Advances in Intra-Articular Injection Hydrogel Drug Delivery Systems in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
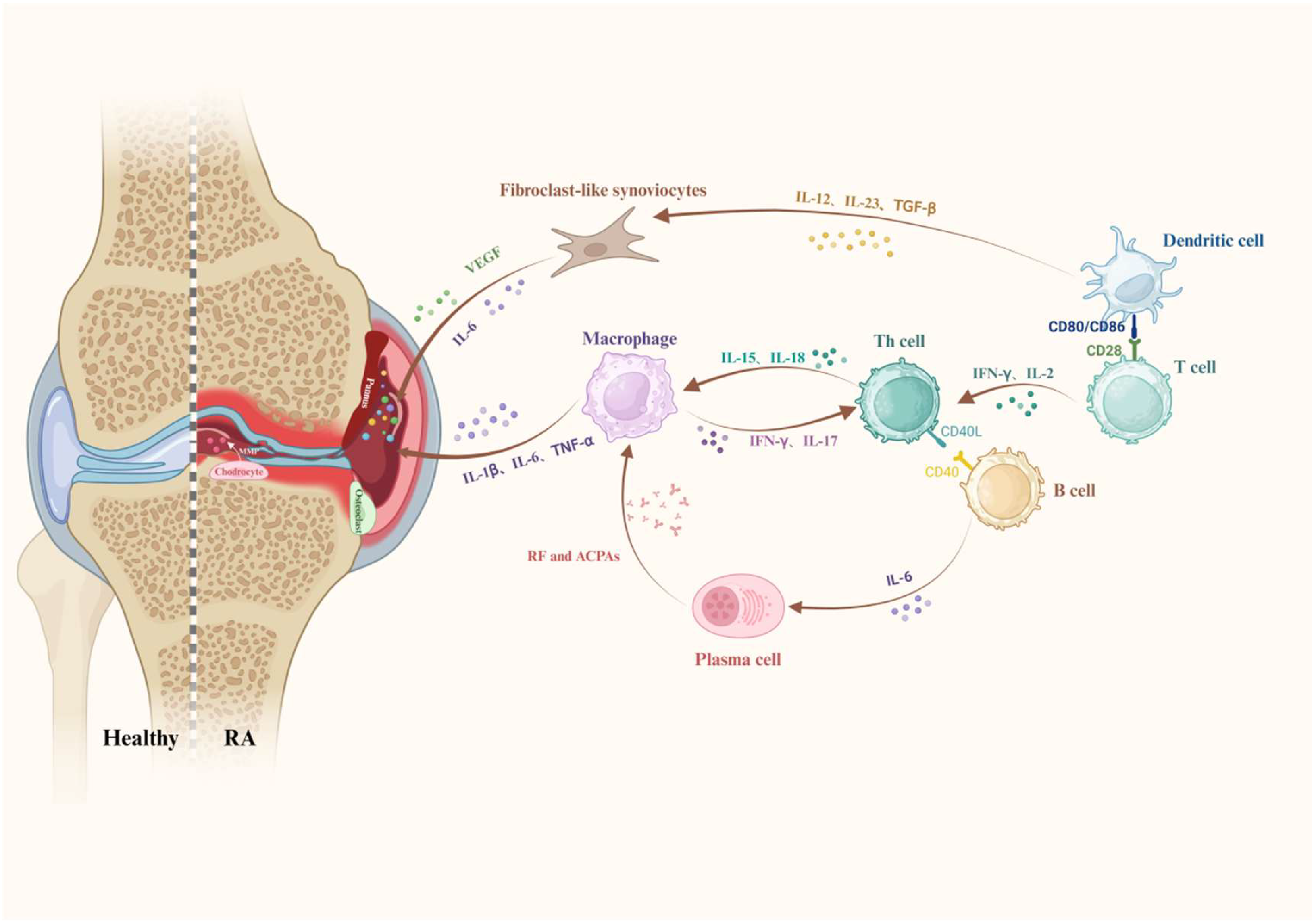
2. Histopathological Changes and Associated Cellular and Molecular Events in RA
2.1. Heterogeneous Infiltration of Inflammatory Cells
2.1.1. T Cells
2.1.2. Monocytes and Macrophages
2.1.3. B Cells
2.1.4. Neutrophils
2.1.5. DCs
2.2. Pathological Changes in Synovial and Joint Tissues
2.2.1. Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes (FLSs)
2.2.2. Pannus
2.2.3. Metabolic Dysregulation and Oxidative Stress
2.3. Inflammatory Mediators and Signaling Pathways
2.3.1. Pro-Inflammatory Factors
2.3.2. Growth Factor
2.3.3. Autoantibodies and the Complement System
2.3.4. MMPs
2.3.5. Signaling Pathways
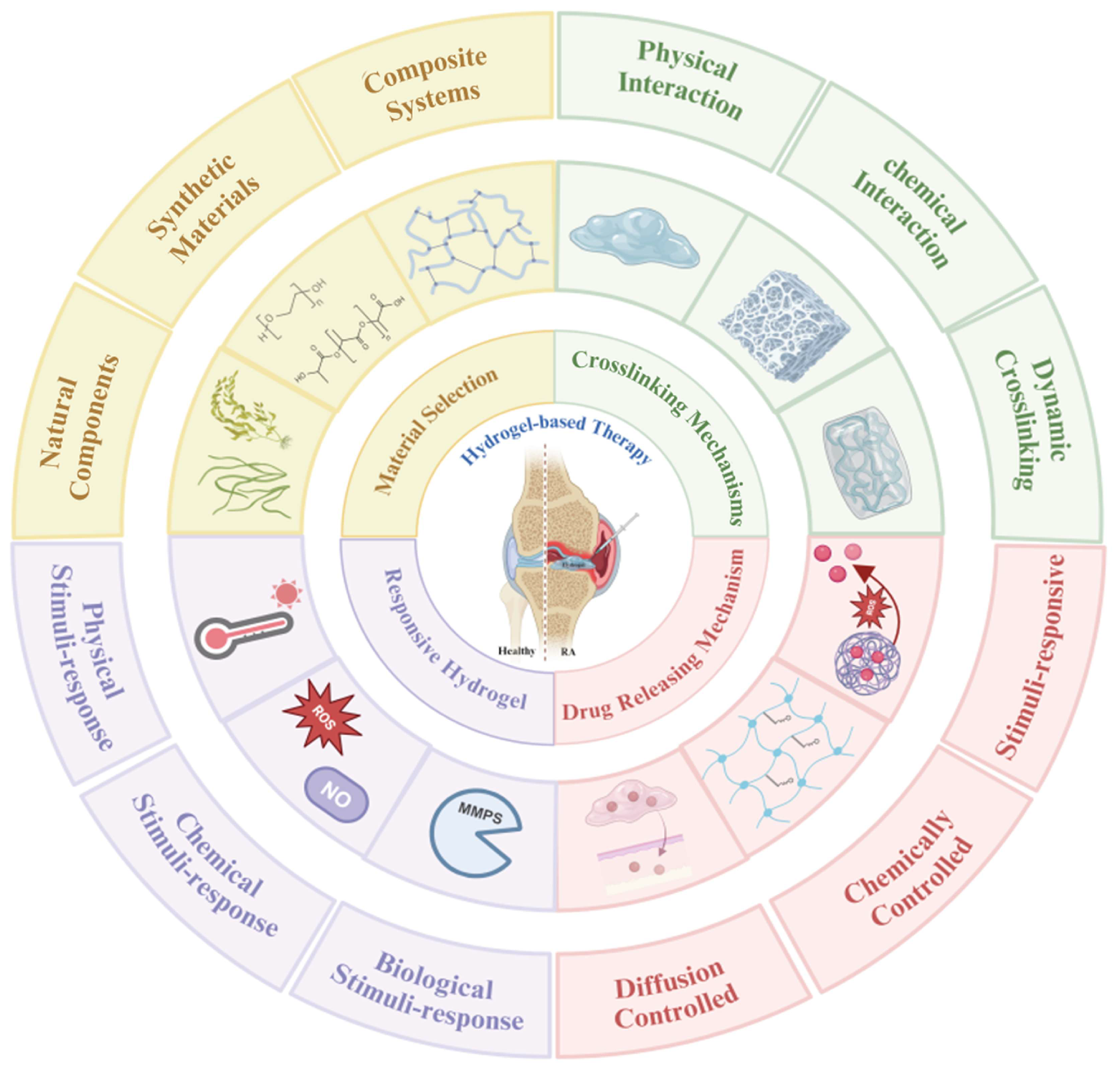
3. Basic Properties of Hydrogels
4. Design and Optimization of Hydrogels
4.1. Material Selection
4.2. Crosslinking-Driven Hydrogel Customization
4.3. Drug-Loading and Release Mechanisms
4.4. Responsive Hydrogels
5. Injectable Hydrogel Systems for RA Management
5.1. Immunologically Targeted Therapies for RA
5.1.1. Modulation of Immune Cell Activity and Inflammation
5.1.2. Cytokine Network Modulation and Inflammatory Cascade Regulation
5.2. Restoration of Joint Microenvironment Homeostasis
5.2.1. Modulation of Oxidative Stress
5.2.2. Modulation of Tissue Repair and Regeneration
5.3. Smart Hydrogels with On-Demand Microenvironment Responsiveness
5.3.1. Pathological Factor-Triggered Hydrogel Platforms
5.3.2. Prodrug-Mimicking Nanoparticle-Loaded Hydrogel Platforms
5.4. Innovative Hydrogel Therapies: Gas-, Sound-, Light-, and 3D Printing-Based Approaches
5.4.1. PTT/PDT
5.4.2. Gas Therapy
5.4.3. SDT
5.4.4. Printing-Based Therapy
6. Challenges and Insights into Future Developments
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Di Matteo, A.; Bathon, J.M.; Emery, P. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2023, 402, 2019–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravallese Ellen, M.; Firestein Gary, S. Rheumatoid Arthritis—Common Origins, Divergent Mechanisms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finckh, A.; Gilbert, B.; Hodkinson, B.; Bae, S.-C.; Thomas, R.; Deane, K.D.; Alpizar-Rodriguez, D.; Lauper, K. Global epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, S.L.; Abate, D.; Abate, K.H.; Abay, S.M.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasi, N.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdela, J.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negi, S.; Tandel, N.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, R.; Tyagi, R.K. Aceclofenac and methotrexate combination therapy could influence Th1/Th17 axis to modulate rheumatoid-arthritis-induced inflammation. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapa-Villarreal, F.A.; Stephens, M.; Pavlicin, R.; Beussman, M.; Peppas, N.A. Therapeutic delivery systems for rheumatoid arthritis based on hydrogel carriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2024, 208, 115300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckner, J.H. Antigen-specific immunotherapies for autoimmune disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2025, 21, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Liu, R.; Zhang, L. Advance in bone destruction participated by JAK/STAT in rheumatoid arthritis and therapeutic effect of JAK/STAT inhibitors. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, J.; Drescher, E.; Simón-Campos Jesus, A.; Emery, P.; Greenwald, M.; Kivitz, A.; Rha, H.; Yachi, P.; Kiley, C.; Nirula, A. A Phase 2 Trial of Peresolimab for Adults with Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivellese, F.; Surace, A.E.A.; Goldmann, K.; Sciacca, E.; Çubuk, C.; Giorli, G.; John, C.R.; Nerviani, A.; Fossati-Jimack, L.; Thorborn, G.; et al. Rituximab versus tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis: Synovial biopsy-based biomarker analysis of the phase 4 R4RA randomized trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1256–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, K.S.; Bit Mansour, A.; Raychaudhuri, S.P. What’s new on the horizon for rheumatoid arthritis management. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2025, 39, 102038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konzett, V.; Aletaha, D. Management strategies in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2024, 20, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.A.; Cameron, C.; Noorbaloochi, S.; Cullis, T.; Tucker, M.; Christensen, R.; Ghogomu, E.T.; Coyle, D.; Clifford, T.; Tugwell, P.; et al. Risk of serious infection in biological treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2015, 386, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.B.M.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Burmester, G.R.; Dougados, M.; Kerschbaumer, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Sepriano, A.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; de Wit, M.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giollo, A.; Fuzzi, E.; Doria, A. Methotrexate in early rheumatoid arthritis: Is the anchor drug still holding? Autoimmun. Rev. 2022, 21, 103031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Hu, W.; Cai, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Dong, S. Advanced application of stimuli-responsive drug delivery system for inflammatory arthritis treatment. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 14, 100223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraenkel, L.; Bathon, J.M.; England, B.R.; St. Clair, E.W.; Arayssi, T.; Carandang, K.; Deane, K.D.; Genovese, M.; Huston, K.K.; Kerr, G.; et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2021, 73, 924–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Xu, Y.; Dong, X.; Mu, Q.; Chen, X.; Yu, Y.; Su, G. Nanotechnology-empowered combination therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: Principles, strategies, and challenges. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Nossent, J.; Pavlos, N.J.; Xu, J. Rheumatoid arthritis: Pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res. 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Venrooij, W.J.; van Beers, J.J.B.C.; Pruijn, G.J.M. Anti-CCP antibodies: The past, the present and the future. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, J.; Ekwall, A.-K.H.; Mark, L.; Bergström, B.; Andersson, K.; Gjertsson, I.; Lundell, A.-C.; Rudin, A. T helper cells in synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis primarily have a Th1 and a CXCR3+Th2 phenotype. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Su, R.; Guo, Q.; Su, R.; Gao, C.; Li, X.; Wang, C. Differential immunological profiles in seronegative versus seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: Th17/Treg dysregulation and IL-4. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1447213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firestein, G.S.; McInnes, I.B. Immunopathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunity 2017, 46, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetti, M.; Spreafico, R.; Consolaro, A.; Leong, J.Y.; Chua, C.; Massa, M.; Saidin, S.; Magni-Manzoni, S.; Arkachaisri, T.; Wallace, C.A.; et al. TCR repertoire sequencing identifies synovial Treg cell clonotypes in the bloodstream during active inflammation in human arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Craft, J. T follicular helper cell heterogeneity: Time, space, and function. Immunol. Rev. 2019, 288, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Niu, X. T follicular helper cells in autoimmune diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2023, 134, 102976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, P.B.; Marcovecchio, P.; Hamers, A.A.J.; Hedrick, C.C. Nonclassical Monocytes in Health and Disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 37, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Alivernini, S. Synovial tissue macrophages in joint homeostasis, rheumatoid arthritis and disease remission. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, G.; Firestein, G.S. Restoring synovial homeostasis in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 316–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misharin, A.V.; Cuda, C.M.; Saber, R.; Turner, J.D.; Gierut, A.K.; Haines, G.K., III; Berdnikovs, S.; Filer, A.; Clark, A.R.; Buckley, C.D.; et al. Nonclassical Ly6C− Monocytes Drive the Development of Inflammatory Arthritis in Mice. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Deng, T.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, S.; Li, H.; Li, J.; You, S.; Xie, H.Q.; Shen, B. A versatile platform based on matrix metalloproteinase-sensitive peptides for novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies in arthritis. Bioact. Mater. 2025, 47, 100–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hascoët, E.; Blanchard, F.; Blin-Wakkach, C.; Guicheux, J.; Lesclous, P.; Cloitre, A. New insights into inflammatory osteoclast precursors as therapeutic targets for rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis. Bone Res. 2023, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ah Kioon, M.D.; Laurent, P.; Chaudhary, V.; Du, Y.; Crow, M.K.; Barrat, F.J. Modulation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells response in inflammation and autoimmunity. Immunol. Rev. 2024, 323, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udalova, I.A.; Mantovani, A.; Feldmann, M. Macrophage heterogeneity in the context of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwa, Y.; Nagafuchi, Y.; Yamada, S.; Fujio, K. The role of dendritic cells and their immunometabolism in rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1161148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Gevezova, M.; Sarafian, V.; Maes, M. Redox regulation of the immune response. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 1079–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, M.; Jia, S. Macrophage: Key player in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1080310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, B.; Klareskog, L.; Robinson, W.H.; Malmström, V.; Grönwall, C. The peculiar features, diversity and impact of citrulline-reactive autoantibodies. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2024, 20, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghazali, T.; Saleh, R.O.; Uthirapathy, S.; Ballal, S.; Abullais, S.S.; Kalia, R.; Arya, R.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, A.; Abdulamer, R.S. Rheumatoid arthritis unmasked: The power of B cell depletion therapy. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2025, 52, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertsinidou, E.; Saevarsdottir, S.; Manivel, V.A.; Klareskog, L.; Alfredsson, L.; Mathsson-Alm, L.; Hansson, M.; Cornillet, M.; Serre, G.; Holmdahl, R.; et al. In early rheumatoid arthritis, anticitrullinated peptide antibodies associate with low number of affected joints and rheumatoid factor associates with systemic inflammation. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Pellegrini, C.; Masi, S.; Puxeddu, I.; Blandizzi, C. Ectopic Lymphoid Organs and Immune-Mediated Diseases: Molecular Basis for Pharmacological Approaches. Trends Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascão, R.; Rosário, H.S.; Souto-Carneiro, M.M.; Fonseca, J.E. Neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis: More than simple final effectors. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 9, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fresneda Alarcon, M.; McLaren, Z.; Wright, H.L. Neutrophils in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Same Foe Different M.O. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 649693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, H.L.; Lyon, M.; Chapman, E.A.; Moots, R.J.; Edwards, S.W. Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fluid Neutrophils Drive Inflammation Through Production of Chemokines, Reactive Oxygen Species, and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 584116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frade-Sosa, B.; Sanmartí, R. Neutrophils, neutrophil extracellular traps, and rheumatoid arthritis: An updated review for clinicians. Reumatol. Clin. 2023, 19, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandpur, R.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; Vivekanandan-Giri, A.; Gizinski, A.; Yalavarthi, S.; Knight, J.S.; Friday, S.; Li, S.; Patel, R.M.; Subramanian, V.; et al. NETs Are a Source of Citrullinated Autoantigens and Stimulate Inflammatory Responses in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, ra140–ra178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Xia, J.; Gao, H.; Jiang, R.; Xiao, L.; Sheng, H.; Lin, J. IL33-induced neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) mediate a positive feedback loop for synovial inflammation and NET amplification in rheumatoid arthritis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 2602–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutant, F. Pathogenic effects of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis—Role for glycosylation. Jt. Bone Spine 2019, 86, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebre, M.C.; Jongbloed, S.L.; Tas, S.W.; Smeets, T.J.; McInnes, I.B.; Tak, P.P. Rheumatoid arthritis synovium contains two subsets of CD83−DC-LAMP− dendritic cells with distinct cytokine profiles. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 940–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongbloed, S.L.; Lebre, M.C.; Fraser, A.R.; Gracie, J.A.; Sturrock, R.D.; Tak, P.P.; McInnes, I.B. Enumeration and phenotypical analysis of distinct dendritic cell subsets in psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, G.; Miossec, P. Paired synovium and lymph nodes from rheumatoid arthritis patients differ in dendritic cell and chemokine expression. J. Pathol. 2004, 204, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottini, N.; Firestein, G.S. Duality of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in RA: Passive responders and imprinted aggressors. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, N.; Takayanagi, H. Mechanisms of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis-immune cell–fibroblast–bone interactions. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karouzakis, E.; Raza, K.; Kolling, C.; Buckley, C.D.; Gay, S.; Filer, A.; Ospelt, C. Analysis of early changes in DNA methylation in synovial fibroblasts of RA patients before diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaltskan, V.; Firestein, G.S. Targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2022, 67, 102304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, T.; Liang, W. The association between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 2237–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, M.J.; Karami, J.; Aslani, S.; Tahmasebi, M.N.; Vaziri, A.S.; Jamshidi, A.; Farhadi, E.; Mahmoudi, M. Transformation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis; from a friend to foe. Autoimmun. Highlights 2021, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufino, A.T.; Freitas, M.; Proença, C.; Ferreira de Oliveira, J.M.P.; Fernandes, E.; Ribeiro, D. Rheumatoid arthritis molecular targets and their importance to flavonoid-based therapy. Med. Res. Rev. 2024, 44, 497–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Deng, R. Angiogenesis as a potential treatment strategy for rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 910, 174500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veale, D.J.; Orr, C.; Fearon, U. Cellular and molecular perspectives in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearon, U.; Canavan, M.; Biniecka, M.; Veale, D.J. Hypoxia, mitochondrial dysfunction and synovial invasiveness in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearon, U.; Hanlon, M.M.; Floudas, A.; Veale, D.J. Cellular metabolic adaptations in rheumatoid arthritis and their therapeutic implications. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, Ó.C.; O’Neill, L.A.J. Metabolic Reprogramming in Stromal and Immune Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis: Therapeutic Possibilities. Eur. J. Immunol. 2025, 55, e202451381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fan, D.; Cao, X.; Ye, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, C. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in the Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Synovial Microenvironment. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardeş, S.; Karagülle, M.; Durak, İ.; Avcı, A.; Karagülle, M.Z. Association of oxidative stress with clinical characteristics in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, S.; Knedla, A.; Tennie, C.; Kampmann, A.; Wunrau, C.; Dinser, R.; Korb, A.; Schnäker, E.M.; Tarner, I.H.; Robbins, P.D.; et al. Synovial fibroblasts spread rheumatoid arthritis to unaffected joints. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trejo-Zambrano, M.I.; Gómez-Bañuelos, E.; Andrade, F. Redox-Mediated Carbamylation As a Hapten Model Applied to the Origin of Antibodies to Modified Proteins in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2022, 36, 389–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, R.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Rawat, R.; Rashid, S.; Vargas-De-La-Cruz, C.; Yadav, S.; Bungau, S.G.; Behl, T. Current trends in epigenetic, cellular and molecular pathways in management of rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 1577–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, J.S.; Holland, L.; López, M.; Meyers, K.; Cumbie, W.G.; McClain, A.; Ignatowicz, A.; Nelson, D.; Shashidharamurthy, R. Prostaglandin E2 and IL-23 interconnects STAT3 and RoRγ pathways to initiate Th17 CD4+ T-cell development during rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koper-Lenkiewicz, O.M.; Sutkowska, K.; Wawrusiewicz-Kurylonek, N.; Kowalewska, E.; Matowicka-Karna, J. Proinflammatory Cytokines (IL-1, -6, -8, -15, -17, -18, -23, TNF-α) Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Rheumatoid Arthritis-A Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Qiu, H.; Wen, R.; Zou, X.; Sun, X.; Yu, L.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Lan, F. Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species—“Nanosweeper” for Rheumatoid Arthritis Theranostics by Macrophage Reprogramming. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 70322–70338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, R.; Bansal, Y.; Bansal, G. Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitors: A comprehensive update. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 823–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oza, P.P.; Kashfi, K. The Triple Crown: NO, CO, and H2S in cancer cell biology. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 249, 108502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripodi, G.; Lombardo, M.; Kerav, S.; Aiello, G.; Baldelli, S. Nitric Oxide in Parkinson’s Disease: The Potential Role of Dietary Nitrate in Enhancing Cognitive and Motor Health via the Nitrate-Nitrite-Nitric Oxide Pathway. Nutrients 2025, 17, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierońska, J.M.; Cieślik, P.; Kalinowski, L. Nitric Oxide-Dependent Pathways as Critical Factors in the Consequences and Recovery after Brain Ischemic Hypoxia. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellam, J.; Berenbaum, F. The role of synovitis in pathophysiology and clinical symptoms of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz-Späh, J.; Jakobsson, P.J. The anti-inflammatory and vasoprotective properties of mPGES-1 inhibition offer promising therapeutic potential. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2023, 27, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.Y.; Chang, Y.; Sun, X.J.; Dai, X.; Wei, W. The role of prostaglandin E2 receptor signaling of dendritic cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 23, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Pillinger, M.H.; Abramson, S.B. Prostaglandin E2 synthesis and secretion: The role of PGE2 synthases. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 119, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; You, X.; Yan, Y.; Singh, G.K.; Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Liu, W.; Zhang, F.; Lv, Y.; Yang, L. Cyclic mechanical stretch downregulates IL-1β-induced COX-2 expression and PGE2 production in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Connect. Tissue Res. 2011, 52, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, M.M.; Reader, J.; Fulton, A.M. Eicosanoids in Cancer: Prostaglandin E2 Receptor 4 in Cancer Therapeutics and Immunotherapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehbi, V.L.; Taskén, K. Molecular Mechanisms for cAMP-Mediated Immunoregulation in T cells—Role of Anchored Protein Kinase A Signaling Units. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, K.D.; Holers, V.M.; Emery, P.; Mankia, K.; El-Gabalawy, H.; Sparks, J.A.; Costenbader, K.H.; Schett, G.; van der Helm-van Mil, A.; van Schaardenburg, D.; et al. Therapeutic interception in individuals at risk of rheumatoid arthritis to prevent clinically impactful disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2025, 84, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brito Rocha, S.; Baldo, D.C.; Andrade, L.E.C. Clinical and pathophysiologic relevance of autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv. Rheumatol. 2019, 59, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, M.; van Schie, K.A.; van der Woude, D. Autoantibodies and B Cells: The ABC of rheumatoid arthritis pathophysiology. Immunol. Rev. 2020, 294, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucks, A.; Maerz, T.; Hankenson, K.; Moeser, A.; Colbath, A. The multifaceted role of mast cells in joint inflammation and arthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2023, 31, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coss, S.L.; Zhou, D.; Chua, G.T.; Aziz, R.A.; Hoffman, R.P.; Wu, Y.L.; Ardoin, S.P.; Atkinson, J.P.; Yu, C.Y. The complement system and human autoimmune diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2023, 137, 102979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hysa, E.; Cutolo, C.A.; Gotelli, E.; Paolino, S.; Cimmino, M.A.; Pacini, G.; Pizzorni, C.; Sulli, A.; Smith, V.; Cutolo, M. Ocular microvascular damage in autoimmune rheumatic diseases: The pathophysiological role of the immune system. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, W.Y.; Tsai, W.C. Rethink About the Role of Rheumatoid Factor and Anti-citrullinated Protein Antibody in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatol. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Chen, H.; Xie, K.; Xiang, J.; Chen, J.; Lin, Z. Cathepsin B serves as a potential prognostic biomarker and correlates with ferroptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 128, 111502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clanchy, F.I.L.; Borghese, F.; Bystrom, J.; Balog, A.; Penn, H.; Taylor, P.C.; Stone, T.W.; Mageed, R.A.; Williams, R.O. Disease status in human and experimental arthritis, and response to TNF blockade, is associated with MHC class II invariant chain (CD74) isoform expression. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 128, 102810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokry, A.A.; El-Shiekh, R.A.; Kamel, G.; Bakr, A.F.; Sabry, D.; Ramadan, A. Anti-arthritic activity of the flavonoids fraction of ivy leaves (Hedera helix L.) standardized extract in adjuvant induced arthritis model in rats in relation to its metabolite profile using LC/MS. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yin, G.; Zhao, H.; Ling, H.; Xie, Z.; Xiao, C.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, T.; Jin, S.; et al. Secreted KIAA1199 promotes the progression of rheumatoid arthritis by mediating hyaluronic acid degradation in an ANXA1-dependent manner. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnihotri, P.; Saquib, M.; Joshi, L.; Malik, S.; Chakraborty, D.; Sarkar, A.; Kumar, U.; Biswas, S. Integrative metabolomic-proteomic analysis uncovers a new therapeutic approach in targeting rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2024, 26, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, T.; Nie, Z.; Han, H.; Zhong, S.; Yin, Z.; Sun, S.; Xie, J.; Shen, J.; et al. Role and Therapeutic Potential for Targeting Fibroblast Growth Factor 10/FGFR1 in Relapsed Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Zhou, C.; Nandakumar, K.S. Molecular and Cellular Pathways Contributing to Joint Damage in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 3830212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ma, H.; Zhang, H.; Deng, C.; Xin, P. Recent advances on signaling pathways and their inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 230, 108793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noort, A.R.; Tak, P.P.; Tas, S.W. Non-canonical NF-κB signaling in rheumatoid arthritis: Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde? Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, D.A.; Poenariu, I.S.; Crînguș, L.I.; Vreju, F.A.; Turcu-Stiolica, A.; Tica, A.A.; Padureanu, V.; Dumitrascu, R.M.; Banicioiu-Covei, S.; Dinescu, S.C.; et al. JAK/STAT pathway in pathology of rheumatoid arthritis (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 3498–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Pujol, E.J.; Martínez, G.; Casado-Jurado, D.; Vázquez, J.; León-Barberena, J.; Rodríguez-Lucena, D.; Torres, Y.; Alcudia, A.; Begines, B. Hydrogels and Nanogels: Pioneering the Future of Advanced Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, K. Current hydrogel advances in physicochemical and biological response-driven biomedical application diversity. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Xiao, M.; Chen, S.; Huang, Y.; Hou, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, L. Innovative applications of natural polysaccharide polymers in intravesical therapy of bladder diseases. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 354, 123307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, K.; Samiraninezhad, N.; Akbarizadeh, A.R.; Amini, A.; Gholami, A. Stimuli-responsive hydrogel based on natural polymers for breast cancer. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1325204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.C.; Chang, C.C.; Chan, H.P.; Chung, T.W.; Shu, C.W.; Chuang, K.P.; Duh, T.H.; Yang, M.H.; Tyan, Y.C. Hydrogels: Properties and Applications in Biomedicine. Molecules 2022, 27, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Atif, M.; Haseen, M.; Kamal, S.; Khan, M.S.; Shahid, S.; Nami, S.A.A. Synthesis, classification and properties of hydrogels: Their applications in drug delivery and agriculture. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 170–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, B.G.; Nguyen, A.K.; Gooding, J.J.; Kilian, K.A. Advancing Synthetic Hydrogels through Nature-Inspired Materials Chemistry. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2404235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Han, F.; Chen, P.; Zhang, R.; Tao, Y. Injectable and drug-loaded gelatin methacrylate and carboxymethylated-sulfated xanthan gum hydrogels as biomimetic mineralization constructs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 355, 123354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Cheng, X.; Pan, R.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Liang, W.; Xie, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Yu, K.; et al. Polyvinyl pyrrolidone/carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel loaded with Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis extracellular vesicles promotes wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 306, 141782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Tan, Z.; Weng, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, G.; Sun, F.; Zhao, Y. Locally Injectable Chitosan/β-Glycerophosphate Hydrogel Doped with Triptolide-Human Serum Albumin Nanoparticles for Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, J.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y.; Lv, H.; Zhou, Y. Spatiotemporal controlled released hydrogels for multi-system regulated bone regeneration. J. Control. Release 2024, 372, 846–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Long, F.; Bai, S.; Wang, Y. Dynamic supramolecular hydrogels mediated by chemical reactions. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 14236–14248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, X.; Zou, Z.; Chen, X.; He, C. Injectable, self-healing hydrogel adhesives with firm tissue adhesion and on-demand biodegradation for sutureless wound closure. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadh4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, R.; Fan, W.; Wang, L.; Zhan, J.; Cao, T.; Liu, Q.; Piao, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, W.; et al. Spermidine-Functionalized Injectable Hydrogel Reduces Inflammation and Enhances Healing of Acute and Diabetic Wounds In Situ. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2310162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, W.; Huang, L.; Xian, Y.; Ma, W.; Fan, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, D. Injectable pathological microenvironment-responsive anti-inflammatory hydrogels for ameliorating intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomaterials 2024, 306, 122509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajendiran, M.; Rhee, J.S.; Kim, K. Recent Developments in Thiolated Polymeric Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2018, 24, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
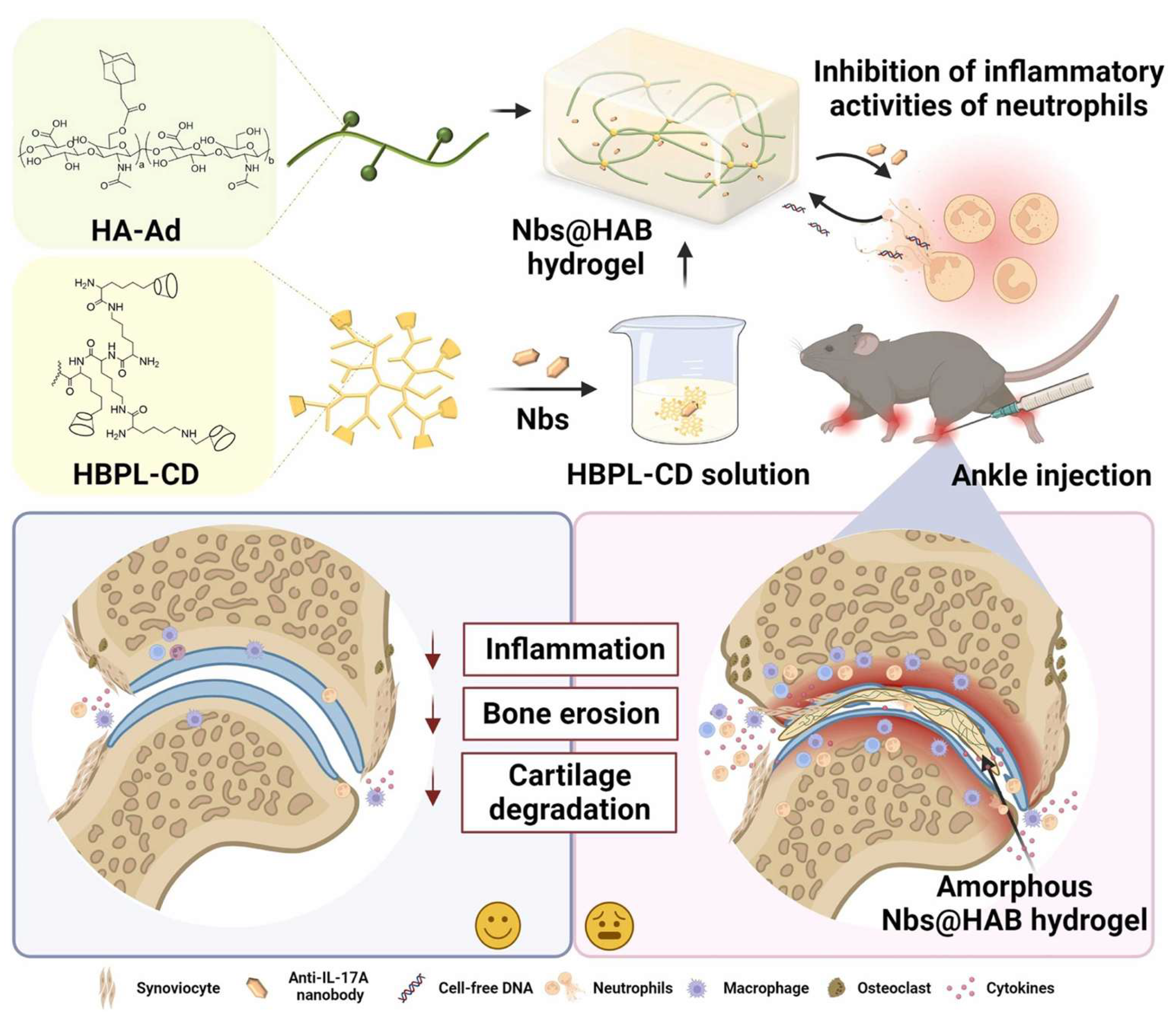
- Wang, Q.; Cheng, Q.; Yao, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zeng, Z.; Jia, L.; Du, Y.; Xue, J.; Gao, C. A cationic hydrogel with anti-IL-17A-specific nanobodies for rheumatoid arthritis treatment via inhibition of inflammatory activities of neutrophils. Nano Today 2024, 59, 102507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovers, M.M.; Rogkoti, T.; Bakker, B.K.; Bakal, K.J.; van Genderen, M.H.P.; Salmeron-Sanchez, M.; Dankers, P.Y.W. Using a Supramolecular Monomer Formulation Approach to Engineer Modular, Dynamic Microgels, and Composite Macrogels. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2405868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolabi, H.; Davari, N.; Khajehmohammadi, M.; Malektaj, H.; Nazemi, K.; Vahedi, S.; Ghalandari, B.; Reis, R.L.; Ghorbani, F.; Oliveira, J.M. Progress of Microfluidic Hydrogel-Based Scaffolds and Organ-on-Chips for the Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2208852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Qin, X.; Yang, R.; Qin, J.; Li, W.; Luan, K.; Wu, Z.; Song, L. Intra-articular Administration of Chitosan Thermosensitive In Situ Hydrogels Combined with Diclofenac Sodium-Loaded Alginate Microspheres. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ge, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Tian, T.; Wei, J.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, Q.; Wu, J.; et al. Synovium microenvironment-responsive injectable hydrogel inducing modulation of macrophages and elimination of synovial fibroblasts for enhanced treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Jadhav, K.; Kamboj, R.; Malhotra, H.; Ray, E.; Jhilta, A.; Dhir, V.; Verma, R.K. Self-actuating inflammation responsive hydrogel microsphere formulation for controlled drug release in rheumatoid arthritis (RA): Animal trials and study in human fibroblast like synoviocytes (hFLS) of RA patients. Biomater. Adv. 2024, 160, 213853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terriac, L.; Helesbeux, J.J.; Maugars, Y.; Guicheux, J.; Tibbitt, M.W.; Delplace, V. Boronate Ester Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: Challenges and Opportunities. Chem. Mater. 2024, 36, 6674–6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Z.; Dong, X.; Qi, H.; Tao, R.; Zhang, P. Carbon Quantum Dots with High Photothermal Conversion Efficiency and Their Application in Photothermal Modulated Reversible Deformation of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogel. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023, 6, 3395–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikani, T.; Dave, S.; Thakore, S. Functionalization of hyaluronic acid for development of self-healing hydrogels for biomedical applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Y.W.; Loukanov, A.; Tsai, H.-C. State-of-the-Art Synthesis of Porous Polymer Materials and Their Several Fantastic Biomedical Applications: A Review. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 2024, 2403743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zeng, B.; Liu, C.; Gong, L.; Wu, H.; Chen, L.; Jin, M.; Guo, J.; et al. Triple Cross-linked Dynamic Responsive Hydrogel Loaded with Selenium Nanoparticles for Modulating the Inflammatory Microenvironment via PI3K/Akt/NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2303167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Ren, R.; Wei, X.; Jia, Z.; Chen, N.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Lele, S.M.; Zhong, H.A.; Goldring, M.B.; et al. Thermoresponsive polymeric dexamethasone prodrug for arthritis pain. J. Control. Release 2021, 339, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Lin, Y.; Shuai, Z.; Duan, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Jiang, J.; Wu, J.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Nanocomposite hydrogel to deliver the immunomodulator lenalidomide and anti-inflammatory hesperidin locally to joints affected by rheumatoid arthritis. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 476, 146270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ge, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Tian, T.; Wei, J.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, Q.; Wu, J.; et al. Microenvironment Responsive Hydrogel Exerting Inhibition of Cascade Immune Activation and Elimination of Synovial Fibroblasts for Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy. J. Control. Release 2024, 370, 747–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Xie, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Ai, Y.; Zheng, W.; Ding, M.; Gao, J.; Wang, J.; Liang, Q. Nitrite-Responsive Hydrogel: Smart Drug Release Depending on the Severity of the Nitric Oxide-Related Disease. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 51185–51197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Fu, T.; Zhang, C.; An, Z.; Yan, J.; Lu, Z.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Qiu, L.; Shi, L.; et al. Prolonged, staged, and self-regulated methotrexate release coupled with ROS scavenging in an injectable hydrogel for rheumatoid arthritis therapy. J. Control. Release 2024, 375, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Gao, R.; Liu, Y.; Fu, L.; Zhou, J.; Li, L. Stimulus-Responsive Hydrogels as Drug Delivery Systems for Inflammation Targeted Therapy. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2306152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, Y.; Hussain, Z.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Ullah, I.; Lu, Z.; Osaka, A.; Lin, J.; et al. An Injectable Hydrogel Composing Anti-Inflammatory and Osteogenic Therapy toward Bone Erosions Microenvironment Remodeling in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, e2304668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ma, J.; Song, W.; Zhao, C. An injectable hydrogel to disrupt neutrophil extracellular traps for treating rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Deliv. 2023, 30, 2173332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Yan, L.; Xu, T.; Zhang, K.; Lu, X.; Xie, C.; Fu, W. Injectable bioadhesive hydrogel as a local nanomedicine depot for targeted regulation of inflammation and ferroptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Biomaterials 2024, 311, 122706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Seo, J.; Kim, Y.H.; Ju, H.J.; Kim, S.; Ji, Y.B.; Lee, H.B.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, S.; Kim, M.S. Enhanced intra-articular therapy for rheumatoid arthritis using click-crosslinked hyaluronic acid hydrogels loaded with toll-like receptor antagonizing peptides. Acta Biomater. 2023, 172, 188–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Park, S.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, B.K.; Lee, B.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.S. An injectable, electrostatically interacting drug depot for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomaterials 2018, 154, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Du, Y.; Lv, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhuang, P.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Cui, W.; Chen, W. Injectable Amphipathic Artesunate Prodrug-Hydrogel Microsphere as Gene/Drug Nano-Microplex for Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2206261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Song, S.; Wang, D.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Ren, X.; Zhao, Y. Nanozyme-reinforced hydrogel as a H2O2-driven oxygenerator for enhancing prosthetic interface osseointegration in rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Zhao, J.; Tao, B.; Yang, Y.; Duan, Q.; Gao, P.; He, T.; Liu, S.; Feng, Q.; Zhao, P.; et al. Regulation of rheumatoid arthritis microenvironment via a self-healing injectable hydrogel for improved inflammation elimination and bone repair. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 36, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wu, X.; Liu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, L. ECM-Inspired Hydrogels with ADSCs Encapsulation for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2206253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Qi, W.; Xue, Z.; Wu, K.; Jiang, L.; Wu, C.; Huang, Z.; Li, Q.; Lu, Y. A multifunctional supramolecular hydrogel that rapidly binds TNF-α for efficient reduction of synovial inflammation and cartilage destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 147125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Hao, W.; Yao, J.; Zhu, T.; Sun, M.; Lu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Loh, J.L.C. Anti-inflammatory supramolecular hydrogel loaded chicoric acid based on graphene oxide modified hyaluronic acid and polyethylene glycol for rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 287, 138610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Yang, P.; Guo, W.; Lu, P.; Huang, C.; Cai, Z.; Jiang, X.; Yang, G.; Du, Y.; Zhao, F. Supramolecular Hydrogel Dexamethasone-Diclofenac for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S.; Park, S.J.; Yang, J.A.; Jeon, J.H.; Bhang, S.H.; Kim, B.S.; Hahn, S.K. Injectable hyaluronic acid-tyramine hydrogels for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Liu, R.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, D.; Yu, L.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, Z.; Hua, Z.; et al. Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels Hybridized with Au-Triptolide Nanoparticles for Intraarticular Targeted Multi-Therapy of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 849101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Tao, C.; Sun, L.; Qi, S.; Le, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J. In Situ Forming Injectable Hydrogel for Encapsulation of Nanoiguratimod and Sustained Release of Therapeutics. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 8725–8738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, K.; Tang, X.; Shen, Z.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, S.; Che, N.; Tian, J.; Ling, J.; Yang, Y. Exosome inspired photo-triggered gelation hydrogel composite on modulating immune pathogenesis for treating rheumatoid arthritis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, C.; Wei, Y.; Yan, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, W.; Sun, L.; Zhang, T. Bone-derived MSCs encapsulated in alginate hydrogel prevent collagen-induced arthritis in mice through the activation of adenosine A(2A/2B) receptors in tolerogenic dendritic cells. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2778–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Han, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Sheng, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Tan, H.; Bai, L.; et al. Polymer-modified DNA hydrogels for living mitochondria and nanozyme delivery in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Bioact. Mater. 2025, 47, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gao, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Feng, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, B.; Lin, Q. Infliximab-based self-healing hydrogel composite scaffold enhances stem cell survival, engraftment, and function in rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Acta Biomater. 2021, 121, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.-W.; Hsiao, Y.-C.; Jheng, P.-R.; Chen, C.-H.; Manga, Y.B.; Lekha, R.; Chao, K.-M.; Ho, Y.-C.; Chuang, E.-Y. Strontium ranelate-laden near-infrared photothermal-inspired methylcellulose hydrogel for arthritis treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 123, 111980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Jori, C.; Kanika; Kumar, A.; Vyawahare, A.; Kumar, J.; Kumar, B.; Ahmad, A.; Fareed, M.; Ali, N.; et al. A bioactive and biodegradable vitamin C stearate-based injectable hydrogel alleviates experimental inflammatory arthritis. Biomater. Sci. 2024, 12, 3389–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Yan, J.; Levy, S.; Bhagchandani, S.; Slaughter, K.V.; Sherman, N.E.; Amirault, J.; Wang, Y.; Riegel, L.; He, X.; et al. Towards an arthritis flare-responsive drug delivery system. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Yin, C.; Ye, X.; Chen, Q.; Wu, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Duan, C.; Lu, A.; et al. A Metabolic Driven Bio-Responsive Hydrogel Loading Psoralen for Therapy of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Small 2023, 19, e2207319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
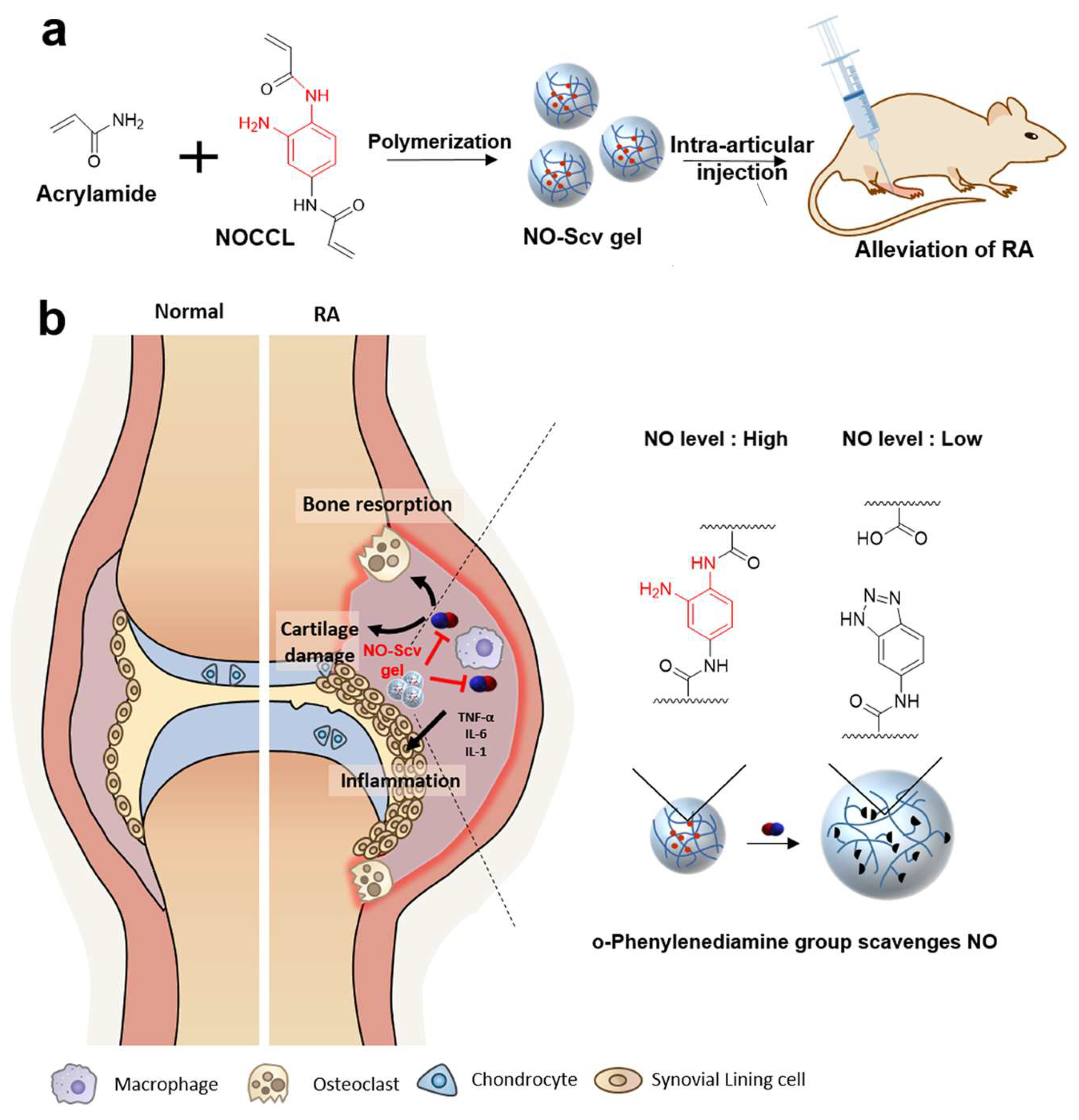
- Kim, T.; Suh, J.; Kim, W.J. Polymeric Aggregate-Embodied Hybrid Nitric-Oxide-Scavenging and Sequential Drug-Releasing Hydrogel for Combinatorial Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2008793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, J.; Lee, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Park, D.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; Kim, W.J. Nitric Oxide-Scavenging Nanogel for Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 6716–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Deng, D.; Li, C.; Huang, G.; Zhang, W.; Liang, T.; Liang, R.; Liang, M.; Su, Y.; Lin, C.; et al. The combination of modified acupuncture needle and melittin hydrogel as a novel therapeutic approach for rheumatoid arthritis treatment. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Fei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yue, O.; Wang, X.; Jiang, H. Locally Injectable, ROS-Scavenging, and ROS-/pH-Responsive Polymeric-Micelles-Embedded Hydrogels for Precise Minimally Invasive and Long-Lasting Rheumatoid Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, e2403579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.S.; Xu, B.X.; Fan, K.J.; Li, Y.W.; Wu, J.; Wang, T.Y. Dexamethasone-Loaded Thermosensitive Hydrogel Suppresses Inflammation and Pain in Collagen-Induced Arthritis Rats. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 4101–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Dai, C.; Li, Y.; Yin, Y.; Gong, L.; Machuki, J.O.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, S.; Guo, K.; Gao, F. PRP-chitosan thermoresponsive hydrogel combined with black phosphorus nanosheets as injectable biomaterial for biotherapy and phototherapy treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomaterials 2020, 239, 119851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Choi, S.; Kim, M.S. Intra-articular hydrogel formulation prolongs the in vivo stability of Toll-like receptor antagonistic peptides for rheumatoid arthritis treatment. J. Control. Release 2024, 372, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Qin, J.; Ma, X.; Wang, Q.; Wu, W.; Huang, H.; Cai, L. Chitosan-based self-healing thermosensitive hydrogel loaded with siHMGB1 for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis via macrophage repolarization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 137102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Hua, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y. Fabrication of a novel macrophage-targeted biomimetic delivery composite hydrogel with multiple-sensitive properties for tri-modal combination therapy of rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 665, 124708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makled, S.; Abbas, H.; Ali, M.E.; Zewail, M. Melatonin hyalurosomes in collagen thermosensitive gel as a potential repurposing approach for rheumatoid arthritis management via the intra-articular route. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 661, 124449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, R.; Yin, D. Imperative and effective reversion of synovial hyperplasia and cartilage destruction in rheumatoid arthritis through multiple synergistic effects of O2 and Ca2+. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 114, 111058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Gao, H.; Ding, J.; He, Z. Intraarticular Injection of Infliximab-Loaded Thermosensitive Hydrogel Alleviates Pain and Protects Cartilage in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 3315–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, C.; Fang, Z.; Bahatibieke, A.; Fan, D.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Xie, Y.; Qiao, K.; Xiao, C.; et al. A dual dynamically cross-linked hydrogel promotes rheumatoid arthritis repair through ROS initiative regulation and microenvironment modulation-independent triptolide release. Mater. Today Bio 2024, 26, 101042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahatibieke, A.; Zhao, J.; Fan, D.; Zhou, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, T.; Fang, Z.; Xie, Y.; et al. Sea-Island Micelle Structured Hydrogel Scaffold: A Dual-Action Approach to Combat Cartilage Damage under RA Conditions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 2911–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, N.; Guo, X.; Sun, R.; Liu, H.; Tang, L.; Gou, J.; Yin, T.; He, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X. Intra-articular injection of indomethacin-methotrexate in situ hydrogel for the synergistic treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 993–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, W.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, L.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; et al. In Situ-Activated Phospholipid-Mimic Artemisinin Prodrug via Injectable Hydrogel Nano/Microsphere for Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy. Research 2022, 2022, 0003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Liu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, L. Hierarchical Microcarriers Loaded with Peptide Dendrimer-Grafted Methotrexate for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment. Small Sci. 2024, 4, 2300097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-ElNour, M.; Soliman, M.E.; Skouras, A.; Casettari, L.; Geneidi, A.S.; Ishak, R.A.H. Microparticles-in-Thermoresponsive/Bioadhesive Hydrogels as a Novel Integrated Platform for Effective Intra-articular Delivery of Triamcinolone Acetonide. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 1963–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, K.; Zhang, S.; Chen, B.; Liu, H.; Tong, F.; Peng, F.; Tu, Y.; et al. Magnesium-Based Micromotors as Hydrogen Generators for Precise Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 1982–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Zhao, K.; Xu, L.; Cui, J.; Ruan, L.; Bei, S.; Cao, J.; Qi, X.; Shen, S. Macrophages-mediated delivery of protoporphyrin for sonodynamic therapy of rheumatoid arthritis. Ultrason. Sonochem 2024, 107, 106928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Song, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, M.; Lu, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, N. Mutual-reinforcing sonodynamic therapy against Rheumatoid Arthritis based on sparfloxacin sonosensitizer doped concave-cubic rhodium nanozyme. Biomaterials 2021, 276, 121063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshabrawy, H.A.; Abo Dena, A.S.; El-Sherbiny, I.M. Triple-layered platform utilizing electrospun nanofibers and 3D-printed sodium alginate-based hydrogel for effective topical treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, J.R.; Adebowale, K.; Zhao, Z.; Mitragotri, S. Hydrogels in the clinic: An update. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2024, 9, e10680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, R.; Furst, D.E. Safety of repository corticotropin injection as an adjunctive therapy for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2020, 19, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

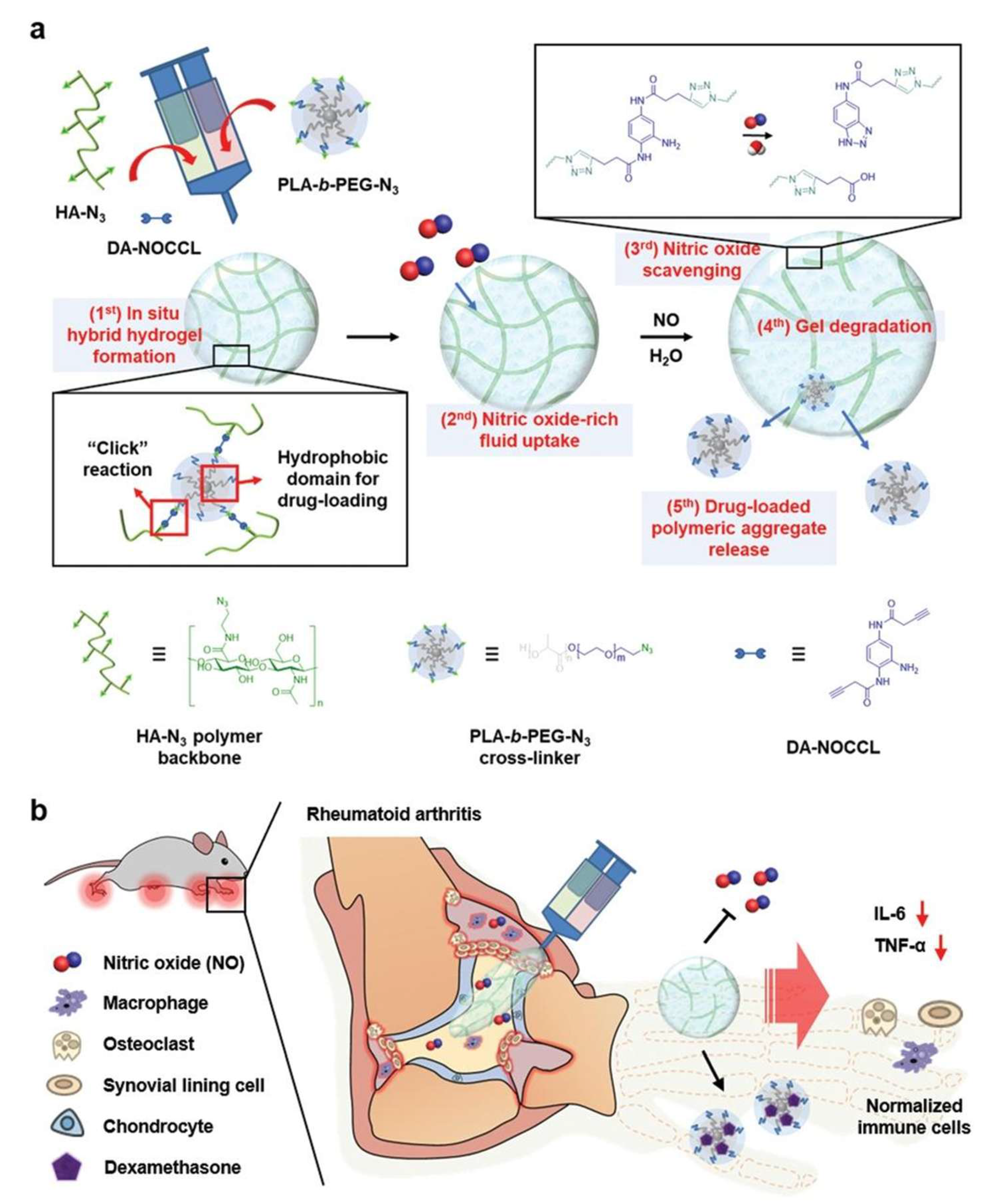

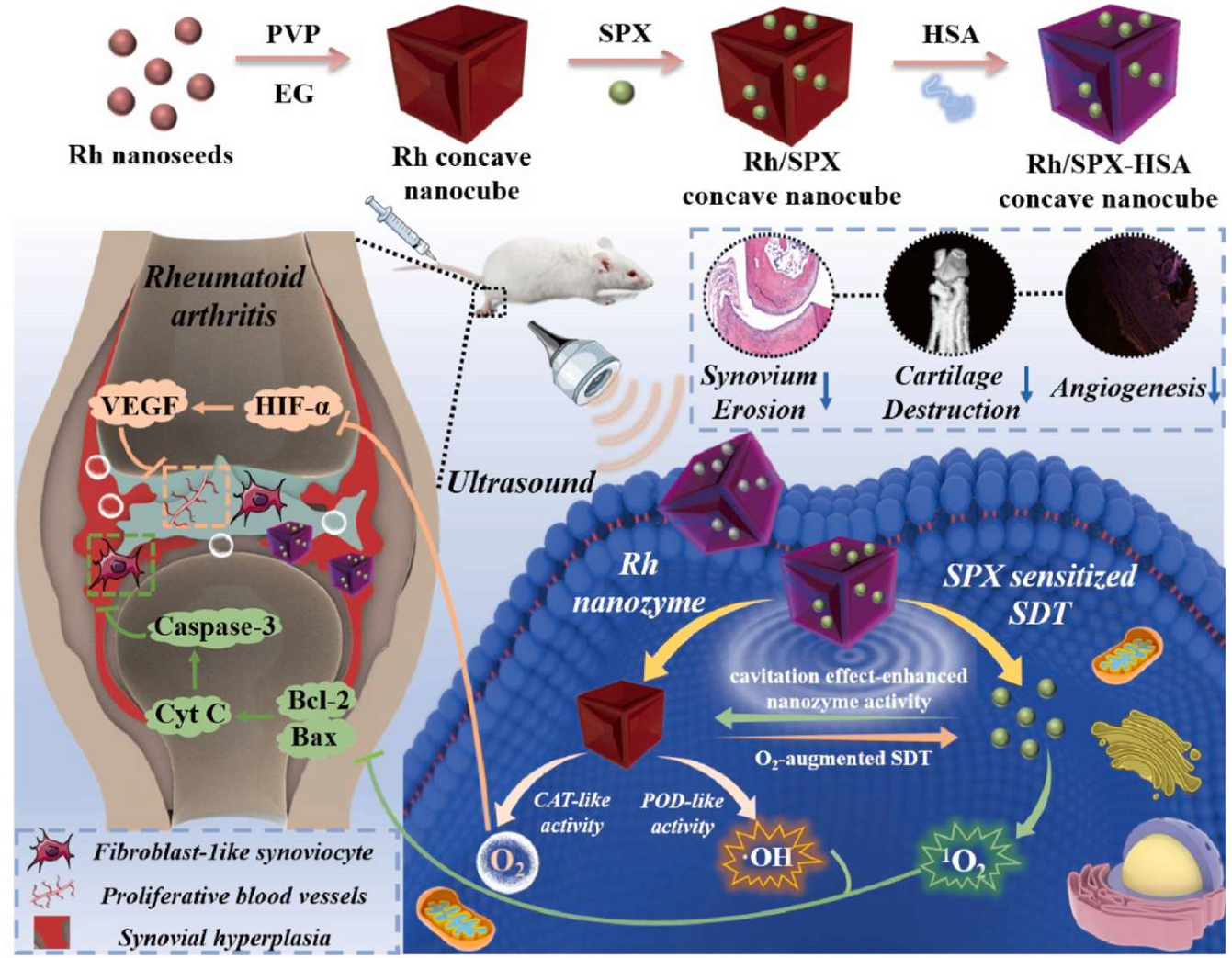

| Hydrogel Material(s) | Hydrogel Formation Mechanism | Bioactive Agent(s) | Inflammatory Arthritis Model(s) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collagen and HA | Electrostatic interactions | BP-HA/Zn-nrBCP | CIA rabbit model; RA femur defect model | [134] |
| DNase-OHA/CMCS | Schiff base reaction | MTX/DNase I | CIA mouse model | [135] |
| Gelatin/PEGDA | Phase separation | Fol-PDA@Leonurine NPs | CIA rat model | [136] |
| Click-HA | Click chemistry | TLR2-antag-Pep2 | CIA rat model | [137] |
| mPEG-(PCL-ran-PLLA)-COOH | Electrostatic interactions | MINO/SSZ | CIA rat model | [138] |
| HAMA | UV-initiated crosslinking | Gene/ART-NMPs | modified AIA rat model | [139] |
| CS/β-GP | Electrostatic/H-bond interactions | DCF-Alg-MS | AIA rabbit model | [120] |
| HA-Hyd/HA-Ald | Schiff base reaction | MnCoO nanozyme | OVA/Freund’s adjuvant-induced RA rabbit model | [140] |
| HA-SH/DNRS copolymer | Click chemistry | MTX/H2S | CIA rat model | [141] |
| β-CD-HP/Ada-HA | Host–guest interactions | Anti-IL17A-Nb | CIA mouse model | [117] |
| Dendritic PLL/HA | Schiff base reaction | ADSCs | CIA mouse model | [142] |
| Nap-DFDFDEGPIRRSDS | Non-covalent interactions | Met@hCuS-NPs | AIA rat model | [143] |
| β-CD-GO-HA/Ada-4armPEG | Non-covalent interactions | Chicoric acid | AIA rat model | [144] |
| Dex/DCF/CaCl2 | Ionic coordination | DMT/DCF | AIA rat model | [145] |
| HA-Tyr | Radical crosslinking | DMT | CIA rat model | [146] |
| HA-AAc/(SH-PEG-SH) | Michael addition | Iguratimod | CIA mouse model | [147] |
| Silk fibroin | Photo-crosslinking | OE-MSC-Exos | CIA rat model | [148] |
| Alginate/CaCl2 | Ionic crosslinking | BMSCs | CIA mouse model | [149] |
| CS/β-GP | H-bonding/electrostatics | LEN/HSP | CIA mouse model | [150] |
| DNA/PAAm matrix | Watson–Crick base pairing | PBzyme/Mito | CIA rat model | [129] |
| HA-Hyd/HA-Ald | Schiff base reaction | Infliximab | CIA mouse model | [151] |
| Methylcellulose | Hydrophobic interactions | Sr-ranelate | AIA rabbit model | [152] |
| Collagen and HA | Electrostatic interactions | BP-HA/Zn-nrBCP | Zymosan-induced RA rat model | [153] |
| Hydrogel Material(s) | Hydrogel Formation Mechanism | Internal Stimulus | Bioactive Agent(s) | Inflammatory Arthritis Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9AA-SA-AA | Hydrophobic interactions | MMPs | SA-AA/9AA amphiphiles | CIA rat model | [154] |
| TGMS | Hydrophobic interactions | MMPs | Triamcinolone acetonide | K/BxN mouse model | [155] |
| Gelatin/Soy lecithin | Chemical crosslinking | MMPs | MTX | AIA rat model | [122] |
| TGMS | Hydrophobic interactions | MMPs | Psoralen/CaO2 | CIA rat model | [156] |
| PEG-PLA-N3/HA-N3 | Click chemistry | NO | DMT | CIA mouse model | [157] |
| AAm/NO-cleavable linker | Polymerization | NO | AAm/linker | CIA mouse model | [158] |
| DHP/AAm | Radical polymerization | NO | MTX | AIA rat model | [131] |
| IOK peptide | Physical interactions | pH | MTX/Bi nanosheets | AIA rat model | [121] |
| CS/β-GP/HA | H-bonding/hydrophobic | pH | Melittin | CIA mouse model | [159] |
| Nap-FFKRGH | π-π stacking | pH | siRNA/MTX-PEI/bismuthene | CIA rat model | [130] |
| HA/PEG | Bioorthogonal chemistry | ROS | MPDA/MTX | CIA rat model | [132] |
| DA-HA/SCS | Schiff base | ROS/pH | MTX | CIA rat model | [160] |
| PBA-PLL/Odex/SeNPs | Multiple bonding interactions | ROS/pH | SeNPs | CIA rat model | [127] |
| CS/Gly/borax | Intermolecular interactions | Temperature | DMT | CIA rat model | [161] |
| PRP-CS | Electrostatic/H-bonding | Temperature | BP nanosheets | CIA mouse model | [162] |
| HPMAm | Thermal phase transition | Temperature | DMT | AIA rat model | [128] |
| mPEG-PCL-PLLA | Hydrophobic interactions | Temperature | Phage peptides | CIA rat model | [163] |
| CS/β-GP/OCS | Schiff base | Temperature | Apoferritin/siHMGB1 | CIA rat model | [164] |
| CS/β-GP | Non-covalent interactions | Temperature | Triptolide | CIA mouse model | [110] |
| PF127 | Thermogelation | Temperature | ICG/CAT/SIN | CIA mouse model | [165] |
| Collagen/poloxamer | Sol–gel transition | Temperature | Melatonin | AIA rat model | [166] |
| CS/β-GP | Non-covalent interactions | Temperature | Crocin I/Dex-liposomes | AIA rat model | [160] |
| PLGA-PEG-PLGA | Thermogelation | Temperature | CaO2 | CIA rat model | [167] |
| PF127/HA/PGA | Hydrophobic interactions | Temperature | Infliximab | AIA rabbit model | [168] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, M.-H.; Yan, Y.; Chen, B.; Gong, L.; Chen, L.; Feng, J.; Han, M.; Liu, C.; Xiao, C.; Jin, M.; et al. Advances in Intra-Articular Injection Hydrogel Drug Delivery Systems in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091118
Song M-H, Yan Y, Chen B, Gong L, Chen L, Feng J, Han M, Liu C, Xiao C, Jin M, et al. Advances in Intra-Articular Injection Hydrogel Drug Delivery Systems in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(9):1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091118
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Mong-Hsiu, Yuxuan Yan, Bohan Chen, Liming Gong, Liqing Chen, Jing Feng, Mingfeng Han, Chenfei Liu, Congcong Xiao, Mingji Jin, and et al. 2025. "Advances in Intra-Articular Injection Hydrogel Drug Delivery Systems in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 9: 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091118
APA StyleSong, M.-H., Yan, Y., Chen, B., Gong, L., Chen, L., Feng, J., Han, M., Liu, C., Xiao, C., Jin, M., Gao, Z., & Huang, W. (2025). Advances in Intra-Articular Injection Hydrogel Drug Delivery Systems in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Pharmaceutics, 17(9), 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091118









