Synthesis of Terminal-Alkylated PEGs with Imine Spacer to Form Iminium Mono-Ion Complexes for pDNA Delivery into Skeletal Muscle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
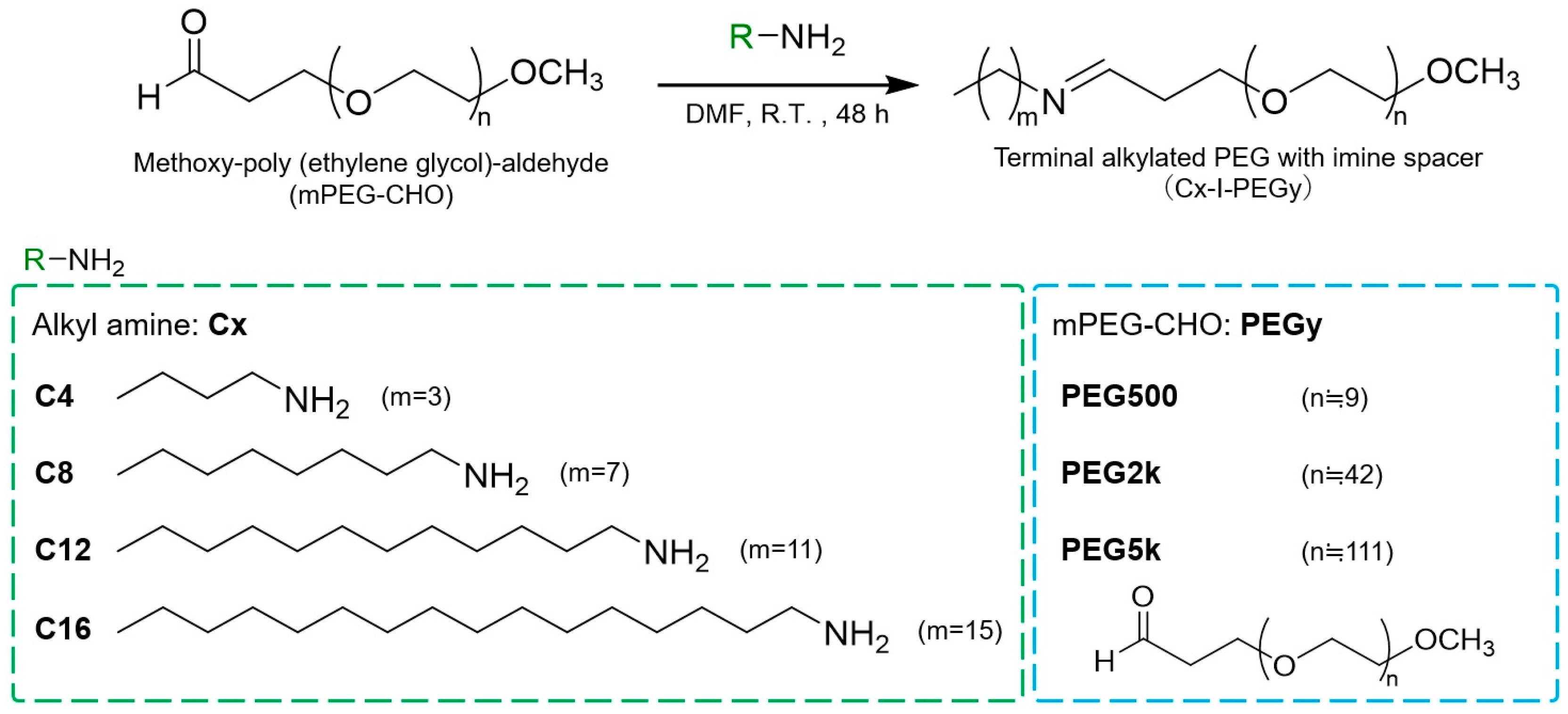
2.2. Synthesis of Cx-I-PEGy
2.3. 1H NMR Spectroscopy
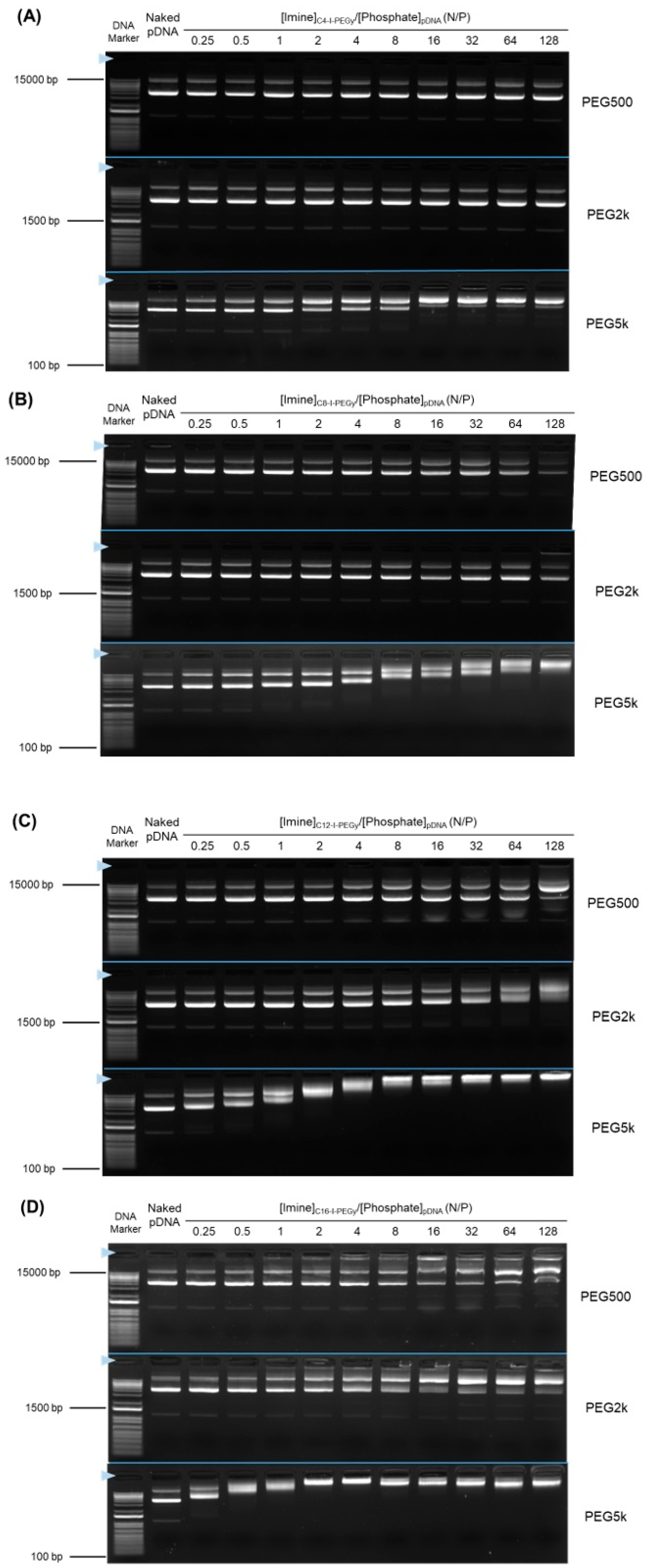
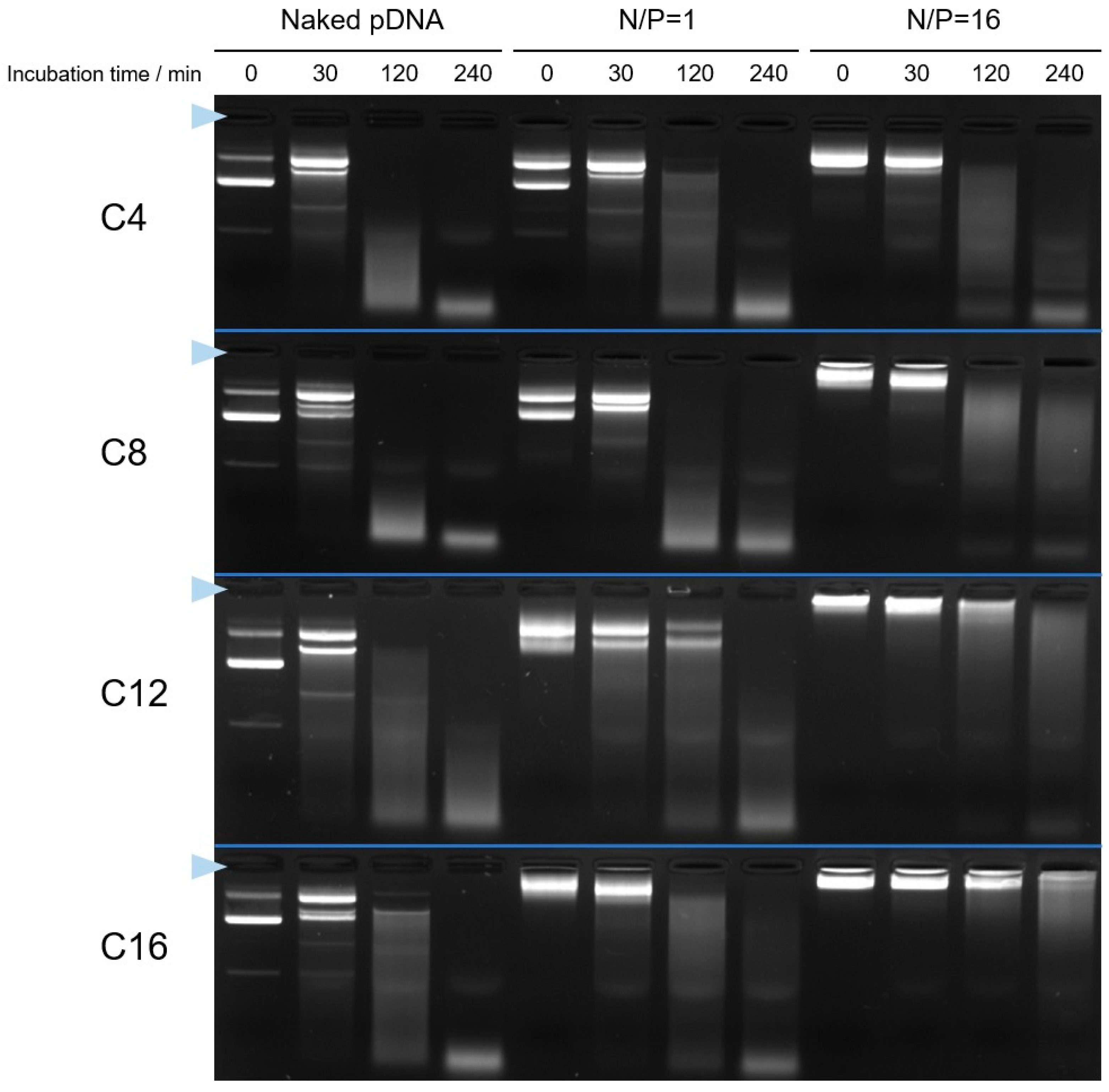
2.4. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis to Confirm the I-MIC Formation
2.5. Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC) Measurement
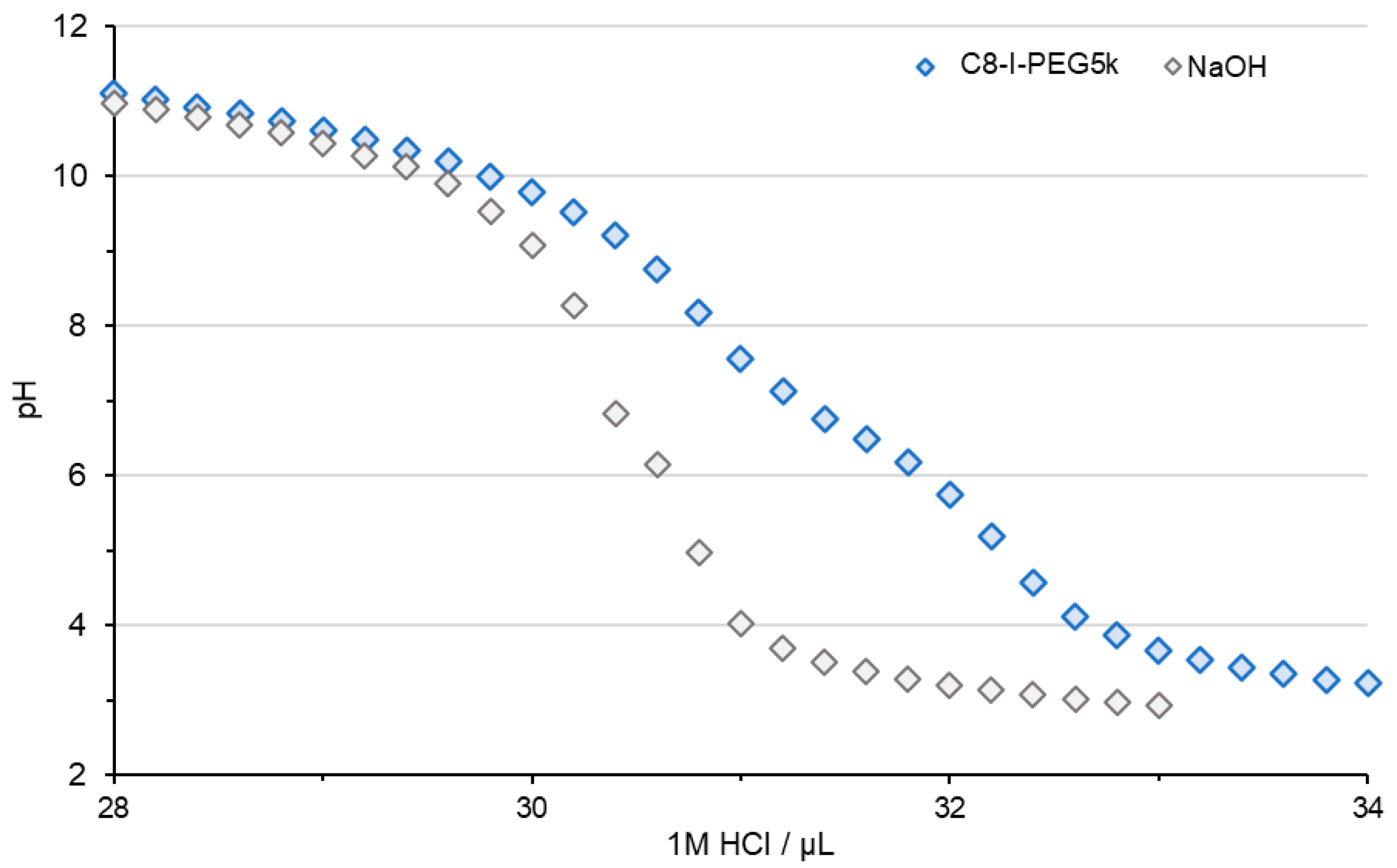
2.6. Acid–Base Titration
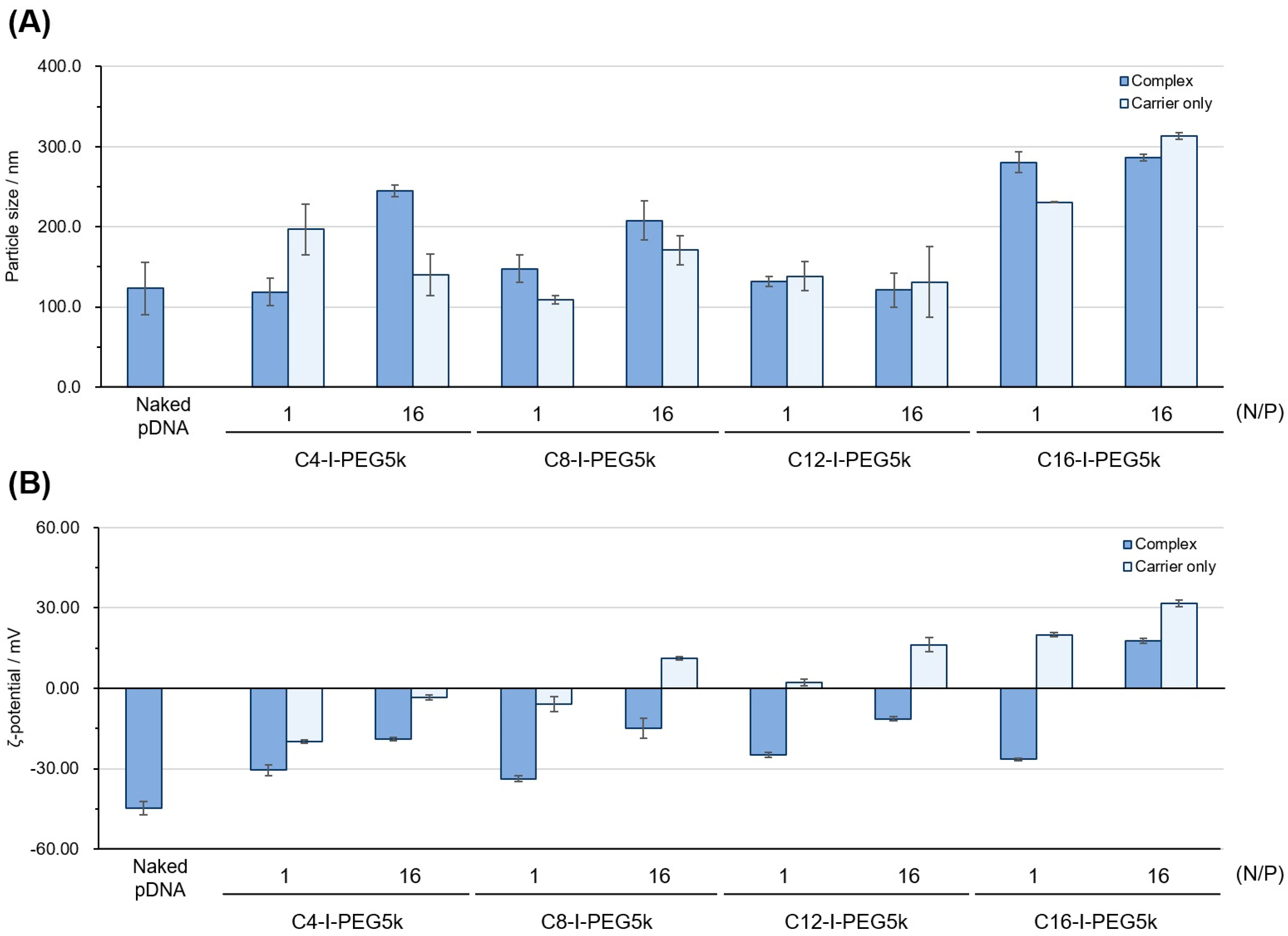
2.7. Particle Size and Zeta (ζ) Potential Measurement
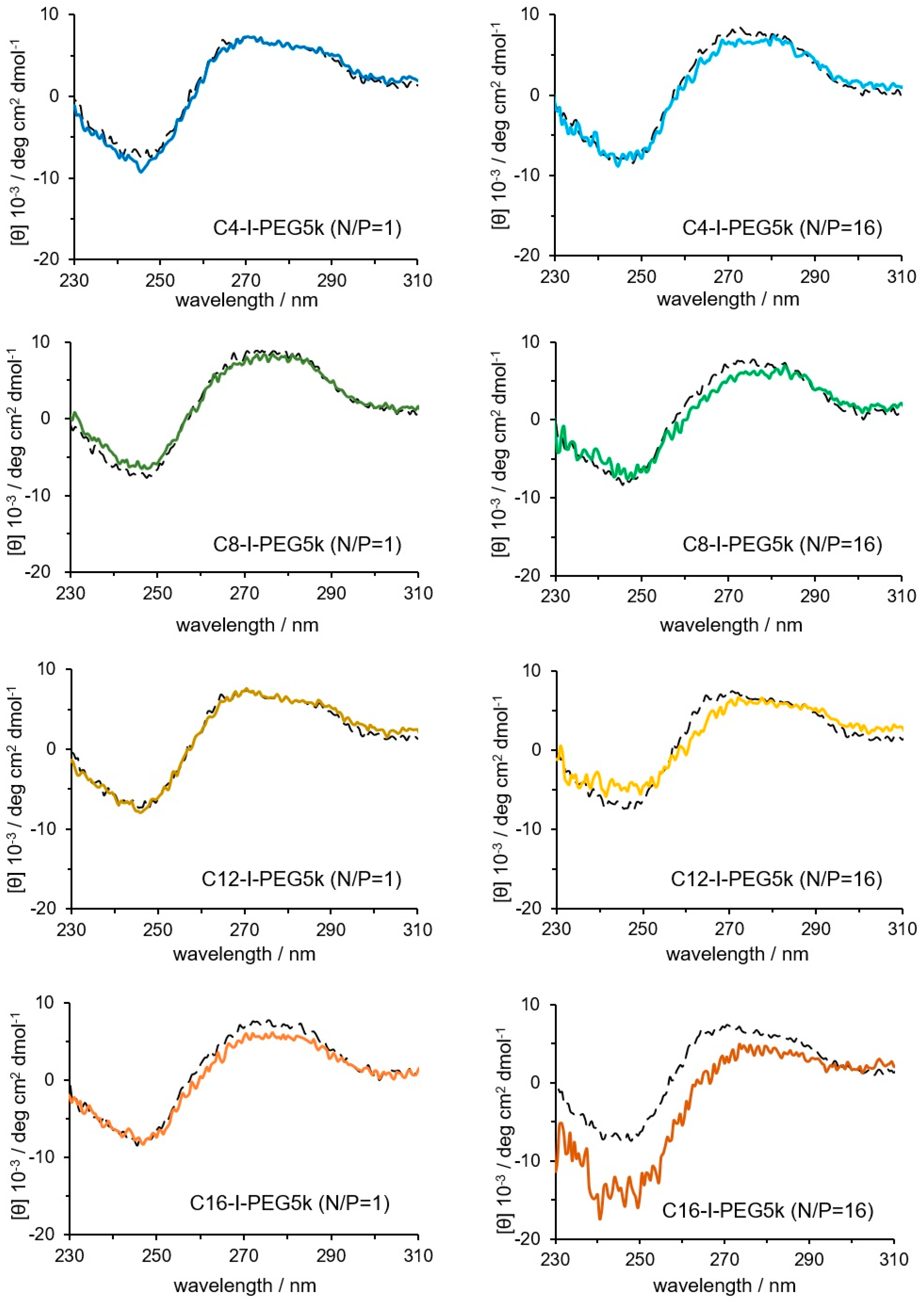
2.8. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectrum Measurement
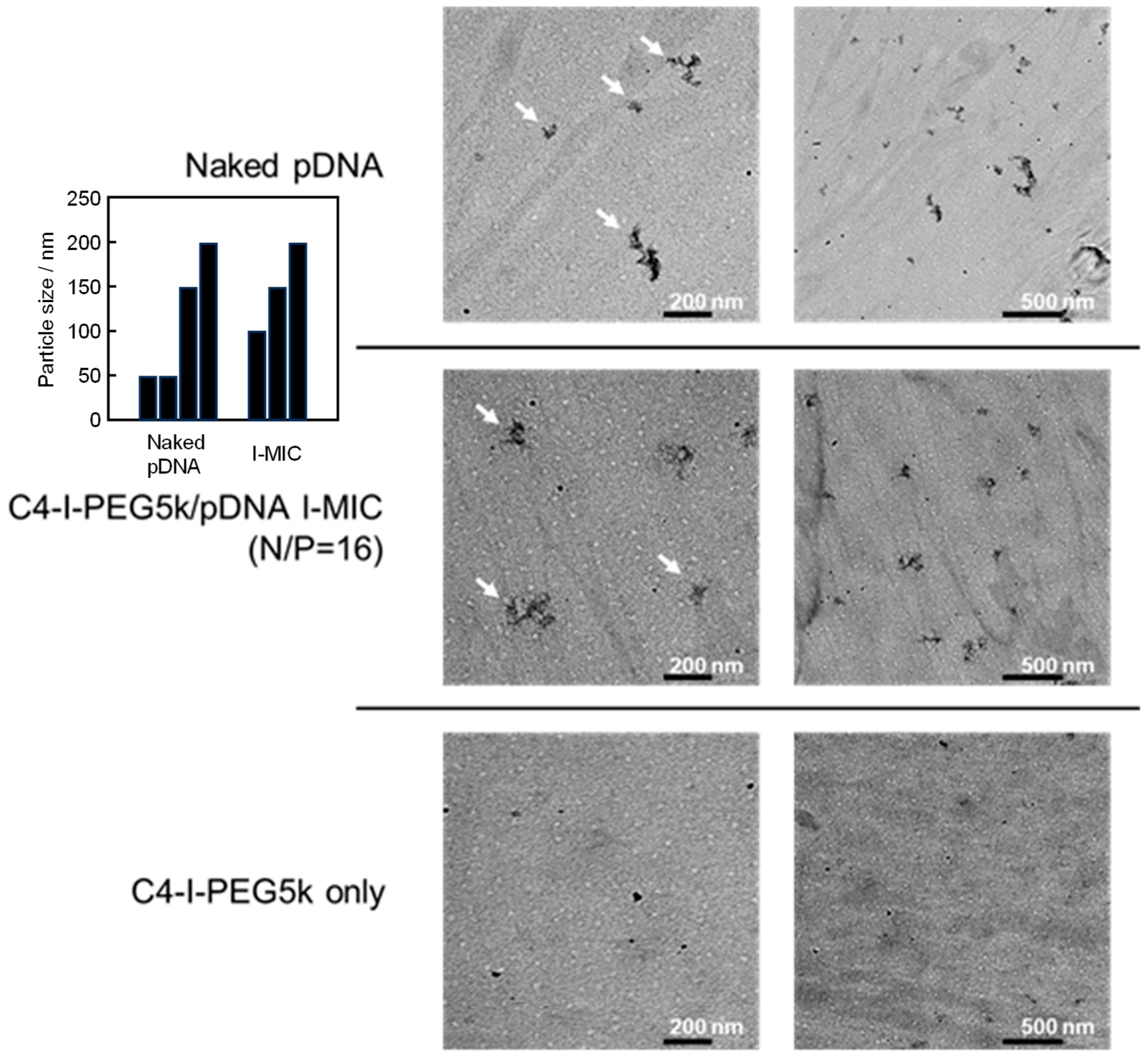
2.9. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Observation
2.10. Cell Viability Assay
2.11. Hemolysis Assay
2.12. In Vitro Gene Transfection Activity
2.13. In Vivo Gene Transfection Activity
2.14. In Vivo Imaging System (IVIS)
2.15. Animals
2.16. Statical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Screening by pDNA Complex Formation Ability of Cx-I-PEGy
3.2. How to Form pDNA Complex with Cx-I-PEG5k
3.3. Physicochemical Properties of the Cx-I-PEG5k/pDNA I-MICs
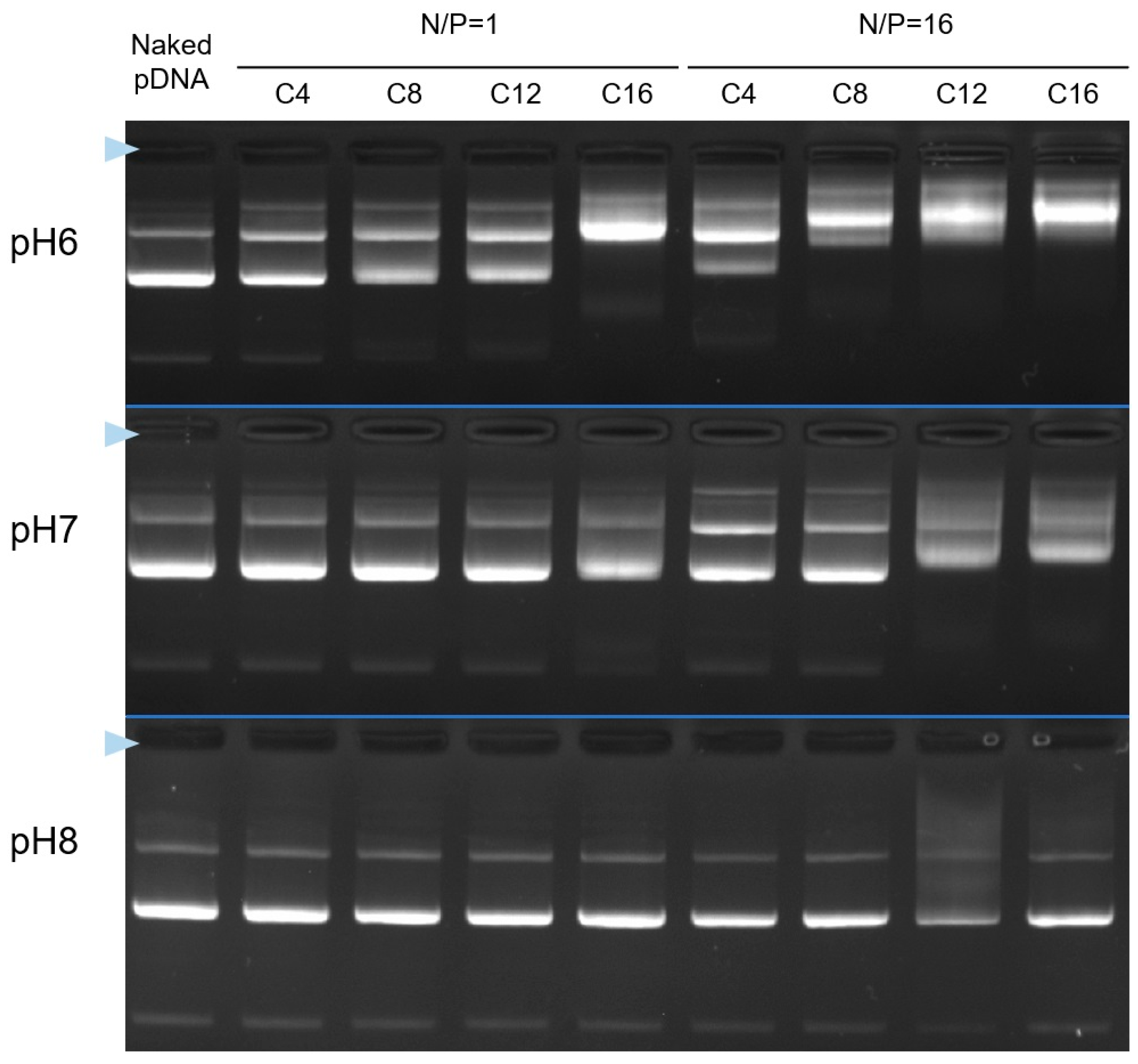
3.4. Stability of Cx-I-PEG5k/pDNA I-MICs
3.5. Pharmaceutical Properties of Cx-I-PEG5k/pDNA I-MICs In Vitro
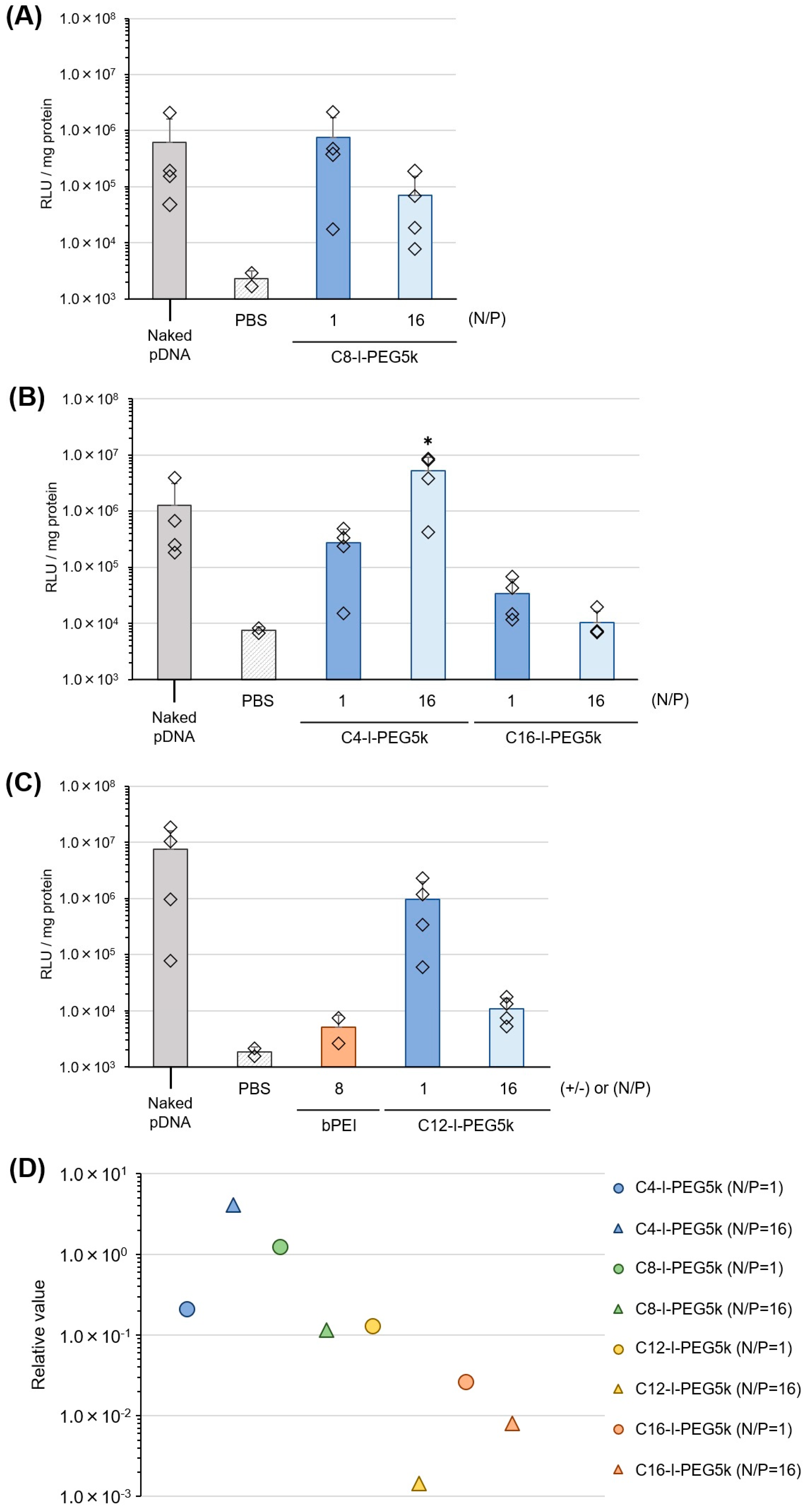
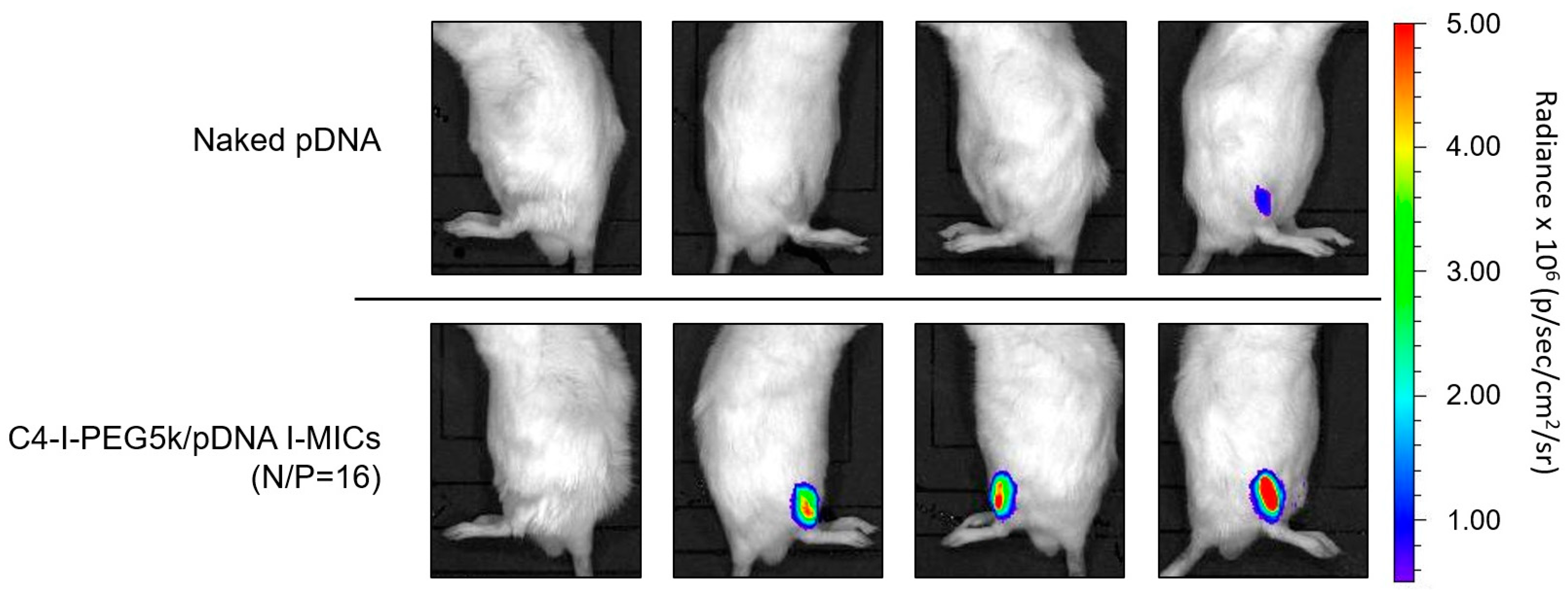
3.6. Pharmaceutical Properties of Cx-I-PEG5k/pDNA I-MICs In Vivo
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morishita, R.; Aoki, M.; Hashiya, N.; Makino, H.; Yamasaki, K.; Azuma, J.; Sawa, Y.; Matsuda, H.; Kaneda, Y.; Ogihara, T. Safety evaluation of clinical gene therapy using hepatocyte growth factor to treat peripheral arterial disease. Hypertension 2004, 44, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigematsu, H.; Yasuda, K.; Iwai, T.; Sasajima, T.; Ishimaru, S.; Ohashi, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ogihara, T.; Morishita, R. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of hepatocyte growth factor plasmid for critical limb ischemia. Gene Ther. 2010, 17, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asayama, S. Molecular design of polymer-based carriers for plasmid DNA delivery in vitro and in vivo. Chem. Lett. 2020, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, M.; Shimoda, S.; Wakabayashi, R.; Kunisawa, Y.; Ishii, T.; Osada, K.; Itaka, K.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K.; Nakano, K.J. Effective transgene expression without toxicity by intraperitoneal administration of PEG-detachable polyplex micelles in mice with peritoneal dissemination. Control Release 2012, 160, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Cheng, T.; Chu, L.; Xu, H.; Meng, A.; Fan, S.; Shi, L.; Liu, J. The impact of PEGylation patterns on the in vivo biodistribution of mixed shell micelles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4229–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Osada, K.; Ishii, T.; Oba, M.; Uchida, S.; Tockary, T.A.; Endo, T.Z.; Ge, Z.; Kinoh, H.; Kano, M.R.; et al. Homo-catiomer integration into PEGylated polyplex micelle from block-catiomer for systemic anti-angiogenic gene therapy for fibrotic pancreatic tumors. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 4722–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nance, E.; Zhang, C.; Shih, T.; Xu, Q.; Schuster, B.S.; Hanes, J. Brain-penetrating nanoparticles improve paclitaxel efficacy in malignant glioma following local administration. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 10655–10664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asayama, S.; Nohara, A.; Negishi, Y.; Kawakami, H. Alkylimidazolium end-modified poly(ethylene glycol) to form the mono-ion complex with plasmid DNA for in vivo gene delivery. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asayama, S.; Nohara, A.; Negishi, Y.; Kawakami, H. Plasmid DNA mono-ion complex stabilized by hydrogen bond for in vivo diffusive gene delivery. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 1226–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalba, S.; Ten Hagen, T.L.M.; Burgui, C.; Garrido, M.J. Stealth nanoparticles in oncology: Facing the PEG dilemma. J. Control Release 2022, 351, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.P.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.H.; Chen, X.C.; Yu, Q.Y.; Luan, C.R.; Zhang, J.H.; Wei, X.; Yu, X.Q. Ring-opening polymerization of diepoxides as an alternative method to overcome PEG dilemma in gene delivery. Polymer 2018, 134, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, H.; Akita, H.; Harashima, H. A multifunctional envelope type nano device (MEND) for gene delivery to tumours based on the EPR effect: A strategy for overcoming the PEG dilemma. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Taneichi, S.; Kawakami, H.; Negishi, Y.; Asayama, S. Plasmid DNA mono-ion complex for in vivo sustainable gene expression. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 11464–11471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nirasawa, K.; Negishi, Y.; Asayama, S. Structure-activity relationship of mono-ion complexes for plasmid DNA delivery by muscular injection. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, R.; Mori, A.; Asayama, S. Synthesis of diethylamino end-modified poly(ethylene glycol) with imine spacer to form mono-ion complexes with pDNA. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2024, 35, e70025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Jiao, Y. Hydrophobic modifications of cationic polymers for gene delivery. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1144–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, Z.; Qiao, H.; Liu, M.; Shen, M.; Yuan, T.; Chen, J.; Dionysiou, D.D. Spectroscopic study on interaction between three cationic surfactants with different alkyl chain lengths and DNA. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 151, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, F.A.; Albuquerque, L.J.C.; Sales, M.N.; Christoffolete, M.A.; Bellettini, I.C.; Giacomelli, F.C. Balancing gene transfection and cytotoxicity of nucleic acid carriers with focus on ocular and hepatic disorders: Evaluation of hydrophobic and hydrophilic polyethyleneimine derivatives. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 4556–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddard, E.D.; Turro, N.J.; Kuo, P.L. Fluorescence probes for critical micelle concentration determination. Langmuir 1985, 1, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, M.; Zhao, C.L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, R.; Winnik, M.A.; Mura, J.L.; Riess, G.; Croucher, M.D. Poly(styrene-ethylene oxide) block copolymer micelle formation in water: A fluorescence probe study. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, S.; Osada, K.; Hiki, S.; Dirisala, A.; Ishii, T.; Kataoka, K. Polyplex micelles with double-protective compartments of hydrophilic shell and thermoswitchable palisade of poly(oxazoline)-based block copolymers for promoted gene transfection. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsworth, J.M.; Rose, F.R.A.J.; Wright, E.; Scotchford, C.A.; Shakesheff, K.M. Seeding cells into needled felt scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2003, 66, 425–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, H.; Han, J.; Yang, L.; Li, S.; Jia, Q.; Fang, J.; Ling, P.; Wang, S. Synthesis and antitumor activity of ultra-low molecular weight hyaluronic acid-decorated camptothecin conjugates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 351, 123144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, L.; Yan, X.; Ding, J.; Cheng, B.; Yang, J.; Li, B.; Wang, X.J. Attapulgite microspheres coated with poly(lactic acid-glycolic acid) nanoparticles form satellite structure to enhance doxorubicin delivery in bone cancer therapy. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 104, 106509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi, Y.; Matsuo, K.; Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Matsuki, Y.; Takagi, N.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; Aramaki, Y. Delivery of an angiogenic gene into ischemic muscle by novel bubble liposomes followed by ultrasound exposure. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asayama, S.; Akaike, T.; Maruyama, A. Bi-phasic polycation for the DNA carrier responding to endosomal pH. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2001, 22, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittimalla, C.; Zammut-Italiano, L.; Zuber, G.; Behr, J.P. Monomolecular DNA nanoparticles for intravenous delivery of genes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 11436–11441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, Y.; Yang, W.; Chen, P.; Masuda, K.; Hong, T.; Cabral, H. Tryptophan intercalation in siRNA drives the formation of polymeric micelles with enhanced delivery efficiency. RCS Pharm. 2024, 1, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, A.F.; Röder, R.; Kos, P.; Dias, R.S.; Wagner, E.; Pais, A.A. Combining polyethylenimine and Fe(III) for mediating pDNA transfection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierrat, P.; Wang, R.; Kereselidze, D.; Lux, M.; Didier, P.; Kichler, A.; Pons, F.; Lebeau, L. Efficient in vitro and in vivo pulmonary delivery of nucleic acid by carbon dot-based nanocarriers. Biomaterials 2015, 51, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Nirasawa, K.; Negishi, Y.; Asayama, S. Noncorrelative relation between in vitro and in vivo for plasmid DNA transfection by succinylated polyethylenimine muscular injection. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2021, 32, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, J.A.; Malone, R.W.; Williams, P.; Chong, W.; Acsadi, G.; Jani, A.; Felgner, P.L. Direct gene transfer into mouse muscle in vivo. Science 1990, 247, 1465–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiraishi, K.; Hamano, M.; Ma, H.; Kawano, K.; Maitani, Y.; Aoshi, T.; Ishii, K.J.; Yokoyama, M.J. Hydrophobic blocks of PEG-conjugates play a significant role in the accelerated bloos clearance (ABC) phenomenon. Control Release 2013, 165, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oba, R.; Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Negishi, Y.; Asayama, S. Synthesis of Terminal-Alkylated PEGs with Imine Spacer to Form Iminium Mono-Ion Complexes for pDNA Delivery into Skeletal Muscle. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081054
Oba R, Endo-Takahashi Y, Negishi Y, Asayama S. Synthesis of Terminal-Alkylated PEGs with Imine Spacer to Form Iminium Mono-Ion Complexes for pDNA Delivery into Skeletal Muscle. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(8):1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081054
Chicago/Turabian StyleOba, Riku, Yoko Endo-Takahashi, Yoichi Negishi, and Shoichiro Asayama. 2025. "Synthesis of Terminal-Alkylated PEGs with Imine Spacer to Form Iminium Mono-Ion Complexes for pDNA Delivery into Skeletal Muscle" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 8: 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081054
APA StyleOba, R., Endo-Takahashi, Y., Negishi, Y., & Asayama, S. (2025). Synthesis of Terminal-Alkylated PEGs with Imine Spacer to Form Iminium Mono-Ion Complexes for pDNA Delivery into Skeletal Muscle. Pharmaceutics, 17(8), 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081054





