Tertiary Amine Oxide-Containing Zwitterionic Polymers: From Material Design to Biomedical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Synthetic Strategies and Structural Characteristics
2.1. Controlled Polymerization Techniques for TAO-Based Polymer Backbones
2.2. Polymer Functionalization Design
3. Structural Characteristics
3.1. Zwitterionic Properties
3.2. Dynamic Cell Membrane Affinity
3.3. Topological Variability
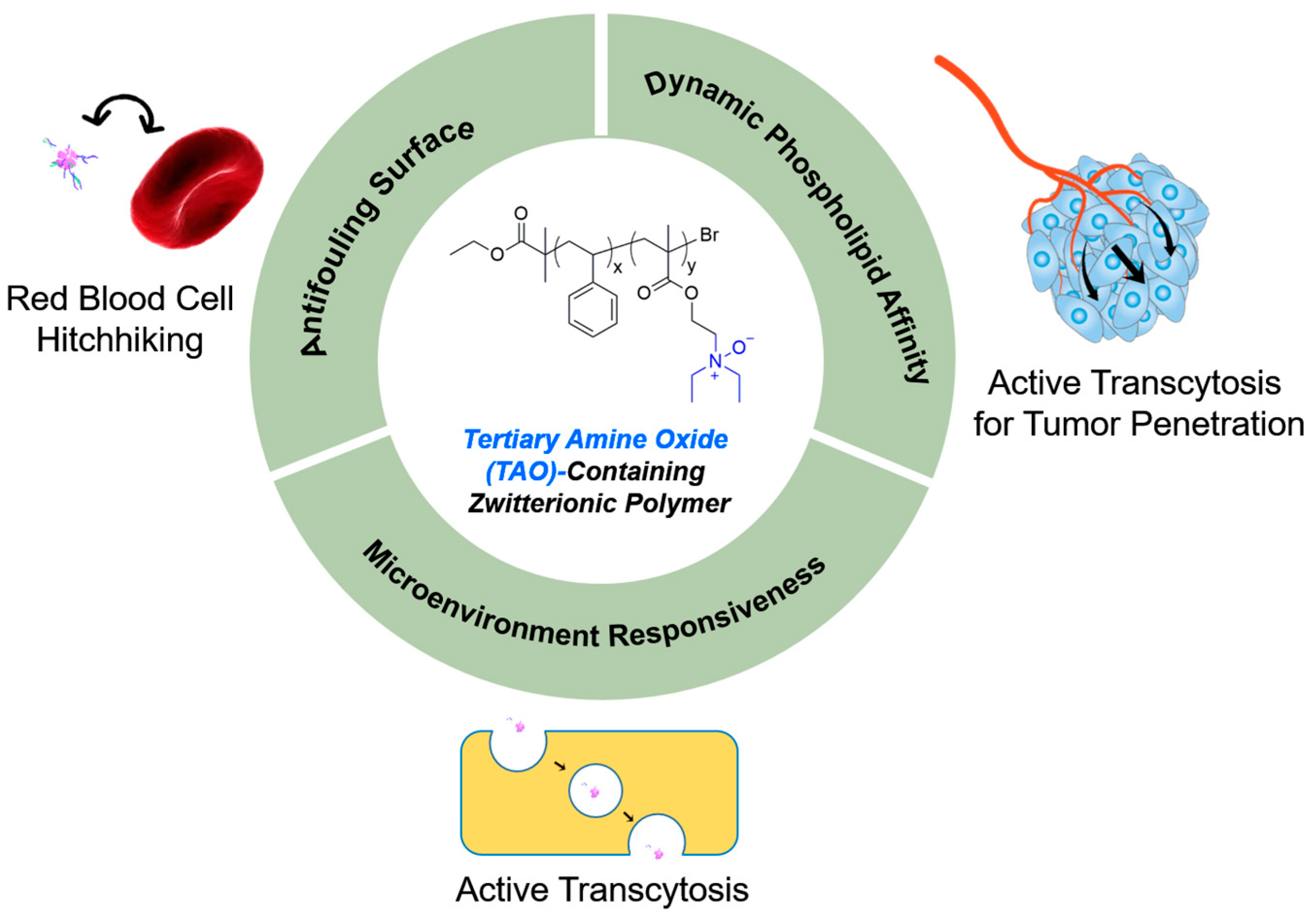
4. Core Structural Advantages and Applications
4.1. Zwitterionic Properties to Minimize Nonspecific Protein Adsorption
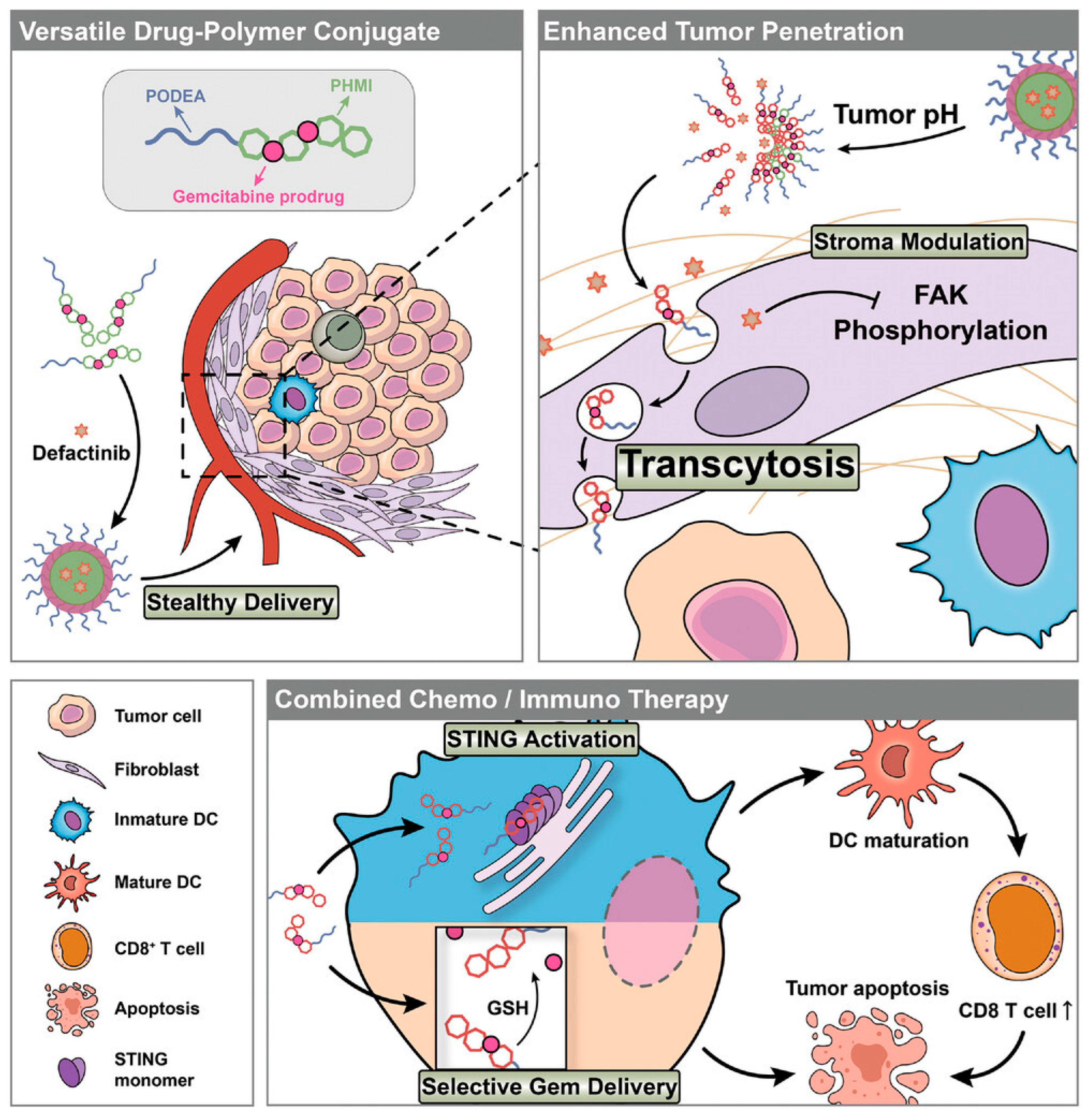
4.2. Dynamic Phospholipid Affinity
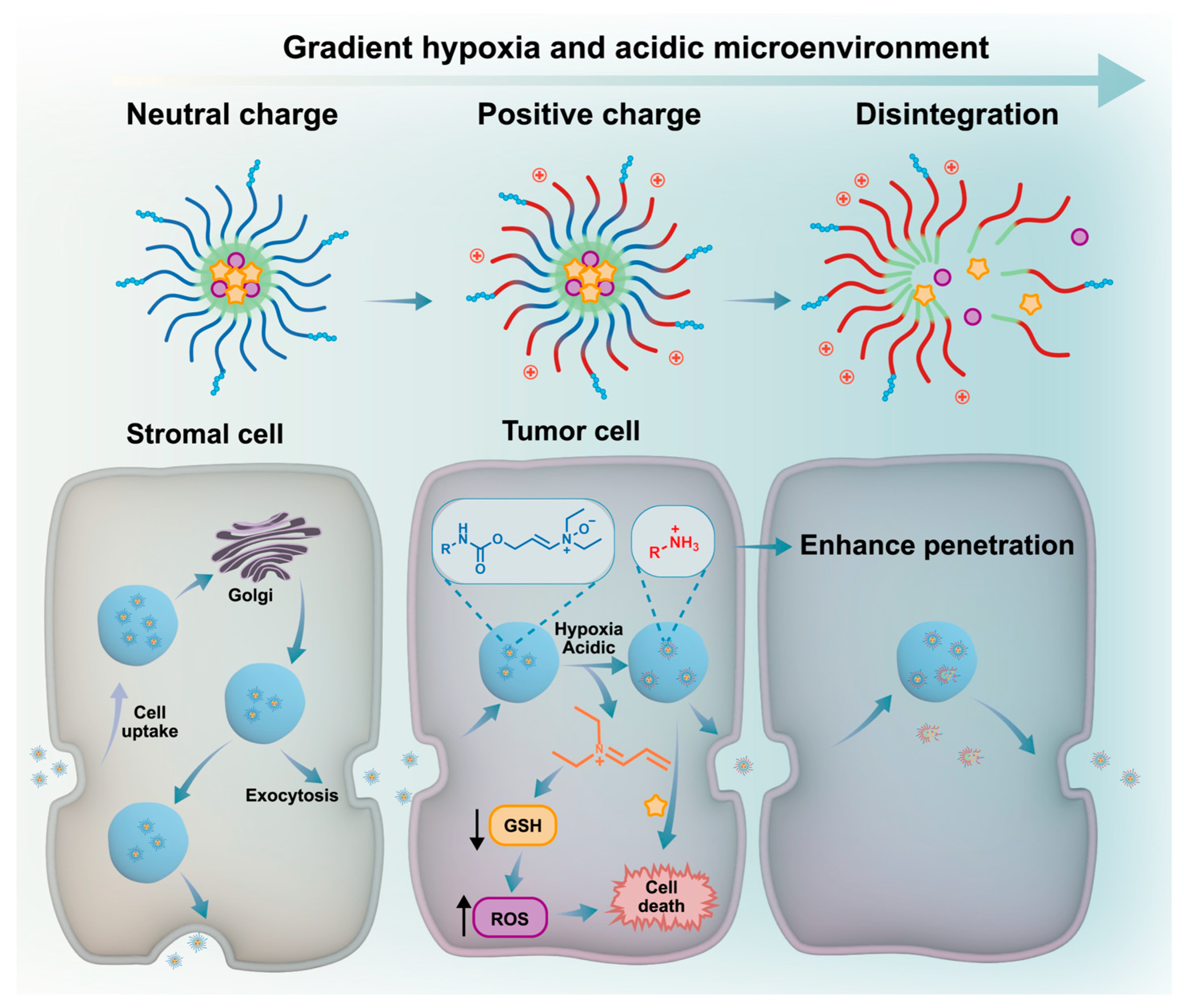
4.3. Microenvironment Responsiveness
5. Challenges and Future Outlook
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Serda, M.; Li, Q.; Sun, T. Recent Advancements on Self-Immolative System Based on Dynamic Covalent Bonds for Delivering Heterogeneous Payloads. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2300138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, X. Deformable nanocarriers for enhanced drug delivery and cancer therapy. Exploration 2024, 4, 20230037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, H.; Fu, Q. Stimuli-responsive polymer-based nanosystems for cancer theranostics. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 23223–23261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhong, Y.; Fan, W.; Xiang, J.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, J.; Geng, Y.; Sun, R.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Enhanced tumour penetration and prolonged circulation in blood of polyzwitterion–drug conjugates with cell-membrane affinity. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 1019–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Deventer, S.; Arp, A.B.; van Spriel, A.B. Dynamic plasma membrane organization: A complex symphony. Trends Cell Biol. 2021, 31, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Cheung, S.T.; Wong-Rolle, A.; Kim, J. Enamine N-Oxides: Synthesis and application to hypoxia-responsive prodrugs and imaging agents. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobus, M.; Friedrich, T.; Zorn, E.; Burmeister, N.; Maison, W. Medicinal chemistry of drugs with N-Oxide functionalities. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 5168–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, L.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wu, R.; Liu, X.; Zhou, R.; Huang, Y. Complying with the physiological functions of Golgi apparatus for secretory exocytosis facilitated oral absorption of protein drugs. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gao, H.; Bao, G. Physical principles of nanoparticle cellular endocytosis. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 8655–8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhwani, S.; Syed, A.M.; Ngai, J.; Kingston, B.R.; Maiorino, L.; Rothschild, J.; MacMillan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Rajesh, N.U.; Hoang, T.; et al. The entry of nanoparticles into solid tumours. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Pan, Y.; Jiao, G.; Xu, M.; Fan, D.; Hu, Z.; Wu, J.; Chen, T.; Liu, M.; Bao, X.; et al. A bioorthogonal decaging chemistry of N-Oxide and silylborane for prodrug activation both in vitro and in vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 24698–24706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, Q.; Piao, Y.; Shao, S.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, J.; Xiang, J.; Shen, Y. Synergistic combination of oral transcytotic nanomedicine and histone demethylase inhibitor for enhanced cancer chemoimmunotherapy. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 33729–33742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahadian, S.; Finbloom, J.A.; Mofidfar, M.; Diltemiz, S.E.; Nasrollahi, F.; Davoodi, E.; Hosseini, V.; Mylonaki, I.; Sangabathuni, S.; Montazerian, H.; et al. Advancing microphysiological systems for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 157, 37–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, G.; Wei, W. Simulation of nanoparticles interacting with a cell membrane: Probing the structural basis and potential biomedical application. NPG Asia Mater. 2021, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyjaszewski, K.; Xia, J. Atom transfer radical polymerization. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 2921–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Yuan, P.; Yu, W.; Lin, J.; Xu, A.; Xu, X.; Lou, J.; Yu, T.; Qian, C.; Liu, B.; et al. Mitochondria-targeting polymer micelle of dichloroacetate induced pyroptosis to enhance osteosarcoma immunotherapy. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 10327–10340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luc, V.-S.; Lin, C.-C.; Wang, S.-Y.; Lin, H.-P.; Li, B.-R.; Chou, Y.-N.; Chang, C.-C. Antifouling properties of amine-oxide-containing zwitterionic polymers. Biomacromolecules 2023, 24, 5467–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Kim, H.; Li, X.; Yoon, J. A hypoxia-triggered bioreduction of hydrophilic type I photosensitizer for switchable in vivo photoacoustic imaging and high-specificity cancer phototherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202506412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Li, M.; Nie, X.; Meng, H.; Shosei, S.; Liu, L.; Yang, Q.; Shen, M.; Li, Y. A pH-triggered N-oxide polyzwitterionic nano-drug loaded system for anti-tumor immunity activation research. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, W.; Wang, P.; Hou, S.; Niu, W.; Shi, Y.; Kang, G.; Yu, C.-Y.; Wei, H. Fabrication of GSH-responsive poly(tertiary amine-oxide)-based nanomedicines for enhanced anticancer drug release. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2024, 225, 2300335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Fang, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Tian, Z.; You, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yang, X.; Bi, Y.; et al. PROTAC-loaded nanocapsules degrading BRD4 for radio-chemotherapy sensitization in glioblastoma. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2025, 15, 2309–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Sun, H.; He, N.; Xu, C.; Du, L.; Ji, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Gu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Glutathione depletion-induced versatile nanomedicine for potentiating ferroptosis to overcome solid tumor radioresistance and enhance immunotherapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2303412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wen, C.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Cheng, G.; Bai, J.; Xu, T.; Ji, J.; et al. Zwitterionic biomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 17073–17154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Cui, H.; Tian, X.; Du, W.; Yang, Z.; Wan, D.; Qiu, Z.; Liu, C.; et al. Precision-guided stealth missiles in biomedicine: Biological carrier-mediated nanomedicine hitchhiking strategy. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2504672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Qi, Y.; Liu, G.; Song, Y.; Jiang, X.; Du, B. Size-dependent in vivo transport of nanoparticles: Implications for delivery, targeting, and clearance. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 20825–20849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, Y.; Xin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, K.; Luo, Y.; Wang, B. Red blood cells in biology and translational medicine: Natural vehicle inspires new biomedical applications. Theranostics 2024, 14, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fu, Q. Nanomaterials for disease treatment by modulating the pyroptosis pathway. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2301266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Li, J.; Xiang, J.; Shao, S.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, J.; Shen, Y. Transcytosis-enabled active extravasation of tumor nanomedicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 189, 114480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, M.; Chen, C. Nano-bio interactions: A major principle in the dynamic biological processes of nano-assemblies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 186, 114318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liang, T.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Geng, Z.; Zhu, B. A universal and versatile zwitterionic coating for blood-contacting catheters with long lengths and complex geometries. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2502411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Liu, Y.; Yan, J.; Fang, Z.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Y. Zwitterionic polymers: Structure design and emerging applications. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2025, 216, e00106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Huang, S.; Hu, Q.; He, W.; Wei, Z.; Wang, L.; Lu, J.; Yue, X.; Men, S.; Miao, C.; et al. Recent advances in zwitterionic polymers-based non-fouling coating strategies for biomedical applications. Mater. Today Chem. 2024, 40, 102232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, J.; Shao, S.; Shen, Y. Multipotent poly(tertiary amine-oxide) micelles for efficient cancer drug delivery. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2200173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Xiang, J.; Wei, Q.; Tang, Y.; Piao, Y.; Shao, S.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, J.; Li, Z.-C.; Shen, Y. Role of micelle size in cell transcytosis-based tumor extravasation, infiltration, and treatment efficacy. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 3904–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; You, H.; Fan, H.; Chen, Y.; Song, H.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Wu, Y.; et al. Transcytosis-triggering nanoparticles for overcoming stromal barriers and reversing immunosuppression in pancreatic cancer combinatorial therapy. Nano Lett. 2025, 25, 2949–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Dong, X. Dynamic polymeric materials via hydrogen-bond cross-linking: Effect of multiple network topologies. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2024, 151, 101890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shi, X.; Parak, W.J.; Pich, A. Transvascular transport of nanocarriers for tumor delivery. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Shen, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lian, Z.; Xie, H.; Ling, S.; Xie, C.; et al. Rapamycin-loaded nanoparticles elicit local liver immunosuppressive and remote anti-tumor efficacy. Nano Today 2025, 61, 102589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, G.; Yang, H.; Lv, H.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Fu, Y.; Sun, F.; Feng, Y.; et al. Inhalable metal-organic framework-mediated cuproptosis combined with PD-L1 checkpoint blockade for lung metastasis synergistic immunotherapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 2281–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Si, J.; Huang, G.; Ji, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ge, Z. Multifunctional zwitterionic N-oxide polymers to overcome cascade physiological barriers for efficient anticancer drug delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, 2403852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Song, H.; Luo, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Luo, F.; Fan, H.; Li, X.; Sun, T.; et al. Transcytosis mediated deep tumor penetration for enhanced chemotherapy and immune activation of pancreatic cancer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Wei, Q.; Xiang, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Geng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, R.; Xu, L.; Wang, G.; et al. Mucus penetrating and cell-binding polyzwitterionic micelles as potent oral nanomedicine for cancer drug delivery. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2109189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, J.; Huang, W.; Zhang, S.; Deng, X.; Gao, W. Hypoxia-triggered bioreduction of poly(N-oxide)-drug conjugates enhances tumor penetration and antitumor efficacy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, S.K.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Advanced hitchhiking nanomaterials for biomedical applications. Theranostics 2023, 13, 4781–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Feng, Y.; Xiang, J.; Liu, J.; Piao, Y.; Shao, S.; Tang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, Y. Screening of zwitterionic liposomes with red blood cell-hitchhiking and tumor cell-active transporting capability for efficient tumor entrance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sun, Y.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, H.; Xie, C.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; et al. Mitochondria-targeted icaritin nanoparticles induce immunogenic cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 2899–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Xiang, J.; Shao, S.; Tang, J.; Shen, Y. Mitochondria-targeted polymer-celastrol conjugate with enhanced anticancer efficacy. J. Control. Release 2022, 342, 122–133. [Google Scholar]
- You, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Su, B.; Li, X.; Guo, Y.; et al. Engineered bacterial outer membrane vesicles-based doxorubicin and CD47-siRNA co-delivery nanoplatform overcomes immune resistance to potentiate the immunotherapy of glioblastoma. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, e2418053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, S.; Piao, Y.; Yin, W.; Lu, H.; Shen, Y. A neutral water-soluble mitochondria-targeting polymer. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 10015–10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jing, H.; Vong, L.B.; Wang, J.; Li, N. Recent advances in targeted stimuli-responsive nano-based drug delivery systems combating atherosclerosis. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 1705–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Guo, M.; Guan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, M.; Li, H.; Qiao, G.; Yang, Q.; Shen, M.; Li, Y. ROS-responsive simvastatin nano-prodrug based on tertiary amine-oxide zwitterionic polymer for atherosclerotic therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 176. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, F.; Guo, R.; Pan, K.; Xu, H.; Chu, X. Mucus and mucin: Changes in the mucus barrier in disease states. Tissue Barriers 2025, 13, 2499752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Ali, B.; Kong, N.; Xie, T.; Koo, S. Oral nanomedicine: Challenges and opportunities. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2306081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Fu, X.; Shao, M.; Chang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z. Eyedrop delivery of therapeutic proteins with zwitterionic polymers to treat dry age-related macular degeneration. Biomaterials 2024, 305, 122429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, S.; Xia, W.; Lundergan, L.; Yuan, H.; Xu, J. Zwitterionic polymers for biomedical applications: Antimicrobial and antifouling strategies toward implantable medical devices and drug delivery. Langmuir 2024, 40, 23125–23145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Zhu, C.; Yuan, G.; Jin, J.; Zhang, J.; Fan, W.; Piao, Y.; Shao, S.; Lin, S.; Xiang, J.; et al. Active trans-corneal drug delivery with ocular adhesive micelles for efficient glaucoma therapy. J. Control. Release 2025, 377, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhan, Y.; Xu, X.; Zeng, Q.; Liang, J.; Chen, X. Hypoxia-activated prodrugs and redox-responsive nanocarriers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 6551–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, R.; Dračínský, M.; Slavětínská, L.; Buděšínský, M. The observed and calculated 1H and 13C chemical shifts of tertiary amines and their N-oxides. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2011, 49, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadh, M.J.; Mustafa, M.A.; Qassem, L.Y.; Ghadir, G.K.; Alaraj, M.; Alubiady, M.H.S.; Al-Abdeen, S.H.Z.; Shakier, H.G. Targeting hypoxic and acidic tumor microenvironment by nanoparticles: A review. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 95, 105660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xu, C.; Geng, Y.; Shen, Y.; Qiu, N. Endoplasmic reticulum-targeted polymer-manganese nanocomplexes for tumor immunotherapy. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 4959–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Arambula, J.F.; Koo, S.; Kumar, R.; Singh, H.; Sessler, J.L.; Kim, J.S. Hypoxia-targeted drug delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 771–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chu, Y.; Luo, Y.; You, H.; Su, B.; Li, C.; Guo, Q.; Sun, T.; et al. Penetrating micelle for reversing immunosuppression and drug resistance in pancreatic cancer treatment. Small 2022, 18, e2107712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Xu, X.; Shi, X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, H.; Piao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Slater, N.K.H.; Tang, J. A dual-channel fluorescent ratio probe with hypoxia targeting and hypoxia activation capacity for tumour imaging. Polym. Chem. 2022, 13, 3358–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, J.G.M.; Rovers, M.M.; Rutten, M.G.T.A.; Dankers, P.Y.W. Engineering supramolecular hydrogen bonding interactions into dynamic covalent polymers to obtain double dynamic biomaterials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 12345–12356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Fan, Q.; Wang, C. Recent applications of immunomodulatory biomaterials for disease immunotherapy. Exploration 2022, 2, 20210157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, W.; Liang, P.; Ni, L.; Lv, X.; Fan, J.; Shi, F. High molecular weight polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum attenuates inflammatory responses, gut microbiota, and liver metabolomic in lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 287, 138400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.C.; Than, N.; Min, S.; Shin, W.; Kim, H.J. Modelling host–microbiome interactions in organ-on-a-chip platforms. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2024, 2, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre-Franco, M.F.; Kouider, R.; Kassir Al-Karany, R.; Cuerda-Correa, E.M.; Al-Kassir, A. Recent advances in polymer science and fabrication processes for enhanced microfluidic applications: An overview. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Mottafegh, A.; Joo, J.U.; Kang, J.H.; Wang, L.; Kim, D.P. Toward microfluidic continuous-flow and intelligent downstream processing of biopharmaceuticals. Lab Chip 2024, 24, 2861–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, J.; Sun, T.; Bi, Y. Tertiary Amine Oxide-Containing Zwitterionic Polymers: From Material Design to Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070846
Shen J, Sun T, Bi Y. Tertiary Amine Oxide-Containing Zwitterionic Polymers: From Material Design to Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(7):846. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070846
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Jian, Tao Sun, and Yunke Bi. 2025. "Tertiary Amine Oxide-Containing Zwitterionic Polymers: From Material Design to Biomedical Applications" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 7: 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070846
APA StyleShen, J., Sun, T., & Bi, Y. (2025). Tertiary Amine Oxide-Containing Zwitterionic Polymers: From Material Design to Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics, 17(7), 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070846








