Impact of Pharmacogenetics on High-Dose Methotrexate Toxicity in Pediatric Oncology
Abstract
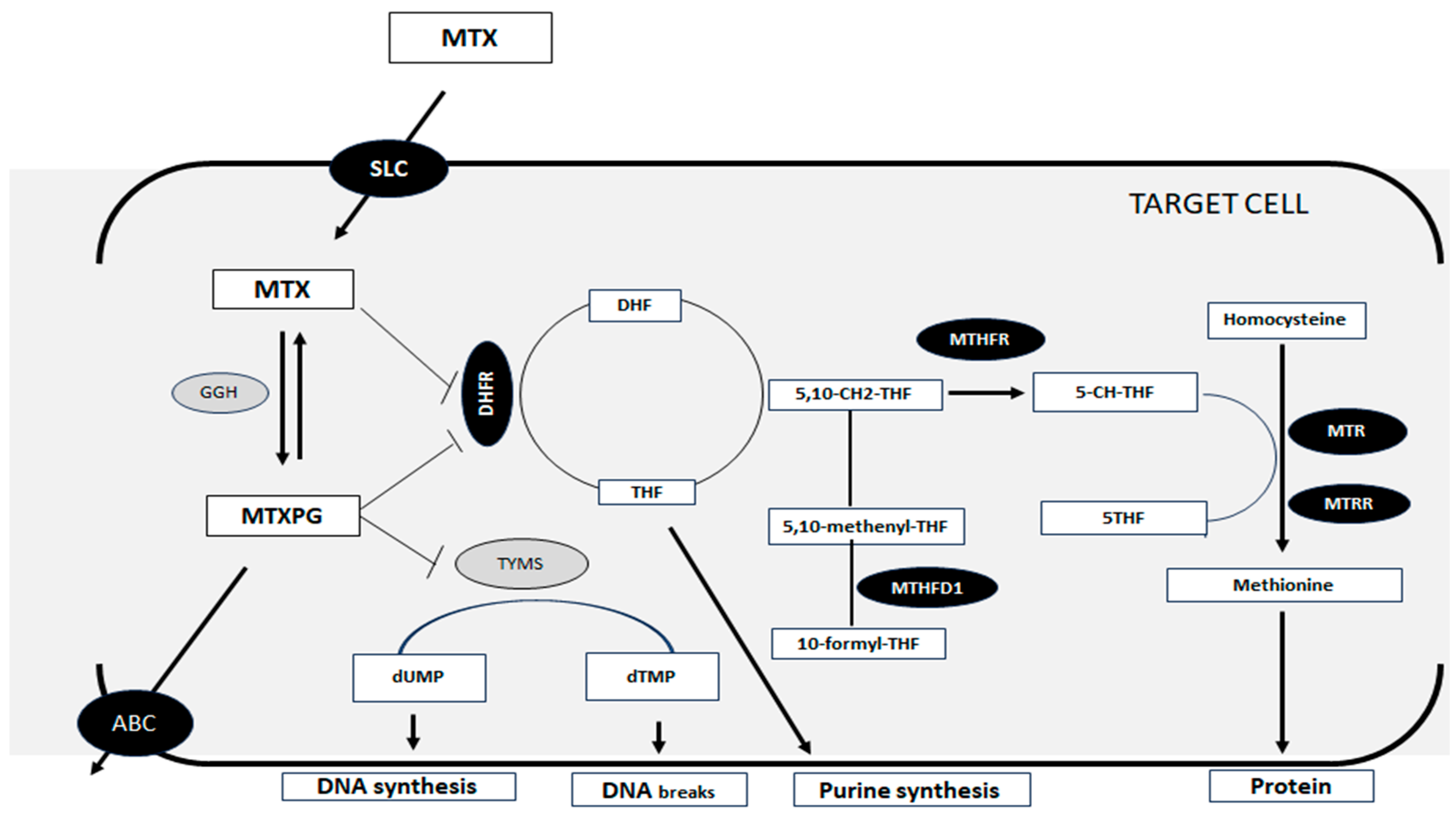
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Ethics Statements
2.4. Sociodemographic and Clinical Variables
2.5. Genetic Variables
2.5.1. DNA Isolation
2.5.2. Detection of Genetic Polymorphisms
2.5.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sociodemographic and Clinical Variables
3.2. Sociodemographic and Clinical Variables Associated with HDMTX Toxicity
3.3. Genotype Distribution
3.4. Polymorphisms Associated with Toxicity
4. Discussion
4.1. Sex
4.2. MTHFD1 rs2236225
4.3. MTHFR rs1801133
4.4. GSTP1 rs1695
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Erdmann, F.; Frederiksen, L.E.; Bonaventure, A.; Mader, L.; Hasle, H.; Robison, L.L.; Winther, J.F. Childhood Cancer: Survival, Treatment Modalities, Late Effects and Improvements over Time. Cancer Epidemiol. 2021, 71, 101733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabassa-Blanco, J.; Brunet-Llobet, L.; Marcote-Sinclair, P.; Balsells-Mejía, S.; Correa-Llano, M.G.; Miranda-Rius, J. Prevalence of, and Risk Factors for, Dental Sequelae in Adolescents Who Underwent Cancer Therapy during Childhood. Oral. Dis. 2024, 30, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, K.A.; Scott, S.; Firth, A.U.; Sung, H.; Henley, S.J.; Sherman, R.L.; Siegel, R.L.; Anderson, R.N.; Kohler, B.A.; Benard, V.B.; et al. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, Part 1: National Cancer Statistics. Cancer 2022, 128, 4251–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, F.; Jin, R. The Influence of MTHFR Genetic Polymorphisms on Methotrexate Therapy in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Open Life Sci. 2021, 16, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Luo, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, F.; Ma, Y.; Xu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Luo, L.; Shi, C.; et al. Association of MTHFR and ABCB1 Polymorphisms with MTX-Induced Mucositis in Chinese Paediatric Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia, Lymphoma or Osteosarcoma-A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2021, 46, 1557–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, S.; Kotur, N.; Stankovic, B.; Zukic, B.; Gasic, V.; Dokmanovic, L. Pharmacogenomic and Pharmacotranscriptomic Profiling of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Paving the Way to Personalized Treatment. Genes 2019, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodidela, S.; Suresh Chandra, P.; Dubashi, B. Pharmacogenetics of Methotrexate in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: Why Still at the Bench Level? Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 70, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Li, W. Genomics and Pharmacogenomics of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2018, 126, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmiegelow, K. Advances in Individual Prediction of Methotrexate Toxicity: A Review. Br J. Haematol. 2009, 146, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Drokow, E.K.; Waqas Ahmed, H.A.; Song, J.; Akpabla, G.S.; Kumah, M.A.; Agyekum, E.B.; Neku, E.A.; Sun, K. The Relationship between Methionine Synthase Rs1805087 Polymorphism and Hematological Cancers Risk. Future Oncol. 2020, 16, 2219–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongaro, A.; De Mattei, M.; Della Porta, M.G.; Rigolin, G.; Ambrosio, C.; Di Raimondo, F.; Pellati, A.; Masieri, F.F.; Caruso, A.; Catozzi, L.; et al. Gene Polymorphisms in Folate Metabolizing Enzymes in Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Effects on Methotrexate-Related Toxicity and Survival. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, T.S.; Thorn, C.F.; Yang, J.J.; Ulrich, C.M.; French, D.; Zaza, G.; Dunnenberger, H.M.; Marsh, S.; McLeod, H.L.; Giacomini, K.; et al. PharmGKB Summary: Methotrexate Pathway. Pharmacogenetics Genom. 2011, 21, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, P.; Culverhouse, R.; Marsh, S.; Mody, A.; Scott-Horton, T.J.; Brasington, R.; Joseph, A.; Reddy, V.; Eisen, S.; McLeod, H.L. Methotrexate (MTX) Pathway Gene Polymorphisms and Their Effects on MTX Toxicity in Caucasian and African American Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 572–579. [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto, S.; Yanagimachi, M.; Tanoshima, R.; Urayama, K.Y.; Tanaka, F.; Aida, N.; Goto, H.; Ito, S. Influence of ADORA2A Gene Polymorphism on Leukoencephalopathy Risk in MTX-Treated Pediatric Patients Affected by Hematological Malignancies. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 1983–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liu, S.; Jiang, D.; Yi, Z.; Benjamin, M.M.; Zhao, R. The Role of Genetic Polymorphisms in High-Dose Methotrexate Toxicity and Response in Hematological Malignancies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 757464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, S.C.; McCormick, J.; Pui, C.-H.; Buddington, R.K.; Harvey, R.D. Preventing and Managing Toxicities of High-Dose Methotrexate. Oncologist 2016, 21, 1471–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Liu, Y.W.; Wang, S.Z.; Li, X.L.; Nie, X.L.; Yu, X.T.; Zhao, L.B.; Wang, X.L. Associations between the C677T and A1298C Polymorphisms of MTHFR and the Toxicity of Methotrexate in Childhood Malignancies: A Meta-Analysis. Pharmacogenomics J. 2018, 18, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erculj, N.; Kotnik, B.F.; Debeljak, M.; Jazbec, J.; Dolzan, V. The Influence of Folate Pathway Polymorphisms on High-Dose Methotrexate-Related Toxicity and Survival in Children with Non-Hodgkin Malignant Lymphoma. Radiol. Oncol. 2014, 48, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metayer, C.; Scélo, G.; Chokkalingam, A.P.; Barcellos, L.F.; Aldrich, M.C.; Chang, J.S.; Guha, N.; Urayama, K.Y.; Hansen, H.M.; Block, G.; et al. Genetic Variants in the Folate Pathway and Risk of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Causes Control 2011, 22, 1243–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colella, G.; Boschetti, C.E.; Vitagliano, R.; Colella, C.; Jiao, L.; King-Smith, N.; Li, C.; Nuoh Lau, Y.; Lai, Z.; Mohammed, A.I.; et al. Interventions for the Prevention of Oral Mucositis in Patients Receiving Cancer Treatment: Evidence from Randomised Controlled Trials. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangavi, R.; Pandiyan, I. Unveiling the Multifaceted Management of Oral Mucositis in Cancer Patients: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e55213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, G.; Liu, B.; Guo, Y.; Peng, N.; Li, T. Correlation between Gene Polymorphism and Adverse Reactions of High-Dose Methotrexate in Osteosarcoma Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 22, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, C.; Liu, X.; Hao, F.; Hu, C. Association between High-Dose Methotrexate-Induced Toxicity and Polymorphisms within Methotrexate Pathway Genes in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1003812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, Z.L.; Vang, J.; Lopez-Lopez, E.; Oosterom, N.; Mikkelsen, T.; Ramsey, L.B. Systematic Review of Pharmacogenetic Factors That Influence High-Dose Methotrexate Pharmacokinetics in Pediatric Malignancies. Cancers 2021, 13, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaili, M.A.; Kazemi, A.; Faranoush, M.; Mellstedt, H.; Zaker, F.; Safa, M.; Mehrvar, N.; Rezvany, M.R. Polymorphisms within Methotrexate Pathway Genes: Relationship between Plasma Methotrexate Levels, Toxicity Experienced and Outcome in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Iran J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagimachi, M.; Naruto, T.; Hara, T.; Kikuchi, M.; Hara, R.; Miyamae, T.; Imagawa, T.; Mori, M.; Kaneko, T.; Morita, S.; et al. Influence of Polymorphisms within the Methotrexate Pathway Genes on the Toxicity and Efficacy of Methotrexate in Patients with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 71, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hu, X.; Xu, L. Impact of Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR) Polymorphisms on Methotrexate-Induced Toxicities in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Meta-Analysis. Tumour Biol. 2012, 33, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dm, T.; Kd, T. The Role of Glutathione-S-Transferase in Anti-Cancer Drug Resistance. Oncogene 2003, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treviño, L.R.; Shimasaki, N.; Yang, W.; Panetta, J.C.; Cheng, C.; Pei, D.; Chan, D.; Sparreboom, A.; Giacomini, K.M.; Pui, C.-H.; et al. Germline Genetic Variation in an Organic Anion Transporter Polypeptide Associated with Methotrexate Pharmacokinetics and Clinical Effects. JCO 2009, 27, 5972–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relling, M.V.; Schwab, M.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Suarez-Kurtz, G.; Pui, C.-H.; Stein, C.M.; Moyer, A.M.; Evans, W.E.; Klein, T.E.; Antillon-Klussmann, F.G.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for Thiopurine Dosing Based on TPMT and NUDT15 Genotypes: 2018 Update. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 105, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) | Protocol Development | CTEP. Available online: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm#ctc_50 (accessed on 26 April 2025).
- Sherry, S.T.; Ward, M.-H.; Kholodov, M.; Baker, J.; Phan, L.; Smigielski, E.M.; Sirotkin, K. dbSNP: The NCBI Database of Genetic Variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbarino, J.M.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. PharmGKB: A Worldwide Resource for Pharmacogenomic Information. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst. Biol. Med. 2018, 10, e1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annotation of RNPGx Guideline for Methotrexate and ABCB1, MTHFR, SLC19A1, SLCO1B1. Available online: https://www.pharmgkb.org/guidelineAnnotation/PA166202781 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Artika, I.M.; Dewi, Y.P.; Nainggolan, I.M.; Siregar, J.E.; Antonjaya, U. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction: Current Techniques, Applications, and Role in COVID-19 Diagnosis. Genes 2022, 13, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R: The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Wiczer, T.; Dotson, E.; Tuten, A.; Phillips, G.; Maddocks, K. Evaluation of Incidence and Risk Factors for High-Dose Methotrexate-Induced Nephrotoxicity. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2016, 22, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeske, K.A.; Ji, L.; Freyer, D.R.; Gaynon, P.; Ruccione, K.; Butturini, A.; Avramis, V.I.; Siegel, S.; Matloub, Y.; Seibel, N.L.; et al. Comparative Toxicity by Sex Among Children Treated for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Report From the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2015, 62, 2140–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, K.E.; Rohlicek, C.V.; Andelfinger, G.U.; Michaud, J.; Bigras, J.-L.; Richter, A.; Mackenzie, R.E.; Rozen, R. The MTHFD1 p.Arg653Gln Variant Alters Enzyme Function and Increases Risk for Congenital Heart Defects. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 30, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rs2236225 RefSNP Report—dbSNP—NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp/rs2236225 (accessed on 23 August 2024).
- Chen, Y.; Shen, Z. Gene Polymorphisms in the Folate Metabolism and Their Association with MTX-Related Adverse Events in the Treatment of ALL. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 4913–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erčulj, N.; Kotnik, B.F.; Debeljak, M.; Jazbec, J.; Dolžan, V. Influence of Folate Pathway Polymorphisms on High-Dose Methotrexate-Related Toxicity and Survival in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2012, 53, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajinovic, M.; Lemieux-Blanchard, É.; Chiasson, S.; Primeau, M.; Costea, I.; Moghrabi, A. Role of Polymorphisms in MTHFR and MTHFD1 Genes in the Outcome of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Pharmacogenomics J. 2004, 4, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germline Genetic Polymorphisms May Influence Chemotherapy Response and Disease Outcome in Osteosarcoma—Windsor—2012—Cancer—Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cncr.26472 (accessed on 23 August 2024).
- Goyette, P.; Pai, A.; Milos, R.; Frosst, P.; Tran, P.; Chen, Z.; Chan, M.; Rozen, R. Gene Structure of Human and Mouse Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR). Mamm. Genome 1998, 9, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Feng, C.; Zhou, X.; Tu, C.; Li, Z. MTHFR Polymorphism Is Associated with Severe Methotrexate-Induced Toxicity in Osteosarcoma Treatment. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 781386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpa, V.; Kalinderi, K.; Fidani, L.; Tragiannidis, A. Association of microRNA Polymorphisms with Toxicities Induced by Methotrexate in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Hematol. Rep. 2023, 15, 634–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Liang, L.; Ji, L.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ongaro, A. MTHFR Gene Polymorphisms and Methotrexate Toxicity in Adult Patients with Hematological Malignancies: A Meta-Analysis. Pharmacogenomics 2016, 17, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Lopez, E.; Martin-Guerrero, I.; Ballesteros, J.; Garcia-Orad, A. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of MTHFR Polymorphisms in Methotrexate Toxicity Prediction in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Pharmacogenomics J. 2013, 13, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Guo, Y.; Su, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hui, W.; Zhao, H.; Hu, R.; Sun, W. Influence of MTHFR C677T Polymorphism on High-Dose Methotrexate-Related Toxicity in Patients with Primary Central Nervous System Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 21, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aráoz, H.V.; D’Aloi, K.; Foncuberta, M.E.; Sanchez La Rosa, C.G.; Alonso, C.N.; Chertkoff, L.; Felice, M. Pharmacogenetic Studies in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Argentina. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Kong, Q.; Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Mai, H.; Zhen, Z.; Zhou, D.; Chen, H. Relationship between Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Gene Polymorphisms and Methotrexate Drug Metabolism and Toxicity. Transl. Pediatr. 2023, 12, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giletti, A.; Vital, M.; Lorenzo, M.; Cardozo, P.; Borelli, G.; Gabus, R.; Martínez, L.; Díaz, L.; Assar, R.; Rodriguez, M.N.; et al. Methotrexate Pharmacogenetics in Uruguayan Adults with Hematological Malignant Diseases. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 109, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.A.; Stewart, R.K.; Smith, G.B.; Massey, T.E.; Bell, D.A. Human Glutathione S-Transferase P1 Polymorphisms: Relationship to Lung Tissue Enzyme Activity and Population Frequency Distribution. Carcinogenesis 1998, 19, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Cho, Y.-A.; Kim, D.-C.; Lee, K.-E. Association between Genetic Polymorphism of GSTP1 and Toxicities in Patients Receiving Platinum-Based Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocedi, A.; Noce, A.; Marrone, G.; Noce, G.; Cattani, G.; Gambardella, G.; Di Lauro, M.; Di Daniele, N.; Ricci, G. Glutathione Transferase P1-1 an Enzyme Useful in Biomedicine and as Biomarker in Clinical Practice and in Environmental Pollution. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishi, S.; Cheng, C.; French, D.; Pei, D.; Das, S.; Cook, E.H.; Hijiya, N.; Rizzari, C.; Rosner, G.L.; Frudakis, T.; et al. Ancestry and Pharmacogenetics of Antileukemic Drug Toxicity. Blood 2007, 109, 4151–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.-Y.; Peng, S.-Y.; Xing, K.; Fan, L.; Tan, S.-L.; Luo, Z.-Y.; Yuan, H.-Y.; Xu, P.; Luo, J.-Q. Evaluating the Role of GSTP1 Genetic Polymorphism (Rs1695, 313A>G) as a Predictor in Cyclophosphamide-Induced Toxicities. Medicine 2021, 100, e24423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sociodemographic and Clinical Variables | Sex | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female 49 (45.79%) | Male 58 (54.21%) | ||||||
| n | % | Median (p25–p75) | n | % | Median (p25–p75) | ||
| Family history of cancer | 21 | 42.86 | 27 | 46.55 | 0.70 | ||
| Cancer diagnosis | |||||||
| Acute lymphoblastic leukemia | 32 | 65.31 | 34 | 58.62 | 0.53 | ||
| Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma | 7 | 14.29 | 12 | 20.69 | |||
| Osteosarcoma | 7 | 14.29 | 10 | 17.24 | |||
| Ependymoma | 3 | 6.12 | 1 | 1.72 | |||
| Undifferentiated sarcoma of small cells | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 1.72 | |||
| Age at diagnosis | 6 (4–8) | 6.9 (3–11.5) | 0.24 | ||||
| Concomitantly administered antineoplastic drug * | 37 | 75.51 | 45 | 77.59 | 0.80 | ||
| Elimination > 48 h | 36 | 73.47 | 36 | 62.07 | 021 | ||
| General toxicity grade I–IV | 33 | 67.35 | 50 | 86.21 | 0.02 | ||
| General toxicity grade III–IV | 30 | 61.22 | 42 | 72.41 | 0.23 | ||
| Hematologic toxicity | |||||||
| Hematologic toxicity grade I–IV | 26 | 53.06 | 40 | 68.97 | 0.09 | ||
| Neutropenia grade I–IV | 25 | 51.02 | 39 | 67.24 | 0.09 | ||
| Thrombocytopenia grade I–IV | 12 | 24.49 | 27 | 46.55 | 0.02 | ||
| Hematologic toxicity grade III–IV | 22 | 44.9 | 33 | 56.90 | 0.21 | ||
| Gastrointestinal toxicity | |||||||
| Gastrointestinal toxicity grade I–IV | 26 | 53.6 | 39 | 67.24 | 0.13 | ||
| Diarrhea grade I–IV | 6 | 12.24 | 9 | 15.52 | 0.62 | ||
| Mucositis grade I–IV | 7 | 14.29 | 19 | 32.76 | 0.03 | ||
| Nausea and vomiting grade I–IV | 20 | 40.82 | 25 | 43.10 | 0.81 | ||
| Gastrointestinal toxicity grade III–IV | 4 | 8.16 | 15 | 25.86 | 0.02 | ||
| Liver toxicity | |||||||
| Liver toxicity grade I–VI | 18 | 36.73 | 20 | 34.48 | 0.80 | ||
| Liver toxicity grade III–IV | 14 | 28.57 | 13 | 22.41 | 0.33 | ||
| Kidney toxicity | |||||||
| Kidney toxicity grade I–VI | 2 | 4.08 | 5 | 8.62 | 0.34 | ||
| Kidney toxicity grade III–IV | 2 | 4.08 | 2 | 3.45 | 0.86 | ||
| Pulmonary toxicity | 4 | 8.16 | 4 | 6.90 | 0.80 | ||
| Skin toxicity | 1 | 2.04 | 8 | 12.07 | 0.14 | ||
| Sociodemographic and Clinical Variables | Toxicity | OR | 95%CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex | General toxicity (grades I–IV) | 2.30 | 1.06–9.07 | 0.02 |
| Gastrointestinal toxicity (grades III–IV) | 3.87 | 1.11–17.32 | 0.02 | |
| Mucositis (grades I–IV) | 2.89 | 1.02–9.07 | 0.03 | |
| Thrombocytopenia (grades I–IV) | 2.66 | 1.09–6.78 | 0.02 | |
| Diagnosis of ALL | Hepatic toxicity (grades III–IV) | 5.81 | 1.07–108.36 | <0.01 |
| MTX clearance > 48 h | 3.16 | 1.11–9.34 | 0.02 | |
| Diagnosis of NHL | Gastrointestinal toxicity (grades III–IV) | 3.93 | 1.20–12.85 | 0.03 |
| Mucositis (grades I–IV) | 5.60 | 1.90–17.37 | <0.01 | |
| Diagnosis of OS | Gastrointestinal toxicity (grades I–IV) | 7.96 | 2.03–53.13 | <0.01 |
| Nausea and vomiting (grades I–IV) | 10.00 | 2.89–48.86 | <0.01 | |
| Hepatic toxicity (grades III–IV) | 3.11 | 1.23–6.11 | <0.01 | |
| Clearance MTX > 48 h | 6.41 | 1.49–35.20 | 0.02 | |
| Age at diagnosis | Gastrointestinal toxicity (grades I–IV) | 1.71 | 1.05–1.31 | <0.01 |
| Nausea and vomiting (grades I–IV) | 1.20 | 1.09–1.34 | <0.01 | |
| Concomitant antineoplastic agent * | Hematologic toxicity (grades III–IV) | 2.96 | 1.06–8.91 | 0.02 |
| Variables | q-Value | p-Value | OR | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal toxicity (grades III–IV) | ||||
| MTHFD1 rs2236225 (AA vs. AG/GG) | 0.06 | 0.03 | 6.15 | 1.29–35.41 |
| Sex (male vs. female) | 0.06 | 0.03 | 3.71 | 1.20–14.10 |
| Hematological toxicity (grades I–IV) | ||||
| MTHFR rs1801133 (A vs. GG) | 0.02 | <0.01 | 4.23 | 1.73–10.98 |
| GSTP1 rs1695 (AA vs. G) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 2.88 | 1.23–7.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marangoni-Iglecias, L.M.; Sánchez-Martin, A.; Pineda-Lancheros, L.E.; Cura, Y.; Marquez-Pete, N.; Gálvez-Navas, J.M.; Báez-Gutiérrez, N.; Jara-Vera, A.M.d.L.; Urrutia-Maldonado, E.; Pérez-Ramírez, C.; et al. Impact of Pharmacogenetics on High-Dose Methotrexate Toxicity in Pediatric Oncology. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050585
Marangoni-Iglecias LM, Sánchez-Martin A, Pineda-Lancheros LE, Cura Y, Marquez-Pete N, Gálvez-Navas JM, Báez-Gutiérrez N, Jara-Vera AMdL, Urrutia-Maldonado E, Pérez-Ramírez C, et al. Impact of Pharmacogenetics on High-Dose Methotrexate Toxicity in Pediatric Oncology. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(5):585. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050585
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarangoni-Iglecias, Luciana Maria, Almudena Sánchez-Martin, Laura Elena Pineda-Lancheros, Yasmín Cura, Noelia Marquez-Pete, José María Gálvez-Navas, Nerea Báez-Gutiérrez, Adrián Manuel de La Jara-Vera, Emilia Urrutia-Maldonado, Cristina Pérez-Ramírez, and et al. 2025. "Impact of Pharmacogenetics on High-Dose Methotrexate Toxicity in Pediatric Oncology" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 5: 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050585
APA StyleMarangoni-Iglecias, L. M., Sánchez-Martin, A., Pineda-Lancheros, L. E., Cura, Y., Marquez-Pete, N., Gálvez-Navas, J. M., Báez-Gutiérrez, N., Jara-Vera, A. M. d. L., Urrutia-Maldonado, E., Pérez-Ramírez, C., & Jiménez-Morales, A. (2025). Impact of Pharmacogenetics on High-Dose Methotrexate Toxicity in Pediatric Oncology. Pharmaceutics, 17(5), 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050585







