Computer-Aided Drug Design in Research on Chinese Materia Medica: Methods, Applications, Advantages, and Challenges
Abstract
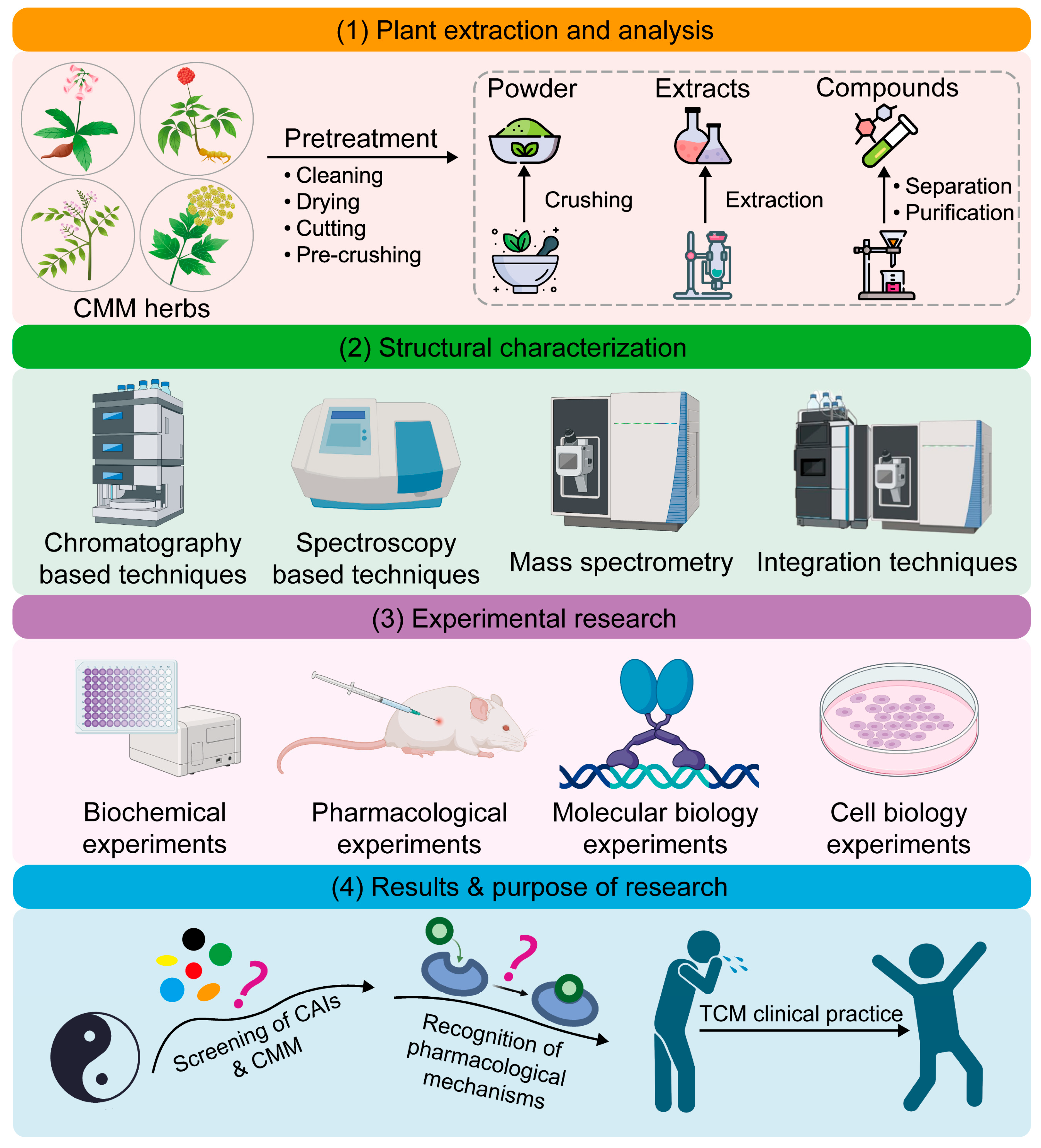
1. Introduction
2. Computational Chemistry in CMM Research
2.1. QC
2.1.1. Brief Introduction to QC
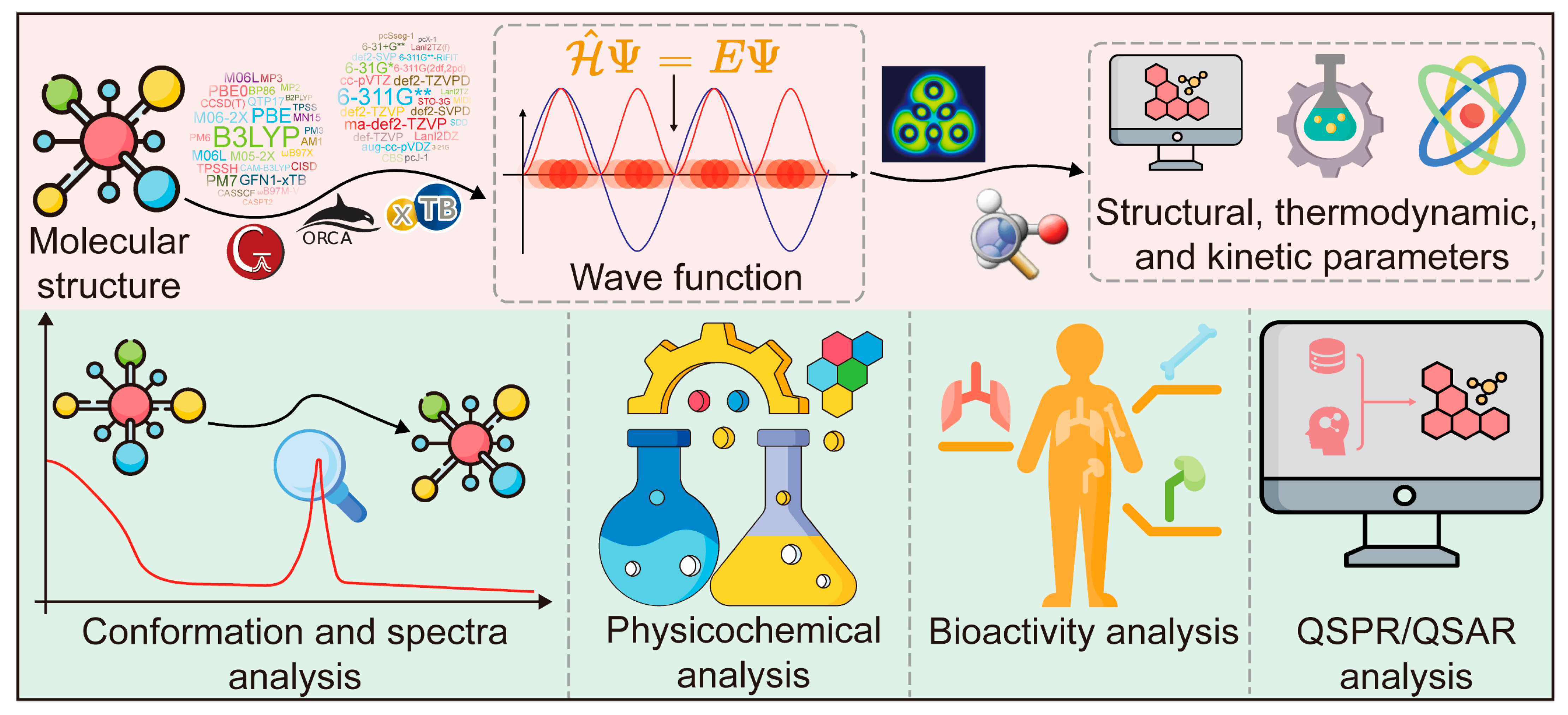
2.1.2. Applications of QC in CMM Research
- Conformation and spectra analysis of CAIs
- 2.
- Physicochemical analysis of CAIs
- 3.
- Bioactivity analysis of CAIs
- 4.
- Quantitative structure–property relationship (QSPR) and quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) analysis of CAIs
2.2. MM
2.2.1. Brief Introduction to MM
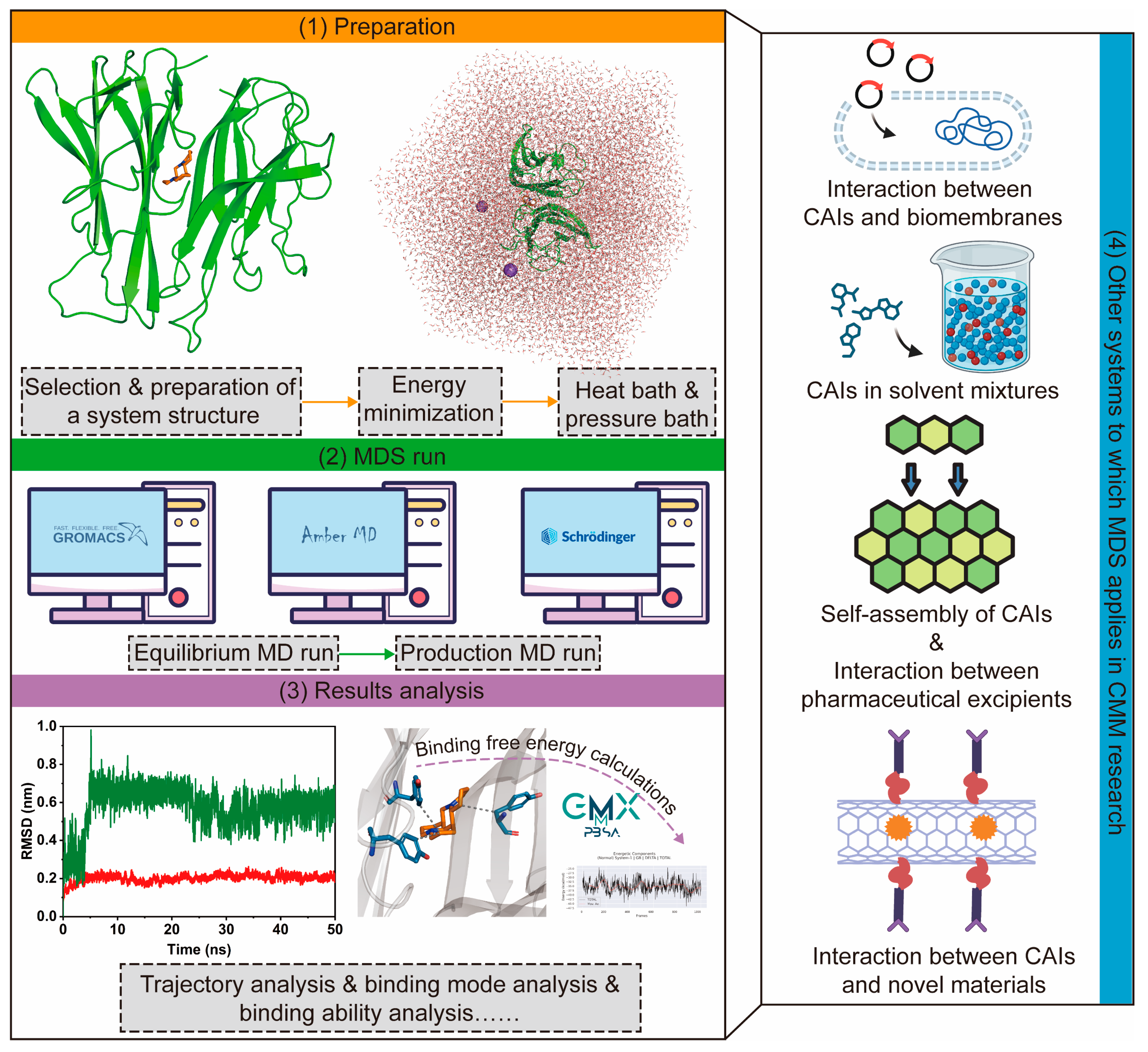
2.2.2. Applications of MM in CMM Research
- Virtual screening of CAIs
- 2.
- MDS for various systems related to CMM research
2.3. QM/MM
2.3.1. Brief Introduction to QM/MM
2.3.2. Applications of QM/MM in CMM Research
3. Informatics
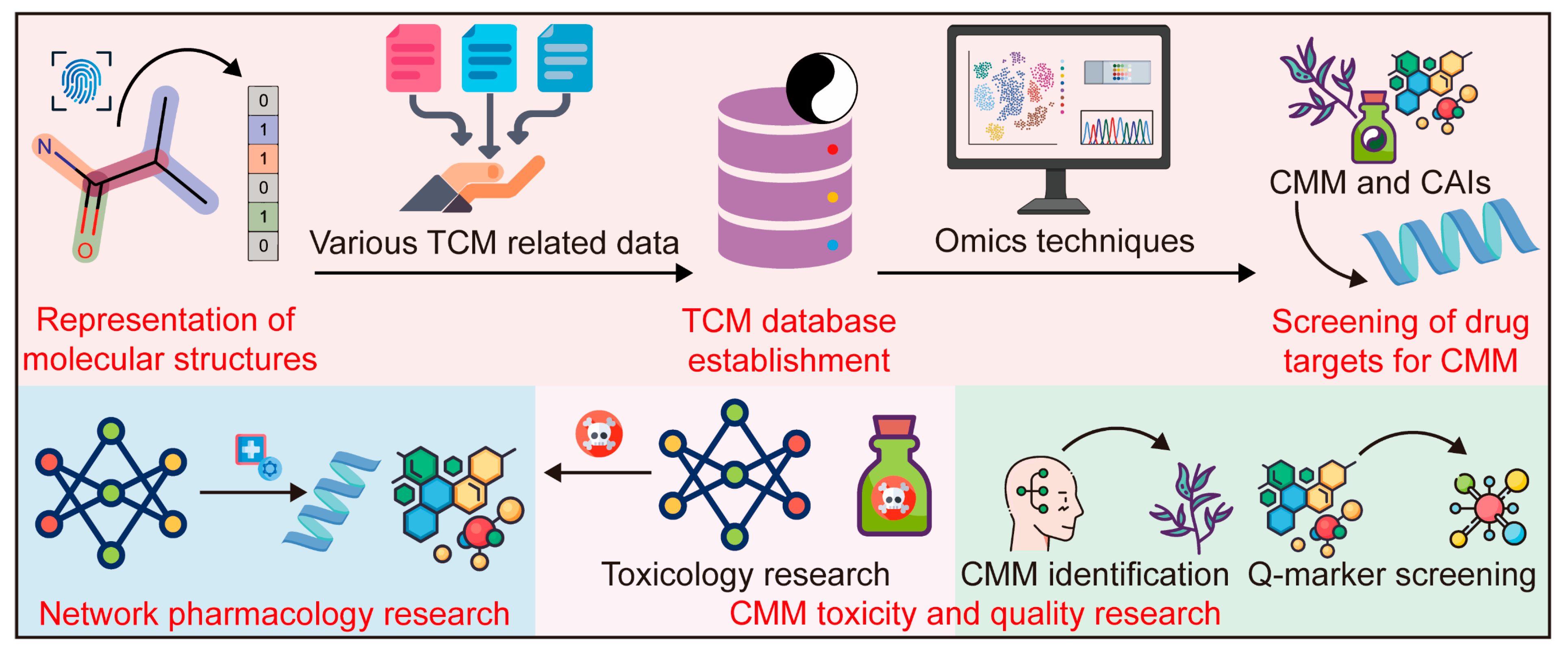
3.1. Cheminformatics and Bioinformatics
3.1.1. Brief Introduction to Cheminformatics and Bioinformatics
3.1.2. Application of Cheminformatics and Bioinformatics in CMM Research
- TCM database establishment
| Database | Number of Formulae | Number of Herbs | Number of Ingredients | Number of Targets | Number of Cases | Website | Accessibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BATMAN-TCM [138] | 54,832 | 8404 | 39,171 | 2,319,272 | - | http://bionet.ncpsb.org.cn/batman-tcm/#/home | Yes |
| CancerHSP [139] | - | 2439 | 3575 | - | - | https://old.tcmsp-e.com/CancerHSP.php | Yes |
| CEMTDD [140] | - | 621 | 4060 | 2163 | - | http://www.cemtdd.com/index.html | No |
| CMAUP [141] | - | 7865 | 60,222 | 758 | - | https://www.bidd.group/CMAUP/ | Yes |
| CMCR | - | - | - | - | 111,653 | https://cmcr.yiigle.com/ | Yes |
| CPMCP [142] | 656 | 1560 | 27,928 | 20,965 | - | http://cpmcp.top | No |
| ETCM [143] | 3959 | 402 | 7284 | 2266 | - | http://www.tcmip.cn/ETCM/ | Yes |
| ETM-DB [144] | 573 | 1054 | 4285 | - | - | http://biosoft.kaist.ac.kr/etm/home.php | No |
| Herb [145] | - | 7263 | 49,258 | 12,933 | - | http://herb.ac.cn/ | Yes |
| HIT [146] | - | 1250 | 1237 | 2208 | - | http://www.badd-cao.net:2345/ | Yes |
| IGTCM [147] | - | 83 | 1033 | - | - | http://yeyn.group:96/ | Yes |
| iTCM [148] | 25,875 | 8454 | 43,430 | 18,851 | - | http://itcm.biotcm.net/ | Yes |
| LTM-TCM [149] | 48,126 | 9122 | 34,967 | 13,109 | - | http://cloud.tasly.com/#/tcm/home | No |
| SuperTCM [150] | - | 6516 | 55,772 | 543 | - | http://tcm.charite.de/supertcm | Yes |
| SymMap [151] | - | 698 | 25,975 | 20,965 | - | https://www.symmap.org | No |
| TCM@taiwan [152] | - | 352 | 37,170 | - | - | http://tcm.cmu.edu.tw/ | No |
| TCMBank [153] | - | 9193 | 61,965 | 32,529 | - | https://tcmbank.cn/ | No |
| TCM-ID [154] | 7443 | 2751 | 7375 | 768 | - | https://www.bidd.group/TCMID/ | Yes |
| TCMID [155] | 99,582 | 10,846 | 43,413 | - | - | https://www.megabionet.org/tcmid/ | No |
| TCMIO [156] | 1493 | 618 | 16,437 | 400 | - | http://tcmio.xielab.net | Yes |
| TCMIP V2.0 | 3959 | 402 | 7284 | 2266 | - | http://www.tcmip.cn/ | Yes |
| TCMM [157] | 48,043 | 8932 | 69,816 | 76,449 | www.tcmm.net.cn/zh-hans/ | Yes | |
| TCM-Mesh [158] | - | 6235 | 383,840 | - | - | http://mesh.tcm.microbioinformatics.org/ | No |
| TCMSID [159] | - | 499 | 20,015 | 3270 | - | https://tcm.scbdd.com/ | No |
| TCMSP [160] | - | 499 | 29,384 | 3311 | - | https://old.tcmsp-e.com/tcmsp.php | Yes |
| TCMSSD [161] | 133,518 | 8259 | 43,413 | 17,602 | - | http://tcmssd.ratcm.cn/ | Yes |
| TCM-suite [162] | 6692 | 7322 | 704,321 | - | - | http://tcm-suite.aimicrobiome.cn/ | Yes |
| TM-MC [163] | 5075 | 635 | 34,656 | 13,971 | - | https://tm-mc.kr/material.do | Yes |
| YaTCM [164] | 1813 | 6220 | 47,696 | 18,697 | - | http://cadd.pharmacy.nankai.edu.cn/yatcm/home | No |
| Imedbooks | 95,260 | 8980 | - | - | - | https://www.imedbooks.com/ | Yes |
| TCMkb | - | - | - | - | 465,784 | http://www.tcmkb.cn/consiliaweb/ | Yes |
| Shoudao Zhongyi | - | - | - | - | 400,000 | https://www.shoudaozhongyi.com/ | Yes |
| Yian | 586 | 895 | - | - | 30 | http://www.zhongyoo.com/yian/ | Yes |
| Yideng Xuyan | 400,000 | - | - | - | 102,000 | http://db.yidxy.com/prescriptions | Yes |
| TCMdoc | 80,000 | 11,239 | - | - | 60,000 | http://www.tcmdoc.cn/YiAn/index.aspx | Yes |
- 2.
- Screening of drug targets for CMM
- 3.
- CMM network pharmacology (CMM-NP) research
- 4.
- CMM toxicity and quality research
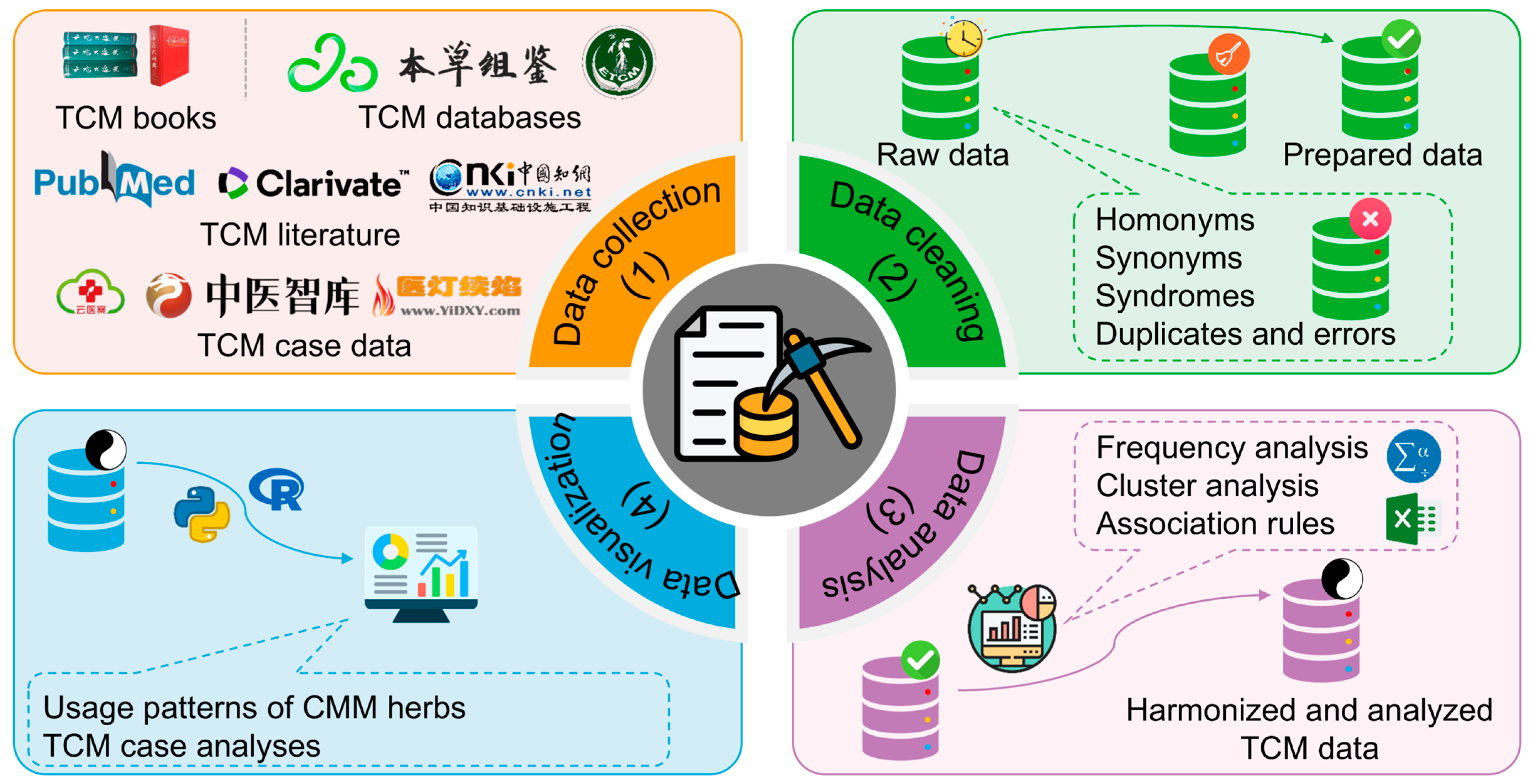
3.2. Data Mining
3.2.1. Brief Introduction to Data Mining
3.2.2. Application of Data Mining in CMM Research
4. Advantages and Challenges of CADD in CMM Research
4.1. Advantages of CADD in CMM Research
4.1.1. Enhancing the Accuracy and Reliability of CMM Research
4.1.2. Improving the Efficiency and Reducing the Cost of CMM Research
4.1.3. Promoting the Modernization and Internationalization of CMM Research
4.2. Challenges of CADD in CMM Research
4.2.1. Inadequate Computational Accuracy and Computational Resources
4.2.2. Difficulties in Data Collection and Data Quality Control
4.2.3. Insufficient Adaptability and Interpretability of AI Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADMET | absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity |
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| AIDD | artificial intelligence drug design |
| CADD | computer-aided drug design |
| CAIs | Chinese materia medica active ingredients |
| CD | circular dichroism |
| CMM | Chinese materia medica |
| CMM-NP | Chinese materia medica network pharmacology |
| CNKI | China National Knowledge Infrastructure |
| CPUs | central processing units |
| DEGs | differentially expressed genes |
| DFT | density functional theory |
| DL | deep learning |
| ESP | molecular surface electrostatic potentials |
| FDA | US Food and Drug Administration |
| GO | gene ontology |
| GPUs | graphics processing units |
| GWAS | genome-wide association studies |
| HIV | human immunodeficiency virus |
| HOMO | highest occupied molecular orbital |
| InChI | International Chemical Identifier |
| IR | infrared |
| IRC | intrinsic reaction coordinates |
| KRR | kernel ridge regression |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| LBDD | ligand-based drug design |
| LUMO | lowest unoccupied molecular orbital |
| MD | molecular dynamics |
| MDS | molecular dynamics simulation |
| ML | machine learning |
| MM | molecular mechanics |
| MM/PB(GB)SA | molecular mechanics Poisson–Boltzmann/generalized Born surface area |
| MS | mass spectrometry |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
| NPA | natural population analysis |
| NSFC | National Natural Science Foundation of China |
| NPs | natural products |
| PPI | protein–protein interaction |
| QC | quantum chemistry |
| QCC | quantum chemical calculation |
| QM | quantum mechanics |
| QM/MM | quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics |
| Q-markers | quality markers |
| QSAR | quantitative structure–activity relationship |
| QSPR | quantitative structure–property relationship |
| SBDD | structure-based drug design |
| SMILES | simplified molecular input line entry system |
| TCM | traditional Chinese medicine |
| UV–Vis | ultraviolet–visible |
| WGCNA | weighted gene co-expression network analysis |
| WM | Western medicine |
References
- Li, C.; Sun, H.; Kong, R. Traditional Chinese Medicine and Self-Molding of National Image. Asia-Pac. Tradit. Med. 2024, 20, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Cyranoski, D. Why Chinese Medicine Is Heading for Clinics around the World. Nature 2018, 561, 448–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, M.; Xu, H.; Han, L.; Sun, R. Stable Support from National Nature Science Foundation for Innovative Development of Basic Research in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Bull. Natl. Nat. Sci. Found. China 2024, 38, 378–382. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.C.; Fei, Y.T.; Lai, X.Z.; Lan, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z.W.; Fang, H.; Liu, J.P.; Rong, H.G. Progress and Challenges in Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine in China from 2002 to 2021. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1425940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Dang, Y.; Chen, X.; Hai; Yao, W.; Kou, W.; Zhang, J.; Shi, J.; Dong, Y.; Li, J. Quercetin 7-Rhamnoside from Sorbaria Sorbifolia Exerts Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Effect via DHRS13/Apoptotic Pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 135, 156031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Song, X.; Tang, X.; Qian, X.; Du, Z.; Hu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, M. Synergistic Effect of Constituent Drugs of Baibutang on Improving Yin-Deficiency Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 306, 116050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humblet, C.; Marshall, G.R. Three-Dimensional Computer Modeling as an Aid to Drug Design. Drug Dev. Res. 1981, 1, 409–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, K.M.; Ringe, D.; Reynolds, C.H. Drug Design: Structure- and Ligand-Based Approaches; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, B.; Shen, Y.Q. Computer Especially AI-Assisted Drug Virtual Screening and Design in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Phytomedicine 2022, 107, 154481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vemula, D.; Jayasurya, P.; Sushmitha, V.; Kumar, Y.N.; Bhandari, V. CADD, AI and ML in Drug Discovery: A Comprehensive Review. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 181, 106324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, I.N.; Busch, D.H.; Shull, H. Quantum Chemistry; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision C.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Neese, F.; Wennmohs, F.; Becker, U.; Riplinger, C. The ORCA Quantum Chemistry Program Package. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 224108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannwarth, C.; Caldeweyher, E.; Ehlert, S.; Hansen, A.; Pracht, P.; Seibert, J.; Spicher, S.; Grimme, S. Extended Tight-Binding Quantum Chemistry Methods. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2021, 11, e1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.T.; Huang, Z.P.; Xu, X.R.; Li, S.H.; Xu, Y.X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.M. Two New Diketopiperazines from the Cordyceps Fungus Samsoniella Sp. XY4. J. Antibiot. 2023, 76, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.S.; Zheng, Y.L.; Mo, J.X.; Liu, X.; Li, X.H.; Zhou, C.X. Sesquiterpene Lactones from the Root Tubers of Lindera Aggregata. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Liang, J.; Wei, D.; Cui, H.L. Molecular and Crystalline Vibration Characteristics of Baicalin Investigated by Terahertz Spectroscopy and Density Functional Theory. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Gao, Z.; He, D.; Zhang, L.; Ke, G. Data-Driven Quantum Chemical Property Prediction Leveraging 3D Conformations with Uni-Mol+. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, P.J.; McCann, D.M.; Devlin, F.J.; Smith, A.B. Determination of the Absolute Configurations of Natural Products via Density Functional Theory Calculations of Optical Rotation, Electronic Circular Dichroism, and Vibrational Circular Dichroism: The Cytotoxic Sesquiterpene Natural Products Quadrone, Suberosenone, Suberosanone, and Suberosenol a Acetate. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Adrjan, B.; Wlodarz, J.; Li, J.; Jackowski, K.; Roszak, S. NMR Measurements and DFT Studies of Nuclear Magnetic Shielding in Emodin and Chuanxiongzine Molecules. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1166, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wu, J.; Ning, Z.; Jian, J.; Zhao, T.; Liang, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Size-Tunable Au@ag Nanoparticles for Colorimetric and SERS Dual-Mode Sensing of Palmatine in Traditional Chinese Medicine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 174, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, Y.; Liu, F.; Huang, J.; Li, P.; Wang, B.; Zhao, W.; Chen, M.; Xu, S.; Guan, F.; et al. Comprehensive Investigation of Structural Properties (X-Ray Diffraction, IR, Hirshfeld, MEP and FMOs) and in Silico Screening of Potential Biological Activity of Euphorbia Factor L1. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1246, 131237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Ranjan, R.; Shukla, M. Molecular Interaction of Curcumin with Silver Nanocluster: A DFT Study. Vib. Spectrosc. 2023, 129, 103604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, C.; Zhao, L.; Gong, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Hu, P. Identifying Isomers in Chinese Traditional Medicine via Density Functional Theory and Ion Fragmentation Simulation Software QCxMS. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1730, 465122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zeng, J.; Cai, R.; Li, C. New UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS/MS-Based Library-Comparison Method Simultaneously Distinguishes 22 Phytophenol Isomers from Desmodium Styracifolium. Microchem. J. 2023, 191, 108938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Qiu, M. Machine Learning-Assisted Structure Annotation of Natural Products Based on MS and NMR Data. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2023, 40, 1735–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.H.; Amichetti, M.; Zanardi, M.M.; Grimson, R.; Daranas, A.H.; Sarotti, A.M. ML-J-DP4: An Integrated Quantum Mechanics-Machine Learning Approach for Ultrafast NMR Structural Elucidation. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 7487–7491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Qian, H.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Yu, S.; Xiao, X. Thermodynamic Estimate of pKa Values of the Carboxylic Acids in Aqueous Solution with the Density Functional Theory. Chin. J. Chem. 2010, 28, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Lui, R.; Matthews, S. LogP Prediction Performance with the SMD Solvation Model and the M06 Density Functional Family for SAMPL6 Blind Prediction Challenge Molecules. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2020, 34, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tang, W.; Liu, S.; Han, D.; Liu, Y.; Gong, J. Solubility of Benzoin in Three Binary Solvent Mixtures and Investigation of Intermolecular Interactions by Molecular Dynamic Simulation. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 243, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Cai, R.; Zeng, J.; Hu, Y.; Su, J.; Chen, S. Reconstruction of Quality Marker System for Ginkgo Folium Tablet Using UHPLC-Q-orbitrap MS, Quantum Chemical Calculation, Network Pharmacology, and Molecular Simulation. Phytochem. Anal. 2024, 35, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Su, J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, S.; Ouyang, X.; Cai, R.; Li, X. Antioxidant Mechanisms and Products of Four 4′,5,7-Trihydroxyflavonoids with Different Structural Types. RSC Med. Chem. 2022, 14, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredas, J.L. Mind the Gap! Mater. Horiz. 2014, 1, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; McGann, M.; Enyedy, I.J. The Influence of Calculated Physicochemical Properties of Compounds on Their ADMET Profiles. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 36, 127825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.N.; Chen, L.M.; Liu, Y.; Ma, H.Y.; Hu, Q.; Cao, Z.X.; Han, L.; Xu, R.C.; Yang, M.; Tian, Y.; et al. New Understanding of Aconitine Hydrolysis Pathway: Isolation, Identification and Toxicity Evaluation Based on Intermediate Products. Arabian J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104255. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Li, D.; Hu, Y.; You, X.; Guo, X.; Li, X.; Chen, B. A Novel C6-Sulfonated Celastrol Analog as a Tyrosinase and Melanin Inhibitor: Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Simulation. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1283, 135288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halabi Diaz, A.; Duque-Noreña, M.; Chamorro, E. Unveiling an Electronic LogP Analogue within the Conceptual Density Functional Theory Framework. Chem. Phys. 2024, 584, 112346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, H.; Bohle, F.; Bursch, M.; Hansen, A.; Grimme, S. Benchmark Study of Electrochemical Redox Potentials Calculated with Semiempirical and DFT Methods. J. Phys. Chem. A 2020, 124, 7166–7176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, B.M.; Byrd, E.F.C. Evaluation of Electrostatic Descriptors for Predicting Crystalline Density. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 2146–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, E.F.C.; Rice, B.M. Improved Prediction of Heats of Formation of Energetic Materials Using Quantum Mechanical Calculations. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.S.; Lane, P.; Brinck, T.; Paulsen, K.; Grice, M.E.; Politzer, P. Relationships of Critical Constants and Boiling Points to Computed Molecular Surface Properties. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 9369–9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.A.F.; Hachmann, J. Benchmarking DFT Approaches for the Calculation of Polarizability Inputs for Refractive Index Predictions in Organic Polymers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 4452–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Meng, J. Nuclear Magnetic Moments in Covariant Density Functional Theory. Front. Phys. 2018, 13, 132109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennington, R.; Keith, T.A.; Millam, J.M. GaussView, Version 6; Semichem Inc.: Shawnee Mission, KS, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T. A Comprehensive Electron Wavefunction Analysis Toolbox for Chemists, Multiwfn. J. Chem. Phys. 2024, 161, 082503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Guo, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Yan, H.; Jin, R.; Tang, Y. Evodiamine and Rutaecarpine as Potential Anticancer Compounds: A Combined Computational Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Asikaer, A.; Chen, Q.; Wang, F.; Lan, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, L.; Zhao, H.; Duan, H. Network Pharmacology and in Vitro Experimental Verification Unveil Glycyrrhizin from Glycyrrhiza Glabra Alleviates Acute Pancreatitis via Modulation of MAPK and STAT3 Signaling Pathways. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2024, 24, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.Z.; Cheng, P.G.; Abdulrahman, A.Y.; Teoh, T.C. The Identification of Active Compounds in Ganoderma Lucidum Var. Antler Extract Inhibiting Dengue Virus Serine Protease and Its Computational Studies. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 4273–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, C.Y.; Zhu, H.J.; Pittman, C.U.; Shou, J.W.; Cao, F. The First Dimeric Indole-Diterpenoids from a Marine-Derived Penicillium Sp. Fungus and Their Potential for Anti-Obesity Drugs. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2025, 7, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cui, H.; Liu, K.; Yang, X.; Xing, S.; Li, W. Unveiling Anti-Diabetic Potential of Baicalin and Baicalein from Baikal Skullcap: LC–MS, In Silico, and In Vitro Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paukku, Y.; Rasulev, B.; Syrov, V.; Khushbaktova, Z.; Leszczynski, J. Structure-hepatoprotective Activity Relationship Study of Sesquiterpene Lactones: A QSAR Analysis. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2009, 109, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.Z.; Wang, B.C.; Fan, Y.; Tan, J.; Yang, X. QSAR Study of Flavonoid-Metal Complexes and Their Anticancer Activities. J. Struct. Chem. 2015, 56, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ding, J.; Pan, L.; Cao, D.; Jiang, H.; Ding, X. Quantum Chemical Descriptors in Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship Models and Their Applications. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2021, 217, 104384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Rhabori, S.; El Aissouq, A.; Chtita, S.; Khalil, F. QSAR, Molecular Docking and ADMET Studies of Quinoline, Isoquinoline and Quinazoline Derivatives against Plasmodium falciparum Malaria. Struct. Chem. 2023, 34, 585–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornig, M.; Klamt, A. COSMOfrag: A Novel Tool for High-Throughput ADME Property Prediction and Similarity Screening Based on Quantum Chemistry. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2005, 45, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Júnior, E.F.; Aquino, T.M.; Araujo-Junior, J.X. Quantum Mechanical (QM) Calculations Applied to ADMET Drug Prediction: A Review. Curr. Drug Metab. 2017, 18, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.A.; Yang, S.; Mai, H.; Cheng, A.C. Exploring Deep Learning of Quantum Chemical Properties for Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion Predictions. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 6336–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropsha, A.; Isayev, O.; Varnek, A.; Schneider, G.; Cherkasov, A. Integrating QSAR Modelling and Deep Learning in Drug Discovery: The Emergence of Deep QSAR. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2024, 23, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liang, J.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Xia, B.; Shi, M.; Zeng, J.; Huang, H.; Yang, L.; He, J. Exploring Antithrombotic Mechanisms and Effective Constituents of Lagopsis Supina Using an Integrated Strategy Based on Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, Metabolomics, and Experimental Verification in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 336, 118717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hehre, W.J. A Guide to Molecular Mechanics and Quantum Chemical Calculations; Wavefunction, Inc.: Irvine, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Karplus, M.; Petsko, G.A. Molecular Dynamics Simulations in Biology. Nature 1990, 347, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornak, V.; Abel, R.; Okur, A.; Strockbine, B.; Roitberg, A.; Simmerling, C. Comparison of Multiple Amber Force Fields and Development of Improved Protein Backbone Parameters. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinf. 2006, 65, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudrapal, M.; Issahaku, A.R.; Agoni, C.; Bendale, A.R.; Nagar, A.; Soliman, M.E.S.; Lokwani, D. In Silico Screening of Phytopolyphenolics for the Identification of Bioactive Compounds as Novel Protease Inhibitors Effective against SARS-CoV-2. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 10437–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Shadrack, D.M.; Joseph, F.M.; Ndensendo, V.M.K. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Bioactive Compounds of Withania Somnifera Leaf Extract as DNA Gyrase Inhibitor. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 9279–9286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponder, J.W.; Wu, C.; Ren, P.; Pande, V.S.; Chodera, J.D.; Schnieders, M.J.; Haque, I.; Mobley, D.L.; Lambrecht, D.S.; DiStasio, R.A.; et al. Current Status of the AMOEBA Polarizable Force Field. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 2549–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenzado, J.L.; Benito, C.; Atilhan, M.; Aparicio, S. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Cineole and Organic Acids. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 377, 121322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanommeslaeghe, K.; Raman, E.; MacKerell, A. Automation of the CHARMM General Force Field (CGenFF) II: Assignment of Bonded Parameters and Partial Atomic Charges. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 3155–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiannis, T.C.; Ververis, K.; Liang, J.J.; Pitsillou, E.; Kagarakis, E.A.; Yi, D.T.; Xu, V.; Hung, A.; El-Osta, A. Investigation of the Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Bioactive Compounds from Olea Europaea: In Silico Evaluation of Cyclooxygenase Enzyme Inhibition and Pharmacokinetic Profiling. Molecules 2024, 29, 3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuhri, U.M.; Purwaningsih, E.H.; Fadilah, F.; Yuliana, N.D. Network Pharmacology Integrated Molecular Dynamics Reveals the Bioactive Compounds and Potential Targets of Tinospora crispa Linn. as Insulin Sensitizer. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0251837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanommeslaeghe, K.; Hatcher, E.; Acharya, C.; Kundu, S.; Zhong, S.; Shim, J.; Darian, E.; Guvench, O.; Lopes, P.; Vorobyov, I.; et al. CHARMM General Force Field: A Force Field for Drug-like Molecules Compatible with the CHARMM All-atom Additive Biological Force Fields. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 671–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramani, N.K.; Venugopal, S. Molecular Docking and Dynamic Simulation Studies of Bioactive Compounds from Traditional Medicinal Compounds against Exfoliative Toxin B from Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2024, 15, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and Testing of a General Amber Force Field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, F.J.; Zahid, S.; Amber, S.; Jabeen, H.; Asim, N.; Ali Shah, S.A. Multitargeted Molecular Docking and Dynamic Simulation Studies of Bioactive Compounds from Rosmarinus Officinalis against Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2022, 27, 7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes-Pérez, A.F.; Herrera-Calderon, O.; Quintero-Saumeth, J. Uncaria Tomentosa (Cat’s Claw): A Promising Herbal Medicine against SARS-CoV-2/ACE-2 Junction and SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Based on Molecular Modeling. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 2227–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschner, K.N.; Yongye, A.B.; Tschampel, S.M.; González-Outeiriño, J.; Daniels, C.R.; Foley, B.L.; Woods, R.J. GLYCAM06: A Generalizable Biomolecular Force Field. Carbohydrates. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 622–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitapunkul, K.; Toochinda, P.; Lawtrakul, L. Molecular Dynamic Simulation Analysis on the Inclusion Complexation of Plumbagin with β-Cyclodextrin Derivatives in Aqueous Solution. Molecules 2021, 26, 6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostenbrink, C.; Villa, A.; Mark, A.E.; Van Gunsteren, W.F. A Biomolecular Force Field Based on the Free Enthalpy of Hydration and Solvation: The GROMOS Force-field Parameter Sets 53A5 and 53A6. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1656–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad Rosdi, M.N.; Mohd Arif, S.; Abu Bakar, M.H.; Razali, S.A.; Mohamed Zulkifli, R.; Ya’akob, H. Molecular Docking Studies of Bioactive Compounds from Annona Muricata Linn as Potential Inhibitors for Bcl-2, Bcl-w and Mcl-1 Antiapoptotic Proteins. Apoptosis 2018, 23, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, P.; Velmurugan, Y.; Arputharaj, D.S.; Savaridasson, J.K.; Hemamalini, M.; Venkatachalam, R. In Vitro Contraceptive Activities, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics, MM-PBSA, Non-Covalent Interaction and DFT Studies of Bioactive Compounds from Aegle Marmelos. Linn., Leaves. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1096177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrink, S.J.; Risselada, H.J.; Yefimov, S.; Tieleman, D.P.; De Vries, A.H. The MARTINI Force Field: Coarse Grained Model for Biomolecular Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 7812–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurella, L.C.; Moglioni, A.G.; Martini, M.F. Molecular Study of Endo and Phytocannabinoids on Lipid Membranes of Different Composition. Colloid. Surface. B 2023, 221, 113020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halgren, T.A. Merck Molecular Force Field. I. Basis, Form, Scope, Parameterization, and Performance of MMFF94. J. Comput. Chem. 1996, 17, 490–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.M.; Hong, P.H.; Su, J.H.; Hwang, T.L.; Lu, M.C.; Fang, L.S.; Wu, Y.C.; Li, J.J.; Chen, J.J.; Wang, W.H. Bioactive Compounds from a Gorgonian Coral Echinomuricea Sp.(Plexauridae). Marine Drugs 2012, 10, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolok, N.; Sumiwi, S.A.; Muhtadi, A.; Susilawati, Y.; Hendriani, R.; Ramadhan, D.S.F.; Levita, J.; Sahidin, I. Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Studies of Bioactive Compounds Contained in Noni Fruit (Morinda Citrifolia L.) against Human Pancreatic α-Amylase. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 7091–7098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.; Ali, S.; Lim, J.H.; Chun, H.J.; Ahmad, K.; Ahmad, S.S.; Hwang, Y.C.; Han, K.S.; Kim, N.R.; Lee, E.J. Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitory Potentials of Glycyrrhiza Uralensis and Its Bioactive Compounds Licochalcone a and Licochalcone B: An in Silico and in Vitro Study. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 1024764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Maxwell, D.S.; Tirado-Rives, J. Development and Testing of the OPLS All-Atom Force Field on Conformational Energetics and Properties of Organic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 11225–11236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patidar, K.; Deshmukh, A.; Bandaru, S.; Lakkaraju, C.; Girdhar, A.; Vr, G.; Banerjee, T.; Nayarisseri, A.; Singh, S.K. Virtual Screening Approaches in Identification of Bioactive Compounds Akin to Delphinidin as Potential HER2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 2291–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugesan, S.; Kottekad, S.; Crasta, I.; Sreevathsan, S.; Usharani, D.; Perumal, M.K.; Mudliar, S.N. Targeting COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) Main Protease through Active Phytocompounds of Ayurvedic Medicinal Plants–Emblica Officinalis (Amla), Phyllanthus Niruri Linn.(Bhumi Amla) and Tinospora Cordifolia (Giloy)–a Molecular Docking and Simulation Study. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 136, 104683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.; Cramer, R.D.; Van Opdenbosch, N. Validation of the General Purpose Tripos 5.2 Force Field. J. Comput. Chem. 1989, 10, 982–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.; Ahmad, S.; Iqbal, M.N.; Khurshid, U.; Saleem, H.; Alamri, A.; Anwar, S.; Alamri, A.S.; Chohan, T.A. Phytochemical, Pharmacological, and in-Silico Molecular Docking Studies of Strobilanthes Glutinosus Nees: An Unexplored Source of Bioactive Compounds. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 147, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Goodsell, D.S.; Halliday, R.S.; Huey, R.; Hart, W.E.; Belew, R.K.; Olson, A.J. Automated Docking Using a Lamarckian Genetic Algorithm and an Empirical Binding Free Energy Function. J. Comput. Chem. 1998, 19, 1639–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 1. Method and Assessment of Docking Accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, S.; Cozza, G.; Moro, S. Medicinal Chemistry and the Molecular Operating Environment (MOE): Application of QSAR and Molecular Docking to Drug Discovery. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 1555–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, T.J.; Makino, S.; Skillman, A.G.; Kuntz, I.D. DOCK 4.0: Search Strategies for Automated Molecular Docking of Flexible Molecule Databases. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2001, 15, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.A.; Cheatham III, T.E.; Darden, T.; Gohlke, H.; Luo, R.; Merz Jr, K.M.; Onufriev, A.; Simmerling, C.; Wang, B.; Woods, R.J. The Amber Biomolecular Simulation Programs. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1668–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J.C. GROMACS: Fast, Flexible, and Free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, M.; Hünenberger, P.H.; Bakowies, D.; Baron, R.; Bürgi, R.; Geerke, D.P.; Heinz, T.N.; Kastenholz, M.A.; Kräutler, V.; Oostenbrink, C.; et al. The GROMOS Software for Biomolecular Simulation: GROMOS05. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1719–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Luo, C.; Jiang, H. Computational Methods for Drug Design and Discovery: Focus on China. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Wang, D.; Li, R.L.; He, L.Y.; Ai, L.; Wu, C.J. Current Strategies and Technologies for Finding Drug Targets of Active Components from Traditional Chinese Medicine. Front. Biosci. 2021, 26, 572–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Li, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Hu, G.; Wu, H. Solution Structure of BmKK2, a New Potassium Channel Blocker from the Venom of Chinese Scorpion Buthus Martensi Karsch. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinf. 2004, 55, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao Weina; Li Yun; Zhang Rui; Gao Hui; Xu Weiren; Li Aixiu; Du Qishi; Zhang Xin; Wei Dongqing Screening of new HIV inhibitors based on the database of traditional Chinese medicine. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2006, 41, 241–246.
- Fan, J.; Fu, A.; Zhang, L. Progress in Molecular Docking. Quant. Biol. 2019, 7, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paggi, J.M.; Pandit, A.; Dror, R.O. The Art and Science of Molecular Docking. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2024, 93, 389–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Rusnac, D.-V.; Park, H.; Canzani, D.; Nguyen, H.M.; Stewart, L.; Bush, M.F.; Nguyen, P.T.; Wulff, H.; Yarov-Yarovoy, V.; et al. An Artificial Intelligence Accelerated Virtual Screening Platform for Drug Discovery. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, F.; Junaid, M.; Almalki, A.H.; Almaghrabi, M.; Ghazanfar, S.; Tahir ul Qamar, M. Deep Learning Pipeline for Accelerating Virtual Screening in Drug Discovery. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, M.J.; McCammon, J.A. Free Energy Difference Calculations by Thermodynamic Integration: Difficulties in Obtaining a Precise Value. J. Comput. Chem. 1991, 12, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Thomas, L.L. Perspective on Free-Energy Perturbation Calculations for Chemical Equilibria. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, T.; Marelius, J.; Åqvist, J. Ligand Binding Affinity Prediction by Linear Interaction Energy Methods. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 1998, 12, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genheden, S.; Ryde, U. The MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA Methods to Estimate Ligand-Binding Affinities. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Gao, Y.; Guo, J.; Tian, Y.; Lin, Z.; Wang, X. Discovery of Natural 15-LOX Small Molecule Inhibitors from Chinese Herbal Medicine Using Virtual Screening, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Dynamics Studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 115, 105197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Shi, J.; Cao, H.; Ye, T.; Yue, M.; Ye, F.; Fu, Y. Virtual Screening Based on Pharmacophore Model for Developing Novel HPPD Inhibitors. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 184, 105109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Peng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Duan, J.; Mao, X.; Tang, Z.; et al. Insights into the Penetration of PhACs in TCM during Ultrafiltration: Effects of Fouling Mechanisms and Intermolecular Interactions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 295, 121205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Shi, X.; Ding, H.; Dai, X.; Wan, G.; Qiao, Y. Interactions of Borneol with DPPC Phospholipid Membranes: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 20365–20381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Wang, R.; Wu, Z.; Guo, S.; Yang, C.; Ma, L.; Chen, L.; Shi, X.; Qiao, Y. Permeation-enhancing Effects and Mechanisms of Borneol and Menthol on Ligustrazine: A Multiscale Study Using in Vitro and Coarse-grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation Methods. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 92, 1830–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Yang, Y.; Wen, W.; Luo, Y.; Wu, J.; Xiang, L.; Hu, Y.; Xu, S.; Chen, S.; Wang, P. Vanillin Enhances the Passive Transport Rate and Absorption of Drugs with Moderate Oral Bioavailability in Vitro and in Vivo by Affecting the Membrane Structure. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Liu, Z.; Fan, R.; Zhao, M.; Luo, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Tang, J.; Luo, A.; et al. A New Methodology of Understanding the Mechanism of High Shear Wet Granulation Based on Experiment and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 638, 122923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Pan, S.; Li, J.; Ding, X.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, W. Formulation Design and Evaluation of Ginsenoside Compound K Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Pharm. Innov. 2024, 19, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Shi, X.; Ding, H.; Yin, Q.; Qiao, Y. Dissipative Particle Dynamics Simulation of Ginsenoside Ro Vesicular Solubilization Systems. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2014, 11, 2046–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Wen, J.; Sun, Y.; Ren, M.; Qiao, R.; Li, C. Self-Assembled Herbal Hydrogel for Rectal Administration Therapy in Ulcerative Colitis. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 503, 158477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, X.; Zhang, R.; Hao, D.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; Chai, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Unraveling the Mechanism of the Supramolecular Self-Assembly during the in Vivo Metabolism of Geniposide from Chinese Medicine. Mater. Des. 2023, 225, 111546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Luo, W.; Wu, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, J.; et al. Natural Products from Herbal Medicine Self-assemble into Advanced Bioactive Materials. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2403388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prašnikar, E.; Ljubič, M.; Perdih, A.; Borišek, J. Machine Learning Heralding a New Development Phase in Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warshel, A.; Levitt, M. Theoretical Studies of Enzymic Reactions: Dielectric, Electrostatic and Steric Stabilization of the Carbonium Ion in the Reaction of Lysozyme. J. Mol. Biol. 1976, 103, 227–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühne, T.D.; Iannuzzi, M.; Del Ben, M.; Rybkin, V.V.; Seewald, P.; Stein, F.; Laino, T.; Khaliullin, R.Z.; Schütt, O.; Schiffmann, F.; et al. CP2K: An Electronic Structure and Molecular Dynamics Software Package—Quickstep: Efficient and Accurate Electronic Structure Calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 194103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Su, X.; Yu, W.; Liu, J.; Hou, K.; Wang, C. Efficient Production of Neohesperidin Enabled by Protein Engineering of Rhamnosyltransferase Cm1,2RhaT. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 1960–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Pezeshki, S.; Duster, A.W.; Wang, B.; Wu, X.P.; Zheng, S.W.; Gagliardi, L.; Truhlar, D.G. QMMM 2023: A Program for Combined Quantum Mechanical and Molecular Mechanical Modeling and Simulations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2024, 295, 108987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xue, H.; Yu, R.; Bao, Y.O.; Kuang, Y.; Chai, Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, J.; Shi, X.; et al. Schaftoside Inhibits 3CLpro and PLpro of SARS-CoV-2 Virus and Regulates Immune Response and Inflammation of Host Cells for the Treatment of COVID-19. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 4154–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodun, D.S.; Omoboyowa, D.A.; Omotuyi, O.I.; Olugbogi, E.A.; Balogun, T.A.; Ezeh, C.J.; Omirin, E.S. QSAR-Based Virtual Screening of Traditional Chinese Medicine for the Identification of Mitotic Kinesin Eg5 Inhibitors. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2023, 104, 107865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, T.; Li, A.; Xu, H.; Pan, J.; Xing, B.; Wu, R.; Dickschat, J.S.; Yang, D.; Ma, M. Structural Insights into Three Sesquiterpene Synthases for the Biosynthesis of Tricyclic Sesquiterpenes and Chemical Space Expansion by Structure-Based Mutagenesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 8474–8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Ma, X.; Qiu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Shen, S.; Li, Y.; Gao, H.; Chen, K.; Zhou, J.; Hu, T.; et al. Structural and Catalytic Insight into the Unique Pentacyclic Triterpene Synthase TwOSC. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202313429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, W.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, W.; Mo, T.; Cui, X.; Li, J.; et al. Molecular Characterization and Structure Basis of a Malonyltransferase with Both Substrate Promiscuity and Catalytic Regiospecificity from Cistanche Tubulosa. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 2333–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Pei, J. Chinese Herbal Medicine Meets Biological Networks of Complex Diseases: A Computational Perspective. Evid.-Based Compl. Alt. 2017, 2017, 7198645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, T.; Tsugawa, H.; Miyagawa, H.; Fukusaki, E. Integrated Strategy for Unknown EI-MS Identification Using Quality Control Calibration Curve, Multivariate Analysis, EI-MS Spectral Database, and Retention Index Prediction. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6766–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-López, E.; Bajorath, J.; Medina-Franco, J.L. Informatics for Chemistry, Biology, and Biomedical Sciences. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Jin, C.; Li, D.; Deng, Y.; Yao, L.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.L.; Wang, T. Multi-Level Advances in Databases Related to Systems Pharmacology in Traditional Chinese Medicine: A 60-Year Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1289901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Cai, R.; Li, C.; Hu, Y.; Su, J.; Lei, T. Database-aided Ultrahigh-performance Liquid Chromatography Q-exactive-orbitrap Tandem Mass Spectrometry Putatively Identifies 16 Unexpected Compounds and Three Anticounterfeiting Pharmacopoeia Quality Markers for Perillae Fructus. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2024, 38, e9762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Diao, L.; Gu, J.; Wang, W.; Li, D.; et al. BATMAN-TCM: A Bioinformatics Analysis Tool for Molecular mechANism of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Li, B.; Gao, S.; Bai, Y.; Shar, P.A.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Z.; Sun, K.; Fu, Y.; Huang, C.; et al. CancerHSP: Anticancer Herbs Database of Systems Pharmacology. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, W.; Xie, T.; Yao, H.; Pang, X.; Sun, F.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, J. CEMTDD: The Database for Elucidating the Relationships among Herbs, Compounds, Targets and Related Diseases for Chinese Ethnic Minority Traditional Drugs. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17675–17684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Lin, H.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, K.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; et al. CMAUP Database Update 2024: Extended Functional and Association Information of Useful Plants for Biomedical Research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1508–D1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Huang, J.; Tang, R.; Li, M.; Yuan, H.; Wang, Y.; Wei, J.M.; Liu, J. CPMCP: A Database of Chinese Patent Medicine and Compound Prescription. Database 2022, 2022, baac073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.M.; Chen, T.; Lv, C.Y.; Tang, S.H.; Zhang, X.B.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhou, R.R.; et al. ETCM: An Encyclopaedia of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D976–D982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bultum, L.E.; Woyessa, A.M.; Lee, D. ETM-DB: Integrated Ethiopian Traditional Herbal Medicine and Phytochemicals Database. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Dong, L.; Liu, L.; Guo, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Bu, D.; Liu, X.; Huo, P.; Cao, W.; et al. HERB: A High-Throughput Experiment- and Reference-Guided Database of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1197–D1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Ye, L.; Kang, H.; Zhang, D.; Tao, L.; Tang, K.; Liu, X.; Zhu, R.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.Z.; et al. HIT: Linking Herbal Active Ingredients to Targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D1055–D1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Liang, D.; Yi, J.; Jin, S.; Zeng, Z. IGTCM: An Integrative Genome Database of Traditional Chinese Medicine Plants. Plant Genome 2023, 16, e20317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, S.; Wang, Q.; Lv, C.; Wang, J.; Fang, J.; Fu, L.; Yang, J.; Zu, X.; et al. Exploring Pharmacological Active Ingredients of Traditional Chinese Medicine by Pharmacotranscriptomic Map in ITCM. Briefings Bioinf. 2023, 24, bbad027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ren, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Wu, J.; Sun, H.; Zhou, S.; Yan, K.; Yan, X.; et al. LTM-TCM: A Comprehensive Database for the Linking of Traditional Chinese Medicine with Modern Medicine at Molecular and Phenotypic Levels. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 178, 106185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Springer, L.; Gohlke, B.O.; Goede, A.; Dunkel, M.; Abel, R.; Gallo, K.; Preissner, S.; Eckert, A.; Seshadri, L.; et al. SuperTCM: A Biocultural Database Combining Biological Pathways and Historical Linguistic Data of Chinese Materia Medica for Drug Development. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 144, 112315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, K.; Fang, S.; Bu, D.; Li, H.; Sun, L.; Hu, H.; Gao, K.; Wang, W.; et al. SymMap: An Integrative Database of Traditional Chinese Medicine Enhanced by Symptom Mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1110–D1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.C. TCM Database@taiwan: The World’s Largest Traditional Chinese Medicine Database for Drug Screening In Silico. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Chen, G.; He, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, K.; Chen, C.Y.C. TCMBank-the Largest TCM Database Provides Deep Learning-Based Chinese-Western Medicine Exclusion Prediction. Signal Transduct. Tar. 2023, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Y.B.; Wang, J.F.; Li, H.; Ung, C.Y.; Han, L.Y.; Cao, Z.W.; Chen, Y.Z. Database of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Its Application to Studies of Mechanism and to Prescription Validation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 149, 1092–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yi, Z.; Wen, C.; Shi, T. TCMID: Traditional Chinese Medicine Integrative Database for Herb Molecular Mechanism Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D1089–D1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cai, C.; Du, J.; Liu, B.; Cui, L.; Fan, X.; Wu, Q.; Fang, J.; Xie, L. TCMIO: A Comprehensive Database of Traditional Chinese Medicine on Immuno-Oncology. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, H. TCMM: A Unified Database for Traditional Chinese Medicine Modernization and Therapeutic Innovations. Comput. Struct. Biotec. 2024, 23, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yu, S.; Bai, H.; Ning, K. TCM-Mesh: The Database and Analytical System for Network Pharmacology Analysis for TCM Preparations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.X.; Dong, J.; Wei, H.; Shi, S.H.; Lu, A.P.; Deng, G.M.; Cao, D.S. TCMSID: A Simplified Integrated Database for Drug Discovery from Traditional Chinese Medicine. J. Cheminf. 2022, 14, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.; Huang, C.; Li, P.; Guo, Z.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. TCMSP: A Database of Systems Pharmacology for Drug Discovery from Herbal Medicines. J. Cheminf. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, Q.; Duan, Q.; Shi, W.; Li, D.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, M.; Kuang, H.; et al. TCMSSD: A Comprehensive Database Focused on Syndrome Standardization. Phytomedicine 2024, 128, 155486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Lang, J.; Li, H.; Lu, J.; Lin, H.; Tian, G.; Bai, H.; Yang, J.; Ning, K. TCM-suite: A Comprehensive and Holistic Platform for Traditional Chinese Medicine Component Identification and Network Pharmacology Analysis. iMeta 2022, 1, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Lee, M.K.; Jang, H.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, S.; Jang, Y.; Jang, H.; Kim, A. TM-MC 2.0: An Enhanced Chemical Database of Medicinal Materials in Northeast Asian Traditional Medicine. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2024, 24, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Ma, C.; Zhao, X.; Hu, Z.; Du, T.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Lin, J. YaTCM: Yet Another Traditional Chinese Medicine Database for Drug Discovery. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Tao, Q.; Cao, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhang, L.; Luo, Y.; Wang, L. Kaempferol Has Potential Anti-Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Targets Based on Bioinformatics Analyses and Pharmacological Effects on Endotoxin-Induced Cytokine Storm. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 2290–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yoo, M.; Shin, J.; Kim, H.; Kang, J.; Tan, A.C. Systems Pharmacology-Based Approach of Connecting Disease Genes in Genome-Wide Association Studies with Traditional Chinese Medicine. Int. J. Genom. 2018, 2018, 7697356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Qiang, W.; Gui, Y.; Tan, X.; Pei, T.; Lin, K.; Cai, S.; Sun, L.; Ning, G.; Wang, J.; et al. A Large-Scale Transcriptional Study Reveals Inhibition of COVID-19 Related Cytokine Storm by Traditional Chinese Medicines. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Lee, K.; Deng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Wei, C.; Yang, S.; Wang, T.; Wong, N.J.; et al. Arctigenin Attenuates Diabetic Kidney Disease through the Activation of PP2A in Podocytes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Guo, S.; Jia, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, M. Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis to Decipher Molecular Mechanism of Compound Kushen Injection for Esophageal Cancer by Combining WGCNA with Network Pharmacology. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yu, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, B.; Fan, Y.; Ruan, B.; Zhang, X.; Dai, H.; Mei, W.; Jie, W.; et al. Integrated Analysis of Dendrobium Nobile Extract Dendrobin a against Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Based on Network Pharmacology, Bioinformatics, and Validation Experiments. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1079539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, H.; Qi, J.; Tang, D.; Chen, X.; Wan, J.; Li, P.; Hu, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y. Natural Formulas and the Nature of Formulas: Exploring Potential Therapeutic Targets Based on Traditional Chinese Herbal Formulas. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhao, X.; Lu, X.; Zhao, L.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, M.; Feng, S.; Fan, T.; et al. A Deep Learning-Driven Discovery of Berberine Derivatives as Novel Antibacterial against Multidrug-Resistant Helicobacter Pylori. Signal Transduct. Tar. 2024, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Rasteh, A.M.; Dong, A.; Wang, P.; Liu, H. Identification of Molecular Targets of Hypericum Perforatum in Blood for Major Depressive Disorder: A Machine-Learning Pharmacological Study. Chin. Med. 2024, 19, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Lin, Z.; Miao, Q.; Lin, L.; Wang, S.; Lu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, Q.; Kong, W.; Wu, K.; et al. Mechanisms of QingRe HuoXue Formula in Atherosclerosis Treatment: An Integrated Approach Using Bioinformatics, Machine Learning, and Experimental Validation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 141, 112890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Ren, W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Yin, Z.; Li, D. Exploring the Underlying Mechanism of Shenyankangfu Tablet in the Treatment of Glomerulonephritis through Network Pharmacology, Machine Learning, Molecular Docking, and Experimental Validation. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 4585–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S. Framework and Practice of Network-Based Studies for Chinese Herbal Formula. J. Chin. Integr. Med. 2007, 5, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.L. Network Pharmacology. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1110–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, N.; Chen, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Q. Network Pharmacology, a Promising Approach to Reveal the Pharmacology Mechanism of Chinese Medicine Formula. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 309, 116306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Liao, J.; Chen, Q.; Lu, X.; Fan, X. Network Pharmacology Approaches for Research of Traditional Chinese Medicines. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2023, 21, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Hong, W.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Fang, Z. Mechanism of Herb Pair Containing Astragali Radix and Spatholobi Caulis in the Treatment of Myelosuppression Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Investigation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Tian, L.; Xia, Z.Q.; Wang, K.; Chen, T.; Wang, R.; Feng, Z.; Shi, G.; et al. Wumei Wan Attenuates Angiogenesis and Inflammation by Modulating RAGE Signaling Pathway in IBD: Network Pharmacology Analysis and Experimental Evidence. Phytomedicine 2023, 111, 154658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, F.; Xiao, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Yang, S. Mechanism of Sijunzi Decoction in the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 302, 115876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, M.H.; Abdullah, Z.L.; Mohamed Yusof, N.I.S.; Mohd Fauzi, F. In Silico Toxicity Studies of Traditional Chinese Herbal Medicine: A Mini Review. Curr. Opin. Struc. Biol. 2023, 80, 102588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, Y.; Yao, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fu, D. Potential Molecular Mechanisms and Drugs for Aconitine-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Zebrafish through RNA Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e924092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yu, L.; Xiang, C.; Yang, M. Exploring the Mechanism of Alisma Orientale for the Treatment of Pregnancy Induced Hypertension and Potential Hepato-Nephrotoxicity by Using Network Pharmacology, Network Toxicology, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1027112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.Y.; Gao, H.Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, T.Y.; Wang, S.T.; Yang, J.B.; Hao, R.R.; Pang, F.; Wei, F.; Liu, Z.G.; et al. Integrated Spatially Resolved Metabolomics and Network Toxicology to Investigate the Hepatotoxicity Mechanisms of Component D of Polygonum Multiflorum Thunb. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 298, 115630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J. Network Toxicology and Molecular Docking Analyses on Strychnine Indicate CHRM1 Is a Potential Neurotoxic Target. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.C.; Qian, Q.; Gao, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Li, Y.X.; Wang, X.; Fu, Y.; Ma, Y.M.; Wang, Q. Toxic Effects of Tripterygium Glycoside Tablets on the Reproductive System of Male Rats by Metabolomics, Cytotoxicity, and Molecular Docking. Phytomedicine 2023, 114, 154813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Li, X. Omics and bioinformatics studies of the brain toxicity of Sophorae Tonkinensis Radix et Rhizoma in mice. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ. 2023, 40, 343–349. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, M.; You, L.; Zheng, R.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, R.; Sun, Y.; Pan, H.; He, T.; et al. Developing an Artificial Intelligence Method for Screening Hepatotoxic Compounds in Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine Combination. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Bu, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chu, Y.; Li, Y.; Cai, T. Model-guided research strategies for safe use of traditional Chinese medicine: Quantitative toxicology of traditional Chinese medicine. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2023, 54, 359–366. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, P.; Sun, D.; Zhou, W.; Gao, Y. Research progress in toxicity prediction of traditional Chinese medicines. Chin. J. Pharmacovigil. 2023, 20, 473–479. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Pang, X.; Liao, B.; Yao, H.; Song, J.; Chen, S. An Authenticity Survey of Herbal Medicines from Markets in China Using DNA Barcoding. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Liu, Q.; Qiu, S.; Dai, J.; Gao, X. DNA Barcoding: An Efficient Technology to Authenticate Plant Species of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Recent Advances. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wang, Y.; Bai, M.; Peng, T.; Li, H.; Xu, H.J.; Guo, G.; Bai, H.; Rong, N.; Sahu, S.K.; et al. Soil Conditions and the Plant Microbiome Boost the Accumulation of Monoterpenes in the Fruit of Citrus Reticulata ‘Chachi. ’ Microbiome 2023, 11, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Shi, M.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, L.; Sun, Y. Research Progress on Quality Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Genuine Medicinal Materials. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2022, 53, 6931–6947. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Guo, D. Quality Marker of TCMs: Concept and Applications. Phytomedicine 2018, 44, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fan, J.; Cheng, X.; Jin, H.; Wang, Y.; Wei, F.; An, F.; Ma, S. New Revolution for Quality Control of TCM in Industry 4.0: Focus on Artificial Intelligence and Bioinformatics. Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 181, 118023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xu, E.; Bai, M.; Miao, M. Analysis of Characteristics of Traditional Chinese Medicine External Treatment for Dyspepsia Based on Data Mining. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2208, 020010. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Bai, L.; Miao, M. Analysis of Characteristics of Traditional Chinese Medicines for Treating Dysmenorrhea Based on Data Mining. DEStech Trans. Soc. Sci. Edu. Hum. Sci. 2019, 1, 28154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Lu, A.; Zhong, L.; Zheng, G.; Bian, Z. Chinese Herbal Medicine for Hyperlipidaemia: A Review Based on Data Mining from 1990 to 2016. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2017, 15, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Shen, D.; Lu, P.; Yang, H. Advances in researches made via traditional Chinese medicine inheritance support system. China J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2015, 30, 329–331. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Jiang, S.S.; Ding, X.; Wei, H.J.; Liang, T.X.; Zhao, X.D.; Jiang, L.D. Study on the medication pattern of traditional Chinese medicine against new coronavirus pneumonia based on the cloud platform of ancient and modern medical cases. J. Beijing Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2023, 39, 800–805. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.Y.; Kang, L.; Liu, J.; Xing, Y.H.; Yang, C.; Yang, L.; Li, X.Y.; Lei, L. Construction and Application of TCM Miner. Chin. J. Libr. Inf. Sci. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 45, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Liu, W.; Tang, B.; Meng, T.; Yao, J.B.; Hu, W. Design and Implementation of Intelligent Chinese Medicine Data Analysis System. Comput. Knowl. Technol. 2022, 18, 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Kaptchuk, T.; Li, X.; Gao, X.; Yao, J.; Tang, X.; Xu, Z. Acceptability of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Chinese People Based on 10-Year’s Real World Study with Mutiple Big Data Mining. Front. Public Health 2022, 9, 811730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, J.; Xin, L.; Fang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Qi, Y.; He, M.; Fang, D.; Chen, X.; Cong, C. Association between Traditional Chinese Medicine and Osteoarthritis Outcome: A 5-Year Matched Cohort Study. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.; Peng, L.; Yang, L.; Chou, H.; Li, C.; Zuo, Z.; Koon, H.; Cheung, Y. Examining Patterns of Traditional Chinese Medicine Use in Pediatric Oncology: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Data-Mining Study. J. Integr. Med. 2022, 20, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z. A Study of Chinese Herbal Properties Based on Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2015 10th International Conference on Information, Communications and Signal Processing (ICICS), Singapore, 2–4 December 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.H.; Tung, C.W.; Fülöp, F.; Li, J.H. Developing a QSAR Model for Hepatotoxicity Screening of the Active Compounds in Traditional Chinese Medicines. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 78, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jafari, M.; Tang, Y.; Tang, J. Predicting Meridian in Chinese Traditional Medicine Using Machine Learning Approaches. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1007249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekins, S.; Puhl, A.C.; Zorn, K.M.; Lane, T.R.; Russo, D.P.; Klein, J.J.; Hickey, A.J.; Clark, A.M. Exploiting Machine Learning for End-to-End Drug Discovery and Development. Nat. Mater. 2019, 18, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.C.S.; Shan, H.; Dahoun, T.; Vogel, H.; Yuan, S. Advancing Drug Discovery via Artificial Intelligence. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholap, A.D.; Uddin, M.J.; Faiyazuddin, M.; Omri, A.; Gowri, S.; Khalid, M. Advances in Artificial Intelligence in Drug Delivery and Development: A Comprehensive Review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 178, 108702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Yin, Q.; Shi, J.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, P. Deep Learning and Machine Intelligence: New Computational Modeling Techniques for Discovery of the Combination Rules and Pharmacodynamic Characteristics of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 933, 175260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Writing Group of Recommendations of Expert Panel from Chinese Geriatrics Society on the Clinical Use of Compound Danshen Dripping Pills. Recommendations on the Clinical Use of Compound Danshen Dripping Pills. Chin. Med. J. 2017, 130, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foresight Industry Research Institute. Report of Market Prospective and Investment Strategy Planning on Traditional Chinese Medicine Industry (2024-2029); Foresight Industry Research Institute: Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yao Zhi Zixun. China Pharmaceutical R&D Blue Book (2024); Yao Zhi Zixun: Chongqing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, S. Artificial Intelligence for Drug Discovery: Resources, Methods, and Applications. Mol. Ther. Nucl. Acids 2023, 31, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirlekar, B.U.; Nuthi, A.; Singh, K.D.; Murty, U.S.; Dixit, V.A. An Overview of Compound Properties, Multiparameter Optimization, and Computational Drug Design Methods for PARP-1 Inhibitor Drugs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 252, 115300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Li, W.H.; Wang, D. Machine Learning: The Trends of Developing High-Efficiency Single-Atom Materials. Chem. Catal. 2021, 1, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, A.; Yun, T.; Nayak, N.V.; Merullo, J.; Bach, S.H.; Sun, C.; Pavlick, E. $100K or 100 Days: Trade-Offs When Pre-Training with Academic Resources. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.23261. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, D.; Xie, Z.; Dong, K.; Zhang, W.; Chen, G.; Bi, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.K.; et al. DeepSeek-Coder: When the Large Language Model Meets Programming—The Rise of Code Intelligence. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.14196. [Google Scholar]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate Structure Prediction of Biomolecular Interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, R.; Dave, D.; Naik, H.; Singhal, S.; Omer, R.; Patel, P.; Qian, B.; Wen, Z.; Shah, T.; Morgan, G.; et al. Explainable AI (XAI): Core Ideas, Techniques, and Solutions. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Force Field Name | Description | Applicable Systems | CMM Research Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMBER [62] | A well-known and widely used force field for various systems. It contains many versions, such as AMBER84, AMBER86, AMBER94, AMBER96, AMBER98, AMBER99, AMBER03, AMBER03UA, AMBER99SB, AMBER99SB-ILDN, AMBER14SB, and AMBER19SB. | Proteins, nucleic acids, and some organic small molecules. | [63,64] |
| AMOEBA [65] | It introduces polarization effects to more accurately describe intermolecular interactions. It addresses the limitations of the traditional fixed-charge force field and proposes a more complex polarization model to improve the accuracy of the description of molecular properties. | Biological macromolecules and organic small molecules in solution environments. | [66] |
| CGenFF [67] | A fully CHARMM-compatible force field dedicated to the simulation of organic small molecules. | Organic small molecules. | [68,69] |
| CHARMM [70] | It was originally dedicated to the CHARMM program. After being updated with various versions, such as CHARMM16, CHARMM19, CHARMM22, CHARMM27, and CHARMM36, it is now supported by many programs. | Proteins, nucleic acids, phospholipids, and sugars. | [71] |
| GAFF [72] | It is fully compatible with the AMBER force field and can describe a variety of organic small molecules. It is a simple force field with better structural description accuracy than some complex force fields. | Organic small molecules. | [73,74] |
| GLYCAM [75] | It is fully compatible with the AMBER force field and can be used in the AMBER program to research glycoproteins. It includes various versions, such as GLYCAM93, GLYCAM2000, GLYCAM06, and GLYCAM06-LP. | Proteins and sugars. | [76] |
| GROMOS [77] | A force field with a simple energy functional and extensive applications. It contains many versions, most of which are supported only by the GROMOS program and the Gromacs program. | Condensed-phase simulation of proteins, nucleic acids, sugars, phospholipids, and organic small molecules. | [78,79] |
| MARTINI [80] | It improves the computational efficiency by simplifying the representation of atoms, combining multiple atoms into a single “coarse-grained” particle. | Large-scale biophysical systems such as membranes, biopolymers, and complex fluids. | [81] |
| MM [82] | A high-precision force field developed by the Merk Group for the simulation of organic molecules. It is suitable for conformational searches and unsuitable for condensed-phase simulations. It also includes various versions, such as MM1, MM2, MM3, MM4, MM+, and MM2X. | Organic small molecules. | [83] |
| MMFF94 [82] | An improved version of the MM series force fields for calculations of organic molecules and condensed phases. | Organic small molecules. | [84,85] |
| OPLS [86] | A force field that initially specialized in condensed-phase simulations. Its versions include OPLS-UA, OPLS-AA, and OPLS-AA/M. Starting with OPLS 2.0, the force field is exclusive to Schrödinger, Inc. and has been developed into various simulation systems. | Proteins, sugars, and organic small molecules. | [87,88] |
| Tripos [89] | The force field parameters are carefully optimized to provide a high-precision description based on QCC and experimental data. | Organic small molecules and proteins. | [90] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, B.; Liu, S.; Xia, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Computer-Aided Drug Design in Research on Chinese Materia Medica: Methods, Applications, Advantages, and Challenges. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030315
Chen B, Liu S, Xia H, Li X, Zhang Y. Computer-Aided Drug Design in Research on Chinese Materia Medica: Methods, Applications, Advantages, and Challenges. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(3):315. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030315
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ban, Shuangshuang Liu, Huiyin Xia, Xican Li, and Yingqing Zhang. 2025. "Computer-Aided Drug Design in Research on Chinese Materia Medica: Methods, Applications, Advantages, and Challenges" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 3: 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030315
APA StyleChen, B., Liu, S., Xia, H., Li, X., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Computer-Aided Drug Design in Research on Chinese Materia Medica: Methods, Applications, Advantages, and Challenges. Pharmaceutics, 17(3), 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030315






