PLA-Based Electrospun Nanofibrous Mats Towards Application as Antibiotic Carriers: Processing Parameters, Fabrication and Characterization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Solution Preparation and Electrospinning Process
2.3. Structural-Morphological Characterization & In Vitro Drug Release Testing
2.3.1. Attenuated Total Reflection Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.3.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.3.3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.5. Porosity Calculation
2.3.6. In Vitro Degradation Testing
2.3.7. Drug Loading and In Vitro Drug Release
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preliminary Evaluation of Process Parameters and Morphology
3.2. Morphological Analysis
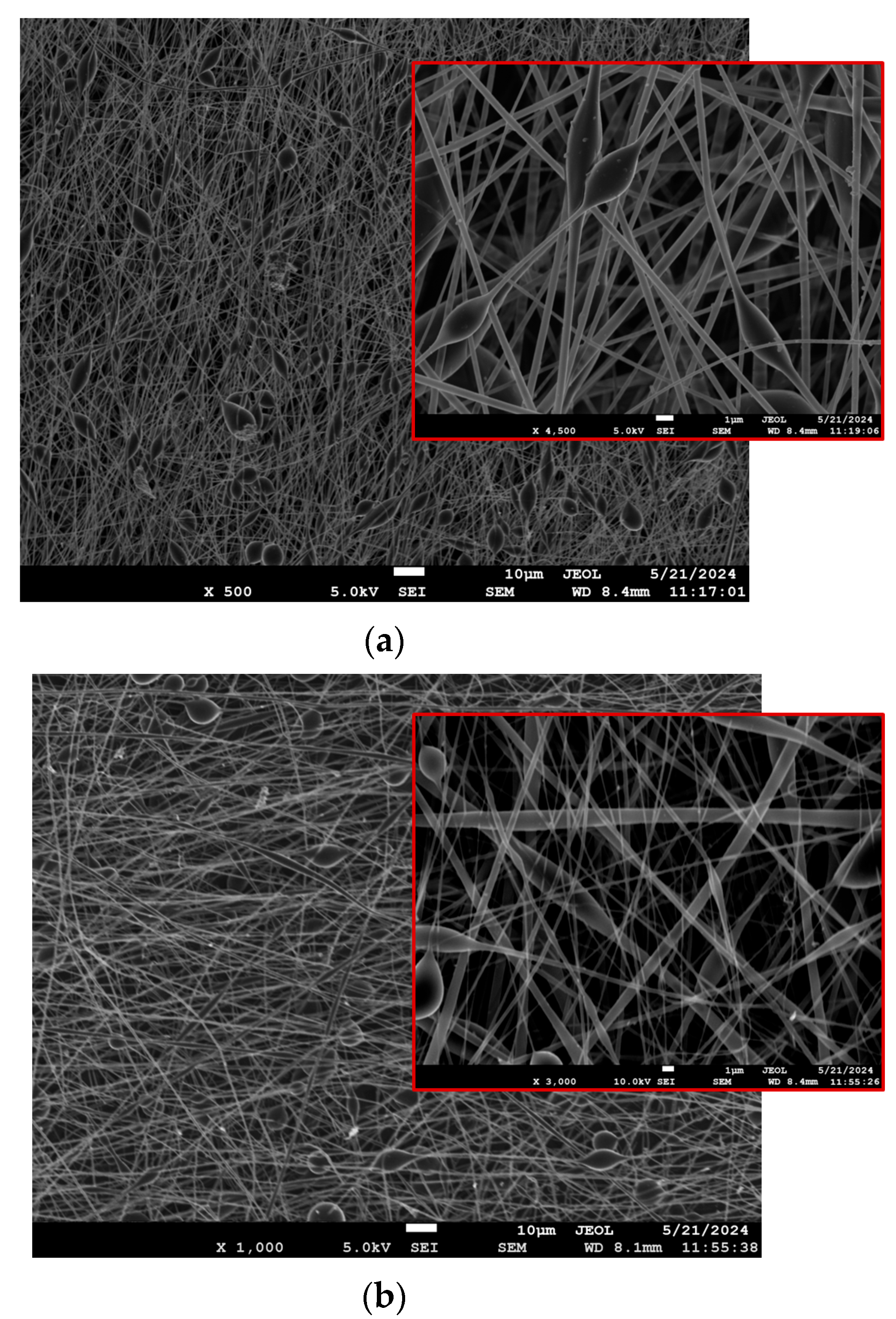
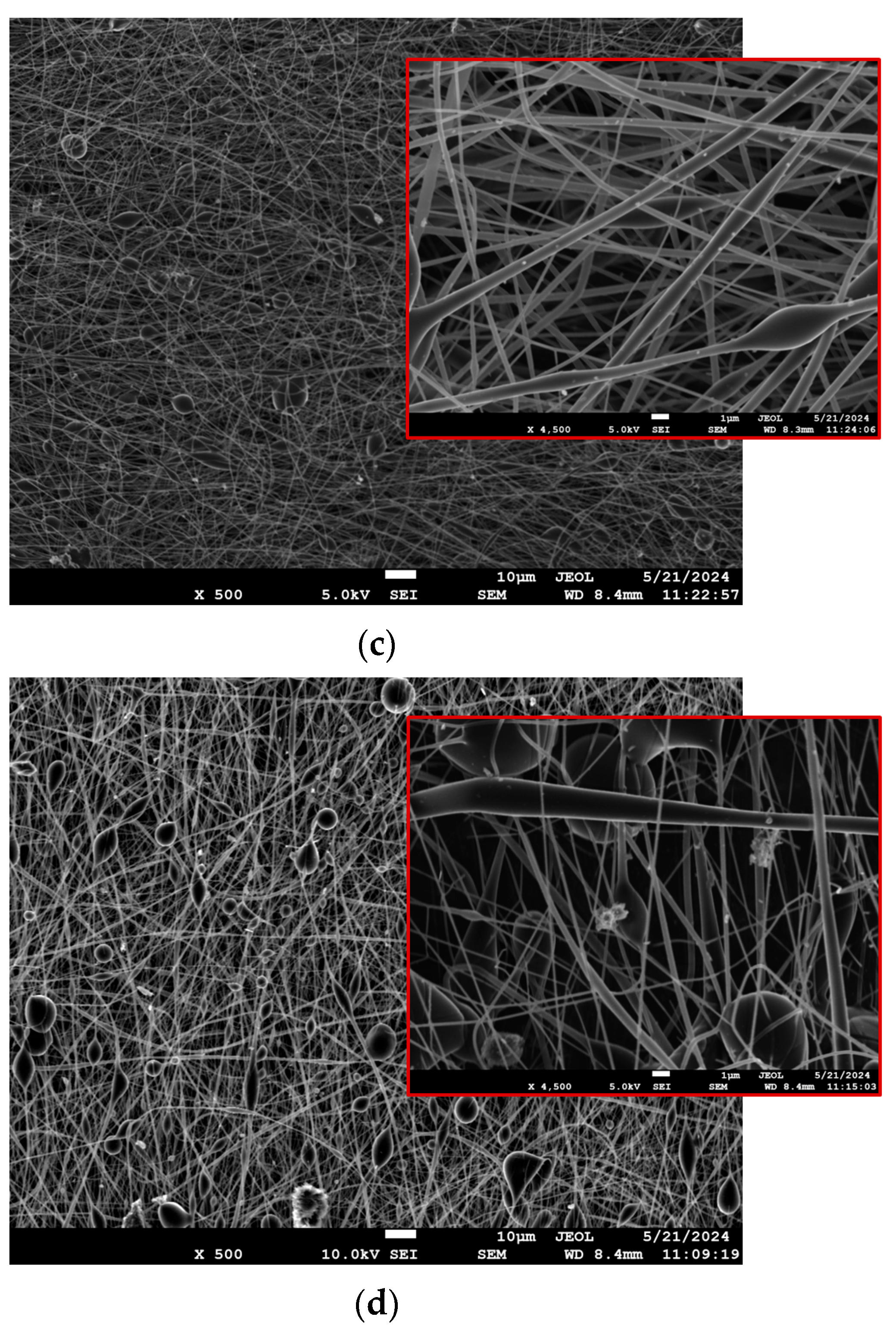
3.2.1. SEM
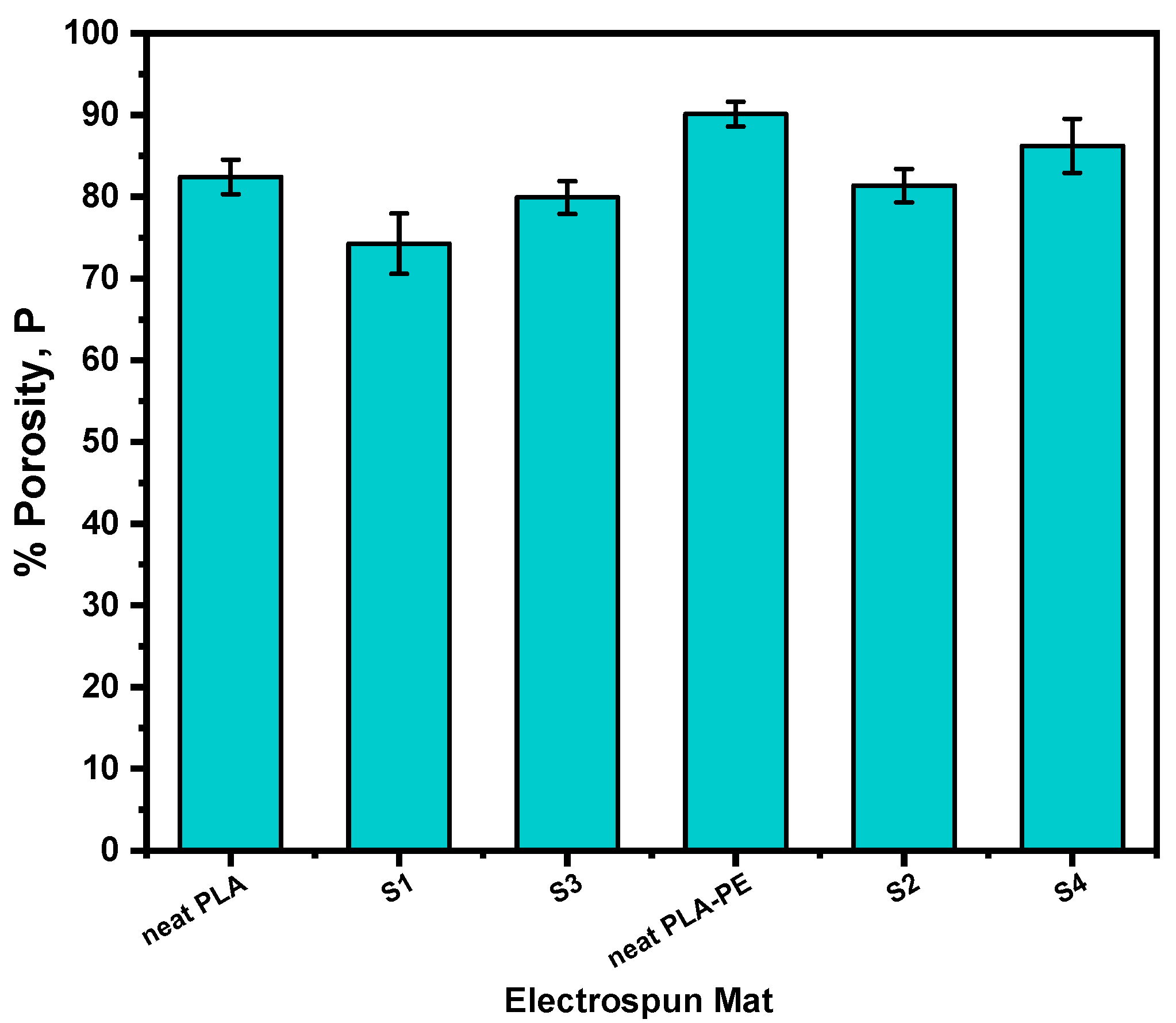
3.2.2. Porosity Calculations
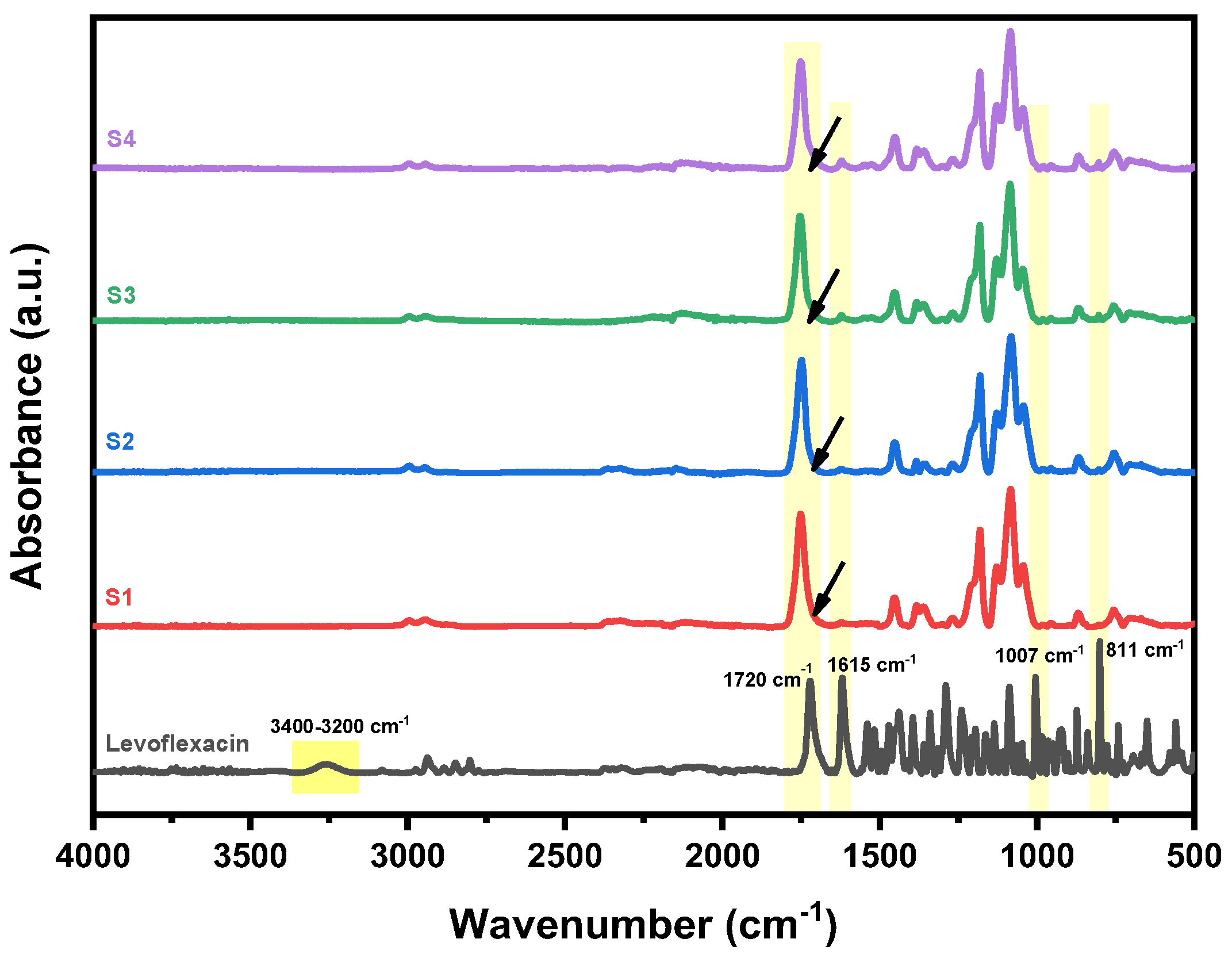
3.3. Structural Investigation (ATR-FTIR)
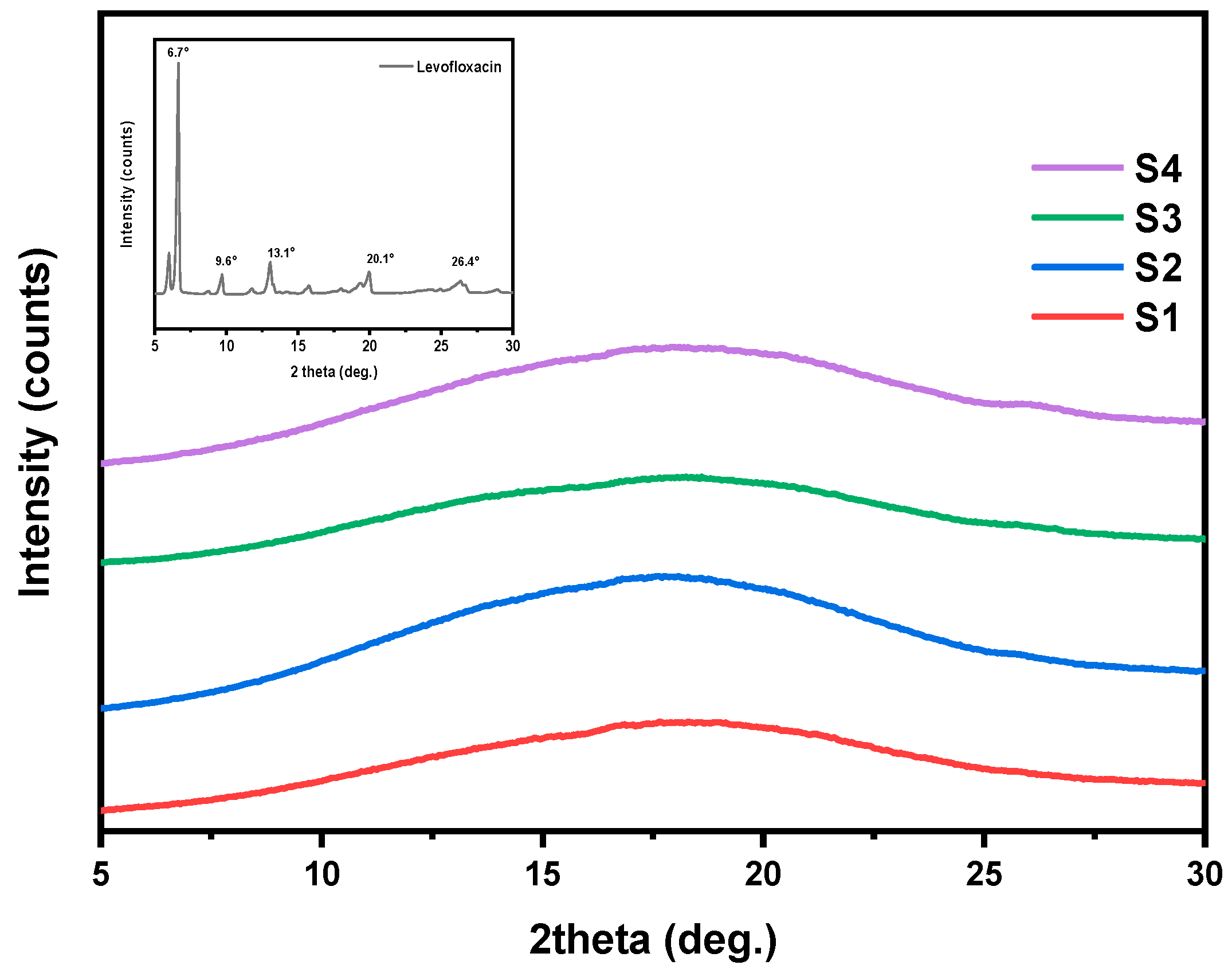
3.4. Crystalline Structure Assessment (XRD)
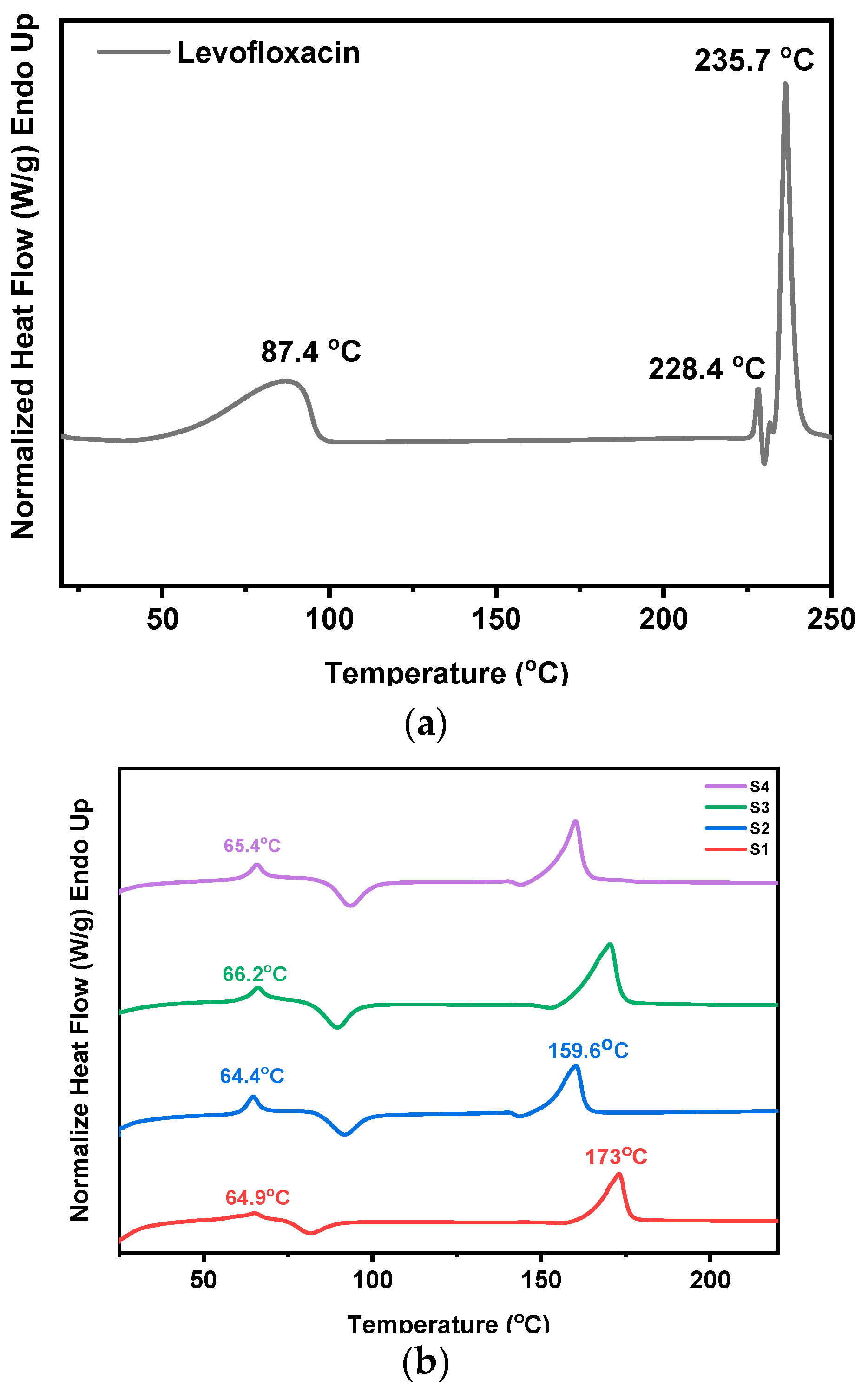
3.5. Investigation of Thermal Transitions (DSC)
3.6. Estimation of Degradation Rate
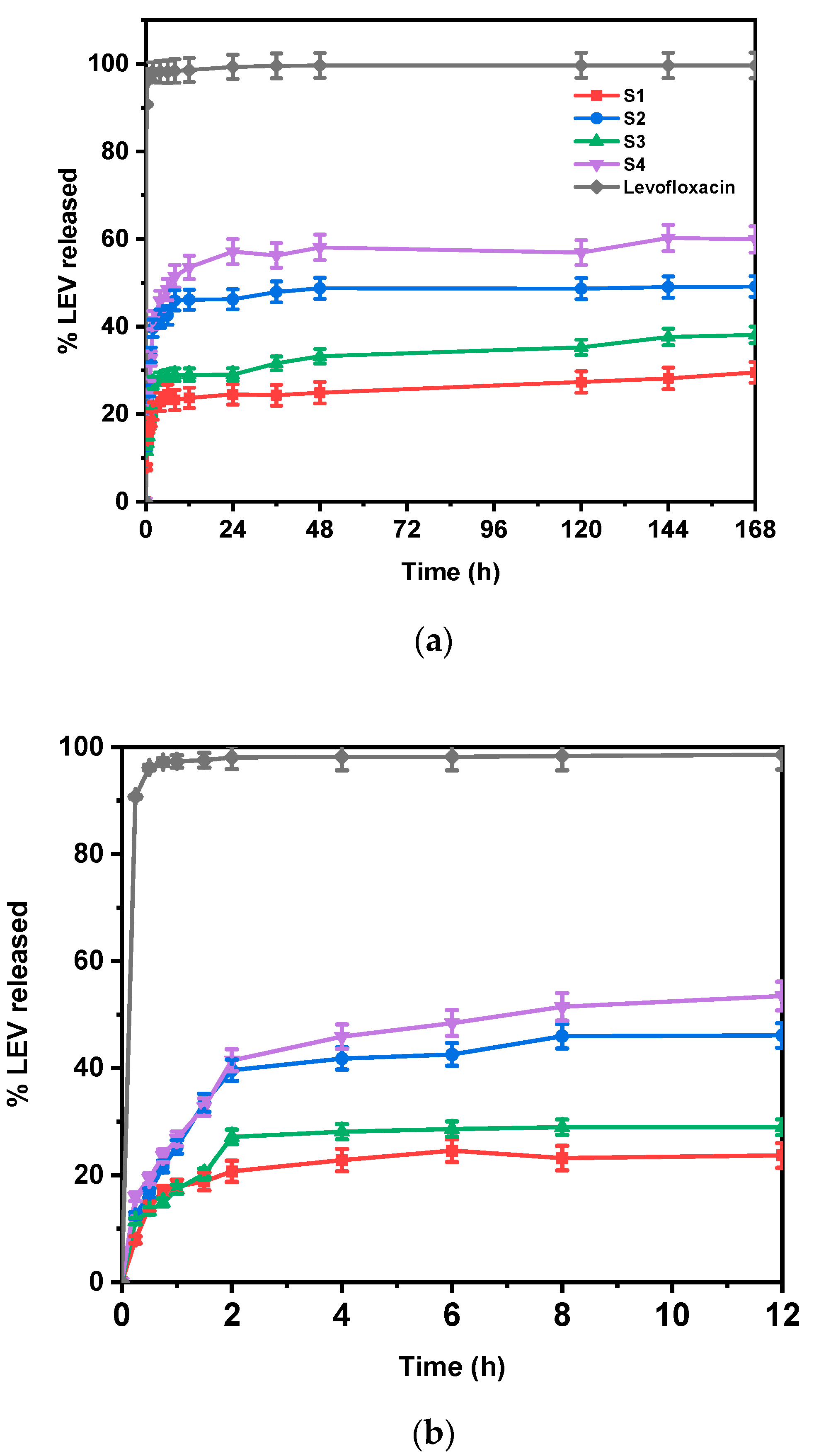
3.7. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeong, W.Y.; Kwon, M.; Choi, H.E.; Kim, K.S. Recent Advances in Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems: A Review. Biomater. Res. 2021, 25, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phatale, V.; Vaiphei, K.K.; Jha, S.; Patil, D.; Agrawal, M.; Alexander, A. Overcoming Skin Barriers through Advanced Transdermal Drug Delivery Approaches. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkilani, A.Z.; Nasereddin, J.; Hamed, R.; Nimrawi, S.; Hussein, G.; Abo-Zour, H.; Donnelly, R.F. Beneath the Skin: A Review of Current Trends and Future Prospects of Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, L.; Verma, S.; Joshi, K.; Utreja, P.; Sharma, S. Nanofiber as a Novel Vehicle for Transdermal Delivery of Therapeutic Agents: Challenges and Opportunities. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 7, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, F.; Kim, B.S. Recent Advances in Polymeric Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems. J. Control. Release 2022, 341, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Ullah, M.; Saeed, S.; Saleh, E.A.M.; Kassem, A.F.; Arbi, F.M.; Wahab, A.; Rehman, M.; ur Rehman, K.; Khan, D. Nanotherapeutic Approaches for Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems and Their Biomedical Applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 207, 112819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, M.; Bidgoli, S.A.; Rezayat, S.M. Electrospun Polymeric Nanofibers for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Nanomed. J. 2017, 4, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillova, A.; Yeazel, T.R.; Asheghali, D.; Petersen, S.R.; Dort, S.; Gall, K.; Becker, M.L. Fabrication of Biomedical Scaffolds Using Biodegradable Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 11238–11304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, N.; Lopes, D.; Lopes, J.; Macário-Soares, A.; Dan, A.K.; Ghanbari, R.; Kahkesh, K.H.; Peixoto, D.; Giram, P.S.; Raza, F. Natural Polymeric Nanofibers in Transdermal Drug Delivery. Appl. Mater. Today 2023, 30, 101726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiwrale, A.; Bharati, S.; Pingale, P.; Rajput, A. Nanofibers: A Current Era in Drug Delivery System. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, H.; Li, G.; Cho, H.; Jiang, M.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, X. Developments of Advanced Electrospinning Techniques: A Critical Review. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yan, C.; Li, G.; Cheng, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Mao, Q.; Cho, H.; Gao, Q.; Gao, C. Recent Developments of Electrospun Nanofibers for Electrochemical Energy Storage and Conversion. Energy Storage Mater. 2024, 65, 103111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, K.; Liu, T.; Padilla, D.J.; Nelson, M.; Landorf, C.W.; Patel, R.J.; Ballentine, M.L.; Kennedy, A.J.; Shih, W.-S.; Scotch, A. Nanofibers Enabled Advanced Gas Sensors: A Review. Adv. Sens. Energy Mater. 2024, 3, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esentürk, İ.; Erdal, M.S.; Güngör, S. Electrospinning Method to Produce Drug-Loaded Nanofibers for Topical/Transdermal Drug Delivery Applications. J. Fac. Pharm. Istanb. Univ. 2016, 46, 49–69. [Google Scholar]
- Gaydhane, M.K.; Sharma, C.S.; Majumdar, S. Electrospun Nanofibres in Drug Delivery: Advances in Controlled Release Strategies. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 7312–7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abduljabbar, A.; Farooq, I. Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers: Processing, Properties, and Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouroutzidou, G.K.; Lazaridou, M.; Papoulia, C.; Tsamesidis, I.; Chrissafis, K.; Vourlias, G.; Paraskevopoulos, K.M.; Bikiaris, D.; Kontonasaki, E. Electrospun PLGA Membranes with Incorporated Moxifloxacin-Loaded Silica-Based Mesoporous Nanocarriers for Periodontal Regeneration. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhussain, R.; Adebisi, A.; Conway, B.R.; Asare-Addo, K. Electrospun Nanofibers: Exploring Process Parameters, Polymer Selection, and Recent Applications in Pharmaceuticals and Drug Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 90, 105156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, M.; Poursorkhabi, V.; Mohanty, A.K.; Gregori, S.; Misra, M. Electrospinning Highly Oriented and Crystalline Poly (Lactic Acid) Fiber Mats. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 2430–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmaz, D.; Toprakci, H.A.K.; Olmez, H.; Toprakci, O. Electrospun Polylactic Acid Based Nanofibers for Biomedical Applications. Mater. Sci. Res. India 2018, 15, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, E.; Daniilidis, V.; Karlioti, G.; Kalamas, T.; Stefanidou, M.; Bikiaris, N.D.; Vlachopoulos, A.; Koumentakou, I.; Bikiaris, D.N. Poly(Lactic Acid): A Versatile Biobased Polymer for the Future with Multifunctional Properties—From Monomer Synthesis, Polymerization Techniques and Molecular Weight Increase to PLA Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachopoulos, A.; Karlioti, G.; Balla, E.; Daniilidis, V.; Kalamas, T.; Stefanidou, M.; Bikiaris, N.D.; Christodoulou, E.; Koumentakou, I.; Karavas, E.; et al. Poly(Lactic Acid)-Based Microparticles for Drug Delivery Applications: An Overview of Recent Advances. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, F.; Ramezani Dana, H. Poly Lactic Acid (PLA) Polymers: From Properties to Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2022, 71, 1117–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, H.; Azimi, B.; Ismaeilimoghadam, S.; Danti, S. Poly (Lactic Acid)-Based Electrospun Fibrous Structures for Biomedical Applications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, S.; Dorati, R.; Conti, B.; Modena, T.; Bruni, G.; Genta, I. Design of Copolymer PLA-PCL Electrospun Matrix for Biomedical Applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 124, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnier, X.; Delpouve, N.; Basson, N.; Guinault, A.; Domenek, S.; Saiter, A.; Mallon, P.E.; Dargent, E. Molecular Dynamics in Electrospun Amorphous Plasticized Polylactide Fibers. Polymer 2015, 73, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, M.P.; Perdiguero, M.; Fiori, S.; Kenny, J.M.; Peponi, L. Biodegradable Electrospun PLA-PHB Fibers Plasticized with Oligomeric Lactic Acid. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 179, 109226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonés, A.; Salaris, V.; Mujica-Garcia, A.; Arrieta, M.P.; Lopez, D.; Lieblich, M.; Kenny, J.M.; Peponi, L. PLA Electrospun Fibers Reinforced with Organic and Inorganic Nanoparticles: A Comparative Study. Molecules 2021, 26, 4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaris, V.; San Félix García-Obregón, I.; López, D.; Peponi, L. Fabrication of PLA-Based Electrospun Nanofibers Reinforced with ZnO Nanoparticles and in Vitro Degradation Study. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allizond, V.; Banche, G.; Salvoni, M.; Malandrino, M.; Cecone, C.; Cuffini, A.M.; Bracco, P. Facile One-Step Electrospinning Process to Prepare AgNPs-Loaded PLA and PLA/PEO Mats with Antibacterial Activity. Polymers 2023, 15, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, A.; Brzezinski, M.; Lapienis, G.; Biela, T. Star-Shaped and Branched Polylactides: Synthesis, Characterization, and Properties. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 89, 159–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrientos, I.J.H.; Paladino, E.; Brozio, S.; Passarelli, M.K.; Moug, S.; Black, R.A.; Wilson, C.G.; Lamprou, D.A. Fabrication and Characterisation of Drug-Loaded Electrospun Polymeric Nanofibers for Controlled Release in Hernia Repair. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 517, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangole, S.; Salave, S.; Rana, D.; Shah, S.; Medhe, T.P.; Benival, D. Electrospun Nanofiber Composite for Levofloxacin in Ocular Drug Delivery. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2022, 10, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monavari, M.; Sohrabi, R.; Motasadizadeh, H.; Monavari, M.; Fatahi, Y.; Ejarestaghi, N.M.; Fuentes-Chandia, M.; Leal-Egaña, A.; Akrami, M.; Homaeigohar, S. Levofloxacin Loaded Poly (Ethylene Oxide)-Chitosan/Quercetin Loaded Poly (D, L-Lactide-Co-Glycolide) Core-Shell Electrospun Nanofibers for Burn Wound Healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1352717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajdič, S.; Planinšek, O.; Gašperlin, M.; Kocbek, P. Electrospun Nanofibers for Customized Drug-Delivery Systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 51, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelb, M.B.; Punia, A.; Sellers, S.; Kadakia, P.; Ormes, J.D.; Khawaja, N.N.; Wylie, J.; Lamm, M.S. Effect of Drug Incorporation and Polymer Properties on the Characteristics of Electrospun Nanofibers for Drug Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 68, 103112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikiaris, N.D.; Klonos, P.A.; Ioannidis, R.O.; Saranti, P.; Barmpalexis, P.; Kyritsis, A. Molecular Mobility and Thermal Transitions Study in Renewable PLA-Polyols Star-like Copolymers. Polymer 2024, 292, 126635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachou, M.; Bolbasis, G.-M.; Trikali, A.-E.; Protopapa, C.; Siamidi, A.; Sakellaropoulou, A.; Christodoulou, E.; Bikiaris, N.D. Release Behavior of the Pineal Hormone Melatonin from Modified Matrix Tablets Based on Poly (L-Lactic Acid) and Its Derivatives. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Vicini, S.; Sionkowska, A. Electrospun Materials Based on Polymer and Biopolymer Blends—A Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, N.; Gunn, J.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Controlled, Localized Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-Y.; Lee, I.-H. Controlled Release of Ketoprofen from Electrospun Porous Polylactic Acid (PLA) Nanofibers. J. Polym. Res. 2011, 18, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Ren, Z.; Han, G.; Mao, C. Synthesis of CaTiO3 Nanofibers with Controllable Drug-release Kinetics. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 2015, 4532–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant, S.; Thommes, M.; Hildgen, P. Microporous Structure and Drug Release Kinetics of Polymeric Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2008, 24, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandari, S.; Dronam, V.R.; Eedara, B.B. Development and Preliminary Characterization of Levofloxacin Pharmaceutical Cocrystals for Dissolution Rate Enhancement. J. Pharm. Investig. 2017, 47, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiotaki, C.; Koumentakou, I.; Christodoulou, E.; Bikiaris, N.D.; Vlachou, M.; Karavas, E.; Tourlouki, K.; Kehagias, N.; Barmpalexis, P. Fabrication of PLA-Based Nanoneedle Patches Loaded with Transcutol-Modified Chitosan Nanoparticles for the Transdermal Delivery of Levofloxacin. Molecules 2024, 29, 4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pásztor, N.; Rédai, E.; Szabó, Z.-I.; Sipos, E. Preparation and Characterization of Levofloxacin-Loaded Nanofibers as Potential Wound Dressings. Acta Marisiensis-Ser. Medica 2017, 63, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaly, N.; Yameen, B.; Wu, J.; Farokhzad, O.C. Degradable Controlled-Release Polymers and Polymeric Nanoparticles: Mechanisms of Controlling Drug Release. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2602–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundrat, V.; Cernekova, N.; Kovalcik, A.; Enev, V.; Marova, I. Drug Release Kinetics of Electrospun PHB Meshes. Materials 2019, 12, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaharwar, A.K.; Mihaila, S.M.; Kulkarni, A.A.; Patel, A.; Di Luca, A.; Reis, R.L.; Gomes, M.E.; van Blitterswijk, C.; Moroni, L.; Khademhosseini, A. Amphiphilic Beads as Depots for Sustained Drug Release Integrated into Fibrillar Scaffolds. J. Control. Release 2014, 187, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Name | Tm °C | Tg °C | Tc °C | [η] (dL/g) | Mn (g/mol) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | 175.9 | 56 | 116 | 1.32 | 55,500 | 2.18 |
| PLA-PE | 150 | 51 | 118 | 0.47 | 25,000 | 1.81 |
| Polymer | Polymer Concentration (% w/v) | Voltage (kV) | Rotation Speed (rpm) | Distance (cm) | Flow Rate (μL/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | 5 | 22 | 500 | 10 | 1000 |
| 5 | 22 | 5000 | 10 | 1000 | |
| 10 | 20 | 1000 | 12 | 750 | |
| 10 | 20 | 1000 | 12 | 1000 | |
| 15 | 20 | 1000 | 12 | 750 | |
| 15 | 20 | 1000 | 12 | 750 | |
| PLA-PE | 10 | 20 | 500 | 10 | 1500 |
| 10 | 22 | 500 | 10 | 1500 | |
| 15 | 20 | 1000 | 12 | 1000 | |
| 15 | 22 | 1000 | 12 | 1000 | |
| 20 | 20 | 1000 | 12 | 750 | |
| 20 | 22 | 1000 | 12 | 750 |
| Sample Name | Polymer Concentration (% w/v) | LEV Concentration (% w/w) | Voltage (kV) | Rotation Speed (rpm) | Flow Rate (μL/h) | Average Fiber Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA10LEV10 (S1) | 10 | 10 | 20 | 1000 | 750 | 334.8 ± 12.2 |
| PLAPE20LEV10 (S2) | 20 | 10 | 20 | 1000 | 750 | 526.3 ± 18.8 |
| PLA10LEV20 (S3) | 10 | 20 | 20 | 1000 | 750 | 442.7 ± 10.6 |
| PLAPE20LEV20 (S4) | 20 | 20 | 20 | 1000 | 750 | 665.2 ± 24.1 |
| Sample Name | % Drug Loading | % Encapsulation Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | 17.91 ± 1.47 | 78.21 ± 0.82 |
| S2 | 28.52 ± 1.93 | 64.28 ± 2.81 |
| S3 | 22.32 ± 0.98 | 81.32 ± 1.27 |
| S4 | 34.78 ± 2.81 | 58.29 ± 2.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Christodoulou, E.; Chondromatidou, A.; Bikiaris, N.D.; Balla, E.; Vlachou, M.; Barmpalexis, P.; Bikiaris, D.N. PLA-Based Electrospun Nanofibrous Mats Towards Application as Antibiotic Carriers: Processing Parameters, Fabrication and Characterization. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050589
Christodoulou E, Chondromatidou A, Bikiaris ND, Balla E, Vlachou M, Barmpalexis P, Bikiaris DN. PLA-Based Electrospun Nanofibrous Mats Towards Application as Antibiotic Carriers: Processing Parameters, Fabrication and Characterization. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(5):589. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050589
Chicago/Turabian StyleChristodoulou, Evi, Anastasia Chondromatidou, Nikolaos D. Bikiaris, Evangelia Balla, Marilena Vlachou, Panagiotis Barmpalexis, and Dimitrios N. Bikiaris. 2025. "PLA-Based Electrospun Nanofibrous Mats Towards Application as Antibiotic Carriers: Processing Parameters, Fabrication and Characterization" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 5: 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050589
APA StyleChristodoulou, E., Chondromatidou, A., Bikiaris, N. D., Balla, E., Vlachou, M., Barmpalexis, P., & Bikiaris, D. N. (2025). PLA-Based Electrospun Nanofibrous Mats Towards Application as Antibiotic Carriers: Processing Parameters, Fabrication and Characterization. Pharmaceutics, 17(5), 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050589












