Killer Peptide-Containing Polyelectrolytic Nanocomplexes to Fight Toxoplasma gondii Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Production of KP Loaded Nanoparticles by Microfluidics
2.3. Characterization of NPs by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Measurement of Z-Potential
2.4. Determination of Nanoparticles Composition and Encapsulation Efficiency
2.5. Stability of Nanoparticles and Encapsulated KP
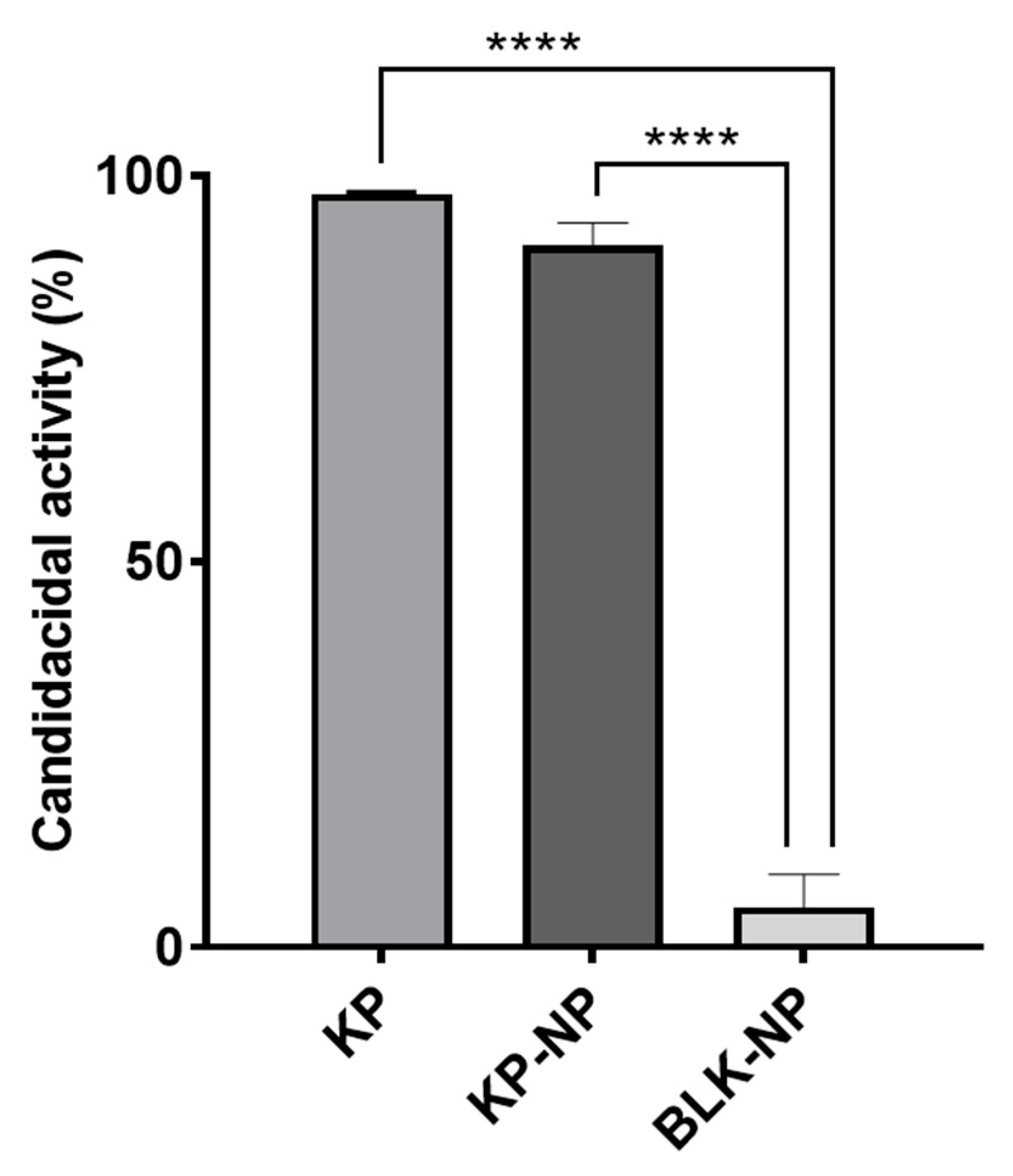
2.6. In Vitro Testing on Candida Albicans
2.7. In Vitro Toxicity and Efficacy Tests on the Target Parasite Toxoplasma Gondii and Infected HFF Cells
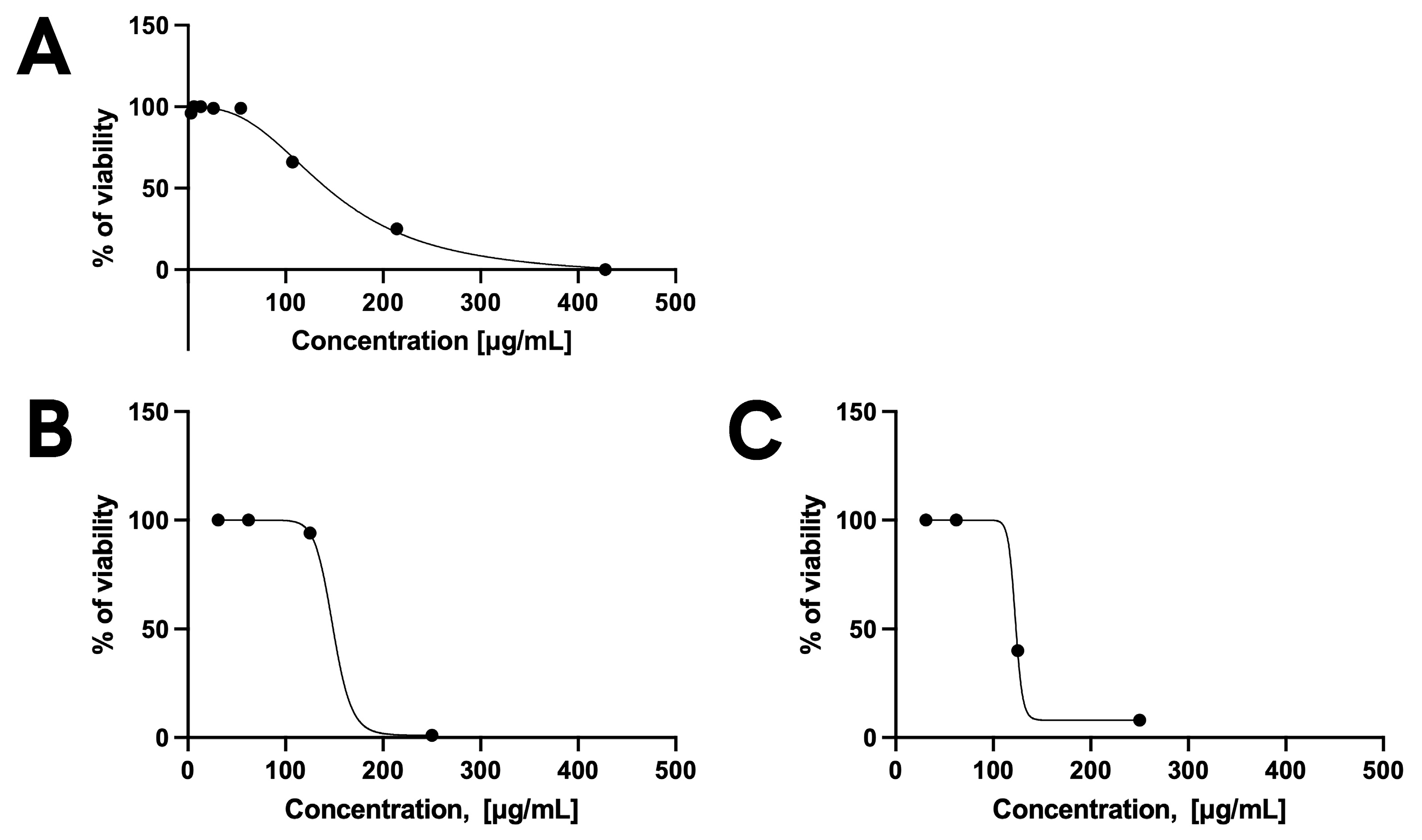
2.7.1. Resazurin Reduction Assay (Alamar Blue)
2.7.2. Toxo-β-Gal Assay
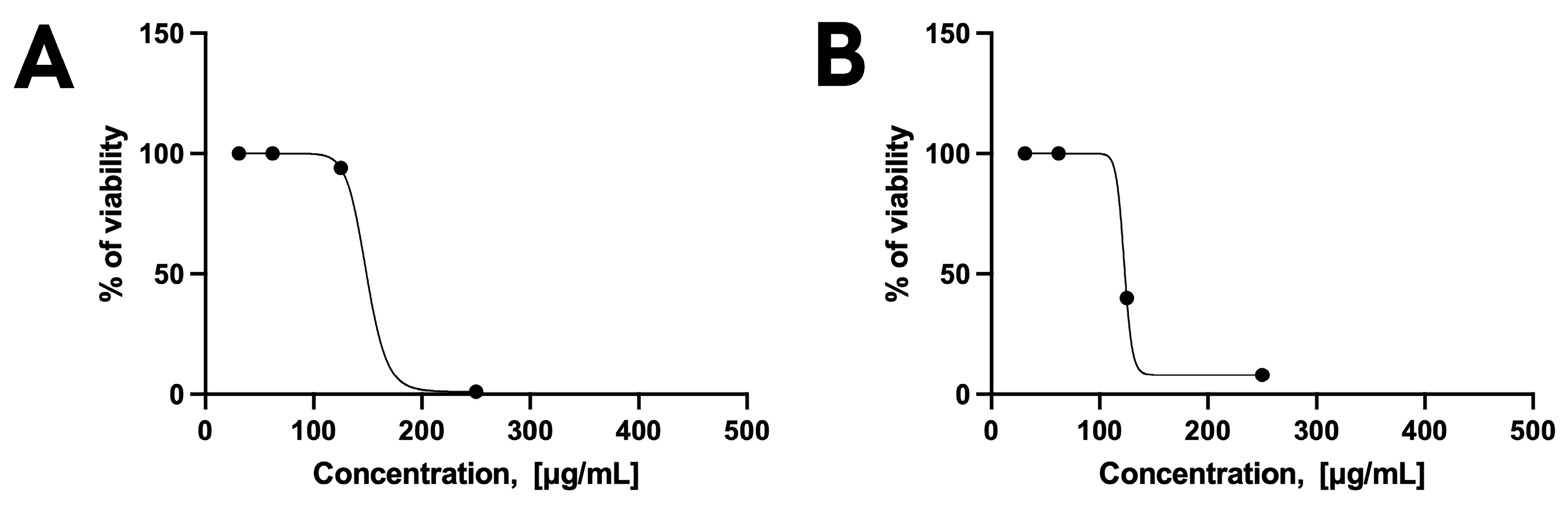
2.7.3. In Vitro Testing on the Free Form of the Parasite (Tachyzoites)
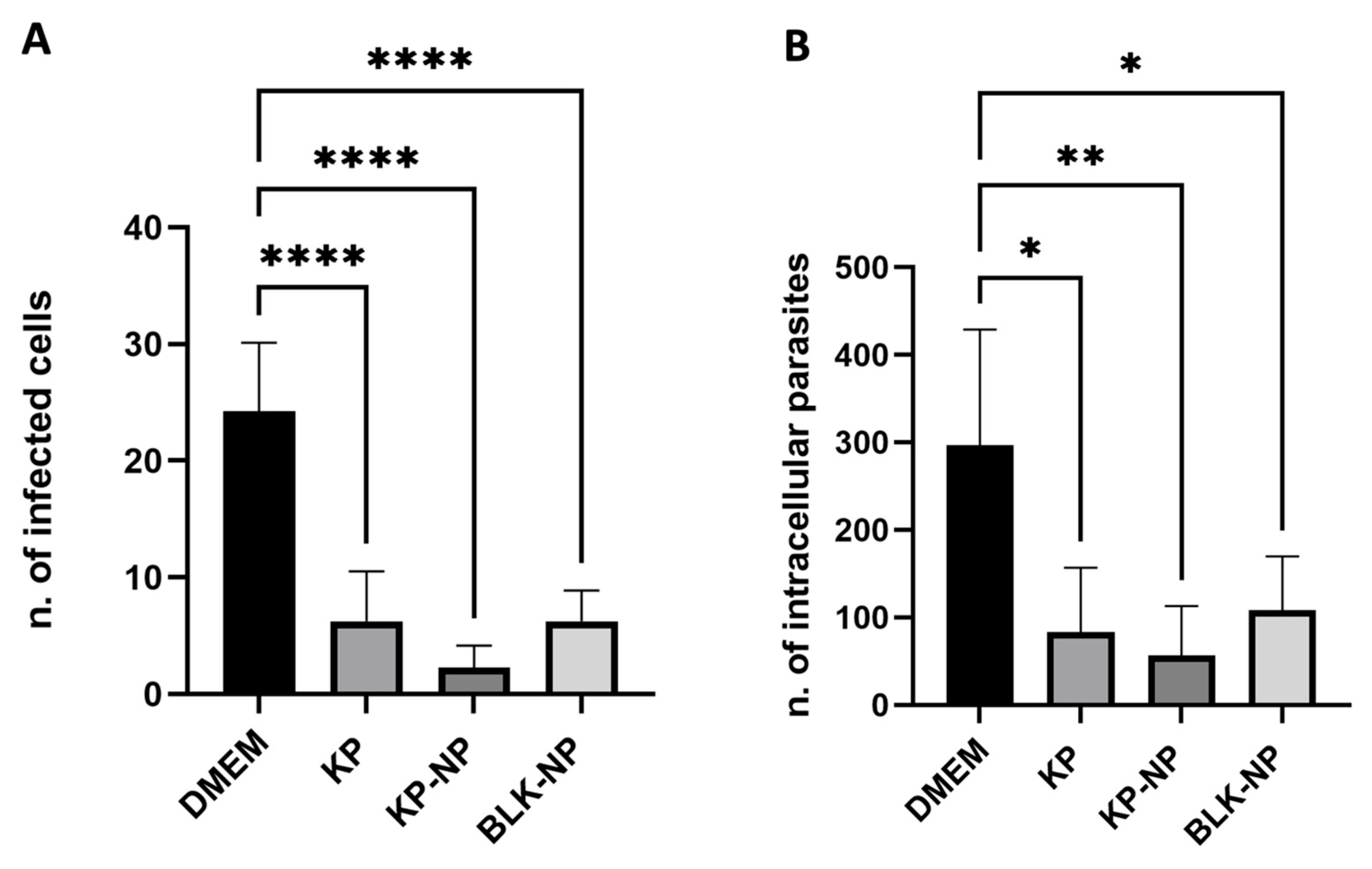
- Number of infected cells;
- Number of intracellular parasites.
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. KP Solubility in Different Solvents
3.2. Production, Characterization, and Stability of NPs
3.3. Tests on Candida Albicans Model
3.4. Tests on T. gondii
3.4.1. Toxicity and Efficacy on HFF Cells and T. gondii
3.4.2. Efficacy on Free Tachyzoites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Vismarra, A.; Kramer, L.; Genchi, M. Toxoplasmosis. In Encyclopedia of Infection and Immunity; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 2, pp. 724–740. ISBN 9780128187319. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega-Barria, E.; Boothroyd, J.C. A Toxoplasma Lectin-like Activity Specific for Sulfated Polysaccharides Is Involved in Host Cell Infection. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzouz, N.; Kamena, F.; Laurino, P.; Kikkeri, R.; Mercier, C.; Cesbron-Delauw, M.F.; Dubremetz, J.F.; De Cola, L.; Seeberger, P.H. Toxoplasma Gondii Secretory Proteins Bind to Sulfated Heparin Structures. Glycobiology 2013, 23, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Murata, F.H.A.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Villena, I. Congenital Toxoplasmosis in Humans: An Update of Worldwide Rate of Congenital Infections. Parasitology 2021, 148, 1406–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima Bessa, G.; de Almeida Vitor, R.W.; dos Santos Martins-Duarte, E. Toxoplasma Gondii in South America: A Differentiated Pattern of Spread, Population Structure and Clinical Manifestations. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 3065–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Medeiros Brito, R.M.; de Lima Bessa, G.; Bastilho, A.L.; Dantas-Torres, F.; de Andrade-Neto, V.F.; Bueno, L.L.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Magalhães, L.M.D. Genetic Diversity of Toxoplasma Gondii in South America: Occurrence, Immunity, and Fate of Infection. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, F.; Händel, U.; Angenstein, F.; Goldschmidt, J.; Kreutzmann, P.; Lison, H.; Fischer, K.D.; Scheich, H.; Wetzel, W.; Schlüter, D.; et al. Toxoplasma Gondii Actively Inhibits Neuronal Function in Chronically Infected Mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halonen, S.K.; Weiss, L.M. Toxoplasmosis. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 114, 125–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virus, M.A.; Ehrhorn, E.G.; Lui, L.A.M.; Davis, P.H. Neurological and Neurobehavioral Disorders Associated with Toxoplasma Gondii Infection in Humans. J. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 2021, 6634807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunay, I.R.; Gajurel, K.; Dhakal, R.; Liesenfeld, O.; Montoya, J.G. Treatment of Toxoplasmosis: Historical Perspective, Animal Models, and Current Clinical Practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00057-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.C.; Goulart, C.; Hayward, J.A.; Kupz, A.; Miller, C.M.; van Dooren, G.G. Control of Human Toxoplasmosis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2021, 51, 95–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polonelli, L.; Magliani, W.; Conti, S.; Bracci, L.; Lozzi, L.; Neri, P.; Adriani, D.; De Bernardis, F.; Cassone, A. Therapeutic Activity of an Engineered Synthetic Killer Antiidiotypic Antibody Fragment against Experimental Mucosal and Systemic Candidiasis. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 6205–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovati, L.; Santinoli, C.; Mangia, C.; Vismarra, A.; Belletti, S.; D’Adda, T.; Fumarola, C.; Ciociola, T.; Bacci, C.; Magliani, W.; et al. Novel Activity of a Synthetic Decapeptide against Toxoplasma Gondii Tachyzoites. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertinhez, T.A.; Conti, S.; Ferrari, E.; Magliani, W.; Spisni, A.; Polonelli, L. Reversible Self-Assembly: A Key Feature for a New Class of Autodelivering Therapeutic Peptides. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 6, 1036–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, L.; Martelli, P.; Saleri, R.; De Angelis, E.; Ferrarini, G.; Cavalli, V.; Passeri, B.; Bazzoli, G.; Ogno, G.; Magliani, W.; et al. An Engineered Anti-Idiotypic Antibody-Derived Killer Peptide (KP) Early Activates Swine Inflammatory Monocytes, CD3+CD16+ Natural Killer T Cells and CD4+CD8α+ Double Positive CD8β+ Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Associated with TNF-α and IFN-γ Secretion. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 72, 101523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unno, A.; Kitoh, K.; Takashima, Y. Up-Regulation of Hyaluronan Receptors in Toxoplasma Gondii-Infected Monocytic Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blass, S.L.; Puré, E.; Hunter, C.A. A Role for CD44 in the Production of IFN-Gamma and Immunopathology during Infection with Toxoplasma Gondii. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 5726–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Unno, A.; Baba, M.; Ohno, T.; Kitoh, K.; Takashima, Y. CD44 Mediated Hyaluronan Adhesion of Toxoplasma Gondii-Infected Leukocytes. Parasitol. Int. 2014, 63, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattheolabakis, G.; Milane, L.; Singh, A.; Amiji, M.M. Hyaluronic Acid Targeting of CD44 for Cancer Therapy: From Receptor Biology to Nanomedicine. J. Drug Target. 2015, 23, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchera, A.; Bettini, R. Polysaccharide Nanoparticles for Oral Controlled Drug Delivery: The Role of Drug-Polymer and Interpolymer Interactions. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzzarelli, R.A.A. Colorimetric Determination of Chitosan. Anal. Biochem. 1998, 260, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oueslati, N.; Leblanc, P.; Harscoat-Schiavo, C.; Rondags, E.; Meunier, S.; Kapel, R.; Marc, I. CTAB Turbidimetric Method for Assaying Hyaluronic Acid in Complex Environments and under Cross-Linked Form. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliani, W.; Conti, S.; Ciociola, T.; Giovati, L.; Zanello, P.P.; Pertinhez, T.; Spisni, A.; Polonelli, L. Killer Peptide: A Novel Paradigm of Antimicrobial, Antiviral and Immunomodulatory Auto-Delivering Drugs. Future Med. Chem. 2011, 3, 1209–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonelli, L.; Ciociola, T.; Sperindè, M.; Giovati, L.; D’Adda, T.; Galati, S.; Travassos, L.R.; Magliani, W.; Conti, S. Fungicidal Activity of Peptides Encoded by Immunoglobulin Genes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desiatkina, O.; Boubaker, G.; Anghel, N.; Amdouni, Y.; Hemphill, A.; Furrer, J.; Păunescu, E. Synthesis, Photophysical Properties and Biological Evaluation of New Conjugates BODIPY: Dinuclear Trithiolato-Bridged Ruthenium(II)-Arene Complexes. ChemBioChem 2022, 23, e202200536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Păunescu, E.; Boubaker, G.; Desiatkina, O.; Anghel, N.; Amdouni, Y.; Hemphill, A.; Furrer, J. The Quest of the Best—A SAR Study of Trithiolato-Bridged Dinuclear Ruthenium(II)-Arene Compounds Presenting Antiparasitic Properties. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 222, 113610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barna, F.; Debache, K.; Vock, C.A.; Küster, T.; Hemphill, A. In Vitro Effects of Novel Ruthenium Complexes in Neospora Caninum and Toxoplasma Gondii Tachyzoites. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5747–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Gao, Y.; N’da, D.D.; Xuan, X. In Vitro Anti-Toxoplasma Gondii Efficacy of Synthesised Benzyltriazole Derivatives. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2021, 88, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.; Viscardi, M.; Sgroi, G.; D’Alessio, N.D.; Veneziano, V.; Pellicano, R.; Brunetti, R.; Fusco, G. Real-Time PCR Detection of Toxoplasma Gondii in Tissue Samples of Wild Boars (Sus Scrofa) from Southern Italy Reveals High Prevalence and Parasite Load. Parasites. Vectors 2019, 12, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copy Number Calculator/Technology Networks. Available online: https://www.technologynetworks.com/tn/tools/copynumbercalculator (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Knudson, W.; Chow, G.; Knudson, C.B. CD44-Mediated Uptake and Degradation of Hyaluronan. Matrix Biol. 2002, 21, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, E.; Greco, A.; Riva, F.; Dorati, R.; Conti, B.; Modena, T.; Genta, I. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Nanoparticles for Protein Delivery: Systematic Examination of Microfluidic Production Conditions. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, E.; Riva, F.; Dorati, R.; Greco, A.; Ricci, S.; Pisani, S.; Patrini, M.; Modena, T.; Conti, B.; Genta, I. On-Chip Synthesis of Hyaluronic Acid-Based Nanoparticles for Selective Inhibition of CD44+ Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Proliferation. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.L.; Deng, F.S.; Chuang, C.Y.; Lin, C.H. Antimicrobial Actions and Applications of Chitosan. Polymers 2021, 13, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagras, N.A.-E.; Allam, A.F.; Farag, H.F.; Osman, M.M.; Shalaby, T.I.; Fawzy Hussein Mogahed, N.M.; Tolba, M.M.; Shehab, A.Y. Successful Treatment of Acute Experimental Toxoplasmosis by Spiramycin-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles. Exp. Parasitol. 2019, 204, 107717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmi, T.; Rahimi Esboei, B.; Sadeghi, F.; Zamani, Z.; Didehdar, M.; Fakhar, M.; Chabra, A.; Hajialiani, F.; Namazi, M.J.; Tabatabaie, F. In Vitro Antiprotozoal Effects of Nano-Chitosan on Plasmodium Falciparum, Giardia Lamblia and Trichomonas Vaginalis. Acta Parasitol. 2021, 66, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, N.S.; Araújo, N.K.; Daniele-Silva, A.; de Freitas Oliveira, J.W.; de Medeiros, J.M.; Araújo, R.M.; Ferreira, L.D.S.; Rocha, H.A.O.; Silva-Junior, A.A.; Silva, M.S.; et al. Antimicrobial Activity of Chitosan Oligosaccharides with Special Attention to Antiparasitic Potential. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wodecka, B.; Albogami, B. Evaluation of the Antiparasitic, Antihepatotoxicity, and Antioxidant Efficacy of Quercetin and Chitosan, Either Alone or in Combination, against Infection Induced by Giardia Lamblia in Male Rats. Life 2023, 13, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teimouri, A.; Azami, S.J.; Keshavarz, H.; Esmaeili, F.; Alimi, R.; Mavi, S.A.; Shojaee, S. Anti-Toxoplasma Activity of Various Molecular Weights and Concentrations of Chitosan Nanoparticles on Tachyzoites of RH Strain. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villavedra, M.; Battistoni, J.J.; Rossi, S.; Carol, H.; Nieto, A. Avidity Analysis of the Human Immune Response to a Chitin Binding Protein of Toxoplasma Gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 2001, 31, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Fernandez, A.; Avlonitis, N.; Vande Velde, G.; Bradley, M.; Read, N.D.; Vendrell, M. Searching for the Optimal Fluorophore to Label Antimicrobial Peptides. ACS Comb. Sci. 2016, 18, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciociola, T.; Magliani, W.; De Simone, T.; Pertinhez, T.A.; Conti, S.; Cozza, G.; Marin, O.; Giovati, L. In Silico Predicted Antifungal Peptides: In Vitro and In Vivo Anti-Candida Activity. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, A.; Ricchi, F.; Giovati, L.; Conti, S.; Ciociola, T.; Cermelli, C. Anti-Herpetic Activity of Killer Peptide (KP): An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etewa, S.E.; El-Maaty, D.A.A.; Hamza, R.S.; Metwaly, A.S.; Sarhan, M.H.; Abdel-Rahman, S.A.; Fathy, G.M.; El-Shafey, M.A. Assessment of Spiramycin-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Treatment on Acute and Chronic Toxoplasmosis in Mice. J. Parasit. Dis. 2017, 42, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubaker, G.; Bernal, A.; Vigneswaran, A.; Imhof, D.; de Sousa, M.C.F.; Hänggeli, K.P.A.; Haudenschild, N.; Furrer, J.; Păunescu, E.; Desiatkina, O.; et al. In Vitro and in Vivo Activities of a Trithiolato-DiRuthenium Complex Conjugated with Sulfadoxine against the Apicomplexan Parasite Toxoplasma Gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2024, 25, 100544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semeraro, M.; Boubaker, G.; Scaccaglia, M.; Imhof, D.; de Sousa, M.C.F.; Hänggeli, K.P.A.; Löwe, A.; Genchi, M.; Kramer, L.H.; Vismarra, A.; et al. In Vivo Safety and Efficacy of Thiosemicarbazones in Experimental Mice Infected with Toxoplasma Gondii Oocysts. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.R.; Pechere, J.C.F. In Vitro Effects of Four Macrolides (Roxithromycin, Spiramycin, Azithromycin [CP-62,993], and A-56268) on Toxoplasma Gondii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1988, 32, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaafar, M.R.; Mady, R.F.; Diab, R.G.; Shalaby, T.I. Chitosan and Silver Nanoparticles: Promising Anti-Toxoplasma Agents. Exp. Parasitol. 2014, 143, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Formulation | Particle Size (nm) | Z-Potential (mV) | KP EE (%w/w) | Chitosan Involved (% w/w)) | HA Involved (% w/w) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BLK-NPs | 242 ± 81 | −13.1 ± 1.6 | - | 70 ± 6 | 90.1 ± 0.9 |
| KP-NPs | 392 ± 100 | −14.6 ± 1.03 | 76 ± 9 | 88 ± 4 | 94.6 ± 0.7 |
| Temperature (°C) | Day | Particle Size (nm) | KP Content (% w/w) | Chitosan Content (% w/w) | HA Content (% w/w) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 379 ± 36 | 63.0 ± 1.6 | 93.9 ± 6.3 | 93.7 ± 0.1 | |
| 4 | 2 | 357 ± 37 | 62.6 ± 1.1 | 84.9 ± 3.6 | 93.4 ± 1.7 |
| 3 | 384 ± 45 | 64.3 ± 4.1 | 85.7 ± 0.4 | 93.9 ± 1.0 | |
| 1 | 235 ± 29 | 63.4 ± 2.4 | 80.9 ± 8.4 | 90.1 ± 7.2 | |
| 25 | 2 | 564 ± 108 | 63.5 ± 2.5 | 93.3 ± 8.8 | 93.1 ± 0.4 |
| 3 | 359 ± 48 | 64.4 ± 4.2 | 93.2 ± 8.8 | 92.8 ± 0.4 | |
| 1 | 295 ± 34 | 63.1 ± 1.8 | 95.6 ± 3.8 | 95.7 ± 1.3 | |
| 37 | 2 | 320 ± 43 | 62.2 ± 0.8 | 90.3 ± 2.9 | 93.9 ± 1.5 |
| 3 | 302 ± 33 | 65.4 ± 6.4 | 79.9 ± 0.2 | 94.6 ± 0.3 |
| Treatment | Particle Size (nm) |
|---|---|
| Room temperature | 404 ± 107 |
| 60 °C | 734 ± 342 |
| 0.1 N HCl, 60 °C | 213 ± 70 |
| 0.1 N NaOH, 60 °C | 478 ± 157 |
| Sodium Hyaluronate Solution | Acetic Acid | Chitosan Solution | BLK-NPs | KP-NPs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viable HFFs | 95% (±0.06) -> nontoxic | 0% (±0.06) -> toxic | 0% (±0.50) -> toxic | 84% (±1.6) -> nontoxic | 93% (±2.29) -> nontoxic |
| Sodium Hyaluronate Solution | BLK-NPs | KP-NPs | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viable extracellular tachyzoites | 24% (±0.50) -> effective | 9% (±0.38) -> effective | 9% (±0.33) -> effective |
| Viable intracellular tachyzoites | 8% (±0.20) -> effective | 7% (±0.20) -> effective | 8% (±0.09) -> effective |
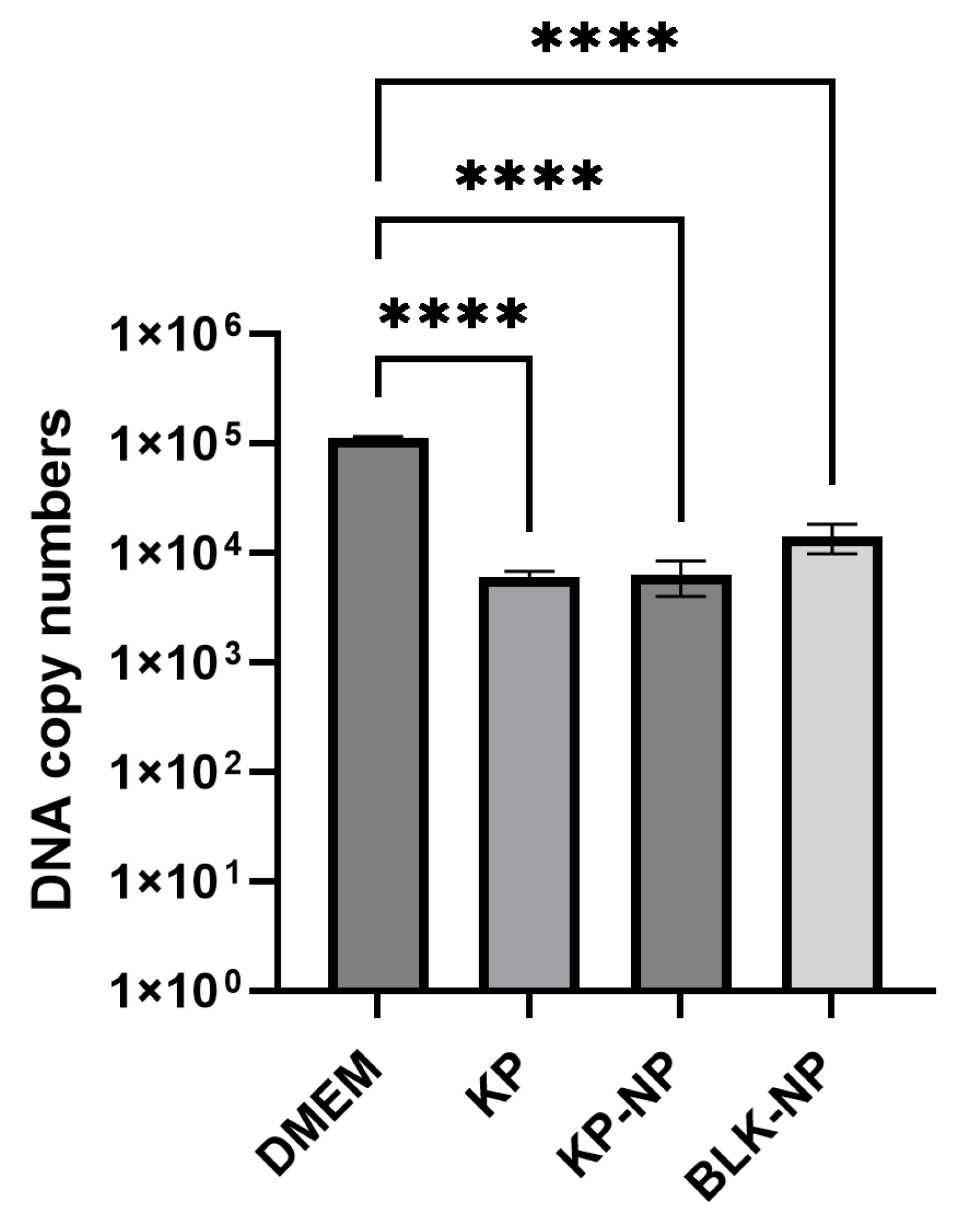
| Sample | Cq Mean | Cq Std. Dev | SQ | Log SQ | SQ Mean | SQ Std. Dev | ΔCq | FC | % Reduction Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMEM CTR | 24.37 | 0.688 | 48,677 | 4.687 | 111,373 | 4194.25 | |||
| KP | 28.17 | 0.177 | 5512 | 3.741 | 6041 | 747.92 | 3.80 | 0.072 | 94.6 |
| KP-NPs | 28.17 | 0.530 | 4668 | 3.669 | 6252 | 2240.29 | 3.79 | 0.072 | 94.4 |
| BLK-NPs | 26.99 | 0.22 | 16,977 | 4.230 | 14,022 | 4179.11 | 2.62 | 0.163 | 87.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bucella, A.; Semeraro, M.; Giovati, L.; Artesani, L.; Bettini, R.; Bianchera, A.; Vismarra, A. Killer Peptide-Containing Polyelectrolytic Nanocomplexes to Fight Toxoplasma gondii Infection. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081075
Bucella A, Semeraro M, Giovati L, Artesani L, Bettini R, Bianchera A, Vismarra A. Killer Peptide-Containing Polyelectrolytic Nanocomplexes to Fight Toxoplasma gondii Infection. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(8):1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081075
Chicago/Turabian StyleBucella, Arianna, Manuela Semeraro, Laura Giovati, Lorenza Artesani, Ruggero Bettini, Annalisa Bianchera, and Alice Vismarra. 2025. "Killer Peptide-Containing Polyelectrolytic Nanocomplexes to Fight Toxoplasma gondii Infection" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 8: 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081075
APA StyleBucella, A., Semeraro, M., Giovati, L., Artesani, L., Bettini, R., Bianchera, A., & Vismarra, A. (2025). Killer Peptide-Containing Polyelectrolytic Nanocomplexes to Fight Toxoplasma gondii Infection. Pharmaceutics, 17(8), 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081075










