Pectosomes and Chitosomes as Delivery Systems for Metronidazole: The One-Pot Preparation Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Viscosity of Polymer Solutions
2.3. Preparation of Liposomes
2.4. Vesicle Size Reduction
2.5. Entrapment Efficiency
2.6. Phosphorus Assay
2.7. Particle Size Analysis
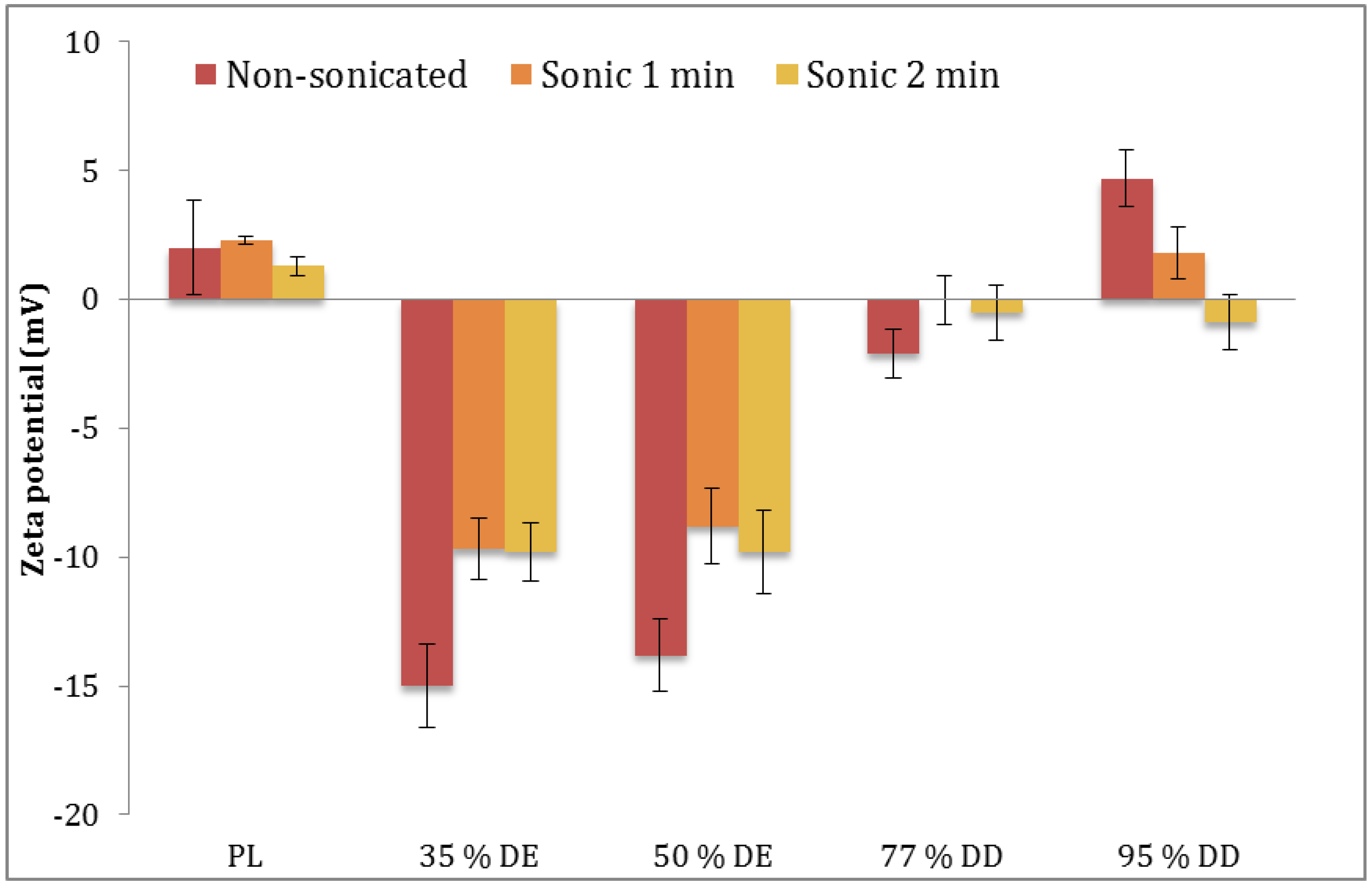
2.8. Zeta Potential
2.9. pH Measurements
2.10. Stability Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Viscosity of the Polymer Solutions
| Polymer type | Conc. (%, w/w) | Viscosity (mPas) |
|---|---|---|
| Pectin (35% DE) | 0.50 | 0.85 |
| Pectin (50% DE) | 0.50 | 0.67 |
| Chitosan (77% DD) | 0.17 | 0.75 |
| Chitosan (95% DD) | 0.05 | 0.49 |
3.2. Entrapment Efficiency
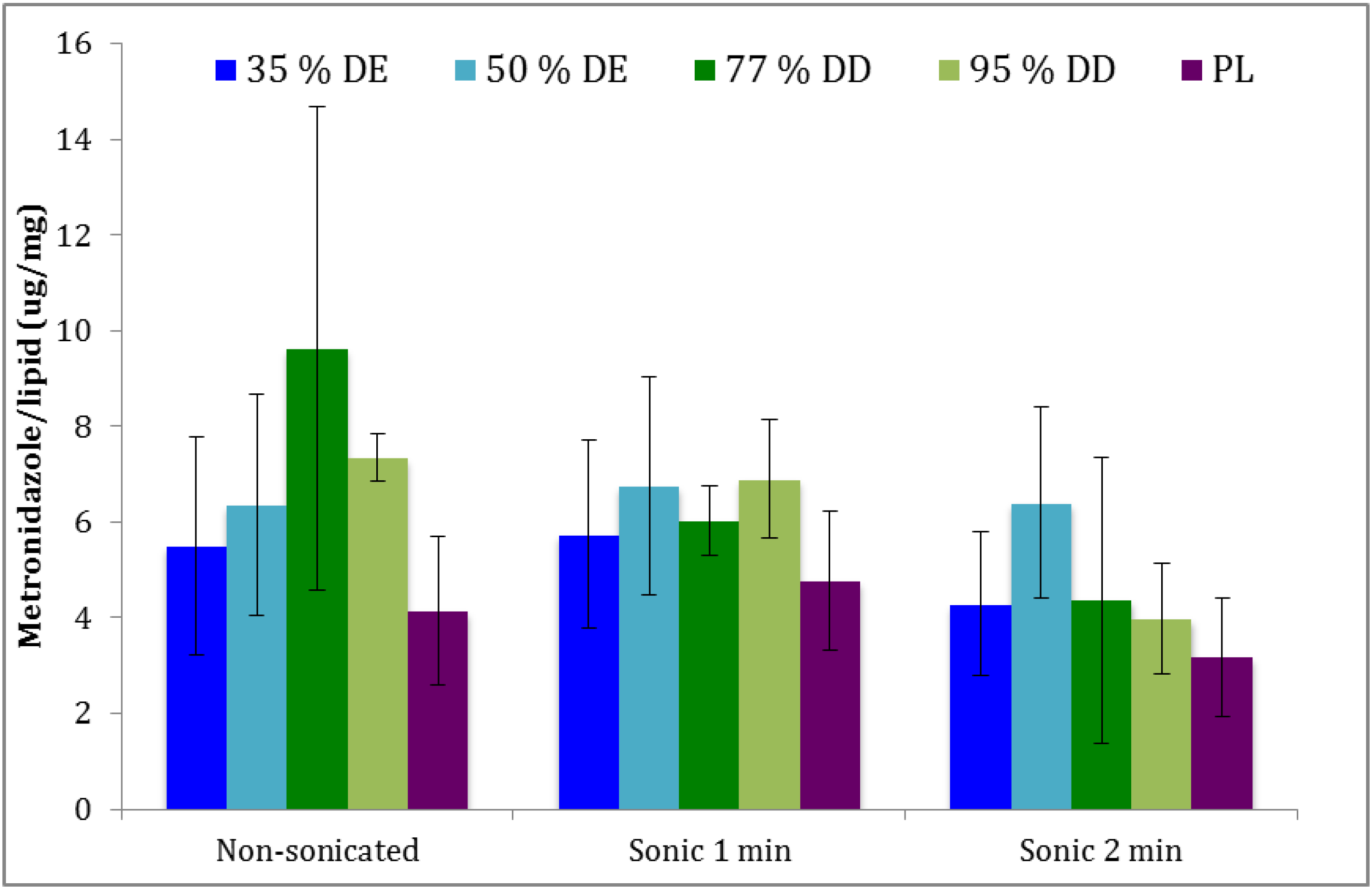
3.3. Characteristics of Vesicles
| Type of liposomes | Sonication time | Peak 1 | Peak 2 | PI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (nm) | % | Size (nm) | % | |||
| Freshly prepared | ||||||
| Pectosomes (35% DE) | 1 min | 148 | 13 | 626 | 86 | 0.373 |
| 2 min | 91 | 14 | 324 | 84 | 0.287 | |
| Pectosomes (50% DE) | 1 min | 222 | 11 | 847 | 82 | 0.446 |
| 2 min | 166 | 12 | 718 | 86 | 0.397 | |
| Chitosomes (77% DD) | 1 min | 62 | 30 | 239 | 72 | 0.315 |
| 2 min | 58 | 21 | 193 | 76 | 0.384 | |
| Chitosomes (95% DD) | 1 min | 194 | 14 | 733 | 86 | 0.442 |
| 2 min | 67 | 10 | 290 | 91 | 0.421 | |
| Plain | 1 min | 91 | 18 | 450 | 83 | 0.329 |
| 2 min | 82 | 12 | 415 | 89 | 0.446 | |
| Stored for 1 month | ||||||
| Pectosomes (35% DE) | 1 min | 115 | 14 | 497 | 85 | 0.324 |
| 2 min | 69 | 14 | 265 | 85 | 0.275 | |
| Pectosomes (50% DE) | 1 min | 113 | 10 | 508 | 90 | 0.390 |
| 2 min | 126 | 16 | 473 | 83 | 0.347 | |
| Chitosomes (77% DD) | 1 min | 68 | 23 | 310 | 75 | 0.360 |
| 2 min | 122 | 29 | 410 | 69 | 0.320 | |
| Chitosomes (95% DD) | 1 min | 115 | 6 | 625 | 93 | 0.525 |
| 2 min | 108 | 3 | 774 | 98 | 0.217 | |
| Plain | 1 min | 69 | 15 | 316 | 85 | 0.367 |
| 2 min | 47 | 7 | 222 | 93 | 0.454 | |
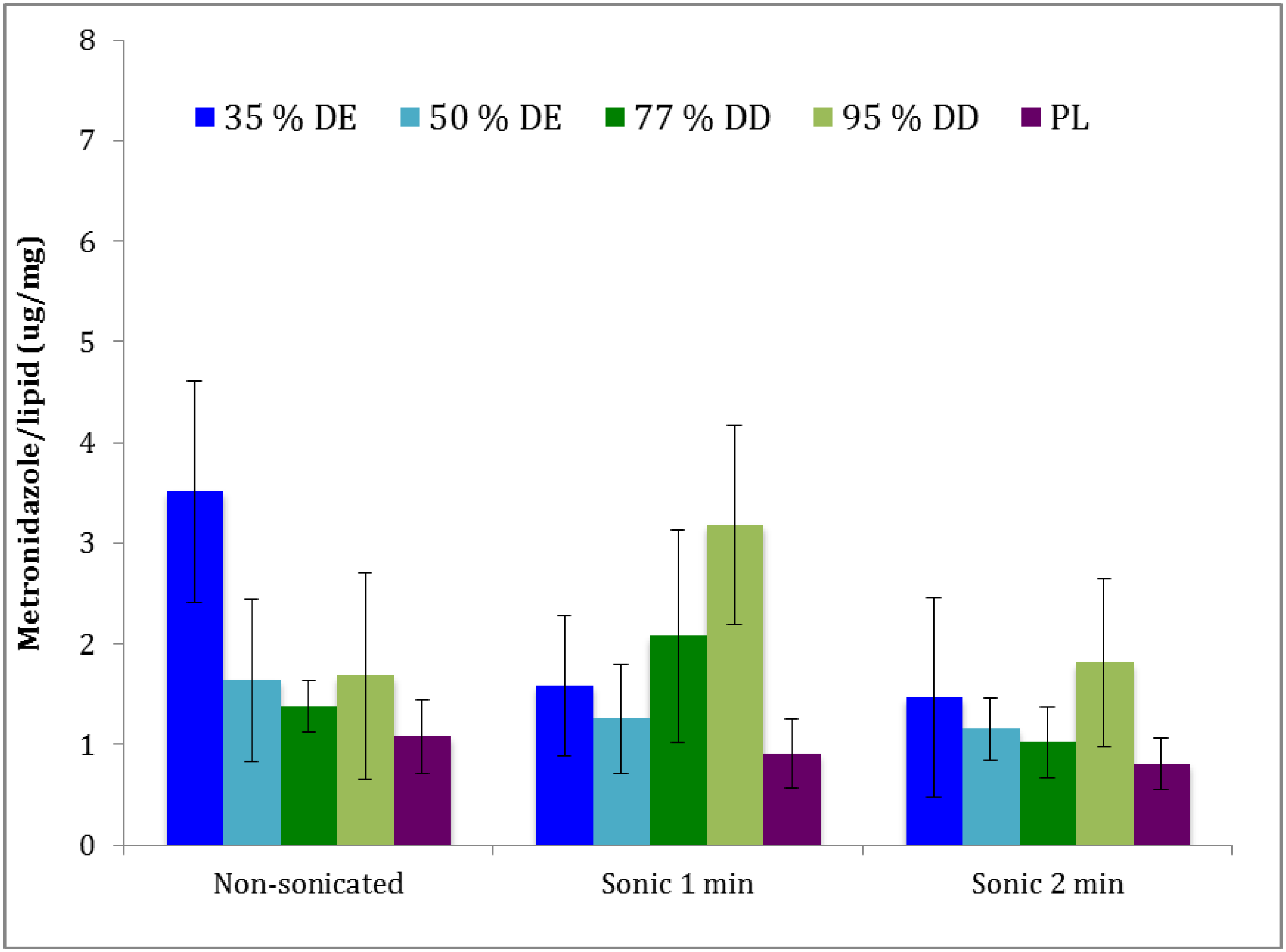
3.4. Storage Stability
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hainer, B.L.; Gibson, M.V. Vaginitis: Diagnosis and treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2011, 83, 807–815. [Google Scholar]
- Vanić, Ž.; Škalko-Basnet, N. Nanopharmaceuticals for improved topical vaginal delivery: Can they deliver? Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Neves, J.; Amiji, M.; Sarmento, B. Mucoadhesive nanosystems for vaginal microbicide development: Friend or foe? Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 3, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenta, C. The use of mucoadhesive polymers in vaginal delivery. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2005, 57, 1692–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Dünnhaupt, S. Chitosan-based drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagesaether, E.; Sande, S.A. In vitro measurements of mucoadhesive properties of six types of pectin. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2007, 33, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriamornsak, P. Application of pectin in oral drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemetsrud, T.; Jonassen, H.; Hiorth, M.; Kjøniksen, A.-L.; Smistad, G. Studies on pectin-coated liposomes and their interaction with mucin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 103, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogończyk, D.; Siek, M.; Garstecki, P. Microfluidic formulation of pectin microbeads for encapsulation and controlled release of nanoparticles. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 013405:1–013405:12. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.; Ahujaa, M.; Kaur, H. Thiolated pectin nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization and ex vivo corneal permeation study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1606–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burapapadha, K.; Kumpugdee-Vollrathc, M.; Chantasartd, D.; Sriamornsak, P. Fabrication of pectin-based nanoemulsions loaded with itraconazole for pharmaceutical application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.; Alund, S.J.; Hiorth, M.; Kjøniksen, A.-L.; Smistad, G. Studies on pectin coating of liposomes for drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 88, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karn, P.R.; Vanić, Ž.; Pepić, I.; Škalko-Basnet, N. Mucoadhesive liposomal delivery systems: The choice of coating material. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2011, 37, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Niwa, T.; Hino, T.; Kawashima, Y. Mucoadhesion of polymer-coated liposomes to rat intestine in vitro. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 42, 1954–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manconi, M.; Mura, S.; Manca, M.L.; Fadda, A.M.; Dolz, M.; Hernandez, M.J.; Casanovas, A.; Díez-Sales, O. Chitosomes as drug delivery systems for C-phycocyanin: Preparation and characterization. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 392, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanić, Ž.; Hafner, A.; Bego, M.; Škalko-Basnet, N. The characterization of various deformable liposomes with metronidazole. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentine, P.; Bubel, A.; Crucifix, C.; Bourel-Bonnet, L.; Frisch, B. Manufacture of liposomes by isopropanol injection: Characterisation of the method. J. Liposome Res. 2012, 22, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, G.R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J. Biol. Chem. 1959, 234, 466–468. [Google Scholar]
- Škalko, N.; Čajkovac, M.; Jalšenjak, I. Liposomes with metronidazole for topical use: The choice of preparation method and vehicle. J. Liposome Res. 1998, 8, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cagno, M.; Styskala, J.; Hlaváč, J.; Brandl, M.; Bauer-Brandl, A.; Škalko-Basnet, N. Liposomal solubilization of new 3-hydroxy-quinolinone derivatives with promising anticancer activity: A screening method to identify maximum incorporation capacity. J. Liposome Res. 2011, 21, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, P.; Hussain, H.; Tho, I.; Škalko-Basnet, N. Liposomal delivery system enhances anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Andersen, T.; Vanić, Ž.; Flaten, G.E.; Mattsson, S.; Tho, I.; Škalko-Basnet, N. Pectosomes and Chitosomes as Delivery Systems for Metronidazole: The One-Pot Preparation Method. Pharmaceutics 2013, 5, 445-456. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics5030445
Andersen T, Vanić Ž, Flaten GE, Mattsson S, Tho I, Škalko-Basnet N. Pectosomes and Chitosomes as Delivery Systems for Metronidazole: The One-Pot Preparation Method. Pharmaceutics. 2013; 5(3):445-456. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics5030445
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndersen, Toril, Željka Vanić, Gøril Eide Flaten, Sofia Mattsson, Ingunn Tho, and Nataša Škalko-Basnet. 2013. "Pectosomes and Chitosomes as Delivery Systems for Metronidazole: The One-Pot Preparation Method" Pharmaceutics 5, no. 3: 445-456. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics5030445
APA StyleAndersen, T., Vanić, Ž., Flaten, G. E., Mattsson, S., Tho, I., & Škalko-Basnet, N. (2013). Pectosomes and Chitosomes as Delivery Systems for Metronidazole: The One-Pot Preparation Method. Pharmaceutics, 5(3), 445-456. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics5030445