Fabricating Oral Disintegrating Tablets Without Disintegrant Using Powder-Based 3D Printing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
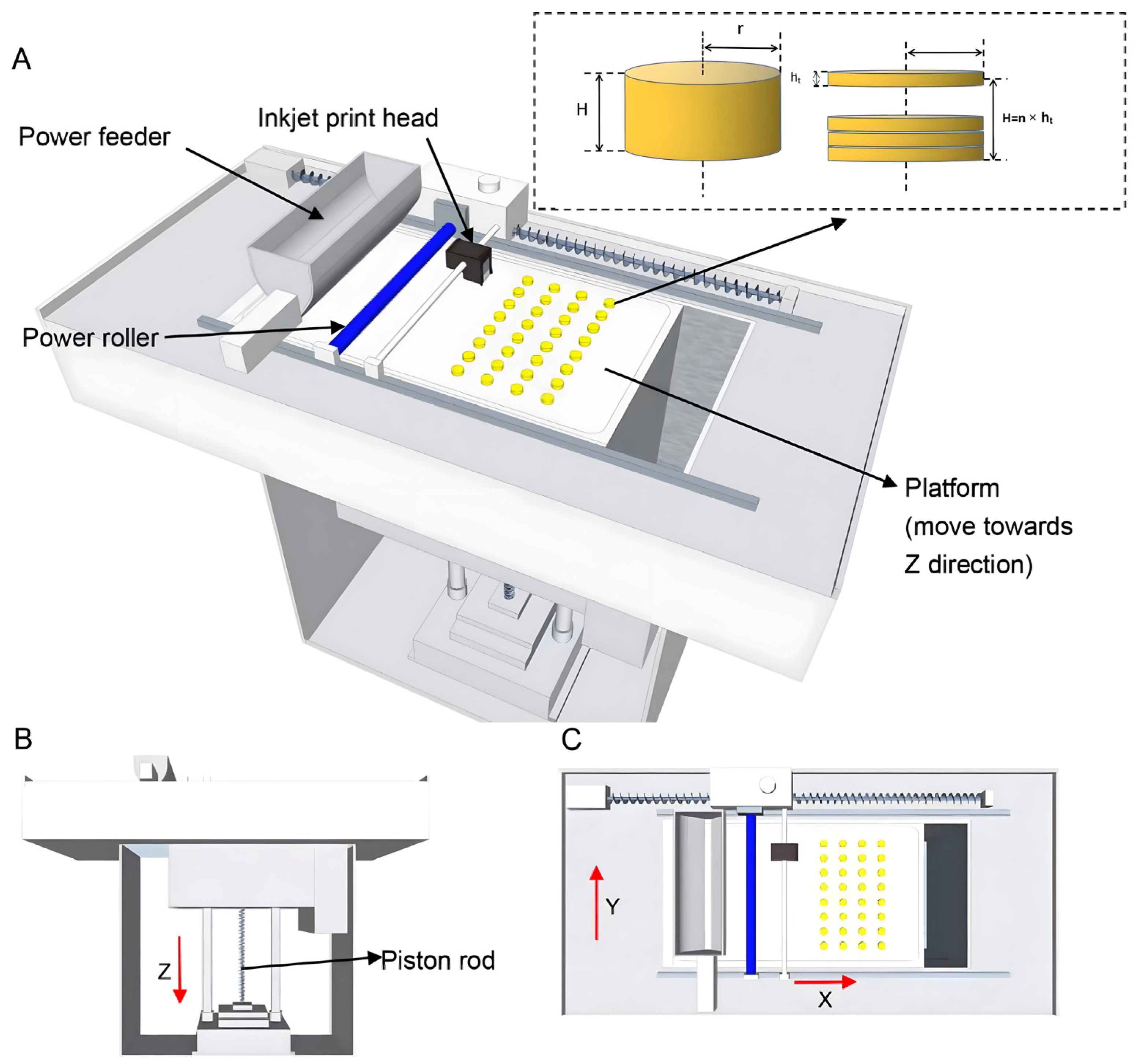
2.2. Method of Preparation of 3DP Clozapine ODTs
2.3. The Formulation Optimization of 3D Powder-Based Clozapine ODTs
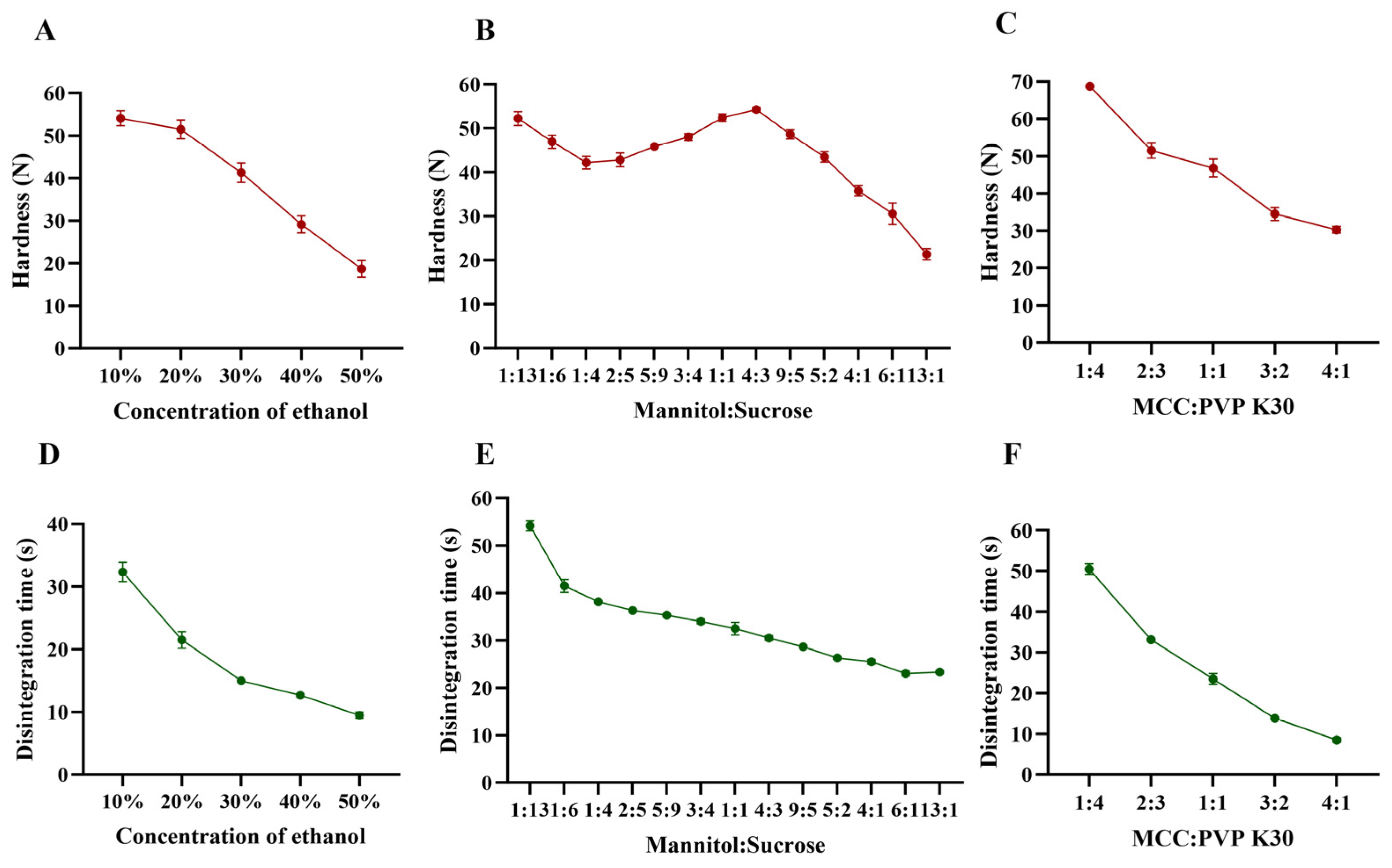
2.3.1. Single-Factor Experiments
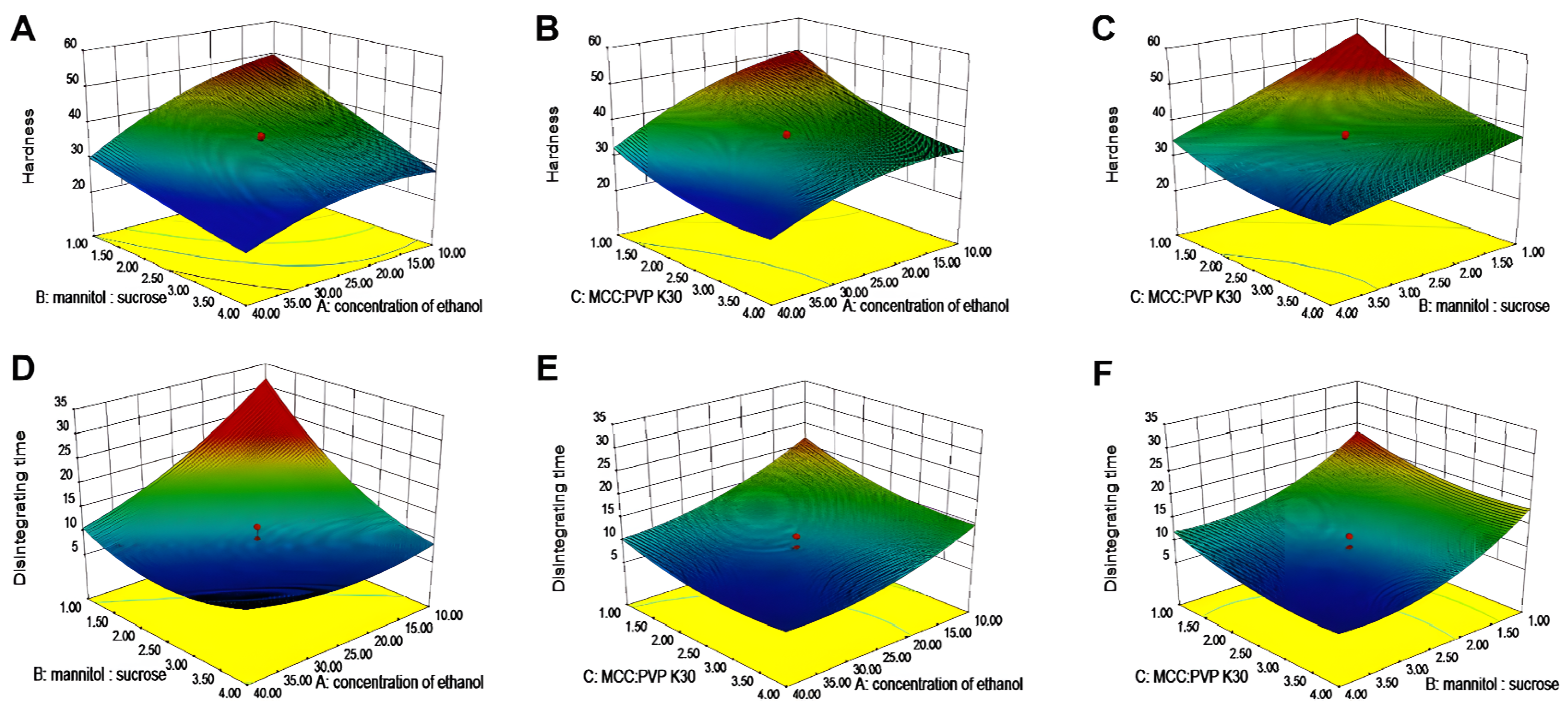
2.3.2. Central Composite Design (CCD)
2.4. Characterization of ODTs
2.4.1. Hardness
2.4.2. Determination of Drug Content
2.4.3. Contact Angle Testing
2.4.4. In Vitro Disintegration by Texture Analyzer
2.4.5. In Vitro Dissolution Test
2.4.6. Porosity Measurement Method
2.4.7. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.4.8. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.4.9. X-Ray Powder Diffraction
2.4.10. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.4.11. Disintegration Process
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Result of Formulation Optimization for 3D Powder-Based Clozapine ODTs
3.2. Formulation Optimization by the CCD
3.3. Characterization Study of ODTs
3.3.1. Content Uniformity and Hardness
3.3.2. Clozapine and Excipient Interactions
3.4. Characteristic Difference Between 3DP ODTs and Directed Tablets
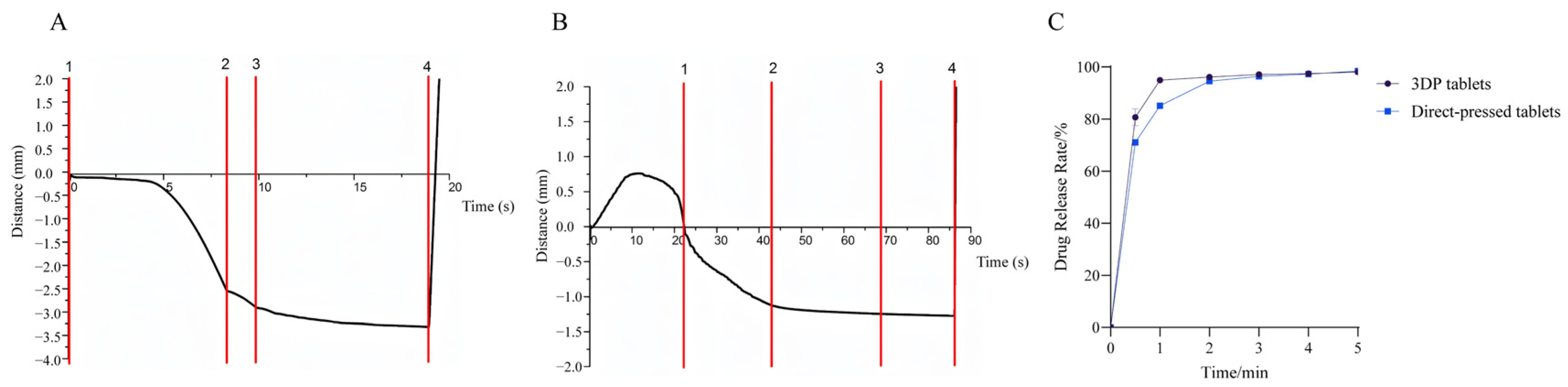
3.4.1. Disintegration Speed
3.4.2. Disintegration and Dissolution Tests
3.4.3. Appearance and Contact Angle
3.4.4. SEM
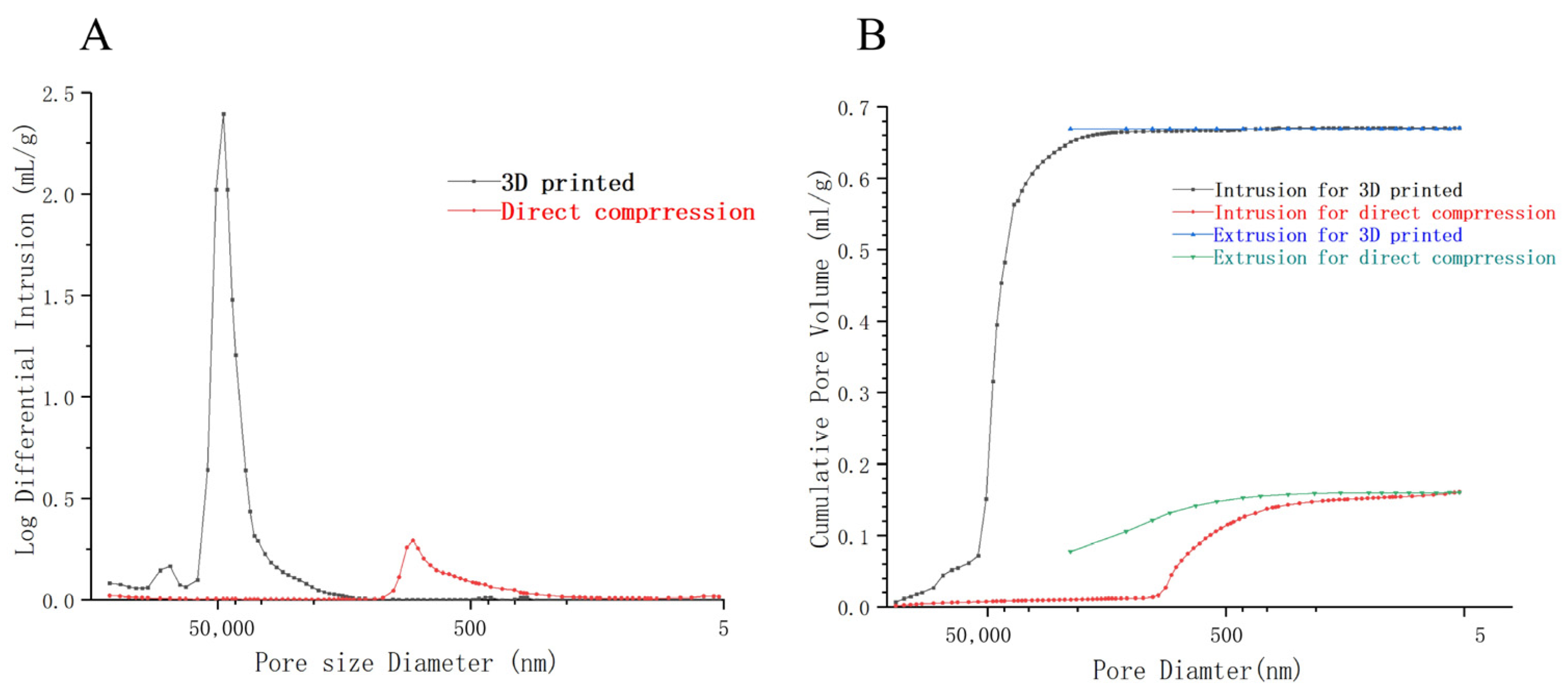
3.4.5. Porosity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, P.; Mishra, B. An Overview of Recent Patents on Oral Osmotic Drug Delivery Systems. Recent. Pat. Drug Deliv. Formul. 2007, 1, 236–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, S.-E.; Kwon, K.B.; Kim, S.H.; Lim, S.-J. The Prevalence, Risk Factors and Prognostic Implications of Dysphagia in Elderly Patients Undergoing Hip Fracture Surgery in Korea. BMC Geriatr. 2019, 19, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariff, Z.B.; Dahmash, D.T.; Kirby, D.J.; Missaghi, S.; Rajabi-Siahboomi, A.; Maidment, I.D. Does the Formulation of Oral Solid Dosage Forms Affect Acceptance and Adherence in Older Patients? A Mixed Methods Systematic Review. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 1015–1023.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drumond, N.; van Riet-Nales, D.A.; Karapinar-Çarkit, F.; Stegemann, S. Patients’ Appropriateness, Acceptability, Usability and Preferences for Pharmaceutical Preparations: Results from a Literature Review on Clinical Evidence. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 521, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, S.M.; AbdAlla, F.I.; Abdelgawad, N.M. Preparation and Optimization of Fast-Disintegrating Tablet Containing Naratriptan Hydrochloride Using D-Optimal Mixture Design. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 2472–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwerfalli, A.M.; Al-Kinani, A.; Alany, R.G.; ElShaer, A. Nano-Engineering Chitosan Particles to Sustain the Release of Promethazine from Orodispersables. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 131, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, Y.H.; Jayakrishnan, A.; Razif, M.R.F.M.; Yee, K.M.; Kee, P.E.; Goh, B.H.; Uddin, A.H.; Lakshminarayanan, V.; Liew, K.B. A Comprehensive Review of Challenges in Oral Drug Delivery Systems and Recent Advancements in Innovative Design Strategies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2024, 31, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comoglu, T.; Dilek Ozyilmaz, E. Orally Disintegrating Tablets and Orally Disintegrating Mini Tablets–Novel Dosage Forms for Pediatric Use. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2019, 24, 902–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, Y.; Irisawa, Y.; Okimoto, K.; Osawa, T.; Yamashita, S. Further Improvement of Orally Disintegrating Tablets Using Micronized Ethylcellulose. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 423, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Ho, M.J.; Jeong, C.K.; Kang, M.J. Novel Bioequivalent Tablet of Solifenacin Succinate Prepared Using Direct Compression Technique for Improved Chemical Stability. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khattawi, A.; Mohammed, A.R. Challenges and Emerging Solutions in the Development of Compressed Orally Disintegrating Tablets. Expert. Opin. Drug Discov. 2014, 9, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, C.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Mu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Shen, L. A Comprehensive Understanding of Disintegrants and Disintegration Quantification Techniques: From the Perspective of Tablet Microstructure. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 104891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotta, S.; Nair, A.; Alsabeelah, N. 3D Printing Technology in Drug Delivery: Recent Progress and Application. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 5039–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Kuang, H.; Huang, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, R.; Shang, G.; Wang, Z.; Liao, Y.; He, J.; Li, D. 3D Printing of Drug Delivery Systems Enhanced with Micro/Nano-Technology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2025, 216, 115479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, C.R.M.; Okafor-Muo, O.L.; Hassanin, H.; ElShaer, A. 3DP Printing of Oral Solid Formulations: A Systematic Review. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, K. Oral Disintegrating Tablets-An Updated Patent Perspective. Recent. Pat. Drug Deliv. Formul. 2020, 14, 166–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.-G.; Shen, X.-X.; Branford-White, C.; Zhu, L.-M.; White, K.; Yang, X.L. Novel Oral Fast-Disintegrating Drug Delivery Devices with Predefined Inner Structure Fabricated by Three-Dimensional Printing. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Rabel, S.; Bukhtar, Q.; Qadir, M.I.; Jabeen, F.; Khan, A. Orally Disintegrating Films: A Modern Expansion in Drug Delivery System. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyna-Orlewicz, K.; Brniak, W.; Tatara, W.; Strzebońska, M.; Haznar-Garbacz, D.; Szafraniec-Szczęsny, J.; Antosik-Rogóż, A.; Wojteczko, K.; Strózik, M.; Kurek, M.; et al. Investigating the Impact of Co-Processed Excipients on the Formulation of Bromhexine Hydrochloride Orally Disintegrating Tablets (ODTs). Pharm. Res. 2023, 40, 2947–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quodbach, J.; Kleinebudde, P. Performance of Tablet Disintegrants: Impact of Storage Conditions and Relative Tablet Density. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2015, 20, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, E.; Morelli, L.; Salvioni, L.; Giustra, M.; De Santes, B.; Spena, F.; Barbieri, L.; Garbujo, S.; Viganò, M.; Novati, B.; et al. Co-Processed Materials Testing as Excipients to Produce Orally Disintegrating Tablets (ODT) Using Binder Jet 3D-Printing Technology. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2024, 194, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shore, D.; Matthews, S.; Cott, J.; Lieberman, J.A. Clinical Implications of Clozapine Discontinuation: Report of an NIMH Workshop. Schizophr. Bull. 1995, 21, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zeng, F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Shi, K.; Zong, L. Formulation and in Vivo Evaluation of Orally Disintegrating Tablets of Clozapine/Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes. AAPS PharmSciTech 2013, 14, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.-G.; Branford-White, C.; Yang, Y.-C.; Zhu, L.-M.; Welbeck, E.W.; Yang, X.-L. A Novel Fast Disintegrating Tablet Fabricated by Three-Dimensional Printing. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2009, 35, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.; Poddar, A.; Sawant, K. Formulation of Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex-Based Orally Disintegrating Tablet of Eslicarbazepine Acetate for Improved Oral Bioavailability. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 58, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Thakkar, R.; Zhang, J.; Lu, A.; Duggal, I.; Pillai, A.; Wang, J.; Aghda, N.H.; Maniruzzaman, M. Investigating the Use of Magnetic Nanoparticles as Alternative Sintering Agents in Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D Printing of Oral Tablets. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 2924–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovanov, R.; Cornilă, A.; Bogdan, C.; Hales, D.; Tomuță, I.; Achim, M.; Tăut, A.; Iman, N.; Casian, T.; Iurian, S. Testing the Disintegration and Texture-Related Palatability Predictions for Orodispersible Tablets Using an Instrumental Tool Coupled with Multivariate Analysis: Focus on Process Variables and Analysis Settings. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 198, 106801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Xie, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chang, X.; Shan, L.; Sun, L.; Huang, X.; Gao, C. Effects of Polyvinylpyrrolidone Both as a Binder and Pore-Former on the Release of Sparingly Water-Soluble Topiramate from Ethylcellulose Coated Pellets. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 465, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerk, C.F.; Bolhuis, G.K.; de Boer, A.H. Effect of Microcrystalline Cellulose on Liquid Penetration in and Disintegration of Directly Compressed Tablets. J. Pharm. Sci. 1979, 68, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.-Y.; Chung, Y.-Y.; Cheah, X.-Z.; Tan, E.Y.-L.; Quah, J. The Characterization and Dissolution Performances of Spray Dried Solid Dispersion of Ketoprofen in Hydrophilic Carriers. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khattawi, A.; Koner, J.; Rue, P.; Kirby, D.; Perrie, Y.; Rajabi-Siahboomi, A.; Mohammed, A.R. A Pragmatic Approach for Engineering Porous Mannitol and Mechanistic Evaluation of Particle Performance. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 94, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markl, D.; Zeitler, J.A. A Review of Disintegration Mechanisms and Measurement Techniques. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 890–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quodbach, J.; Kleinebudde, P. A Critical Review on Tablet Disintegration. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2015, 21, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohel, M.; Patel, M.; Amin, A.; Agrawal, R.; Dave, R.; Bariya, N. Formulation Design and Optimization of Mouth Dissolve Tablets of Nimesulide Using Vacuum Drying Technique. AAPS PharmSciTech 2004, 5, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapolu, K.; Sanka, K.; Vemula, P.K.; Aatipamula, V.; Mohd, A.B.; Diwan, P.V. Optimization and Characterization of Gastroretentive Floating Drug Delivery System Using Box-Behnken Design. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 1928–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, K.; Mehta, T.; Sansare, S.; Sharifi, L.; Ma, A.W.K.; Chaudhuri, B. Pharmaceutical Applications of Powder-Based Binder Jet 3D Printing Process-A Review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 177, 113943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilha Dezena, R.M.; Tardim, B.G. Disintegration Mechanism of Pharmaceutical Tablets: The Chemistry behind Excipients. Pharm. Pharmacol. Int. J. 2022, 10, 76–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fina, F.; Madla, C.M.; Goyanes, A.; Zhang, J.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Fabricating 3D Printed Orally Disintegrating Printlets Using Selective Laser Sintering. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 541, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markl, D.; Strobel, A.; Schlossnikl, R.; Bøtker, J.; Bawuah, P.; Ridgway, C.; Rantanen, J.; Rades, T.; Gane, P.; Peiponen, K.-E.; et al. Characterisation of Pore Structures of Pharmaceutical Tablets: A Review. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 538, 188–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Ou, Z.; Yang, G. 3D Printed Tablets with Internal Scaffold Structure Using Ethyl Cellulose to Achieve Sustained Ibuprofen Release. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 115, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashed, N.; Chan, S.; Lam, M.; Ghafourian, T.; Nokhodchi, A. Effect of pH, Ionic Strength and Agitation Rate on Dissolution Behaviour of 3D-Printed Tablets, Tablets Prepared from Ground Hot-Melt Extruded Filaments and Physical Mixtures. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, X.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, L.; Shen, L. Exploring the Disintegration Mechanism of Dissolved Natural Plant Products Tablets Based on Pore Structure Control. Adv. Powder Technol. 2024, 35, 104586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorhaydari, K. A Comprehensive Examination of High-Temperature Hydrogen Attack—A Review of over a Century of Investigations. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 7875–7908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


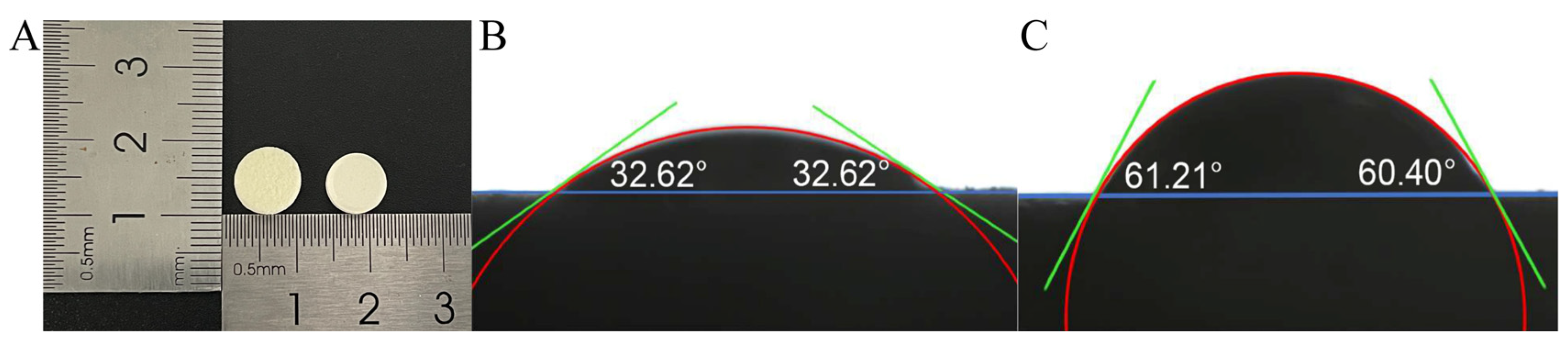
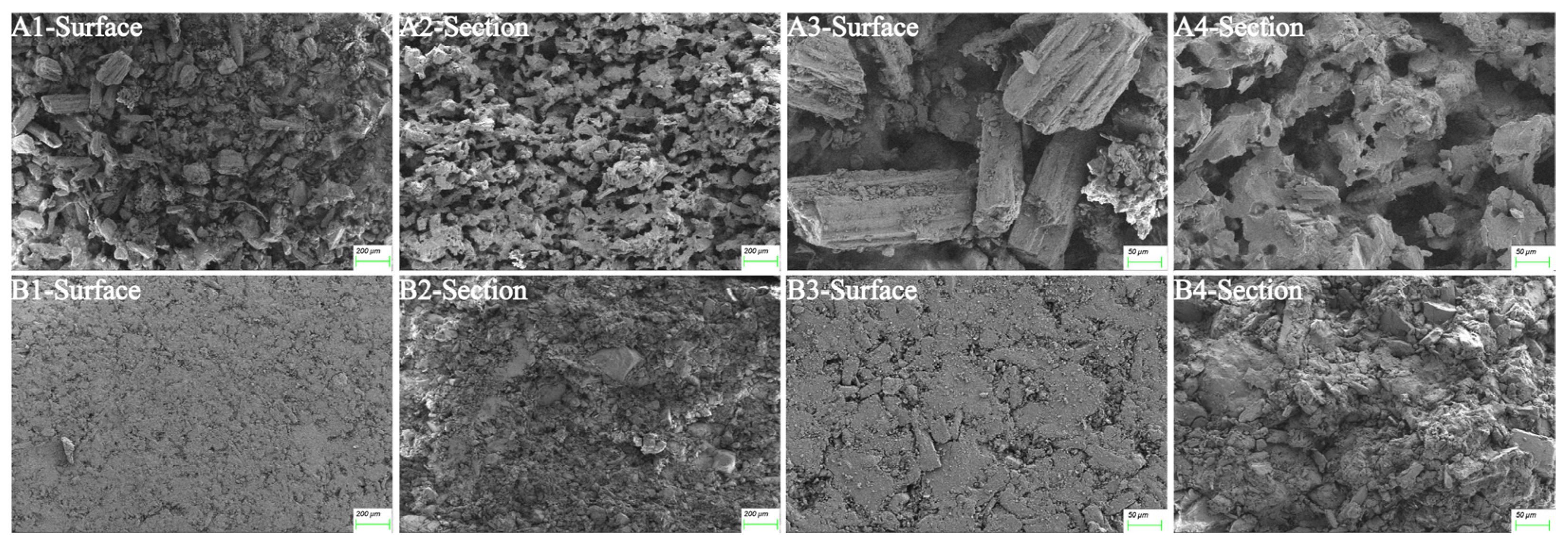
| Prescription Components | Proportion (w/w, %) |
|---|---|
| Clozapine | 20% |
| Mannitol and sucrose | 70% |
| PVP K30 and MCC | 10% |
| Type | Total Intrusion Volume [103 mL/mg] | Median Pore Diameter V (nm) | Median Pore Diameter A (nm) | Average Pore Diameter (4 V/A) | Porosity (%) | Permeabilitiy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D printed ODT | 0.67 | 44,560.80 | 11,615.44 | 20,992.19 | 48.97 | 4606.38 |
| Direct pressing ODT | 0.16 | 971.14 | 10.25 | 138.91 | 19.06 | 0.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Lin, M.; Chen, P.; Yi, H.; Lv, Z.; Liu, Y. Fabricating Oral Disintegrating Tablets Without Disintegrant Using Powder-Based 3D Printing. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040435
Wang J, Liu S, Lin M, Chen P, Yi H, Lv Z, Liu Y. Fabricating Oral Disintegrating Tablets Without Disintegrant Using Powder-Based 3D Printing. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(4):435. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040435
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiu, Shunfang Liu, Minmei Lin, Peihong Chen, Huagui Yi, Zhufen Lv, and Yuanfen Liu. 2025. "Fabricating Oral Disintegrating Tablets Without Disintegrant Using Powder-Based 3D Printing" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 4: 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040435
APA StyleWang, J., Liu, S., Lin, M., Chen, P., Yi, H., Lv, Z., & Liu, Y. (2025). Fabricating Oral Disintegrating Tablets Without Disintegrant Using Powder-Based 3D Printing. Pharmaceutics, 17(4), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040435









