Engineering a Dual-Function Starch–Cellulose Composite for Colon-Targeted Probiotic Delivery and Synergistic Gut Microbiota Regulation in Type 2 Diabetes Therapeutics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Construction and Characterization of Pueraria Lobata-Based Carrier for CTDS
2.3. Construction and Characterization of Pueraria Lobata-Based CTDS for Probiotics (CDTS@probiotics)
2.4. Resistance to Simulated Gastric Fluid and Probiotics Release in Simulated Intestinal Fluid
2.5. In Vivo Probiotics Distribution and Colonization
2.6. Effects of Probiotic-Loading CTDS on T2DM Model Rats
2.7. Storage and Heat Stability
2.8. Tablet Preparation and Probiotic Release Profile
2.9. Experimental Animal Ethics
2.10. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microwave–Hydrothermal and Cooling Processing Caused Physical Property Changes in Pueraria Lobata Powder Through Starch Gelatinization and Retrogradation
3.2. Microwave–Hydrothermal- and Cooling-Processed Pueraria Lobata Powder Can Serve as the Carrier Material of an Oral Probiotics Delivery System
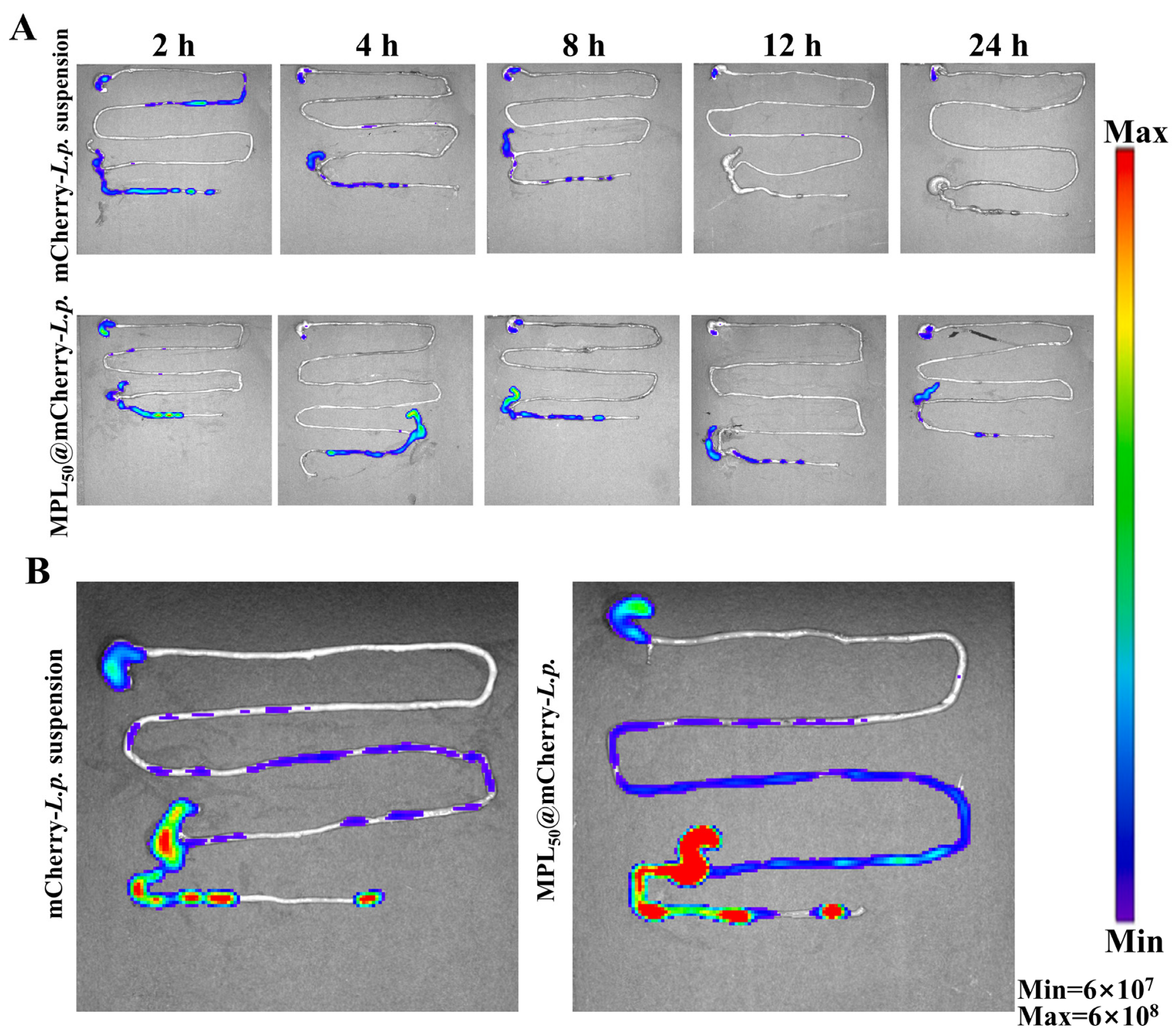
3.3. Oral Probiotic Delivery System Could Enhance Colonization of L.p. in GI Tract
3.4. Colon-Targeting Probiotic Delivery System Could Improve Oral Glucose Tolerance and Restore Dyslipidemia in T2DM Model Rats
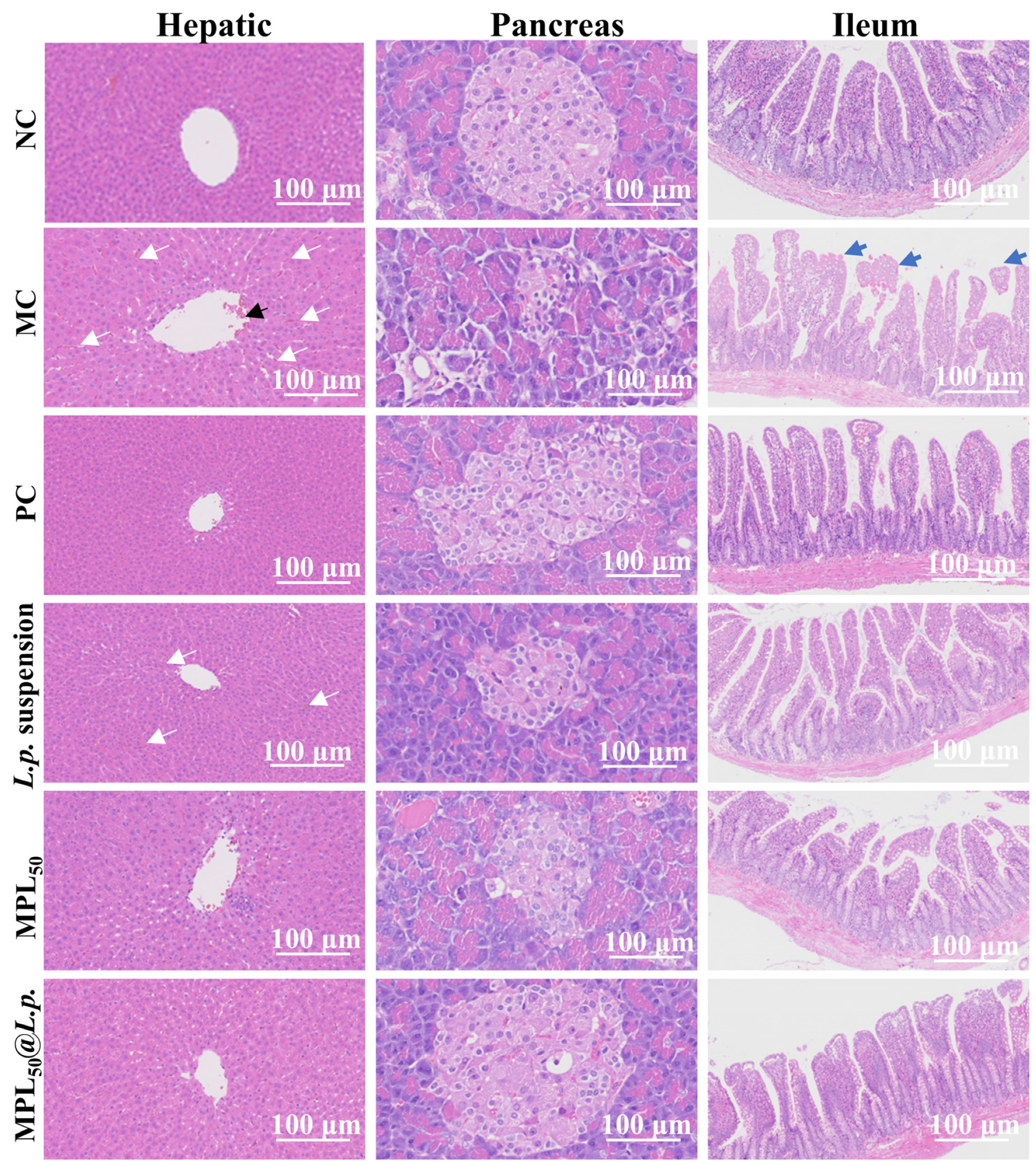
3.5. Colon-Targeting Probiotic Delivery System Restored Histological Abnormality of Liver, Pancreas, and Ileum in T2DM Model Rats
3.6. Colon-Targeting Probiotic Delivery System Promoted Proliferation of Probiotics and Facilitated Production of SCFAs
3.7. MPL50@L.p. Powder Had Comparable Storage and Thermal Stabilities with Lyophilized L.p. Powder and Could Easily Be Tableted
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CTDS | Colon-targeting delivery system |
| FBG | Fasting blood glucose |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LEfSe | Linear discriminant analysis effect size |
| MPLs | Microwave Pueraria lobata samples |
| OGTT | Oral glucose tolerance test |
| SCFA | Short-chain fatty acid |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| SGF | Simulated gastric fluid |
| SIF | Simulated intestinal fluid |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TG | Triglyceride |
References
- Lee, S.H.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, C.S. Insulin resistance: From mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Diabetes Metab. J. 2022, 46, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdinand, K.C.; Izzo, J.L.; Lee, J.; Meng, L.; George, J.; Salsali, A.; Seman, L. Antihyperglycemic and blood pressure effects of empagliflozin in black patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Circulation 2019, 139, 2098–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portincasa, P.; Bonfrate, L.; Vacca, M.; De Angelis, M.; Farella, I.; Lanza, E.; Khalil, M.; Wang, D.Q.H.; Sperandio, M.; Di Ciaula, A. Gut microbiota and short chain fatty acids: Implications in glucose homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Ning, J.; Bao, X.-q.; Shang, M.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, D. Fecal microbiota transplantation protects rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease mice via suppressing inflammation mediated by the lipopolysaccharide-TLR4 signaling pathway through the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Microbiome 2021, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H.S.; McDonough, C.M.; Huang, G. Gut microbiome in neuroendocrine and neuroimmune interactions: The case of genistein. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 402, 115130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitetta, L.; Gorgani, N.N.; Vitetta, G.; Henson, J.D. Prebiotics progress shifts in the intestinal microbiome that benefits patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Neng, Q.; Li, Y.; Kang, Y.; Guo, L.; Huang, X.; Chen, M.; Yang, F.; Hong, J.; Zhou, S.; et al. Gastrointestinal autonomic neuropathy exacerbates gut microbiota dysbiosis in adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 804733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makki, K.; Deehan, E.C.; Walter, J.; Bäckhed, F. The impact of dietary fiber on gut microbiota in host health and disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.K.; Rossi, M.; Bajka, B.; Whelan, K. Dietary fibre in gastrointestinal health and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayib, M.; Larson, J.; Slavin, J. Dietary fibers reduce obesity-related disorders: Mechanisms of action. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2020, 23, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, R.G.O.F.; Banzato, L.R.; Galendi, J.S.C.; Mendes, A.L.; Bolfi, F.; Veroniki, A.A.; Thabane, L.; Nunes-Nogueira, V.d.S. Effectiveness of non-pharmacological strategies in the management of type 2 diabetes in primary care: A protocol for a systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e034481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, H.; Mao, W.; Qian, X.; Liu, Y. The oral delivery system of modified GLP-1 by probiotics for T2DM. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Yen, H.R.; Lu, W.L.; Ho, H.H.; Lin, W.Y.; Kuo, Y.W.; Huang, Y.Y.; Tsai, S.Y.; Lin, H.C. Adjuvant probiotics of Lactobacillus salivarius subsp. salicinius AP-32, L. johnsonii MH-68, and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis CP-9 attenuate glycemic levels and inflammatory cytokines in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 754401. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, L.; Wu, J.; Lam, Y.Y.; Kwan, H.Y.; Bian, Z.-X.; Wong, H.L.X. Gut-microbial metabolites, probiotics and their roles in type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, M.; Xiao, Z.; Ruan, G.; Wei, Y. Gut microbiota: A new target for T2DM prevention and treatment. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 958218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantzourani, I.; Chondrou, P.; Bontsidis, C.; Karolidou, K.; Terpou, A.; Alexopoulos, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E.; Galanis, A.; Plessas, S. Assessment of the probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria isolated from kefir grains: Evaluation of adhesion and antiproliferative properties in in vitro experimental systems. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, L.M.; Halal, S.L.M.E.; Dias, A.R.G.; Zavareze, E.d.R. Physical modification of starch by heat-moisture treatment and annealing and their applications: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 274, 118665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, K.; Song, H.; Guan, X. Exploring the remarkable effects of microwave treatment on starch modification: From structural evolution to changed physicochemical and digestive properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 343, 122412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Boye, J.I. Research advances on the formation mechanism of resistant starch type III: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 60, 276–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.a.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, K.; Cao, H.; Sun, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Z.; Guan, X. Different multi-scale structural features of oat resistant starch prepared by ultrasound combined enzymatic hydrolysis affect its digestive properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 96, 106419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Guan, Y.; Dong, H.; Yang, M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Naeem, A.; Zhu, W. Study on structural characteristics and physicochemical properties of starches extracted from three varieties of kudzu root (Pueraria lobata starch). J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 1048–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wei, P.; Jia, M.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shi, L. Research progress in modifications, bioactivities, and applications of medicine and food homologous plant starch. Foods 2024, 13, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Miao, M.; Sun, J.; Fang, H.; Liu, L.; Xu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Lai, Q.; Tang, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Structure and physicochemical properties of starches from six accessions of the genus Pueraria in China. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzadeh, M.; Keshavarz Lelekami, A.; Khedmat, L. Plant/algal polysaccharides extracted by microwave: A review on hypoglycemic, hypolipidemic, prebiotic, and immune-stimulatory effect. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 266, 118134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Sun, C.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, Y. A multihole nozzle controls recrystallization of high-moisture extruded maize starches: Effect of cooling die temperature. Food Res. Int. 2024, 184, 114267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Qin, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, B.; Wan, F.; Tang, M.; Pan, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. A pH-/Enzyme-Responsive Nanoparticle Selectively Targets Endosomal Toll-like Receptors to Potentiate Robust Cancer Vaccination. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 2978–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, G.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Hu, A.; Zheng, J. Structural and physicochemical properties of resistant starch under combined treatments of ultrasound, microwave, and enzyme. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 232, 123331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.-D.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-M.; Kim, D.-K. Puerarin inhibits inflammation and oxidative stress in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mice model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 124, 109847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Lu, Y.; Xie, J.; Fei, Y.; Zheng, G.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Lv, L.; Ling, Z.; Berglund, B.; et al. Probiotic gastrointestinal transit and colonization after oral administration: A long journey. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 609722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghurabi, H.; Tagami, T.; Ogawa, K.; Ozeki, T. Preparation, Characterization and in vitro evaluation of Eudragit S100-coated bile salt-containing liposomes for oral colonic delivery of budesonide. Polymers 2022, 14, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, K.; Wu, H.; Neish, A.S.; Champion, J.A. Alginate/chitosan microparticles for gastric passage and intestinal release of therapeutic protein nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2019, 295, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Hong, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, C. Structural features and digestibility of corn starch with different amylose content. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 692673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobosz, A.; Sikora, M.; Krystyjan, M.; Tomasik, P.; Lach, R.; Borczak, B.; Berski, W.; Lukasiewicz, M. Short- and long-term retrogradation of potato starches with varying amylose content. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 99, 2393–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zeng, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Du, F.; Chen, Y.; Shen, J.; et al. Starch from Pueraria lobata and the amylose fraction alleviates dextran sodium sulfate induced colitis in mice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 302, 120329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, D.J. Structure and growth of plant cell walls. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 25, 340–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, H.; Shad, M.A.; Saleem, S.; Khan, M.U.A.; Nishan, U.; Rasheed, T.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Characteristics of starch isolated from microwave heat treated lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) seed flour. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Li, J.; Song, R.; Zhou, B.; Li, B.; Liang, H. Carboxymethylpachymaran/alginate gel entrapping of natural pollen capsules for the encapsulation, protection and delivery of probiotics with enhanced viability. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Wang, W.; Xiang, Q.; Pan, C.; Qiu, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, D.; Ouyang, J.; Jia, R.; Shi, M.; et al. Engineered probiotic ameliorates ulcerative colitis by restoring gut microbiota and redox homeostasis. Cell Host Microbe 2024, 32, 1502–1518.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB14924.3–2010; Laboratory Animals—Nutrients for Formula Feeds. National Standards of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Sharma, M.; Chan, H.K.; Lavilla, C.A.; Uy, M.M.; Froemming, G.R.A.; Okechukwu, P.N. Induction of a single dose of streptozotocin (50 mg) in rat model causes insulin resistance with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 37, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Gong, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Qian, J.-Y.; Zhu, W. Effect of rice protein on the gelatinization and retrogradation properties of rice starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 125061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodayari, A.; Hirn, U.; Spirk, S.; Ogawa, Y.; Seveno, D.; Thielemans, W. Advancing plant cell wall modelling: Atomistic insights into cellulose, disordered cellulose, and hemicelluloses—A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 343, 122415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, B.; Liang, Y.; Jia, M.; Yun, J.; Niu, J.; Li, H.; Ren, G.; Qin, P.; et al. Starch chain-length distributions affect the processing and digestion characteristics of proso millet starch. Food Chem. 2024, 457, 140104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iuga, M.; Mironeasa, S. A review of the hydrothermal treatments impact on starch based systems properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 60, 3890–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, G.; Awika, J.M. Effect of protein–starch interactions on starch retrogradation and implications for food product quality. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 2081–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Blum, N.T.; Lin, J.; Qu, J.; Huang, P. Biomaterial scaffold-based local drug delivery systems for cancer immunotherapy. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 1489–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cui, S.W.; Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Liang, R.; Xu, F.; Zhong, F. Protective approaches and mechanisms of microencapsulation to the survival of probiotic bacteria during processing, storage and gastrointestinal digestion: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2863–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; He, X.; Zhao, R.; Shi, Q.; Nian, Y.; Hu, B. Hydrogels as promising carriers for the delivery of food bioactive ingredients. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1006520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.; Alric, M.; Blanquet-Diot, S.; Bornhorst, G.; Cueva, C.; Deglaire, A.; Denis, S.; Ferrua, M.; Havenaar, R.; Lelieveld, J.; et al. Can dynamicin vitrodigestion systems mimic the physiological reality? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 59, 1546–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Escalera, S.; Wellejus, A. Evaluation of Caco-2 and human intestinal epithelial cells as in vitro models of colonic and small intestinal integrity. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2022, 31, 101314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.K.; Parab, S.; Dabholkar, N.; Agrawal, M.; Singhvi, G.; Alexander, A.; Bapat, R.A.; Kesharwani, P. Oral peptide delivery: Challenges and the way ahead. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 931–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foretz, M.; Guigas, B.; Viollet, B. Understanding the glucoregulatory mechanisms of metformin in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 569–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, M.; Li, H.; Fu, Z.; Li, Q. Centenarian-sourced Lactobacillus casei combined with dietary fiber complex ameliorates brain and gut function in aged mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.-J.; Lee, H.G.; Seo, K.-H.; Yokoyama, W.; Kim, H. Antiobesity effect of prebiotic polyphenol-rich grape seed flour supplemented with probiotic kefir-derived lactic acid bacteria. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12498–12511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Han, L.; Ma, J.; Wu, T.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, L.; Tong, X. Exploring the synergistic and complementary effects of berberine and paeoniflorin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus by network pharmacology. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 919, 174769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H. A comprehensive review of the factors influencing the formation of retrograded starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tian, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Luo, T.; Dai, J. Characteristics of the gut microbiome in patients with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konikoff, T.; Gophna, U. Oscillospira: A central, enigmatic component of the Human gut microbiota. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 523–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, D.B.G.; Go, J.R.; Fida, M.; Saleh, O.A. Management and treatment of Aerococcus bacteremia and endocarditis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 102, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; He, C.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Jing, X.; Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Suo, L.; Kalds, P.; et al. Taxonomic and functional adaption of the gastrointestinal microbiome of goats kept at high altitude (4800 m) under intensive or extensive rearing conditions. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiab009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, T.; Xu, W.; Huang, Y.; Ran, L.; Yan, Y.; Mi, J.; Lu, L.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, X.; et al. The polysaccharides from the fruits of Lycium barbarum L. confer anti-diabetic effect by regulating gut microbiota and intestinal barrier. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, A.; Alkan, Z.; Stephensen, C.B.; Newman, J.W.; Kable, M.E.; Lemay, D.G. Diet, microbiome, and inflammation predictors of fecal and plasma short-chain fatty acids in humans. J. Nutr. 2024, 154, 3298–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González Hernández, M.A.; Canfora, E.E.; Jocken, J.W.E.; Blaak, E.E. The short-chain fatty acid acetate in body weight control and insulin sensitivity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Jian, Y.-P.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Li, Y.; Gu, L.-T.; Sun, H.-H.; Liu, M.-D.; Zhou, H.-L.; Wang, Y.-S.; Xu, Z.-X. Short-chain fatty acids in diseases. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
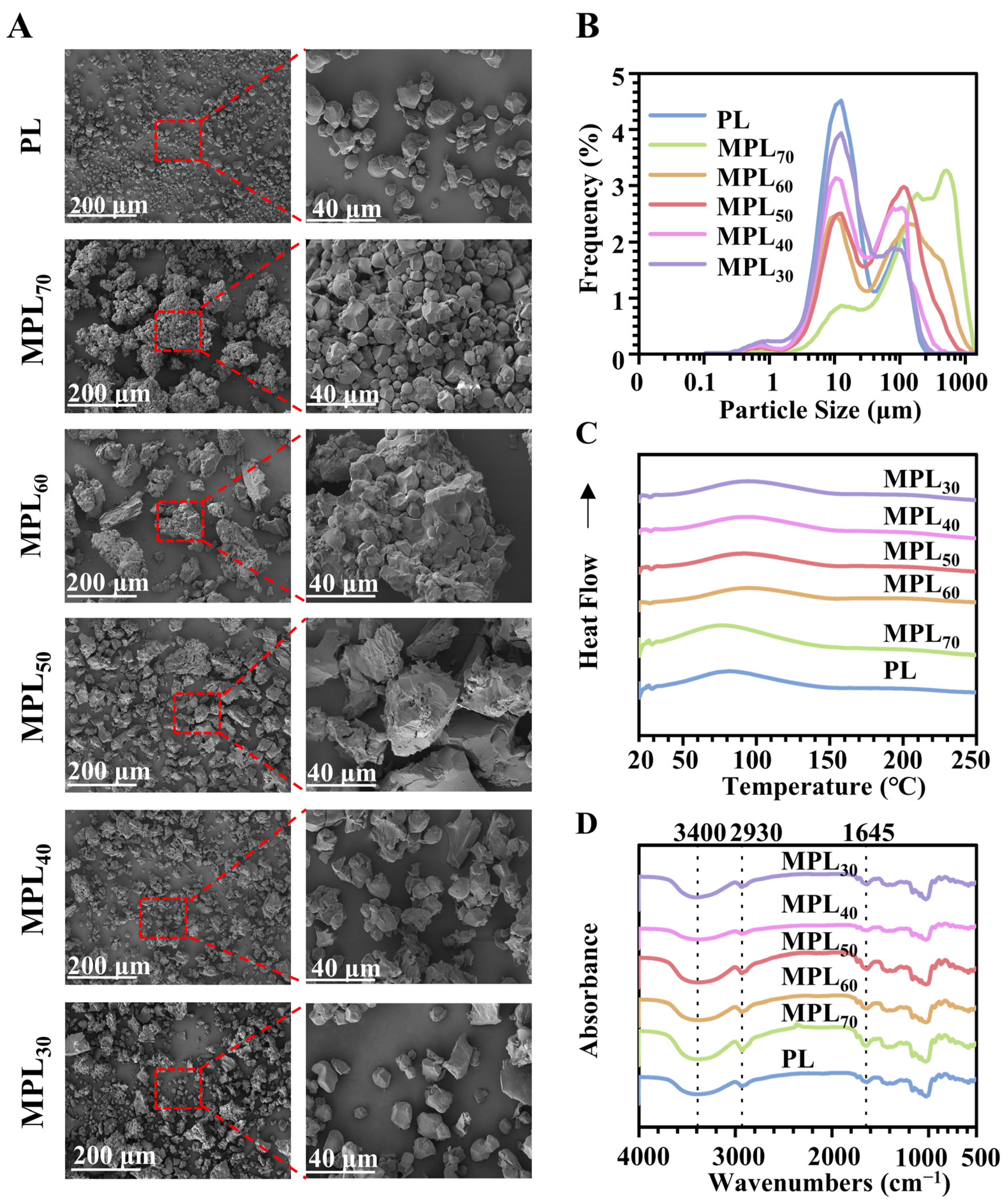




| Samples | D (10)/μm | D (50)/μm | D (90)/μm | D [2,3]/μm | D [3,4]/μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL | 5.58 ± 0.12 a | 15.40 ± 0.40 a | 102.23 ± 0.61 a | 9.83 ± 0.23 a | 34.26 ± 0.50 a |
| MPL70 | 16.33 ± 0.96 c | 199.77 ± 20.34 c | 748.80 ± 101.38 d | 41.18 ± 2.24 c | 304.80 ± 37.02 d |
| MPL60 | 6.55 ± 0.08 b | 66.93 ± 5.13 b | 429.30 ± 20.80 c | 14.22 ± 0.30 b | 149.10 ± 7.64 c |
| MPL50 | 7.21 ± 0.34 b | 57.90 ± 8.36 b | 285.50 ± 71.23 b | 16.49 ± 1.57 b | 109.69 ± 21.37 b |
| MPL40 | 5.29 ± 0.69 a | 18.06 ± 7.78 a | 125.87 ± 23.19 a | 9.66 ± 1.67 a | 44.32 ± 11.14 a |
| MPL30 | 5.29 ± 0.17 a | 16.74 ± 0.22 a | 99.19 ± 4.21 a | 8.93 ± 0.25 a | 35.53 ± 1.21 a |
| Samples | Porosity/% | Average Pore Size/nm | Total Pore Volume /mL·g−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PL | 52.53 | 2998 | 0.7834 |
| MPL70 | 56.68 | 2138 | 0.9634 |
| MPL60 | 63.43 | 5248 | 1.2883 |
| MPL50 | 69.41 | 6598 | 1.6232 |
| MPL40 | 64.18 | 5214 | 1.2786 |
| MPL30 | 53.00 | 3408 | 0.8692 |
| Samples | To/°C | Tp/°C | Tc/°C |
|---|---|---|---|
| MPL30 | 35.50 | 79.17 | 149.17 |
| MPL40 | 34.33 | 95.00 | 155.50 |
| MPL50 | 36.50 | 91.50 | 156.50 |
| MPL60 | 36.00 | 93.33 | 159.67 |
| MPL70 | 37.17 | 93.67 | 169.50 |
| PL | 35.17 | 82.17 | 152.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, R.; Ding, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yan, G.; Yin, D.; Yang, Y. Engineering a Dual-Function Starch–Cellulose Composite for Colon-Targeted Probiotic Delivery and Synergistic Gut Microbiota Regulation in Type 2 Diabetes Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050663
Liu R, Ding Y, Xu Y, Wu Q, Chen Y, Yan G, Yin D, Yang Y. Engineering a Dual-Function Starch–Cellulose Composite for Colon-Targeted Probiotic Delivery and Synergistic Gut Microbiota Regulation in Type 2 Diabetes Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(5):663. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050663
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ruixiang, Yikang Ding, Yujing Xu, Qifeng Wu, Yanan Chen, Guiming Yan, Dengke Yin, and Ye Yang. 2025. "Engineering a Dual-Function Starch–Cellulose Composite for Colon-Targeted Probiotic Delivery and Synergistic Gut Microbiota Regulation in Type 2 Diabetes Therapeutics" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 5: 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050663
APA StyleLiu, R., Ding, Y., Xu, Y., Wu, Q., Chen, Y., Yan, G., Yin, D., & Yang, Y. (2025). Engineering a Dual-Function Starch–Cellulose Composite for Colon-Targeted Probiotic Delivery and Synergistic Gut Microbiota Regulation in Type 2 Diabetes Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics, 17(5), 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050663





