Novel Drug–Drug Cocrystalline Forms of Carbamazepine with Sulfacetamide: Preparation, Characterization, and In Vitro/In Vivo Performance Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
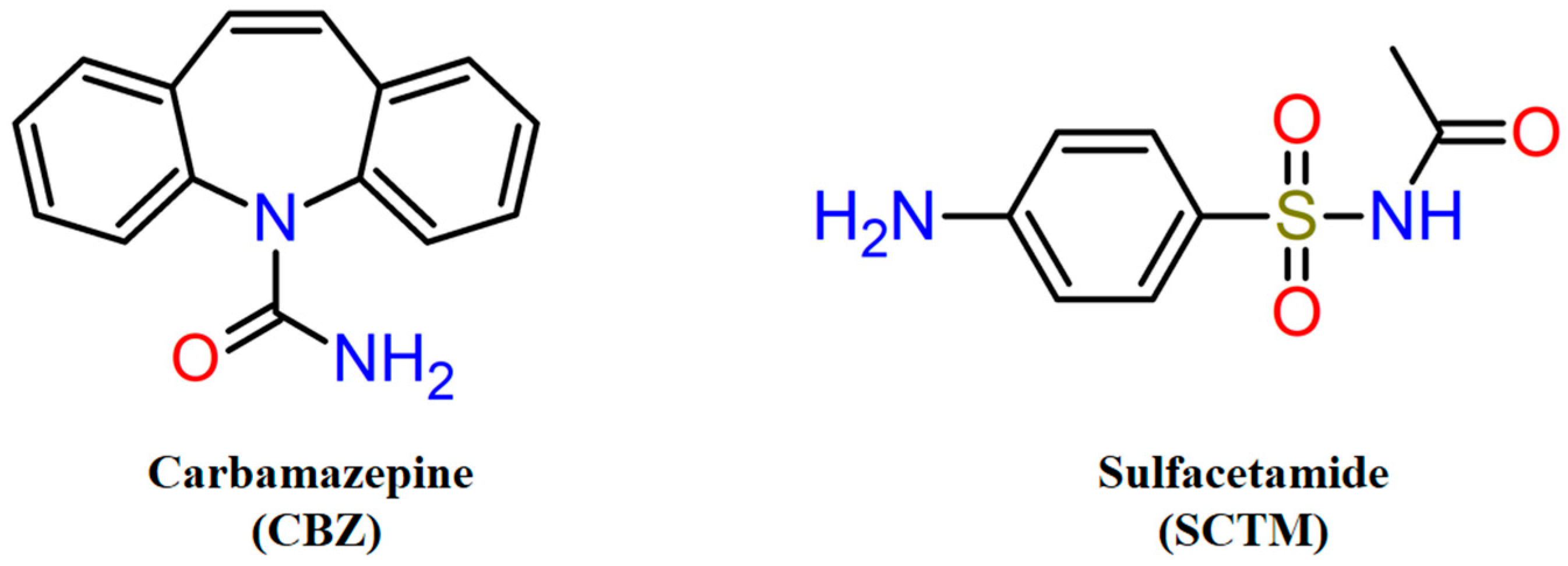
2.1. Materials
2.2. Screening and Preparation of Solid Phases
2.2.1. Grinding Method
2.2.2. Solution Crystallization
2.2.3. Slurry
2.3. Powder X-Ray Diffraction (PXRD)
2.4. Single-Crystal X-Ray Diffraction (SCXRD)
2.5. Thermal Analysis
2.5.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.5.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.6. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.7. Determination of the Binary and Ternary Phase Diagrams
2.8. In Vitro Studies
2.8.1. Solubility Experiments
2.8.2. Powder Dissolution Under Non-Sink Conditions
2.8.3. Diffusion Tests
2.9. In Vivo Pharmacokinetics
3. Results and Discussion
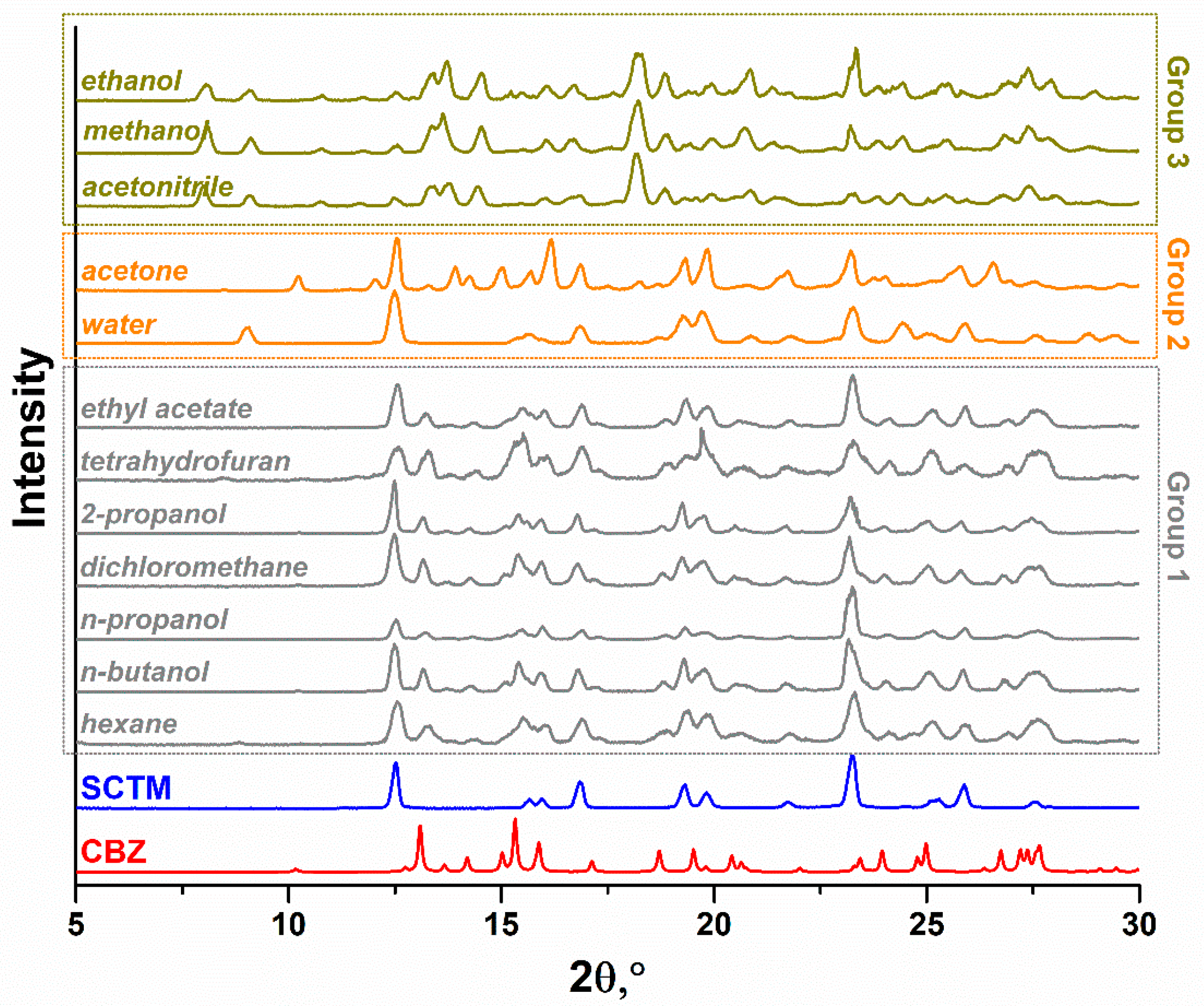
3.1. Effect of Solvents on Cocrystallization of CBZ and SCTM by Grinding
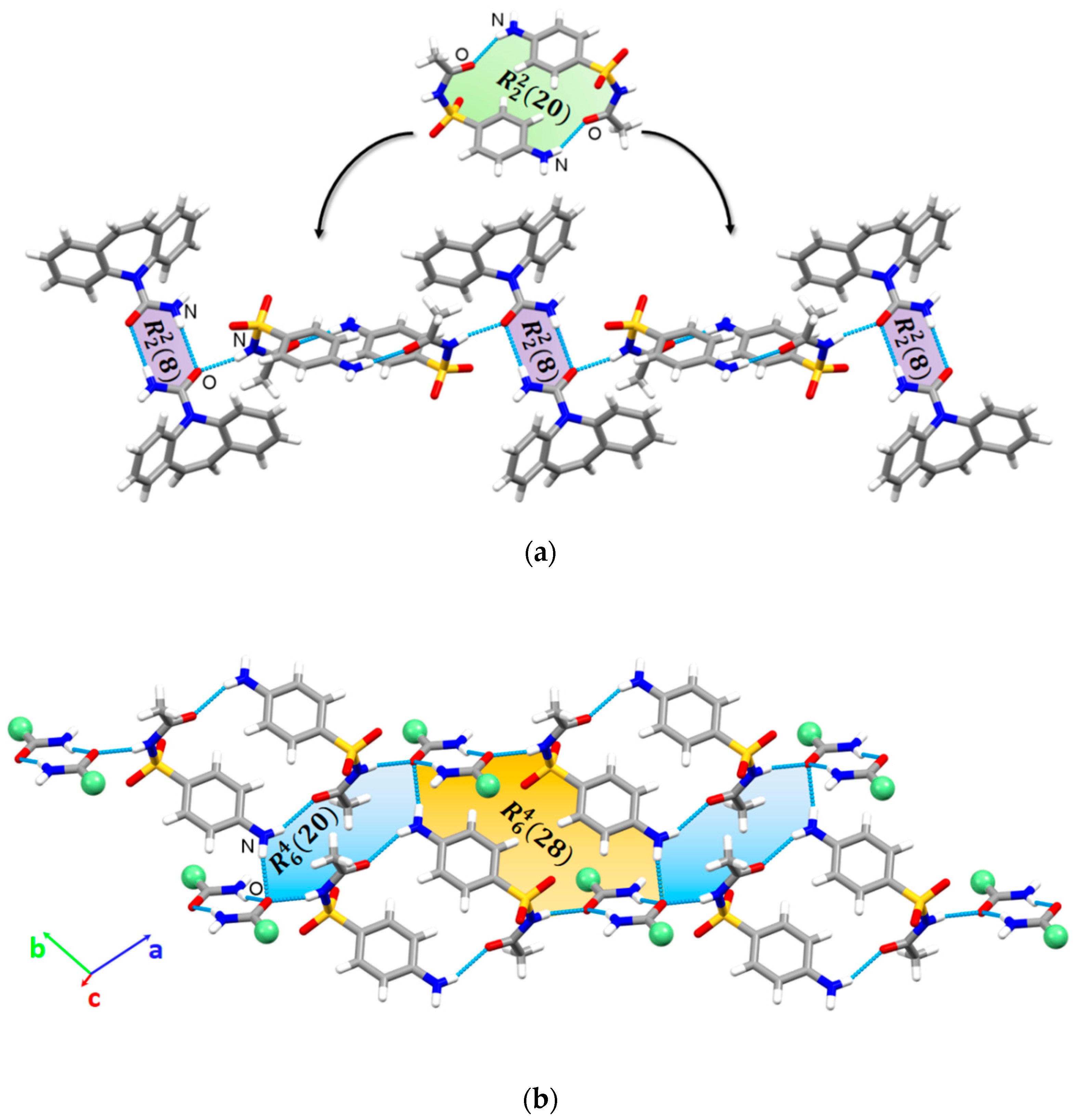
3.2. Crystal Structure Analysis
3.3. Thermal Analysis
3.4. Design of the Cocrystal Hydrate Preparation Approach
3.5. Effect of pH on Stability and Solubility of Cocrystal Hydrate
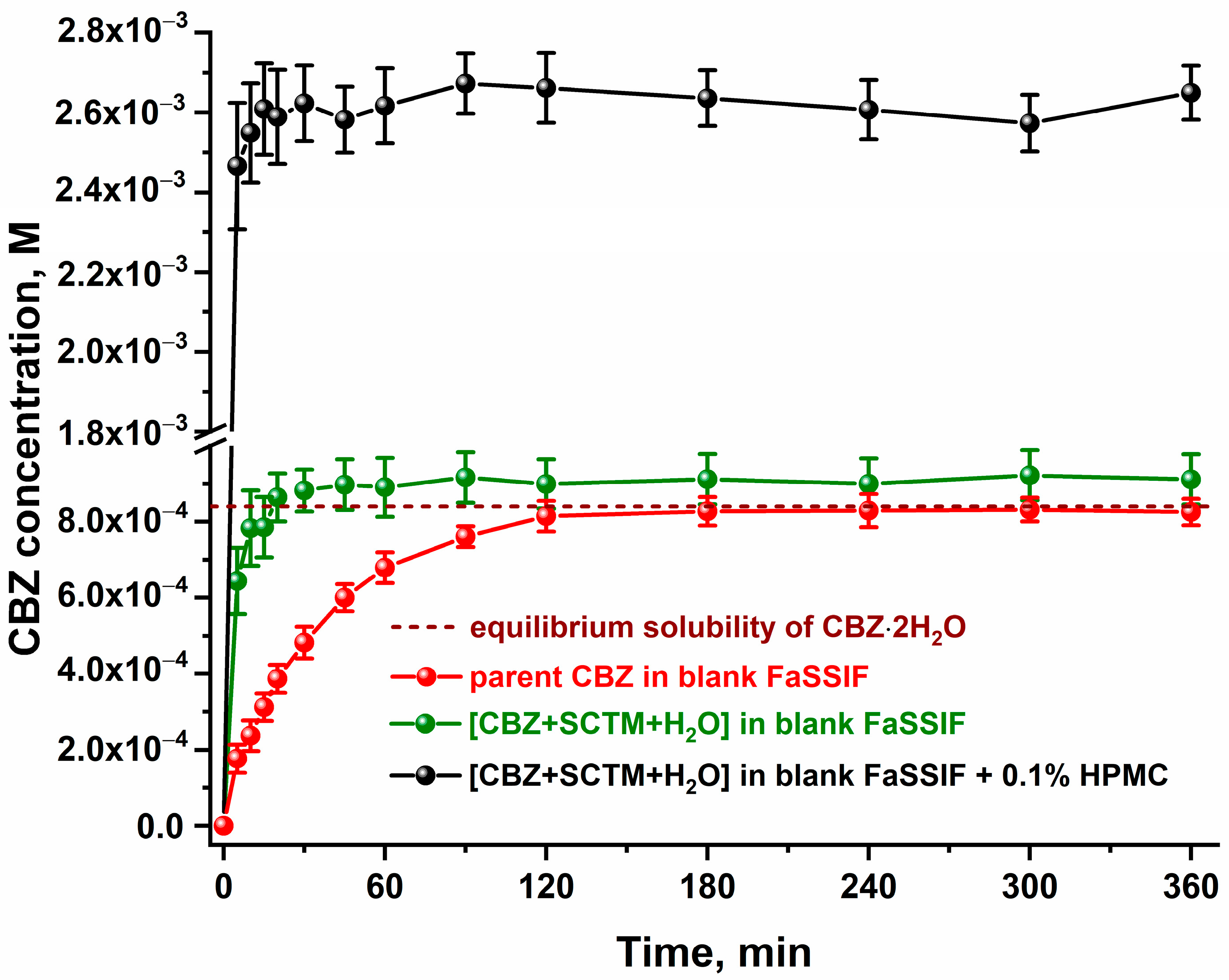
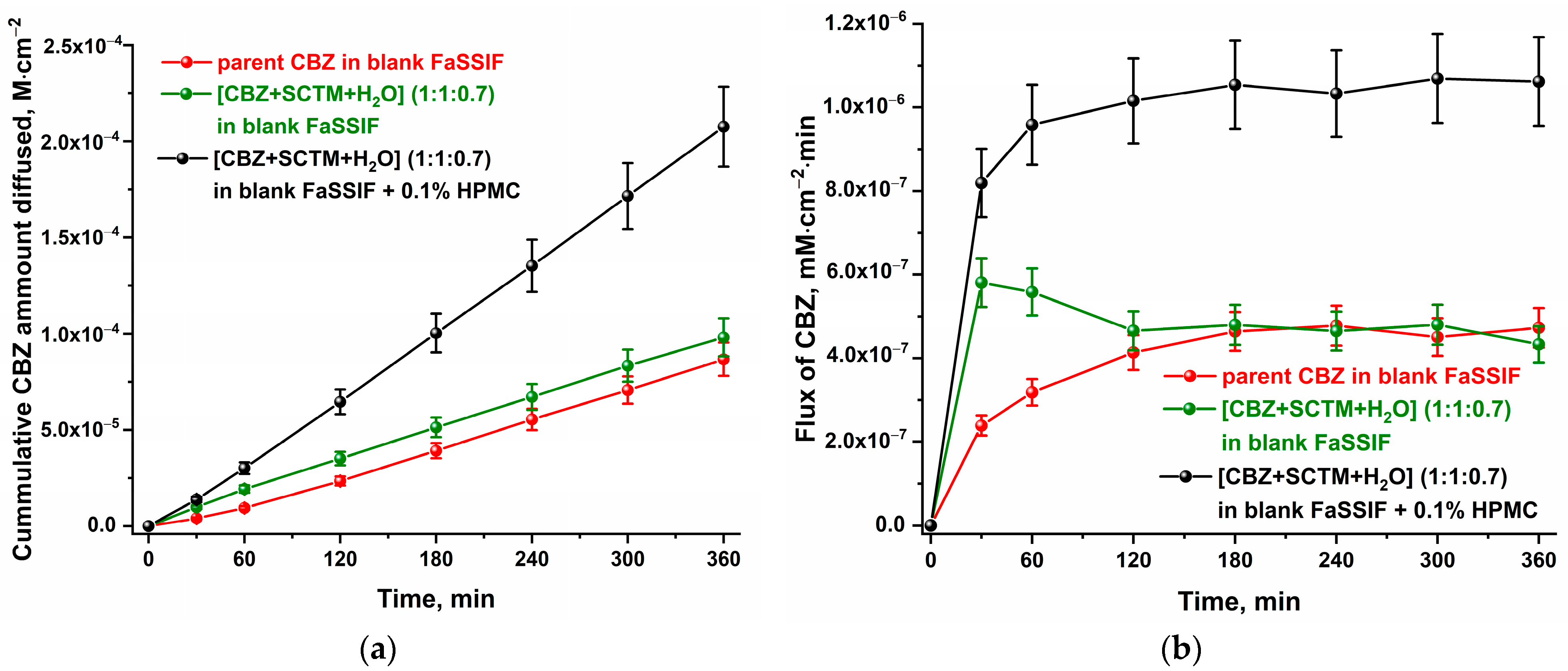
3.6. In Vitro Dissolution and Diffusion Tests
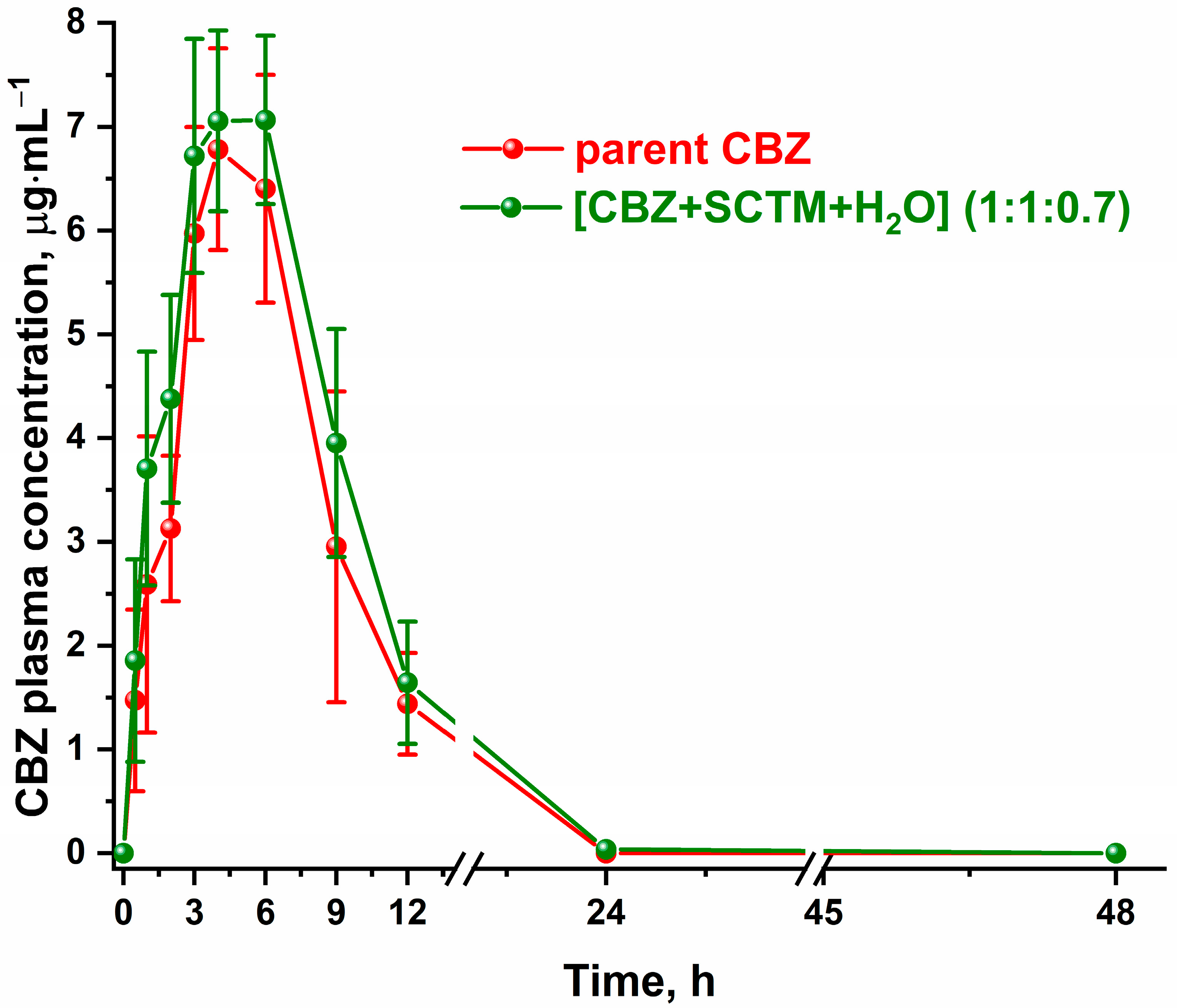
3.7. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolla, G.; Sarma, B.; Nangia, A.K. Crystal Engineering of Pharmaceutical Cocrystals in the Discovery and Development of Improved Drugs. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 11514–11603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozd, K.V.; Manin, A.N.; Boycov, D.E.; Perlovich, G.L. Simultaneous Improvement of Dissolution Behavior and Oral Bioavailability of Antifungal Miconazole via Cocrystal and Salt Formation. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.-L.; Wu, C.; Li, J.-H.; Liu, L.-C.; He, X.; Lu, T.-B.; Chen, J.-M. Modulating the solubility and pharmacokinetic properties of 5-fluorouracil via cocrystallization. CrystEngComm 2020, 22, 3670–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Tan, F.; Yao, J.; Cui, Y.; Feng, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gong, W.; Yang, M.; et al. Preparation, characterization, and pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban cocrystals with enhanced in vitro and in vivo properties in beagle dogs. Int. J. Pharm. X 2022, 4, 100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, C.; Antoniciello, F.; Roncarati, D.; Scarlato, V.; Grepioni, F.; Braga, D. Levofloxacin and Ciprofloxacin Co-Crystals with Flavonoids: Solid-State Investigation for a Multitarget Strategy against Helicobacter pylori. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šilić, D.; Cetina-Čižmek, B.; Antonijevic, M.; Douroumis, D. One-Step Synthesis of a Drug–Drug Cocrystal Hydrate Using Hot Melt Extrusion. Cryst. Growth Des. 2024, 24, 8044–8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemchuk, O.; d’Agostino, S.; Fiore, C.; Sambri, V.; Zannoli, S.; Grepioni, F.; Braga, D. Natural Antimicrobials Meet a Synthetic Antibiotic: Carvacrol/Thymol and Ciprofloxacin Cocrystals as a Promising Solid-State Route to Activity Enhancement. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 20, 6796–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A. API co-crystals—Trends in CMC-related aspects of pharmaceutical development beyond solubility. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devogelaer, J.-J.; Brugman, S.J.T.; Meekes, H.; Tinnemans, P.; Vlieg, E.; de Gelder, R. Cocrystal design by network-based link prediction. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 6875–6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Mondal, P.K.; Wu, Y.; Gong, W.; Mirmehrabi, M.; Rohani, S. Virtual Multicomponent Crystal Screening: Hydrogen Bonding Revisited. Cryst. Growth Des. 2021, 21, 5862–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, L.; Yuan, P.; An, Q.; Su, B.; Yu, M.; Chen, T.; Hu, K.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; et al. Cocrystal virtual screening based on the XGBoost machine learning model. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, H. Efficient cocrystal coformer screening based on a Machine learning Strategy: A case study for the preparation of imatinib cocrystal with enhanced physicochemical properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2024, 196, 114201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Ding, Y.; Su, J.; Li, J.; Ji, Y. Unlocking the Potential of Machine Learning in Co-crystal Prediction by a Novel Approach Integrating Molecular Thermodynamics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202502410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemli, B.; Pál, S.; Salem, A.; Széchenyi, A. Prioritizing Computational Cocrystal Prediction Methods for Experimental Researchers: A Review to Find Efficient, Cost-Effective, and User-Friendly Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Baptista, B.; Lopes, J.A.; Sarraguça, M.C. Pharmaceutical cocrystallization techniques. Advances and challenges. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 547, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemchuk, O.; Spoletti, E.; Braga, D.; Grepioni, F. Solvent Effect on the Preparation of Ionic Cocrystals of dl-Amino Acids with Lithium Chloride: Conglomerate versus Racemate Formation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2021, 21, 3438–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Quan, S.; Fu, X.; Meng, S.; Jiang, L.; Fan, X. Study on the effect of solvent on cocrystallization of CL-20 and HMX through theoretical calculations and experiments. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 21255–21263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surov, A.O.; Churakov, A.V.; Perlovich, G.L. Three Polymorphic Forms of Ciprofloxacin Maleate: Formation Pathways, Crystal Structures, Calculations, and Thermodynamic Stability Aspects. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 6556–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozd, K.V.; Manin, A.N.; Churakov, A.V.; Perlovich, G.L. Drug-drug cocrystals of antituberculous 4-aminosalicylic acid: Screening, crystal structures, thermochemical and solubility studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 99, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasankar, A.; Reddy, L.S.; Bethune, S.J.; Rodríguez-Hornedo, N. Role of Cocrystal and Solution Chemistry on the Formation and Stability of Cocrystals with Different Stoichiometry. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyssens, T.; Springuel, G.; Montis, R.; Candoni, N.; Veesler, S. Importance of Solvent Selection for Stoichiometrically Diverse Cocrystal Systems: Caffeine/Maleic Acid 1:1 and 2:1 Cocrystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 1520–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, D.; Svärd, M.; Rasmuson, Å.C. Investigation of solid–liquid phase diagrams of the sulfamethazine–salicylic acid co-crystal. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 2863–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surov, A.O.; Voronin, A.P.; Drozd, K.V.; Volkova, T.V.; Vasilev, N.; Batov, D.; Churakov, A.V.; Perlovich, G.L. Extending the Range of Nitrofurantoin Solid Forms: Effect of Molecular and Crystal Structure on Formation Thermodynamics and Physicochemical Properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 2022, 22, 2569–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, H.; Haynes, D.A.; le Roex, T. Solvate formation in lutidinium pamoate salts: A systematic study. CrystEngComm 2011, 13, 2227–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sládková, V.; Skalická, T.; Skořepová, E.; Čejka, J.; Eigner, V.; Kratochvíl, B. Systematic solvate screening of trospium chloride: Discovering hydrates of a long-established pharmaceutical. CrystEngComm 2015, 17, 4712–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, J.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, H. Piroxicam–clonixin drug–drug cocrystal solvates with enhanced hydration stability. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 4145–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozd, K.V.; Manin, A.N.; Churakov, A.V.; Perlovich, G.L. Novel drug–drug cocrystals of carbamazepine with para-aminosalicylic acid: Screening, crystal structures and comparative study of carbamazepine cocrystal formation thermodynamics. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 4273–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodowska, K.; Parczewski, A. Organic solvents in the pharmaceutical industry. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2010, 67, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Guideline, I.C.H.H.T. Impurities: Guideline for residual solvents Q3C (R5). Curr. Step 2005, 4, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Healy, A.M.; Worku, Z.A.; Kumar, D.; Madi, A.M. Pharmaceutical solvates, hydrates and amorphous forms: A special emphasis on cocrystals. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 117, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunze, A.; Amann, B.L.; Grunze, H. Efficacy of Carbamazepine and Its Derivatives in the Treatment of Bipolar Disorder. Medicina 2021, 57, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.A. Successful treatment of painful traumatic mononeuropathy with carbamazepine: Insights into a possible molecular pain mechanism. J. Neurol. Sci. 1997, 152, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grześk, G.; Stolarek, W.; Kasprzak, M.; Grześk, E.; Rogowicz, D.; Wiciński, M.; Krzyżanowski, M. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Carbamazepine: A 20-Year Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.A.; Cristofoletti, R.; Abrahamsson, B.; Groot, D.W.; Parr, A.; Polli, J.E.; Mehta, M.; Shah, V.P.; Tomakazu, T.; Dressman, J.B.; et al. Biowaiver Monograph for Immediate-Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms: Carbamazepine. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 1935–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.M.; Dressman, J.B. The Developability Classification System: Application of Biopharmaceutics Concepts to Formulation Development. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 4940–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, M.; Akogyeram, C.O.; Scott, K.R.; Potti, G.K.; Gallelli, J.F.; Habib, M.J. Development of carbamazepine:phospholipid solid dispersion formulations. J. Control. Release 1993, 23, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, M.; Xiong, L.; Feng, W.; Williams, R.O. Bioavailability Improvement of Carbamazepine via Oral Administration of Modified-Release Amorphous Solid Dispersions in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medarević, D.P.; Kyriakos, K.; Miodrag, M.; Jelena, D.; Zorica, D.; Ibrić, S. Dissolution rate enhancement and physicochemical characterization of carbamazepine-poloxamer solid dispersions. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2016, 21, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nokhodchi, A.; Al-Hamidi, H.; Antonijevic, M.D.; Owusu-Ware, S.; Kaialy, W. Dissolution and solid state behaviours of carbamazepine-gluconolactone solid dispersion powders: The potential use of gluconolactone as dissolution enhancer. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 100, 452–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffens, K.E.; Wagner, K.G. Dissolution enhancement of carbamazepine using twin-screw melt granulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 148, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S.; Nelson, K.F. Improvement of oral bioavailability of carbamazepine by inclusion in 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 1992, 85, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.S.; MacRae, R.J.; Snowden, M.J. Effect of SBE7-β-cyclodextrin complexation on carbamazepine release from sustained release beads. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 60, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolten, D.; Türk, M. Micronisation of carbamazepine through rapid expansion of supercritical solution (RESS). J. Supercrit. Fluids 2012, 62, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, S.; Bansal, M.; H, V.; Gupta, R.K. Formulation and Evaluation of Nanosuspension Containing Carbamazepine. J. Biomed. Pharm. Res. 2024, 13, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Löbmann, K.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T. Transformations between Co-Amorphous and Co-Crystal Systems and Their Influence on the Formation and Physical Stability of Co-Amorphous Systems. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasim, M.; Mannan, A.; Asad, M.H.H.B.; Amirzada, M.I.; Shafique, M.; Hussain, I. Fabrication of Carbamazepine Cocrystals: Characterization, In Vitro and Comparative In Vivo Evaluation. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6685806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayanfar, A.; Asadpour-Zeynali, K.; Jouyban, A. Solubility and dissolution rate of a carbamazepine–cinnamic acid cocrystal. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 187, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boycov, D.E.; Drozd, K.V.; Manin, A.N.; Churakov, A.V.; Vlasov, M.Y.; Sokolova, I.V.; Perlovich, G.L. Two novel drug-nutraceutical cocrystal hydrates of carbamazepine: The influence of isomerism in trihydroxybenzoic acids on the in vitro/in vivo properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 420, 126784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.V.; Cruz-Cabeza, A.J.; Steed, J.W. What Has Carbamazepine Taught Crystal Engineers? Cryst. Growth Des. 2024, 24, 7342–7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thipparaboina, R.; Kumar, D.; Chavan, R.B.; Shastri, N.R. Multidrug co-crystals: Towards the development of effective therapeutic hybrids. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaï, B.; Fournier, B.; Dahaoui, S.; Gillet, J.-M.; Ghermani, N.-E. Crystal and Electron Properties of Carbamazepine–Aspirin Co-crystal. Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 19, 1308–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, M.; Buckton, G.; Rawlinson-Malone, C.; Williams, A.C.; Spillman, M.J.; Shankland, N.; Shankland, K. A carbamazepine-indomethacin (1:1) cocrystal produced by milling. CrystEngComm 2011, 13, 6327–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devogelaer, J.-J.; Meekes, H.; Tinnemans, P.; Vlieg, E.; de Gelder, R. Co-crystal Prediction by Artificial Neural Networks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 21711–21718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Cai, P.; Luo, M.; Guo, M.; Cai, T. Melt Crystallization of Celecoxib-Carbamazepine Cocrystals with the Synchronized Release of Drugs. Pharm. Res. 2023, 40, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delori, A.; Galek, P.T.A.; Pidcock, E.; Patni, M.; Jones, W. Knowledge-based hydrogen bond prediction and the synthesis of salts and cocrystals of the anti-malarial drug pyrimethamine with various drug and GRAS molecules. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 2916–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljohani, M.; Pallipurath, A.R.; McArdle, P.; Erxleben, A. A Comprehensive Cocrystal Screening Study of Chlorothiazide. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 5223–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makadia, J.; Seaton, C.C.; Li, M. Apigenin Cocrystals: From Computational Prescreening to Physicochemical Property Characterization. Cryst. Growth Des. 2023, 23, 3480–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Chan, H.C.S.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Lv, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Z. Phase solubility investigation and theoretical calculations on drug-drug cocrystals of carbamazepine with Emodin, Paeonol. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 329, 115604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsughayer, A.; Elassar, A.-Z.A.; Mustafa, S.; Al Sagheer, F. Synthesis, Structure Analysis and Antibacterial Activity of New Potent Sulfonamide Derivatives. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 2, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, F.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Pinard, M.; Ghelardini, C.; Scozzafava, A.; McKenna, R.; Supuran, C.T. A class of sulfonamide carbonic anhydrase inhibitors with neuropathic pain modulating effects. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 1828–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romdhani, A.; Martínez, F.; Almanza, O.A.; Peña, M.A.; Jouyban, A.; Acree, W.E. Solubility of sulfacetamide in (ethanol + water) mixtures: Measurement, correlation, thermodynamics, preferential solvation and volumetric contribution at saturation. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeliński, T.; Maciej, P.; Cysewski, P. Solubility advantage of sulfanilamide and sulfacetamide in natural deep eutectic systems: Experimental and theoretical investigations. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G. SADABS, Program for Scaling and Correction of Area Detector Data; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1997; Volume 33. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Crystallogr. 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. PLATON SQUEEZE: A tool for the calculation of the disordered solvent contribution to the calculated structure factors. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C 2015, 71, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, I.C.B.; Emmerling, F. Carbamazepine Dihydroxybenzoic Acid Cocrystals: Exploring Packing Interactions and Reaction Kinetics. Cryst. Growth Des. 2021, 21, 6961–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boycov, D.E.; Drozd, K.V.; Manin, A.N.; Churakov, A.V.; Perlovich, G.L. Rational Design of the Carbamazepine Ternary Cocrystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2024, 24, 4862–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Han, Y.; Xie, Y.-f.; Gong, N.-b.; Guo, F. Carbamazepine cocrystals with several aromatic carboxylic acids in different stoichiometries: Structures and solid state characterization. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1168, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajbongshi, T.; Sarmah, K.K.; Das, S.; Deka, P.; Saha, A.; Saha, B.K.; Puschmann, H.; Reddy, C.M.; Thakuria, R. Non-stoichiometric carbamazepine cocrystal hydrates of 3,4-/3,5-dihydroxybenzoic acids: Coformer–water exchange. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 3902–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surov, A.O.; Drozd, K.V.; Ramazanova, A.G.; Churakov, A.V.; Vologzhanina, A.V.; Kulikova, E.S.; Perlovich, G.L. Polymorphism of Carbamazepine Pharmaceutical Cocrystal: Structural Analysis and Solubility Performance. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskins, M.M.; Zaworotko, M.J. Screening and Preparation of Cocrystals: A Comparative Study of Mechanochemistry vs Slurry Methods. Cryst. Growth Des. 2021, 21, 4141–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischman, S.G.; Kuduva, S.S.; McMahon, J.A.; Moulton, B.; Bailey Walsh, R.D.; Rodríguez-Hornedo, N.; Zaworotko, M.J. Crystal Engineering of the Composition of Pharmaceutical Phases: Multiple-Component Crystalline Solids Involving Carbamazepine. Cryst. Growth Des. 2003, 3, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalpiaz, A.; Ferretti, V.; Bertolasi, V.; Pavan, B.; Monari, A.; Pastore, M. From Physical Mixtures to Co-Crystals: How the Coformers Can Modify Solubility and Biological Activity of Carbamazepine. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childs, S.L.; Rodríguez-Hornedo, N.; Reddy, L.S.; Jayasankar, A.; Maheshwari, C.; McCausland, L.; Shipplett, R.; Stahly, B.C. Screening strategies based on solubility and solution composition generate pharmaceutically acceptable cocrystals of carbamazepine. CrystEngComm 2008, 10, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.-Y.; Dai, X.-L.; Lu, T.-B.; Chen, J.-M. Cocrystal formation by anti-solvent slurry. CrystEngComm 2023, 25, 5882–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.A.; Peterson, M.L.; Klein, D. Continuously Substituted Solid Solutions of Organic Co-Crystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2008, 8, 4487–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manin, A.N.; Voronin, A.P.; Drozd, K.V.; Manin, N.G.; Bauer-Brandl, A.; Perlovich, G.L. Cocrystal screening of hydroxybenzamides with benzoic acid derivatives: A comparative study of thermal and solution-based methods. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 65, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korde, S.; Pagire, S.; Pan, H.; Seaton, C.; Kelly, A.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Coates, P.; Paradkar, A. Continuous Manufacturing of Cocrystals Using Solid State Shear Milling Technology. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 2297–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fateixa, S.; Nogueira, H.I.S.; Trindade, T. Carbamazepine polymorphism: A re-visitation using Raman imaging. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 617, 121632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia-Sá, L.; Soares, C.; Freitas, O.M.; Moreira, M.M.; Nouws, H.P.; Correia, M.; Paíga, P.; Rodrigues, A.J.; Oliveira, C.M.; Figueiredo, S.A.; et al. A Three-Dimensional Electrochemical Process for the Removal of Carbamazepine. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surov, A.O.; Ramazanova, A.G.; Voronin, A.P.; Drozd, K.V.; Churakov, A.V.; Perlovich, G.L. Virtual Screening, Structural Analysis, and Formation Thermodynamics of Carbamazepine Cocrystals. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MartÍnez, F.; GÓmez, A. Estimation of the Solubility of Sulfonamides in Aqueous Media from Partition Coefficients and Entropies of Fusion. Phys. Chem. Liq. 2002, 40, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, D.J.; Rodríguez-Hornedo, N. Solubility Advantage of Pharmaceutical Cocrystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 2252–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasani, M.S.; Kale, D.P.; Singh, I.P.; Bansal, A.K. Influence of Drug–Polymer Interactions on Dissolution of Thermodynamically Highly Unstable Cocrystal. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| [CBZ+SCTM+H2O] (1:1:0.7) a | [CBZ+SCTM+MeOH] (1:1:0.352) | |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C15H12N2O·C8H10N2O3S | C15H12N2O·C8H10N2O3S·0.352(CH4O) |
| Mr | 450.50 | 461.73 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P-1 | Triclinic, P-1 |
| Temperature, K | 120 | 100 |
| a, Å | 10.0803 (5) | 10.0837 (4) |
| b, Å | 10.2836 (6) | 10.1781 (4) |
| c, Å | 11.8893 (7) | 11.7782 (5) |
| α, ° | 106.1941 (19) | 106.2160 (13) |
| β, ° | 99.903 (2) | 99.5884 (14) |
| γ, ° | 95.703 (2) | 95.9646 (14) |
| V (Å3) | 1151.70 (11) | 1129.98 (8) |
| Z | 2 | 2 |
| Dcalc, g·cm−3 | 1.299 | 1.357 |
| μ, mm−1 | 0.18 | 0.18 |
| Reflection collected | 18,645 | 19,269 |
| Independent reflections | 5011 | 6905 |
| Reflections with I > 2(I) | 4357 | 5620 |
| Rint | 0.032 | 0.031 |
| R1[F2 > 2σ(F2)], wR2(F2), S | 0.0544, 0.1211, 1.097 | 0.0432, 0.1108, 1.042 |
| Parameters | 377 | 431 |
| Largest diff. peak/hole, e·Å−3 | 0.33, −0.47 | 0.38, −0.53 |
| CCDC | 2442631 | 2442630 |
| pHinitial | pHeq | Solids in Equilibrium with the Solution | Keu | SCC, M |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.6 | 3.6 | [CBZ+SCTM+H2O], CBZ·2H2O | 26.4 ± 0.5 | (9.32 ± 0.15)·10−3 |
| 6.5 | 4.5 | CBZ·2H2O | - | - |
| 6.5 | 4.5 | CBZ·2H2O, SCTM | - | - |
| 6.5 | 4.4 | CBZ·2H2O, SCTM | - | - |
| CBZ * | [CBZ+SCTM+H2O] (1:1:0.7) | |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax, μg·mL−1 | 7.7 ± 1.1 | 7.8 ± 0.5 |
| tmax, h | 5.3 ± 1.2 | 4.7 ± 1.2 |
| AUC0–∞, μg·h·mL−1 | 58 ± 9 | 68 ± 11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boycov, D.E.; Drozd, K.V.; Manin, A.N.; Churakov, A.V.; Vlasov, M.Y.; Kachalkina, I.V.; Perlovich, G.L. Novel Drug–Drug Cocrystalline Forms of Carbamazepine with Sulfacetamide: Preparation, Characterization, and In Vitro/In Vivo Performance Evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050678
Boycov DE, Drozd KV, Manin AN, Churakov AV, Vlasov MY, Kachalkina IV, Perlovich GL. Novel Drug–Drug Cocrystalline Forms of Carbamazepine with Sulfacetamide: Preparation, Characterization, and In Vitro/In Vivo Performance Evaluation. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(5):678. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050678
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoycov, Denis E., Ksenia V. Drozd, Alex N. Manin, Andrei V. Churakov, Mikhail Yu. Vlasov, Irina V. Kachalkina, and German L. Perlovich. 2025. "Novel Drug–Drug Cocrystalline Forms of Carbamazepine with Sulfacetamide: Preparation, Characterization, and In Vitro/In Vivo Performance Evaluation" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 5: 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050678
APA StyleBoycov, D. E., Drozd, K. V., Manin, A. N., Churakov, A. V., Vlasov, M. Y., Kachalkina, I. V., & Perlovich, G. L. (2025). Novel Drug–Drug Cocrystalline Forms of Carbamazepine with Sulfacetamide: Preparation, Characterization, and In Vitro/In Vivo Performance Evaluation. Pharmaceutics, 17(5), 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050678









