Modeling Shear-Thinning Flow in Twin-Screw Extrusion Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
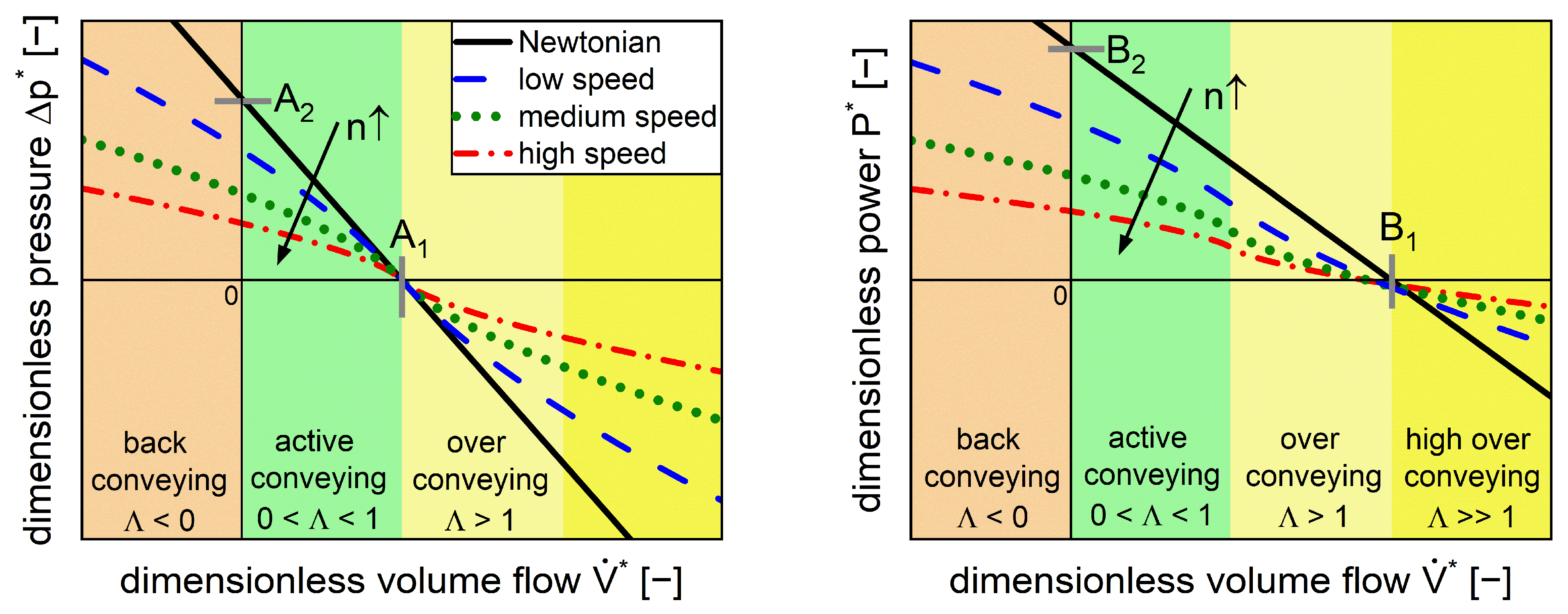
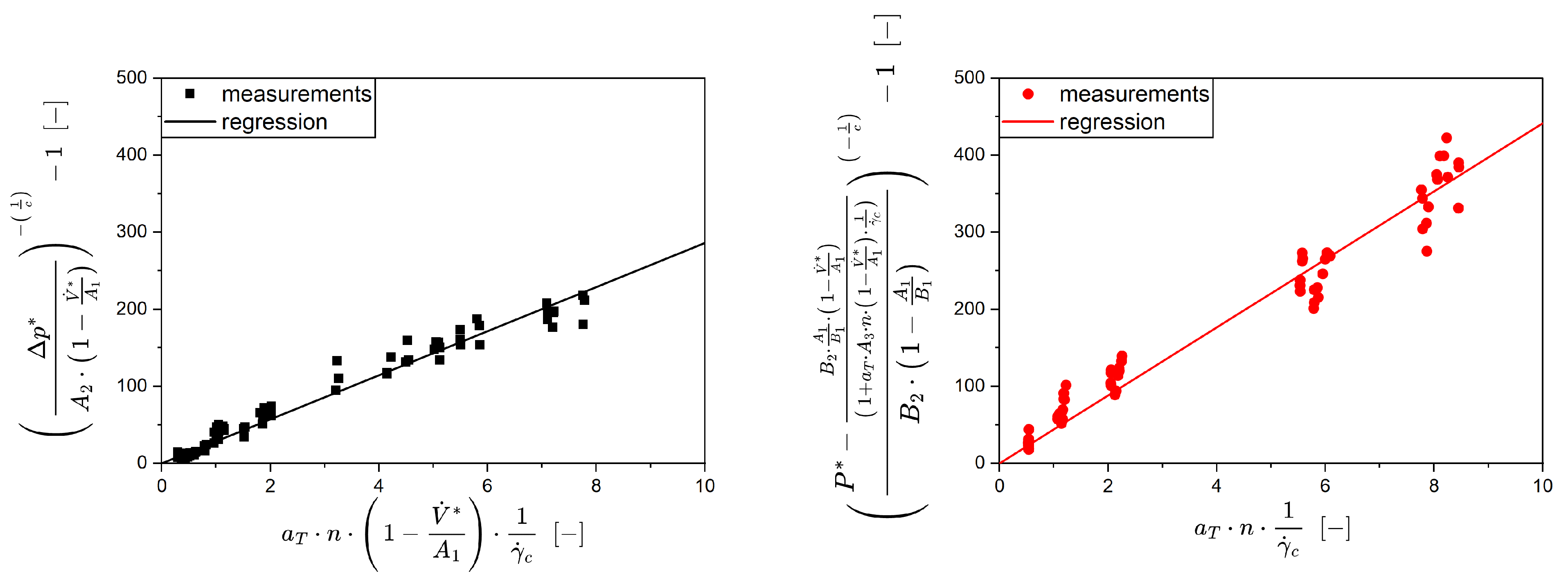
2. Theoretical Framework
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Rheology Measurement Method
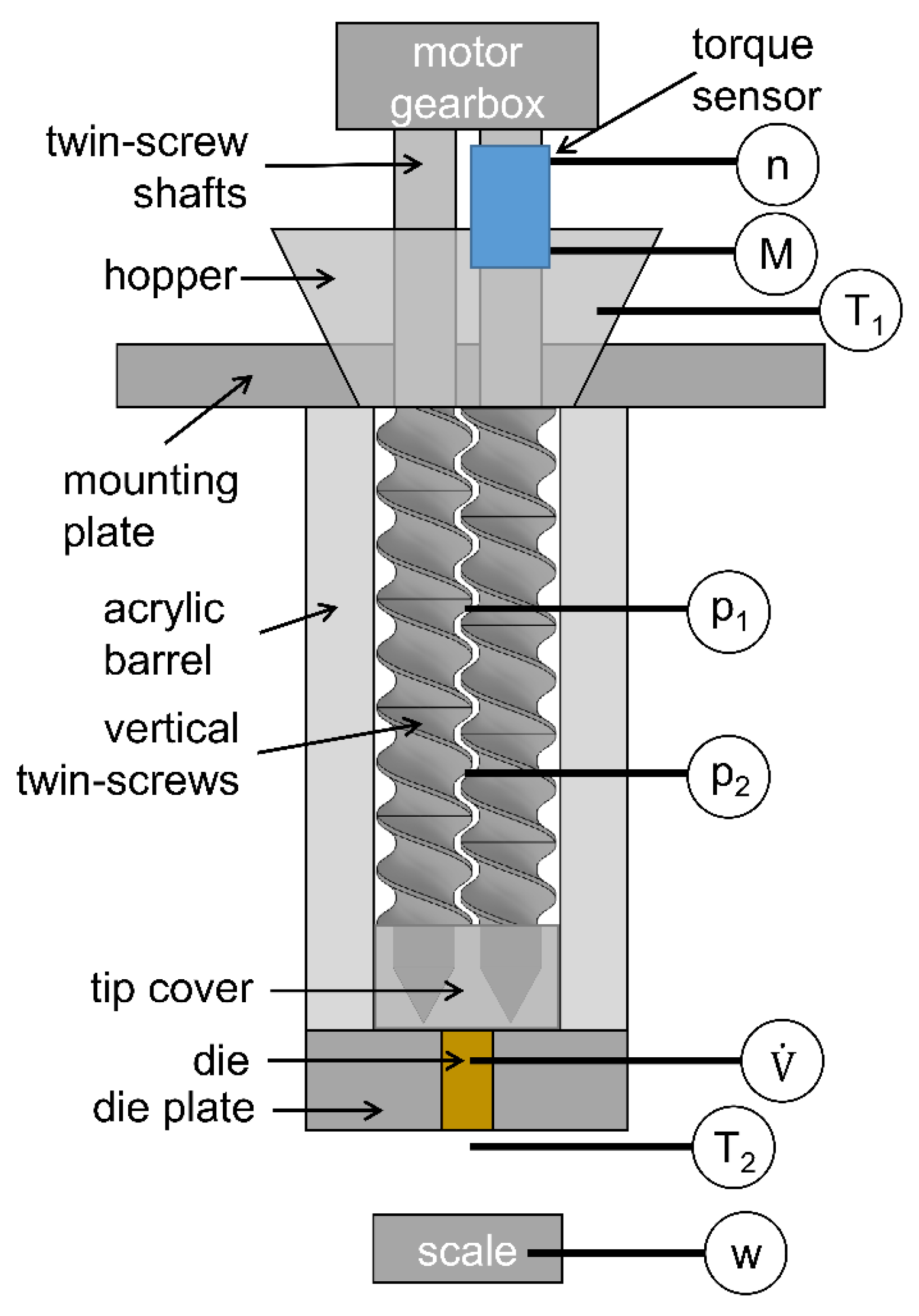
3.3. Extrusion Screw Test Rig Method
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Rheology of Model Fluids
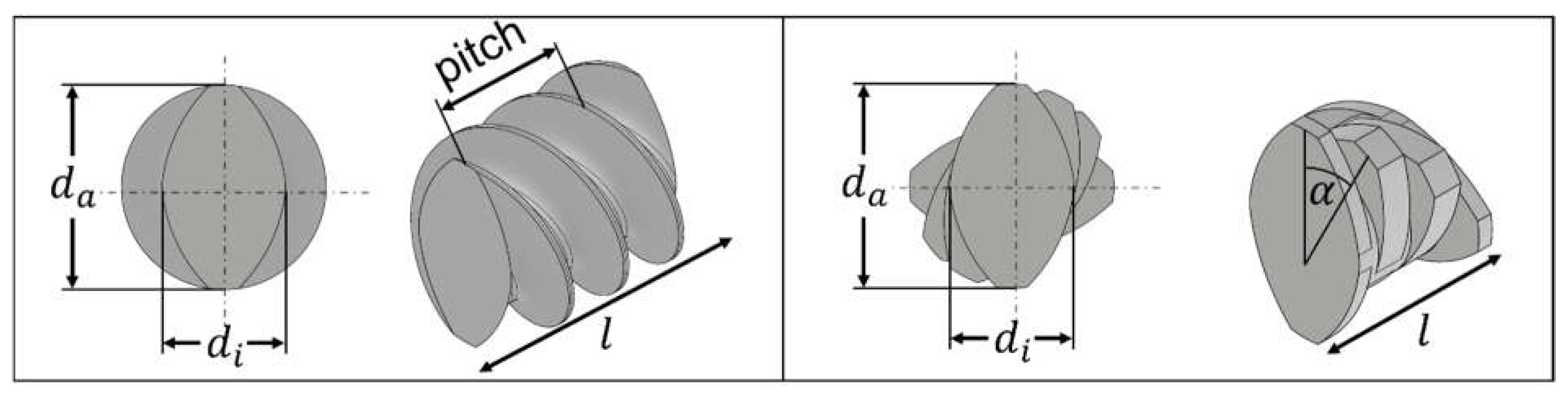
4.2. Selected Screw Elements
4.3. Optimization of Extrusion Test Rig
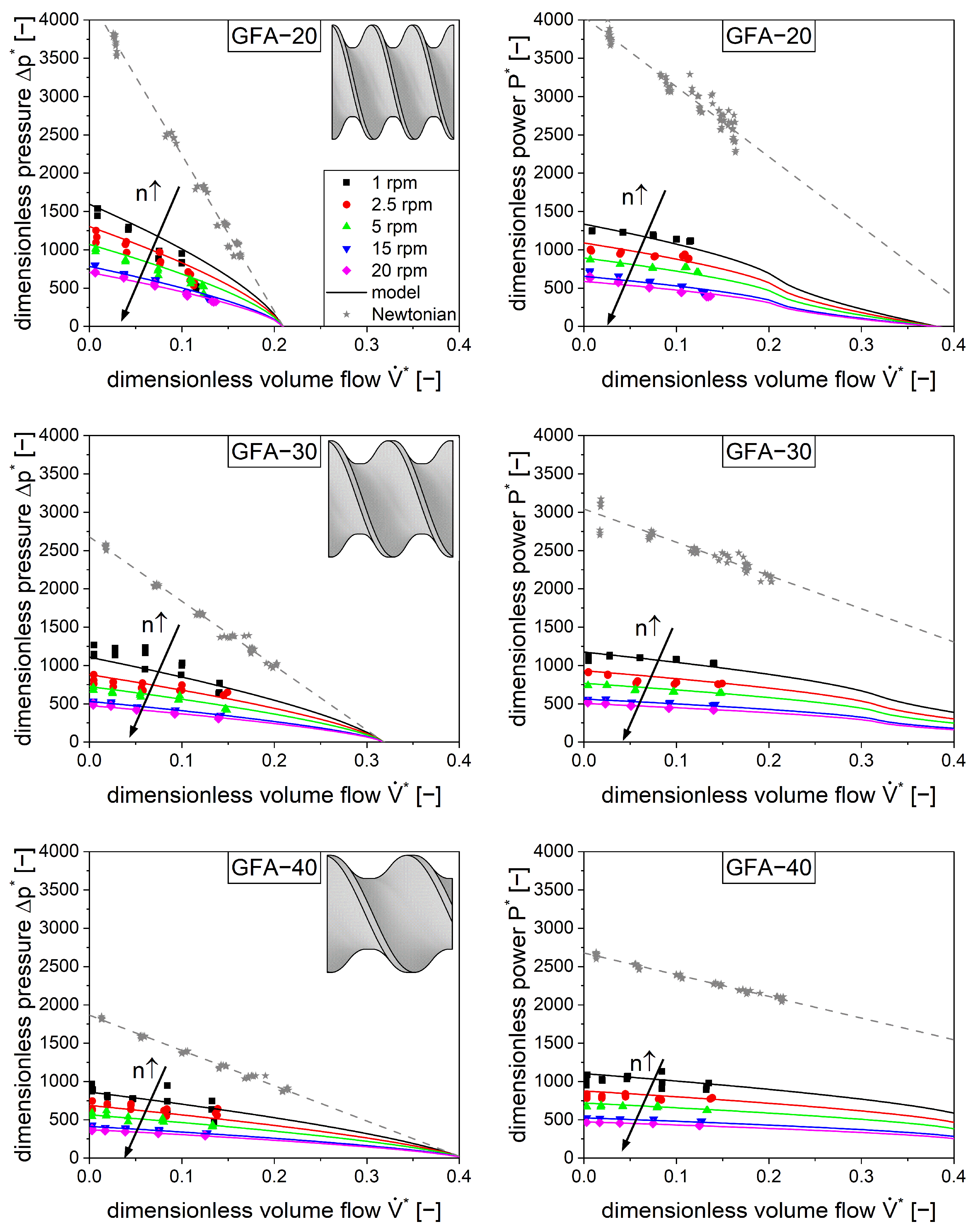
4.4. Characterization of Conveying Elements
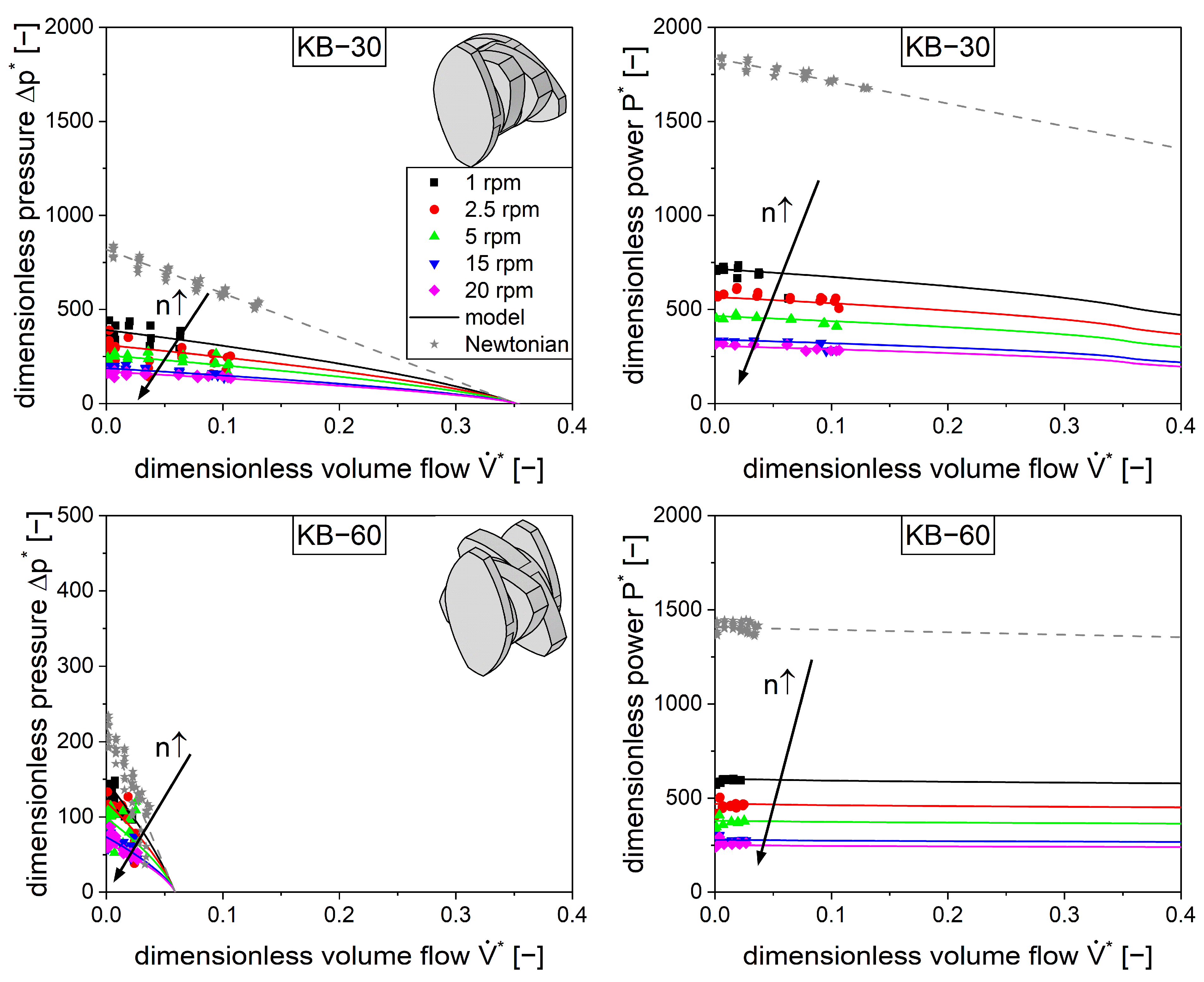
4.5. Kneading Elements
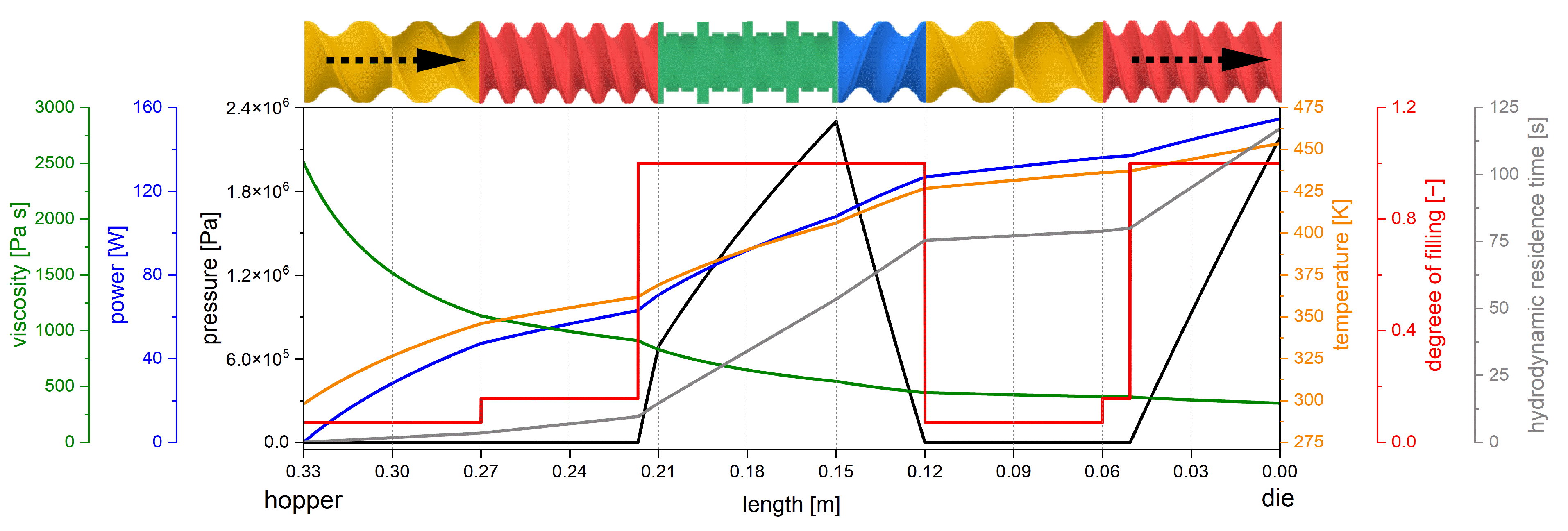
4.6. Utilization of the Screw Parameters
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Latin Symbols | Definition | Unit |
| dimensionless pressure parameters | ||
| dimensionless power parameters | ||
| dimensionless shear parameters | ||
| temperature shift factor | ||
| centerline distance | ||
| flow index | ||
| barrel diameter | ||
| screw outer diameter | ||
| screw inner diameter | ||
| Arrhenius activation energy | ||
| axial length | ||
| torque | ||
| screw speed | ||
| power | ||
| dimensionless power | ||
| pressure | ||
| dimensionless pressure | ||
| ideal gas constant | ||
| temperature | ||
| reference temperature | ||
| volume flow | ||
| dimensionless volume flow | ||
| weight | ||
| Greek symbols | definition | unit |
| shear rate | ||
| critical shear rate | ||
| representative shear rate | ||
| difference | ||
| viscosity | ||
| zero shear rate viscosity | ||
| dynamic viscosity | ||
| conveying parameter | ||
| Abbreviations | definition | |
| 1D | one-dimensional | |
| 3D | three-dimensional | |
| HEC | hydroxyethylcellulose | |
| Note: Tradenames and trademarks are used without particular labeling. | ||
Appendix A

| Dimension | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| diameter ratio | 1.66 | |
| conveying element screw diameter | 28.25 * | |
| kneading element screw diameter | 27.97 * | |
| barrel diameter | 28.45 * | |
| centerline distance | 23 | |
| conveying element length | 30 | |
| kneading element length | 15 | |
| pitch | 20, 30, 40 | |
| staggering angle | 30, 60, 90 |
References
- Patil, H.; Tiwari, R.V.; Repka, M.A. Hot-Melt Extrusion: From Theory to Application in Pharmaceutical Formulation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repka, M.A.; Battu, S.K.; Upadhye, S.B.; Thumma, S.; Crowley, M.M.; Zhang, F.; Martin, C.; McGinity, J.W. Pharmaceutical applications of hot-melt extrusion: Part II. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2007, 33, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, M.M.; Zhang, F.; Repka, M.A.; Thumma, S.; Upadhye, S.B.; Battu, S.K.; McGinity, J.W.; Martin, C. Pharmaceutical applications of hot-melt extrusion: Part I. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2007, 33, 909–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauwendaal, C. Polymer Extrusion, 5th ed.; Hanser: München, Germany, 2014; ISBN 978-1-56990-516-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kohlgrüber, K.; Bierdel, M.; Rust, H. Polymer-Aufbereitung und Kunststoff-Compoundierung: Grundlagen, Apparate, Maschinen, Anwendungstechnik; Hanser: München, Germany, 2019; ISBN 978-3-446-45832-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kohlgrüber, K. Co-Rotating Twin-Screw Extruders: Fundamentals, Technology, and Applications, 1st ed.; Hanser: München, Germany, 2008; ISBN 978-3-446-41372-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, H.; Matić, J.; Khinast, J. Characteristic parameters and process maps for fully-filled twin-screw extruder elements. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 230, 116202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitzlmayr, A.; Khinast, J. Co-rotating twin-screw extruders: Detailed analysis of conveying elements based on smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Part 1: Hydrodynamics. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 134, 861–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitzlmayr, A.; Khinast, J. Co-rotating twin-screw extruders: Detailed analysis of conveying elements based on smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Part 2: Mixing. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 134, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stritzinger, U.; Roland, W.; Berger-Weber, G.; Steinbichler, G. Modeling melt conveying and power consumption of co-rotating twin-screw extruder kneading blocks: Part A. Data generation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 3721–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, J.; Helmig, J.; Möller, M.; Elgeti, S. Boundary-conforming finite element methods for twin-screw extruders using spline-based parameterization techniques. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020, 361, 112740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Amano, T.; Kihara, S.-I.; Funatsu, K. Flow patterns and mixing mechanisms in the screw mixing element of a co-rotating twin-screw extruder. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2002, 42, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.; Seong, J. Comparison of effects on technical variances of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software based on finite element and finite volume methods. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2014, 78, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayser, K.; Monschke, M.; Wagner, K.G. ASD Formation Prior to Material Characterization as Key Parameter for Accurate Measurements and Subsequent Process Simulation for Hot-Melt Extrusion. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emin, M.A.; Wittek, P.; Schwegler, Y. Numerical analysis of thermal and mechanical stress profile during the extrusion processing of plasticized starch by non-isothermal flow simulation. J. Food Eng. 2021, 294, 110407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potente, H.; Bastian, M.; Gehring, A.; Stephan, M.; Ptschke, P. Experimental investigation of the morphology development of polyblends in corotating twin-screw extruders. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 76, 708–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergnes, B.; Della Valle, G.; Delamare, L. A global computer software for polymer flows in corotating twin screw extruders. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1998, 38, 1781–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitzlmayr, A.; Koscher, G.; Reynolds, G.; Huang, Z.; Booth, J.; Shering, P.; Khinast, J. Mechanistic modeling of modular co-rotating twin-screw extruders. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 474, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochmann, E.S.; Steffens, K.E.; Gryczke, A.; Wagner, K.G. Numerical simulation of hot-melt extrusion processes for amorphous solid dispersions using model-based melt viscosity. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 124, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, V. Modeling of Pharmaceutical Twin Screw Extrusion Processes Using Experimental Dimensionless Numbers; 14th European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE): Berlin, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bawiskar, S.; White, J.L. Melting model for modular self wiping co-rotating twin screw extruders. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1998, 38, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawiskar, S.; White, J.L. A Composite Model for Solid Conveying, Melting, Pressure and Fill Factor Profiles in Modular Co -Rotating Twin Screw Extruders. Int. Polym. Process. 1997, 12, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potente, H.; Hanhart, W.; Reski, T. Design and processing optimization of extruder screws. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1994, 34, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flecke, J.; Potente, H.; Kretschmer, K. A Physico-Mathematical Model for the Dispersion Process in a Co-Rotating Intermeshing Twin Screw Extruder. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2002, 21, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, T.; David, C.; Dannemiller, D. Twin screw extruder simulation programs-what can they offer? Plast. Addit. Compd. 2002, 4, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, J. Grundlagen des fördertechnischen Verhaltens einspindeliger Schnecken bei Newtonschen Flüssigkeiten. Chem. Ing. Tech. 1967, 39, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, J. Die Ähnlichkeitstheorie in Der Physikalisch-Technischen Forschung; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1971; ISBN 978-3-642-65096-3. [Google Scholar]
- Düphans, V.; Kimmel, V.; Messing, L.; Schaldach, G.; Thommes, M. Experimental and Numerical Characterization of Screw Elements Used in Twin-Screw Extrusion. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2024, 29, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eitzlmayr, A.; Khinast, J.; Hörl, G.; Koscher, G.; Reynolds, G.; Huang, Z.; Booth, J.; Shering, P. Experimental characterization and modeling of twin-screw extruder elements for pharmaceutical hot melt extrusion. AIChE J. 2013, 59, 4440–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezger, T. Das Rheologie Handbuch: Für Anwender von Rotations- und Oszillations-Rheometern, 5th ed.; Vincentz Network: Hannover, Germany, 2016; ISBN 978-3-74860-012-1. [Google Scholar]
- Osswald, T.A.; Rudolph, N. Polymer Rheology: Fundamentals and Applications; Hanser: Munich, Germany, 2015; ISBN 978-1-56990-517-3. [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson, A.; Bird, R.B. Non-Newtonian Flow in Annuli. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1958, 50, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, V.; Ercolin, E.; Zimmer, R.; Yörük, M.; Winck, J.; Thommes, M. Measuring and Modeling of Melt Viscosity for Drug Polymer Mixtures. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker Chemie AG. Technical Data Sheet Elastosil LR3003/10: Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR). Available online: https://www.wacker.com/h/en-us/medias/ELASTOSIL-LR-300310-TR-AB-en-2024.06.16.pdf (accessed on 22 July 2024).
- Elkem Bluestar Silicones. Rhodorsil® Oils 47: Technical Information. Available online: https://www.silitech.ch/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/32.pdf (accessed on 22 July 2024).
- Boutelier, D.; Cruden, A.; Saumur, B. Density and visco-elasticity of Natrosol 250 HH solutions: Determining their suitability for experimental tectonics. J. Struct. Geol. 2016, 86, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochmann, E.S.; Gryczke, A.; Wagner, K.G. Validation of Model-Based Melt Viscosity in Hot-Melt Extrusion Numerical Simulation. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebre-Sellassie, I.; Martin, C.; Zhang, F.; DiNunzio, J. (Eds.) Pharmaceutical Extrusion Technology, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-0-367-73508-1. [Google Scholar]
- Stritzinger, U.; Roland, W.; Berger-Weber, G.; Steinbichler, G. Modeling melt conveying and power consumption of co-rotating twin-screw extruder kneading blocks: Part B. Prediction models. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2023, 63, 841–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza Gonzalez, J.F.; Nirschl, H. Numerical Investigation of the Local Shear Rate in a Twin-Screw Extruder for the Continuous Processing of Li-Ion Battery Electrode Slurries. Energy Technol. 2023, 11, 2201517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitzlmayr, A.; Matić, J.; Khinast, J. Analysis of flow and mixing in screw elements of corotating twin-screw extruders via SPH. AIChE J. 2017, 63, 2451–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badruddoza, A.Z.M.; Moseson, D.E.; Lee, H.-G.; Esteghamatian, A.; Thipsay, P. Role of rheology in formulation and process design of hot melt extruded amorphous solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 664, 124651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaval, M.; Sharma, S.; Dudhat, K.; Chavda, J. Twin-Screw Extruder in Pharmaceutical Industry: History, Working Principle, Applications, and Marketed Products: An In-depth Review. J. Pharm. Innov. 2022, 17, 294–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, T.; Özbay, C.; Feuerbach, T.; Thommes, M. Predicting Throughput and Melt Temperature in Pharmaceutical Hot Melt Extrusion. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Silicone Oil | Silicone Rubber | HEC Solution | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 96 ± 0.1 | 224 ± 11 | 107 ± 1 | |
| - | 0.043 ± 0.004 | 0.260 ± 0.007 | |
| - | 0.316 ± 0.003 | 0.598 ± 0.004 | |
| 14,327 ± 218 | 24,512 ± 4206 | 39,569 ± 695 | |
| 25 | 25 | 25 | |
| 973 [34] | 1070 [35] | 1008 [36] |
| Measured Conveying Elements | König [6] | Eitzlmayr [29] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Label | GFA-20 | GFA-30 | GFA-40 | - | - | - | 16/16 | 24/24 |
| Pitch/d [-] | 0.70 | 1.05 | 1.40 | 0.70 | 1.05 | 1.40 | 0.89 | 1.33 |
| A1 | 0.210 ± 0.007 | 0.319 ± 0.011 | 0.406 ± 0.013 | 0.203 | 0.319 | 0.416 | 0.2257 | 0.3593 |
| A2 | 4278 ± 55 | 2677 ± 29 | 1866 ± 15 | 4437 | 2545 | 1956 | 808.6 | 766.5 |
| A3 | 37.60 ± 1.86 | 28.62 ± 0.77 | 18.45 ± 0.44 | n/a | n/a | n/a | 41.49 | 39.33 |
| B1 | 0.443 ± 0.035 | 0.702 ± 0.071 | 0.947 ± 0.033 | 0.722 | 1.040 | 1.384 | n/a | n/a |
| B2 | 4039 ± 75 | 3041 ± 56 | 2677 ± 12 | 3085 | 2737 | 2719 | n/a | n/a |
| B3 | 82.70 ± 7.81 | 44.15 ± 1.24 | 37.88 ± 0.97 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Measured Kneading Elements | Stritzinger [10] | Eitzlmayr [29] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Label | KB-30 | KB-60 | KB-90 | 30° | 60° | 90° | KB 45/5/8 |
| 1.05 | 2.11 | 3.16 | 1.03 | 2.05 | 3.08 | 2.5 | |
| A1 | 0.352 ± 0.028 | 0.059 ± 0.01 | 0 | 0.444 | 0.107 | n/a | 0.1545 |
| A2 | 818 ± 13 | 220 ± 12 | 0 | 826 | 280 | 1.83 | 259.1 |
| A3 | 17.02 ± 1.21 | 5.14 ± 0.59 | 0 | n/a | n/a | n/a | 13.29 |
| B1 | 1.53 ± 0.153 | 10.834 ± 3.455 | 2.131 | 3.262 | n/a | n/a | |
| B2 | 1834 ± 10 | 1407 ± 13 | 1358 ± 28 | 3518 | 2453 | 2775 | n/a |
| B3 | 42.43 ± 1.89 | 27.89 ± 0.91 | 22.63 ± 1.73 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kimmel, V.; Gräfe, L.; Grieser, L.; Lips, A.; Hennig, R.; Winck, J.; Thommes, M. Modeling Shear-Thinning Flow in Twin-Screw Extrusion Processes. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030353
Kimmel V, Gräfe L, Grieser L, Lips A, Hennig R, Winck J, Thommes M. Modeling Shear-Thinning Flow in Twin-Screw Extrusion Processes. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(3):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030353
Chicago/Turabian StyleKimmel, Vincent, Lorena Gräfe, Luca Grieser, Alexey Lips, Robert Hennig, Judith Winck, and Markus Thommes. 2025. "Modeling Shear-Thinning Flow in Twin-Screw Extrusion Processes" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 3: 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030353
APA StyleKimmel, V., Gräfe, L., Grieser, L., Lips, A., Hennig, R., Winck, J., & Thommes, M. (2025). Modeling Shear-Thinning Flow in Twin-Screw Extrusion Processes. Pharmaceutics, 17(3), 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030353






