Optimization of Lipoplexes Functionalized with a Sialic Acid Mimetic (F9-PEG) to Target the C1858T PTPN22 Variant for Preclinical Assessment of a Novel Immunotherapy in Endocrine Autoimmunity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. siRNA Design
2.2. Liposome/Lipoplex Preparation and Characterization
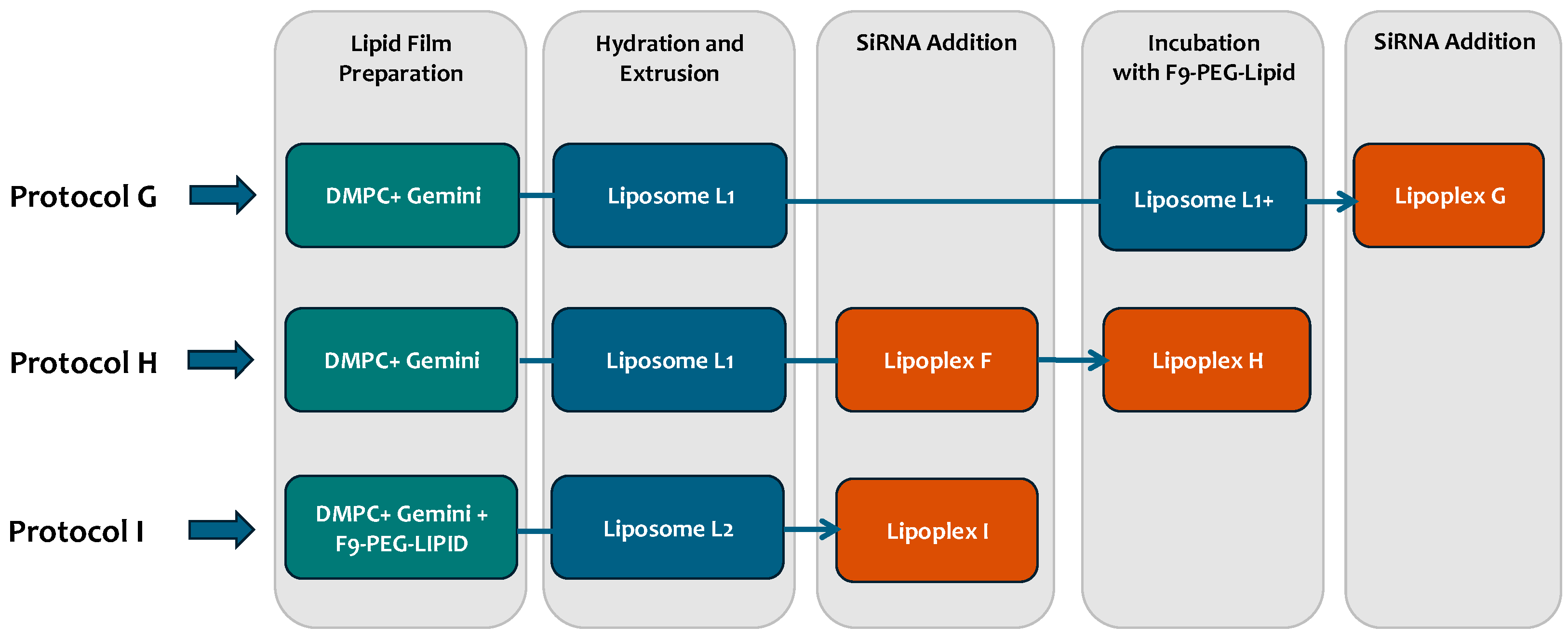
2.2.1. General Liposome and Lipoplex Preparations
2.2.2. Optimization of the Lipid/siRNA Ratio
2.2.3. Functionalization of Lipoplexes with Siglec-10 Ligand F9
2.2.4. Labeling of Lipoplexes with ATTO740 Fluorescent Dye
2.3. Binding Efficiency of siRNA to Liposomes
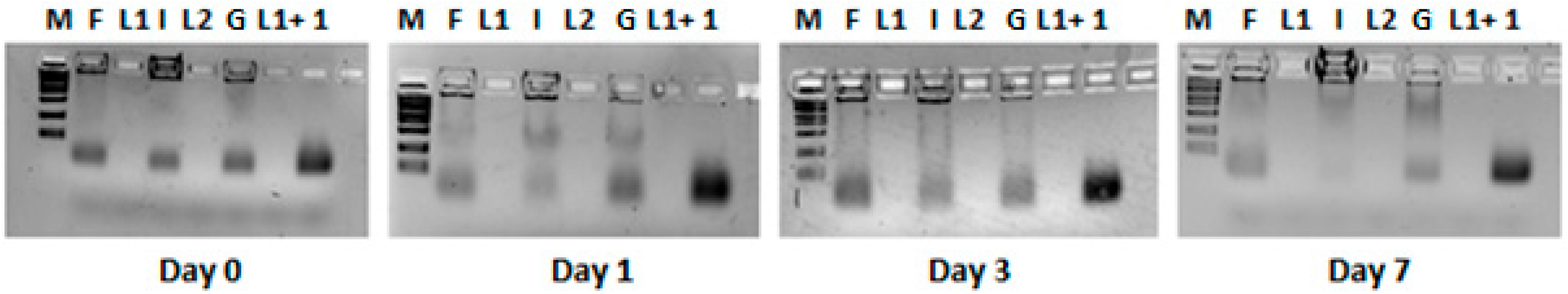
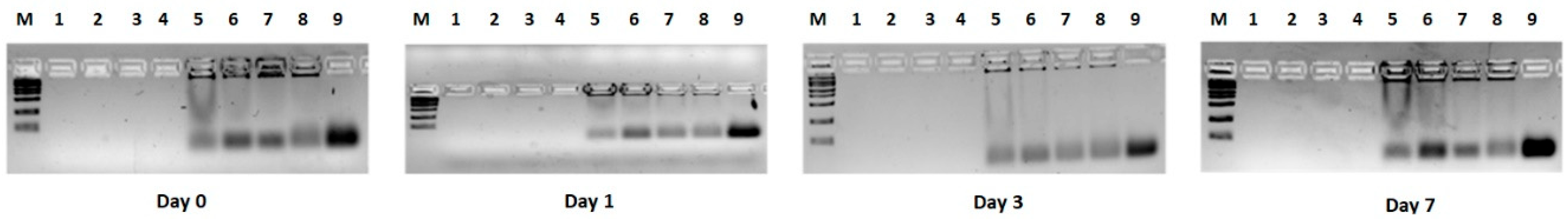
2.3.1. Electrophoresis
2.3.2. HPLC Determination
3. Results
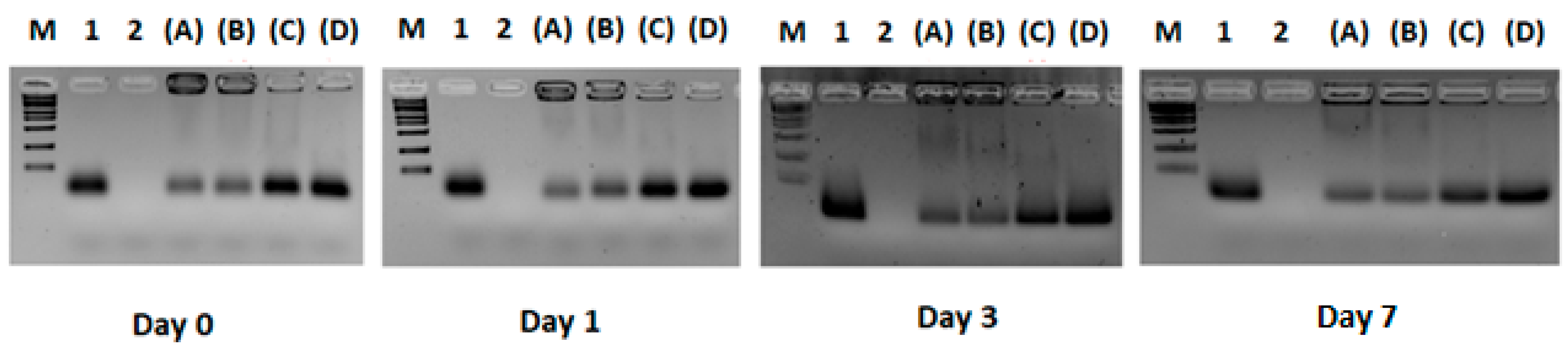
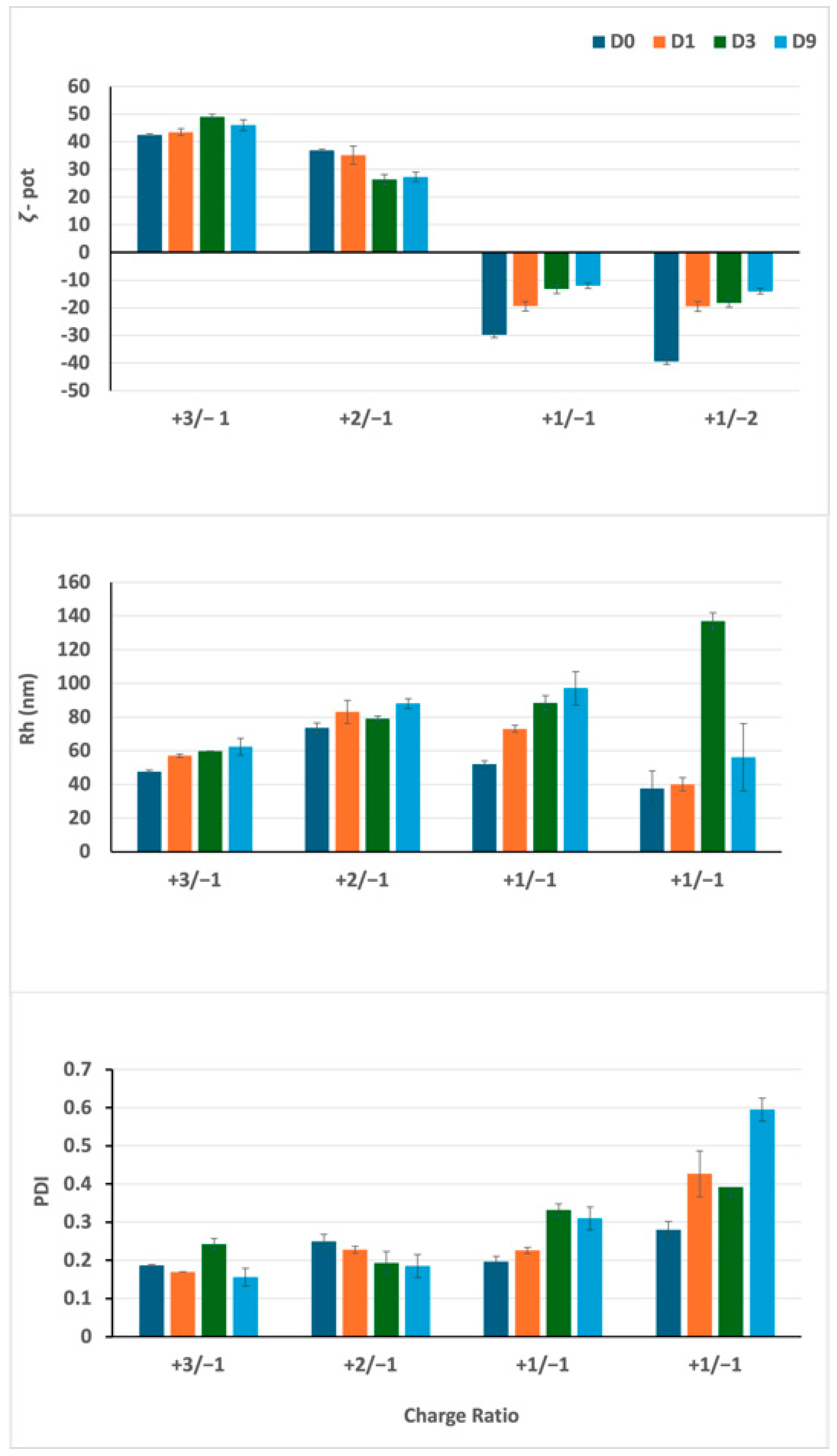
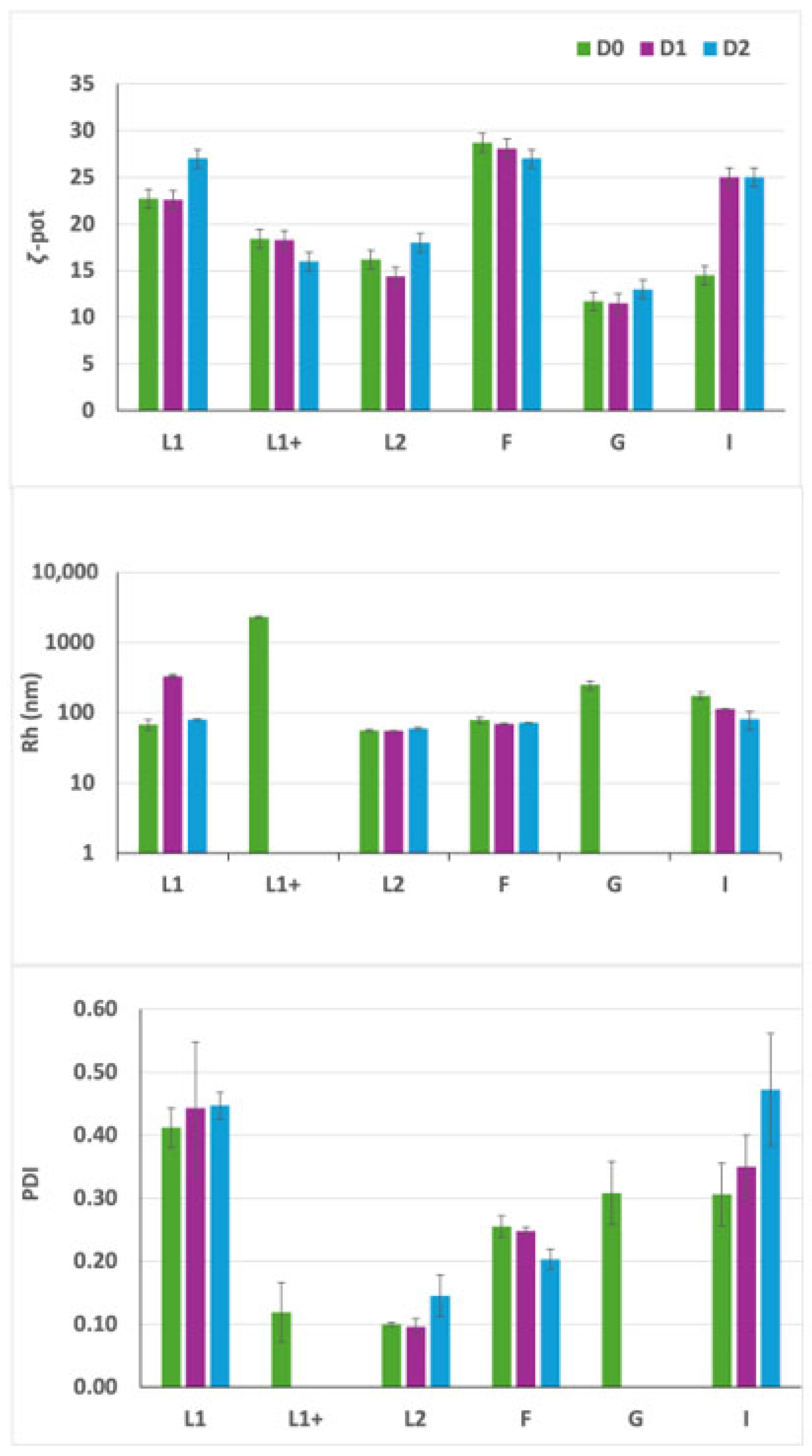
3.1. Experiment 1: Definition of the Optimal Lipid/siRNA Ratio
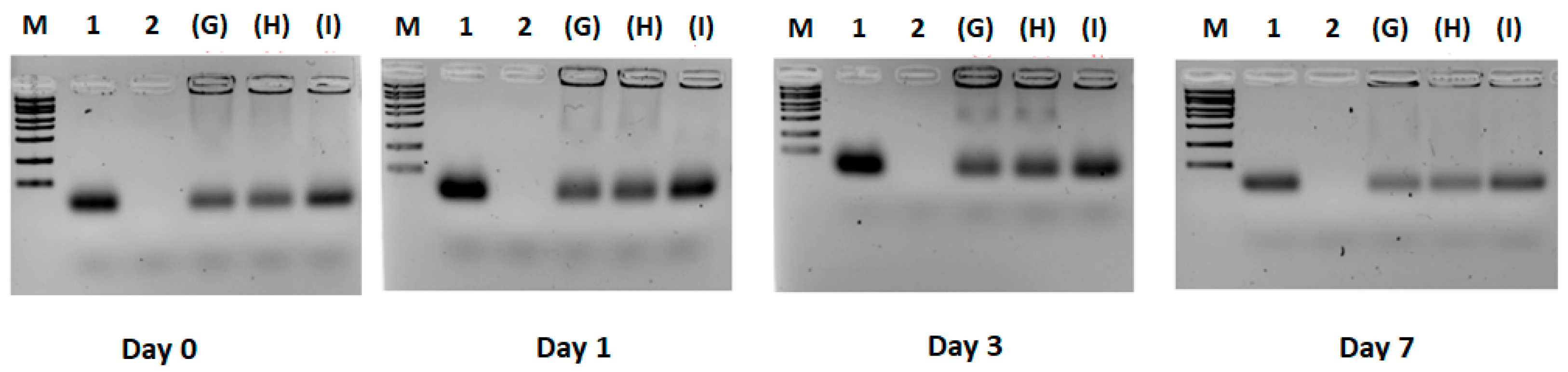
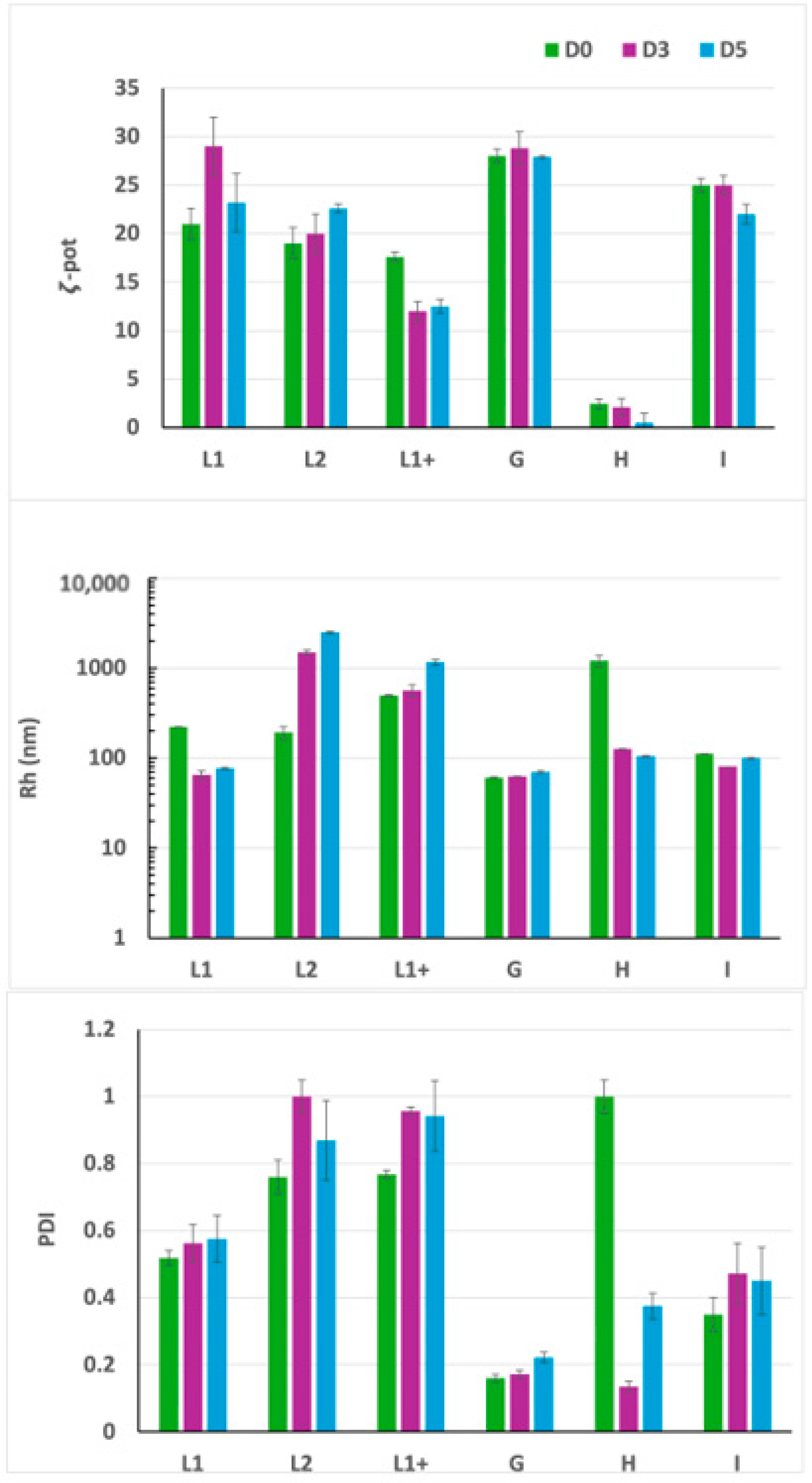
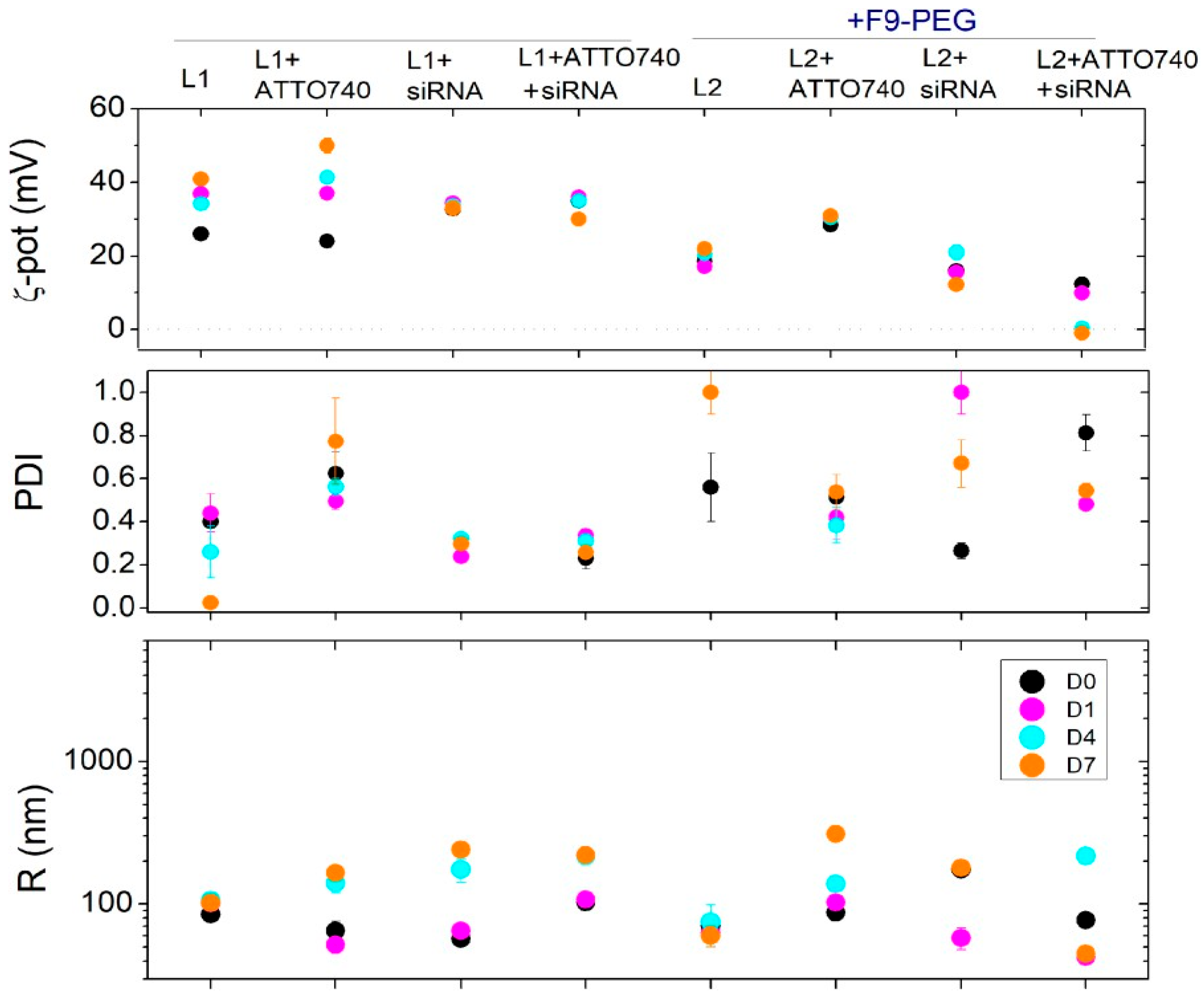
3.2. Experiment 2: Effect of F9-PEG Lipid on Lipoplex Stability
3.3. Experiment 3: Effect of ATTO740 on Lipoplex Stability
3.4. HPLC Analyses of Free siRNA and Lipoplex Preparations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATD | Autoimmune thyroid disease |
| T1D | Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus |
| APS3v | Polyglandular syndrome Type 3 variant |
| L-T4 | Levo-thyroxine |
| PTPN22 | protein tyrosine phosphatase N22 gene |
| min | minutes |
| aCD3 | Anti-CD3 |
| TCR | T cell antigen receptor |
| CSK | C-terminal Src kinase |
| PBMC | Peripheral blood T lymphocytes |
| PBS | phosphate buffer solution |
| mAbs | Monoclonal antibodies |
| TLR | Toll-Like receptor |
| ASO | Antisense oligonucleotides |
| RNAi | RNA interference |
| siRNA | small interfering RNA |
| SAM | Affinity Siglec-10 sialoside mimetic |
| DMPC | Dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine |
| O/N | Overnight |
| DLS | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| DELS | Dielectrophoretic Light Scattering |
| CD | Circular dichroism spectroscopy |
| ζ-pot | ζ-potential |
| Sig10L | Siglec-10 ligand |
| L2 | Liposome + F9-PEG-lipid (2.8%) |
| L1+ | Functionalized liposomes, Liposome used to prepare G |
| L1 | DMPC/gemini liposomes, Liposome used to prepare F |
| F | Lipoplexes/ATTO740 |
| HPLC | High-pressure liquid chromatography |
| PDI | Polydispersity index |
| R | Hydrodynamic size |
| LP | Liposome |
| M | Marker |
References
- Redondo, M.J.; Morgan, N.G. Heterogeneity and endotypes in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmar, M.; Kahaly, G.J. Genetics of the autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type 3 variant. Thyroid 2010, 20, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, J.M.; Johnson, R.K.; Stene, L.C. Type 1 diabetes-early life origins and changing epidemiology. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapini, N.; Schiaffini, R.; Fierabracci, A. Immunotherapy strategies for the prevention and treatment of distinct stages of type 1 diabetes: An overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woittiez, N.J.; Roep, B.O. Impact of disease heterogeneity on treatment efficacy of immunotherapy in type 1 diabetes: Different shades of gray. Immunotherapy 2015, 7, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianchecchi, E.; Palombi, M.; Fierabracci, A. The putative role of the C1858T polymorphism of protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN22 gene in autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vang, T.; Congia, M.; Macis, M.D.; Musumeci, L.; Orrù, V.; Zavattari, P.; Nika, K.; Tautz, L.; Taskén, K.; Cucca, F.; et al. Autoimmune-associated lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase is a gain-of-function variant. Nat. Gen. 2005, 37, 1317–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianchecchi, E.; Crino, A.; Giorda, E.; Luciano, R.; Perri, V.; Lo Russo, A.; Cappa, M.; Rosado, M.M.; Fierabracci, A. Altered B cell homeostasis and toll-like receptor 9-driven response in type 1 diabetes carriers of the C1858T PTPN22 allelic variant: Implications in the disease pathogenesis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 110755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, L.J.; Rossi, J.J. Approaches for the sequence-specific knockdown of mRNA. Nat. Biotech. 2003, 21, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottini, N.; Musumeci, L.; Alonso, A.; Rahmouni, S.; Nika, K.; Rostamkhani, M.; Rostamkhani, M.; MacMurray, J.; Meloni, G.F.; Lucarelli, P.; et al. A functional variant of lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase is associated with type I diabetes. Nat. Gen. 2004, 36, 337–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perri, V.; Pellegrino, M.; Ceccacci, F.; Scipioni, A.; Petrini, S.; Gianchecchi, E.; Lo Russo, A.; De Santis, S.; Mancini, G.; Fierabracci, A. Use of short interfering RNA delivered by cationic liposomes to enable efficient down-regulation of PTPN22 gene in human T lymphocytes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 0175784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrino, M.; Ceccacci, F.; Petrini, S.; Scipioni, A.; De Santis, S.; Cappa, M.; Mancini, G.; Fierabracci, A. Exploiting novel tailored immunotherapies of type 1 diabetes: Short interfering RNA delivered by cationic liposomes enables efficient down- regulation of variant PTPN22 gene in T lymphocytes. Nanomedicine 2019, 18, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arena, A.; Belcastro, E.; Accardo, A.; Sandomenico, A.; Pagliarosi, O.; Rosa, E.; Petrini, S.; Conti, L.A.; Giorda, E.; Corsetti, T.; et al. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of RITUXfab-decorated lipoplexes to improve delivery of siRNA targeting C1858T PTPN22 variant in B lymphocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büll, C.; Heise, T.; Adema, G.J.; Boltje, T.J. Sialic acid mimetics to target the sialic acid–Siglec axis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rillahan, C.D.; Schwartz, E.; McBride, R.; Fokin, V.V.; Paulson, J.C. Click and pick: Identification of sialoside analogues for Siglec-based cell targeting. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 11014–11018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arena, A.; Belcastro, E.; Ceccacci, F.; Petrini, S.; Conti, L.A.; Pagliarosi, O.; Giorda, E.; Sennato, S.; Schiaffini, R.; Wang, P.; et al. Improvement of lipoplexes with a sialic acid mimetic to target the C1858T PTPN22 variant for immunotherapy in endocrine autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 838331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, C.; Bombelli, C.; Borocci, S.; di Profio, P.; Mancini, G. Role of the spacer stereochemistry on the aggregation properties of cationic gemini surfactants. Langmuir 2006, 22, 9333–9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seebach, D.; Kalinowski, H.-O.; Bastani, B.; Crass, G.; Daum, H.; Dörr, H.; DuPreez, N.P.; Ehrig, V.; Langer, W.; Nüssler, C.; et al. Preparation of auxiliaries for asymmetric synthesis from tartaric acid. Addition of butyllithium to aldehydes in chiral media. Helv. Chim. Acta 1977, 60, 301–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, M.J.; Nayar, R.; Mayer, L.D.; Cullis, P.R. Reduction of liposome size and preparation of unilamellar vesicles by extrusion techniques. Liposome Technol. 1993, 1, 123–139. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, S.-H.; Hsieh, Y.-C.; Huang, L.-C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Hsu, K.-W.; Hsieh, W.-S.; Chi, W.-M.; Lee, C.-H. A rapid and quantitative method to detect human circulating tumor cells in a preclinical animal model. Cancer Sci. 2025, 116, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sennato, S.; Paldino, G.; Bombelli, C.; Mezzani, I.; Petrini, S.; Delfino, D.V.; Fiorentino, F.; Marianecci, C.; Ciogli, A.; Rotili, D.; et al. Optimization of Lipoplexes Functionalized with a Sialic Acid Mimetic (F9-PEG) to Target the C1858T PTPN22 Variant for Preclinical Assessment of a Novel Immunotherapy in Endocrine Autoimmunity. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060710
Sennato S, Paldino G, Bombelli C, Mezzani I, Petrini S, Delfino DV, Fiorentino F, Marianecci C, Ciogli A, Rotili D, et al. Optimization of Lipoplexes Functionalized with a Sialic Acid Mimetic (F9-PEG) to Target the C1858T PTPN22 Variant for Preclinical Assessment of a Novel Immunotherapy in Endocrine Autoimmunity. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(6):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060710
Chicago/Turabian StyleSennato, Simona, Giorgia Paldino, Cecilia Bombelli, Irene Mezzani, Stefania Petrini, Domenico Vittorio Delfino, Francesco Fiorentino, Carlotta Marianecci, Alessia Ciogli, Dante Rotili, and et al. 2025. "Optimization of Lipoplexes Functionalized with a Sialic Acid Mimetic (F9-PEG) to Target the C1858T PTPN22 Variant for Preclinical Assessment of a Novel Immunotherapy in Endocrine Autoimmunity" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 6: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060710
APA StyleSennato, S., Paldino, G., Bombelli, C., Mezzani, I., Petrini, S., Delfino, D. V., Fiorentino, F., Marianecci, C., Ciogli, A., Rotili, D., Ceccacci, F., & Fierabracci, A. (2025). Optimization of Lipoplexes Functionalized with a Sialic Acid Mimetic (F9-PEG) to Target the C1858T PTPN22 Variant for Preclinical Assessment of a Novel Immunotherapy in Endocrine Autoimmunity. Pharmaceutics, 17(6), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060710











