Intravenous Administration of sRNA Nanoparticles for Treatment of Osteoporosis in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. LNP Formulation Details
2.2.1. Lipid Nanoparticle Preparation
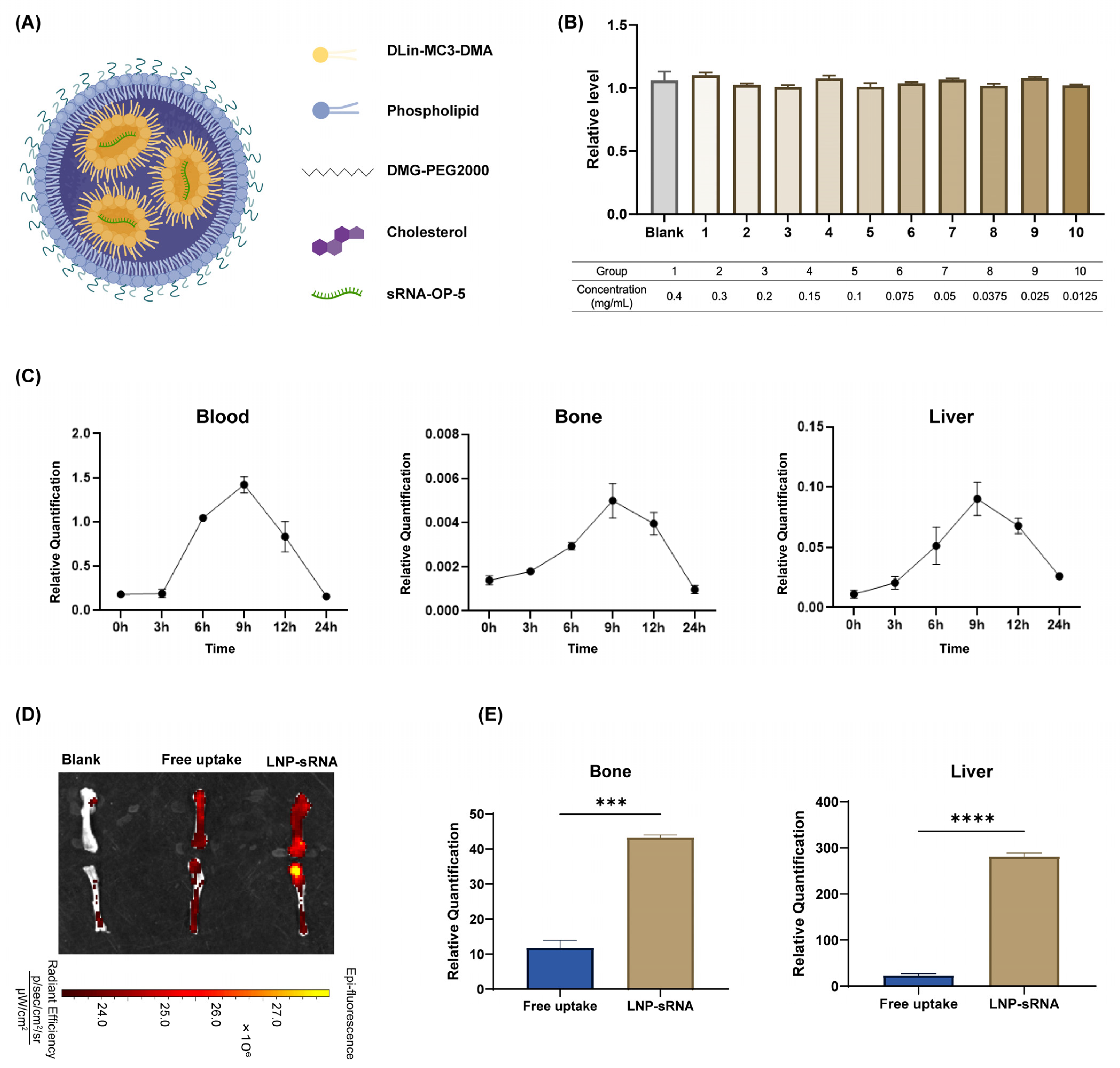
2.2.2. Particle Size and Zeta Potential
2.2.3. Entrapment Efficiency Percentage and Loading Efficiency
2.3. In Vitro Evaluation
2.3.1. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
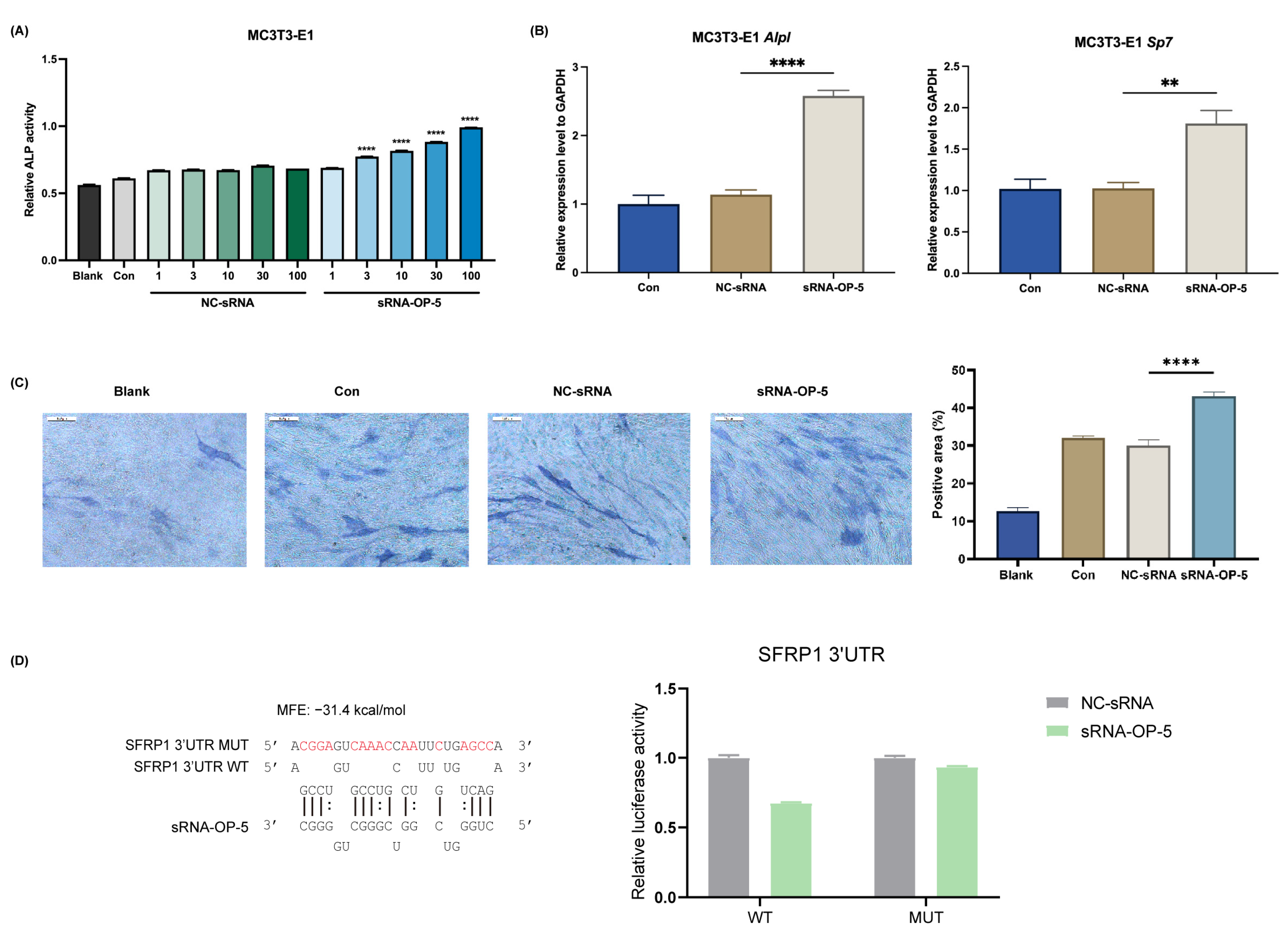
2.3.2. RT-qPCR
2.3.3. ALP Activity Assay and ALP Staining
2.4. In Vivo Study
2.4.1. Animals
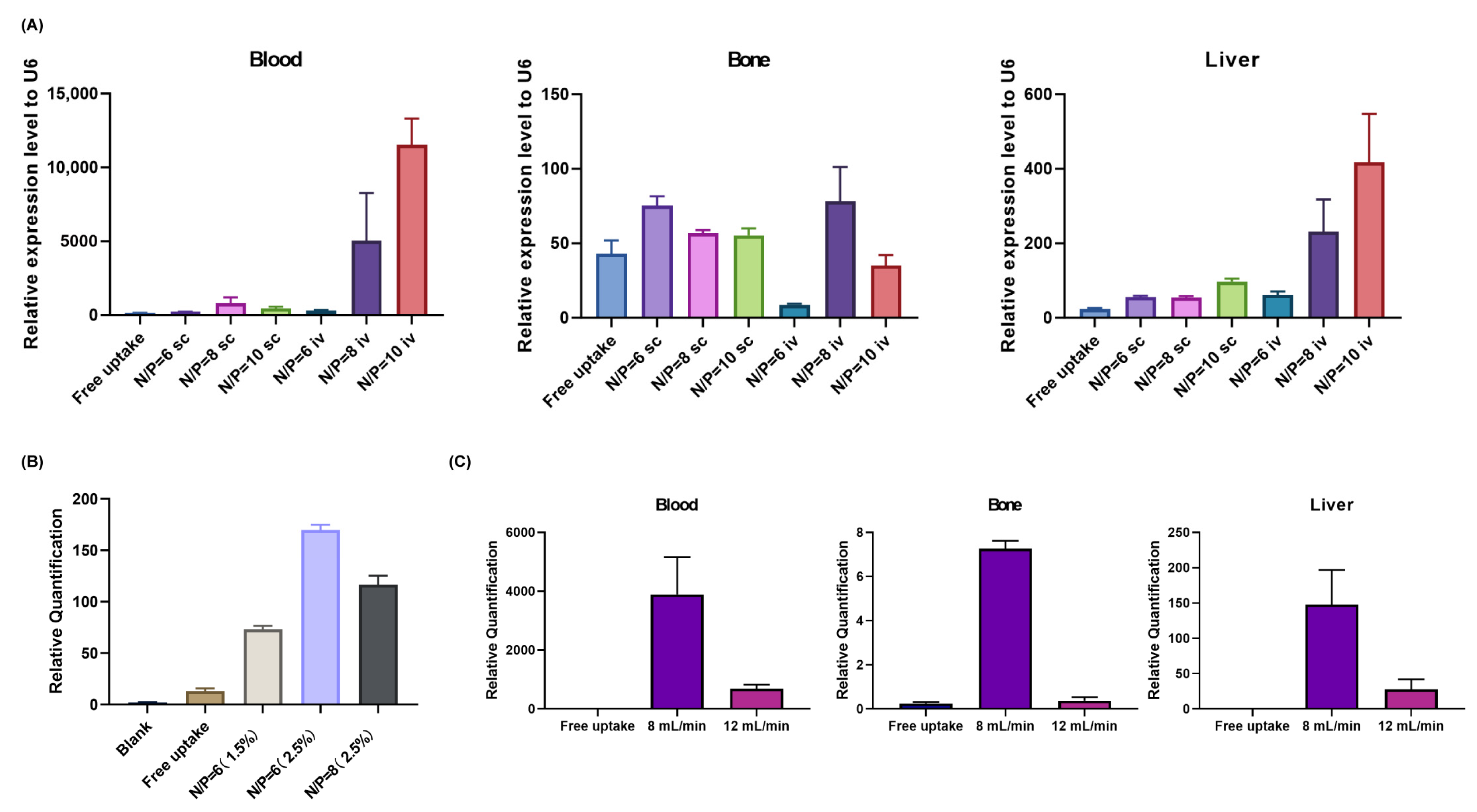
2.4.2. In Vivo Distribution of LNP-sRNA
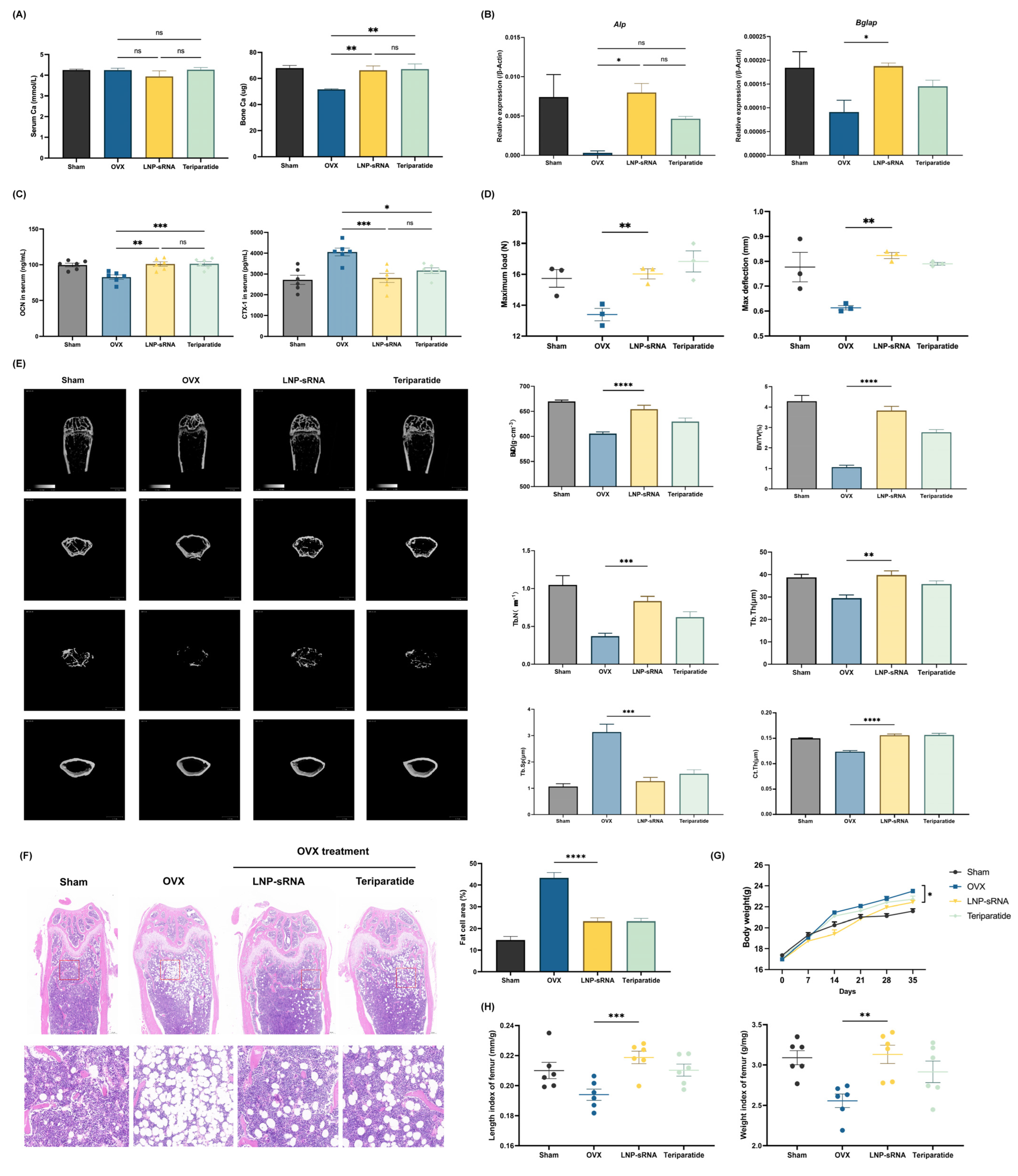
2.4.3. In Vivo Efficacy Studies—Osteoporosis Model
Model Development
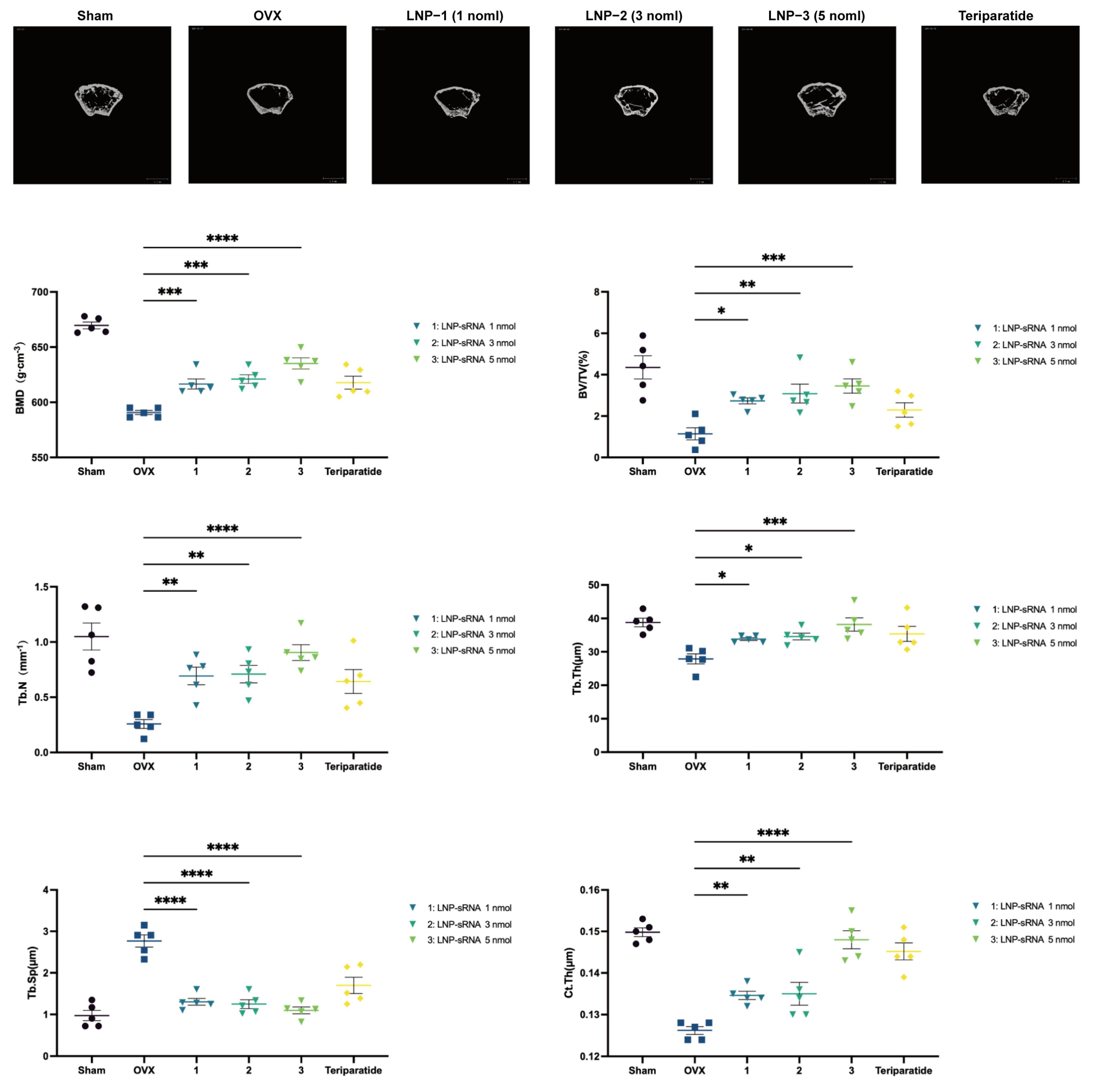
Micro Computed Tomography (Micro-CT) Analysis
Three-Point Bending Test
Histology Analysis
Analysis of Serum and Bone Tissues
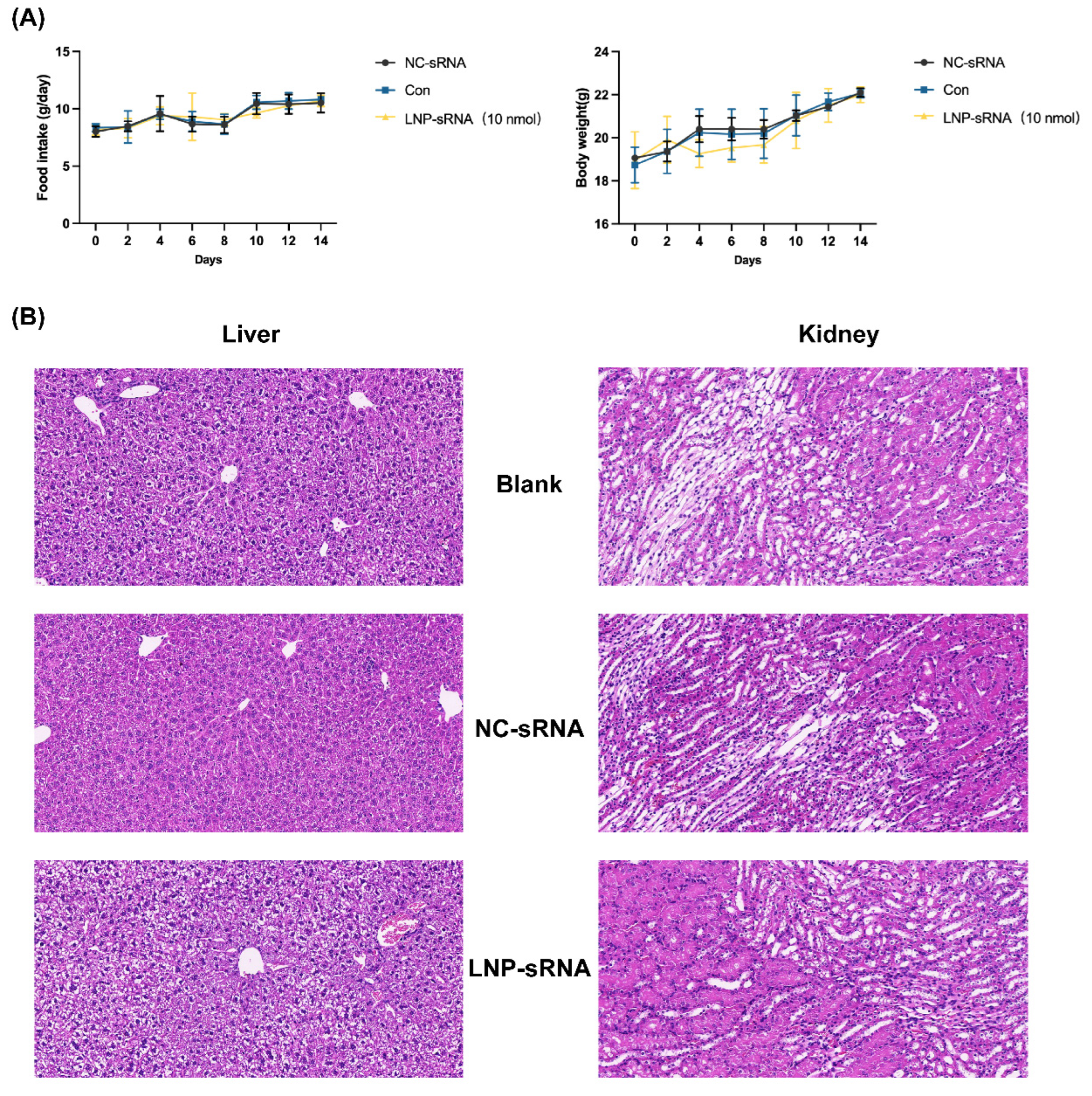
2.4.4. In Vivo Toxicity Evaluation—Acute Oral Toxicity Study
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. sRNA-OP-5 Exhibits Anti-Osteoporotic Effects at the Cellular Level
3.2. Optimization of LNP Formulation Parameters
3.3. Characterization and Biodistribution of Optimized LNP-sRNA Formulation
3.4. Therapeutic Efficacy in OVX-Induced Osteoporosis Model
3.5. Safety Profile of LNP-sRNA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodan, G.A.; Martin, T.J. Therapeutic approaches to bone diseases. Science 2000, 289, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Perche, F.; Logeart-Avramoglou, D.; Pichon, C. Rna-based therapy for osteogenesis. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118594. [Google Scholar]
- Svedbom, A.; Hernlund, E.; Ivergård, M.; Compston, J.; Cooper, C.; Stenmark, J.; McCloskey, E.V.; Jönsson, B.; Kanis, J.A. Osteoporosis in the European Union: A compendium of country-specific reports. Arch. Osteoporos. 2013, 8, 137. [Google Scholar]
- Khosla, S.; Hofbauer, L.C. Osteoporosis treatment: Recent developments and ongoing challenges. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cosman, F.; Crittenden, D.B.; Adachi, J.D.; Binkley, N.; Czerwinski, E.; Ferrari, S.; Hofbauer, L.C.; Lau, E.; Lewiecki, E.M.; Miyauchi, A.; et al. Romosozumab treatment in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1532–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Billington, E.; Aghajafari, F.; Skulsky, E.; Kline, G.A. Bisphosphonates. BMJ 2024, 386, e076898. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bandeira, L.; Lewiecki, E.M. Anabolic therapy for osteoporosis: Update on efficacy and safety. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 66, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdahl, B.L. Overview of treatment approaches to osteoporosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 1891–1906. [Google Scholar]
- Jadhav, V.; Vaishnaw, A.; Fitzgerald, K.; Maier, M.A. Rna interference in the era of nucleic acid therapeutics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Zhong, L.; Weng, Y.; Peng, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, X.J. Therapeutic sirna: State of the art. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 101. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, D.; Gonzalez-Duarte, A.; O’Riordan, W.D.; Yang, C.C.; Ueda, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Tournev, I.; Schmidt, H.H.; Coelho, T.; Berk, J.L.; et al. Patisiran, an rnai therapeutic, for hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lu, Z.; Wientjes, M.G.; Au, J.L. Delivery of sirna therapeutics: Barriers and carriers. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 492–503. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. Bone site-specific delivery of sirna. J. Biomed. Res. 2016, 30, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Guo, Y.; Kong, L.; Shi, J.; Liu, P.; Li, R.; Geng, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, D. A bone-targeted engineered exosome platform delivering sirna to treat osteoporosis. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 10, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ding, P.; Meng, Y.; Lin, T.; Zhang, Z.; Shu, H.; Ma, J.; Cohen Stuart, M.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Rational polyelectrolyte nanoparticles endow preosteoclast-targeted sirna transfection for anabolic therapy of osteoporosis. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade7379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C. Potential oligonucleotide drugs in bencao srna atlas (Ii). Sci. China Life Sci. 2025, 68, 1834. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Liu, J.; Du, S.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, C. Potential oligonucleotide drugs in Bencao srna Atlas. Sci. China Life Sci. 2023, 66, 2943–2945. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Sun, N.; Du, X.; Dong, Y.; Mei, S.; Deng, X.; Li, X.; Guo, X.; Tang, K.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of the Bencao (herbal) small Rna Atlas reveals novel Rna therapeutics for treating human diseases. Sci. China Life Sci. 2023, 66, 2380–2398. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, C.; Kriaucionis, S.; Kessler, B.M.; Jiang, C. From herbal small Rnas to one medicine. Sci. China Life Sci. 2019, 62, 285–287. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Guo, S.; Mu, X.; Mei, S.; Yang, R.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, J. Bencaosome [16:0 Lyso Pa+Xlgb28-Srna] improves osteoporosis by simultaneously promoting osteogenesis and inhibiting osteoclastogenesis in mice. IUBMB Life 2024, 76, 832–844. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, J.A.; Cullis, P.R.; van der Meel, R. Lipid nanoparticles enabling gene therapies: From concepts to clinical utility. Nucleic Acid. Ther. 2018, 28, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hald Albertsen, C.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Witzigmann, D.; Lind, M.; Petersson, K.; Simonsen, J.B. The role of lipid components in lipid nanoparticles for vaccines and gene therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 188, 114416. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, N.; Maeki, M.; Sato, Y.; Ishida, A.; Tani, H.; Harashima, H.; Tokeshi, M. Development of a microfluidic-based post-treatment process for size-controlled lipid nanoparticles and application to sirna delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 34011–34020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roces, C.B.; Lou, G.; Jain, N.; Abraham, S.; Thomas, A.; Halbert, G.W.; Perrie, Y. Manufacturing considerations for the development of lipid nanoparticles using microfluidics. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Wu, C.; Chen, J.; Xiao, Y. Nanotechnology in the targeted drug delivery for bone diseases and bone regeneration. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 2305–2317. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Guo, B.; Wu, H.; Tang, T.; Zhang, B.T.; Zheng, L.; He, Y.; Yang, Z.; Pan, X.; Chow, H.; et al. A delivery system targeting bone formation surfaces to facilitate Rnai-based anabolic therapy. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 307–314. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.D.; Toh, K.; Martin, M.R.; Chen, P.; Wang, C.; Igarashi, K.; Mpekris, F.; Stylianopoulos, T.; Stuber, M.D.; Kataoka, K.; et al. Bone marrow vessels are hyperpermeable to macromolecules and nanoscale medicine in a size-dependent manner. J. Control. Release 2025, 382, 113669. [Google Scholar]
- Choe, J.A.; Moseman, J.E.; Jones, J.M.; Burger, J.C.; Weichmann, A.M.; McNeel, D.G.; Murphy, W.L. Hydroxyapatite binding peptide lipid nanoparticles for biomimetic mrna delivery to bone. Adv. Ther. 2025, 8, 2400505. [Google Scholar]
- Sabnis, S.; Kumarasinghe, E.S.; Salerno, T.; Mihai, C.; Ketova, T.; Senn, J.J.; Lynn, A.; Bulychev, A.; McFadyen, I.; Chan, J.; et al. A novel amino lipid series for mrna delivery: Improved endosomal escape and sustained pharmacology and safety in non-human primates. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar]
- Ghandehari, H.; Chan, H.K.; Harashima, H.; MacKay, J.A.; Minko, T.; Schenke-Layland, K.; Shen, Y.; Vicent, M.J. Advanced drug delivery 2020—Parts 1,2 and 3. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 156, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Love, K.T.; Chen, Y.; Eltoukhy, A.A.; Kastrup, C.; Sahay, G.; Jeon, A.; Dong, Y.; Whitehead, K.A.; Anderson, D.G. Rapid discovery of potent sirna-containing lipid nanoparticles enabled by controlled microfluidic formulation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6948–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinc, A.; Querbes, W.; De, S.; Qin, J.; Frank-Kamenetsky, M.; Jayaprakash, K.N.; Jayaraman, M.; Rajeev, K.G.; Cantley, W.L.; Dorkin, J.R.; et al. Targeted delivery of rnai therapeutics with endogenous and exogenous ligand-based mechanisms. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaraman, M.; Ansell, S.M.; Mui, B.L.; Tam, Y.K.; Chen, J.; Du, X.; Butler, D.; Eltepu, L.; Matsuda, S.; Narayanannair, J.K.; et al. Maximizing the potency of sirna lipid nanoparticles for hepatic gene slencing in vivo. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 8529–8533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, I.R.; Billington, E.O. Drug therapy for osteoporosis in older adults. Lancet 2022, 399, 1080–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöttler, S.; Becker, G.; Winzen, S.; Steinbach, T.; Mohr, K.; Landfester, K.; Mailänder, V.; Wurm, F.R. Protein adsorption is required for stealth effect of poly(ethylene glycol)- and poly(phosphoester)-coated nanocarriers. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodine, P.V.; Zhao, W.; Kharode, Y.P.; Bex, F.J.; Lambert, A.J.; Goad, M.B.; Gaur, T.; Stein, G.S.; Lian, J.B.; Komm, B.S. The Wnt Antagonist Secreted Frizzled-Related Protein-1 Is a Negative Regulator of Trabecular Bone Formation in Adult Mice. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 1222–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, R.; Kneissel, M. Wnt signaling in bone homeostasis and disease: From human mutations to treatments. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, V.; Bryant, H.U.; Macdougald, O.A. Regulation of bone mass by wnt signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saag, K.G.; Petersen, J.; Brandi, M.L.; Karaplis, A.C.; Lorentzon, M.; Thomas, T.; Maddox, J.; Fan, M.; Meisner, P.D.; Grauer, A. Romosozumab or alendronate for fracture prevention in women with osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Jin, H. Rna-based therapeutics: An overview and prospectus. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, X.; Du, X.; Han, H.; Liu, F.; Zheng, Z.; Hao, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Wei, Z.; Huang, C.; et al. Intravenous Administration of sRNA Nanoparticles for Treatment of Osteoporosis in Mice. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060789
Mu X, Du X, Han H, Liu F, Zheng Z, Hao J, Liu L, Liu S, Wei Z, Huang C, et al. Intravenous Administration of sRNA Nanoparticles for Treatment of Osteoporosis in Mice. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(6):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060789
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Xuemeng, Xinyi Du, Huitian Han, Fei Liu, Zhifa Zheng, Jing Hao, Lijin Liu, Su Liu, Ze Wei, Changfa Huang, and et al. 2025. "Intravenous Administration of sRNA Nanoparticles for Treatment of Osteoporosis in Mice" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 6: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060789
APA StyleMu, X., Du, X., Han, H., Liu, F., Zheng, Z., Hao, J., Liu, L., Liu, S., Wei, Z., Huang, C., Liang, A., Zou, W., Zhao, L., Wu, Z., & Zhang, J. (2025). Intravenous Administration of sRNA Nanoparticles for Treatment of Osteoporosis in Mice. Pharmaceutics, 17(6), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060789







