Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC)-Based Topical Formulation of Hesperidin for Effective Treatment of Psoriasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
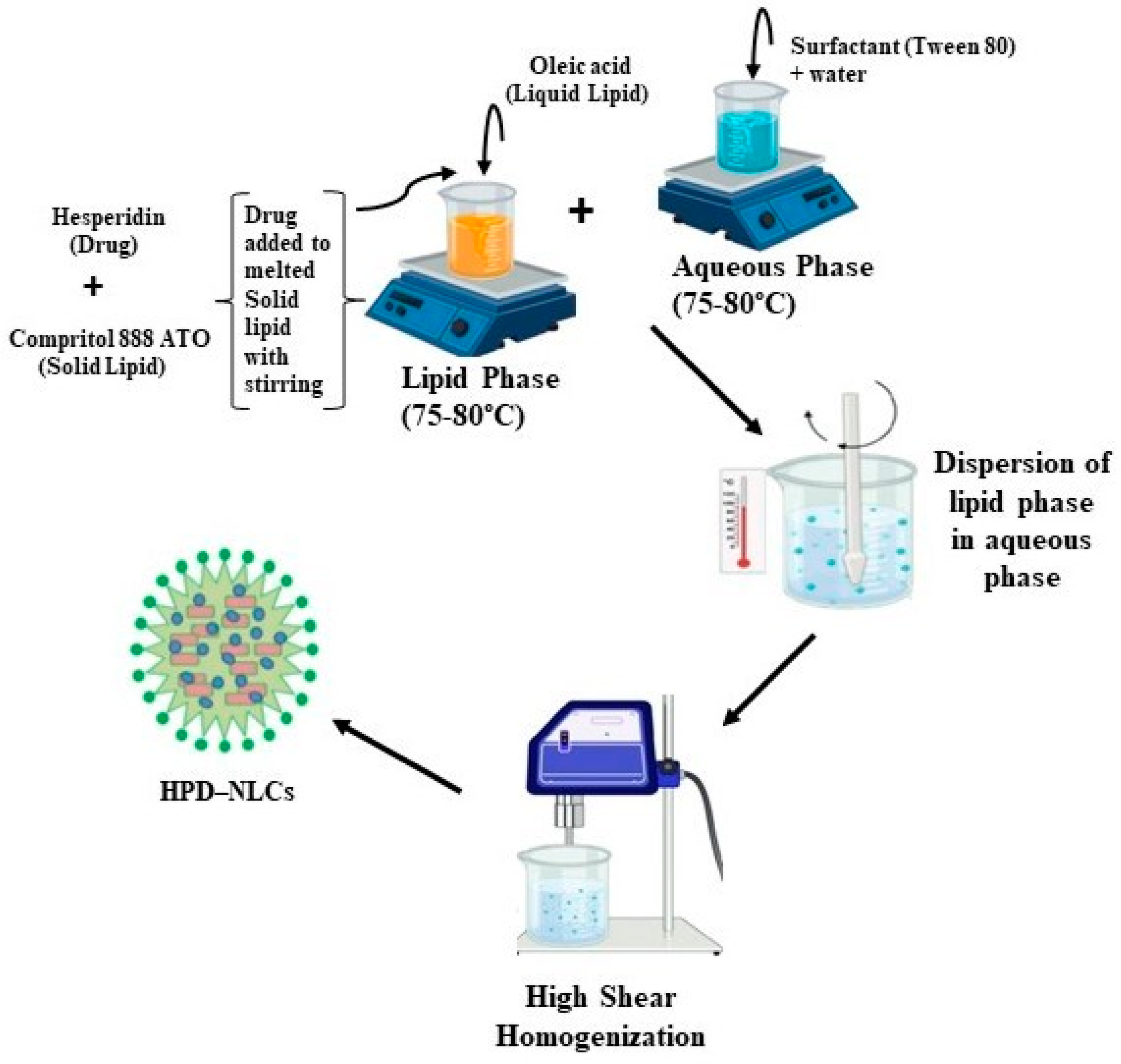
2.1. Fabrication of Hesperidin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (HPD-NLC)
2.2. Statistical Experimental Design
2.3. Lyophilization
2.4. Characterization of HPD-NLC
2.4.1. Particle Size and PDI of Optimized HPD-NLC
2.4.2. EE of Optimized HPD-NLC
2.4.3. High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM) of Optimized HPD-NLC
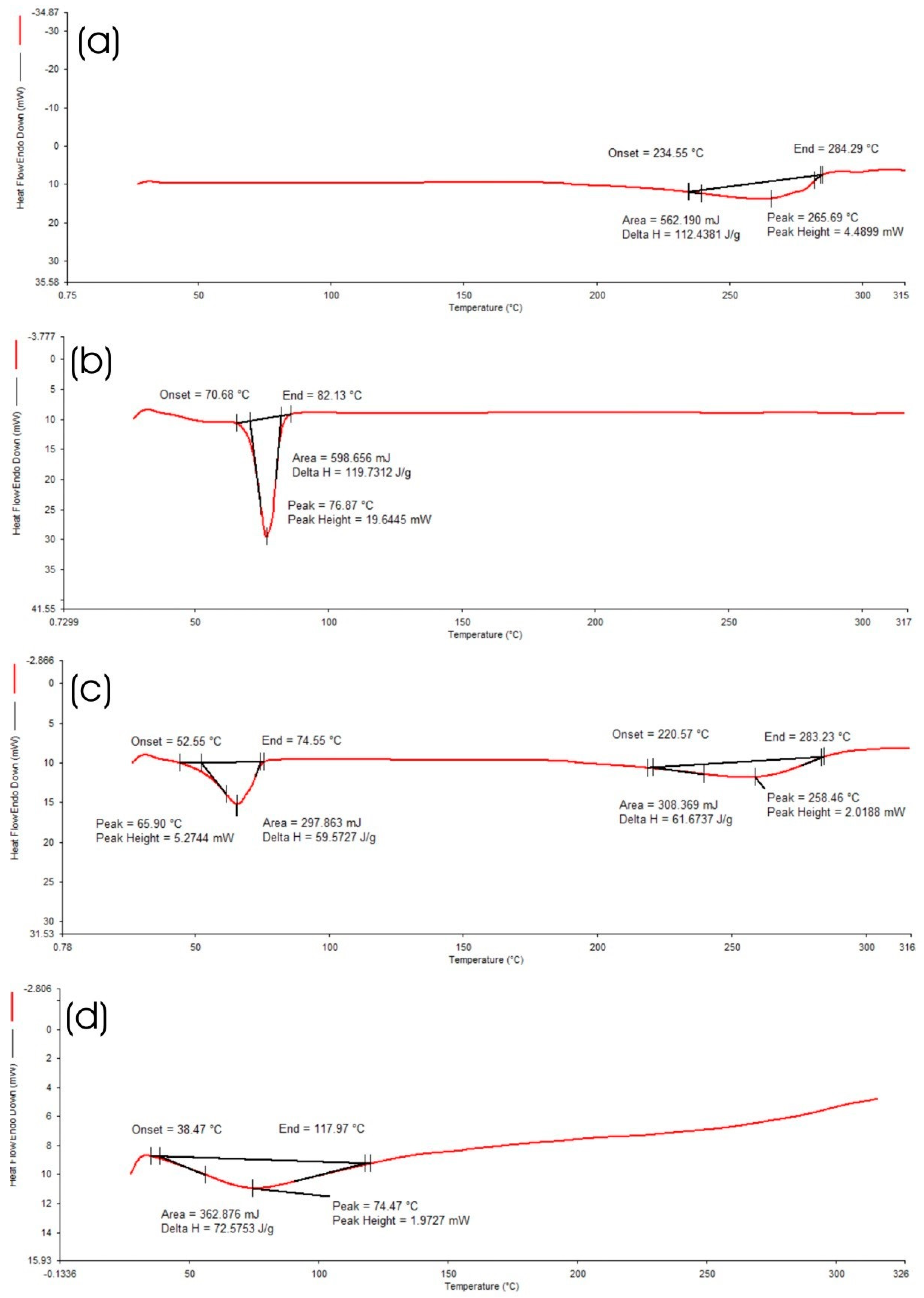
2.4.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) of Optimized HPD-NLC
2.4.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis of Optimized HPD-NLC
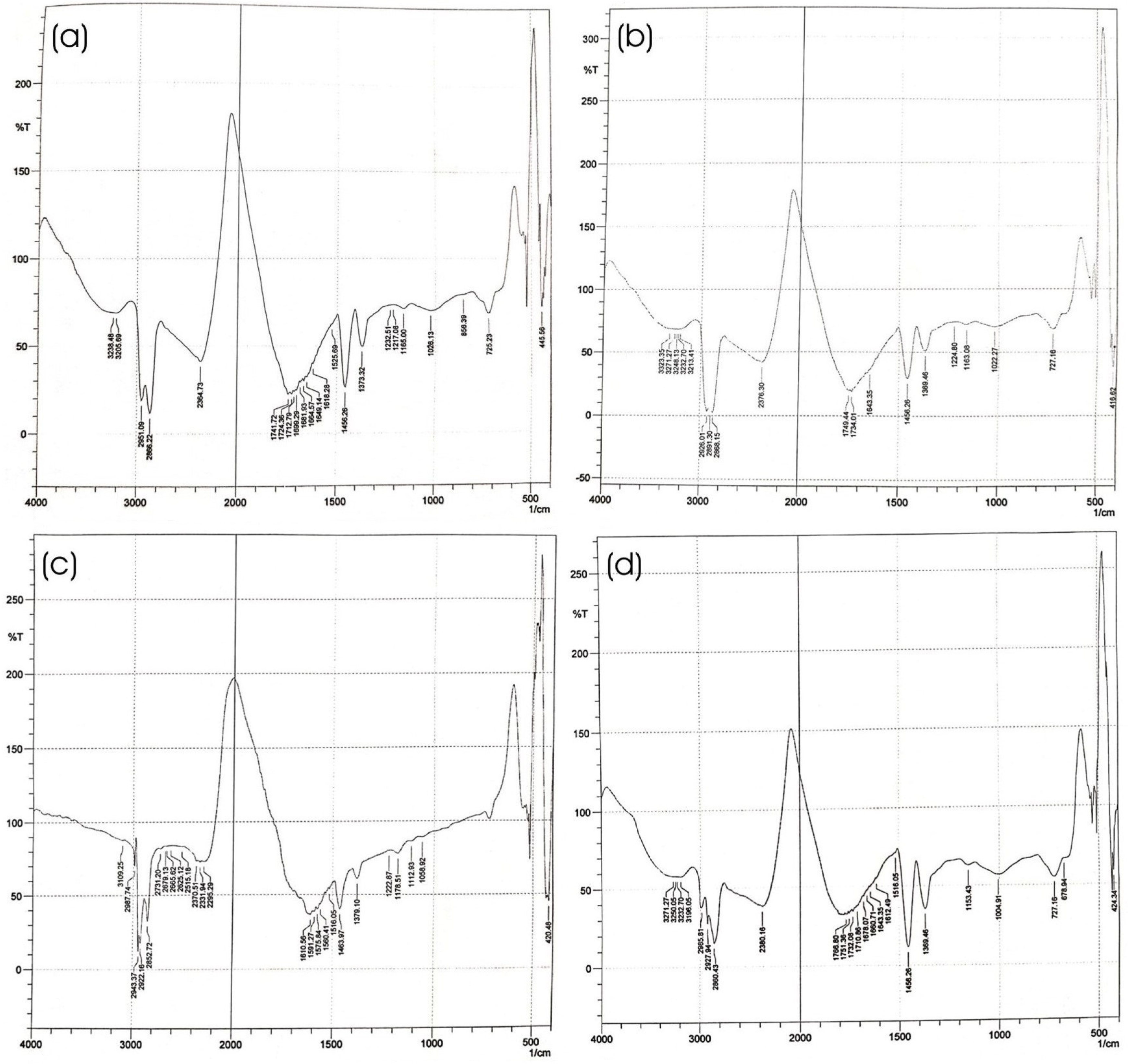
2.4.6. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy of Optimized HPD-NLC
2.5. In Vitro Evaluation of Optimized HPD-NLC
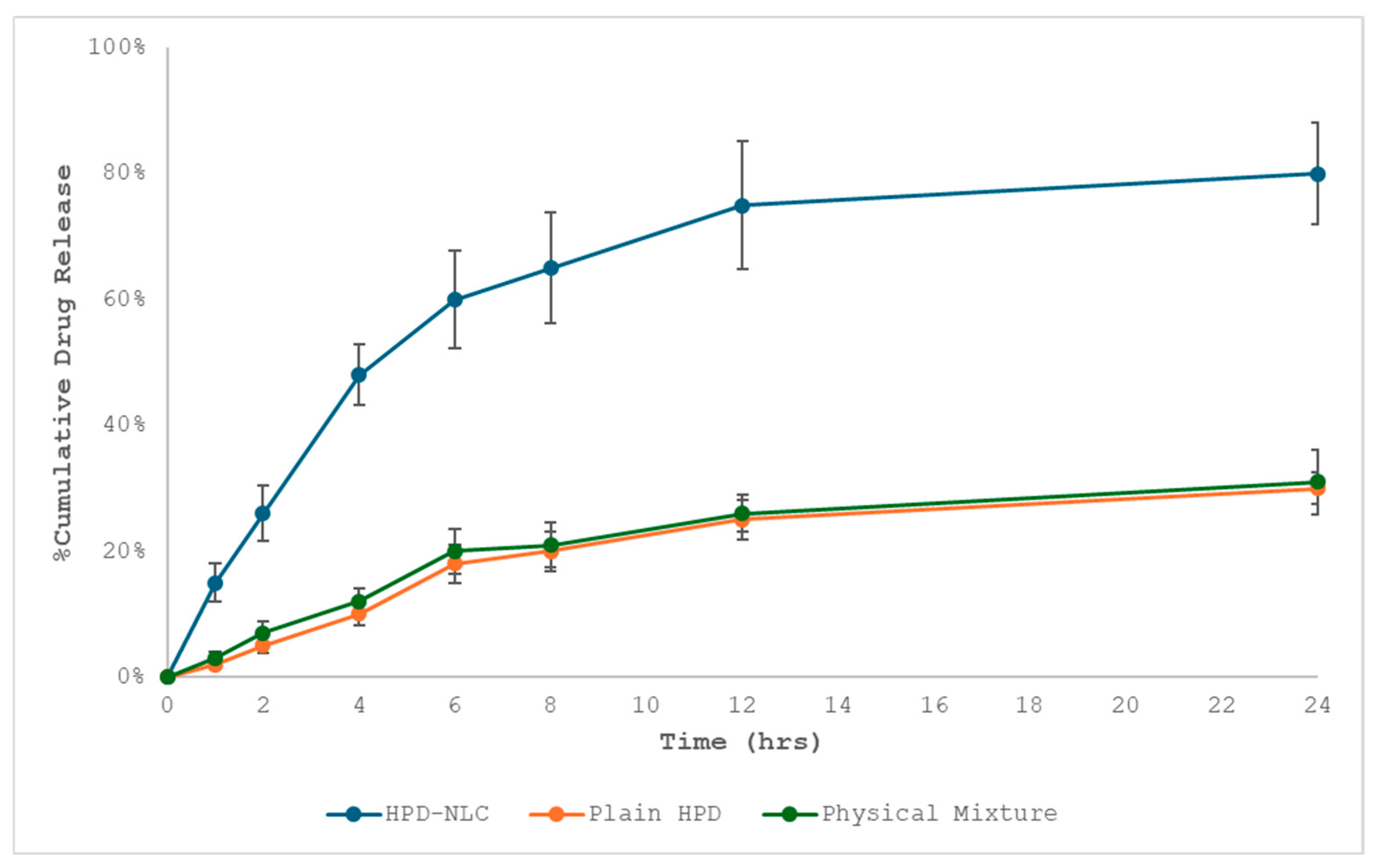
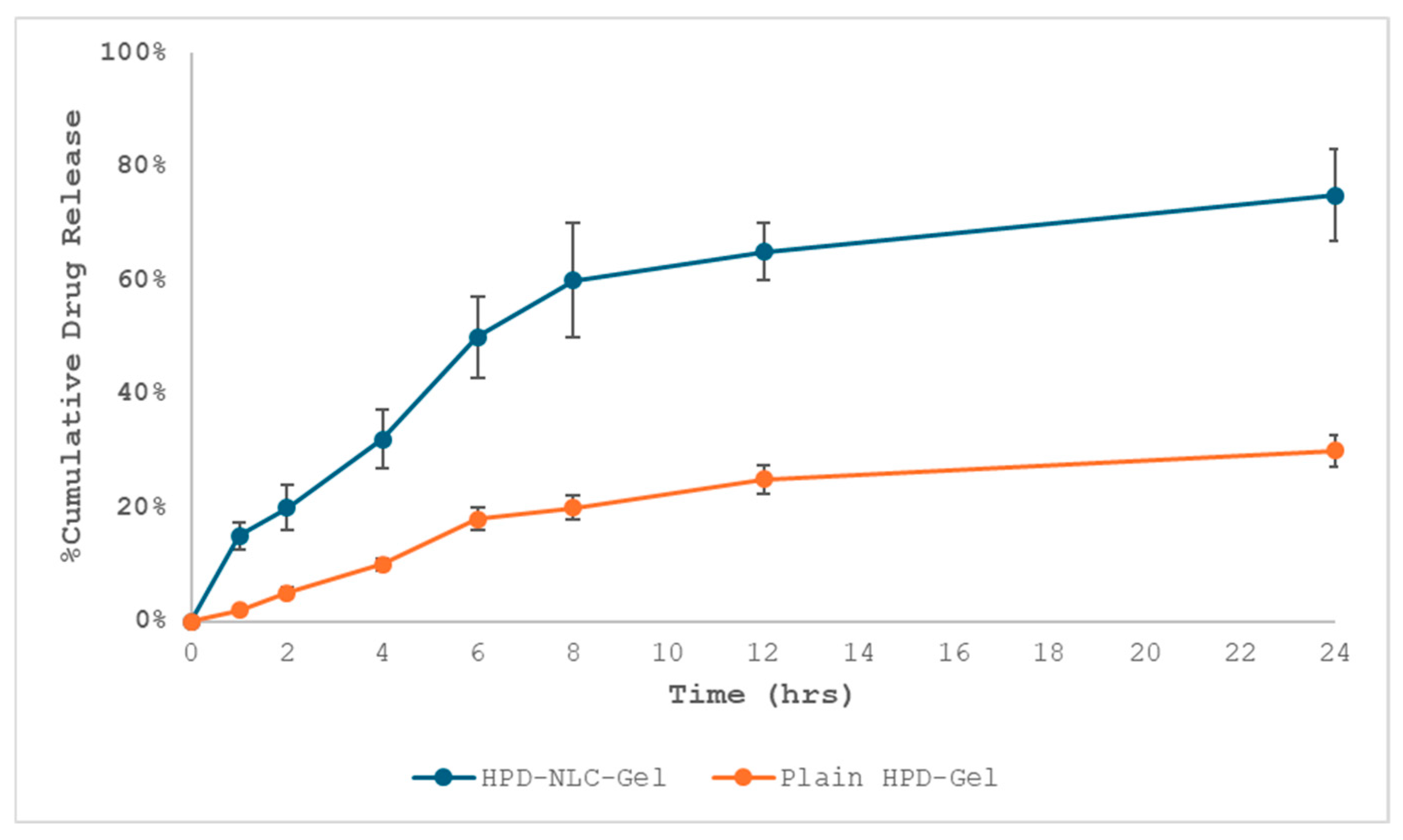
2.5.1. In Vitro Drug Diffusion Study
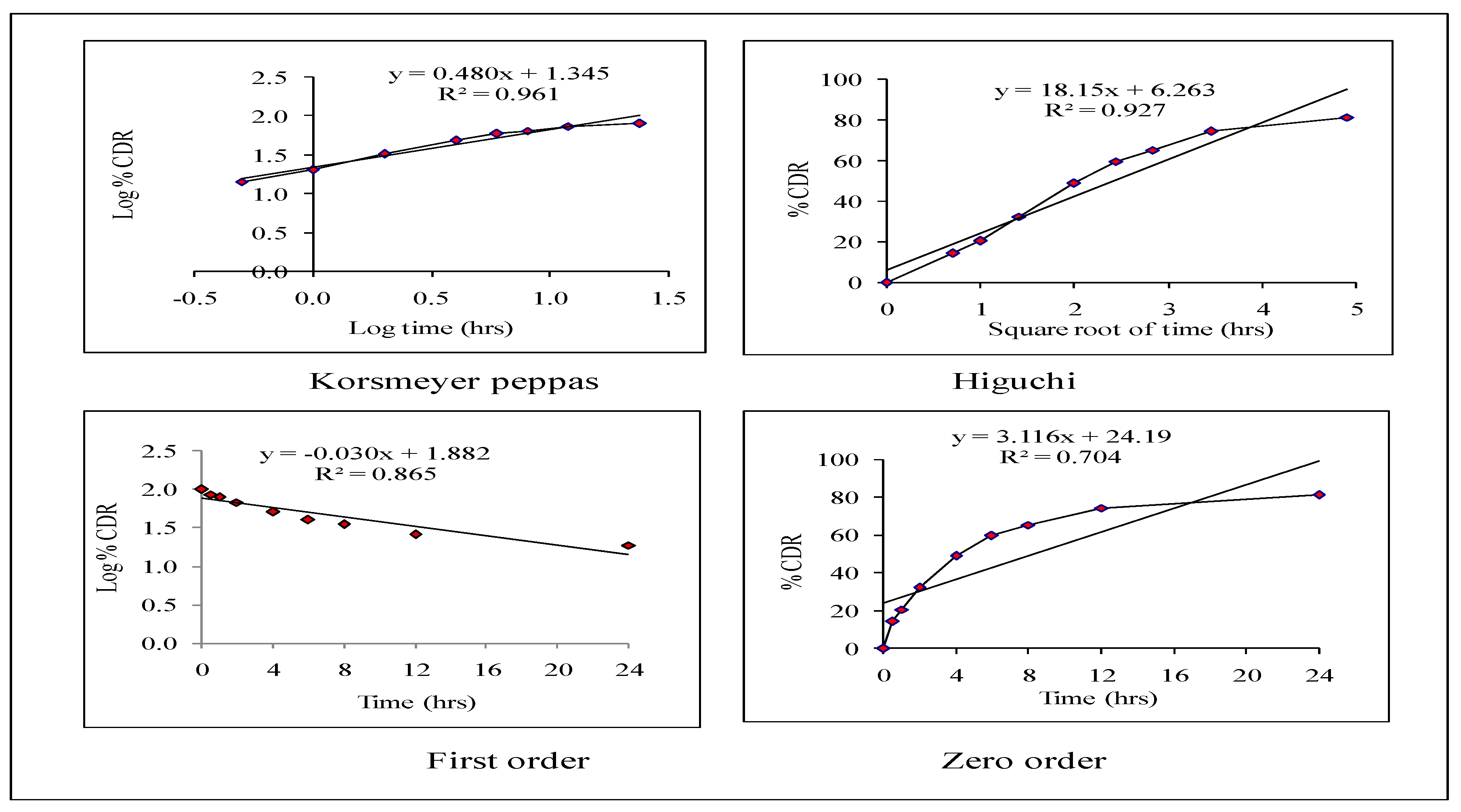
2.5.2. Release Kinetics
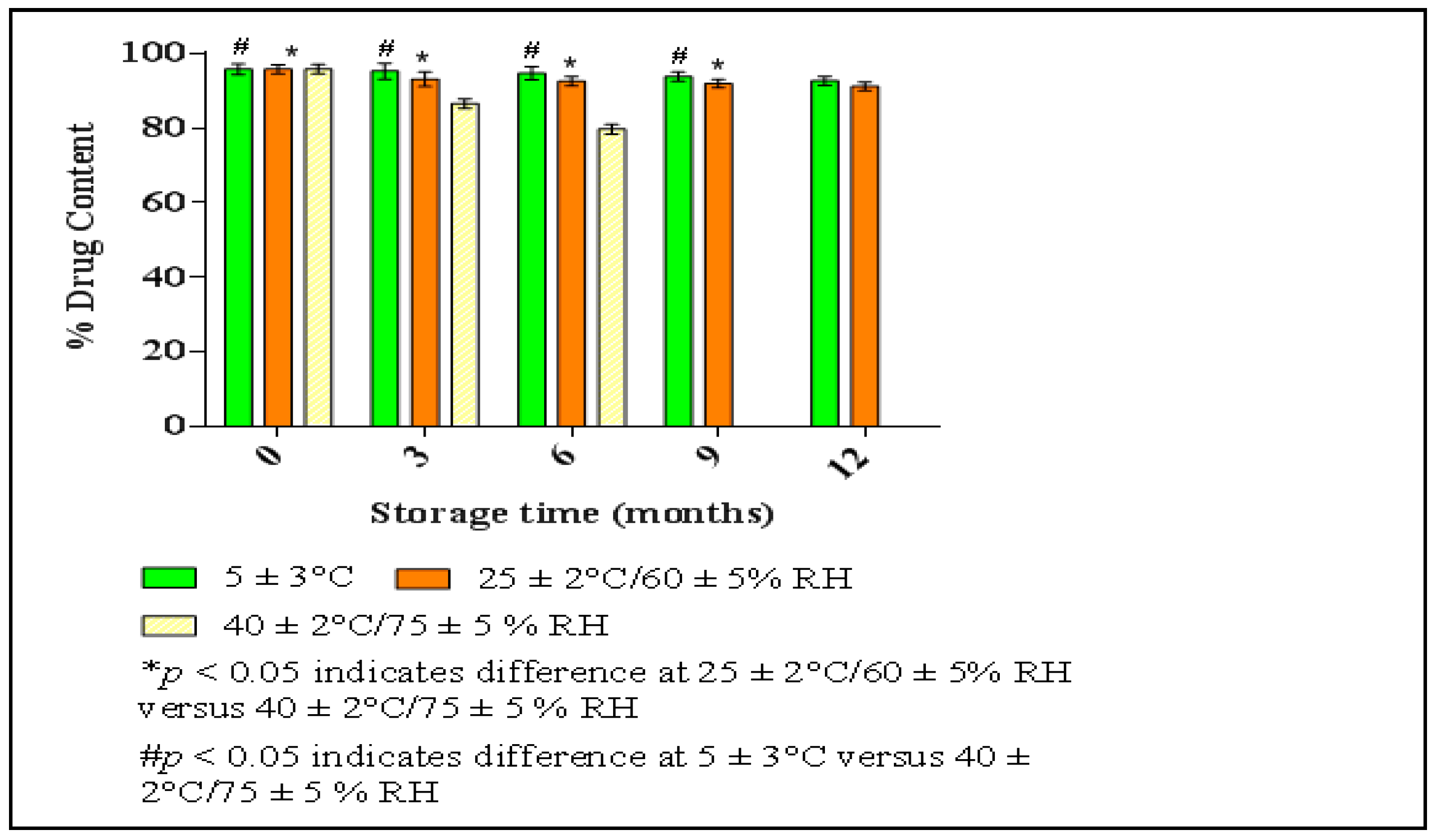
2.5.3. Stability Study of Optimized HPD-NLCs
2.6. Preparation of Optimized HPD-NLC Loaded Topical Gel (HPD-NLC-Gel)
2.7. Characterization of Optimized HPD-NLC-Gel
2.7.1. Determination of the Physical Appearance of HPD-NLC-Gel
2.7.2. Measurement of pH Value
2.7.3. Measurement of Viscosity
2.7.4. Measurement of Spreadability
2.7.5. Drug Content
2.7.6. In Vitro Drug Diffusion Studies of HPD-NLC-Gel
2.7.7. Stability Study of HPD-NLC-Gel
2.8. In Vivo Study of Optimized HPD-NLC-Gel
2.8.1. Animals and Ethics Statement
2.8.2. In Vivo Antipsoriatic Activity
2.8.3. PASI Score
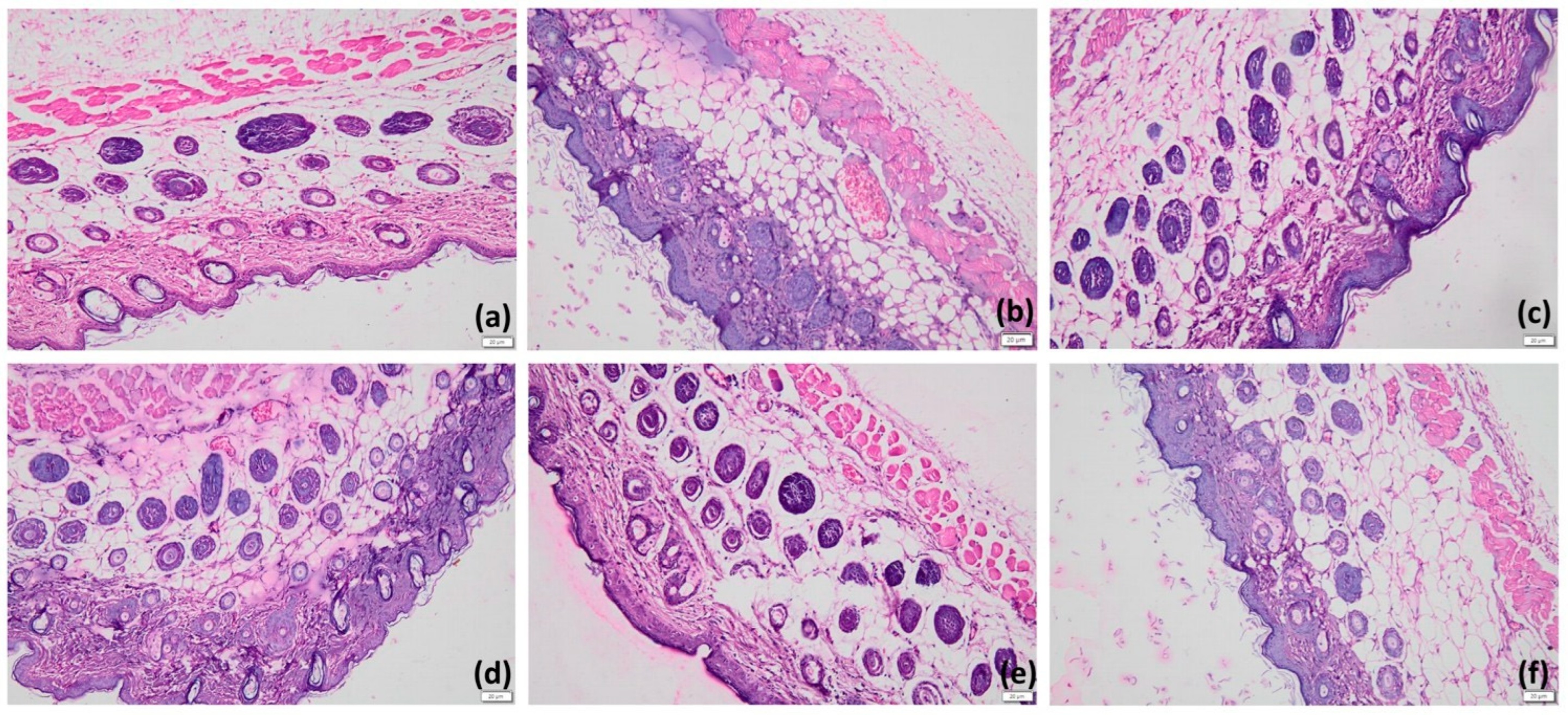
2.8.4. Histopathological Examination
3. Results
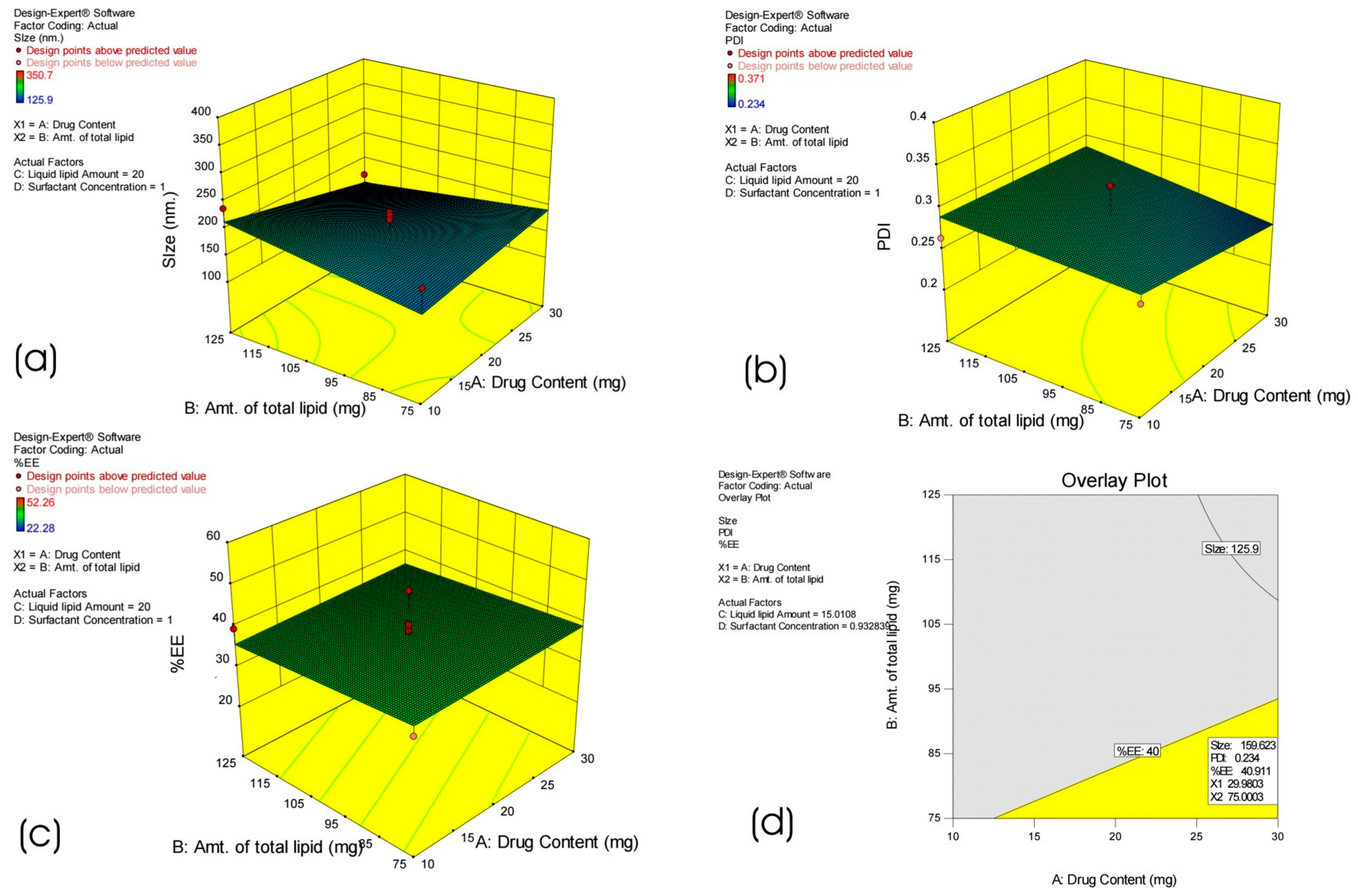
3.1. Optimization of HPD-NLC
3.2. Morphological Characterization of HPD-NLC
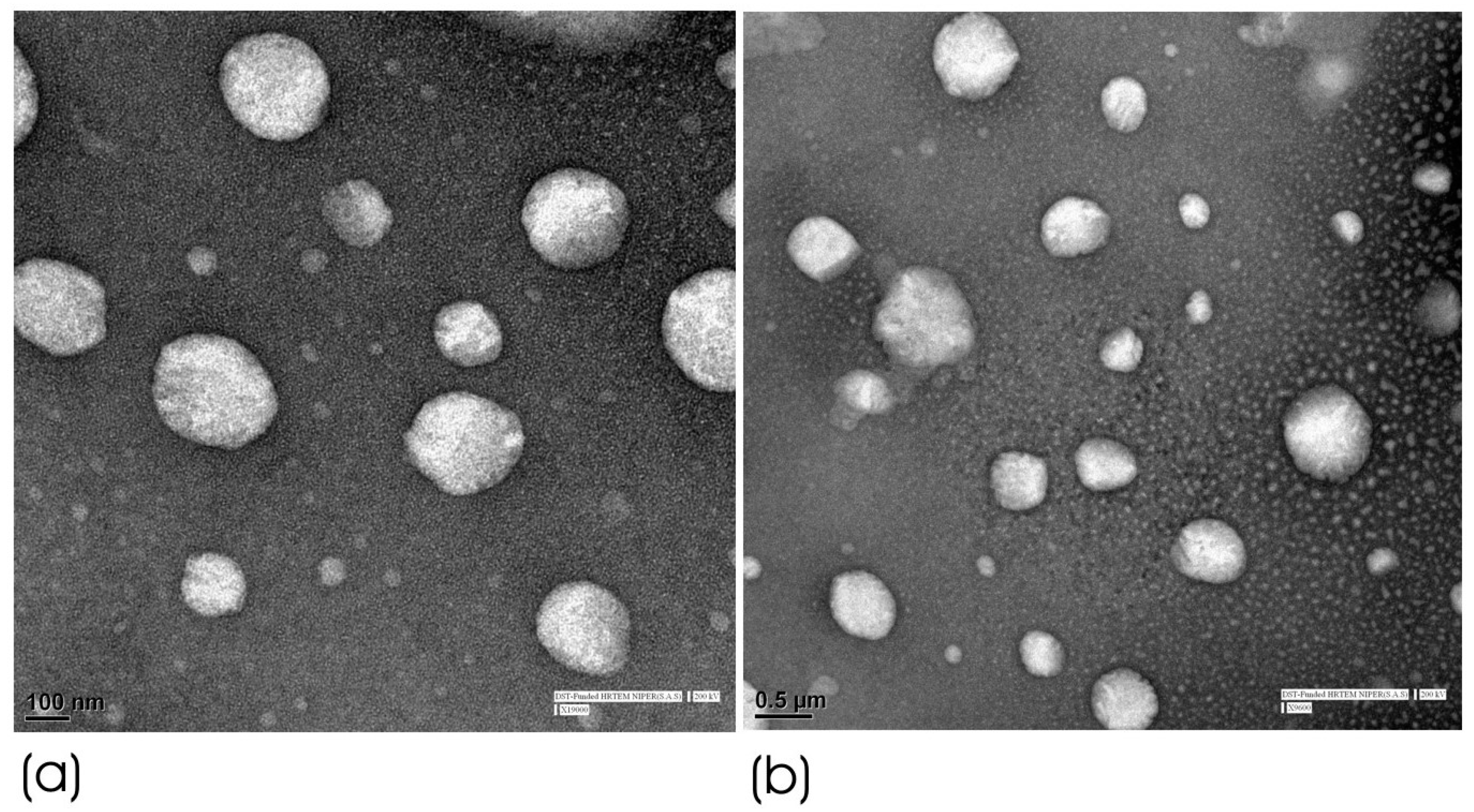
3.2.1. HRTEM
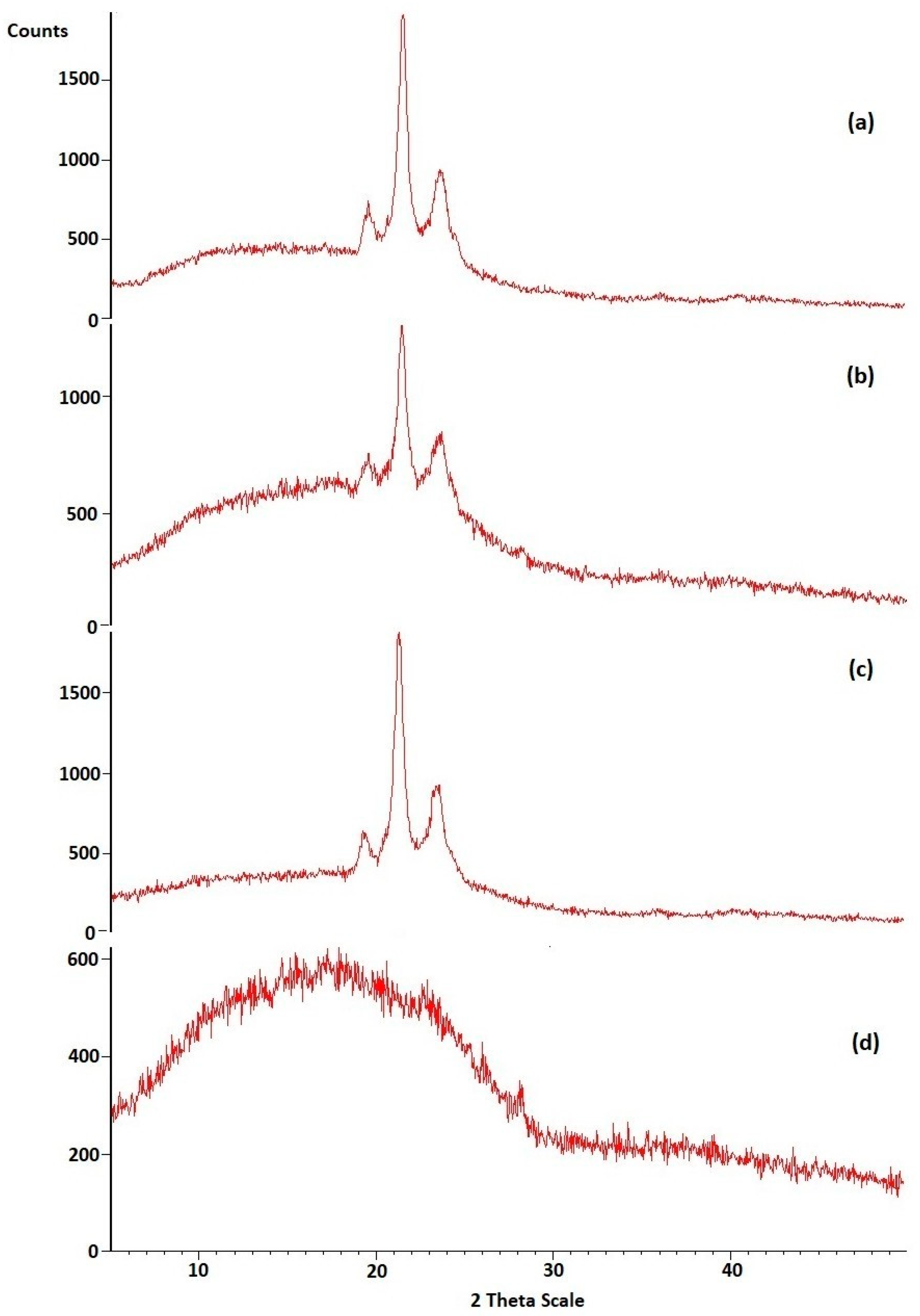
3.2.2. XRD of Optimized HPD-NLC
3.2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Study
3.2.4. DSC Analysis
3.2.5. Particle Size and PDI
3.3. In Vitro Diffusion Study of Optimized HPD-NLC
3.4. Release Kinetics of Optimized HPD-NLC
3.5. Stability Study of Optimized HPD-NLC
3.6. Formulation of Optimized HPD-NLC-Gel
3.7. Physical Characterization of Optimized HPD-NLC-Gel
3.7.1. Determination of the Physical Appearance
3.7.2. Spreadability
3.7.3. pH Value
3.7.4. Viscosity
3.7.5. Stability Study of HPD-NLC-Gel
3.8. In Vitro Drug Release Study of HPD-NLC-Gel
3.9. Release Kinetics from HPD-NLC-Gel
3.10. In Vivo Antipsoriatic Activity of HPD-NLC-Gel
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BBD | Box–Behnken design |
| CCD | Central composite designs |
| CCP | Chitkara college of pharmacy |
| CCSEA | Committee for control and supervision of experiments on animals |
| DSC | Differential scanning calorimetry |
| EE | Entrapment efficiency |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared |
| g | grams |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| HPD | Hesperidin |
| HPMC | Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose |
| HRTEM | High-resolution transmission electron microscopy |
| IAEC | Institutional animal ethical committee |
| ICH | International council on harmonisation |
| NIPER | National institute of pharmaceutical education and research |
| NLCs | Nanostructured lipid carriers |
| OECD | Organisation for economic cooperation and development |
| PASI | Psoriatic area and severity index |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer saline |
| PDI | Polydispersity index |
| QbD | Quality by design |
| RH | Relative humidity |
| SLNs | Solid lipid nanoparticles |
| SLS | Sodium lauryl sulphate |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- Almenara-Blasco, M.; Gracia-Cazaña, T.; Poblador-Plou, B.; Laguna-Berna, C.; Carmona-Pírez, J.; Navarro-Bielsa, A.; Prados-Torres, A.; Gimeno-Miguel, A.; Gilaberte, Y. Multimorbidity of Psoriasis: A Large-Scale Population Study of Its Associated Comorbidities. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, M. Challenges and Future Trends in the Treatment of Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendrisch, F.; Haarhaus, B.; Krieger, N.; Quirin, K.-W.; Schempp, C.M.; Wölfle, U. The Effect of Herbal Medicinal Products on Psoriasis-Like Keratinocytes. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.; Rizwanullah, M.; Mir, S.R.; Amin, S. Statistically Optimized Tacrolimus and Thymoquinone Co-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Gel for Improved Topical Treatment of Psoriasis. Gels 2023, 9, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xie, X.; Zhang, L.; Meng, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, M.; Zhai, C.; Liu, Z.; Di, T.; Zhang, L.; et al. Hesperidin Inhibits Keratinocyte Proliferation and Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Dermatitis via the IRS-1/ERK1/2 Pathway. Life Sci. 2019, 219, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, X. Enhancement of the Water Solubility and Antioxidant Activity of Hesperidin by Chitooligosaccharide. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 2422–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghddam, S.M.M.; Ahad, A.; Aqil, M.; Imam, S.S.; Sultana, Y. Optimization of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Topical Delivery of Nimesulide Using Box–Behnken Design Approach. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Aslam, M.; Khan, A.; Imam, S.S.; Aqil, M.; Sultana, Y. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers of Pioglitazone for Transdermal Application: From Experimental Design to Bioactivity Detail. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avasatthi, V.; Pawar, H.; Dora, C.P.; Bansod, P.; Gill, M.S.; Suresh, S. A Novel Nanogel Formulation of Methotrexate for Topical Treatment of Psoriasis: Optimization, In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2016, 21, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, S.N.A.; Ashari, S.E.; Zainuddin, N.; Hassan, M. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers-Hydrogels System for Drug Delivery: Nanohybrid Technology Perspective. Molecules 2022, 27, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gündoğdu, E.; Demir, E.-S.; Ekinci, M.; Özgenc, E.; Ilem-Özdemir, D.; Şenyigit, Z.; Bermejo, M. An Innovative Formulation Based on Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Imatinib Delivery: Pre-Formulation, Cellular Uptake, and Cytotoxicity Studies. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajiboye, A.L.; Nandi, U.; Galli, M.; Trivedi, V. Olanzapine Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers via High Shear Homogenization and Ultrasonication. Sci. Pharm. 2021, 89, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardouh, A.R.; Faheim, S.H.; Noah, A.T.; Ghorab, M.M. Influence of Formulation Factors on the Size of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers and Nanoemulsions Prepared by High Shear Homogenization. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 10, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solikah, A.; Iskandarsyah; Harmita. Box-Behnken Design for Optimization of Nanostructured Lipid Carrier Sonication Conditions from Mixtures of Palm Stearin and Palm Olein. Indones. J. Pharm. 2021, 32, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, A.M.; Hassan, M.; El-Setouhy, D.A.; Tayel, S.A.; Al-Mahallawi, A.M. Statistical Optimization of Hyaluronic Acid-Enriched Ultra-Deformable Elastomers for Ocular Delivery of Voriconazole via Box–Behnken Design: In Vitro Characterization and In Vivo Evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teja, K.; Spandana, A.K.M.; Patil, A.B.; Preethi, S. Formulation, Optimization, and Evaluation of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers of Resveratrol. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Appl. 2022, 7, 961–987. [Google Scholar]
- Kaithwas, V.; Dora, C.P.; Kushwah, V.; Jain, S. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers of Olmesartan Medoxomil with Enhanced Oral Bioavailability. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 154, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, P.P.; Rajeevan, R.; Maity, S.; Nayak, Y.; Narayan, R.; Mehta, C.H.; Velagacherla, V.; Konuri, A.; Nayak, U.Y. Development of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Loaded Caffeic Acid Topical Cream for Prevention of Inflammation in a Wistar Rat Model. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 13, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, C.H.; Narayan, R.; Acharya, S.; Nayak, U.Y. Design and Development of Surface-Modified Epigallocatechin 3-Gallate NanoCubogel for Localized Delivery to Oral Submucous Fibrosis Therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 66, 102911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorle, A.; Pawar, T.; Mahhirao, J. Design, Development and Characterization of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs) by HPH Method Loaded with Anticancer Drug. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2023, 13, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, H.; Shah, S.U.; Ali, Z.; Khan, A.U.; Rajput, I.B.; Farid, A.; Mohaini, M.A.; Alsalman, A.J.; Al Hawaj, M.A.; Mahmood, S.; et al. In Vitro and Ex Vivo Evaluation of Fluocinolone Acetonide–Acitretin Coloaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Topical Treatment of Psoriasis. Gels 2022, 8, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, A.C.; Yañez, O.; Salas-Huenuleo, E.; Morales, J.O. Development of a Nanostructured Lipid Carrier (NLC) by a Low-Energy Method, Comparison of Release Kinetics and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujjar, S.; Madhavi, B.L.R.; Karki, R. Formulation and Evaluation of Topical Gel Containing Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Dispersion of an Antifungal Drug. Acta Pharm. Sci. 2019, 57, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Sharma, K.; Bedi, N. Topical Nanostructured Lipid Carrier-Based Hydrogel of Mometasone Furoate for the Treatment of Psoriasis. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2018, 6, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madan, J.R.; Khobaragade, S.; Dua, K.; Awasthi, R. Formulation, Optimization, and In Vitro Evaluation of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Topical Delivery of Apremilast. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, K.M.; Jagtap, C.S.; Katare, N.T.; Dhobi, M.; Prasad, S.K. Development of a psoriatic-like skin inflammation rat model using imiquimod as an inducing agent. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2021, 53, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, M.; Shah, F.A.; Sahar, N.U.; Malik, I.; Din, F.U.; Khan, S.A.; Aman, W.; Choi, H.I.; Lim, C.W.; Noh, H.Y.; et al. Formulation Optimization, In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Agomelatine-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Augmented Antidepressant Effects. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 216, 112537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reena, K.; Mittal, S.; Faizan, M.; Jahan, I.; Rahman, Y.; Khan, R.; Singh, L.; Alhalmi, A.; Noman, O.M.; Alahdab, A. Enhancement of Curcumin’s Anti-Psoriatic Efficacy via Formulation into Tea Tree Oil-Based Emulgel. Gels 2023, 9, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, Y.O.; Mahajan, U.B.; Mahajan, H.S.; Ojha, S. Methotrexate-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carrier Gel Alleviates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis by Moderating Inflammation: Formulation, Optimization, Characterization, In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 4763–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Saraf, S.; Pradhan, M.; Patel, R.J.; Singhvi, G.; Ajazuddin, A.A. Design and optimization of curcumin loaded nano lipid carrier system using Box-Behnken design. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woitiski, C.B.; Veiga, F.; Ribeiro, A.; Neufeld, R. Design for Optimization of Nanoparticles Integrating Biomaterials for Orally Dosed Insulin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 73, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, M.; Amiri, S.; Rezazadeh-Bari, M. Optimization of hesperidin extraction using hot methanol method assisted with ultrasound waves from the peel wastes of bitter orange (Citrus aurantium) and Persian orange (Citrus reticulata). Food Meas. 2023, 17, 5582–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Ali, J.; Baboota, S. Enhanced Anti-Psoriatic Activity of Tacrolimus Loaded Nanoemulsion Gel via Omega-3—Fatty Acid (EPA and DHA) Rich Oils—Fish Oil and Linseed Oil. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, A.A.; Abd El-Alim, S.H.; Basha, M.; Salama, A. Phospholipid Complex Enriched Micelles: A Novel Drug Delivery Approach for Promoting the Antidiabetic Effect of Repaglinide. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 99, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Dasgupta, S.; Dey, S.; Ramani, Y.R.; Ray, S.; Mazumder, B. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC)-Based Gel for the Topical Delivery of Aceclofenac: Preparation, Characterization, and In Vivo Evaluation. Sci. Pharm. 2012, 80, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.W.; Sweeney, C.; Dudhipala, N.; Lakhani, P.; Chaurasiya, N.D.; Tekwani, B.L.; Majumdar, S. Primaquine Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN), Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC), and Nanoemulsion (NE): Effect of Lipid Matrix and Surfactant on Drug Entrapment, In Vitro Release, and Ex Vivo Hemolysis. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawbake, G.R.; Shirolkar, S.V. Formulation, Development and Evaluation of Nanostructured Lipid Carrier (NLC) Based Gel for Topical Delivery of Diacerein. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020, 11, 794–802. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, R.S.; da Silva, J.B.; Rosseto, H.C.; Vecchi, C.F.; Campanholi, K.S.S.; Caetano, W.; Bruschi, M.L. Emulgels Containing Propolis and Curcumin: The Effect of Type of Vegetable Oil, Poly(Acrylic Acid) and Bioactive Agent on Physicochemical Stability, Mechanical and Rheological Properties. Gels 2021, 7, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Fits, L.; Mourits, S.; Voerman, J.S.; Kant, M.; Boon, L.; Laman, J.D.; Cornelissen, F.; Mus, A.M.; Florencia, E.; Prens, E.P.; et al. Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5836–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahine, Y.; El-Aal, S.A.; Reda, A.M.; Sheta, E.; Atia, N.M.; Abdallah, O.Y.; Ibrahim, S.S. Diosmin nanocrystal gel alleviates imiquimod-induced psoriasis in rats via modulating TLR7, 8/NF-κB/micro RNA-31, AKT/mTOR/P70S6K milieu, and Tregs/Th17 balance. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 1341–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhalmi, A.; Amin, S.; Khan, Z.; Beg, S.; Al kamaly, O.; Saleh, A.; Kohli, K. Nanostructured Lipid Carrier-Based Codelivery of Raloxifene and Naringin: Formulation, Optimization, In Vitro, Ex Vivo, In Vivo Assessment, and Acute Toxicity Studies. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azmin, M.N.; Stuart, J.F.B.; Calman, K.C.; Florence, A.T. Effects of Polysorbate 80 on the Absorption and Distribution of Oral Methotrexate (MTX) in Mice. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1982, 9, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouton, C.W. Formulation of poorly water-soluble drugs for oral administration: Physicochemical and physiological issues and the lipid formulation classification system. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 29, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, B.W.; Meyer, M.C. The rheological properties of carbopol gels I: Continuous shear and creep properties of carbopol gels. Int. J. Pharm. 1979, 2, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheshala, R.; Ming, N.J.; Kok, Y.Y.; Singh, T.R.R.; Dua, K. Formulation and Characterization of pH Induced in situ Gels Containing Sulfacetamide Sodium for Ocular Drug Delivery: A Combination of Carbopol®/HPMC Polymer. Indian J. Pharm. Educat. Res. 2019, 53, 654–662. [Google Scholar]
- Collamer, A.N.; Guerrero, K.T.; Henning, J.S.; Battafarano, D.F. Psoriatic skin lesions induced by tumor necrosis factor antagonist therapy: A literature review and potential mechanisms of action. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 59, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Trial | Quantity of Drug (mg) (A) | Amount of Total Lipid (mg) (B) | Quantity of Liquid Lipid (mg) (C) | Surfactant Amount (% w/v) (D) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 100 | 20 | 1 |
| 2 | 10 | 75 | 20 | 1 |
| 3 | 20 | 100 | 20 | 1 |
| 4 | 20 | 100 | 15 | 0.5 |
| 5 | 10 | 125 | 20 | 1 |
| 6 | 20 | 100 | 15 | 1.5 |
| 7 | 30 | 125 | 20 | 1 |
| 8 | 20 | 100 | 25 | 0.5 |
| 9 | 20 | 100 | 25 | 1.5 |
| 10 | 30 | 75 | 20 | 1 |
| 11 | 20 | 75 | 25 | 1 |
| 12 | 20 | 75 | 15 | 1 |
| 13 | 30 | 100 | 20 | 1.5 |
| 14 | 20 | 100 | 20 | 1 |
| 15 | 30 | 100 | 20 | 0.5 |
| 16 | 20 | 125 | 15 | 1 |
| 17 | 20 | 100 | 20 | 1 |
| 18 | 10 | 100 | 20 | 1.5 |
| 19 | 20 | 125 | 25 | 1 |
| 20 | 10 | 100 | 20 | 0.5 |
| 21 | 20 | 100 | 20 | 1 |
| 22 | 10 | 100 | 25 | 1 |
| 23 | 30 | 100 | 15 | 1 |
| 24 | 20 | 100 | 20 | 1 |
| 25 | 20 | 125 | 20 | 1.5 |
| 26 | 10 | 100 | 15 | 1 |
| 27 | 20 | 75 | 20 | 0.5 |
| 28 | 20 | 75 | 20 | 1.5 |
| 29 | 20 | 125 | 20 | 0.5 |
| 30 | 30 | 100 | 25 | 1 |
| Trial | Particle Size (nm) (Y1) | Polydispersity Index (PDI) (Y2) | Entrapment Efficiency (%EE) (Y3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 202.4 | 0.239 | 40.21 |
| 2 | 206.5 | 0.267 | 35.81 |
| 3 | 209.4 | 0.271 | 38.29 |
| 4 | 154.2 | 0.246 | 22.28 |
| 5 | 237.8 | 0.264 | 39.54 |
| 6 | 224.5 | 0.265 | 51.82 |
| 7 | 166.3 | 0.261 | 26.22 |
| 8 | 350.7 | 0.371 | 30.85 |
| 9 | 176.1 | 0.234 | 51.5 |
| 10 | 204.6 | 0.338 | 41.43 |
| 11 | 180.4 | 0.285 | 25.62 |
| 12 | 136.8 | 0.264 | 35.08 |
| 13 | 169.8 | 0.314 | 44.27 |
| 14 | 204.3 | 0.261 | 38.54 |
| 15 | 137.6 | 0.251 | 32.81 |
| 16 | 139.4 | 0.287 | 32.25 |
| 17 | 149.5 | 0.269 | 29.52 |
| 18 | 169.4 | 0.274 | 38.11 |
| 19 | 198.7 | 0.365 | 28.54 |
| 20 | 128.5 | 0.244 | 29.52 |
| 21 | 195.4 | 0.314 | 40.12 |
| 22 | 172.5 | 0.291 | 38.06 |
| 23 | 135.8 | 0.243 | 52.26 |
| 24 | 139.5 | 0.261 | 48.24 |
| 25 | 155.0 | 0.275 | 38.95 |
| 26 | 125.9 | 0.248 | 44.57 |
| 27 | 142.8 | 0.262 | 34.28 |
| 28 | 136.4 | 0.277 | 51.25 |
| 29 | 161.8 | 0.284 | 41.08 |
| 30 | 180.2 | 0.289 | 32.43 |
| Pos. [°2θ] | FWHM Total [°2θ] | d-Spacing [Å] | Rel. Int. [%] | Area [cps*°2θ] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19.5482 | 0.2670 | 4.53746 | 23.49 | 13.25 |
| 21.4960 | 0.5660 | 4.13052 | 100.00 | 92.00 |
| 23.6328 | 1.0201 | 3.76166 | 38.47 | 63.91 |
| 35.9834 | 0.8759 | 2.49385 | 1.66 | 2.24 |
| 40.2200 | 0.8514 | 2.24039 | 2.00 | 1.83 |
| Pos. [°2θ] | FWHM Total [°2θ] | d-Spacing [Å] | Rel. Int. [%] | Area [cps*°2θ] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19.4499 | 0.5714 | 4.56019 | 11.91 | 3.40 |
| 21.3946 | 0.5660 | 4.14987 | 100.00 | 44.89 |
| 23.5587 | 1.2221 | 3.77333 | 38.25 | 24.78 |
| 28.2286 | 0.3897 | 3.16143 | 8.06 | 1.50 |
| Pos. [°2θ] | FWHM Total [°2θ] | d-Spacing [Å] | Rel. Int. [%] | Area [cps*°2θ] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19.2804 | 0.5879 | 4.59989 | 13.21 | 7.97 |
| 21.2232 | 0.5656 | 4.18298 | 100.00 | 87.33 |
| 23.3769 | 0.8592 | 3.80225 | 38.17 | 53.88 |
| 35.8121 | 0.7793 | 2.50746 | 2.39 | 1.83 |
| Pos. [°2θ] | FWHM Total [°2θ] | d-Spacing [Å] | Rel. Int. [%] | Area [cps*°2θ] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28.1451 | 0.3960 | 3.16800 | 100.00 | 2.24 |
| Ingredients | HPD-NLC Loaded Gel |
|---|---|
| Carbopol 934 | 1.5% |
| HPMC K4M | 0.5% |
| Glycerol | 5 mL |
| Methyl Paraben | 0.5% |
| Triethanolamine | 2.5 mL |
| 0.1 N NaOH | 2.5 mL |
| Distilled water | q.s. * |
| Storage Time (Months) | Storage Conditions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 ± 3 °C | 25 ± 2 °C/60 ± 5% RH | 40 ± 2 °C/75 ± 5% RH | ||||
| pH | Viscosity (cP) | pH | Viscosity (cP) | pH | Viscosity (cP) | |
| 0 | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 3546 ± 47 | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 3546 ± 47 | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 3546 ± 47 |
| 3 | 6.4 ± 0.5 | 3552 ± 35 | 6.4 ± 0.5 | 3470 ± 52 | 6.6 ± 0.5 | 3157 ± 56 |
| 6 | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 3513 ± 58 | 6.4 ± 0.5 | 3441 ± 34 | 6.3 ± 0.3 | 2889 ± 104 |
| 9 | 6.4 ± 0.5 | 3557 ± 96 | 6.3 ± 0.7 | 3447 ± 28 | - | - |
| 12 | 6.3 ± 0.3 | 3481 ± 35 | 6.4 ± 0.5 | 3385 ± 82 | - | - |
| Group | Erythema | Scaling | Thickness | Average PASI Score | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | |
| I-Normal | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| II-Disease | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2.3 | 2.3 |
| III-Placebo gel | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2.3 | 1.7 |
| IV-HPD-Gel | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2.3 | 1.3 |
| V-Standard | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2.3 | 1 |
| VI-HPD-NLC-Gel | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2.3 | 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rani, A.; Kaur, R.; Aldahish, A.; Vasudevan, R.; Balaji, P.; Dora, C.P.; Chandrasekaran, B.; Singh, T.G.; Sharma, R. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC)-Based Topical Formulation of Hesperidin for Effective Treatment of Psoriasis. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040478
Rani A, Kaur R, Aldahish A, Vasudevan R, Balaji P, Dora CP, Chandrasekaran B, Singh TG, Sharma R. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC)-Based Topical Formulation of Hesperidin for Effective Treatment of Psoriasis. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(4):478. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040478
Chicago/Turabian StyleRani, Anita, Rajwinder Kaur, Afaf Aldahish, Rajalakshimi Vasudevan, Prasanalakshmi Balaji, Chander Parkash Dora, Balakumar Chandrasekaran, Thakur Gurjeet Singh, and Rahul Sharma. 2025. "Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC)-Based Topical Formulation of Hesperidin for Effective Treatment of Psoriasis" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 4: 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040478
APA StyleRani, A., Kaur, R., Aldahish, A., Vasudevan, R., Balaji, P., Dora, C. P., Chandrasekaran, B., Singh, T. G., & Sharma, R. (2025). Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC)-Based Topical Formulation of Hesperidin for Effective Treatment of Psoriasis. Pharmaceutics, 17(4), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040478









