Carbon Dots as a Fluorescent Nanosystem for Crossing the Blood–Brain Barrier with Plausible Application in Neurological Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
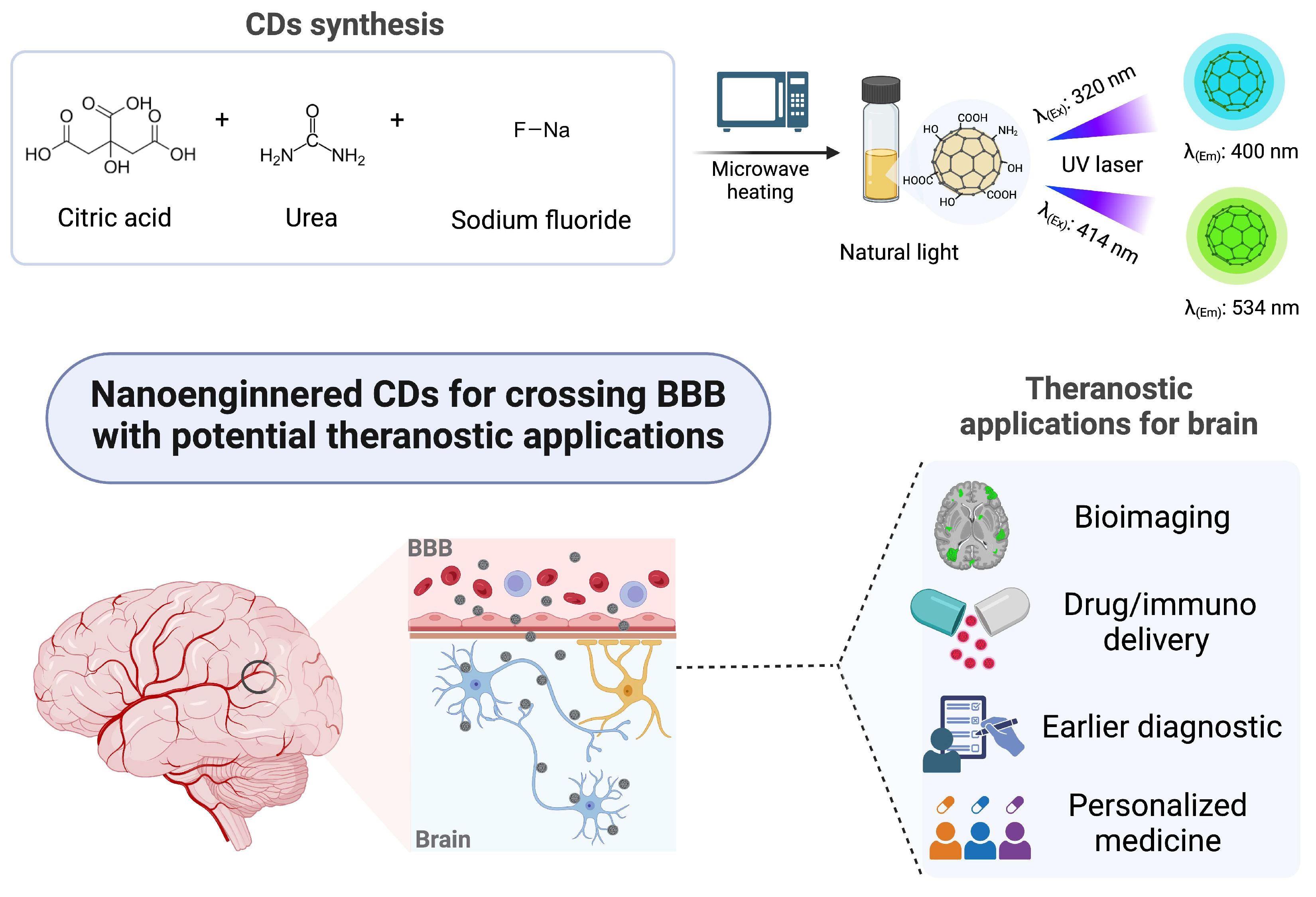
2.1. Synthesis of Carbon Dots (CDs)
2.2. Characterization Techniques
2.3. Cell Culture Line
2.4. Cytotoxicity and Metabolic Assays
2.5. Establishment of Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) In Vitro Model
2.6. Permeability Test in the In Vitro Biomimetic BBB Model
3. Results and Discussion
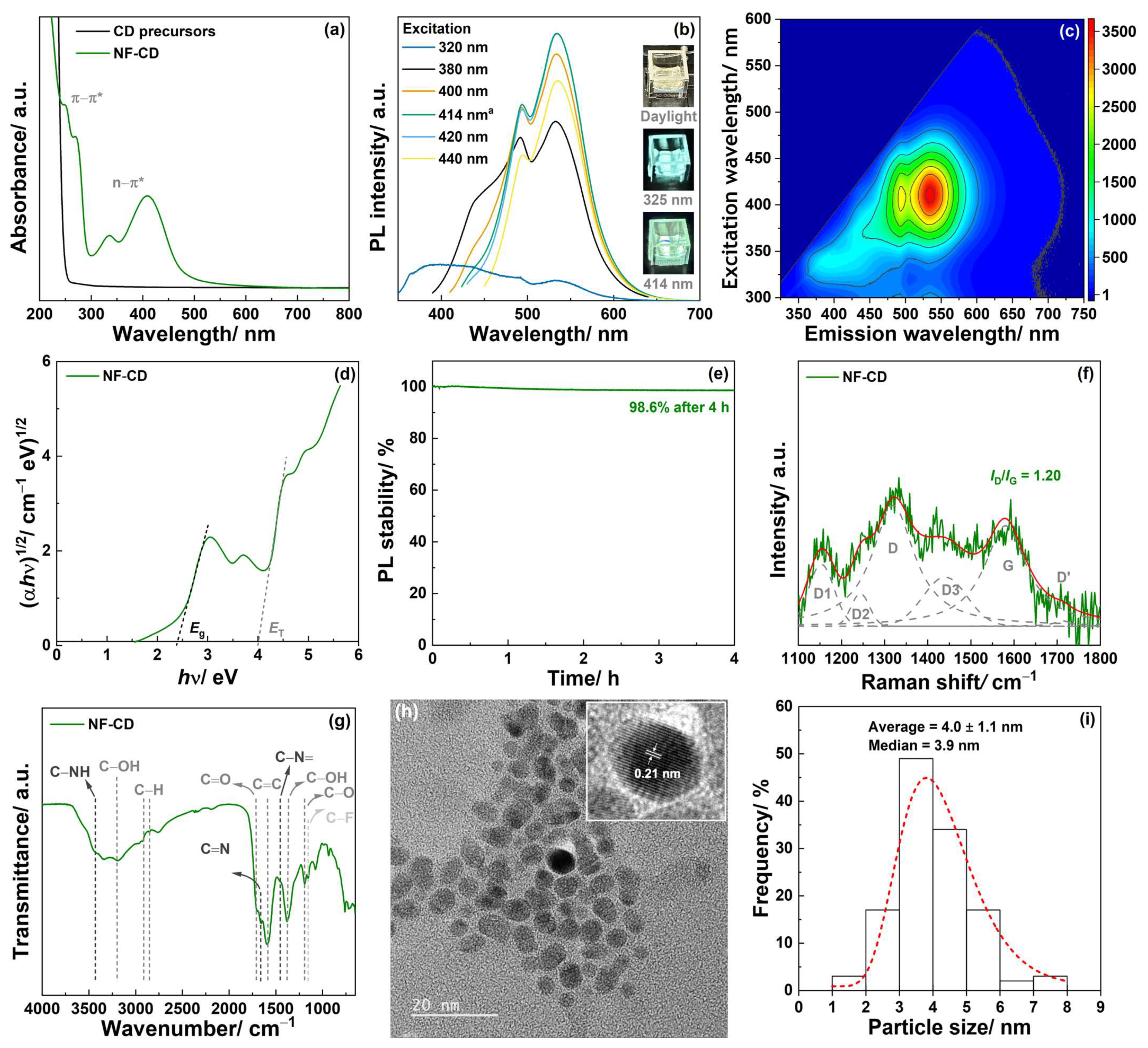
3.1. Characterization of the Carbon Dots (CDs)
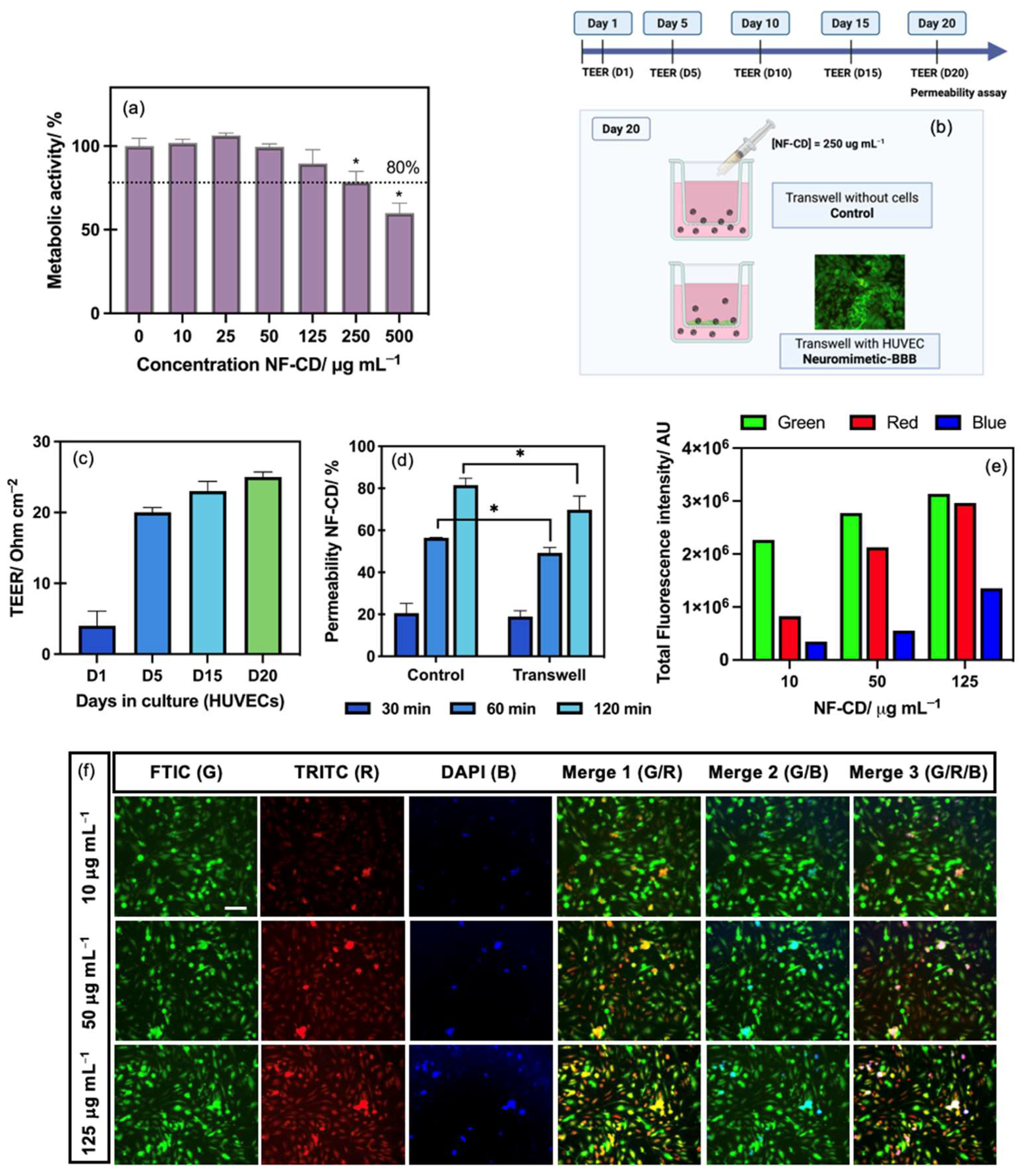
3.2. Cytotoxicity and Metabolic Activity of NF-CD in BBB Model Cells
3.3. BBB Permeability Ability of NF-CD
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATR | Attenuated total reflection |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| CDs | Carbon dots |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| ID | Intensity of the D band in the Raman spectrum |
| ID2 | Intensity of the D2 band in the Raman spectrum |
| ID3 | Intensity of the D3 band in the Raman spectrum |
| IG | Intensity of the G band in the Raman spectrum |
| PL | Photoluminescence |
| QY | Quantum yield |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| UV-Vis | Ultraviolet-visible |
References
- Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chételat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Tang, L.; Li, X.; Fan, F.; Liu, Z. Immunotherapy for glioma: Current management and future application. Cancer Lett. 2020, 476, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, J.Y.; Haney, M.P.; Park, S.I.; McCall, J.G.; Jeong, J.-W. Microfluidic neural probes: In vivo tools for advancing neuroscience. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 1406–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakarpandian, B.; Shen, M.-C.; Nichols, J.B.; Mills, I.R.; Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz, M.; Aschner, M.; Pant, K. SyM-BBB: A microfluidic blood brain barrier model. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griep, L.M.; Wolbers, F.; de Wagenaar, B.; ter Braak, P.M.; Weksler, B.B.; Romero, I.A.; Couraud, P.O.; Vermes, I.; van der Meer, A.D.; van den Berg, A. BBB ON CHIP: Microfluidic platform to mechanically and biochemically modulate blood-brain barrier function. Biomed. Microdevices 2013, 15, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, R.; Yang, B. Carbon dots: A new type of carbon-based nanomaterial with wide applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 2179–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-P.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Pathak, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Harruff, B.A.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7756–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.N.; Baker, G.A. Luminescent carbon nanodots: Emergent nanolights. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6726–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.-P.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Z.; Liang, H.; Shen, X.-C. Recent advances in carbon nanomaterials for cancer phototherapy. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 3993–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.B.; Liu, M.L.; Li, C.M.; Huang, C.Z. Fluorescent carbon dots functionalization. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 270, 165–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Feng, W. Frontiers in carbon dots: Design, properties and applications. Mater. Chem. Front. 2019, 3, 2571–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Dou, X.; Li, H.; Ma, Y.; Lin, J.-M. Nitrite sensing based on the carbon dots-enhanced chemiluminescence from peroxynitrous acid and carbonate. Talanta 2015, 132, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Yu, Q.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Jiang, M.; Yu, R.; Deng, T.; Yu, C. Bioenzyme-responsive l-arginine-based carbon dots: The replenishment of nitric oxide for nonpharmaceutical therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 7432–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintz, K.J.; Mercado, G.; Zhou, Y.; Ji, Y.; Hettiarachchi, S.D.; Liyanage, P.Y.; Pandey, R.R.; Chusuei, C.C.; Dallman, J.; Leblanc, R.M. Tryptophan carbon dots and their ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 176, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seven, E.S.; Seven, Y.B.; Zhou, Y.; Poudel-Sharma, S.; Diaz-Rucco, J.J.; Kirbas Cilingir, E.; Mitchell, G.S.; Van Dyken, J.D.; Leblanc, R.M. Crossing the blood–brain barrier with carbon dots: Uptake mechanism and in vivo cargo delivery. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 3942–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Zhu, Q.; Qi, L.; Guo, M.; Gao, W.; Gao, Q. Synthesis and properties of nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots using lactic acid as carbon source. Materials 2022, 15, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Zheng, J.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, M.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Green functional carbon dots derived from herbal medicine ameliorate blood—Brain barrier permeability following traumatic brain injury. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 9274–9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarra, M.; Soto, J.; Pino-González, M.S.; Gonzalez-Munoz, E.; Dučić, T. Multifunctionalized carbon dots as an active nanocarrier for drug delivery to the glioblastoma cell line. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 13818–13830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, S.D.; Graham, R.M.; Mintz, K.J.; Zhou, Y.; Vanni, S.; Peng, Z.; Leblanc, R.M. Triple conjugated carbon dots as a nano-drug delivery model for glioblastoma brain tumors. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 6192–6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, S.A.; Praveena, P.; Dhanavel, S.; Manikandan, R.; Senthilkumar, S.; Stephen, A. Luminescent chitosan/carbon dots as an effective nano-drug carrier for neurodegenerative diseases. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 24386–24396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Fang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, P. Rational design of nitrogen-doped carbon dots for inhibiting β-amyloid aggregation. Molecules 2023, 28, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Lu, S.; Huang, S. Microwave-assisted one-pot synthesis of highly luminescent N-doped carbon dots for cellular imaging and multi-ion probing. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2429–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, S.; Jiang, C. Fluorescent carbon dots: Rational synthesis, tunable optical properties and analytical applications. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 40973–40989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ma, C.; Zhu, J.-J. Carbon-based dots for electrochemiluminescence sensing. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, H.; Lai, J.; Peng, X.; Hu, Y.; Gu, W.; Ye, L. Carbon dots with red-shifted photoluminescence by fluorine doping for optical bio-imaging. Carbon 2018, 128, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajender, G.; Giri, P.K. Formation mechanism of graphene quantum dots and their edge state conversion probed by photoluminescence and Raman spectroscopy. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 10852–10865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, A.M. Standards for photoluminescence quantum yield measurements in solution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 2213–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolden, C.T.; Skibber, M.A.; Olson, S.D.; Zamorano Rojas, M.; Milewicz, S.; Gill, B.S.; Cox, C.S. Validation and characterization of a novel blood–brain barrier platform for investigating traumatic brain injury. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, K.G. Fluorescence Theory. In Encyclopedia of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry, 2nd ed.; Lindon, J.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 628–634. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.; Zhu, S.; Feng, T.; Yang, M.; Yang, B. Evolution and synthesis of carbon dots: From carbon dots to carbonized polymer dots. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, S.; Wang, X.; Lu, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, L. A biocompatible fluorescent ink based on water-soluble luminescent carbon nanodots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12215–12218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadezky, A.; Muckenhuber, H.; Grothe, H.; Niessner, R.; Pöschl, U. Raman microspectroscopy of soot and related carbonaceous materials: Spectral analysis and structural information. Carbon 2005, 43, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claramunt, S.; Varea, A.; López-Díaz, D.; Velázquez, M.M.; Cornet, A.; Cirera, A. The importance of interbands on the interpretation of the Raman spectrum of graphene oxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 10123–10129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresselhaus, M.S.; Jorio, A.; Hofmann, M.; Dresselhaus, G.; Saito, R. Perspectives on carbon nanotubes and graphene raman spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, M.P.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Fernandes, A.J.S.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Freire, C. Tuning the surface chemistry of graphene flakes: New strategies for selective oxidation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14290–14301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusko, V.; Khannanov, A.; Rakhmatullin, A.; Dimiev, A.M. Unraveling the infrared spectrum of graphene oxide. Carbon 2024, 229, 119507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthoosamy, K.; Bai, R.G.; Abubakar, I.B.; Sudheer, S.M.; Lim, H.N.; Loh, H.S.; Huang, N.M.; Chia, C.H.; Manickam, S. Exceedingly biocompatible and thin-layered reduced graphene oxide nanosheets using an eco-friendly mushroom extract strategy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1505–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, J.L.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Freitas, M.M.A.; Órfão, J.J.M. Modification of the surface chemistry of activated carbons. Carbon 1999, 37, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.J.; Omer, K.M.; Hawaiz, F.E. Deep insights to explain the mechanism of carbon dot formation at various reaction times using the hydrothermal technique: FT-IR, 13C-NMR, 1H-NMR, and UV-visible spectroscopic approaches. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 14340–14349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.T.N.; Shim, J.H. All carbon hybrid N-doped carbon dots/carbon nanotube structures as an efficient catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 12520–12530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Ren, M.; Xiao, H.; Liu, X. Characterization of conformation and locations of C–F bonds in graphene derivative by polarized ATR-FTIR. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 3926–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Yang, S.; Xiao, P.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, X.; Wu, W. Fluorination and betaine modification augment the blood–brain barrier-crossing ability of cylindrical polymer brushes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202201390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Han, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. The blood–brain barrier: Structure, regulation and drug delivery. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.O.; Shin, S.-R.; Bañobre-López, M. Brain-on-a-chip: An emerging platform for studying the nanotechnology-biology interface for neurodegenerative disorders. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, T.; Dong, J.; Lu, Y. The blood–brain barriers: Novel nanocarriers for central nervous system diseases. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandi, D.; Mansingh, S.; Behera, A.; Parida, K. Calculation of relative fluorescence quantum yield and Urbach energy of colloidal CdS QDs in various easily accessible solvents. J. Lumin. 2021, 231, 117792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones II, G.; Jackson, W.R.; Choi, C.Y.; Bergmark, W.R. Solvent effects on emission yield and lifetime for coumarin laser dyes. Requirements for a rotatory decay mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. 1985, 89, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Araújo, C.; Rodrigues, R.O.; Bañobre-López, M.; Silva, A.M.T.; Ribeiro, R.S. Carbon Dots as a Fluorescent Nanosystem for Crossing the Blood–Brain Barrier with Plausible Application in Neurological Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040477
Araújo C, Rodrigues RO, Bañobre-López M, Silva AMT, Ribeiro RS. Carbon Dots as a Fluorescent Nanosystem for Crossing the Blood–Brain Barrier with Plausible Application in Neurological Diseases. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(4):477. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040477
Chicago/Turabian StyleAraújo, Catarina, Raquel O. Rodrigues, Manuel Bañobre-López, Adrián M. T. Silva, and Rui S. Ribeiro. 2025. "Carbon Dots as a Fluorescent Nanosystem for Crossing the Blood–Brain Barrier with Plausible Application in Neurological Diseases" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 4: 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040477
APA StyleAraújo, C., Rodrigues, R. O., Bañobre-López, M., Silva, A. M. T., & Ribeiro, R. S. (2025). Carbon Dots as a Fluorescent Nanosystem for Crossing the Blood–Brain Barrier with Plausible Application in Neurological Diseases. Pharmaceutics, 17(4), 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040477







