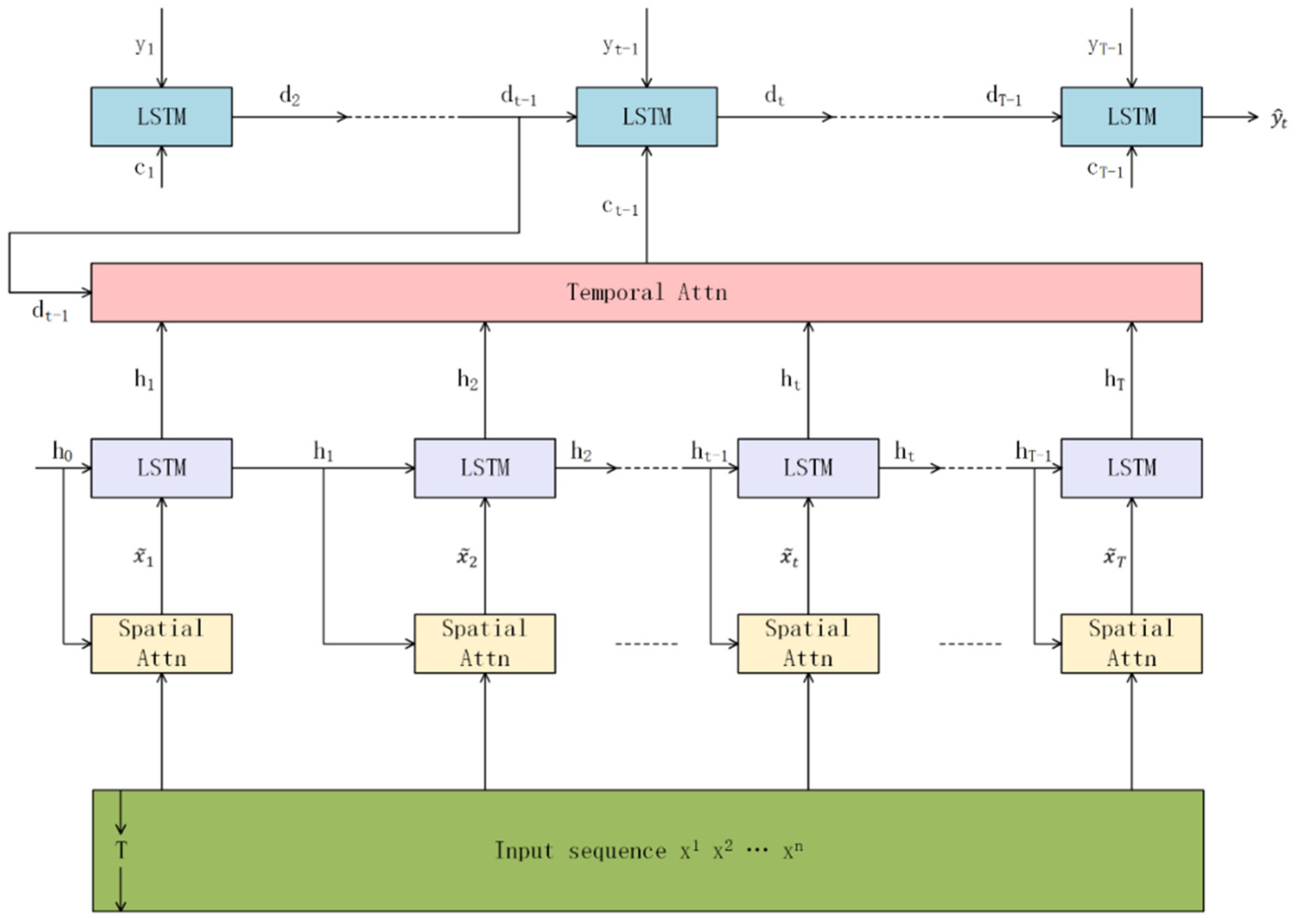
2.2. Model
2.2.1. Encoder with Multidimensional Spatial Attentions
2.2.2. Decoder with Temporal Attentions
3. Experiment and Results
3.1. Datasets
3.2. Evaluation Metrics and Determination of Parameters
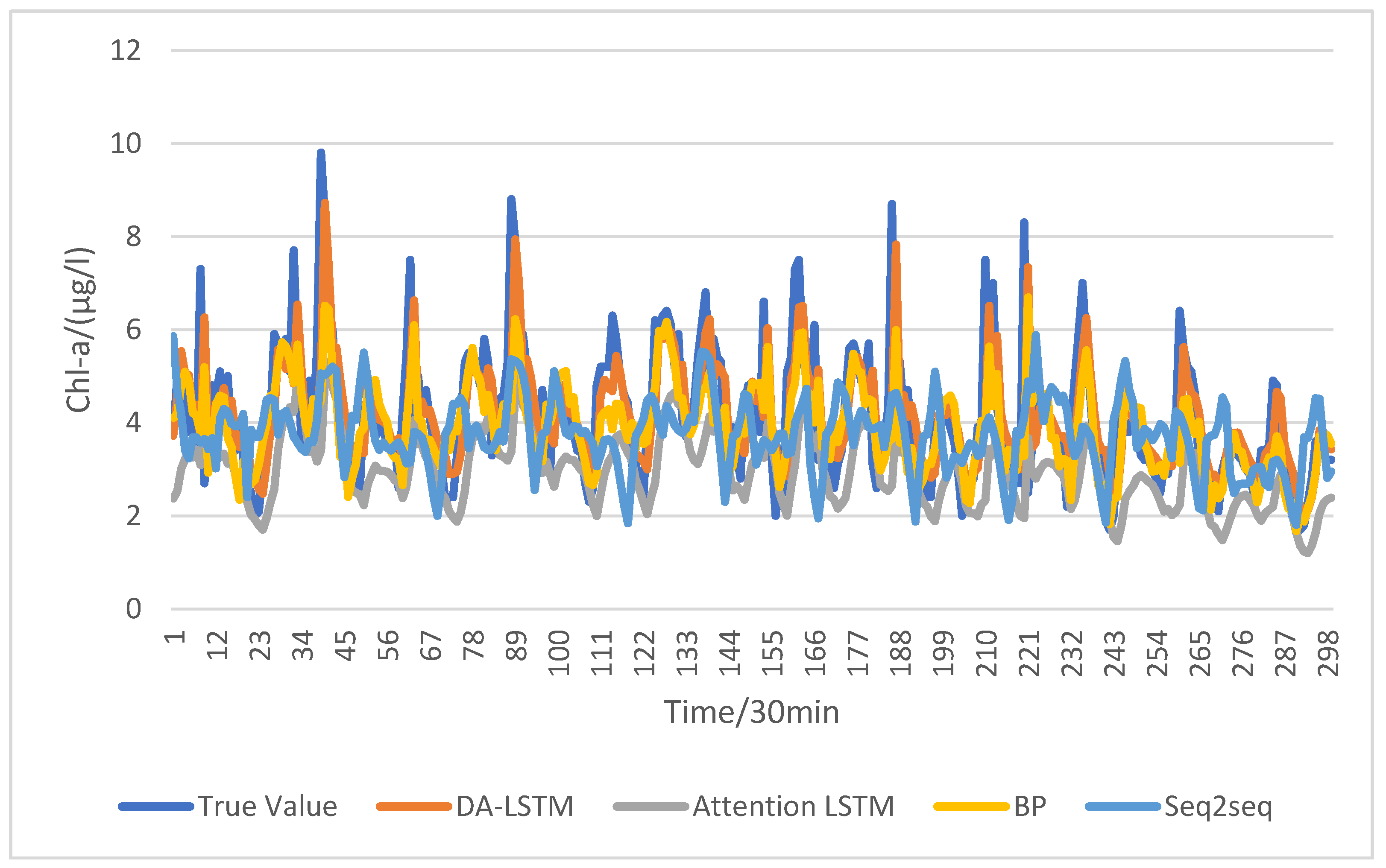
3.3. Experiment-I
- BP: Back-propagation neural network (BP) [9] is the most widely used ML method to predict harmful algal blooms. A lot of studies have shown the efficiency of it.
- Seq2seq: It uses an RNN to encode the input sequences into a feature representation and another RNN to make predictions iteratively [19].
- Attention RNN: Attention RNN is the attention-based encoder decoder network that employs an attention mechanism to select parts of hidden states across all the time steps [12].
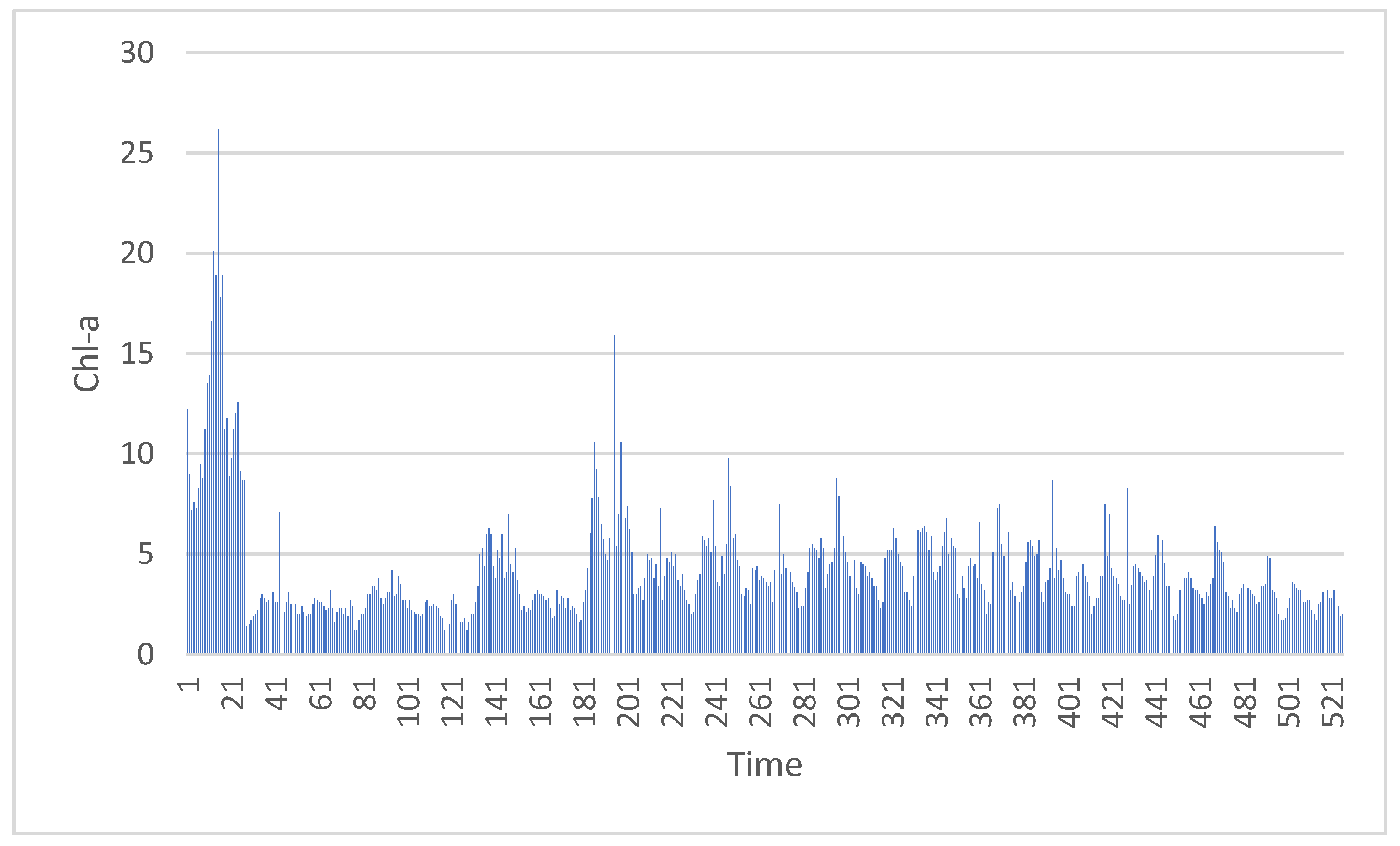
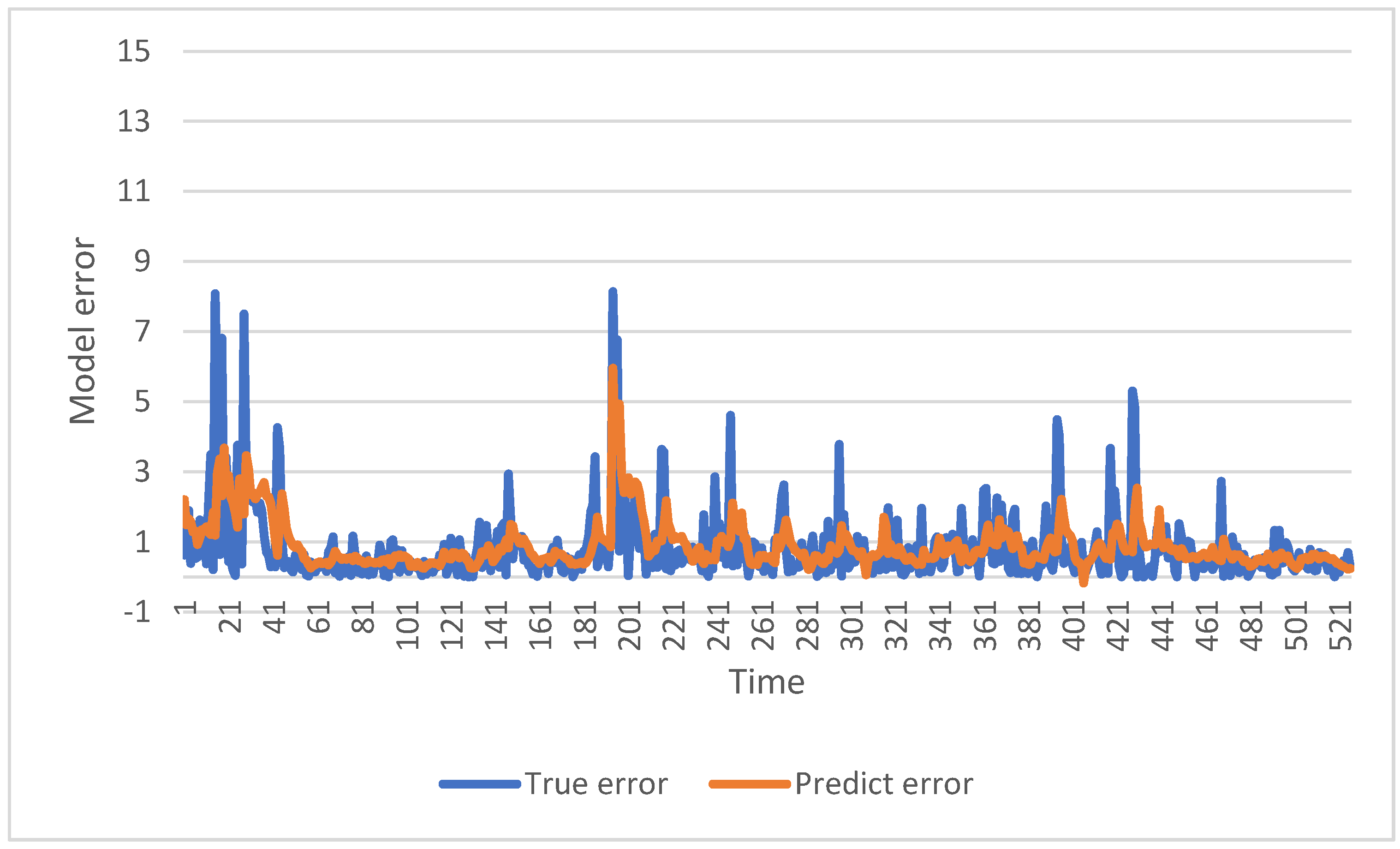
3.4. Experiment-II
4. Discussion
4.1. The Discussion of Experiment-I
4.1.1. The Influence of Temporal Attention
4.1.2. The Influence of Multidimensional Spatial Attention
4.1.3. Comparison with BP Network
4.2. The Discussion of Experiment-II
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amin, R.; Penta, B.; de Rada, S. Occurrence and Spatial Extent of HABs on the West Florida Shelf 2002–Present. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 2080–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Yao, Z. Prediction of algae growth based on BP neural networks. Computer 2005, 21, 167–169. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, R.; Lin, L. Integration of GIS and a Lagrangian Particle-Tracking Model for Harmful Algal Bloom Trajectories Prediction. Water 2019, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokaraju, B.; Durbha, S.S.; King, R.L.; Younan, N.H. A machine learning based spatio-temporal data mining approach for detection of harmful algal blooms in the Gulf of Mexico. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2011, 4, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kwon, J.; Jeong, J.G.; Lee, S.R. Red tides prediction using fuzzy inference and decision tree. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on ICT Convergence (ICTC), Jeju Island, Korea, 15–17 October 2012; pp. 493–498. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Ishizaka, J.; Goes, J.; Gomes, H.; Maúre, E.; Hayashi, M.; Katano, T.; Fujii, N.; Saitoh, K.; Mine, T. Improved MODIS-Aqua chlorophyll-a retrievals in the turbid semi-enclosed Ariake Bay, Japan. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Huang, Y.; Dickman, M.; Jayawardena, A. Neural network modelling of coastal algal blooms. Ecol. Model. 2003, 159, 179–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Sugiura, N.; Maekawa, T. Use of artificial neural network in the prediction of algal blooms. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2022–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werbos, P. Beyond Regression: New Tools for Prediction and Analysis in the Behavioral Sciences. Ph.D. Thesis, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.1078. [Google Scholar]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.0473. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, W. An Improved Approach for Text Sentiment Classification Based on a Deep Neural Network via a Sentiment Attention Mechanism. Future Internet 2019, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lu, R. A Multi-Attention Network for Aspect-Level Sentiment Analysis. Future Internet 2019, 11, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ding, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhao, K.; Chen, Y. Dynamic Group Recommendation Based on the Attention Mechanism. Future Internet 2019, 11, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Song, D.; Chen, H.; Cheng, W.; Jiang, G.; Cottrell, G. A dual-stage attention-based recurrent neural network for time series prediction. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.02971. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Ke, S.; Zhang, J.; Yi, X.; Zheng, Y. GeoMAN: Multi-level Attention Networks for Geo-sensory Time Series Prediction. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-18), Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; pp. 3428–3434. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Han, G.; Gou, Y. TD-LSTM: Temporal Dependence-Based LSTM Networks for Marine Temperature Prediction. Sensors 2018, 18, 3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O.; Le, Q. Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Heess, N.; Graves, A. Recurrent Models of Visual Attention. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 2204–2212. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]

| Dataset | Fujian Marine Forecasts Station | |
| Attributes | 8 | |
| Target Series | Chlorophyll-a | |
| Time Intervals | 30 min | |
| Time Spans | 18/01/2009–27/08/2011 | |
| Size | train | 6337 |
| test | 834 | |
| SDO | DO | Temperature | Air-Temperature | Press | Wind-Speed | Wind-Direction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCC | 0.381 | 0.438 | −0.372 | −0.365 | 0.253 | 0.177 | 0.210 |
| m = p | Prediction Intervals | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 12 | 18 | 24 | ||
| 32 | RMSE | 1.265 | 1.229 | 1.233 | 1.29 |
| MAE | 0.795 | 0.819 | 0.836 | 0.855 | |
| 64 | RMSE | 1.269 | 1.201 | 1.205 | 1.215 |
| MAE | 0.79 | 0.778 | 0.814 | 0.848 | |
| 128 | RMSE | 1.286 | 1.255 | 1.321 | 1.322 |
| MAE | 0.819 | 0.909 | 0.939 | 0.904 | |
| 256 | RMSE | 1.389 | 1.285 | 1.345 | 1.404 |
| MAE | 0.834 | 1.017 | 1.104 | 1.112 | |
| Models | Metrics | Prediction Intervals | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 12 | 18 | 24 | ||
| Seq2seq | RMSE | 1.398 | 1.411 | 1.456 | 1.499 |
| MAE | 0.922 | 0.972 | 0.993 | 1.027 | |
| Attention LSTM | RMSE | 1.29 | 1.254 | 1.305 | 1.32 |
| MAE | 0.837 | 0.855 | 0.894 | 0.902 | |
| BP | RMSE | 1.404 | 1.207 | 1.256 | 1.28 |
| MAE | 1.12 | 0.854 | 0.816 | 0.831 | |
| DA-RNN | RMSE | 1.269 | 1.201 | 1.205 | 1.215 |
| MAE | 0.79 | 0.778 | 0.814 | 0.848 | |
| SDO | DO | Temperature | Air-Temperature | Press | Wind-Speed | Wind-Direction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCC | 0.252 | 0.241 | −0.137 | −0.124 | 0.092 | 0.121 | 0.10 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Xu, L. Unsteady Multi-Element Time Series Analysis and Prediction Based on Spatial-Temporal Attention and Error Forecast Fusion. Future Internet 2020, 12, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12020034
Wang X, Xu L. Unsteady Multi-Element Time Series Analysis and Prediction Based on Spatial-Temporal Attention and Error Forecast Fusion. Future Internet. 2020; 12(2):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12020034
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaofan, and Lingyu Xu. 2020. "Unsteady Multi-Element Time Series Analysis and Prediction Based on Spatial-Temporal Attention and Error Forecast Fusion" Future Internet 12, no. 2: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12020034
APA StyleWang, X., & Xu, L. (2020). Unsteady Multi-Element Time Series Analysis and Prediction Based on Spatial-Temporal Attention and Error Forecast Fusion. Future Internet, 12(2), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12020034




