Novel Alkyl-Polyglucoside-Based Topical Creams Containing Basil Essential Oil (Ocimum basilicum L. Lamiaceae): Assessment of Physical, Mechanical, and Sensory Characteristics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Formulation of APG-Based Emulsions
2.2.2. Physicochemical Properties of Cream Formulations
2.2.3. Mechanical Properties of Cream Formulations
Rheological Analysis
Steady Shear Tests
Dynamic Oscillatory Tests
Texture Analysis of Experimental Creams
Consistency Tests
2.2.4. Sensory Properties of Cream Formulations
2.2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physical Properties of Cream Formulations
3.2. Rheological Analysis
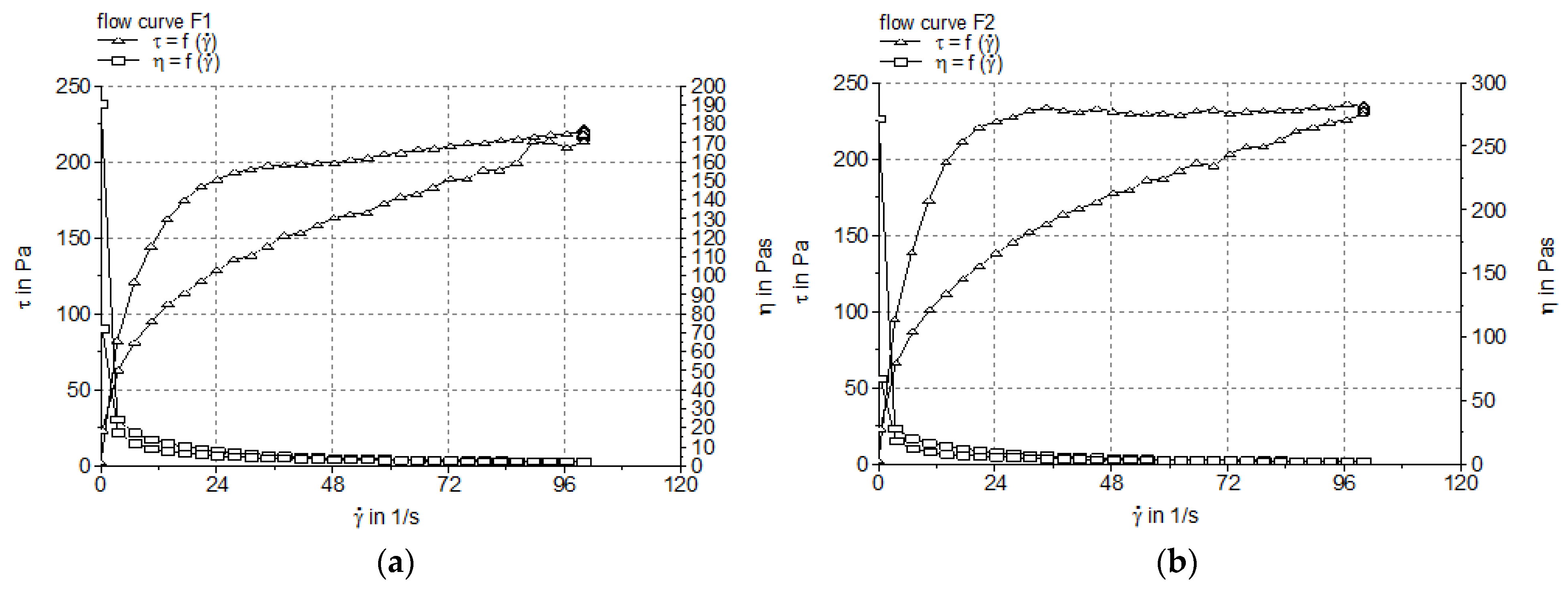
3.2.1. Steady Shear Tests
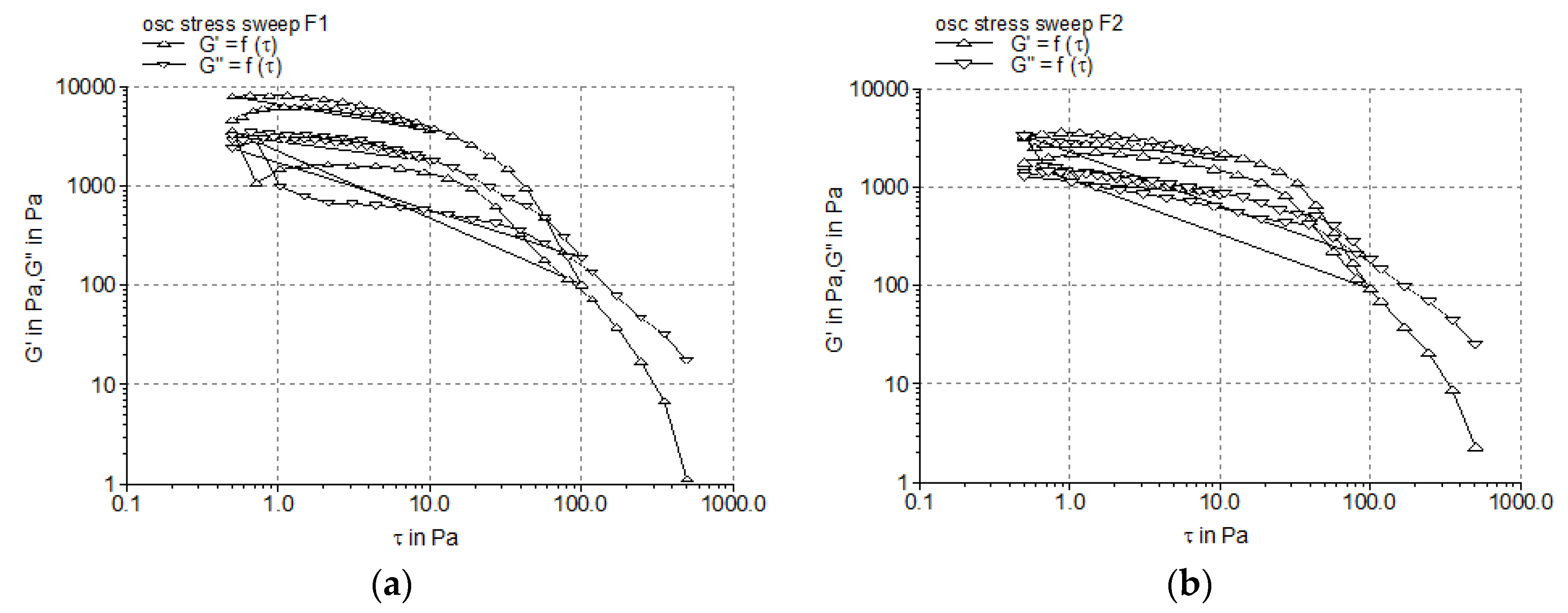
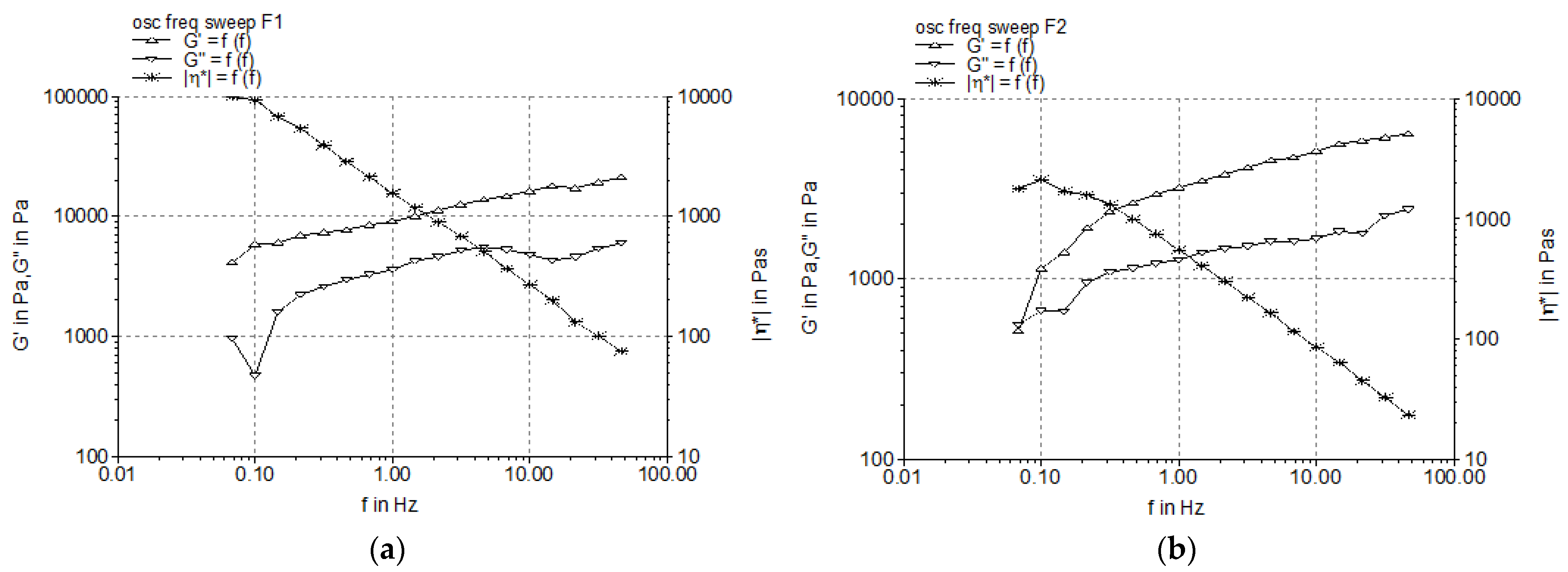
3.2.2. Dynamic Oscillatory Tests
3.3. Texture Analysis
3.4. Consistency Tests
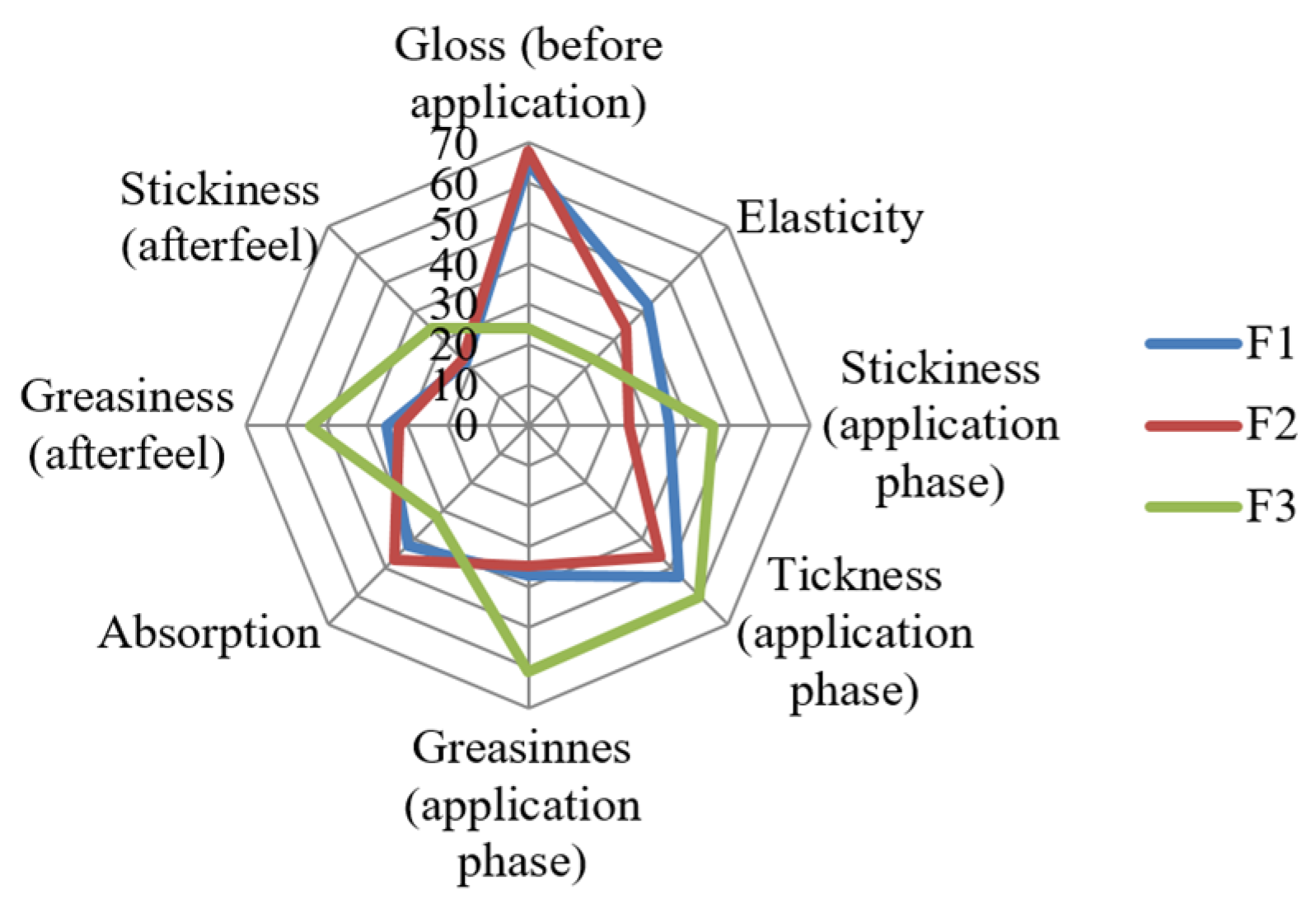
3.5. Sensory Evaluation of Cream Formulations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BEO | Basil essential oil |
| APG | Alkyl polyglucoside |
| O/W | Oil-in-water |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| LVR | Linear viscoelasticity region |
| ICH | International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use |
References
- Zagoto, M.; Cardia, G.F.E.; da Rocha, E.M.T.; Mourão, K.S.M.; Janeiro, V.; Cuman, R.K.N.; Pinto, A.A.; Contiero, R.L.; de Freitas, P.S.L. Biological Activities of Basil Essential Oil: A Review of the Current Evidence. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, e363101220409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Integrating Traditional Medicine in Health Care; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Valiakos, E.; Marselos, M.; Sakellaridis, N.; Constantinidis, T.; Skaltsa, H. Ethnopharmacological Approach to the Herbal Medicines of the “Antidotes” in Nikolaos Myrepsos׳ Dynameron. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 163, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharsono, H.D.A.; Putri, S.A.; Kurnia, D.; Dudi, D.; Satari, M.H. Ocimum Species: A Review on Chemical Constituents and Antibacterial Activity. Molecules 2022, 27, 6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizah, N.S.; Irawan, B.; Kusmoro, J.; Safriansyah, W.; Farabi, K.; Oktavia, D.; Doni, F.; Miranti, M. Sweet Basil (Ocimum Basilicum L.)-A Review of Its Botany, Phytochemistry, Pharmacological Activities, and Biotechnological Development. Plants 2023, 12, 4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakkas, H.; Papadopoulou, C. Antimicrobial Activity of Basil, Oregano, and Thyme Essential Oils. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhakipbekov, K.; Turgumbayeva, A.; Akhelova, S.; Bekmuratova, K.; Blinova, O.; Utegenova, G.; Shertaeva, K.; Sadykov, N.; Tastambek, K.; Saginbazarova, A.; et al. Antimicrobial and Other Pharmacological Properties of Ocimum Basilicum, Lamiaceae. Molecules 2024, 29, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, G.; Sabbah, M.; Caputo, L.; Idbella, M.; De Feo, V.; Porta, R.; Fechtali, T.; Mauriello, G. Basil Essential Oil: Composition, Antimicrobial Properties, and Microencapsulation to Produce Active Chitosan Films for Food Packaging. Foods 2021, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.B.; Oliveira Brito Pereira Bezerra Martins, A.; Cesário, F.R.A.S.; Ferreira E Castro, F.; de Albuquerque, T.R.; Martins Fernandes, M.N.; Fernandes da Silva, B.A.; Quintans Júnior, L.J.; da Costa, J.G.M.; Melo Coutinho, H.D.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Antiedematogenic Activity of the Ocimum Basilicum Essential Oil and Its Main Compound Estragole: In Vivo Mouse Models. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 257, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robu, A.; Kaya, M.G.A.; Antoniac, A.; Kaya, D.A.; Coman, A.E.; Marin, M.-M.; Ciocoiu, R.; Constantinescu, R.R.; Antoniac, I. The Influence of Basil and Cinnamon Essential Oils on Bioactive Sponge Composites of Collagen Reinforced with Hydroxyapatite. Materials 2025, 18, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sestili, P.; Ismail, T.; Calcabrini, C.; Guescini, M.; Catanzaro, E.; Turrini, E.; Layla, A.; Akhtar, S.; Fimognari, C. The Potential Effects of Ocimum Basilicum on Health: A Review of Pharmacological and Toxicological Studies. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2018, 14, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojević, L.; Stanojević, J.; Savić, V.; Cvetkovic, D.; Kolarevic, A.; Marjanović-Balaban, Ž.; Nikolic, L. Peppermint and Basil Essential Oils: Chemical Composition, in Vitro Antioxidant Activity and in Vivo Estimation of Skin Irritation. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2019, 22, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irianto, I.; Ismiyati; Witaningrum, E.; Ayuningtyas, E.; Ulfah, M.; Purwanto, P. Antibacterial Activity of Cream, Ointment, and Emulgel of Ocimum Basilicum L. Essential Oil against Propionibacterium Acnes. Maj. Obat Tradis. 2023, 28, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaksic, I.; Lukic, M.; Malenovic, A.; Reichl, S.; Hoffmann, C.; Müller-Goymann, C.; Daniels, R.; Savic, S. Compounding of a Topical Drug with Prospective Natural Surfactant-Stabilized Pharmaceutical Bases: Physicochemical and in Vitro/in Vivo Characterization—A Ketoprofen Case Study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. Off. J. Arbeitsgemeinschaft Pharm. Verfahrenstechnik EV 2012, 80, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilic, D.; Cvetkovic, M.; Tasic-Kostov, M. Emulsions with Alkyl Polyglucosides as Carriers for Off-Label Topical Spironolactone—Safety and Stability Evaluation. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2021, 26, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MONTANOV 68 MB. Available online: https://www.seppic.com/en-US/product/montanov-68-mb/01tD0000005kfP8IAI (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Jarupinthusophon, S.; Preechataninrat, P.; Anurukvorakun, O. Development of Liquid Crystal Cream Containing Germinated Brown Rice. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How Lamellar Liquid Crystal Emulsion Can Strengthen Skin Barrier? Available online: https://www.seppic.com/en-US/article/how-lamellar-liquid-crystal-emulsion-can-strengthen-skin-barrier#:~:text=MONTANOV%E2%84%A2%20can%20be%20added,formation%20of%20lamellar%20liquid%20crystals (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Sladmin Europäisches und Deutsches Arzneibuch. Available online: https://www.deutsche-apotheker-zeitung.de/daz-az/2006/daz-3-2006/uid-15294 (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Aulton, M.E.; Taylor, K.M. Aulton’s Pharmaceutics: The Design and Manufacture of Medicines, 5th ed; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Directorate for the Quality of Medicines; Healthcare of the Council of Europe. Potentiometric Determination of pH. In European Pharmacopeia; EDQM Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2022; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Directorate for the Quality of Medicines; Healthcare of the Council of Europe. Conductivity 2.2.38. In European Pharmacopoeia; EDQM Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ghica, M.V.; Hîrjău, M.; Lupuleasa, D.; Dinu-Pîrvu, C.-E. Flow and Thixotropic Parameters for Rheological Characterization of Hydrogels. Molecules 2016, 21, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calienni, M.N.; Martínez, L.M.; Izquierdo, M.C.; Alonso, S.d.V.; Montanari, J. Rheological and Viscoelastic Analysis of Hybrid Formulations for Topical Application. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkgreve, M.; Paredes, J.; Denn, M.M.; Bonn, D. On Different Ways of Measuring “the” Yield Stress. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2016, 238, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrot, A.; Mélinge, Y.; Estellé, P.; Rangeard, D.; Lanos, C. The Back Extrusion Test as a Technique for Determining the Rheological and Tribological Behaviour of Yield Stress Fluids at Low Shear Rates. Appl. Rheol. 2019, 21, 53642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directorate for the Quality of Medicines; Healthcare of the Council of Europe. Measurement of Consistency by Penetrometry. In European Pharmacopeia; EDQM Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2022; p. 360. [Google Scholar]
- Parente, M.E.; Ochoa Andrade, A.; Ares, G.; Russo, F.; Jiménez-Kairuz, Á. Bioadhesive Hydrogels for Cosmetic Applications. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2015, 37, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Guide for Two Sensory Descriptive Analysis Approaches for Skin Creams and Lotions. Available online: https://store.astm.org/e1490-19.html (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Tadić, V.M.; Žugić, A.; Martinović, M.; Stanković, M.; Maksimović, S.; Frank, A.; Nešić, I. Enhanced Skin Performance of Emulgel vs. Cream as Systems for Topical Delivery of Herbal Actives (Immortelle Extract and Hemp Oil). Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukic, M.; Jaksic, I.; Krstonosic, V.; Cekic, N.; Savic, S. A Combined Approach in Characterization of an Effective w/o Hand Cream: The Influence of Emollient on Textural, Sensorial and in Vivo Skin Performance. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2012, 34, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.K. Effective Surfactants Blend Concentration Determination for O/W Emulsion Stabilization by Two Nonionic Surfactants by Simple Linear Regression. Indian. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 77, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojiljković, D.; Arsić, I.; Tasić-Kostov, M. The influence of polar and non-polar emollients on the structure and skin moisturizing potential of the emulsions stabilized by mixed emulsifier. Acta Med. Median. 2016, 55, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, B.; Bradic, J.; Petrovic, A.; Ivanovic, D.; Tabakovic, M.; Saric, S.; Jakovljevic, V. Developement and Stability Evaluation of Natural Topical Formulations Containing Pinus sibirica Essential Oil. Exp. Appl. Biomed. Res. (EABR) Sciendo. 2017. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, N.; Gayet, P.; Benoit, J.P.; Saulnier, P. Nano-emulsions and nanocapsules by the PIT method: An investigation on the role of the temperature cycling on the emulsion phase inversion. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 344, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouche, J.; Tyrode, E.; Sadtler, V.; Choplin, L.; Salager, J.L. Simultaneous conductivity and viscosity measurements as a technique to track emulsion inversion by the phase-inversion-temperature method. Langmuir 2004, 20, 2134–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, R.; Wei, Y. A Review of Thixotropy and Its Rheological Modeling. J. Rheol. 2019, 63, 477–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Draft Guideline on Quality and Equivalence of Topical Products; European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2018; pp. 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Block, L.H. Rheology. In Remington Essentials of Pharmaceutics; Felton, L., Ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2012; p. 394. [Google Scholar]
- Magnon, E.; Cayeux, E. Precise Method to Estimate the Herschel-Bulkley Parameters from Pipe Rheometer Measurements. Fluids 2021, 6, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelessidis, V.C.; Maglione, R.; Tsamantaki, C.; Aspirtakis, Y. Optimal determination of rheological parameters for Herschel–Bulkley drilling fluids and impact on pressure drop, velocity profiles and penetration rates during drilling. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2006, 53, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanny, E.; Kohlmann, C. Predicting Tactile Sensory Attributes of Personal Care Emulsions Based on Instrumental Characterizations: A Review. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2024, 46, 1035–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurkevičiūtė, A.; Matulytė, I.; Ivaškienė, M.; Žilius, M. Assessment of Physical, Mechanical, Biopharmaceutical Properties of Emulgels and Bigel Containing Ciclopirox Olamine. Polymers 2022, 14, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, A.; Garcia, A.G.; Young, L.K.; Szoboszlai, M.; Liberatore, M.W.; Baki, G. Measurements Meet Perceptions: Rheology-Texture-Sensory Relations When Using Green, Bio-Derived Emollients in Cosmetic Emulsions. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2021, 43, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidel, J.L.; Bleibaum, R.N.; Clara Tao, K.W. Quantitative Descriptive Analysis. In Descriptive Analysis in Sensory Evaluation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 287–318. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, J. International Conference On Harmonisation Of Technical Requirements For Registration Of Pharmaceuticals For Human Use. In Handbook of Transnational Economic Governance Regimes; Tietje, C., Brouder, A., Eds.; Brill Nijhoff: Leiden, Netherlands, 2010; pp. 1041–1053. ISBN 978-90-04-16330-0. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Yiu, Y.; Lin, M.; Luo, T.; Yao, C. Electrical Conductivity and Stability of O/W Emulsions. Shiyou Xuebao Shiyou JiagongActa Pet. Sin. Pet. Process. Sect. 2008, 24, 592–597. [Google Scholar]
- Salager, J.-L. Emulsion Properties and RelatedKnow-how to Attain Them. In Pharmaceutical Emulsions and Suspensions, 2nd ed.; Revised and Expanded; Nielloud, F., Marti-Mestres, G., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 74–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, D.; Mahmoudi, N.; Heenan, R.K.; Barlow, D.J.; Lawrence, M.J. The Influence of Co-Surfactants on Lamellar Liquid Crystal Structures Formed in Creams. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowska, K.; Walczak, A.; Rostowska, E.; Poleszak, E. Comparison of Sensory and Rheological Properties of Green Cosmetic Creams Prepared on Different Natural, ECOCERT and BDIH Certificated Self-Emulsifying Bases. Curr. Issues Pharm. Med. Sci. 2021, 34, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koruk, H.; Rajagopal, S. A Comprehensive Review on the Viscoelastic Parameters Used for Engineering Materials, Including Soft Materials, and the Relationships between Different Damping Parameters. Sensors 2024, 24, 6137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adejokun, D.A.; Dodou, K. Quantitative Sensory Interpretation of Rheological Parameters of a Cream Formulation. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, H.; Piccerelle, P.; Le Dréau, Y.; Kister, J. A Rheological Method to Evaluate the Physical Stability of Highly Viscous Pharmaceutical Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitek, M.; Medoš, Ž.; Lavrič, Z.; Jeras, M.; Planinšek, O.; Pobirk, A.Z.; Matjaž, M.G. Highly Biocompatible Lamellar Liquid Crystals Based on Hempseed or Flaxseed Oil with Incorporated Betamethasone Dipropionate: A Bioinspired Multi-Target Dermal Drug Delivery System for Atopic Dermatitis Treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 13687–13715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, M.-S.; Ahn, H.-J.; Song, K.-W. Rheological Investigation of Body Cream and Body Lotion in Actual Application Conditions. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2015, 27, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semancik, J.R. Yield Stress Measurements Using Controlled Stress Rheometry. In Rheological Techniques for Yield Stress Analysis; TA Instruments: New Castle, DE, USA; pp. 1–5. Available online: https://www.tainstruments.com/applications-notes/ (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Calderas, F.; Herrera-Valencia, E.E.; Sanchez-Solis, A.; Manero, O.; Medina-Torres, L.; Renteria, A.; Sanchez-Olivares, G. On the Yield Stress of Complex Materials. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2013, 25, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburic, S.; Sisson, H.; Cunningham, N.; Stevic, M.C. Rheological and Texture Analysis Methods for Quantifying Yield Value and Level of Thixotropy. SOFW J. 2017, 143, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, R.; Almeida, I.F. Patient-Centric Design of Topical Dermatological Medicines. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. Guideline on Quality and Equivalence of Locally Applied, Locally Acting Cutaneous Products; European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2014; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, A.; Bianchini, R.; Jachowicz, J. Texture Analysis of Cosmetic/Pharmaceutical Raw Materials and Formulations. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2014, 36, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Smadi, K.; Ali, M.; Zhu, J.; Abdoh, A.; Phan, K.; Mohammed, Y. Advances in Characterization of Transdermal and Topical Products using Texture Analyzer Systems. AAPS PharmSciTech 2025, 26, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemiradzka, W.; Dolińska, B.; Ryszka, F. Development and Study of Semi-Solid Preparations Containing the Model Substance Corticotropin (ACTH): Convenience Application in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2020, 25, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez Soriano, M.M.; Fresno Contreras, M.J.; Sellés Flores, E. Development of a Cream from a Self-Emulsifying Base and Moisturizing Actives. Farm. Soc. Chim. Ital. 1989 2001, 56, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morávková, T.; Filip, P. The Influence of Emulsifier on Rheological and Sensory Properties of Cosmetic Lotions. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 168503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, R.; Verma, G.; Ingle, A.; Kumar, S.; Sarma, H.D.; Dutta, D.; Dutta, B.; Kunwar, A.; Ajish, K.; Bhainsa, K.C.; et al. Structural, Rheological and Therapeutic Properties of Pluronic F127 Hydrogel and Beeswax Based Lavender Oil Ointment Formulations. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 365, 120157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 13299:2016; Sensory Analysis—Methodology—General Guidance for Establishing a Sensory Profile. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Garg, A.; Aggarwal, D.; Garg, S.; Singla, A.K. Spreading of Semisolid Formulations. Pharm. Technol. N. Am. 2002, 26, 84–105. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, N.P.; Meher, J.G.; Pandey, N.; Luqman, S.; Yadav, K.S.; Chanda, D. Enrichment, Development, and Assessment of Indian Basil Oil Based Antiseptic Cream Formulation Utilizing Hydrophilic Lipophilic Balance Approach. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 410686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korhonen, M.; Hirvonen, J.; Yliruusi, J. Rheological properties of creams with four different surfactant combinations—effect of storage time and conditions. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 221, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanno, I.; Centini, M.; Anselmi, C.; Bibiani, C. Green Cosmetic Surfactant from Rice: Characterization and Application. Cosmetics 2015, 2, 322–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Ingredient | Functional Category | Content (w/w %) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | Control Sample | ||
| Oil phase | |||||
| Caprylic/capric triglyceride | Emollient | 10.00 | 10.00 | - | - |
| Cetyl palmitate | Emollient | 6.00 | 6.00 | - | - |
| Almond oil | Emollient | 5.00 | 5.00 | - | - |
| Montanov™ 68 | O/W emulsifier | 5.00 | 7.00 | - | - |
| Tocopheryl acetate | Antioxidant | 0.50 | 0.50 | - | - |
| Water phase | |||||
| Sodium sorbate | Preservative | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | - |
| Xanthan gum | Co-emulsifier | 0.50 | 0.50 | - | - |
| Propylene glycol | Humectant | 4.00 | 4.00 | - | - |
| Active ingredient | |||||
| Basil essential oil | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| Non-ionic hydrophilic base | Base | ||||
| Polysorbate 60 | O/W emulsifier | - | - | - | 2.00 |
| Cetylstearyl alcohol | Co-emulsifier | - | - | - | 4.00 |
| Glycerol | Humectant | - | - | - | 4.00 |
| Vaseline | Emollient | - | - | - | 10.00 |
| Purified water | Solvent | to 100.00 | to 100.00 | to 100.00 | to 100.00 |
| Before the application | Consistency | liquid/semisolid |
| Gloss level | matte/pearl gloss/slightly glossy/gloss/very glossy | |
| Adhesion—the amount of the sample that remains on the index finger after brief contact of 2 s (scale) | 1–10 | |
| Elasticity—the degree of stretching of the sample between the thumb and index finger. | slightly elastic/elastic/very elastic | |
| Texture—the impression of the thickness of the sample when rubbed between the thumb and index finger (scale) | 1–10 | |
| Application phase | Spreadability—the degree of spreadability and melting of the sample when rubbed on the skin of the palm in circular motions 2 times (scale) | 1–10 |
| Stickiness—the force required to separate the finger from the skin | not sticky/slightly sticky/sticky/very sticky | |
| Thickness—the degree of density during application | thin/slightly thick/thick/very thick | |
| Greasiness—the degree of grease during application | not greasy/slightly greasy/greasy/very greasy | |
| Gloss—the degree of gloss during application | not shiny/slightly shiny/shiny/very shiny | |
| Absorption—the impression of the sample absorption rate | slow/moderate/fast | |
| Residual film—the impression of residual film on the skin 10 min after application | no film/moderate/pronounced | |
| After application | Greasiness—the impression of skin being greasy 10 min after application | not greasy/slightly greasy/greasy/very greasy |
| Gloss—the degree of skin gloss after application | not shiny/slightly shiny/shiny/very shiny | |
| Stickiness—the impression of a sticky feeling on the skin 10 min after application | not sticky/slightly sticky/sticky/very sticky |
| Formulation Code | After 7 Days | After 30 Days | After 90 Days | After the Accelerated Aging Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | ||||
| F1 | 6.83 | 6.80 | 6.60 | 6.61 |
| F2 | 6.81 | 6.78 | 6.57 | 6.55 |
| Electrical conductivity | ||||
| F1 | 12.33 | 11.56 | 11.10 | 10.96 |
| F2 | 13.45 | 12.60 | 10.72 | 10.70 |
| Formulation Code | Apparent Viscosity (Pa.s) | Thixotropy Index (%) |
|---|---|---|
| F1 | 2.182 ± 0.064 | 17.961 ± 2.504 |
| F2 | 2.325 ± 0.071 | 22.176 ± 3.016 |
| Formulation Code | Model Correlation Coefficient (R2) | Parameters of Ostwald de Waele Model | Parameters of Herschel–Bulkley Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ostwald de Waele | Herschel–Bulkley | K | n | K | n | τ0 (Pa) | |
| F1 | 0.9330 ± 0.004 | 0.9363 ± 0.003 | 63.83 ± 2.09 | 0.2675 ± 0.012 | 111.5 ± 1.34 | 0.1948 ± 0.011 | −55.78 ± 0.82 |
| F2 | 0.8770 ± 0.007 | 0.884 ± 0.005 | 79.83 ± 1.77 | 0.2346 ± 0.008 | 175.3 ± 1.47 | 0.1433 ± 0.005 | −105.20 ± 1.17 |
| Formulation Code | Elastic Modulus, G’ (Pa) | Viscous Modulus, G” (Pa) | Yield Stress, τ0 (Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 5334.10 ± 105.23 | 2591.20 ± 78.43 | 11.97 ± 0.26 |
| F2 | 2557.95 ± 61.47 | 1211.31 ± 32.86 | 21.25 ± 1.14 |
| Formulation Code | Firmness (g) | Consistency (g·sec) | Cohesiveness (g) | Index of Viscosity (g·sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 596.39 ± 10.71 | 1187.52 ± 15.48 | −242.75 ± 6.81 | −967 ± 9.11 |
| F2 | 3115.02 ± 16.29 | 2823.35 ± 14.87 | −1219.82 ± 12.44 | −1601.72 ± 13.25 |
| Formulation Code | Firmness (g) | Work of Shear (g·sec) |
|---|---|---|
| F1 | 1216.47 ± 12.30 | 1090.03 ± 32.55 |
| F2 | 2153.36 ± 15.37 | 2627.81 ± 20.16 |
| Attribute | χ2 | p | Rank Sum | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | |||
| Before the application Gloss Elasticity | |||||
| 34.939 | <0.001 ** | 65 a | 68 a | 24 b | |
| 20.548 | <0.001 ** | 42 a | 34 b | 23 c | |
| During the application Stickiness Thickness Greasiness Absorption | |||||
| 16.095 7.600 32.281 14.157 | <0.001 ** 0.022 * <0.001 ** 0.001 ** | 36 a 53 37 a 42 a | 25 b 46 a 35 a 47 a | 46 c 60 b 61 b 32 b | |
| Afterfeel phase Greasiness Stickiness | |||||
| 21.815 | <0.001 ** | 35 a | 32 a | 54 b | |
| 16.267 | <0.001 ** | 22 a | 23 a | 34 b | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barjaktarević, A.; Coneac, G.; Cupara, S.; Kostić, O.; Kostić, M.; Olariu, I.; Vlaia, V.; Cotan, A.-M.; Neamu, Ş.; Vlaia, L. Novel Alkyl-Polyglucoside-Based Topical Creams Containing Basil Essential Oil (Ocimum basilicum L. Lamiaceae): Assessment of Physical, Mechanical, and Sensory Characteristics. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070934
Barjaktarević A, Coneac G, Cupara S, Kostić O, Kostić M, Olariu I, Vlaia V, Cotan A-M, Neamu Ş, Vlaia L. Novel Alkyl-Polyglucoside-Based Topical Creams Containing Basil Essential Oil (Ocimum basilicum L. Lamiaceae): Assessment of Physical, Mechanical, and Sensory Characteristics. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(7):934. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070934
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarjaktarević, Ana, Georgeta Coneac, Snežana Cupara, Olivera Kostić, Marina Kostić, Ioana Olariu, Vicenţiu Vlaia, Ana-Maria Cotan, Ştefania Neamu, and Lavinia Vlaia. 2025. "Novel Alkyl-Polyglucoside-Based Topical Creams Containing Basil Essential Oil (Ocimum basilicum L. Lamiaceae): Assessment of Physical, Mechanical, and Sensory Characteristics" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 7: 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070934
APA StyleBarjaktarević, A., Coneac, G., Cupara, S., Kostić, O., Kostić, M., Olariu, I., Vlaia, V., Cotan, A.-M., Neamu, Ş., & Vlaia, L. (2025). Novel Alkyl-Polyglucoside-Based Topical Creams Containing Basil Essential Oil (Ocimum basilicum L. Lamiaceae): Assessment of Physical, Mechanical, and Sensory Characteristics. Pharmaceutics, 17(7), 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070934









