Promising Protocol for In Vivo Experiments with Betulin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Equipment
2.1.1. Animals
2.1.2. Drugs and Chemicals
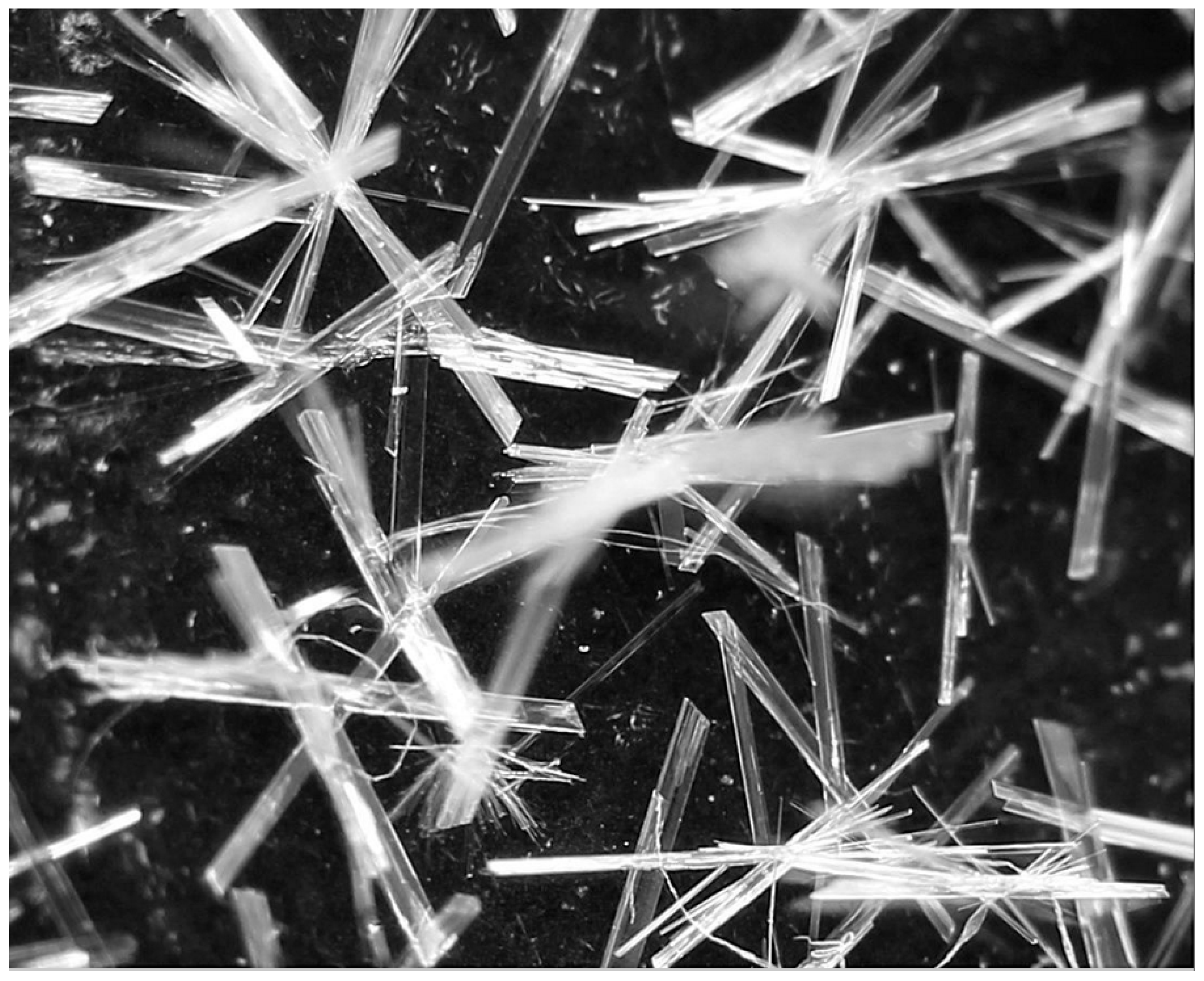
2.1.3. Chromatography
2.1.4. Microscopy
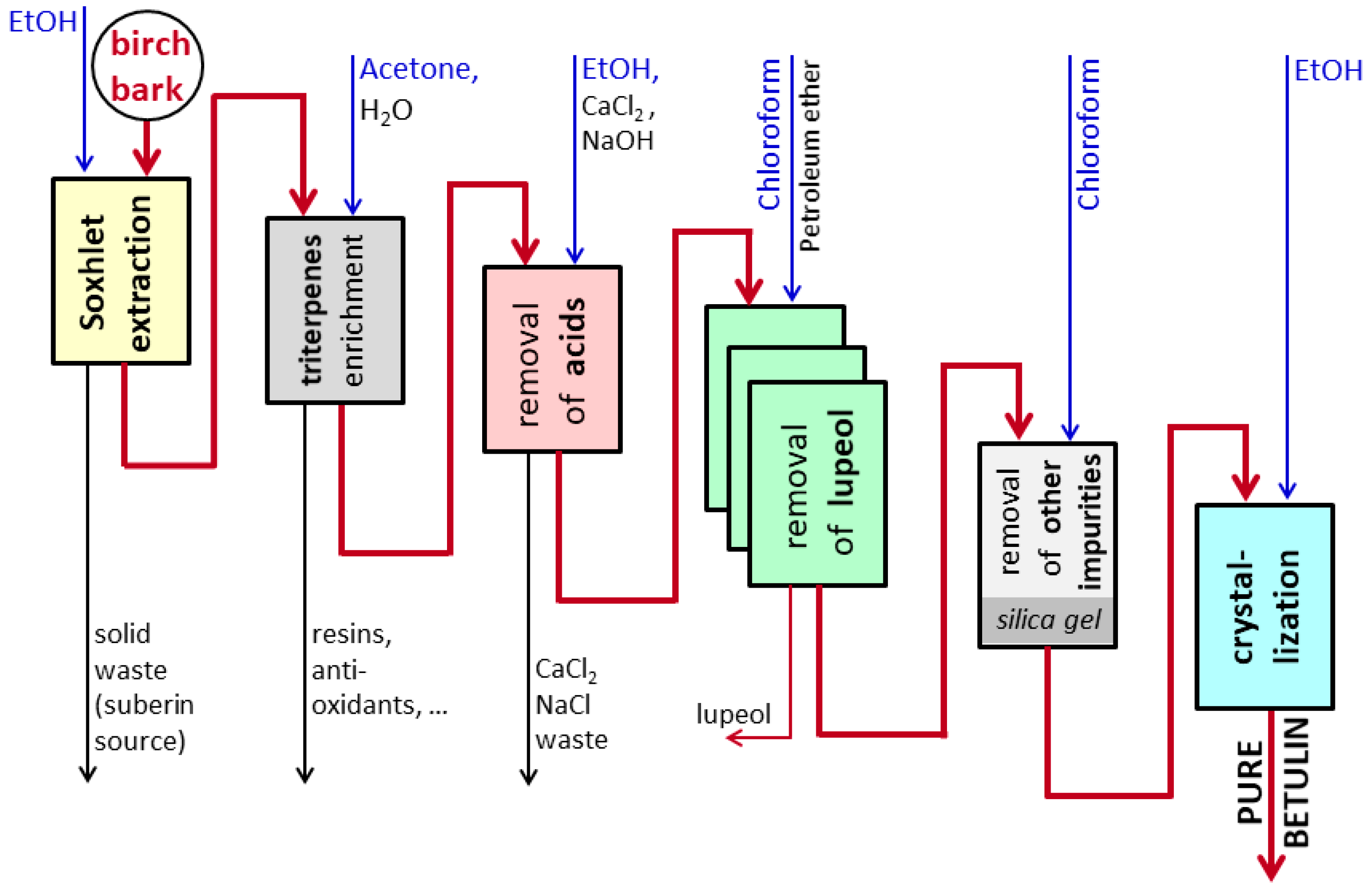
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Administration Form
2.2.2. Administration of Betulin per Os
2.2.3. Administration of Betulin per Rectum
2.2.4. Determination of Betulin Concentrations in Organs
2.2.5. Synergistic Effects of Namitecan and Betulin
2.2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
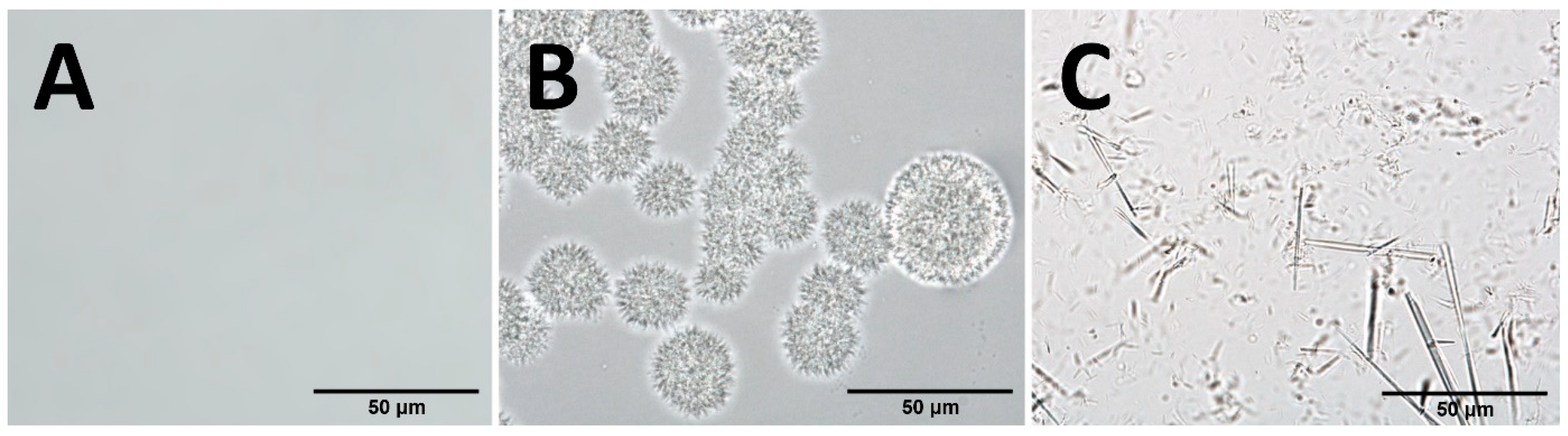
3.1. Administration Form
3.2. Administration of Betulin per Os
3.3. Administration of Betulin per Rectum
3.4. Determination of Betulin Concentrations in Organs
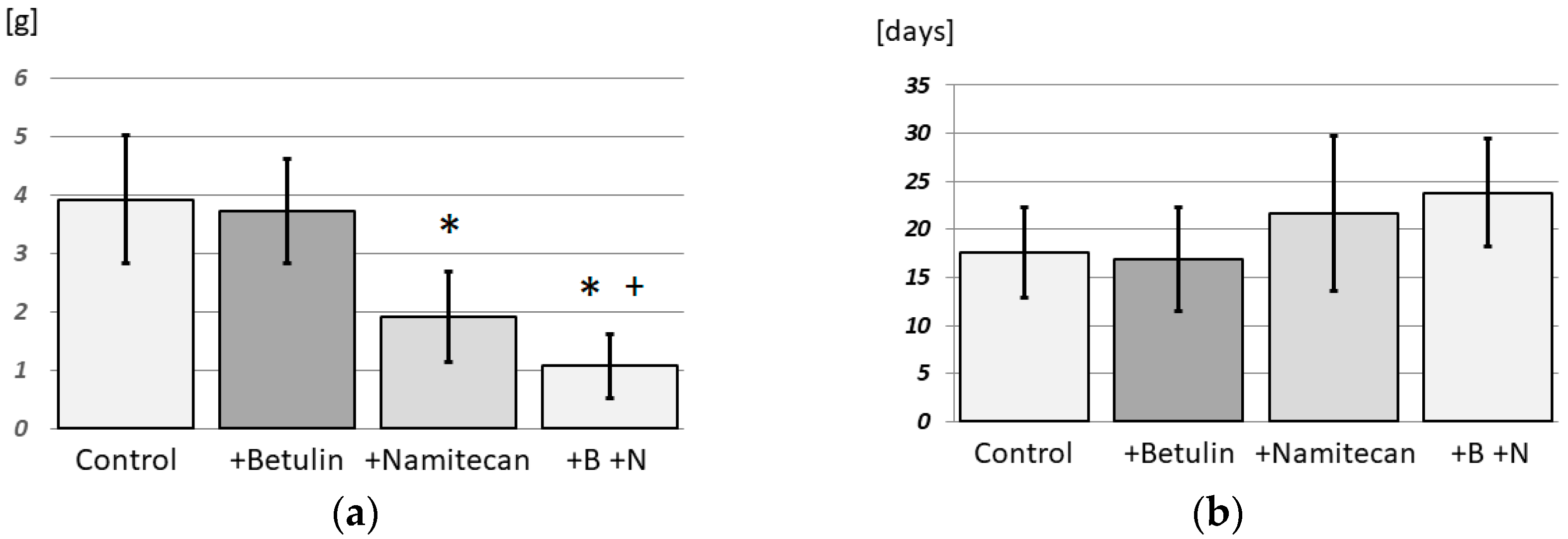
3.5. Synergistic Effects of Namitecan and Betulin
4. Discussion
4.1. Carriers with Betulin
4.2. Determination of Betulin Concentrations in Organs
4.3. Synergistic Effects with Namitecan
4.4. Stability of Pure Betulin and Its Formulation
4.5. Microbial Stability
4.6. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GC-MS | Gas chromatography with mass spectrometry |
| UHPLC-MS | Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography with mass spectroscopy |
| IC50 | Half maximal inhibitory concentration |
References
- Król, S.K.; Kiełbus, M.; Rivero-Müller, A.; Stepulak, A. Comprehensive Review on Betulin as a Potent Anticancer Agent. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 584189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hordyjewska, A.; Ostapiuk, A.; Horecka, A.; Kurzepa, J. Betulin and Betulinic Acid: Triterpenoids Derivatives with a Powerful Biological Potential. Phytochem. Rev. 2019, 18, 929–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuli, H.S.; Sak, K.; Gupta, D.S.; Kaur, G.; Aggarwal, D.; Chaturvedi Parashar, N.; Choudhary, R.; Yerer, M.B.; Kaur, J.; Kumar, M.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Anticancer Properties of Birch Bark-Derived Betulin: Recent Developments. Plants 2021, 10, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adepoju, F.O.; Duru, K.C.; Li, E.; Kovaleva, E.G.; Tsurkan, M.V. Pharmacological Potential of Betulin as a Multitarget Compound. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šiman, P.; Filipová, A.; Tichá, A.; Niang, M.; Bezrouk, A.; Havelek, R. Effective Method of Purification of Betulin from Birch Bark: The Importance of Its Purity for Scientific and Medicinal Use. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, T.; Yin, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, S. Tissue Regeneration Effect of Betulin via Inhibition of ROS/MAPKs/NF-ĸB Axis Using Zebrafish Model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsova, S.A.; Skvortsova, G.P.; Maliar, I.N.; Skurydina, E.S.; Veselova, O.F. Extraction of Betulin from Birch Bark and Study of Its Physico-Chemical and Pharmacological Properties. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2014, 40, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saneja, A.; Arora, D.; Kumar, R.; Dubey, R.D.; Panda, A.K.; Gupta, P.N. Therapeutic Applications of Betulinic Acid Nanoformulations. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1421, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroszewski, B.; Jelonek, K.; Kasperczyk, J. Drug Delivery Systems of Betulin and Its Derivatives: An Overview. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farage, A.E.; Abdo, W.; Osman, A.; Abdel-Kareem, M.A.; Hakami, Z.H.; Alsulimani, A.; Bin-Ammar, A.; Alanazi, A.S.; Alsuwayt, B.; Alanazi, M.M.; et al. Betulin Prevents High Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Mitigating Oxidative Stress and Upregulating Nrf2 and SIRT1 in Rats. Life Sci. 2023, 322, 121688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinay, V.; Sadhana, P. Evaluation of Betulin for Hair Growth Promoting Activity in Rats. Int. J. Pharm. Chem. Anal. 2024, 11, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherbiny, M.; Eisa, N.H.; Abo El-Magd, N.F.; Elsherbiny, N.M.; Said, E.; Khodir, A.E. Anti-Inflammatory/Anti-Apoptotic Impact of Betulin Attenuates Experimentally Induced Ulcerative Colitis: An Insight into TLR4/NF-KB/Caspase Signalling Modulation. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 88, 103750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzeska, A.; Jabłoński, R.; Shlyahtun, A.; Kitlas, P.; Szymańska, N.; Tomulewicz, M. Hypoglycemic Effect of Betulin in Rats With Experimental Diabetes. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2023, 80, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, S.; Laszczyk, M.N.; Scheffler, A. A Preliminary Pharmacokinetic Study of Betulin, the Main Pentacyclic Triterpene from Extract of Outer Bark of Birch (Betulae Alba Cortex). Molecules 2008, 13, 3224–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Guo, N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, W.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Yan, X. Development and Validation of an LC-ESI/MS/MS Method with Precolumn Derivatization for the Determination of Betulin in Rat Plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 939, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pârvănescu (Pană), R.D.; Watz, C.-G.; Moacă, E.-A.; Vlaia, L.; Marcovici, I.; Macașoi, I.G.; Borcan, F.; Olariu, I.; Coneac, G.; Drăghici, G.-A.; et al. Oleogel Formulations for the Topical Delivery of Betulin and Lupeol in Skin Injuries—Preparation, Physicochemical Characterization, and Pharmaco-Toxicological Evaluation. Molecules 2021, 26, 4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, J.S.; Sprecher, E.; Fernandez, M.F.; Schauer, F.; Bodemer, C.; Cunningham, T.; Löwe, S.; Davis, C.; Sumeray, M.; Bruckner, A.L.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Oleogel-S10 (Birch Triterpenes) for Epidermolysis Bullosa: Results from the Phase III Randomized Double-Blind Phase of the EASE Study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2023, 188, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caligiani, A.; Malavasi, G.; Palla, G.; Marseglia, A.; Tognolini, M.; Bruni, R. A simple GC-MS method for the screening of betulinic, corosolic, maslinic, oleanolic and ursolic acid contents in commercial botanicals used as food supplement ingredients. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.; Rasheed, M.; Ali, M.; Ishrat, G.; Ahmed, M. Identification of Five New Triterpenoids from Ethylacetate Bark Extract of Holoptelea integrifolia (Roxb.) Planch by GC-MS. Nat. Prod. Chem. Res. 2018, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, R.H.; Chaudhari, S.R.; Patil, A.S.; Shirkhedkar, A.A. Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-MS/MS (UHPLC-MS/MS) in Practice: Analysis of Drugs and Pharmaceutical Formulations. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joerger, M.; Hess, D.; Delmonte, A.; Gallerani, E.; Fasolo, A.; Gianni, L.; Cresta, S.; Barbieri, P.; Pace, S.; Sessa, C. Integrative Population Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Dose Finding Approach of the New Camptothecin Compound Namitecan (ST1968). Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 80, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, J.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-C.; Hu, Z.-H.; Yao, K.-C.; Yuan, M.-H.; Bao, X.-X.; Zhou, M.-J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.-X.; Lian, L.-H.; et al. Betulin Targets Lipin1/2-Meidated P2X7 Receptor as a Therapeutic Approach to Attenuate Lipid Accumulation and Metaflammation. Biomol. Ther. 2022, 30, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Jung, K.; Lee, D.; Lee, S.R.; Lee, K.R.; Kang, K.S.; Kim, K.H. Protective Effect and Mechanism of Action of Lupane Triterpenes from Cornus Walteri in Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5613–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drąg Zalesińska, M.; Drąg, M.; Poręba, M.; Borska, S.; Kulbacka, J.; Saczko, J. Anticancer Properties of Ester Derivatives of Betulin in Human Metastatic Melanoma Cells (Me 45). Cancer Cell Int. 2017, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassinelli, G.; Zuco, V.; Petrangolini, G.; De Cesare, M.; Tortoreto, M.; Lanzi, C.; Cominetti, D.; Zaffaroni, N.; Passeri, D.; Meco, D.; et al. The Curative Efficacy of Namitecan (ST1968) in Preclinical Models of Pediatric Sarcoma Is Associated with Antiangiogenic Effects. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šiman, P.; Bezrouk, A.; Tichá, A.; Kozáková, H.; Hudcovic, T.; Kučera, O.; Niang, M. Promising Protocol for In Vivo Experiments with Betulin. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081051
Šiman P, Bezrouk A, Tichá A, Kozáková H, Hudcovic T, Kučera O, Niang M. Promising Protocol for In Vivo Experiments with Betulin. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(8):1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081051
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠiman, Pavel, Aleš Bezrouk, Alena Tichá, Hana Kozáková, Tomáš Hudcovic, Otto Kučera, and Mohamed Niang. 2025. "Promising Protocol for In Vivo Experiments with Betulin" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 8: 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081051
APA StyleŠiman, P., Bezrouk, A., Tichá, A., Kozáková, H., Hudcovic, T., Kučera, O., & Niang, M. (2025). Promising Protocol for In Vivo Experiments with Betulin. Pharmaceutics, 17(8), 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081051




