Long-Term Effect of Semaglutide on the Glomerular Filtration Rate Slope in High-Risk Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy: Analysis in Real-World Clinical Practice
Abstract
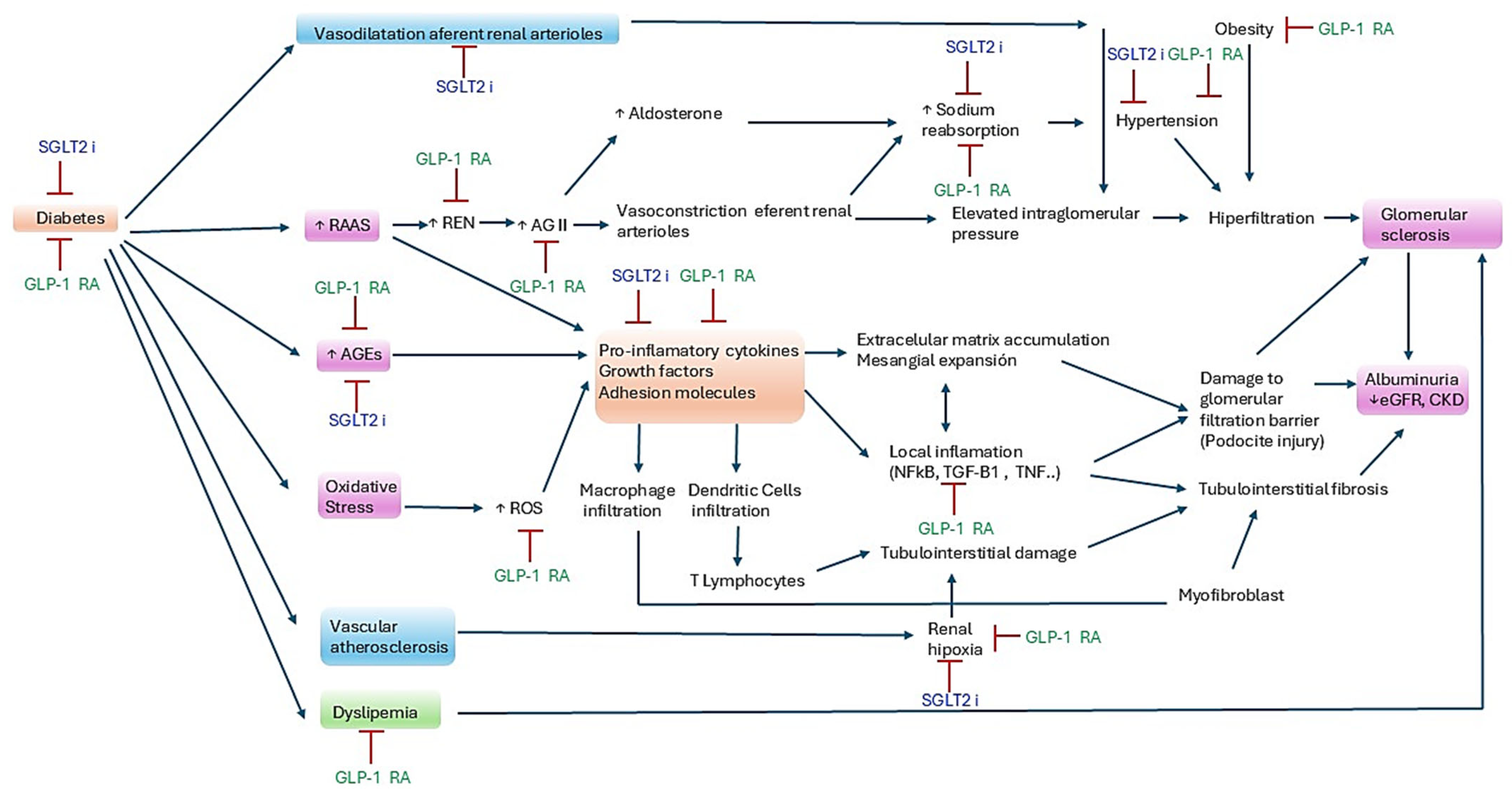
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
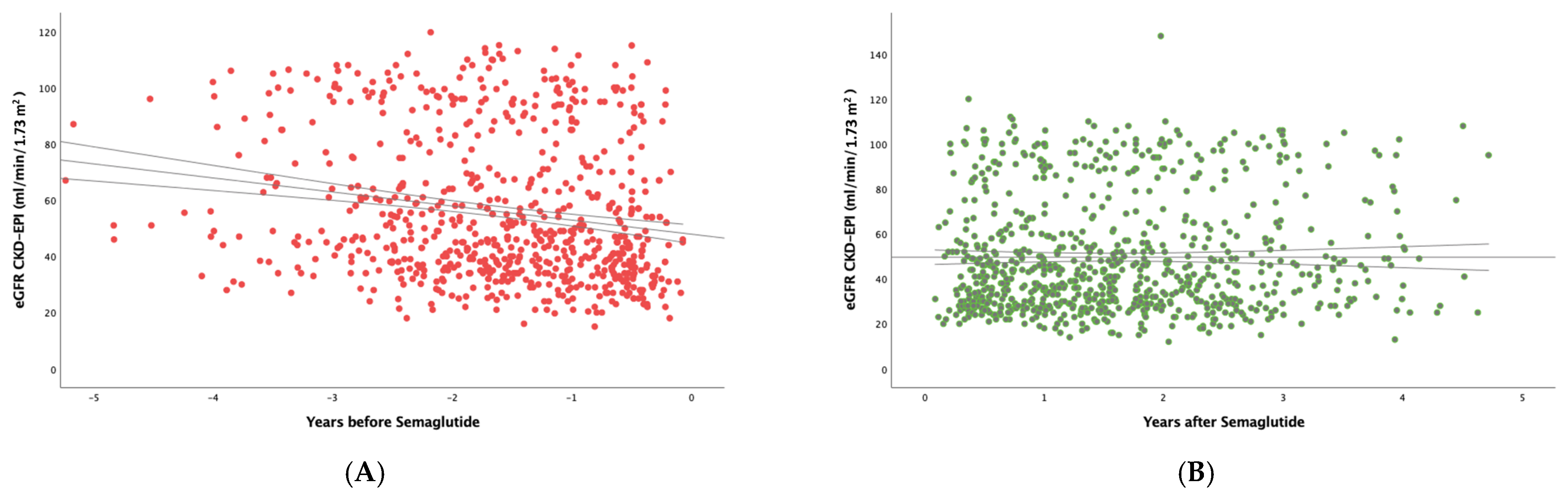
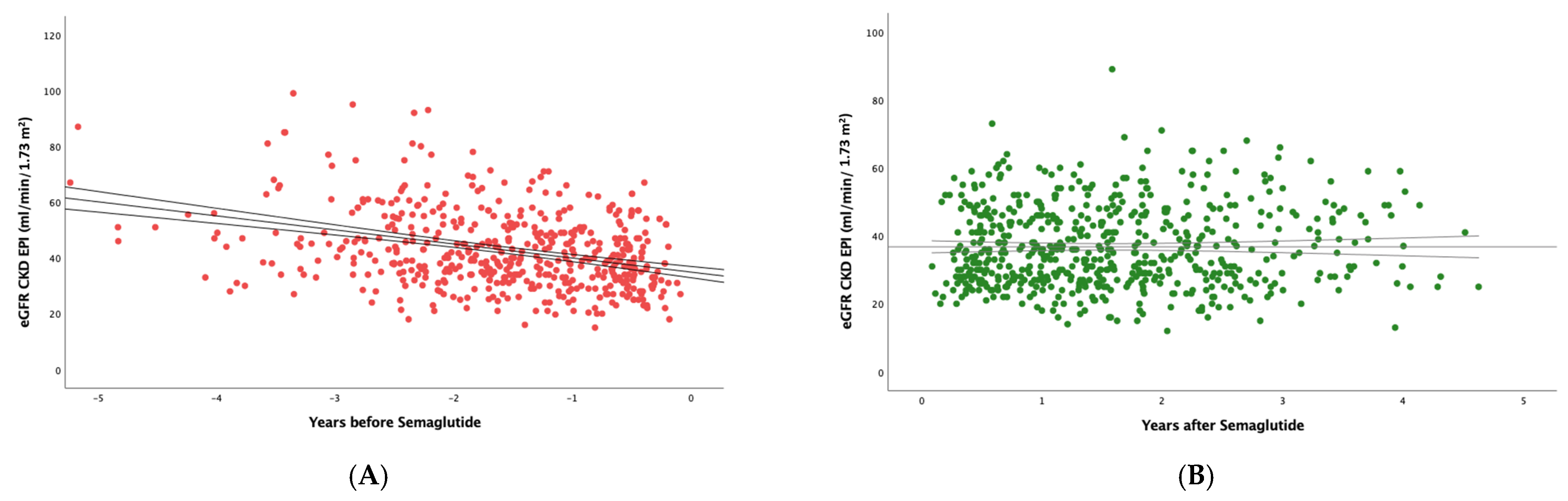
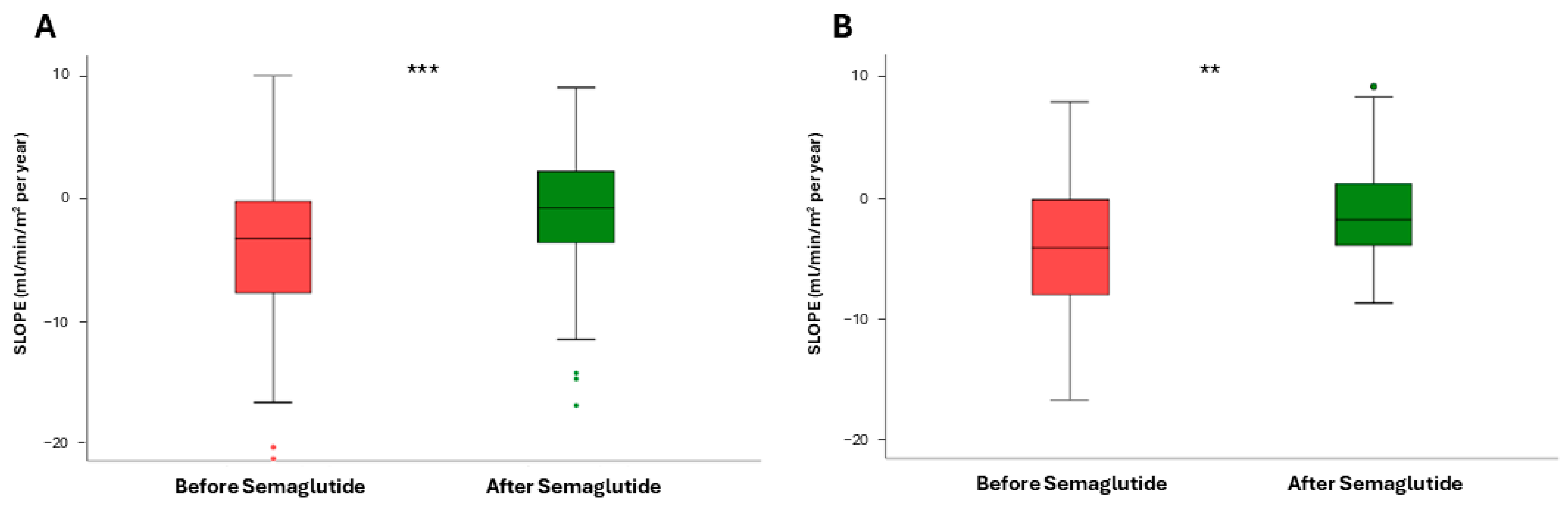
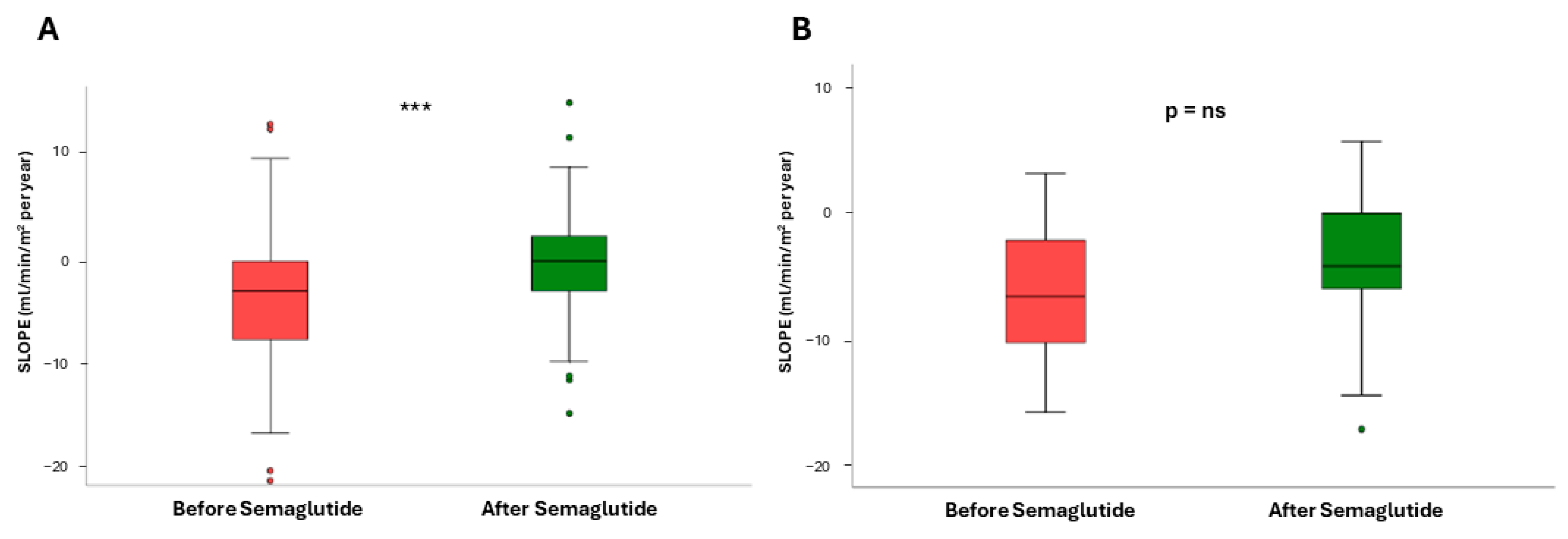
3. Results
3.1. Impact of Semaglutide Treatment on eGFR Slope
3.2. Effect of Semaglutide on Other Clinical Parameters
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| DN | Diabetic nephropathy |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| GLP-1AR | Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist |
| RAASi | Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone axis inhibitors |
| SGLT2i | Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors |
| UACR | Urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio |
References
- Currie, G.; McKay, G.; Delles, C. Biomarkers in diabetic nephropathy: Present and future. World J. Diabetes 2014, 5, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, E.J.; Hunsicker, L.G.; Clarke, W.R.; Berl, T.; Pohl, M.A.; Lewis, J.B.; Ritz, E.; Atkins, R.C.; Rohde, R.; Raz, I.; et al. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Jongs, N.; Chertow, G.M.; Langkilde, A.M.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Rossing, P.; Sjöström, C.D.; Stefansson, B.V.; Toto, R.D.; et al. Effect of dapagliflozin on the rate of decline in kidney function in patients with chronic kidney disease with and without type 2 diabetes: A prespecified analysis from the DAPA-CKD trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Song, Y.; Guo, T.; Xiao, G.; Li, Q. Effect of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists on the renal protection in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. 2022, 48, 101366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.K.; Sperati, C.J.; Thavarajah, S.; Grams, M.E. Reducing Kidney Function Decline in Patients with CKD: Core Curriculum 2021. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 77, 969–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, D.T.W.; Au, I.C.H.; Tang, E.H.M.; Cheung, C.L.; Lee, C.H.; Woo, Y.C.; Wu, T.; Tan, K.C.B.; Wong, C.K.H. Kidney outcomes associated with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors versus glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: A real-world population-based analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2022, 50, 101510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newsome, P.N.; Buchholtz, K.; Cusi, K.; Linder, M.; Okanoue, T.; Ratziu, V.; Sanyal, A.J.; Sejling, A.-S.; Harrison, S.A. A Placebo-Controlled Trial of Subcutaneous Semaglutide in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosenzon, O.; Capehorn, M.S.; de Remigis, A.; Rasmussen, S.; Weimers, P.; Rosenstock, J. Impact of semaglutide on high-sensitivity C-reactive protein: Exploratory patient-level analyses of SUSTAIN and PIONEER randomized clinical trials. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reppo, I.; Jakobson, M.; Volke, V. Effects of Semaglutide and Empagliflozin on Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newsome, P.; Francque, S.; Harrison, S.; Ratziu, V.; van Gaal, L.; Calanna, S.; Hansen, M.; Linder, M.; Sanyal, A. Effect of semaglutide on liver enzymes and markers of inflammation in subjects with type 2 diabetes and/or obesity. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Ren, Q.; Niu, S.; Pan, X.; Yue, L.; Li, Z.; Zhu, R.; Jia, Z.; Chen, X.; et al. Metabolomics Provides Insights into Renoprotective Effects of Semaglutide in Obese Mice. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2022, 16, 3893–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattar, N.; Lee, M.M.Y.; Kristensen, S.L.; Branch, K.R.H.; del Prato, S.; Khurmi, N.S.; Lam, C.S.P.; Lopes, R.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Pratley, R.E.; et al. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, T.; Ying, J.; Vonesh, E.F.; Tighiouart, H.; Levey, A.S.; Coresh, J.; Herrick, J.S.; Imai, E.; Jafar, T.H.; Maes, B.D.; et al. Performance of GFR Slope as a Surrogate End Point for Kidney Disease Progression in Clinical Trials: A Statistical Simulation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 1756–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.S.; Bakris, G.L.; Shahid, I.; Weir, M.R.; Butler, J. Potential Role and Limitations of Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Slope Assessment in Cardiovascular Trials: A Review. JAMA Cardiol. 2022, 7, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inker, L.A.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Tighiouart, H.; Levey, A.S.; Coresh, J.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Simon, A.L.; Ying, J.; Beck, G.J.; Wanner, C.; et al. GFR Slope as a Surrogate End Point for Kidney Disease Progression in Clinical Trials: A Meta-Analysis of Treatment Effects of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, W.; Inker, L.A.; Haaland, B.; Appel, G.B.; Badve, S.V.; Caravaca-Fontán, F.; Chalmers, J.; Floege, J.; Goicoechea, M.; Imai, E.; et al. Evaluation of Variation in the Performance of GFR Slope as a Surrogate End Point for Kidney Failure in Clinical Trials that Differ by Severity of CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 18, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaman, A.M.; Bain, S.C.; Bakris, G.L.; Buse, J.B.; Idorn, T.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Mann, J.F.; Nauck, M.A.; Rasmussen, S.; Rossing, P.; et al. Effect of the Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists Semaglutide and Liraglutide on Kidney Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Pooled Analysis of SUSTAIN 6 and LEADER. Circulation 2022, 145, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, J.F.E.; Hansen, T.; Idorn, T.; Leiter, L.A.; Marso, S.P.; Rossing, P.; Seufert, J.; Tadayon, S.; Vilsbøll, T. Effects of once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide on kidney function and safety in patients with type 2 diabetes: A post-hoc analysis of the SUSTAIN 1–7 randomised controlled trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 880–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.W.; Huang, M.S.; Shyu, Y.C.; Chien, R.N. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase elevation is associated with metabolic syndrome, hepatic steatosis, and fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A community-based cross-sectional study. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2021, 37, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haring, R.; Wallaschofski, H.; Nauck, M.; Dörr, M.; Baumeister, S.E.; Völzke, H. Ultrasonographic hepatic steatosis increases prediction of mortality risk from elevated serum gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase levels. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Hauske, S.; Ono, Y.; Kyaw, M.H.; Steubl, D.; Naito, Y.; Kanasaki, K. Analysis of eGFR index category and annual eGFR slope association with adverse clinical outcomes using real-world Japanese data: A retrospective database study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e052246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Bommel, E.J.M.; Muskiet, M.H.A.; Tonneijck, L.; Kramer, M.H.; Nieuwdorp, M.; van Raalte, D.H. SGLT2 Inhibition in the Diabetic Kidney-From Mechanisms to Clinical Outcome. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosterd, C.M.; Bjornstad, P.; van Raalte, D.H. Nephroprotective effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists: Where do we stand? J. Nephrol. 2020, 33, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Bosch-Traberg, H.; Cherney, D.Z.; Hadjadj, S.; Lawson, J.; Mosenzon, O.; Rasmussen, S.; Bain, S.C. Post hoc analysis of SUSTAIN 6 and PIONEER 6 trials suggests that people with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk treated with semaglutide experience more stable kidney function compared with placebo. Kidney Int. 2023, 103, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klen, J.; Dolžan, V. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity: The Impact of Pharmacological Properties and Genetic Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkovic, V.; Tuttle, K.R.; Rossing, P.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Mann, J.F.; Bakris, G.; Baeres, F.M.; Idorn, T.; Bosch-Traberg, H.; Lausvig, N.L.; et al. Effects of Semaglutide on Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnott, C.; Neuen, B.L.; Heerspink, H.J.; Figtree, G.A.; Kosiborod, M.; Lam, C.S.; Cannon, C.P.; Rosenthal, N.; Shaw, W.; Mahaffey, K.W.; et al. The effects of combination canagliflozin and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist therapy on intermediate markers of cardiovascular risk in the CANVAS program. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 318, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.; Nardi, Y.; Krause, I.; Goldberg, E.; Milo, G.; Garty, M.; Krause, I. A longitudinal assessment of the natural rate of decline in renal function with age. J. Nephrol. 2014, 27, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, M.; Shimbo, T.; Horio, M.; Ando, M.; Yasuda, Y.; Komatsu, Y.; Masuda, K.; Matsuo, S.; Maruyama, S.; Abe, H. Longitudinal Study of the Decline in Renal Function in Healthy Subjects. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhu, J.Y.; Fang, Y.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Liou, H.H.; Chen, M.T.; Tsai, M.H. Enhanced renoprotective effects of combined glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Real-world evidence. J. Diabetes Investig. 2025, 16, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, L.; Bradley, R.M.; Auerbach, P.; Abitbol, A. Real-world impact of adding a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist compared with basal insulin on metabolic targets in adults living with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease already treated with a sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor: The Impact GLP-1 CKD study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 4674–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apperloo, E.M.; Cherney, D.Z.I.; Kuhlman, A.B.; Mann, J.F.E.; Rasmussen, S.; Rossing, P.; Tuttle, K.R.; Vrhnjak, B.; Heerspink, H.J.L. Effect of semaglutide on kidney function across different levels of baseline HbA1c, blood pressure, body weight and albuminuria in SUSTAIN 6 and PIONEER 6. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2025, 40, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, J.F.E.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G.; Belmar, N.; Bosch-Traberg, H.; Busch, R.; Charytan, D.M.; Hadjadj, S.; Gillard, P.; Górriz, J.L.; et al. Effects of semaglutide with and without concomitant SGLT2 inhibitor use in participants with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease in the FLOW trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2849–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Look AHEAD Research Group. Effect of a long-term behavioural weight loss intervention on nephropathy in overweight or obese adults with type 2 diabetes: A secondary analysis of the Look AHEAD randomised clinical trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gervasini, G.; García-Pino, G.; Mota-Zamorano, S.; Luna, E.; García-Cerrada, M.; Tormo, M.Á.; Cubero, J.J. Association of polymorphisms in leptin and adiponectin genes with long-term outcomes in renal transplant recipients. Pharmacogenom. J. 2020, 20, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Pino, G.; Luna, E.; Blanco, L.; Tormo, M.Á.; Mota-Zamorano, S.; González, L.M.; Azevedo, L.; Robles, N.R.; Gervasini, G. Body Fat Distribution, Adipocytokines Levels and Variability in Associated Genes and Kidney Transplant Outcomes. Prog. Transplant. 2022, 32, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota-Zamorano, S.; Luna, E.; Garcia-Pino, G.; González, L.M.; Gervasini, G. Combined donor-recipient genotypes of leptin receptor and adiponectin gene polymorphisms affect the incidence of complications after renal transplantation. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2020, 25, 100648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota-Zamorano, S.; Luna, E.; Garcia-Pino, G.; González, L.M.; Gervasini, G. Variability in the leptin receptor gene and other risk factors for post-transplant diabetes mellitus in renal transplant recipients. Ann. Med. 2019, 51, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cigrovski Berkovic, M.; Rezic, T.; Bilic-Curcic, I.; Mrzljak, A. Semaglutide might be a key for breaking the vicious cycle of metabolically associated fatty liver disease spectrum? World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 6759–6768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barritt, A.S.; Marshman, E.; Noureddin, M. Review article: Role of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, obesity and diabetes-what hepatologists need to know. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 55, 944–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | |
|---|---|
| BMI | 29.1 ± 4.8 |
| Age (years) | 64.3 ± 15.2 |
| Sex (female) | 32.9% |
| Cardiovascular background | 38.2% |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 43.1 (IQR 38.2) |
| HBA1c (%) | 7.3 (IQR 2.1) |
| CRP (mg/L) | 5.3 ± 7.7 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 77.4 ± 30.3 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 219.2 ± 142.7 |
| GGT (mg/dL) | 49.3 ± 72.9 |
| Proteinuria (mg/g Cr) | 362.7 (IQR 866.6) |
| Albuminuria (mg/g Cr) | 145.1 (IQR 499.1) |
| Albuminuria (30–300 mg/g Cr) | 61.8% |
| Albuminuria (300–1000 mg/g Cr) | 21.4% |
| Albuminuria (>1000 mg/g Cr) | 16.8% |
| Use of ACEIs/ARA II | 88.8% |
| Use of SGLT2i | 70.2% |
| Use of MRA | 30.3% |
| Baseline | 6 Month | 1 Year | 2 Years | 3 Years | * p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI | 29.1 ± 4.8 | 28.4 ± 4.8 | 28.1 ± 4.7 | 27.3 ± 3.4 | 26.3 ± 3.4 | 0.04 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 43.1 (IQR 38.2) | 45.5 (36.1) | 42.1 (35.2) | 42.5 (38.2) | 42.4 (37.1) | 0.573 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.3 (IQR 2.1) | 6.7 (1.5) | 6.5 (1.3) | 6.8 (1.9) | 6.6 (1.9) | 0.002 |
| CRP (mgr/L) | 5.3 ± 7.7 | 3.9 ± 3.9 | 3.1 ± 3.1 | 3.4 ± 5.4 | 3.2 ± 0.6 | 0.003 |
| LDL-c (mg/dL) | 77.4 ± 30.3 | 66.3 ± 23.2 | 70.7 ± 28.7 | 66.2 ± 26.2 | 66.1 ± 26.3 | 0.066 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 219.2 ± 142.7 | 190.9 ± 109.4 | 183.5 ± 149.9 | 164.1 ± 82.4 | 162 ± 95.5 | 0.001 |
| GGT (mg/dL) | 49.3 ± 72.9 | 42.8 ± 62.7 | 38.2 ± 42.6 | 37.1 ± 41.7 | 37.1 ± 40.1 | 0.004 |
| Proteinuria (mg/g Cr) | 362.7 (IQR 866.6) | 337.1 (652.2) | 320.2 (996.1) | 328.5 (799.3) | 320 (690.1) | 0.570 |
| Albuminuria (mg/g Cr) | 145.1 (IQR 499.1) | 114.2 (444.1) | 99.5 (661.4) | 98.5 (518.2) | 99.1 (520.2) | 0.584 |
| CKD stage 1–2 | 27.9% | 29.3% | 28.9% | 28.8% | 31.1% | 0.571 |
| CKD stage 3 | 50.6% | 49.3% | 49.3% | 46.2% | 42.2% | |
| CKD stage 4 | 21.5% | 21.3% | 21.8% | 25% | 26.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luna, E.; Álvarez, Á.; Rodriguez-Sabiñón, J.; Villa, J.; Giraldo, T.; Martín, M.V.; Vázquez, E.; Fernández, N.; Ruiz, B.; Garcia-Pino, G.; et al. Long-Term Effect of Semaglutide on the Glomerular Filtration Rate Slope in High-Risk Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy: Analysis in Real-World Clinical Practice. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070943
Luna E, Álvarez Á, Rodriguez-Sabiñón J, Villa J, Giraldo T, Martín MV, Vázquez E, Fernández N, Ruiz B, Garcia-Pino G, et al. Long-Term Effect of Semaglutide on the Glomerular Filtration Rate Slope in High-Risk Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy: Analysis in Real-World Clinical Practice. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(7):943. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070943
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuna, Enrique, Álvaro Álvarez, Jorge Rodriguez-Sabiñón, Juan Villa, Teresa Giraldo, Maria Victoria Martín, Eva Vázquez, Noemi Fernández, Belén Ruiz, Guadalupe Garcia-Pino, and et al. 2025. "Long-Term Effect of Semaglutide on the Glomerular Filtration Rate Slope in High-Risk Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy: Analysis in Real-World Clinical Practice" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 7: 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070943
APA StyleLuna, E., Álvarez, Á., Rodriguez-Sabiñón, J., Villa, J., Giraldo, T., Martín, M. V., Vázquez, E., Fernández, N., Ruiz, B., Garcia-Pino, G., Martínez, C., Azevedo, L., Diaz, R. M., Robles, N. R., & Gervasini, G. (2025). Long-Term Effect of Semaglutide on the Glomerular Filtration Rate Slope in High-Risk Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy: Analysis in Real-World Clinical Practice. Pharmaceutics, 17(7), 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070943







