Application of Nanodrug Delivery Systems in Enhancing Treatment of Gastritis and Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Evaluation of Targeted Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Preparation, Targeted Delivery, and Advantage of Nanomedicine
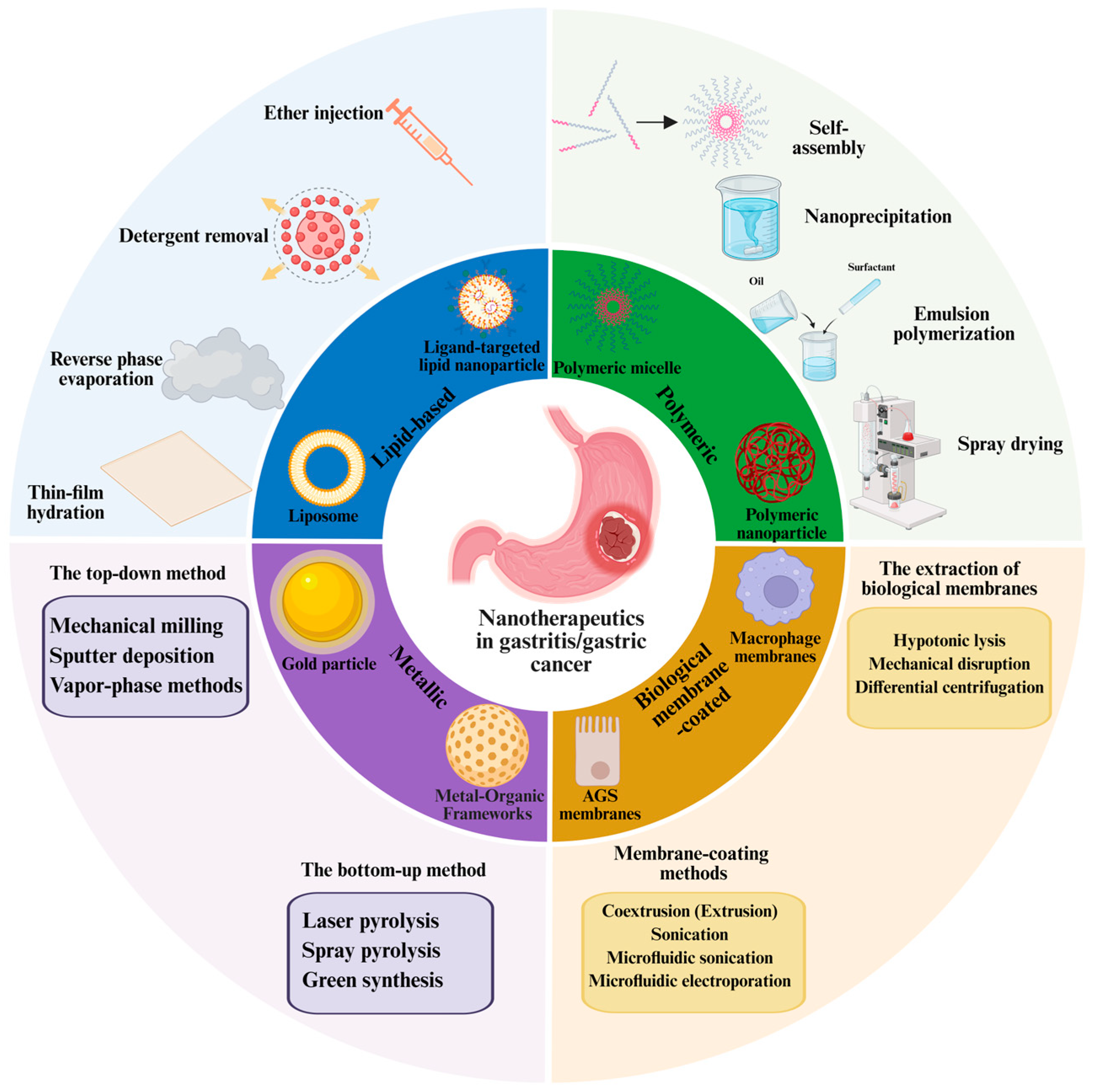
2.1. The Preparation of Nanomedicine
- (1)
- The preparation methods for lipid-based nanoparticles
- (2)
- The preparation methods for polymeric nanoparticles
- (3)
- The preparation methods for metallic nanoparticles
- (4)
- The preparation methods for biomembrane-coated nanoparticles
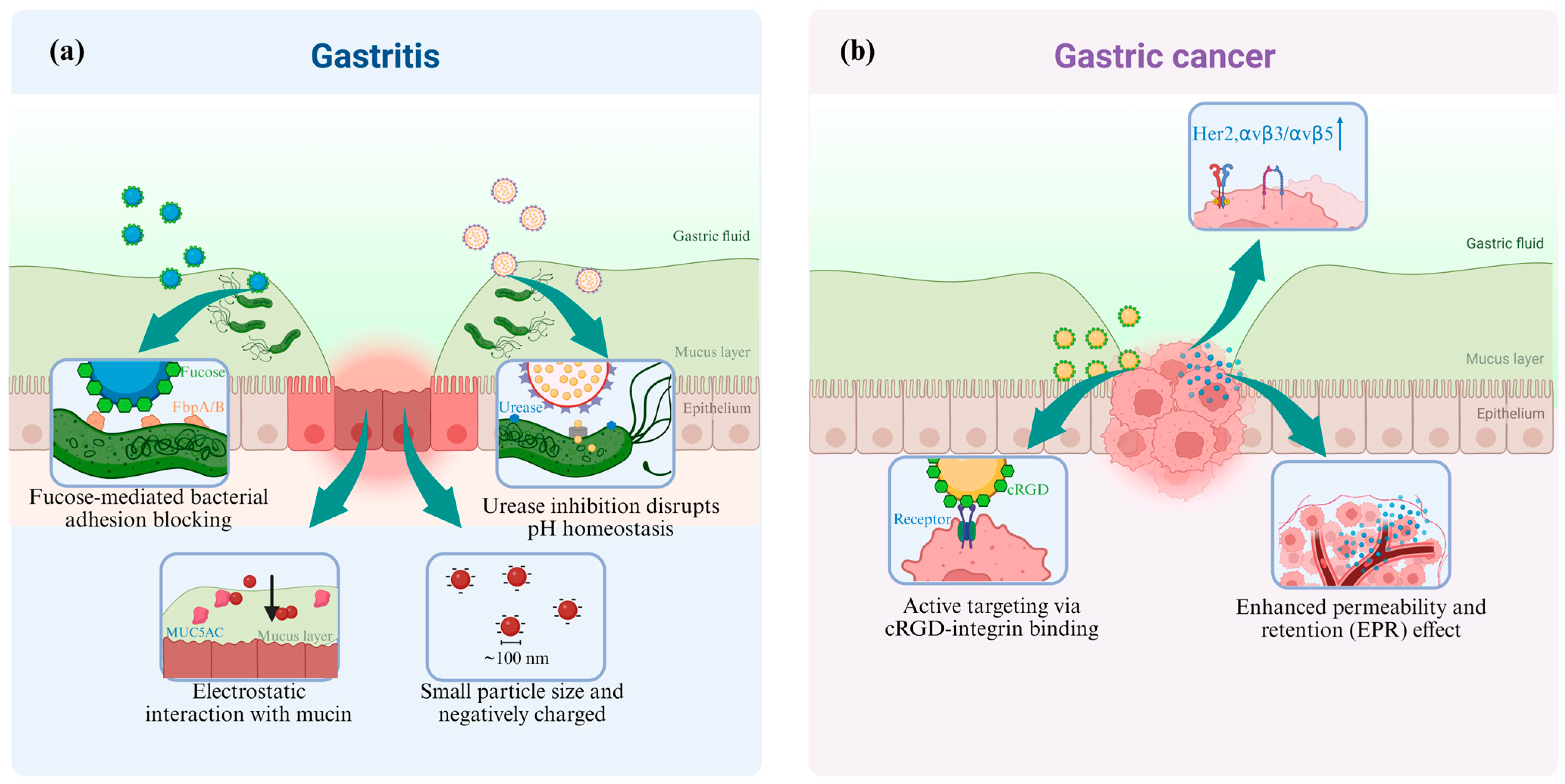
2.2. The Targeted Delivery of Nanomedicine
- (1)
- Nanomedicine targeted to Gastritis
- (2)
- Nanomedicine targeted to Gastric Cancer
2.3. The Advantage of Nanomedicine
3. Therapeutic Applications of Nanomedicine in Gastritis
3.1. Lipid-Based Nanoparticles
3.2. Polymeric Nanoparticles
3.3. Metallic Nanoparticles
3.4. Biomembrane-Coated Nanoparticles
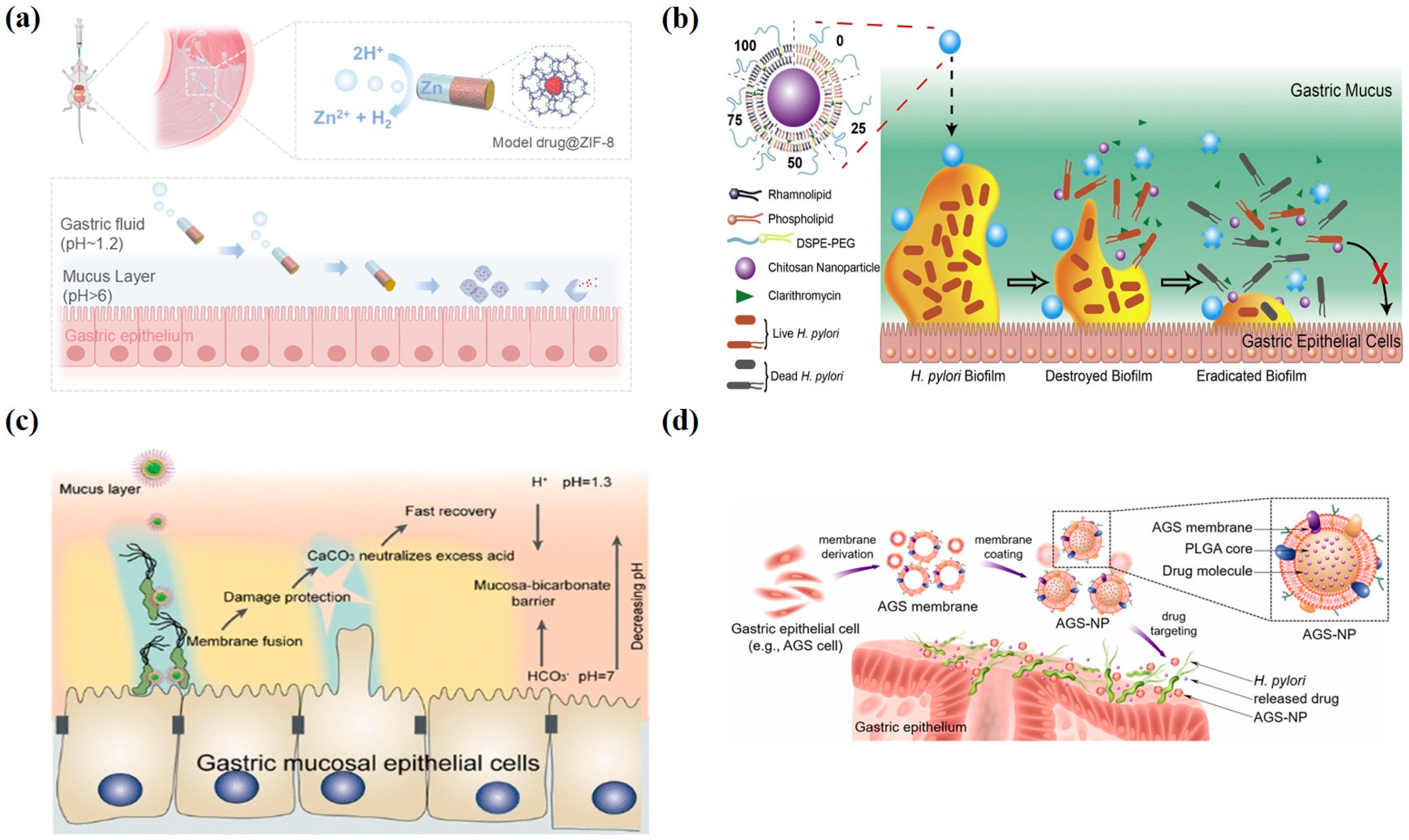
3.5. Recent Advances in Nanomedicine-Based Therapies for Gastritis
4. Therapeutic Applications of Nanomedicine in Gastric Cancer
4.1. Lipid-Based Nanoparticles
4.2. Polymeric Nanoparticles
4.3. Metallic Nanoparticles
4.4. Biomembrance-Coated Nanoparticles
4.5. Recent Advances in Nanomedicine-Based Therapies for Gastric Cancer
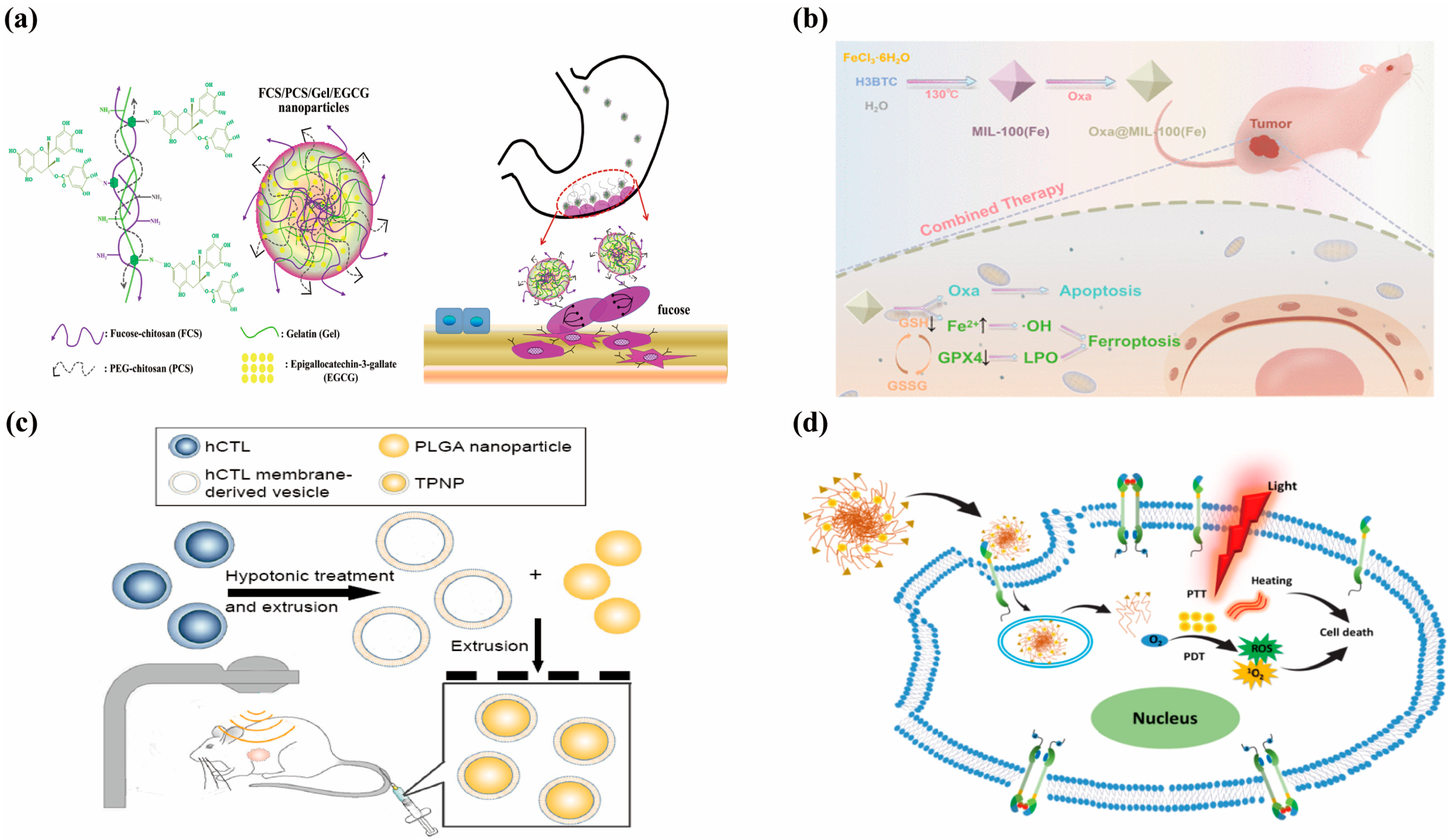
5. Clinical Trials of Nanomedicines in Gastric Cancer
5.1. Liposomal Paclitaxel (L-PTX)
5.2. Albumin-Bound Nanoparticles
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shah, S.C.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Kuipers, E.J.; Li, D. AGA Clinical Practice Update on the Diagnosis and Management of Atrophic Gastritis: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1325–1332.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavros, Y.; Merchant, J.L. The immune microenvironment in gastric adenocarcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenti, M.V.; Rugge, M.; Lahner, E.; Miceli, E.; Toh, B.H.; Genta, R.M.; De Block, C.; Hershko, C.; Di Sabatino, A. Autoimmune gastritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Dou, Y.; Xu, D. Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: Mechanisms and new perspectives. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2025, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Camargo, M.C.; El-Omar, E.; Liou, J.-M.; Peek, R.; Schulz, C.; Smith, S.I.; Suerbaum, S. Helicobacter pylori infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Karhana, S.; Khan, M.A. Nanomedicine for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori: Recent advances, challenges and future perspective. Future Microbiol. 2024, 19, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foegeding, N.J.; Raghunathan, K.; Campbell, A.M.; Kim, S.W.; Lau, K.S.; Kenworthy, A.K.; Cover, T.L.; Ohi, M.D. Intracellular Degradation of Helicobacter pylori VacA Toxin as a Determinant of Gastric Epithelial Cell Viability. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00783-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Lao, Y.-H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yi, K.; Chen, Z.; Han, J.; Song, W.; Tao, Y.; Li, M. Combatting Helicobacter pylori with oral nanomedicines. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 9826–9838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksymova, L.; Pilger, Y.A.; Nuhn, L.; Van Ginderachter, J.A. Nanobodies targeting the tumor microenvironment and their formulation as nanomedicines. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofias, A.M.; Lammers, T. Multidrug nanomedicine. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2023, 18, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaly, N.; Yameen, B.; Wu, J.; Farokhzad, O.C. Degradable Controlled-Release Polymers and Polymeric Nanoparticles: Mechanisms of Controlling Drug Release. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2602–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, L.; Samuel, L.; Patrick, S.; Frederic, L. Specificity of pharmacokinetic modeling of nanomedicines. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 2259–2268. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, A.; Uthaman, S.; Park, I.-K. Utilization of polymer-lipid hybrid nanoparticles for targeted anti-cancer therapy. Molecules 2020, 25, 4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdie, H.; Fateme, H.; Farzaneh, J.; Seyedmohammad, M.; Ali, M. Targeting cell cycle protein in gastric cancer with CDC20siRNA and anticancer drugs (doxorubicin and quercetin) co-loaded cationic PEGylated nanoniosomes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 6575–6585. [Google Scholar]
- Imran, M.; Jha, S.K.; Hasan, N.; Insaf, A.; Shrestha, J.; Shrestha, J.; Devkota, H.P.; Khan, S.; Panth, N.; Warkiani, M.E. Overcoming multidrug resistance of antibiotics via nanodelivery systems. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chen, C.; Feng, W.; Gu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y. Catalase-assembled nanoparticles for PA/CT dual-modality imaging and repair of acute alcoholic gastritis. Biomater. Adv. 2025, 169, 214181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Geng, J.; Wang, H.; Su, J.; Arif, M.; Dong, Q.; Chi, Z.; Liu, C. Ureido-modified carboxymethyl chitosan-graft-stearic acid polymeric nano-micelles as a targeted delivering carrier of clarithromycin for Helicobacter pylori: Preparation and in vitro evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Lin, G.; He, Z.; Wang, Y. Unique flower-like Cur-metal complexes loaded liposomes for primary and metastatic breast cancer therapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 121, 111835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maione-Silva, L.; de Castro, E.G.; Nascimento, T.L.; Cintra, E.R.; Moreira, L.C.; Cintra, B.A.S.; Valadares, M.C.; Lima, E.M. Ascorbic acid encapsulated into negatively charged liposomes exhibits increased skin permeation, retention and enhances collagen synthesis by fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Yang, E.; Chang, P.-S.; Ryu, S. Preparation and characterization of endolysin-containing liposomes and evaluation of their antimicrobial activities against gram-negative bacteria. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2019, 128, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuri, S.; Rhodes, C. Preparation and characterization of liposomes as therapeutic delivery systems: A review. Pharm. Acta Helv. 1995, 70, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Li, D.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Teng, L.; Bunt, C.; Wen, J. Deformable liposomes by reverse-phase evaporation method for an enhanced skin delivery of (+)-catechin. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foged, C.; Nielsen, H.M.; Frokjaer, S. Liposomes for phospholipase A2 triggered siRNA release: Preparation and in vitro test. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 331, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toniazzo, T.; Peres, M.S.; Ramos, A.P.; Pinho, S.C. Encapsulation of quercetin in liposomes by ethanol injection and physicochemical characterization of dispersions and lyophilized vesicles. Food Biosci. 2017, 19, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitor, M.T.; Bergami-Santos, P.C.; Zômpero, R.H.F.; Cruz, K.S.P.; Pinho, M.P.; Barbuto, J.A.M.; de la Torre, L.G. Cationic liposomes produced via ethanol injection method for dendritic cell therapy. J. Liposome Res. 2017, 27, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, B.; Alexandridis, P. Self-assembled block copolymer–nanoparticle hybrids: Interplay between enthalpy and entropy. Langmuir 2012, 28, 15975–15986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepeltier, E.; Bourgaux, C.; Couvreur, P. Nanoprecipitation and the “Ouzo effect”: Application to drug delivery devices. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 71, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Anton, N.; Vandamme, T.F.; Serra, C.A. Microfluidic nanoprecipitation systems for preparing pure drug or polymeric drug loaded nanoparticles: An overview. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1447–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R.; Alwani, S.; Badea, I. Polymeric nanoparticles in gene therapy: New avenues of design and optimization for delivery applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.S.; Czuba, E.; Chen, M.Z.; Yuen, D.; Cupic, K.I.; Yang, S.; Hodgetts, R.Y.; Selby, L.I.; Johnston, A.P.; Such, G.K. pH-responsive transferrin-pHlexi particles capable of targeting cells in vitro. ACS Macro Lett. 2017, 6, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulingam, T.; Foroozandeh, P.; Chuah, J.-A.; Sudesh, K. Exploring various techniques for the chemical and biological synthesis of polymeric nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedroso-Santana, S.; Fleitas-Salazar, N. Ionotropic gelation method in the synthesis of nanoparticles/microparticles for biomedical purposes. Polym. Int. 2020, 69, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Yan, W.; Xu, Z.; Ni, H. Formation mechanism of monodisperse, low molecular weight chitosan nanoparticles by ionic gelation technique. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 90, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamatari, M.; Charisi, A.; Malamataris, S.; Kachrimanis, K.; Nikolakakis, I. Spray drying for the preparation of nanoparticle-based drug formulations as dry powders for inhalation. Processes 2020, 8, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacoff, B.P.; Brown, K.A. Progress in top-down control of bottom-up assembly. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 6508–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Chung, C.H.; Lau, C.M.L.; Chung, J.T.; Chau, Y.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yao, S. Metal–Organic Frameworks-Based Microrockets for Controlled and Sustained Drug Release. Nano Lett. 2025, 25, 5989–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.-H.; Ye, P.-J.; Zhou, Y.-C.; He, D.-X.; Wei, H.; Yu, C.-Y. Cell membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles as drug carriers for cancer therapy. Acta Biomater. 2020, 105, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Chang, J.; Tian, F.; Zhao, F.; Ma, Y.; Sun, J. Microfluidic sonication to assemble exosome membrane-coated nanoparticles for immune evasion-mediated targeting. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 7836–7844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Cabe, M.H.; Ogle, S.D.; Sanchez, V.; Langert, K.A. Optimization of critical parameters for coating of polymeric nanoparticles with plasma membrane vesicles by sonication. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, T. Cell membrane coating technology: A promising strategy for biomedical applications. Nano-Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oroojalian, F.; Beygi, M.; Baradaran, B.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Shahbazi, M.A. Immune cell membrane-coated biomimetic nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Small 2021, 17, 2006484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wu, Q.; Huang, X.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Weitz, D.A.; Song, Y. Synthesis of nanomedicine hydrogel microcapsules by droplet microfluidic process and their pH and temperature dependent release. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 37814–37823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, Y.; Cao, R.; Xu, Y.; Weng, Z.; Ye, J.; He, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X. Metal–organic-framework-based hydrogen-release platform for multieffective Helicobacter pylori targeting therapy and intestinal flora protective capabilities. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2105738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Dong, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ji, Y.; Feng, J.; Yan, P.; Zhu, Y. Mucus and Biofilm Penetrating Nanoplatform as an Ultrasound-Induced Free Radical Initiator for Targeted Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2400363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wong, K.I.; Ma, Y.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Wei, L.; Wang, S.; Yao, M.; Lu, M. Biodegradable Acid-Responsive Nanocarrier for Enhanced Antibiotic Therapy Against Drug-Resistant Helicobacter Pylori via Urease Inhibition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2412893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W.; He, C.; Shu, C.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Fei, X.; Li, N.; Hu, Y.; Xie, C.; et al. Metal-Organic Framework Based Mucoadhesive Nanodrugs for Multifunction Helicobacter Pylori Targeted Eradication, Inflammation Regulation and Gut Flora Protection. Small 2024, 20, 2308286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Guo, Q.; Ding, L.; Fu, H.; Song, H. Precise Targeting Therapy of Orthotopic Gastric Carcinoma by siRNA and Chemotherapeutic Drug Codelivered in pH-Sensitive Nano Platform. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Luo, H.; Luo, Y.-Y.; Zhang, W.; Hong, H.-M.; Deng, M.-S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, B.; Song, G.-B.; Xu, C.-X. Plumbagin-loaded ZIF-90 nanoparticles suppress gastric cancer progression by targeting the YAP1 signaling. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 135369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Sun, L.; Lai, W.-F.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Qin, X.; Qi, X. R11 modified tumor cell membrane nanovesicle-camouflaged nanoparticles with enhanced targeting and mucus-penetrating efficiency for intravesical chemotherapy for bladder cancer. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 834–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Ye, N.; Yang, X.; Li, Z. Boosting nanomedicine efficacy with hyperbaric oxygen therapy. In Bio-Nanomedicine for Cancer Therapy; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 1295, pp. 77–95. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Chen, S.; Hong, Y.; Jia, L.; Zhou, Y.; He, X.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Yang, Z.; Gao, D. Research progress of conjugated nanomedicine for cancer treatment. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, P.; Wei, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, M.; Ge, Y.; Zou, J.; Peng, S.; Jiang, L.; Tian, L. Near-Infrared Light-Triggered MXene Nanocomposite for Tumor-Specific Mild Photothermal-Enhanced Chemodynamic Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2405124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Park, G.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.; Choi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lee, Y.; Choi, T.H. In Vitro and In Vivo Antimicrobial Activity of Antibiotic-Conjugated Carriers with Rapid pH-Responsive Release Kinetics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1900247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Zhou, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, C.; Hou, X. A multifunctional ROS cascade nanoplatform enables common prosperity of O2 and H2O2 for magnetic targeting and fluorescence imaging-guided photodynamic/chemodynamic therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 506, 160178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nem, S.; Jungryun, K.; Jaewon, K.; Kyungwoo, L.; Zehra, Z.; Injun, L.; Eunji, K.; Sung-Gil, C.; Seung, K.J. Covalent organic framework nanomedicines: Biocompatibility for advanced nanocarriers and cancer theranostics applications. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 21, 358–380. [Google Scholar]
- Karavolos, M.; Holban, A.; Eynde, J.J.V. Nanosized Drug Delivery Systems in Gastrointestinal Targeting: Interactions with Microbiota. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.-W.; Jia, Y.-Y.; Wan, N.; Luo, M.; Huan, M.-L.; Kang, T.-B.; Zhou, S.-Y.; Zhang, B.-L. Design and evaluation of novel pH-sensitive ureido-conjugated chitosan/TPP nanoparticles targeted to Helicobacter pylori. Biomaterials 2016, 84, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensign, L.M.; Cone, R.; Hanes, J. Oral drug delivery with polymeric nanoparticles: The gastrointestinal mucus barriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitas, R.; Fonseca, D.R.; Parreira, P.; Martins, M.C.L. Targeted nanotherapeutics for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Biomed. Sci. 2024, 31, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsha, S. Dual drug delivery system for targeting H. pylori in the stomach: Preparation and in vitro characterization of amoxicillin-loaded Carbopol® nanospheres. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 4787–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, X.; Shen, Y.; Li, H.; Zou, Y.; Yuan, G.; Hu, P.; Hu, H. Mucus penetration enhanced lipid polymer nanoparticles improve the eradication rate of Helicobacter pylori biofilm. J. Control. Release 2019, 300, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiyun, D.; Yang, W.; Zhiyong, S.; Shuojun, L.; Moqing, D.; Jiamin, D.; Quan, X.; Liu, D.; Shendy, B.H.; Heyou, H. Tea Polyphenol Liposomes Overcome Gastric Mucus to Treat Helicobacter pylori Infection and Enhance the Intestinal Microenvironment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 13001–13012. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida Furquim de Camargo, B.; Soares Silva, D.E.; Noronha da Silva, A.; Campos, D.L.; Machado Ribeiro, T.R.; Mieli, M.J.; Borges Teixeira Zanatta, M.; Bento da Silva, P.; Pavan, F.R.; Gallina Moreira, C.; et al. New silver (I) coordination compound loaded into polymeric nanoparticles as a strategy to improve in vitro anti-Helicobacter pylori activity. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 2287–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaojing, Y.; Yongkang, L.; Yiqi, D.; Tinglin, Z.; Jie, G.; Zhaoshen, L. Metal-Based Nanoparticles: A Prospective Strategy for Helicobacter pylori Treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 2413–2429. [Google Scholar]
- Panáček, A.; Smékalová, M.; Kilianová, M.; Prucek, R.; Bogdanová, K.; Večeřová, R.; Kolář, M.; Havrdová, M.; Płaza, G.; Chojniak, J.; et al. Strong and Nonspecific Synergistic Antibacterial Efficiency of Antibiotics Combined with Silver Nanoparticles at Very Low Concentrations Showing No Cytotoxic Effect. Molecules 2015, 21, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angsantikul, P.; Thamphiwatana, S.; Zhang, Q.; Spiekermann, K.; Zhuang, J.; Fang, R.H.; Gao, W.; Obonyo, M.; Zhang, L. Coating nanoparticles with gastric epithelial cell membrane for targeted antibiotic delivery against Helicobacter pylori infection. Adv. Ther. 2018, 1, 1800016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Huang, J.; Guo, X.; Zhang, C.; Wei, L.; Wong, K.I.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Lu, M.; Yao, W. An all-in-one therapeutic platform for the treatment of resistant Helicobacter pylori infection. Biomaterials 2024, 308, 122540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.I.; Paget, T.; Moosa, N.Y.; Alghurairy, H.; Elkordy, A.A. Liposomal Drug Delivery against Helicobacter pylori Using Furazolidone and N-Acetyl Cysteine in Augmented Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Hou, Y.; Tian, Y.; Tian, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y. Antimicrobial Peptide Hydrogel with pH-Responsive and Controllable Drug Release Properties for the Efficient Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 51981–51993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, D.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Nie, J.; Ma, G. Acid-Triggered Charge-Switchable Antibacterial Hydrogel for Accelerated Healing of Gastric Mucosal Wounds. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 17533–17553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yu, J.; Bu, C.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Ding, X.; Yuan, P. Antibiotic-Augmented Chemodynamic Therapy for Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection in the Dynamic Stomach Environment. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 14983–14992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Huang, L. Liposomal nanostructures for drug delivery in gastrointestinal cancers. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Ouyang, A.; Fan, L.; Qin, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, P.; Huang, X.; Hao, J.; Zhu, H. Precision Delivery of Binary Cooperative Nanodrugs Self-Assembled by Berberine Glycyrrhetinic Acid Salts for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 58489–58505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, X. Preparation, pharmacokinetics and tumour-suppressive activity of berberine liposomes. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2017, 69, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tian, L.; Khan, M.N.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, Q.; Fu, L.; Liu, J. Ginsenoside Rg3 sensitizes hypoxic lung cancer cells to cisplatin via blocking of NF-κB mediated epithelial–mesenchymal transition and stemness. Cancer Lett. 2018, 415, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.; Wang, D.; Liang, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xia, J.; Qin, J.; Zhan, H.; Wang, J. Novel ginsenoside-based multifunctional liposomal delivery system for combination therapy of gastric cancer. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Chen, Z.-R.; Lai, C.-H.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Feng, C.-L. Active Targeted Nanoparticles for Oral Administration of Gastric Cancer Therapy. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3021–3032. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, A.; Wu, W. Metal-organic frameworks in oral drug delivery. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 19, 100951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Yin, W.; Liu, Z.; Shi, L.; Tang, M. A novel drug delivery system: The encapsulation of naringenin in metal-organic frameworks into liposomes. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Guo, Q.; Xu, L. Study on the Chemotherapeutic Effect and Mechanism of Doxorubicin Hydrochloride on Drug-Resistant Gastric Cancer Cell Lines Using Metal-Organic Framework Fluorescent Nanoparticles as Carriers. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 6681749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, Y. Oxaliplatin-Loaded Mil-100 (Fe) for Chemotherapy–Ferroptosis Combined Therapy for Gastric Cancer. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 16676–16686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, R.; Chen, H.; Wei, J.; Qian, H.; Su, S.; Shao, J.; Wang, L.; Qian, X.; Liu, B. Human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles combined with low-dose irradiation: A new approach to enhance drug targeting in gastric cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 2017, 2129–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zheng, W.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Shen, X.; Chen, Q.; Lu, Y.; Chen, K.; Ai, S.; Zhu, Y. Enhanced photodynamic therapy synergizing with inhibition of tumor neutrophil ferroptosis boosts anti-PD-1 therapy of gastric cancer. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2307870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Shen, H.; SiTu, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, K. Preparation of Bmi-1-siRNA Lipid Nanoparticles and Effects in Gastric Cancer. Nano Biomed. Eng. 2024, 16, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kwak, J.H.; Choi, H.J.; Lee, D.; Park, J.H.; Kim, O.-H.; Kim, S.-J. Enhanced drug delivery in cancer therapy: Role of TMPRSS4 protease in liposomal engineering. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2025, 30, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhi, A.A.; Valizadeh, A.; Sedghizadeh, N.; Beba, L.; Dadashi, H.; Kazempour, M.; Adibkia, K.; Vandghanooni, S.; Eskandani, M. Targeted therapy of gastric cancer with gingerol-loaded hyaluronic acid/PEG-coated PLGA nanoparticles: Development and physicochemical evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 97, 105734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Cai, M.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y.; Jing, X.; Sun, Y.; Chang, R.; Qu, C.; Dong, X. CPP10-targeted photoactivatable MOF nanosystem for combined photodynamic Therapy—Chemotherapy of cancer. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2024, 9, 100761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, Z.; El-kott, A.F.; AlShehri, M.A. Sustainable synthesis of Au nanoparticles templated over chitosan/pectin hydrogel for the treatment of gastric cancer. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1318, 139260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Rao, K.; Xiang, J.; Ning, S.; Zhu, D.; Li, G.; Chen, H. Biomimetic Cascade Nanozyme Catalytic System for the Treatment of Lymph Node Metastasis in Gastric Cancer. Small 2025, 21, 2411576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, T.Y. Recent advances in the bench-to-bedside translation of cancer nanomedicines. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 15, 97–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Sun, B.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Gai, J.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Ma, L. A humanized trivalent Nectin-4-targeting nanobody drug conjugate displays potent antitumor activity in gastric cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Shen, Z.; Yu, N.; Xu, J.; Yuan, X.; Ni, L.; Long, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhang, Y. Efficacy and safety of liposome-paclitaxel/liposome-paclitaxel combined with S-1 in 17 advanced gastric cancer patients with poor performance status. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, S.; De La Fouchardiere, C.; Kim, S.; Cohen, R.; Bachet, J.; Tournigand, C.; Ferraz, J.; Lefevre, M.; Colin, D.; Svrcek, M. Oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil and nab-paclitaxel as perioperative regimen in patients with resectable gastric adenocarcinoma: A GERCOR phase II study (FOXAGAST). Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 107, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.M.; Wang, F.; Jin, Y.; Yuan, S.Q.; Ren, C.; Luo, H.Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Qiu, M.Z.; Wang, Z.X.; Zeng, Z.L. Phase II clinical trial of S-1 plus nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel in untreated patients with metastatic gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 3575–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Type | Loaded Drug | Mechanism of Action | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLA-Bi-ZnO2@Lipo | Lipid-based nanoparticles | Clarithromycin | Antibacterial; alleviate mucosal inflammation and maintain the balance of intestinal flora | [67] |
| Liposomal drug delivery system | Lipid-based nanoparticles | Furazolidone + N-Acetyl Cysteine | Eradicate H. pylori and overcome antibiotic resistance | [68] |
| GE33 Peptide Hydrogel | Polymeric nanoparticles | GE33 Peptide | Improve drug utilization and overcome antibiotic resistance | [69] |
| AASP-CMCS-NAC-C16N-DCA Hydrogel | Polymeric nanoparticles | C16N-DCA | Eradicate H. pylori, protect gastric tissue, and promote wound healing | [36] |
| MOF-based Microrockets | Metallic nanoparticles | Rhodamine 6G | Targeted mucosal drug delivery and continuous drug release | [70] |
| TA-FeHMSN@Amox | Metallic nanoparticles | Amox | Eliminate H. pylori, reduce the dosage of antibiotics, and protect the intestinal flora | [71] |
| Name | Type | Loaded Drug | Mechanism of Action | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLI | Lipid-based nanoparticles | Liproxstatin-1 + Icy7 | Inhibit tumor growth and suppress neutrophil ferroptosis | [83] |
| As@LNPs | Lipid-based nanoparticles | Bmi-1 siRNA | Inhibit tumor growth | [84] |
| TCP-L | Lipid-based nanoparticles | DOX | Inhibit tumors and enhance drug release | [85] |
| Gingerol-HA-NPs | Polymeric nanoparticles | Gingerol | Kill gastric cancer cells | [86] |
| CPP10-PEG@CUR@FT | Metallic nanoparticles | Curcumin | Tumor-targeted, with low side effects and high biosafety | [87] |
| Au NPs@CS-Pec | Metallic nanoparticles | Eliminate free radicals and inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells | [88] | |
| PSC Nanoparticles | Biomembrane-coated nanoparticles | Cisplatin + single-atom nanozymes (SAZ) | High lymphatic tropism and dual-targeting capability. | [89] |
| Drug/Carrier | Experimental Phase | Treatment Plan | ORR | MOS (Month) | Adverse Reactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liposomal paclitaxel | Liposomal Paclitaxel + Cisplatin | 51.43% | 15.3 | Hematologic toxicity, leukopenia (Grade III–IV), gastrointestinal reactions, alopecia (mostly Grade I–II) | |
| Albumin-bound Paclitaxel | Phase II (2018) | Albumin-bound Paclitaxel + FOLFOX | Non-febrile neutropenia (20.4%), nausea (8.2%), diarrhea (8.2%), neuropathy (6.1%) | ||
| Albumin-bound Paclitaxel | Phase II (2018) | Albumin-bound Paclitaxel + S-1 | 58.9% | 14.6 | Neutropenia (12.3%), anemia (5.5%), diarrhea (6.8%), vomiting (2.7%), peripheral neuropathy (1.4%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, M.; Tian, S.; Wang, J.; Gan, S.; Zhang, Z.; Weng, L. Application of Nanodrug Delivery Systems in Enhancing Treatment of Gastritis and Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Evaluation of Targeted Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060683
Xu M, Tian S, Wang J, Gan S, Zhang Z, Weng L. Application of Nanodrug Delivery Systems in Enhancing Treatment of Gastritis and Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Evaluation of Targeted Therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(6):683. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060683
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Miaomiao, Shujie Tian, Jing Wang, Shuqing Gan, Ziting Zhang, and Lixing Weng. 2025. "Application of Nanodrug Delivery Systems in Enhancing Treatment of Gastritis and Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Evaluation of Targeted Therapy" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 6: 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060683
APA StyleXu, M., Tian, S., Wang, J., Gan, S., Zhang, Z., & Weng, L. (2025). Application of Nanodrug Delivery Systems in Enhancing Treatment of Gastritis and Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Evaluation of Targeted Therapy. Pharmaceutics, 17(6), 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060683






