Zein-Based Nanocarriers: Advances in Oral Drug Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
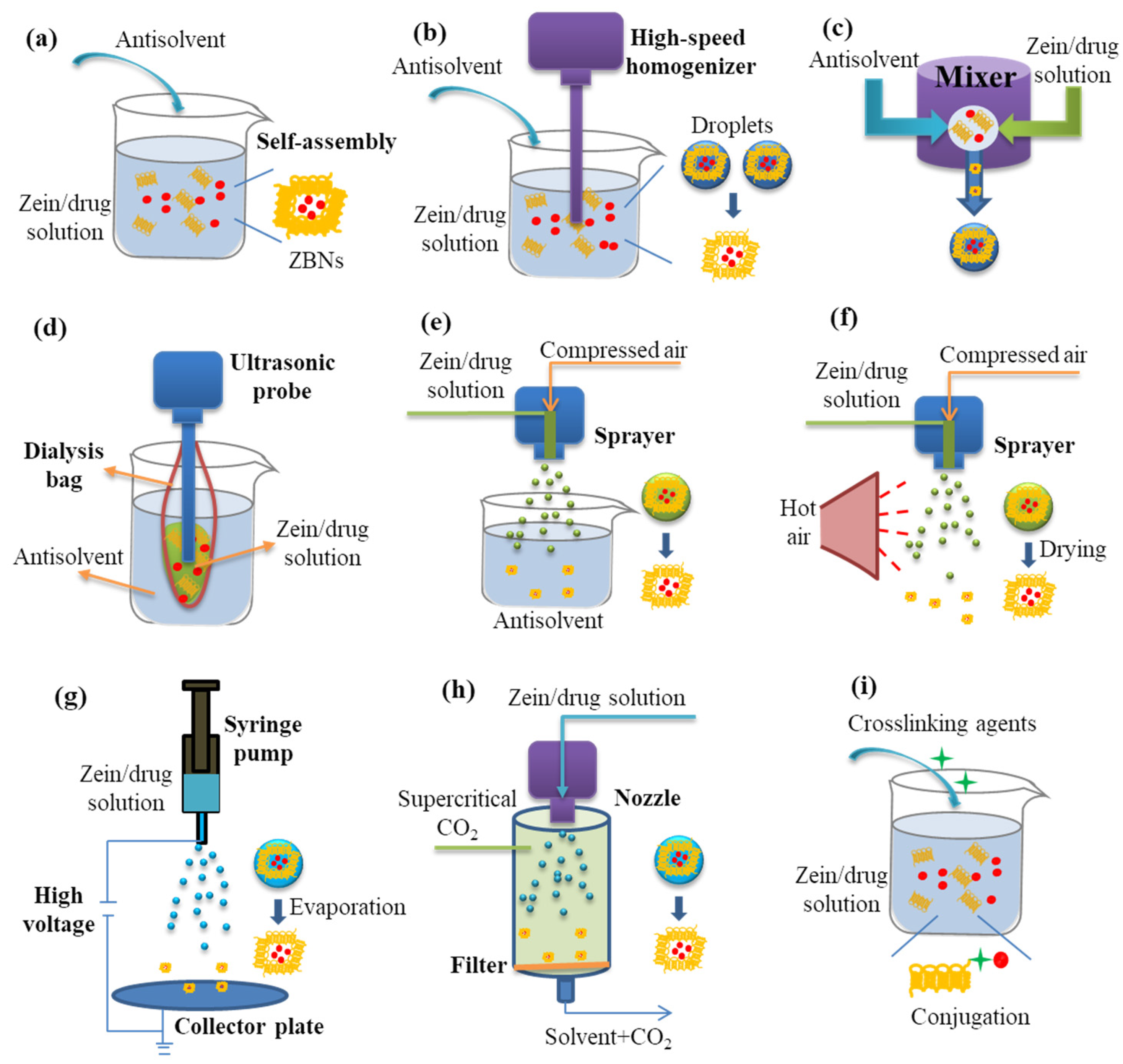
2. Preparation of Zein-Based Nanocarriers
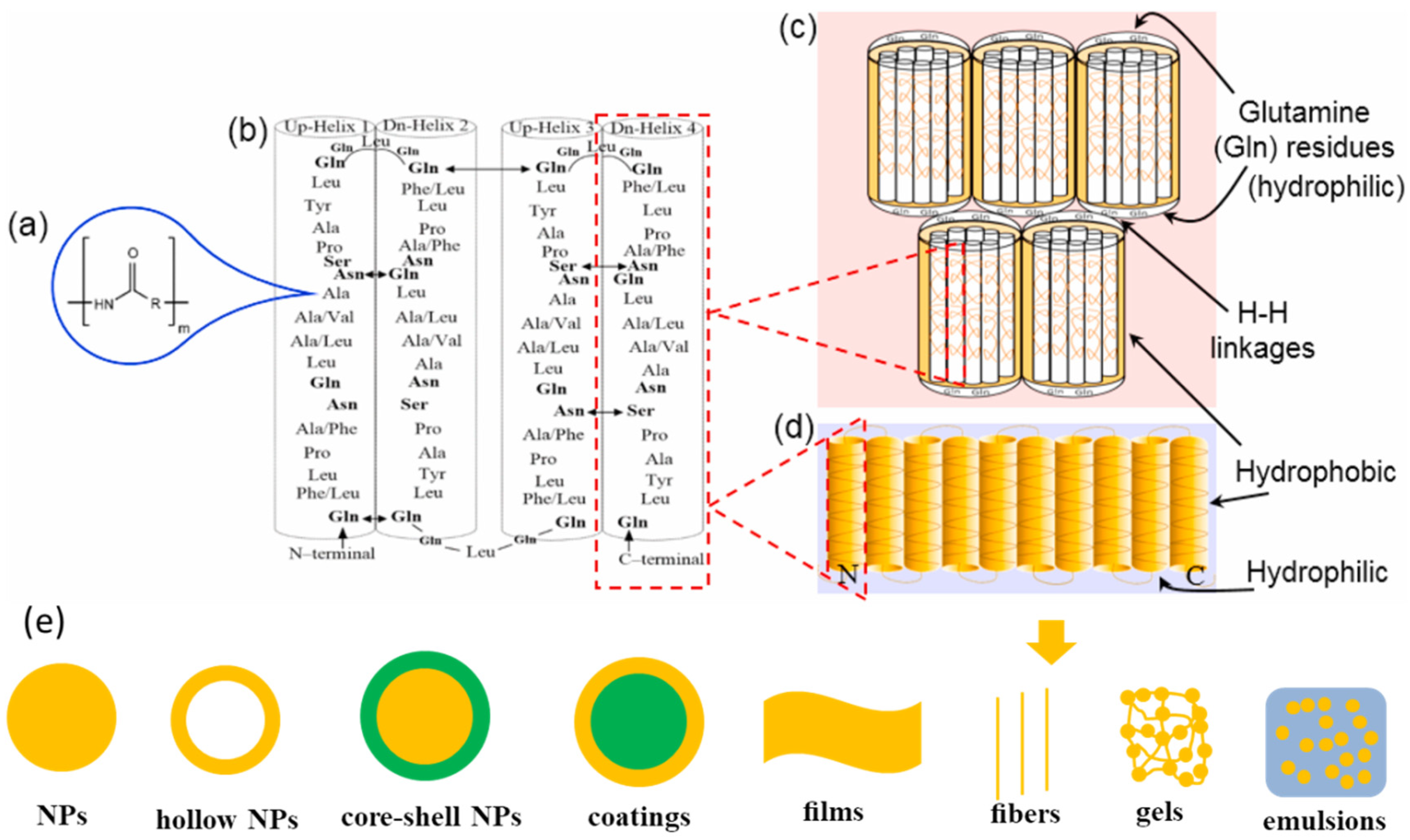
2.1. Characteristics of Zein
2.2. Engineering Zein-Based Nanocarriers
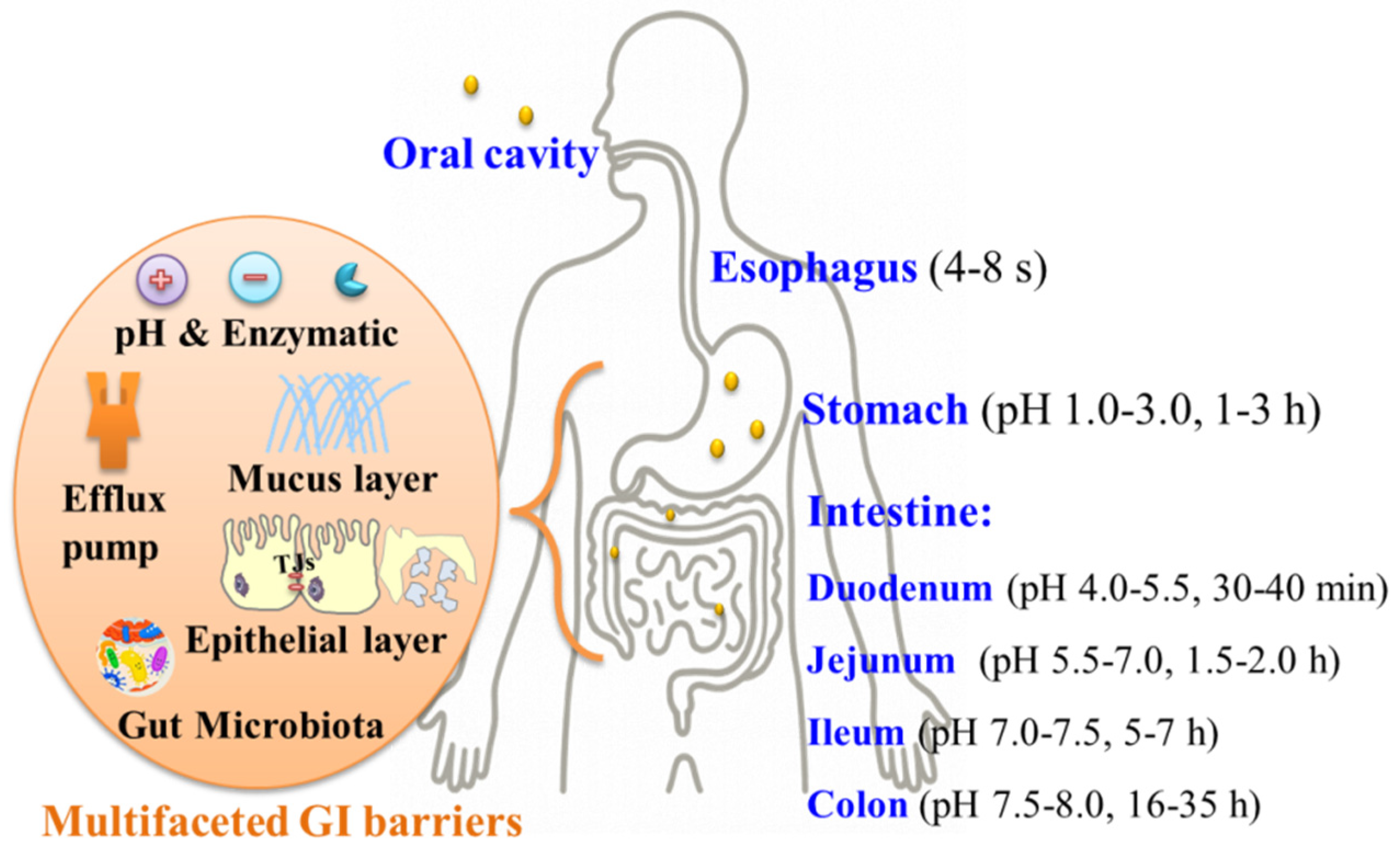
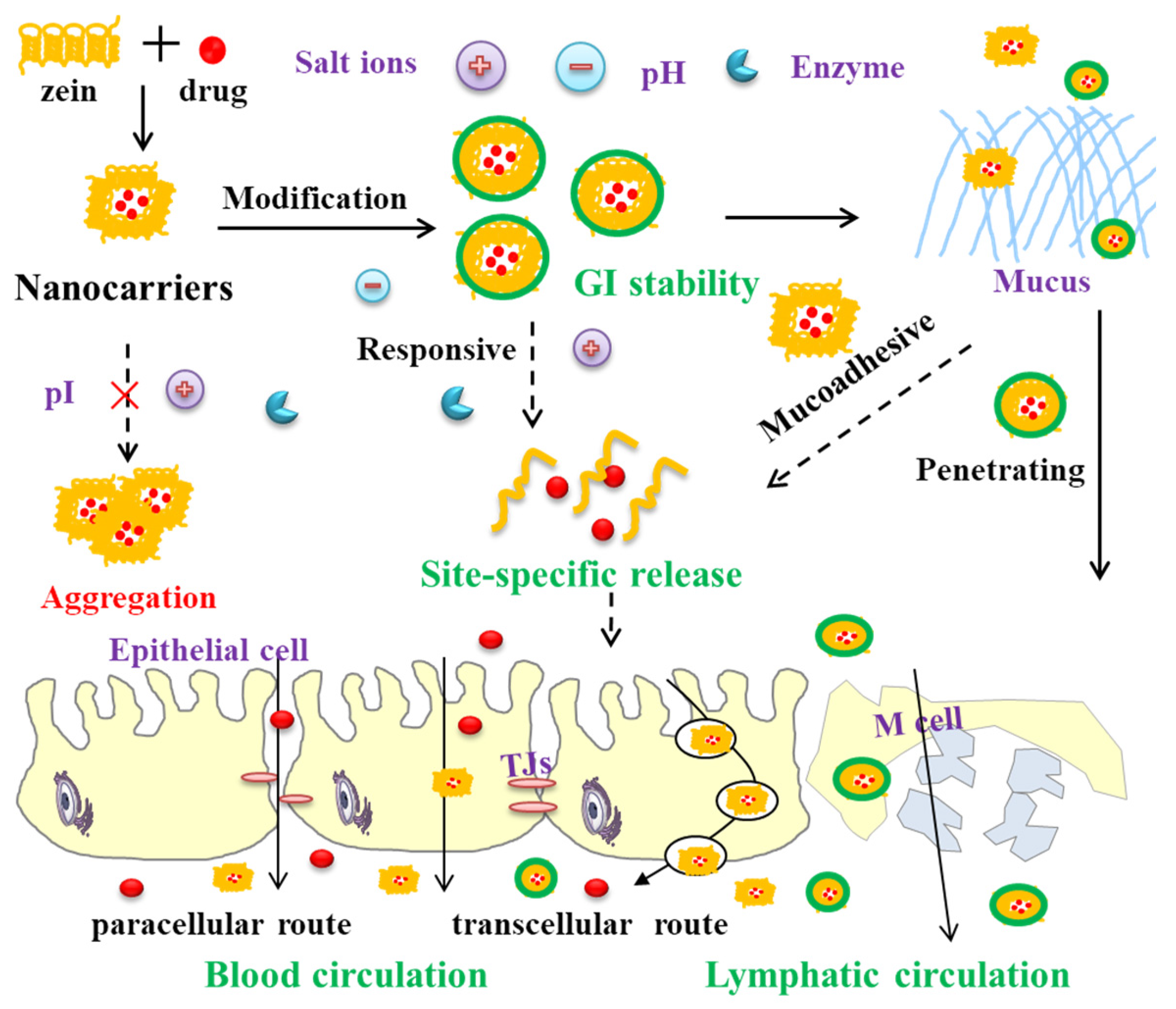
3. Zein-Based Nanocarriers Overcoming GI Barriers
3.1. Stability in GI Tract
3.2. Mucoadhesion/Mucus Penetration
3.3. Paracellular/Transcellular Ttransport
4. Applications of Zein-Based Nanocarriers in Oral Drug Delivery
4.1. Improving Drug Stability
4.2. Enhancing Drug Solubility
4.3. Controlling Drug Release
4.4. Enhancing Drug Absorption
4.5. Enhancing Oral Bioavailability
5. Challenges and Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, S.; Alexander, E.; Liang, H.; Kulchar, R.J.; Singh, R.; Herzog, R.W.; Daniell, H.; Leong, K.W. Synthetic and Biogenic Materials for Oral Delivery of Biologics: From Bench to Bedside. Chem. Rev. 2025, 125, 4009–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; An, D.; Deng, S.; Liu, G. Engineered nanomaterials for overcoming multifaceted gastrointestinal barriers: Toward precision oral delivery of therapeutics. Pharmacol. Res. 2025, 218, 107844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Jiang, Q.; Dong, Z.; Meng, T.; Hu, F.; Wang, J.; Yuan, H. Nanocarriers transport across the gastrointestinal barriers: The contribution to oral bioavailability via blood circulation and lymphatic pathway. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 203, 115130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homayun, B.; Lin, X.; Choi, H.-J. Challenges and Recent Progress in Oral Drug Delivery Systems for Biopharmaceuticals. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán-Lobato, M.; Niu, Z.; Alonso, M.J. Oral Delivery of Biologics for Precision Medicine. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1901935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.D.; Whitehead, K.A.; Mitragotri, S. Materials for oral delivery of proteins and peptides. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, F.; das Neves, J.; Martins, J.P.; Granja, P.L.; Santos, H.A.; Sarmento, B. Functionalized materials for multistage platforms in the oral delivery of biopharmaceuticals. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 89, 306–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Conejos-Sánchez, I.; Griffin, B.T.; O’Driscoll, C.M.; Alonso, M.J. Lipid-based nanocarriers for oral peptide delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 106, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, C.; Nilsen, J.; Grevys, A.; Nunes, R.; Andersen, J.T.; Sarmento, B. Engineered albumin-functionalized nanoparticles for improved FcRn binding enhance oral delivery of insulin. J. Control. Release 2020, 327, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layek, B.; Mandal, S. Natural polysaccharides for controlled delivery of oral therapeutics: A recent update. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 230, 115617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonte, P.; Araújo, F.; Silva, C.; Pereira, C.; Reis, S.; Santos, H.A.; Sarmento, B. Polymer-based nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery: Revisited approaches. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1342–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asad, S.; Jacobsen, A.-C.; Teleki, A. Inorganic nanoparticles for oral drug delivery: Opportunities, barriers, and future perspectives. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2022, 38, 100869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Koo, S.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Yaremenko, A.V.; et al. Oral drug delivery platforms for biomedical applications. Mater. Today 2023, 62, 296–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzoghby, A.O.; Samy, W.M.; Elgindy, N.A. Protein-based nanocarriers as promising drug and gene delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, U.N.; Khandelia, R.; Sanpui, P.; Das, S.; Paul, A.; Chattopadhyay, A. Protein-Based Multifunctional Nanocarriers for Imaging, Photothermal Therapy, and Anticancer Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 19495–19501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.; Qin, Z.; Gao, L.; Zhou, M.; Xue, Y.; Li, Y.; Xie, J. Protein nanoparticles as drug delivery systems for cancer theranostics. J. Control. Release 2024, 371, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, L.; Cakebread, J.A.; Loveday, S.M. Food proteins from animals and plants: Differences in the nutritional and functional properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, B.D. Engineering materials from proteins. AIChE J. 2013, 59, 3558–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fytsilis, V.D.; Urlings, M.J.E.; van Schooten, F.-J.; de Boer, A.; Vrolijk, M.F. Toxicological risks of dairy proteins produced through cellular agriculture: Current state of knowledge, challenges and future perspectives. Future Foods 2024, 10, 100412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaski, A.C.; Schmitz, F.; Horta, R.P.; Cadorin, L.; da Silva, B.J.G.; Andreaus, J.; Paes, M.C.D.; Riegel-Vidotti, I.C.; Zimmermann, L.M. Zein—A plant-based material of growing importance: New perspectives for innovative uses. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 186, 115250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.; Yang, Y. Potential of plant proteins for medical applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irache, J.M.; Gonzalez-Navarro, C.J. Zein nanoparticles as vehicles for oral delivery purposes. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 1209–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, R.; Cheryan, M. Zein: The industrial protein from corn. Ind. Crops Prod. 2001, 13, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, F.F.O.; Luzardo-Álvarez, A.; Blanco-Méndez, J.; Martín-Pastor, M. NMR techniques in drug delivery: Application to zein protein complexes. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 439, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Padua, G.W. Nanoscale characterization of zein self-assembly. Langmuir 2012, 28, 2429–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Ma, M.; Xu, Y.; Wang, D. Surface coating of zein nanoparticles to improve the application of bioactive compounds: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 120, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; An, D.; Li, J.; Deng, S. Zein-based nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization, and pharmaceutical application. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1120251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Yao, F.; Tian, S.; Liu, M.; Liu, G.; Jiang, Y. Recent Advances in Zein-Based Nanocarriers for Precise Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Guzmán, C.J.; Castro-Muñoz, R. A Review of Zein as a Potential Biopolymer for Tissue Engineering and Nanotechnological Applications. Processes 2020, 8, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.H.L.; Duan, W.; Lee, B.-J.; Tran, T.T.D. The use of zein in the controlled release of poorly water-soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 566, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, P.H.L.; Duan, W.; Lee, B.-J.; Tran, T.T.D. Drug stabilization in the gastrointestinal tract and potential applications in the colonic delivery of oral zein-based formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zheng, H.; Lin, M.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, J. Characterization of the protein and peptide of excipient zein by the multi-enzyme digestion coupled with nano-LC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinney, L.L. Zein. In The Encyclopedia of Chemistry; Clark, G.L., Ed.; Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1958; pp. 319–320. [Google Scholar]
- Esen, A. Separation of alcohol-soluble proteins (zeins) from maize into three fractions by differential solubility. Plant Physiol. 1986, 80, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esen, A. A proposed nomenclature for the alcohol-soluble proteins (zeins) of maize (Zea mays L.). J. Cereal Sci. 1987, 5, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.A.; Larkins, B.A. Structural elements regulating zein gene expression. BioEssays 1989, 10, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, C.D.; Manley, R.H. Solvents for Zein. Primary Solvents. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1941, 33, 1416–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manley, R.H.; Evans, C.D. Binary Solvents for Zein. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1943, 35, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.D.; Manley, R.H. Ternary Solvents for Zein. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1944, 36, 408–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giteru, S.G.; Ali, M.A.; Oey, I. Recent progress in understanding fundamental interactions and applications of zein. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argos, P.; Pedersen, K.; Marks, M.; Larkins, B. A structural model for maize zein proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 9984–9990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushima, N.; Danno, G.-i.; Takezawa, H.; Izumi, Y. Three-dimensional structure of maize α-zein proteins studied by small-angle X-ray scattering. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1997, 1339, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forato, L.A.; Doriguetto, A.C.; Fischer, H.; Mascarenhas, Y.P.; Craievich, A.F.; Colnago, L.A. Conformation of the Z19 Prolamin by FTIR, NMR, and SAXS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2382–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momany, F.A.; Sessa, D.J.; Lawton, J.W.; Selling, G.W.; Hamaker, S.A.H.; Willett, J.L. Structural Characterization of α-Zein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Padua, G.W. Formation of Zein Microphases in Ethanol-Water. Langmuir 2010, 26, 12897–12901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Jiang, Q.; Reddy, N.; Yang, Y. Hollow nanoparticles from zein for potential medical applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 18227–18235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Wei, D.; Tang, L.; Deng, S.; Liu, G. Rational Fabrication of Folate-Conjugated Zein/Soy Lecithin/Carboxymethyl Chitosan Core-Shell Nanoparticles for Delivery of Docetaxel. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 13371–13381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Deng, Y.; Ye, L.; Xie, Q.; Jiang, Y. Enhancing hemocompatibility and the performance of Au@silica nanoparticles by coating with cRGD functionalized zein. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 125, 112064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Feng, X.; Gao, C.; Cheng, W.; Meng, L.; Wu, D.; Wang, Z.; Tang, X. Performance enhancing of saturated fatty acids with various carbon chain lengths on the structures and properties of zein films in alkaline solvents. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 155, 110214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, T.M.L.S.; Jansen-Alves, C.; Perleberg, C.; Bueno, D.T.; Leitzke, A.F.; da Silva Gonçalves, R.; Daniel Nörnberg, S.; da Rosa Zavareze, E.; de Pereira, C.M.P. Encapsulation of black soldier fly larvae oil in zein ultrafine fibers via electrospinning: Characterization and antioxidant properties. Food Chem. 2025, 472, 142823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, A.; Zhang, Y.; Hayat, U.; Liu, C.; Song, J.-L.; Shen, N.; Chao, Y.; Wang, H.-J.; Wang, J.-Y. Injectable zein gel with in situ self-assembly as hemostatic material. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 145, 213225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan Türker, D. Influence of charged polysaccharides and zein nanoparticles on the interfacial and emulsification properties of Pickering emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 161, 110887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Li, M.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. Zein-based nano-delivery systems for encapsulation and protection of hydrophobic bioactives: A review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 999373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Liang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, H. Preparation and evaluation of lecithin/zein hybrid nanoparticles for the oral delivery of Panax notoginseng saponins. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 164, 105882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossé, J. Monographie sur une protéine du maïs: La zéine. Ann. Physiol. Veg. 1961, 3, 105–139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Q.; Jin, M. Zein nanoparticles produced by liquid-liquid dispersion. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 2380–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.-K.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Q.; Yin, S.-W.; Yang, X.-Q.; Wen, Q.-B.; Tang, C.-H.; Lai, F.-R. Continuous preparation of zein colloidal particles by Flash NanoPrecipitation (FNP). J. Food Eng. 2014, 127, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wei, D.; Wang, H.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, Y. Self-assembly of zein microspheres with controllable particle size and narrow distribution using a novel built-in ultrasonic dialysis process. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 1094–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Feng, J.; Zhu, W.; Jiang, Y. Zein self-assembly using the built-in ultrasonic dialysis process: Microphase behavior and the effect of dialysate properties. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2018, 296, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.J.L.; Wong, A.I.C.; Xu, Y.; Yuliarti, O. Zein as a water insoluble excipient for spray dry encapsulation of hydrophilic bioactives. J. Food Eng. 2020, 283, 110054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Evangelho, J.A.; Crizel, R.L.; Chaves, F.C.; Prietto, L.; Pinto, V.Z.; Miranda, M.Z.d.; Dias, A.R.G.; Zavareze, E.d.R. Thermal and irradiation resistance of folic acid encapsulated in zein ultrafine fibers or nanocapsules produced by electrospinning and electrospraying. Food Res. Int. 2019, 124, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y. Incorporation of 10-hydroxycamptothecin nanocrystals into zein microspheres. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 155, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Gong, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Deng, H.; Deng, S. Development of nimesulide amorphous solid dispersions via supercritical anti-solvent process for dissolution enhancement. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 152, 105457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Li, J.; Deng, S. Applications of Supercritical Anti-Solvent Process in Preparation of Solid Multicomponent Systems. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Sato, E.; Sato, M.; Koizumi, S.; Unno, K.; Kato, T.; Nakai, K. Novel preparation of zein microspheres conjugated with PS-K available for cancer immunotherapy. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1989, 37, 757–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amidon, G.L.; Lennernäs, H.; Shah, V.P.; Crison, J.R. A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutic drug classification: The correlation of in vitro drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babadi, D.; Dadashzadeh, S.; Osouli, M.; Abbasian, Z.; Daryabari, M.S.; Sadrai, S.; Haeri, A. Biopharmaceutical and pharmacokinetic aspects of nanocarrier-mediated oral delivery of poorly soluble drugs. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 62, 102324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Cho, Y.W.; Park, K. Nanoparticles for oral delivery: Targeted nanoparticles with peptidic ligands for oral protein delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Chalamaiah, M.; Ren, X.; Ma, H.; Wu, J. Identification of New Anti-inflammatory Peptides from Zein Hydrolysate after Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion and Transport in Caco-2 Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berardi, A.; Bisharat, L.; AlKhatib, H.S.; Cespi, M. Zein as a Pharmaceutical Excipient in Oral Solid Dosage Forms: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 2009–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.R.; Bouwens, E.C.; Velikov, K.P. Sodium caseinate stabilized zein colloidal particles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12497–12503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascoli, M.; de Lima, R.; Fraceto, L.F. Zein Nanoparticles and Strategies to Improve Colloidal Stability: A Mini-Review. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, P.; Rawat, K.; Bohidar, H.B. Unraveling anomalous dispersion, and hydrophobic aggregation of zein nanoparticles. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 676, 132123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabra, S.A.; Elzoghby, A.O.; Sheweita, S.A.; Haroun, M.; Helmy, M.W.; Eldemellawy, M.A.; Xia, Y.; Goodale, D.; Allan, A.L.; Rohani, S. Self-assembled amphiphilic zein-lactoferrin micelles for tumor targeted co-delivery of rapamycin and wogonin to breast cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 128, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Ballegooie, C.; Wretham, N.; Ren, T.; Popescu, I.-M.; Yapp, D.T.; Bally, M.B. PEG Conjugated Zein Nanoparticles for In Vivo Use. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Sun, C.; Wang, D.; Gao, Y. The Interaction between Zein and Lecithin in Ethanol-Water Solution and Characterization of Zein-Lecithin Composite Colloidal Nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliardi, A.; Voci, S.; Giuliano, E.; Salvatici, M.C.; Celano, M.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Phospholipid/zein hybrid nanoparticles as promising carriers for the protection and delivery of all-trans retinoic acid. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 128, 112331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, H.; Ling, J.; Ouyang, X.-k.; Song, X. Enhancing the stability of zein/fucoidan composite nanoparticles with calcium ions for quercetin delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 2070–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Deng, S.; Liu, G. Development of carboxymethyl chitosan-coated zein/soy lecithin nanoparticles for the delivery of resveratrol. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 1636–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Xia, G.; Xue, F.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y. Fabrication and characterization of zein/lactoferrin composite nanoparticles for encapsulating 7,8-dihydroxyflavone: Enhancement of stability, water solubility and bioaccessibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heep, G.; Almeida, A.; Marcano, R.; Vieira, D.; Mainardes, R.M.; Khalil, N.M.; Sarmento, B. Zein-casein-lysine multicomposite nanoparticles are effective in modulate the intestinal permeability of ferulic acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariano, A.; Li, Y.O.; Singh, H.; McClements, D.J.; Davidov-Pardo, G. Encapsulation of orange-derived hesperetin in zein/pectin nanoparticles: Fabrication, characterization, stability, and bioaccessibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 153, 110024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lv, S.; Liu, Y.; Deng, S.; Liu, G. Constructing Dendrobium officinale extracts-coated zein nanoparticles as oral delivery vehicles for curcumin. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 211, 118229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Shan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y. Engineering nanomaterials to overcome the mucosal barrier by modulating surface properties. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 124, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Jiang, X.; Gan, Y.; Yu, M. Engineering nanoparticles to overcome the mucus barrier for drug delivery: Design, evaluation and state-of-the-art. Med. Drug Discov. 2021, 12, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tian, C.; Dong, B.; Xia, M.; Cai, Y.; Hu, R.; Chu, X. Models to evaluate the barrier properties of mucus during drug diffusion. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 599, 120415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, D.; Conte, C.; d’Angelo, I.; Miro, A.; Ungaro, F.; Quaglia, F. Mucoadhesive zein/beta-cyclodextrin nanoparticles for the buccal delivery of curcumin. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surendranath, M.; Ramesan, R.M.; Nair, P.; Parameswaran, R. Design and evaluation of propranolol hydrochloride loaded thiolated Zein/PEO electrospun fibrous matrix for transmucosal drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 7778–7791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauluk, D.; Padilha, A.K.; Khalil, N.M.; Mainardes, R.M. Chitosan-coated zein nanoparticles for oral delivery of resveratrol: Formation, characterization, stability, mucoadhesive properties and antioxidant activity. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboredo, C.; González-Navarro, C.J.; Martínez-Oharriz, C.; Martínez-López, A.L.; Irache, J.M. Preparation and evaluation of PEG-coated zein nanoparticles for oral drug delivery purposes. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 597, 120287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inchaurraga, L.; Martínez-López, A.L.; Abdulkarim, M.; Gumbleton, M.; Quincoces, G.; Peñuelas, I.; Martin-Arbella, N.; Irache, J.M. Modulation of the fate of zein nanoparticles by their coating with a Gantrez® AN-thiamine polymer conjugate. Int. J. Pharm. X 2019, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamson, N.G.; Berger, A.; Fein, K.C.; Whitehead, K.A. Anionic nanoparticles enable the oral delivery of proteins by enhancing intestinal permeability. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Bai, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, R.; Li, L.; Wu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Huang, Y. Promoting apical-to-basolateral unidirectional transport of nanoformulations by manipulating the nutrient-absorption pathway. J. Control. Release 2020, 323, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Li, L.; Chunta, S.; Wu, W.; Chen, Z.; Lu, Y. Enhanced oral bioavailability from food protein nanoparticles: A mini review. J. Control. Release 2023, 354, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somaida, A.; Abdelsalam, A.M.; Khedr, S.M.; Mohamed, A.M.; Tariq, I.; Almohsen, N.; Ashraf, O.; Osman, S.K.; Al-Sawahli, M.M.; Engelhardt, K.; et al. Improved oral bioavailability of paclitaxel through folate-engineered zein nanoparticles: Evaluation in intestinal organoid and in vivo models. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 318, 145117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Li, X.; Cui, W.; Xue, M.; Quan, Y.; Guo, X. Glucose-Modified Zein Nanoparticles Enhance Oral Delivery of Docetaxel. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Yin, W.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Chen, F.; Shen, Q.; Hu, X.; Xue, Y.; Ji, J. Zein and Trimethyl Chitosan-Based Core—Shell Nanoparticles for Quercetin Oral Delivery to Enhance Absorption by Paracellular Pathway in Obesity Mice. Biomater. Res. 2025, 29, 0193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Alwahab, N.S.A.; Moazzam, Z.M. Zein-based oral drug delivery system targeting activated macrophages. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 454, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.; Qian, K.; Yao, P. Insulin- and cholic acid-loaded zein/casein—Dextran nanoparticles enhance the oral absorption and hypoglycemic effect of insulin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 6234–6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, A.; Pingale, P.; Telange, D.; Chalikwar, S.; Borse, V. Lymphatic transport system to circumvent hepatic metabolism for oral delivery of lipid-based nanocarriers. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 66, 102934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.-B.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chen, K.-H.; Luo, P.-K.; Chuang, S.-H.; Yu, Y.-T.; Tai, H.-M.; Chen, C.-T.; Lin, K.-J.; Sung, H.-W. Engineering Nano- and Microparticles as Oral Delivery Vehicles to Promote Intestinal Lymphatic Drug Transport. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2104139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Miao, W.; Ji, H.; Lin, Q.; Li, X.; Sang, S.; McClements, D.J.; Jin, Z.; Qiu, C. Interaction of zein/HP-β-CD nanoparticles with digestive enzymes: Enhancing curcumin bioavailability. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Liao, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, H.; Kuang, J.; Li, J.; Guo, J.; Huang, T.; Li, J. Tea saponin-Zein binary complex as a quercetin delivery vehicle: Preparation, characterization, and functional evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Self-Assembly of Zein-Based Microcarrier System for Colon-Targeted Oral Drug Delivery. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 12689–12699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Wu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, J.; Luo, X.; Chang, L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Zou, L.; You, Y.; et al. Colon-specific delivery of isoliquiritigenin by oral edible zein/caseate nanocomplex for ulcerative colitis treatment. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 981055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Sun, C.; Wei, X.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Y. Gastrointestinal pH-Sensitive Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Zein Nanoparticles Coated with Bioactive Glycyrrhizic Acid for Improving Oral Bioaccessibility of Curcumin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 14678–14689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.; Qian, K.; Xu, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Pan, T.; Wang, Z.; Yao, P.; Lin, L. Intestinal epithelium penetration of liraglutide via cholic acid pre-complexation and zein/rhamnolipids nanocomposite delivery. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reboredo, C.; González-Navarro, C.J.; Martínez-López, A.L.; Martínez-Ohárriz, C.; Sarmento, B.; Irache, J.M. Zein-Based Nanoparticles as Oral Carriers for Insulin Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalani, D.V.; Nutan, B.; Kumar, A.; Singh Chandel, A.K. Bioavailability Enhancement Techniques for Poorly Aqueous Soluble Drugs and Therapeutics. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, D. Fabrication and Characterization of Lutein-Loaded Nanoparticles Based on Zein and Sophorolipid: Enhancement of Water Solubility, Stability, and Bioaccessibility. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11977–11985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Han, C.; Tian, Y.; Liu, T. Fabrication of curcumin-loaded zein nanoparticles stabilized by sodium caseinate/sodium alginate: Curcumin solubility, thermal properties, rheology, and stability. Process Biochem. 2020, 94, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Li, Z. A review of drug release mechanisms from nanocarrier systems. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 76, 1440–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouman, J.; Belton, P.; Venema, P.; van der Linden, E.; de Vries, R.; Qi, S. Controlled Release from Zein Matrices: Interplay of Drug Hydrophobicity and pH. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-Bahamonde, J.; Herrera, G.; Lupini, S.; Arabaghian, H.; Rodrigues, D.F. Zein Nanoparticles for Controlled Intestinal Drug Release for the Treatment of Gastrointestinal Infections. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 21707–21720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annappa, H.; Tamatam, A.; Nallamuthu, I.; Ranganathan, K. Formulation of pH-responsive nanoparticles using zein/sodium alginate polymers for enhanced bioavailability of the vitamin D3. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 313, 144140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Sang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Mei, X.; Ren, X. Preparation of gastrointestinal pH-responsive zein coated tea polyphenol-heparin hydrocolloids using for inflammatory bowel disease therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 309, 143135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azman, M.; Sabri, A.H.; Anjani, Q.K.; Mustaffa, M.F.; Hamid, K.A. Intestinal Absorption Study: Challenges and Absorption Enhancement Strategies in Improving Oral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penalva, R.; González-Navarro, C.J.; Gamazo, C.; Esparza, I.; Irache, J.M. Zein nanoparticles for oral delivery of quercetin: Pharmacokinetic studies and preventive anti-inflammatory effects in a mouse model of endotoxemia. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chu, Y.; Tao, X.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Sang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, L. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles-cloaked modified zein nanoparticles for oral delivery of paclitaxel. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2023, 28, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, O.A.A. Development and single dose clinical pharmacokinetics investigation of novel zein assisted- alpha lipoic acid nanoencapsulation of vardenafil. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brotons-Canto, A.; González-Navarro, C.J.; Gil, A.G.; Asin-Prieto, E.; Saiz, M.J.; Llabrés, J.M. Zein Nanoparticles Improve the Oral Bioavailability of Curcumin in Wistar Rats. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brotons-Canto, A.; Gonzalez-Navarro, C.J.; Gurrea, J.; González-Ferrero, C.; Irache, J.M. Zein nanoparticles improve the oral bioavailability of resveratrol in humans. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y.; Freeman, K.; Mchenry, M.A.; Wang, C.; Guo, M. Enhanced Stability and Oral Bioavailability of Cannabidiol in Zein and Whey Protein Composite Nanoparticles by a Modified Anti-Solvent Approach. Foods 2022, 11, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Feng, J.; McClements, D.J.; Hu, K. Impact of calcium-reinforcement on stability, bioavailability, and bioactivity of quercetin-loaded zein/alginate-pectin nanoparticles. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 1771–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Wang, B.; Zhang, C.; Dong, Q.; Qian, J.; Zha, L.; Chen, W.; Hong, L. Preparation and preliminary pharmacokinetics study of GNA-loaded zein nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 1626–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.-F.; Zheng, G.-D.; Wang, W.-J.; Yin, Z.-P.; Chen, J.-G.; Li, J.-E.; Zhang, Q.-F. Physicochemical properties and bioavailability comparison of two quercetin loading zein nanoparticles with outer shell of caseinate and chitosan. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, L.; Wang, B.; Qian, J.; Fletcher, B.; Zhang, C.; Dong, Q.; Chen, W.; Hong, L. Preparation, characterization and preliminary pharmacokinetic study of pH-sensitive Hydroxyapatite/Zein nano-drug delivery system for doxorubicin hydrochloride. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karoshi, V.R.; Nallamuthu, I.; Anand, T. Co-encapsulation of vitamins B6 and B12 using zein/gum arabic nanocarriers for enhanced stability, bioaccessibility, and oral bioavailability. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 9766–9782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashem, F.M.; Al-Sawahli, M.M.; Nasr, M.; Ahmed, O.A. Optimized zein nanospheres for improved oral bioavailability of atorvastatin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 4059–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Y.-T.; Wang, W.-j.; Zheng, G.-D.; Yin, Z.-P.; Chen, J.-G.; Li, J.-E.; Chen, L.-L.; Zhang, Q.-F. In vivo and in vitro comparison of three astilbin encapsulated zein nanoparticles with different outer shells. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 9784–9792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Sharma, G.; Kushwah, V.; Ghoshal, G.; Jain, A.; Singh, B.; Shivhare, U.S.; Jain, S.; Katare, O.P. Beta carotene-loaded zein nanoparticles to improve the biopharmaceutical attributes and to abolish the toxicity of methotrexate: A preclinical study for breast cancer. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Pan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yin, X.; Yu, C.; Kong, W.; Zhang, Y. The Effect of Size, Dose, and Administration Route on Zein Nanoparticle Immunogenicity in BALB/c Mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9917–9928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schofield, T.; Robbins, D.; Miró-Quesada, G. Critical Quality Attributes, Specifications, and Control Strategy. In Quality by Design for Biopharmaceutical Drug Product Development; Jameel, F., Hershenson, S., Khan, M.A., Martin-Moe, S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 511–535. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelsalam, A.M.; Somaida, A.; Ayoub, A.M.; Alsharif, F.M.; Preis, E.; Wojcik, M.; Bakowsky, U. Surface-Tailored Zein Nanoparticles: Strategies and Applications. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Ma, M.; Peng, X.; Xie, Y.; Xie, A.; Deng, B.; Ouyang, J.; Tao, W.; Yang, P.; He, W. Oral Delivery Strategies for Biological Drugs. Small Methods 2025, 2401355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, R.; He, H.; Lu, Y.; Lu, H.; Shen, S.; Wu, W. Oral targeted drug delivery to post-gastrointestinal sites. J. Control. Release 2024, 370, 256–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrero, D.; Pujol-Vila, F.; Vera, D.; Gabriel, G.; Illa, X.; Elizalde-Torrent, A.; Alvarez, M.; Villa, R. Gut-on-a-chip: Mimicking and monitoring the human intestine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 181, 113156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lee, D.; Ma, Y.; Wilhelm, S.; Wang, H.; Kim, B.Y.S.; Jiang, W. Multi-omics approaches to decipher the interactions of nanoparticles and biological systems. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2025, 3, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, R.; Yao, X.; Bai, L.; Hang, R. Evolving biomaterials design from trial and error to intelligent innovation. Acta Biomater. 2025, 197, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutcliffe, R.; Doherty, C.P.A.; Morgan, H.P.; Dunne, N.J.; McCarthy, H.O. Strategies for the design of biomimetic cell-penetrating peptides using AI-driven in silico tools for drug delivery. Biomater. Adv. 2025, 169, 214153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Li, D.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Y.M.; Liao, W. AI-aided design and multi-scale optimization of mechanical metastructures with controllable anisotropy. Eng. Struct. 2024, 310, 118134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Kuang, H.; Huang, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, R.; Shang, G.; Wang, Z.; Liao, Y.; He, J.; Li, D. 3D printing of drug delivery systems enhanced with micro/nano-technology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2025, 216, 115479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Material | Drug | Key Strategy | Key Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zein, lecithin, β-sitosterol | Panax notoginseng saponins (PNSs) | Protection from GI degradation; lecithin coating to mimic lipoprotein structure | Improved PNS stability in GI tract; increased intestinal absorption; 1.71 × higher oral bioavailability than free PNS | [54] |
| Zein, lactoferrin (Lf) | Rapamycin; Wogonin | Active tumor targeting (Lf receptor); synergistic mTOR/PI3K/AKT inhibition | Enhanced cellular uptake and cytotoxicity; superior tumor suppression in breast cancer model; sequential drug release | [74] |
| Zein, soy lecithin, carboxymethyl chitosan (CMC) | Resveratrol | Ternary complex with CMC coating for stability | 2.55 × higher drug dissolution; 2.27 × higher bioaccessibility; 1.69 × higher ABTS+ scavenging; > 68% drug retention after 45-day storage | [79] |
| Zein, pectin | Hesperetin | Pectin shell prevents aggregation in GI tract; zein solubilizes hesperetin for micelle uptake | Improved colloidal stability (pH 2–8, NaCl ≤ 50 mM, 4-week storage); 5.6 × higher bioaccessibility | [82] |
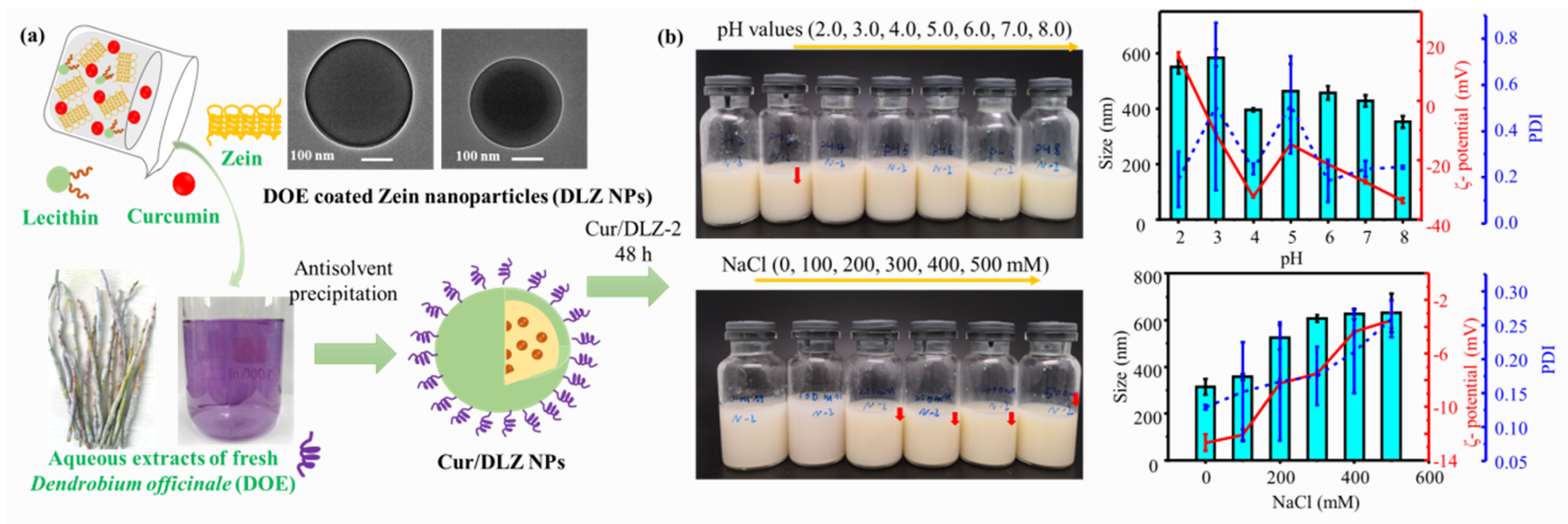
| Zein, dendrobium officinale extracts (DOE), soy lecithin | Curcumin | Plant extract coating for stability and synergistic bioactivity | Good aqueous stability and redispersibility; 3.0 × higher bioaccessibility; 6.8 × higher ABTS+ scavenging; DOE coating enhanced cellular uptake and antitumor activity | [83] |
| Zein, chitosan | Resveratrol | Chitosan (+) binds mucin (-), prolonging residence; zein controls resveratrol release | Improved gastric protection; enhanced mucoadhesion; sustained resveratrol release | [89] |
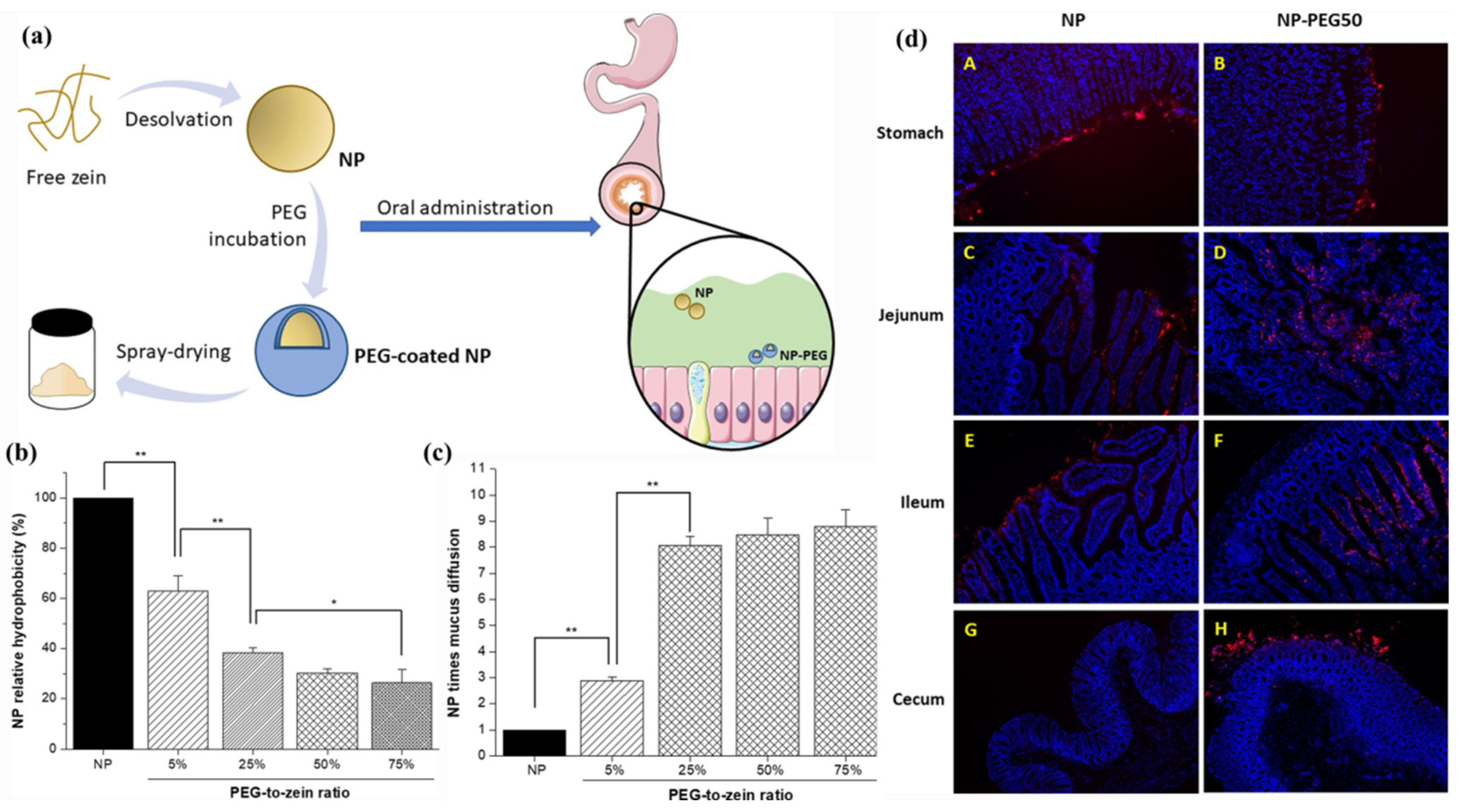
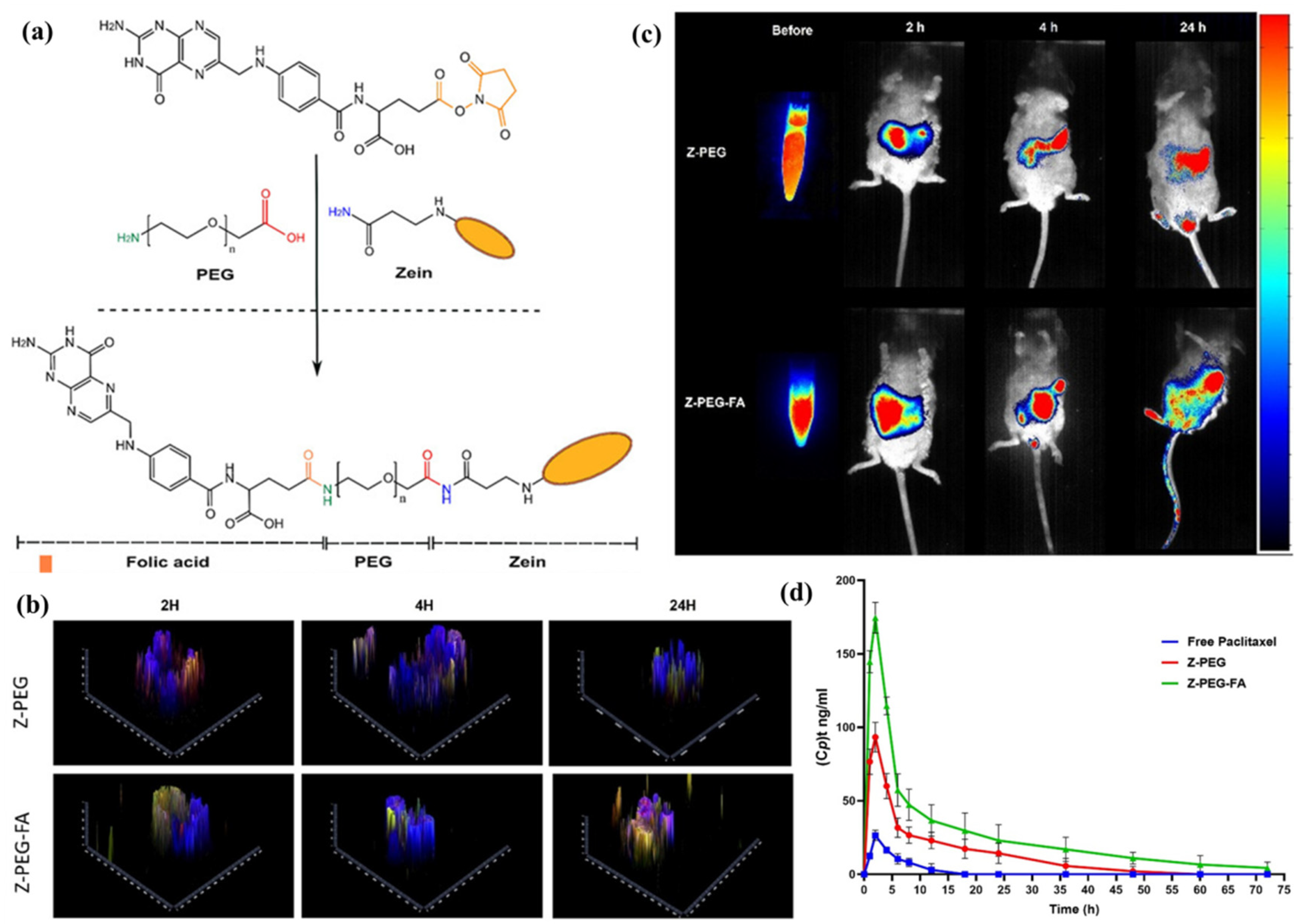
| Zein, PEG, folic acid | Paclitaxel | PEGylation (stability, mucus penetration) and folic acid conjugation (FA-mediated endocytosis/transcytosis) | Enhanced stability in GI fluids; improved uptake in spheroids and intestinal organoids; 7.6 × higher oral bioavailability | [95] |
| Zein, glucose, soybean lecithin | Docetaxel | Glucose modification targets glucose transporters and enhances endocytosis via multiple pathways | 2.19 × increased oral bioavailability; 1.22 × higher cellular uptake; higher tumor distribution and lower systemic toxicity | [96] |
| Zein, hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin | Curcumin | Cyclodextrin complexation to improve solubility; ionic modulation (Ca2+/Na+) to control digestion | Sustained drug release and enhanced mucus penetration; Ca2+-induced stability increased bioavailability | [102] |
| Zein, tea saponin | Quercetin | Coating zein core with amphiphilic surfactant to enhance stability and solubility | 30.16× increased solubility; enhanced thermal/ionic/pH stability; higher oral bioavailability | [103] |
| Zein; polydopamine | Indomethacin | Colon targeting via porous structure and polydopamine coating | Enhanced solubility via polymorph modification; sustained and colon-targeted release | [104]. |
| Zein, sodium caseinate | Isoliquiritigenin | Caseinate stabilizes zein NPs; colon-targeted delivery via pH sensitivity | Enhanced cellular uptake in colonic cells/macrophages; prolonged colon retention; reduced ulcerative colitis symptoms in mice | [105] |
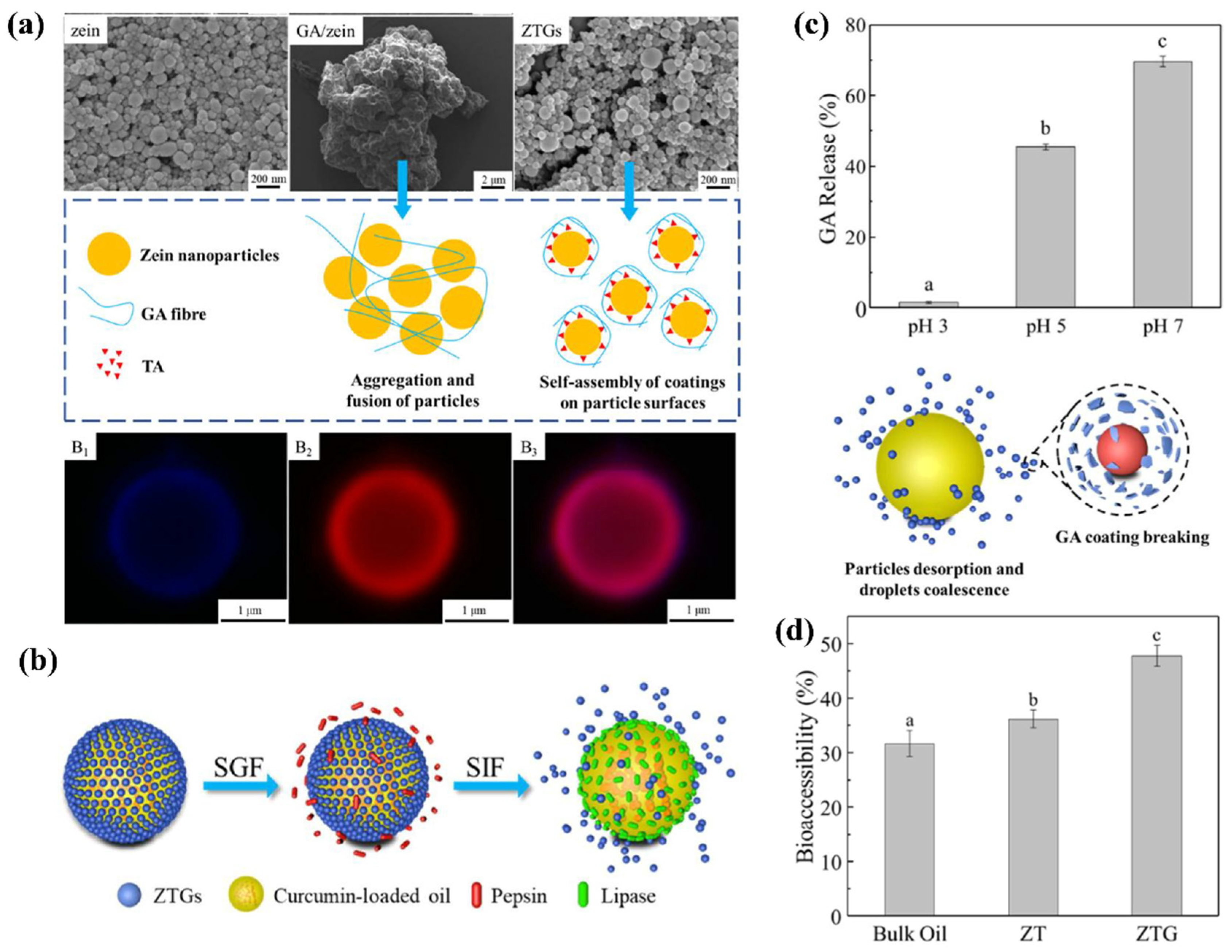
| Zein, glycyrrhizic acid, tannic acid, | Curcumin | pH-responsive glycyrrhizic acid coating for intestine-targeted release | Enhanced stability in gastric fluid; pH-triggered demulsification in intestinal fluid; increased oral bioaccessibility | [106] |
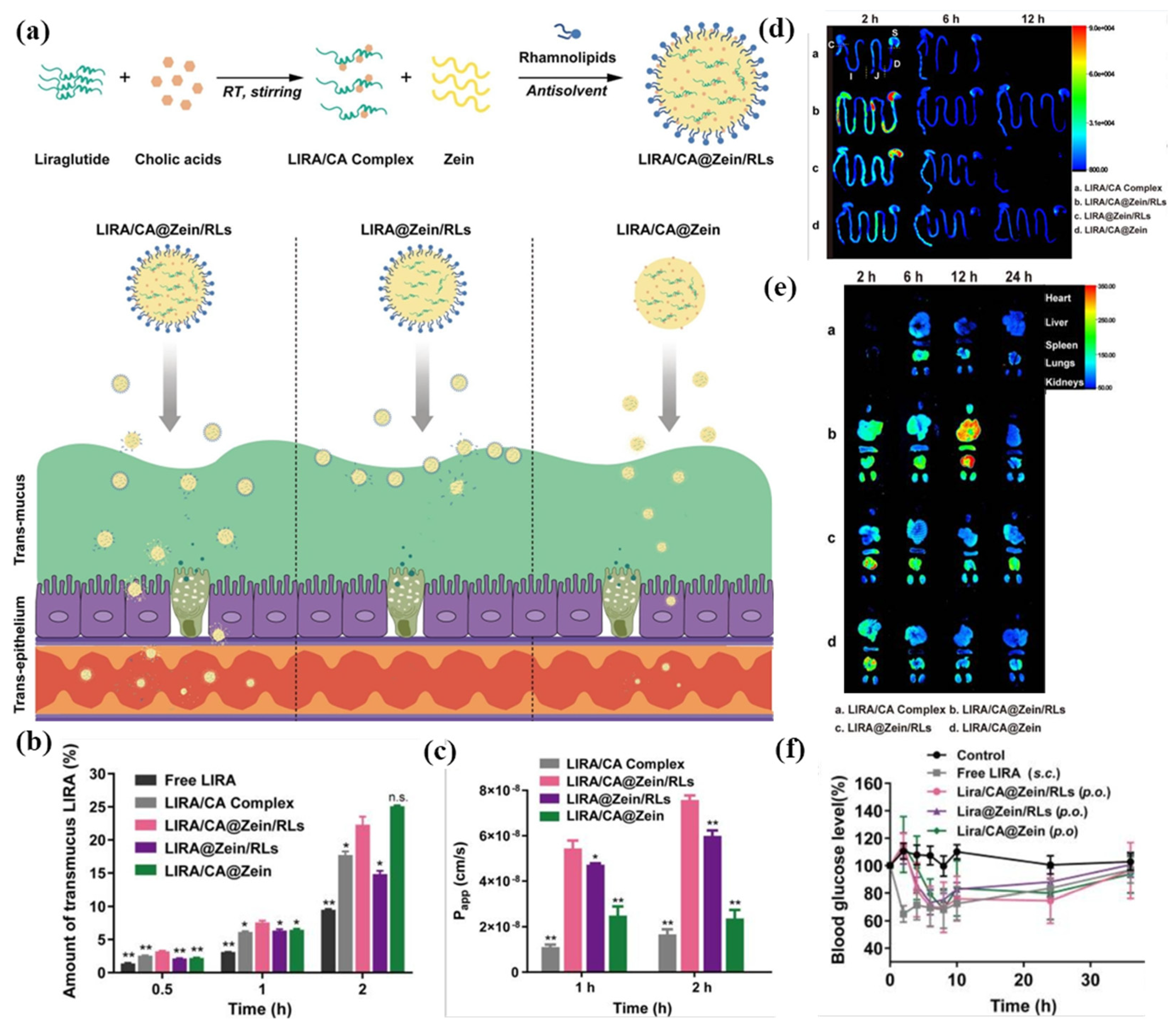
| Zein, rhamnolipids, cholic acid | Liraglutide | Pre-complexation with cholic acid to reduce self-aggregation; rhamnolipids coating for stabilization and endocytosis promotion. | Protection from enzymatic degradation; enhanced intestinal permeability; sustained hypoglycemic effect > 24 h | [107] |
| Zein, PEG | Insulin | PEG coating facilitates mucus penetration | 3.0 × higher pharmacological activity; 2.5 × higher oral bioavailability | [108] |
| Compounds | Carriers | EE (%) | In Vivo Study | Key Bioavailability Parameters # | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paclitaxel | Folate–zein | 87.6 | Rabbits | Cmax (ng/mL): 21.5→162.21 AUC (ng·h/mL):149.75→1147.25 MRT (h): 5.23→5.88 | [95] |
| Docetaxel | Glucose-modified zein | 85 | Sprague Dawley (SD) rats | Fr(%): 43.82→96.04; AUC (ng·h/mL): 3686→8078 MRT (h): 17.45→25.15 | [96] |
| Vitamin D3 | Zein/sodium alginate | 77 | Wistar rats | Plasma concentration: ↑3.4-fold Alkaline phosphatase: ↑1.3-fold | [115] |
| Quercetin | Zein/2-hydroxypropyl- β-cyclodextrin | 80.7 | Wistar rats | Fr (%): 4→57 Cmax (μg/mL): 1.4→3.4 AUC (μg·h/mL): 6.77→94.51 MRT (h): 4.9→25.4 | [118] |
| Paclitaxel | Vesicle-cloaked zein | 93 | SD rats | Cmax (μg/L): 51→132 t½ (h): 4.317→11.708 AUC (mg·h/L): 0.354→2.564 MRT (h): 6.454→17.074 | [119] |
| Vardenafil | Zein/alpha lipoic acid | 69.38 | Humans | Fr: ↑2.49-fold tmax (h): 1→2 AUC (ng·h/mL): 69.24→198.37 MRT (h): 5.72→11.86 | [120] |
| Curcumin | Zein | 98 | Wistar rats | Fr: ↑9.17- fold Cmax (ng/mL): 186.29→1742.97 AUC (μg·h/mL): 2.21→20.27 | [121] |
| Resveratrol | Zein | 87 | Humans | Cmax (resveratrol): 21.80 ng/mL Cmax (metabolite): 986.29 ng/mL | [122] |
| Cannabidiol | Zein/whey protein | 89 | SD rats | Cmax (μg/mL): 0.232→0.466 AUC (μg·h/mL): 1.657→2.912 MRT (h): 6.654→7.136 | [123] |
| Quercetin | zein/alginate–pectin | 84.2 | SD rats | Cmax(mg/L): 1.33→3.13 AUC (mg·min/L):210.75→606.81 MRT (min): 149.9→229.9 | [124] |
| Gambogenic acid | Zein/phospholipid | 76.35 | SD rats | Cmax (mg/L): 0.21→0.42 t½ (min): 69.32→222.52 AUC (mg·min/L): 50.02→243.49 MRT (min): 192.1→420.95 | [125] |
| Quercetin | Zein/caseinate | 82.78 | SD rats | Fr: ↑2.34-fold Feces excretion (%): 70→19.4 | [126] |
| Doxorubicin hcl | Zein/hydroxyapatite | 44.75 | SD rats | t½ (h): 13.91→37.91 AUC (μg·h/mL): 22.47→70.07 | [127] |
| Vitamins | Zein/gum arabic | B6: 61.6 B12: 56.3 | Wistar rats | Fr (B6): ↑4.8-fold Fr (B12): ↑2.2-fold | [128] |
| Atorvastatin | Zein | 29.71 | Wistar albino rats | Cmax (μg/mL): 1.79→8.65 t½ (h): 16.99→20.84 AUC (μg·h/mL): 31.28→117.76 MRT (h): 24.38→27.04 | [129] |
| Astilbin | Zein/chitosan | 84.68 | SD rats | Fr: ↑18.2- fold Cmax (ng/mL): 42→2950 t½ (h): 1.45→2.94 AUC (mg·h/L): 0.29→5.3 | [130] |
| Beta carotene | Zein | 68.8 | Wistar rats | Cmax (μg/mL): 49.21→113.02 t½ (h): 14.35→20.87 AUC (μg·h/mL): 1054.8→2825 MRT (h): 21.37→30.48 | [131] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; An, D.; Meng, X.; Deng, S.; Liu, G. Zein-Based Nanocarriers: Advances in Oral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070944
Liu Y, An D, Meng X, Deng S, Liu G. Zein-Based Nanocarriers: Advances in Oral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(7):944. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070944
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuxin, Dongyu An, Xiangjian Meng, Shiming Deng, and Guijin Liu. 2025. "Zein-Based Nanocarriers: Advances in Oral Drug Delivery" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 7: 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070944
APA StyleLiu, Y., An, D., Meng, X., Deng, S., & Liu, G. (2025). Zein-Based Nanocarriers: Advances in Oral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics, 17(7), 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070944






