Crotoxin-Loaded Silica Nanoparticles: A Nanovenom Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Venom (V)
2.2. Isolation of CTX from C.d.t. Venom
2.3. Synthesis of Silica Nanoparticles (SiNPs)
2.4. Immobilization of CTX on SiNPs (Synthesis of NVs) and Adsorption Studies
2.5. Physicochemical Characterization of SiNPs and NVs
2.6. Analysis of CTX Desorption from NVs by SDS-PAGE
2.7. Study of Biological Activity of SiNPs and NVs
2.7.1. PLA2 Indirect Hemolytic Activity
2.7.2. Cell Proliferation Assay (MTT)
2.7.3. Immunomodulation by NVs on THP-1 Cells
3. Results
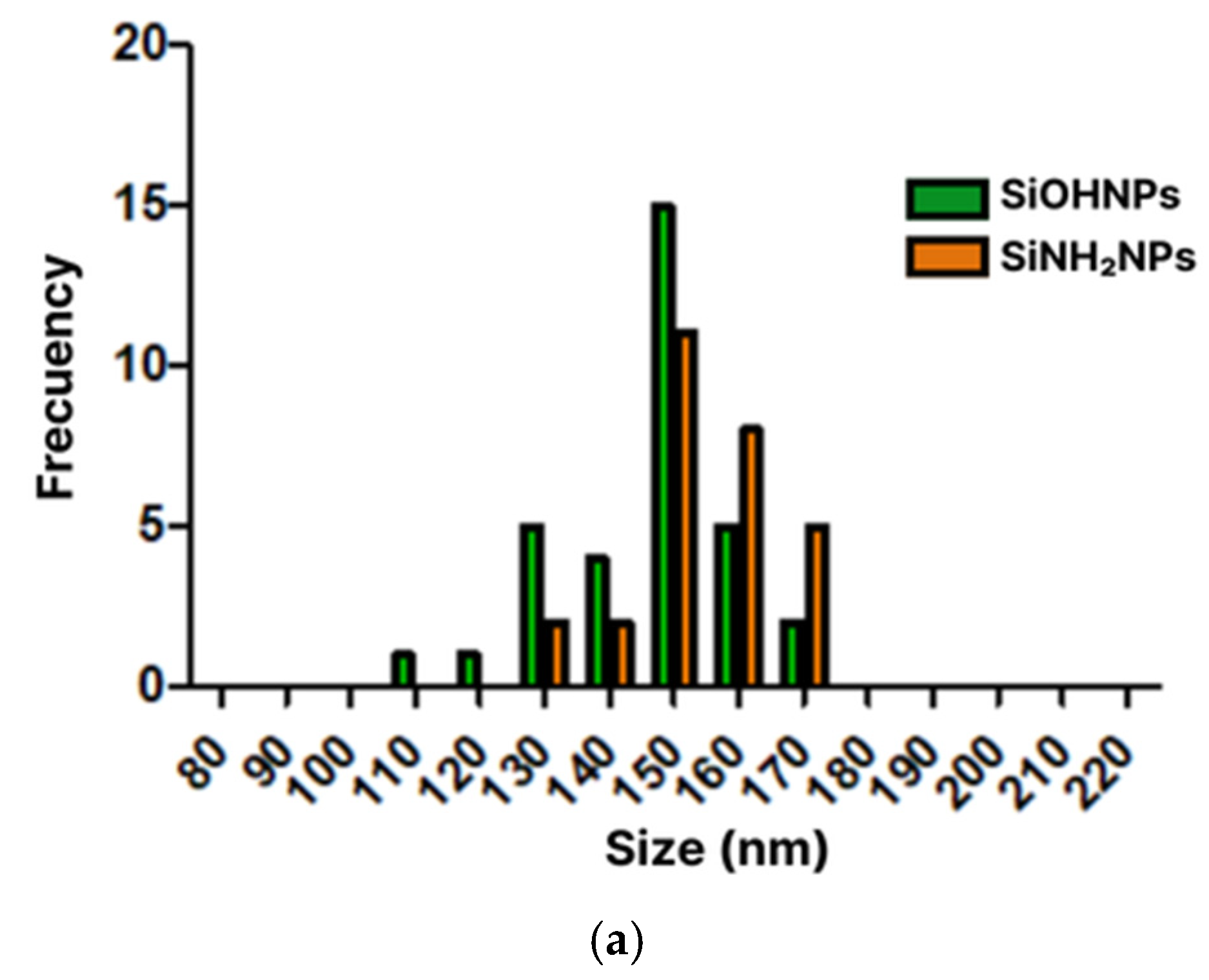
3.1. Characterization of SiNPs
3.2. Isolation and Quantification of CTX
3.3. Immobilization and Characterization of CTX Adsorbed to SiNPs (NVs)
3.4. PLA2 Activity of CTX
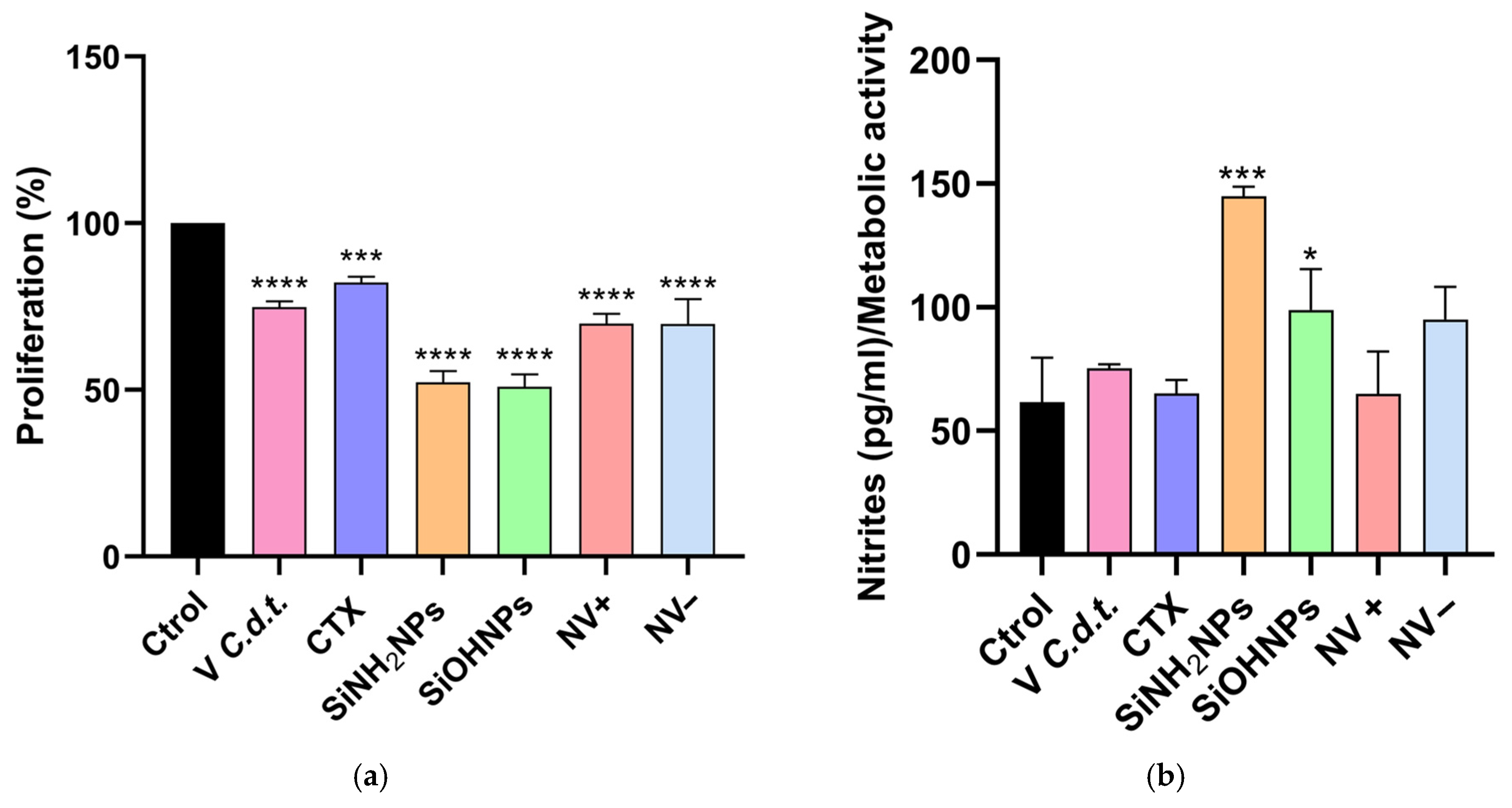
3.5. Cell Proliferation Assay (MTT)
3.6. Cytokine and Nitrite Responses to SiNP and NV Treatments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| C.d.t. | Crotalus durissus terrificus |
| LAAO | L-amino acid oxidase |
| PLA2 | Phospholipase A2 |
| CTX | Crotoxin |
| TLE | Thrombin-like enzyme |
| CVX | Convulxin |
| CTM | Crotamine |
| AV | Antivenom |
| ADJ | Adjuvant |
| NP | Nanoparticle |
| SiNP | Silica nanoparticle |
| NV | Nanovenom |
| V | Venom |
| SN | Supernatant |
| FPLC | Fast protein liquid chromatography |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| TEOS | Tetraethyl orthosilicate |
| ON | Overnight |
| RT | Room temperature |
| APTES | 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane |
| FT-IR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| AC | Adsorbed capacity |
| LC | Load capacity |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscope |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| MTT | Tetrazolium assay |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
References
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Production Control and Regulation of Snake Antivenom Immunoglobulins. 2016. Available online: https://extranet.who.int/prequal/vaccines/guidelines-production-control-and-regulation-snake-antivenom-immunoglobulins (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Amaral, C.F.; Magalhaes, R.A.; de Renzende, N.A. Respiratory involvement secondary to crotalidophidian bite (Crotalus durissus). Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 1991, 33, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranauskas, V.; Dourado, D.M.; Jingguo, Z.; da Cruz-Höfling, M.A. Characterization of the Crotalus durissus terrificus venom by atomic force microscopy. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. Process. Meas. Phenom. 2002, 20, 1317–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, D.; Ohler, M.; Seifert, J.; von Bergen, M.; Arni, R.K.; Genov, N.; Betzel, C. Snake venomic of Crotalus durissus terrificus correlation with pharmacological activities. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 2302–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chippaux, J.P. Snake-bites: Appraisal of the global situation. Bull. World Health Organ. 1998, 76, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kasturiratne, A.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; de Silva, N.; Gunawardena, N.K.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Premaratna, R.; Savioli, L.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, H.J. The global burden of snakebite: A literature analysis and modelling based on regional estimates of envenoming and deaths. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia Denegri, M.E.; Bustillo, S.; Gay, C.C.; Van De Velde, A.; Gomez, G.; Echeverría, S.; Gauna Pereira, M.D.C.; Maruñak, S.; Nuñez, S.; Bogado, F.; et al. Venoms and Isolated Toxins from Snakes of Medical Impact in the Northeast Argentina: State of the Art. Potential Pharmacological Applications. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1962–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebs, D. Snake venoms: Toolbox of the neurobiologist. Endeavour 1989, 13, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markland, F.S. Snake venoms and the hemostatic system. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1749–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.C. Snake venoms. Biochemistry and Pharmacology. Sci. Res. 1976, 32, 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, T.S.; Georgieva, D.; Genov, N.; Murakami, M.T.; Sinha, M.; Kumar, R.P.; Kaur, P.; Kumar, S.; Dey, S.; Sharma, S.; et al. Enzymatic toxins from snake venom: Structural characterization and mechanism of catalysis. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 4544–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, L.S.; Neto, E.B.; Francisco, A.F.; Alfonso, J.; Soares, A.; Pimenta, D.C.; Leiva, L.C. Fast venomic analysis of Crotalus durissus terrificus from northeastern Argentina. Toxicon X 2020, 7, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rádis-Baptista, G.; Kerkis, I. Crotamine, a small basic polypeptide myotoxin from rattlesnake venom with cell-penetrating properties. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 4351–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampaio, S.C.; Hyslop, S.; Fontes, M.R.; Prado-Franceschi, J.; Zambelli, V.O.; Magro, A.J.; Brigatte, P.; Gutierrez, V.P.; Cury, Y. Crotoxin: Novel activities for a classic beta-neurotoxin. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Deenen, L.L.M.; Haas, G.H.D. The substrate specificity of phospholipase A. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Spec. Sect. Lipids Relat. Subj. 1963, 70, 538–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Salud. Guía de Prevención, Diagnóstico, Tratamiento y Vigilancia Epidemiológica de los Envenenamientos Ofídicos; Ministry of Social Welfare; Secretary of State for Public Health; Undersecretary of Health Medicine; National Directorate for Health Promotion and Protection: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2014.
- Ministerio da Saúde. Manual de Diagnóstico e Tratamento de Acidentes por Animais Peçonhentos; Fundacáo Nacional de Saudé: Brasília, Brazil, 2001.
- Rodriguez, J.P.; De Marzi, M.; Maruñak, S.; Malchiodi, E.L.; Leiva, L.C.; Acosta, O. Rabbit IgG antibodies against phospholipase A2 from Crotalus durissus terrificus neutralize the lethal activity of the venom. Medicina 2006, 66, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Torrent, R.M.R.; Bongiovanni, B.; Leiva, L.C.; de Duffard, A.M.E.; Rodríguez, J.P.; de Pérez, O.C.A.; Duffard, R. Neurotoxicological effects of a thrombin-like enzyme isolated from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom (preliminary study). Toxicon 2007, 50, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.A.; Moura-Da-Silva, A.M.; Laing, G.D.; Wu, Y.; Richards, A.; Broadhead, A.; Bianco, A.E.; Theakston, R.D. Antibody from mice immunized with DNA encoding the carboxyl disintegrin and cysteine-rich domain (JD9) of the haemorrhagic metalloprotease, Jararhagin, inhibits the main lethal component of viper venom. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2000, 121, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, L.S.; Rodríguez, J.P.; Teibler, P.; Maruñak, S.; Acosta, O.; Leiva, L. New immunization protocol to produce crotalic antivenom combining Crotalus durissus terrificus venom and its PLA2. Biol. J. Int. Assoc. Biol. Stand. 2015, 43, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudou, F.G.; Litwin, S.; Lanari, L.C.; Laskowicz, R.D.; Damin, C.F.; Chippaux, J.P.; de Roodt, A.R. Antivenom against Crotalus durissus terrificus venom: Immunochemical reactivity and experimental neutralizing capacity. Toxicon 2017, 140, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebert, A.M.; Camporotondi, D.E.; Foglia, M.L.; Alvarez, G.S.; Orihuela, P.L.S.; Diaz, L.E.; Desimone, M.F. Controlling the Interaction between Cells and Silica Nanoparticles. J. Biomater. Tissue Eng. 2013, 3, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, R.R.; Lozano, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Carriers for Therapeutic Biomolecules. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kancha, M.M.; Mehrabi, M.; Bitaraf, F.S.; Vahedi, H.; Alizadeh, M.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Preparation, Characterization, and Anticancer Activity Assessment of Chitosan/TPP Nanoparticles Loaded with Echiscarinatus Venom. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2024, 24, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desimone, M.F.; Jotania, R.B. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications; Materials Research Foundations; Materials Research Forum LLC: Millersville, PA, USA, 2023; Volume 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitarotonda, R.; Giorgi, E.; Desimone, M.F.; De Marzi, M.C. Nanoparticles and immune cells. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 3960–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitarotonda, R.; Giorgi, E.; Eufrasio-da-Silva, T.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Mishra, Y.K.; Khademhosseini, A.; Desimone, M.F.; De Marzi, M.; Orive, G. Immunotherapeutic nanoparticles: From autoimmune disease control to the development of vaccines. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 135, 212726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, C.; Jia, P.; Luo, C.; Pang, J.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, T.; Duan, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z. The size-dependent in vivo toxicity of amorphous silica nanoparticles: A systematic review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 271, 115910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudou, F.G.; Rodriguez, J.P.; Fusco, L.; de Roodt, A.R.; De Marzi, M.C.; Leiva, L. South American snake venoms with abundant neurotoxic components. Composition and toxicological properties. A literatura review. Acta Trop. 2021, 224, 106119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, E.D.; Genovés, S.; Díaz, M.E.; Municoy, S.; Desimone, M.F.; De Marzi, M.C. Adsorption of immunomodulatory proteins over silica nanoparticles and the in vitro effect. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Avila, C.; Rojas, E.; Cerdas, L. An alternative in vitro method for testing the potency of the polyvalent antivenom produced in Costa Rica. Toxicon 1988, 26, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcao, C.B.; Radis-Baptista, G. Crotamine and crotalicidin, membrane active peptides from Crotalus durissus terrificus rattlesnake venom, and their structurally-minimized fragments for applications in medicine and biotechnology. Peptides 2020, 126, 170234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aird, S.D.; Steadman, B.L.; Middaugh, C.R.; Kaiser, I.I. Comparative spectroscopic studies of four crotoxin homologs and their subunits. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1989, 997, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, E.O.V.; Tasima, L.J.; Hatakeyama, D.M.; Serino-Silva, C.; Rodrigues, C.F.B.; Galizio, N.D.C.; Chiarelli, T.; Nishiduka, E.S.; Rocha, M.M.T.D.; Sant’Anna, S.S.; et al. Snake venom color and L-amino acid oxidase: An evidence of long-term captive Crotalus durissus terrificus venom plasticity. Toxicon 2021, 193, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burin, S.M.; Menaldo, D.L.; Sampaio, S.V.; Frantz, F.G.; Castro, F.A. An overview of the immune modulating effects of enzymatic toxins from snake venoms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour Dounighi, N.; Behfar, A.; Ezabadi, A.; Zolfagharian, H.; Heydari, M. Preparation of chitosan nanoparticles containing Naja naja oxiana snake venom. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, F.; Mohammadpour Dounighi, N.; Avadi, M.R.; Rezayat, M. A New Approach to Antivenom Preparation Using Chitosan Nanoparticles Containing EchisCarinatus Venom as A Novel Antigen Delivery System. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2017, 16, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hamzaoui, A.; Laraba-Djebari, F. Development and evaluation of polymeric nanoparticles as a delivery system for snake envenoming prevention. Biol. J. Int. Assoc. Biol. Stand. 2021, 70, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Silva, E.D.; Torres-Rêgo, M.; Gláucia-Silva, F.; Feitosa, R.C.; Lacerda, A.F.; Rocha, H.A.O.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.F.; Silva-Júnior, A.A.D. Cationic PLGA Nanoparticle Formulations as Biocompatible Immunoadjuvant for Serum Production and Immune Response against Bothrops jararaca Venom. Toxins 2022, 14, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudou, F.G.; Fusco, L.; Giorgi, E.; Diaz, E.; Municoy, S.; Desimone, M.F.; Leiva, L.; De Marzi, M.C. Physicochemical and biological characterization of nanovenoms, a new tool formed by silica nanoparticles and Crotalus durissus terrificus venom. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 193, 111128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marzi, M.C.; Saraceno, M.; Mitarotonda, R.; Todone, M.; Fernandez, M.; Malchiodi, E.L.; Desimone, M.F. Evidence of size-dependent effect of silica micro- and nano-particles on basal and specialized monocyte functions. Ther. Deliv. 2017, 8, 1035–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitarotonda, R.; Saraceno, M.; Todone, M.; Giorgi, E.; Malchiodi, E.L.; Desimone, M.F.; De Marzi, M.C. Surface chemistry modification of silica nanoparticles alters the activation of monocytes. Ther. Deliv. 2021, 12, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, B.F.A.; Ferreira, R.S., Jr. Antineoplastic properties and pharmacological applications of Crotalus durissus terrificus snake venom. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2022, 55, e0323-2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Conti, F.S.; Giorgi, E.; Montaldo, L.; Rodríguez, J.P.; De Marzi, M.C.; Baudou, F.G. Crotoxin-Loaded Silica Nanoparticles: A Nanovenom Approach. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070879
Conti FS, Giorgi E, Montaldo L, Rodríguez JP, De Marzi MC, Baudou FG. Crotoxin-Loaded Silica Nanoparticles: A Nanovenom Approach. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(7):879. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070879
Chicago/Turabian StyleConti, Florencia Silvina, Exequiel Giorgi, Laura Montaldo, Juan Pablo Rodríguez, Mauricio Cesar De Marzi, and Federico Gastón Baudou. 2025. "Crotoxin-Loaded Silica Nanoparticles: A Nanovenom Approach" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 7: 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070879
APA StyleConti, F. S., Giorgi, E., Montaldo, L., Rodríguez, J. P., De Marzi, M. C., & Baudou, F. G. (2025). Crotoxin-Loaded Silica Nanoparticles: A Nanovenom Approach. Pharmaceutics, 17(7), 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070879






