Abstract
To obtain the target webpages from many webpages, we proposed a Method for Filtering Pages by Similarity Degree based on Dynamic Programming (MFPSDDP). The method needs to use one of three same relationships proposed between two nodes, so we give the definition of the three same relationships. The biggest innovation of MFPSDDP is that it does not need to know the structures of webpages in advance. First, we address the design ideas with queue and double threads. Then, a dynamic programming algorithm for calculating the length of the longest common subsequence and a formula for calculating similarity are proposed. Further, for obtaining detailed information webpages from 200,000 webpages downloaded from the famous website “www.jd.com”, we choose the same relationship Completely Same Relationship (CSR) and set the similarity threshold to 0.2. The Recall Ratio (RR) of MFPSDDP is in the middle in the four filtering methods compared. When the number of webpages filtered is nearly 200,000, the PR of MFPSDDP is highest in the four filtering methods compared, which can reach 85.1%. The PR of MFPSDDP is 13.3 percentage points higher than the PR of a Method for Filtering Pages by Containing Strings (MFPCS).
1. Introduction
The purpose of filtering webpages is to obtain target webpages in many webpages. The filtered webpages are non-targeted webpages, pornographic webpages, etc. Filtering methods need to be proposed and developed. Some existing studies have proposed many methods to filter webpages [1,2]. Among the existing filtering methods, some are based on structure [1,2]. If programmers use filtering methods based on structure, then programmers should know part of structures of webpages in advance. The structure of webpages must be included in the target webpages, such as a specified node or a specified subtree.
Therefore, we propose a new filtering method based on structure, called a Method for Filtering Pages by Similarity Degree based on Dynamic Programming (MFPSDDP). Compared with other filtering methods based on structure, the biggest innovation of MFPSDDP is that it does not need to know the structures of webpages in advance. MFPSDDP has better accuracy and classifies webpages according to the similarity degree of the structures between two webpages. MFPSDDP considers that the webpage belongs to a specified category in a certain threshold range of similarity. We calculate the similarity of the structures between two webpages, by calculating the node proportion of the same relationship between two nodes. So we propose three definitions of the same relationships between two nodes. Programmers should choose a same relationship among the three relationships that the same relationship leads to the highest accuracy of filtering methods, without concern for the specific structure of webpages.
2. Related Works
The filtering methods of webpages proposed by existing studies can be divided into four types [3,4,5]. The first type is the filtering methods based on Uniform Resource Identifier (URI). The second type is the filtering methods based on contents [6]. The third type is the filtering methods based on structure. The fourth type is the filtering methods based on autonomous learning. Next, we assume that the target pages to be found are the detailed information webpages.
2.1. Filtering Methods Based on URI
This type of filtering method judges the classification of webpages based on the URI [7]. Suppose we want to find out the detailed information pages in many webpages. For example, the URI “https://www.jd.com/book/computer/12343.html” can be judged by “book”, “computer”, and “12343.html” in the URI. The judgement result is that the webpage is a detailed information webpage in the computer book class of the book class. These methods are simple and easy to implement, but they are not suitable for the new mechanism of URI generation and mapping in many websites. To make the URI shorter, many websites map the URI to shorter URI. According to the shorter URI, these methods cannot judge whether the webpage is a detailed information page [8].
2.2. Filtering Methods Based on Contents
This type of filtering method based on contents uses some essential contents as the filtering conditions including specific strings, link ratios of webpages, etc. [8]. For example, the classified navigation bar and the price information must appear in a detailed information page. These methods are applicable to specific websites that require programmers to have a prior understanding of the website contents [9,10].
2.3. Filtering Methods Based on Structure
This type of filtering method uses the tree structures of webpages as the filtering condition including specific tags, specific tree nodes, and specific tree structures in webpages. These methods use the Document Object Model (DOM) model to convert the HyperText Markup Language (HTML) to the eXtensible Markup Language (XML). Some studies calculate the similarity according to the node name in two trees, and give certain weight values to the nodes for the calculation according to the node layer in two trees [11,12]. Some studies traverse the XML tree to get the sequence according to Depth First Search (DFS) or Breadth First Search (BFS), and covert the similarity calculation of two trees to calculate the longest length of the common subsequence of the two sequences [13,14,15]. But many large commercial websites currently use the tags <div>, <span> and the attributes “class” of these tags to improve their development efficiency, so it is difficult to get an ideal similarity threshold.
2.4. Filtering Methods Based on Autonomous Learning
This type of method needs to get some data including the link graphs of webpages, the structure similarity of webpages, etc. These methods train by using a certain training sets of webpages, then uses some learning algorithms to cluster the webpages including K-Means, neural network, etc. [16,17,18]. These methods need not to know the structures of webpages in advance, but it usually takes a large amount of computations, and needs a certain amount of training set [19,20,21,22].
The above four types of filtering methods have been carried out by some researchers in engineering implementation and experimental analysis. In view of the above discussion, we will not consider using the filtering methods based on URI and the filtering methods based on autonomous learning. MFPSDDP proposed by us belongs to the filtering methods of based on structure. According to the tags <span> and <div>, MFPSDDP uses dynamic programming to get the length of longest common subsequence between two XML trees of two webpages, and then calculates the similarity. MFPSDDP needs not to know the structure of webpages in advance, and does not need the training dataset. MFPSDDP sets a similarity threshold, and uses the threshold as the filtering condition [23,24]. We will discuss MFPSDDP in detail, and design the software to realize this method. We make the experiment for comparing MFPSDDP with other filtering methods.
3. Algorithm of MFPSDDP
The key of MFPSDDP is to calculate the similarity between two webpages. Here we propose a method of similarity calculation based on the longest common subsequence. This method obtains the two sequence arrays by traversing two trees of two webpages. Then the dynamic programming method is used to calculate the length of the longest common subsequence. Finally, we obtain the similarity that the length of the longest common subsequence divides to the average of the two arrays.
To get the traversal sequences of two trees of two webpages, we should use the same traversal method, such as BFS. We can use recursive ideas to traverse the trees.
3.1. Same Relationship between Two Nodes
To calculate the length of the longest common subsequence, the same relationship between two nodes is used to judge. We propose the definitions of the same relationships between two nodes.
The same relationship between two nodes of webpages is different from the same relationship between two nodes of common trees. We need to consider the situation that many tags in the tree have the same names. For example, large number of <text> tags and <td> tags exist in the trees of webpages. We should distinguish the types of the same relationships. The types of the same relationships between the node and the node have three types including the Relationship with Same Name (RSN), the Relationship with Partial Same Attributes (RPSA), and the Completely Same Relationship (CSR). The definitions of the three types are followed.
Definition 1.
RSN.Ifandhave the same name, then it indicates RSN is established betweenand. RSN is denoted as,
Definition 2.
RPSA. The establishment of RPSA needs to satisfy two conditions as follows,
Condition 1:.
Condition 2:
Incondition 2,is the attribute set of,is the attribute set of. The equality relationship between the two attributes indicates that they have the same name and value. RPSA is denoted as,
In condition 2,is called the common attribute set between the two nodes.
Definition 3.
CSR.The establishment of CSR needs to satisfy two conditions as follows,
Condition 1:.
Condition 2:
CSR is denoted as,
3.2. Algorithm of MFPSDDP
We suppose that the traversal sequences of two trees of two webpages are respectively the array and the array . We regard the similarity of these two arrays as the similarity of these two webpages. The array indexes start at 0. The following Algorithm 1 is used to calculate the length of the longest common subsequence.
| Algorithm 1: caculateMaxSubSequenceLength (nodeArray1[ ],nodeArray2[ ]) Function: This algorithm calculates the length of the longest common subsequence between nodeArray1[ ] and nodeArray2[ ]. Parameter descriptions: The parameter nodeArray1 is the first node array. The parameter nodeArray2 is the second node array. Return value: This algorithm returns the length of the longest common subsequence between nodeArray1[ ] and nodeArray2[ ]. |
| /*Declare a two-dimensional array for recording the length of the longest common subsequence. The initial value of each element in the array is 0.*/ int lengthArray[ ][ ] = new int[nodeArray1.length + 1][nodeArray2.length + 1] For i = 1 to nodeArray1.length step For j = 1 to nodeArray2.length step 1 //Use CSR to judge the relationship between two nodes If nodeArray1[i] = nodeArray2[j] Then lengthArray[i][j] = lengthArray[i − 1][j − 1] + 1 Else lengthArray[i][j] = max(lengthArray[i][j − 1],lengthArray[i − 1][j]) End If End For End For return lengthArray[nodeArray1.length][nodeArray2.length] |
Algorithm 1 first declares a two-dimensional array for recording the length of the longest common subsequence. Algorithm 1 uses a double loop “” to calculate the length of the longest common subsequence according to the dynamic programming method. The same relationship of two nodes is judged by CSR.
If CSR between the node and the node is established, then the value of is , else the value of is the maximum value between and . Finally, Algorithm 1 returns the last element of the array . The last element is . When Algorithm 1 is finished, the last element of is the length of the longest common subsequence.
The calculation method of similarity is shown in Formula (1). In Formula (1), the molecule represents the length of the longest common subsequence calculated by Algorithm 1; the denominator represents the average of and . Because we adopt the average of and as the denominator, Formula (1) can prevent the phenomenon of high similarity caused by the short length of one of the two arrays.
An example of the similarity analysis between two trees showed in Figure 1. Figure 1a,b are two trees compared. The array and the array are showed in Figure 1c. The array is the node array obtained after traversing the tree showed in Figure 1a by using the traversal method BFS. The array is the node array obtained after traversing the tree showed in Figure 1b by using the traversal method BFS.
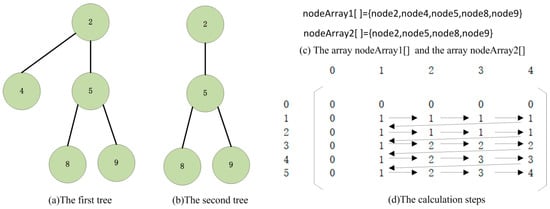
Figure 1.
An example of the similarity analysis between two trees.
According to Algorithm 1, the calculation steps are showed in Figure 1d. The values of elements in and are all 0. The length of the longest common subsequence is calculated from the steps indicated by the arrows started from .
The value of is 4, so the length of the longest common subsequence is 4. Next, we calculate the similarity according to the following steps.
3.3. Selection of Same Relationship between Two Nodes
In MFPSDDP, it is necessary to select a same relationship between RPSA and CSR. We can prepare a certain number of target webpage set and non-target webpage set in advance. The target webpage set is represented by the variable TWPS. The non-target webpage set is represented by the variable NTWPS. We can randomly select a page in TWPS as a template webpage. The template webpage is represented by the variable mwp. Next, we use MFPSDDP and Formula (1) to calculate similarity between a webpage in TWPS ∪ NTWPS and mwp. When using MFPSDDP, the same relationships RPSA and CSR are used respectively to calculate the similarity. Comparing the results of similarity calculation using the same relationships RPSA with CSR, a same relationship with better classification effect is selected.
There are three criteria for better classification effect of a same relationship, as shown below.
- It is easy to find a similarity threshold (e.g., 0.4), which can be used to distinguish the classification of webpages. If the similarity between the webpage and mwp is above the similarity threshold, the webpage is considered to belong to the type of target webpages.
- Compared with the filtering method using another relationship, the filtering method using this relationship has higher Precision Ratio (PR) value. The calculation method of PR is shown in Formula (2):where TAF is the number of target webpages obtained after filtering and AF is the number of webpages obtained after being filtered.
- Compared with the filtering method using another relationship, the filtering method using this relationship has higher Recall Ratio (RR) value. The calculation method of RR is showed in Formula (3).where RUF is the number of target webpages in the pages to be filtered. We use RR and PR as the accuracy indicators of filtering methods.
3.4. Software Design of MFPSDDP
To realize MFPSDDP, we need a buffer for dealing with webpages quickly. Furthermore, we need design the software structure. We adopt double thread to design the software.
3.4.1. Queue Storage and Buffer
The design of the queue storage and buffer is showed in Figure 2. The queue is stored in the table in the database SQL Server. The queue of pages waiting to be filtered is mapped to one table, and the filtered page queue is also mapped to another table. We use the class BasicDataSource in Spring to encapsulate the data source. The elements in these queues take the structure Key-Value. Key is set as the URI of a webpage. Value is set as the content of the webpage. The elements in the queues are all Page objects. The Page object has two properties, one is the property “url” which is the URI of a webpage, and the other is the property “pageContent” which is the content of the webpage. We assume that queues are in the buffer, and a queue has elements, and the length of a URI is bytes, and the content length of a webpage is bytes. Then the buffer size is calculated according to the following formula:
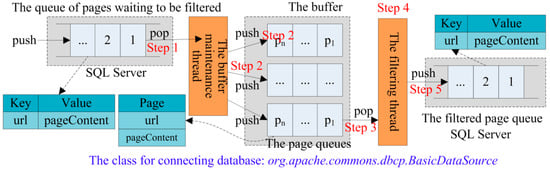
Figure 2.
The software design.
We set , , , , then the buffer size is:
So the buffer takes about 40 MB memory space, which is acceptable for the current configuration of mainstream server.
3.4.2. Double Thread Design
The software design is showed in Figure 2. We design two threads. One is the buffer maintenance thread, and the other is the filtering thread. The process of software implementation is as follows.
Step 1: The buffer maintenance thread pops 500 records of webpages from the database table each time. 500 webpages require about 20 MB memory space. After our test, the software can more stably support the transmission of 20 MB data. When the number of webpages popped is greater than 500, sometimes data transmissions are abnormal. Getting 500 webpages each time can also be supported by the select statement in SQL Server. The software reduces the number of interactions with SQL Server.
Step 2: The buffer maintenance thread pushes 100 webpages as a page queue into the buffer. The buffer maintenance thread maintains 10-page queues in the buffer. A total of 500 webpages can be pushed into the buffer divided into 5 times. The 10-page queues require about 40 MB memory space. The software can support 40 MB memory space without memory overflow.
Step 3: The filtering thread pops 100 webpages once as a queue. After our test, 100 SQL statements need to be executed to process 100 Webpages at a time, and the software can execute more stably. Moreover, one queue is processed each time. Considering that insert statements for database operations are slower than select statements, the software can use five filtering threads to parallel process 5 queues in the buffer.
Step 4: The filtering thread filters the 100 webpages once. The filtering thread uses Algorithm 1 and Formula (1) to calculate the similarity between the webpage to be filtered and the template webpage. The filtering thread determines whether the webpage to be filtered belongs to the type of target webpages according to the similarity threshold in the software configuration.
Step 5: After finishing the filtering operation, the filtering thread pushes once the target webpages in 100 webpages to be filtered into the filtered page queue in SQL Server.
According to the design ideas discussed above, the filtering thread is developed and implemented by Java. Through our experimental analysis, the average processing time of the filtering thread for every 1000 webpages takes only 19.7 s. The filtering thread takes only about 1.1 h for processing 200,000 webpages downloaded from “www.jd.com”. The design ideas of the two threads in Spring’s container are showed in Figure 3.
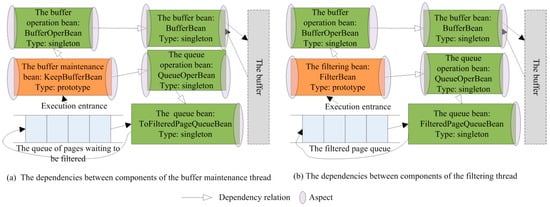
Figure 3.
The Spring’s AOP idea and Spring’s IoC idea in the two threads.
The Spring’s AOP and Spring’s IoC ideas are adopted as shown in Figure 3. Figure 3a is the design of the buffer maintenance thread. Figure 3b is the design of the filtering thread. The Spring’s container supports asynchronous task executor, so the buffer maintenance thread and the filtering thread may not affect each other. The two threads are executed in parallel. The buffer maintenance thread starts up first than the filtering thread.
Take Figure 3a as an example, we describe the dependencies between components. The buffer maintenance bean is the execution entrance of the buffer maintenance thread. We adopt the design idea of Data Access Object (DAO). DAO is embodied in that the operation beans only implement the operation methods, and the data operation is implemented by calling specific entity beans. The buffer maintenance bean depends on the buffer operation bean and the queue operation bean. The buffer operation bean depends on the buffer bean. The queue operation bean depends on the queue bean. The buffer bean encapsulates the buffer. The queue bean encapsulates the queue in SQL Server. Round the methods in each bean, some advices can be carried out including log record, efficiency analysis, etc.
4. Experimental Analysis
The experimental purpose is finding out the detailed information pages in many webpages downloaded from the famous website “www.jd.com”. In advance, we prepared 1000 detailed information pages as TWPS, 1000 non-detailed information webpages as NTWPS. We use these test webpages to choose a same relationship between RPSA and CSR, find out a similarity threshold.
4.1. Selection of Relationships and Determination of Similarity Threshold
We use Algorithm 1 and Formula (1) to calculate the similarity between mwp and the webpages in the set TWPS ∪ NTWPS. The URL of mwp is “https://item.jd.com/6813556.html”.
The same relationship RPSA used by us is as follows,
The above same relationship RPSA indicates that these attributes must be equal between mwp and the webpages in the set TWPS ∪ NTWPS including the attribute class of the tag <div>, the attribute id of the tag <div>, the attribute class of the tag <span>, the attribute id of the tag <span>.
The same relationship CSR used by us is as follows,
The results of similarity calculation are shown in Figure 4. When RPSA is used, we create a scatter plot of similarity between the template webpage mwp and the webpages in TWPS, as showed in Figure 4a; we make a scatter plot of similarity between mwp and the webpages in NTWPS, as showed in Figure 4b. When CSR is used, we create two scatter plots of similarity between mwp and the webpages in TWPS, as showed in Figure 4c,d.
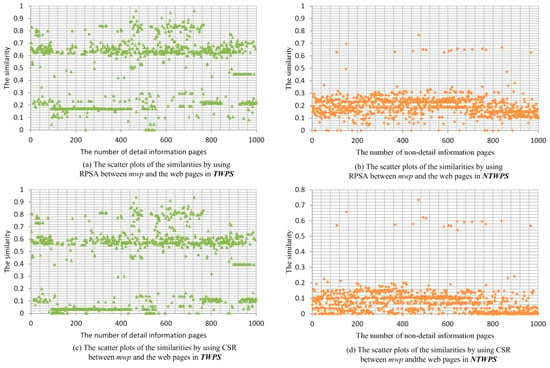
Figure 4.
The scatter plots of the similarities.
From Figure 4a,b, we can see the effect of classification. We can choose the similarity threshold 0.4 when using the relationship RPSA. Similarly, we can choose the similarity threshold 0.2 when using the relationship CSR. Why is the similarity threshold using the relationship CSR lower? Because the conditions of CSR are more stringent, the similarity threshold is lower.
Next, we calculate PRs and RRs according to Formulas (2) and (3), and we can get the results as showed in Table 1.

Table 1.
The RRs and PRs when we use these test webpages.
According to the calculation results in Table 1, both RR and PR using CSR are higher than using RPSA, so we choose CSR and set the similarity threshold to 0.2.
4.2. Comparison with Other Methods
We compare MFPSDDP with three methods including a Method for Filtering Pages by Containing Strings (MFPCS), a Method for Filtering Pages by Containing Tags and Attributes (MFPCTA), a Method for Filtering Pages by Link Ratio (MFPLR).
MFPCS uses string matching to obtain target webpages. MFPCTA traverses the trees of webpages to find a matching tag and the matching attributes of the tag. Link ratio is the ratio of the number of link nodes to the number of all nodes in the tree of a webpage. MFPLR needs to set the most important parameter, which is link ratio. The existing research work mostly set link ratio to 0.25. If the link ratio of a webpage less than 0.25, then we judge the webpage is a detailed information page. The main configurations of four methods are showed in Table 2.

Table 2.
The main configuration of four methods.
We compare MFPSDDP with three other methods by RR and PR. From the experimental results in Figure 5, the RRs and PRs of MFPSDDP can reach more than 70%. The RRs of MFPSDDP show a monotonous rising trend. When the number of webpages filtered is nearly 200,000, the RR of MFPSDDP reaches 92.2%, the PR of MFPSDDP reaches 85.1%.
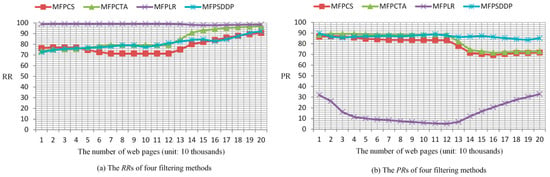
Figure 5.
The experimental results of the accuracies of four filtering methods.
As the number of webpages filtered increases, the RRs of MFPCTA are on the rise. The RR of MFPCTA reaches 96.8% when the number of webpages filtered is nearly 200,000. But the overall PRs of MFPCTA decrease with the increase of the number of webpages, at a minimum of 72%.
The RRs of MFPLR are relatively stable, which have been over 98%, but the PRs of MFPLR are relatively low, and the highest PR of MFPLR is only 32.9%.
When the number of webpages filtered is nearly 200,000, the RRs and PRs of four filtering methods are showed in Table 3. The RR of MFPLR is highest, is 98.5%. But the PR of MFPLR is lowest, only 32.9%. The PR of MFPSDDP is the highest, 85.1%.

Table 3.
The RRs and PRs of four methods when the number of webpages filtered is nearly 200,000.
According to the above analysis, the PR of MFPSDDP is highest in the four filtering methods, and the RR of MFPSDDP is middle in the four filtering methods. In the four filtering methods, MFPLR and MFPSDDP need not to know the structures of webpages in advance, but MFPCS and MFPCTA need to know the structures of webpages in advance.
In addition, we downloaded 200,000 webpages from the famous websites “www.taobao.com”. We still set the similarity threshold to 0.2, and use the webpage “https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?id=561653265544“ as the template page. After our experiments, when the number of webpages filtered is nearly 200,000, the RR of MFPSDDP is 91.6%, the PR of MFPSDDP is 85.7%. These show that MFPSDDP is suitable for large commercial websites with modular development. MFPSDDP can filter out the target webpages with lots of tag <div> and <span>.
5. Conclusions
Based on three same relationships proposed between two nodes, we give the algorithm of MFPSDDP. We use 200,000 webpages downloaded from the famous website “www.jd.com” as experimental data. Through experiments, we choose the same relationship “” and set the similarity threshold to 0.2. The RR of MFPSDDP is middle in the four filtering methods compared. When the number of webpages filtered is nearly 200,000, the PR of MFPSDDP is highest in the four filtering methods compared, can reach 85.1%. The PR of MFPSDDP is 13.3 percentage points higher than the PR of MFPCS. MFPSDDP need not to know the structures of the webpages in advance. MFPSDDP is realized by the software designed by us.
The following study will continue to be carried out in the following stages.
- We will continue to find out some filtering methods with the highly RR and the highly PR by using Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms, such as deep neural networks. We can use thousands of known pages as a training set, get the feature of the training set, and then filter the webpages automatically.
- We continue to improve MFPSDDP. The improved method is to increase the number of template pages, and take the average similarity of multiple template webpages and filtered webpages as the similarity of filtered webpages, so we can get higher RR and PR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.D.; methodology, Z.D.; software, Z.D.; validation, T.H.; formal analysis, T.H.; investigation, Z.D.; resources, Z.D.; data curation, Z.D.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.D.; writing—review and editing, T.H.; project administration, Z.D.; funding acquisition, Z.D.
Funding
This research was funded by “the National Key Technology Support Program of China, grant number 2012BAH09B02”and “the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, grant number 2017JJ5064”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Díaz-Manríquez, A.; Rios, A.B.; Barron-Zambrano, J.H.; Guerrero, T.Y.; Elizondo, J.C. An Automatic Document Classifier System Based on Genetic Algorithm and Taxonomy. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 21552–21559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, V.K.; Kumar, N. An efficient scheme for automatic web pages categorization using the support vector machine. New Rev. Hypermedia Multimedia 2016, 22, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; He, Z.; Wang, H.; You, F.; Li, K. Study on Self-Tuning Tyre Friction Control for Developing Main-Servo Loop Integrated Chassis Control System. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 6649–6660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.; Fotouhi, M.; Khaleghi, M. Intelligent classification of web pages using contextual and visual features. Appl. Soft Comput. 2011, 11, 1638–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.I.; Rahmawy, M.F.; Abulwafa, A.E. A semantic based Web page classification strategy using multi-layered domain ontology. World Wide Web 2017, 20, 939–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranauskas, J.; Netto, O.P.; Nozawa, S.R.; Macedo, A.A. A tree-based algorithm for attribute selection. Appl. Intell. 2018, 48, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, M.; Kim, K.A.; Chung, J.; Ryu, K.H. Emerging Pattern-Based Clustering of Web Users Utilizing a Simple Page-Linked Graph. Sustainability 2016, 8, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilbahar, E.; Cebi, S. Classification of design parameters for e-commerce websites: A novel fuzzy Kano approach. Telematics Inform. 2017, 38, 1814–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, D.A.; Radulescu, D. Approximately similarity measurement of web sites. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Telecommunications & Signal Processing, Istanbul, Turkey, 12 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, G.S.; Krishnaiah, R.V. Clustering algorithm with a novel similarity measure. IOSR J. Comput. Eng. 2012, 4, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crovella, M.E.; Bestavros, A. Self-Similarity in World Wide Web traffic: Evidence and possible causes. IEEE/ACM Trans. Network. 1997, 5, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Zhang, J.; He, T. Automatic combination technology of fuzzy CPN for OWL-S web services in supercomputing cloud platform. Int. J. Pattern Recogit. Artif. Intell. 2017, 31, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Hai, Y. Semantic ranking of web pages based on formal concept analysis. J. Syst. Softw. 2013, 86, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wang, B. Web page recommendation via twofold clustering: Considering user behavior and topic relation. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 29, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, G.; Lou, C. Multiple factor hierarchical clustering algorithm for large scale web page and search engine clickstream data. Ann. Oper. Res. 2012, 197, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.S.; Lu, H.Y.; Lu, J. Web-page recommendation based on web usage and domain knowledge. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2014, 26, 2574–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Pen, Q.; Gao, Z. A topic-specific crawling strategy based on semantics similarity. Data Knowled. Eng. 2013, 88, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussien, A. Comparison of machine learning algorithms to classify web pages. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2017, 8, 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Ruchika, M.; Anjali, S. Quantitative evaluation of web metrics for automatic genre classification of web pages. Int. J. Syst. Assurance Eng. Manag. 2017, 8 (Suppl. 2), 1567–1579. [Google Scholar]
- Kavitha, C.; Sudha, G.; Kiruthika, S. Semantic similarity based web document classification using support vector machine. Int. Arab J. Inf. Technol. 2017, 14, 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, S.A.R. An Automated web page classifier and an algorithm for the extraction of navigational pattern from the web data. J. Web Eng. 2017, 16, 126–144. [Google Scholar]
- Farman, A.; Pervez, K.; Kashif, R. A fuzzy ontology and SVM-based web content classification system. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 25781–25797. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-H.; Yeh, W.-C.; Chuang, M.-C. Web page classification based on a simplified swarm optimization. Appl. Math. Comput. 2015, 270, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, T. An optimized approach for massive web page classification using entity similarity based on semantic network. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2017, 76, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).