Pat-in-the-Loop: Declarative Knowledge for Controlling Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
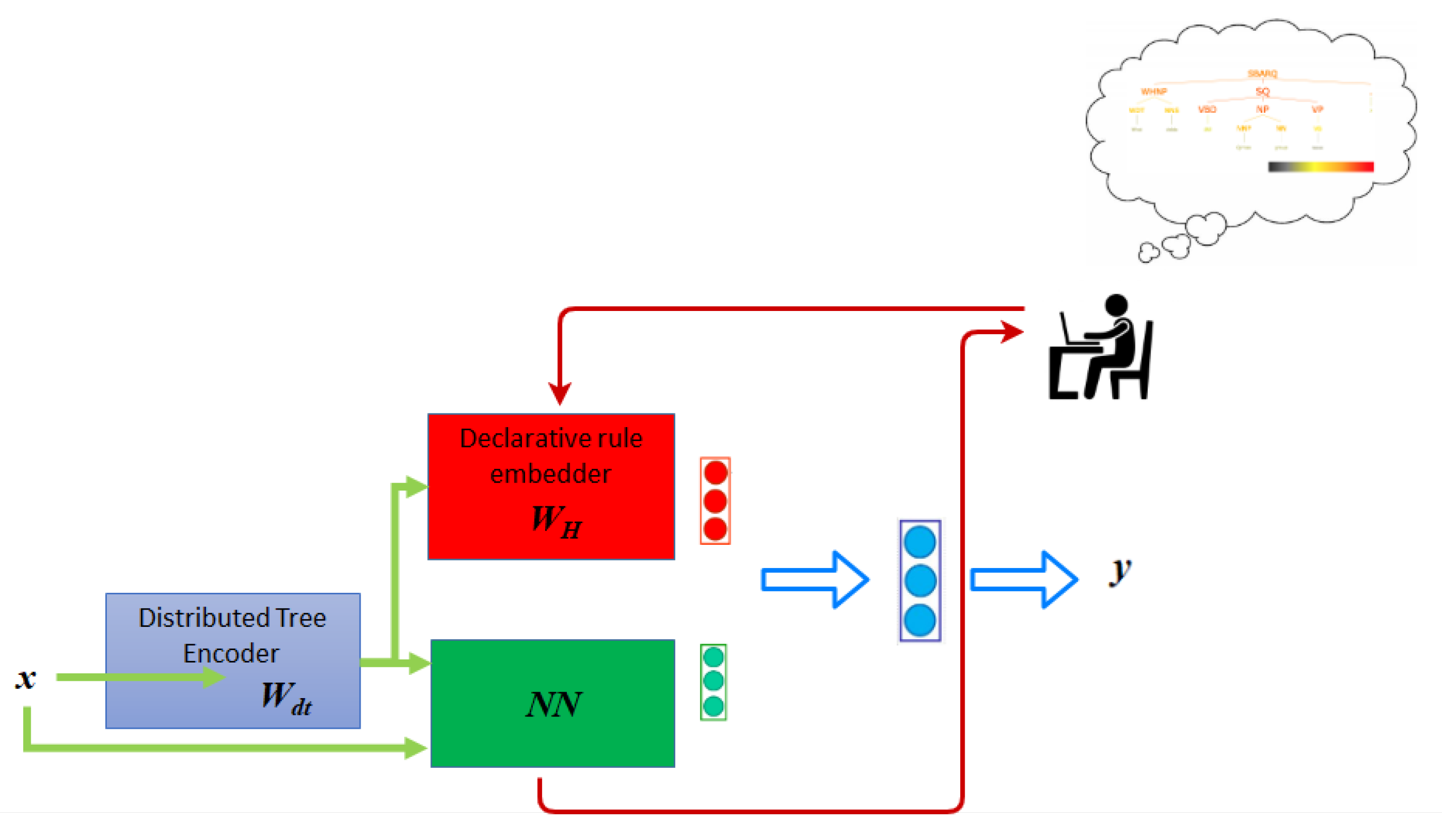
3. The Model
3.1. Preliminary Notation
3.2. Distributed Tree Encoders for Exploiting Parse Trees in Neural Networks
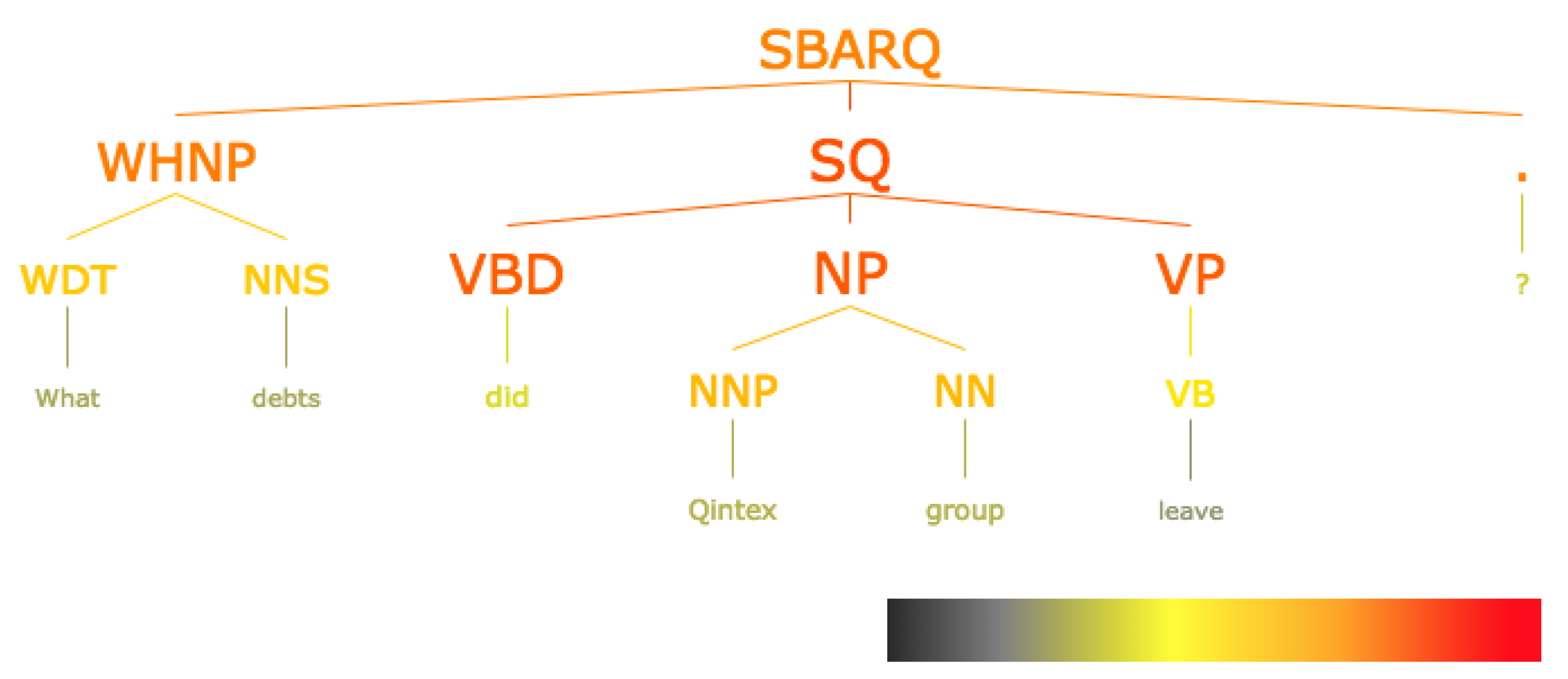
3.3. Visualizing Activation of Parse Trees
3.4. Human-in-the-Loop Layer
4. Pilot Experiment
4.1. Experimental Set-Up
4.2. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, A. Google’s Sentiment Analyzer Thinks Being Gay Is Bad. 2017. Available online: https://motherboard.vice.com/en_us/article/j5jmj8/google-artificial-intelligence-bias (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Jessup, S.; Gibson, A.; Capiola, A.; Alarcon, G.; Borders, M. Investigating the Effect of Trust Manipulations on Affect over Time in Human-Human versus Human-Robot Interactions. 2020. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339027805_Investigating_the_Effect_of_Trust_Manipulations_on_Affect_over_Time_in_Human-Human_versus_Human-Robot_Interactions (accessed on 30 November 2020). [CrossRef]
- Courtland, R. Bias detectives: The researchers striving to make algorithms fair. Nature 2018, 558, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Schiebinger, L. AI can be sexist and racist—It’s time to make it fair. Nature 2018, 559, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiritchenko, S.; Mohammad, S. Examining Gender and Race Bias in Two Hundred Sentiment Analysis Systems. In Proceedings of the Seventh Joint Conference on Lexical and Computational Semantics, *SEM@NAACL-HLT, New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–6 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Agrusti, G.; Damiani, V.; Pasquazi, D.; Carta, P. Reading mathematics at school. Inferential reasoning on the Pythagorean Theorem [Leggere la matematica a scuola. Percorsi inferenziali sul teorema di Pitagora]. Cadmo 2015, 23, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquazi, D. Capacità sensoriali e approccio intuitivo-geometrico nella preadolescenza: Un’indagine nelle scuole. Cadmo 2020, 2020, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S. Analysis of a greedy active learning strategy. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 17; Saul, L.K., Weiss, Y., Bottou, L., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 337–344. [Google Scholar]
- Sener, O.; Savarese, S. Active Learning for Convolutional Neural Networks: A Core-Set Approach. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1708.00489. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, G. Machine Learning: The View from Statistics. In Proceedings of the AAAS Annual Meeting, Houston, TX, USA, 15 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fink, M. Object Classification from a Single Example Utilizing Class Relevance Metrics. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 17; Saul, L.K., Weiss, Y., Bottou, L., Eds.; MIT Press: Vancouver, CA, USA, January 2005; pp. 449–456. [Google Scholar]
- Fei-Fei, L.; Fergus, R.; Perona, P. One-shot learning of object categories. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, Q.; Kwok, J.; Ni, L.M. Generalizing from a Few Examples: A Survey on Few-Shot Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1904.05046. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, K.R.; Myaeng, S.H.; Kim, S.B. Interpretable Word Embedding Contextualization. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Interpretable-Word-Embedding-Contextualization-Jang-Myaeng/b8661fbfe31675f1fc90896458a796aca6c763c5 (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Jacovi, A.; Shalom, O.S.; Goldberg, Y. Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks for Text Classification. pp. 56–65. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334115395_Understanding_Convolutional_Neural_Networks_for_Text_Classification (accessed on 30 November 2020). [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and Understanding Convolutional Networks. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2014; Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 818–833. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, X.; Hovy, E.; Jurafsky, D. Visualizing and Understanding Neural Models in NLP. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–17 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahng, M.; Andrews, P.Y.; Kalro, A.; Chau, D.H. ActiVis: Visual Exploration of Industry-Scale Deep Neural Network Models. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.01942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Y.; Cao, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Song, Y.; Qu, H. Understanding Hidden Memories of Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Visual Analytics Science and Technology (VAST), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 3–6 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Strobelt, H.; Gehrmann, S.; Huber, B.; Pfister, H.; Rush, A.M. LSTMVis: A Tool for Visual Analysis of Hidden State Dynamics in Recurrent Neural Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1606.07461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Vig, J. A multiscale visualization of attention in the transformer model. In Proceedings of the ACL 2019—57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, E.; Tuyls, J.; Wang, J.; Subramanian, S.; Gardner, M.; Singh, S. AllenNLP Interpret: A Framework for Explaining Predictions of NLP Models. In Proceedings of the 2019 EMNLP, Hong Kong, China, 3–7 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hoover, B.; Strobelt, H.; Gehrmann, S. exBERT: A Visual Analysis Tool to Explore Learned Representations in Transformers Models. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.05276. [Google Scholar]
- Smilkov, D.; Thorat, N.; Nicholson, C.; Reif, E.; Viégas, F.B.; Wattenberg, M. Embedding projector: Interactive visualization and interpretation of embeddings. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.05469. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, Z.S.L.; Sharpton, T.J.; Grünwald, N.J. Metacoder: An R package for visualization and manipulation of community taxonomic diversity data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.; Duffy, N. New Ranking Algorithms for Parsing and Tagging: Kernels over Discrete Structures, and the Voted Perceptron. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 6–12 July 2002; pp. 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zanzotto, F.M.; Dell’Arciprete, L. Distributed Tree Kernels. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conferenceon Machine Learning, Edinburgh, UK, 26 June–1 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support Vector Networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristianini, N.; Shawe-Taylor, J. An Introduction to Support Vector Machines and Other Kernel-Based Learning Methods; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, W.; Lindenstrauss, J. Extensions of Lipschitz mappings into a Hilbert space. Contemp. Math. 1984, 26, 189–206. [Google Scholar]
- Plate, T.A. Holographic reduced representations. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1995, 6, 623–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, S.; Binder, A.; Montavon, G.; Klauschen, F.; Müller, K.R.; Samek, W. On pixel-wise explanations for non-linear classifier decisions by layer-wise relevance propagation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Roth, D. Learning Question Classifiers. Available online: https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/C02-1150.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Bojanowski, P.; Grave, E.; Joulin, A.; Mikolov, T. Enriching Word Vectors with Subword Information. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2017, 5, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Keras Homepage. Available online: https://keras.io (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Klein, D.; Manning, C.D. Accurate Unlexicalized Parsing. Available online: https://nlp.stanford.edu/~manning/papers/unlexicalized-parsing.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Zanzotto, F.M.; Santilli, A.; Ranaldi, L.; Onorati, D.; Tommasino, P.; Fallucchi, F. KERMIT: Complementing Transformer Architectures with Encoders of Explicit Syntactic Interpretations. Available online: https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.emnlp-main.18.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Zanzotto, F.M. Viewpoint: Human-in-the-loop Artificial Intelligence. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2019, 64, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Features | ∗ | RNNvis | Emb. Proj. | LSTMVis | ActiVis | BERTviz |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interpretability & | x | x | x | x | x | |
| Explainability | ||||||
| Debbuging & | x | x | x | |||
| Improvement Models | ||||||
| Developer-friendly | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| User-friendly | x | x | x | x | ||
| Algorithm Attribution & | x | x | x | |||
| Features Visualization | ||||||
| During Training | ||||||
| After Training | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| NLP-NN system | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| Target Output o | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dim in | Represented Subtree | ... | ... | |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| (VP,[VBP,([NP,[(DT,[a])]),NN)]) | ... | ... | ||
| (SQ,[(VBD,[did]),NP,VP]) | ... | ... | ||
| (NP,[DT,(NN,[lottery])]) | ... | ... | ||
| (WHNP,[(WDT,[What]),NNS]) | ... | ... | ||
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| f-measure | ||
|---|---|---|
| micro avg | macro avg | |
| BoW | ||
| PureNN | ||
| HumNN | ||
| Class | Rule |
|---|---|
| ABBR | (NP (NP (DT) (JJ full) (NN)) (PP (IN))) |
| ABBR | (SQ (VBZ) (NP) (VP (VB stand) (PP (IN for)))) |
| ABBR | (NN abbrevation) |
| ABBR | (VP (VB mean)) |
| NUM | (WHNP (WDT What) (NNS debts)) |
| NUM | (NP (NP (NNP)(NNP)(POS))(NN)) |
| ABBR | ENTY | DESC | HUM | LOC | NUM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABBR | 6 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ENTY | 0 | 84 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| DESC | 0 | 5 | 133 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| HUM | 0 | 1 | 1 | 63 | 0 | 0 |
| LOC | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 76 | 1 |
| NUM | 0 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 102 |
| ABBR | ENTY | DESC | HUM | LOC | NUM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABBR | 7 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ENTY | 0 | 83 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| DESC | 0 | 3 | 135 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| HUM | 0 | 3 | 0 | 62 | 0 | 0 |
| LOC | 0 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 74 | 1 |
| NUM | 0 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 103 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Onorati, D.; Tommasino, P.; Ranaldi, L.; Fallucchi, F.; Zanzotto, F.M. Pat-in-the-Loop: Declarative Knowledge for Controlling Neural Networks. Future Internet 2020, 12, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12120218
Onorati D, Tommasino P, Ranaldi L, Fallucchi F, Zanzotto FM. Pat-in-the-Loop: Declarative Knowledge for Controlling Neural Networks. Future Internet. 2020; 12(12):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12120218
Chicago/Turabian StyleOnorati, Dario, Pierfrancesco Tommasino, Leonardo Ranaldi, Francesca Fallucchi, and Fabio Massimo Zanzotto. 2020. "Pat-in-the-Loop: Declarative Knowledge for Controlling Neural Networks" Future Internet 12, no. 12: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12120218
APA StyleOnorati, D., Tommasino, P., Ranaldi, L., Fallucchi, F., & Zanzotto, F. M. (2020). Pat-in-the-Loop: Declarative Knowledge for Controlling Neural Networks. Future Internet, 12(12), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12120218







