Sustained Delivery of Liraglutide Using Multivesicular Liposome Based on Mixed Phospholipids
Abstract
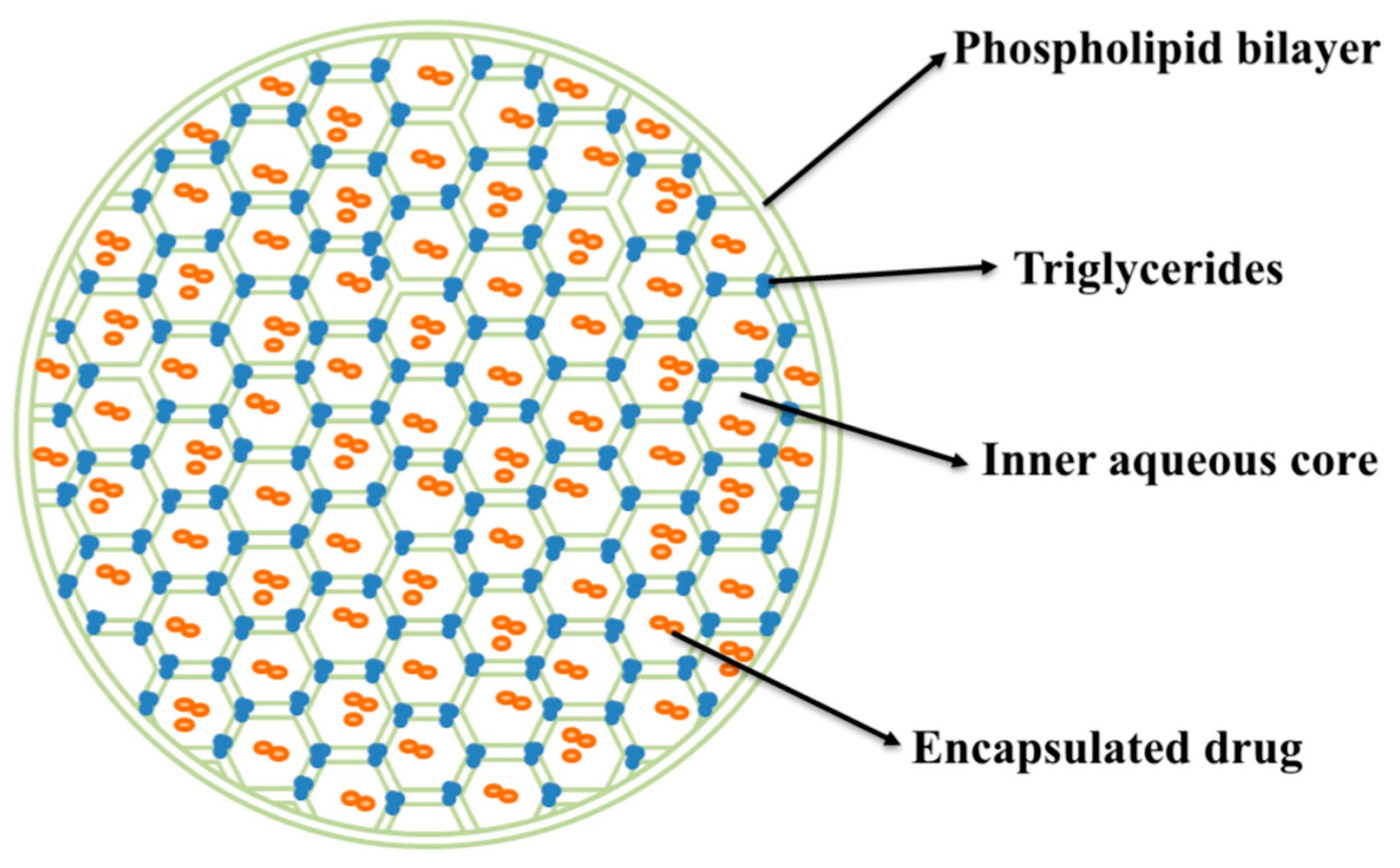
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Lir-MVLs
2.3. Physiochemical Characterization
2.4. Structural Analysis
2.5. Fluidity Analysis
2.6. In Vitro Release
2.7. In Vivo Pharmacodynamics
2.8. The Retention at the Local Injection Site
2.9. Pharmacokinetic
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Basic Characterization of Lir-MVLs
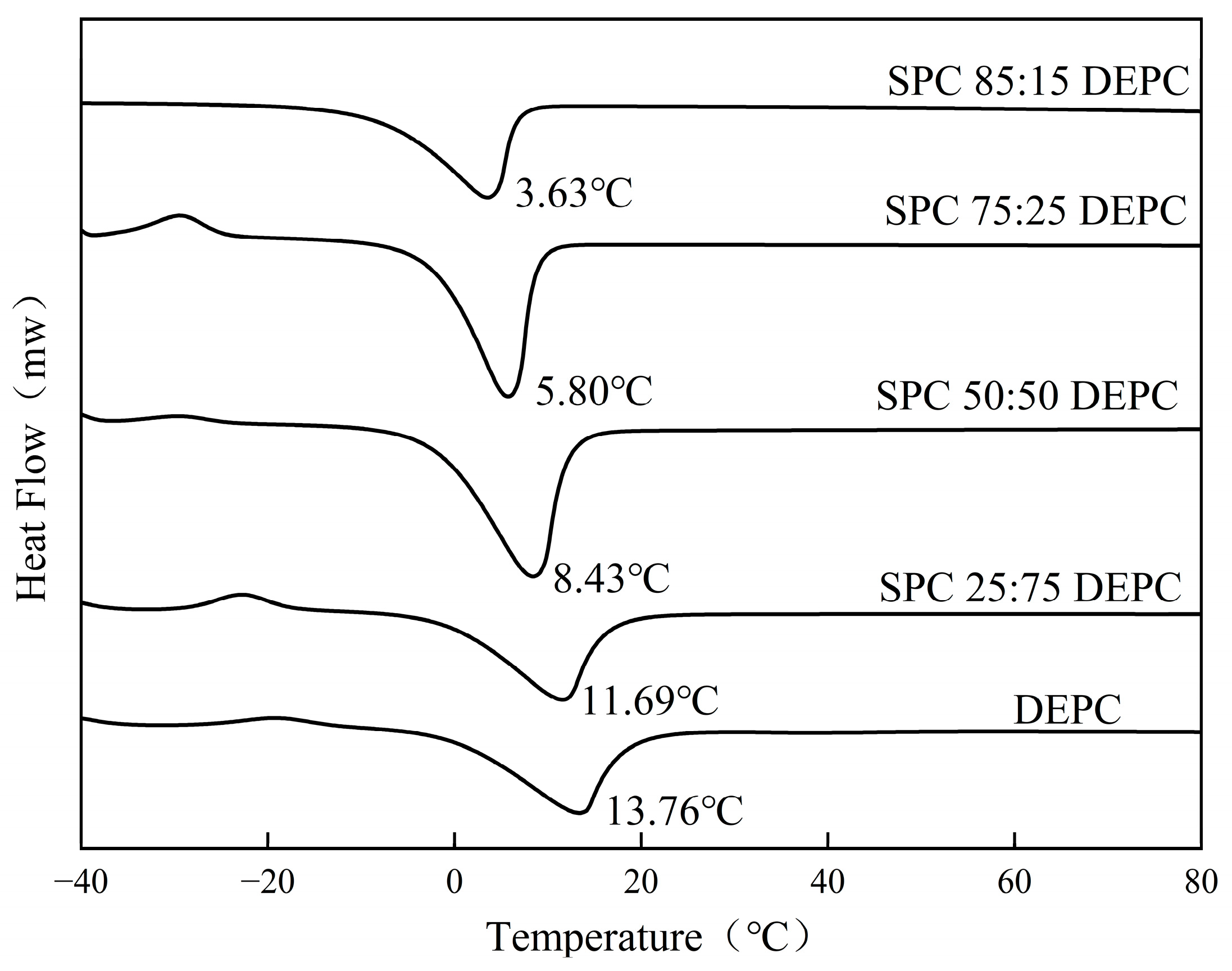
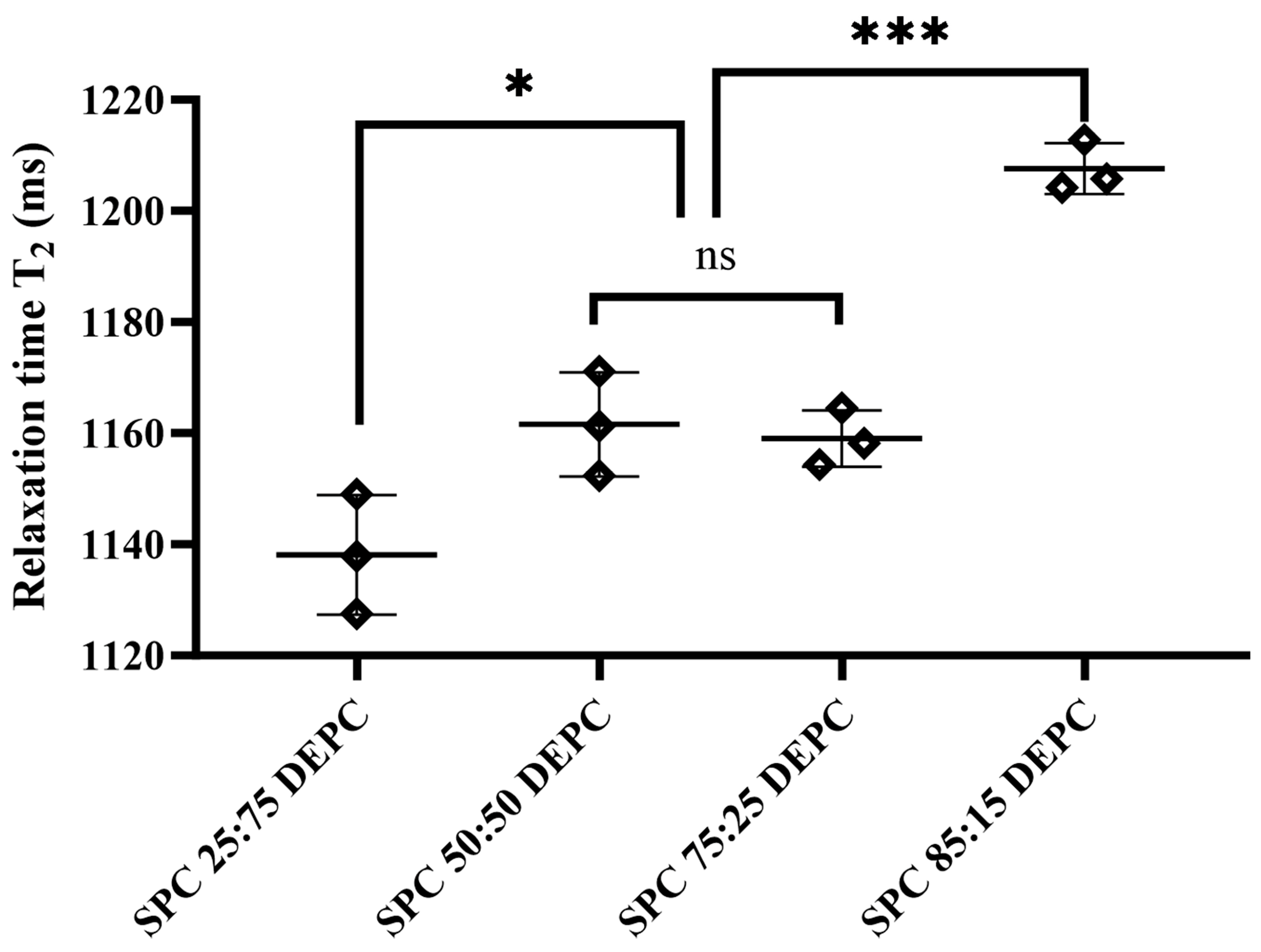
3.2. The Fluidity of Lipid Membranes
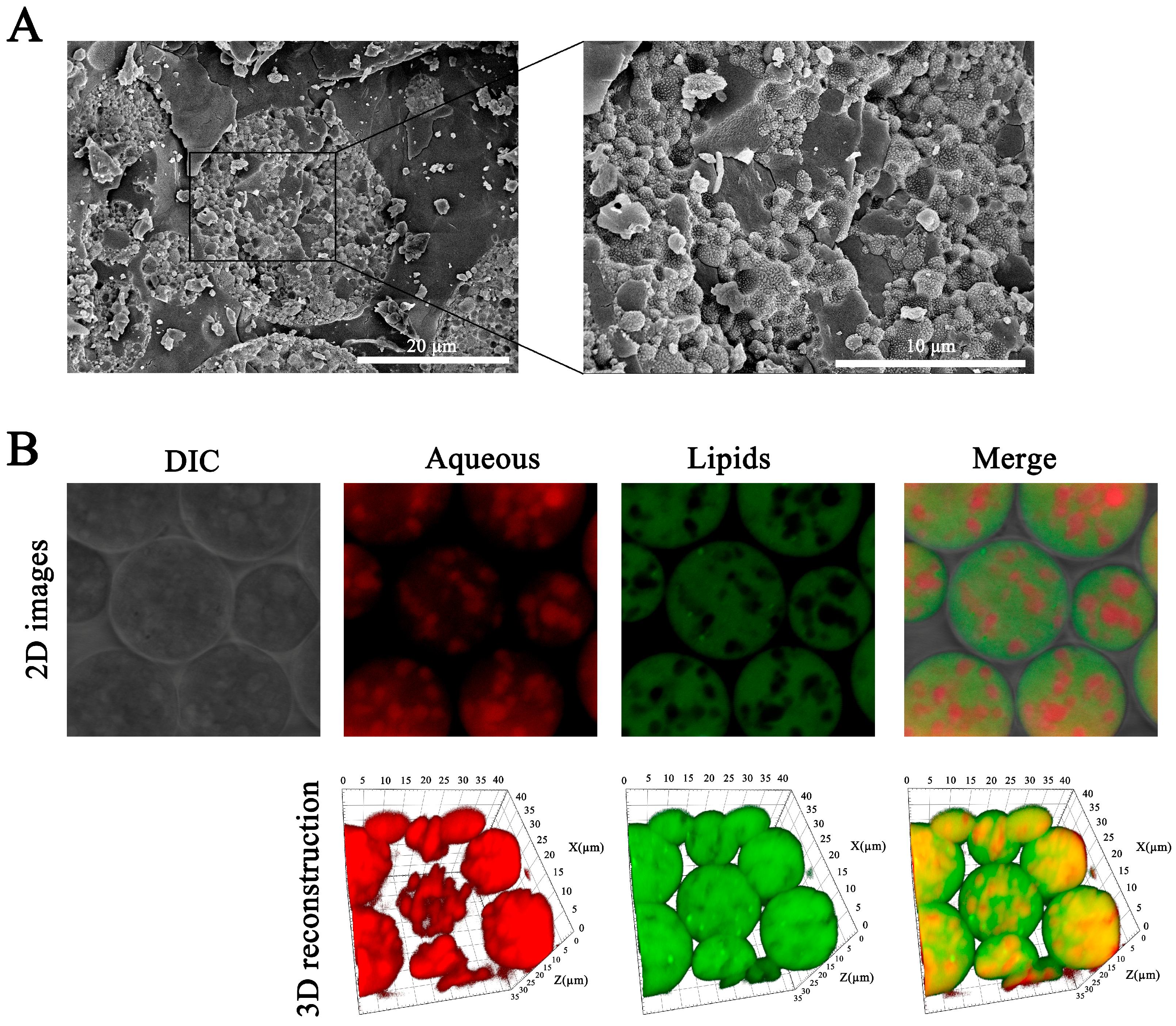
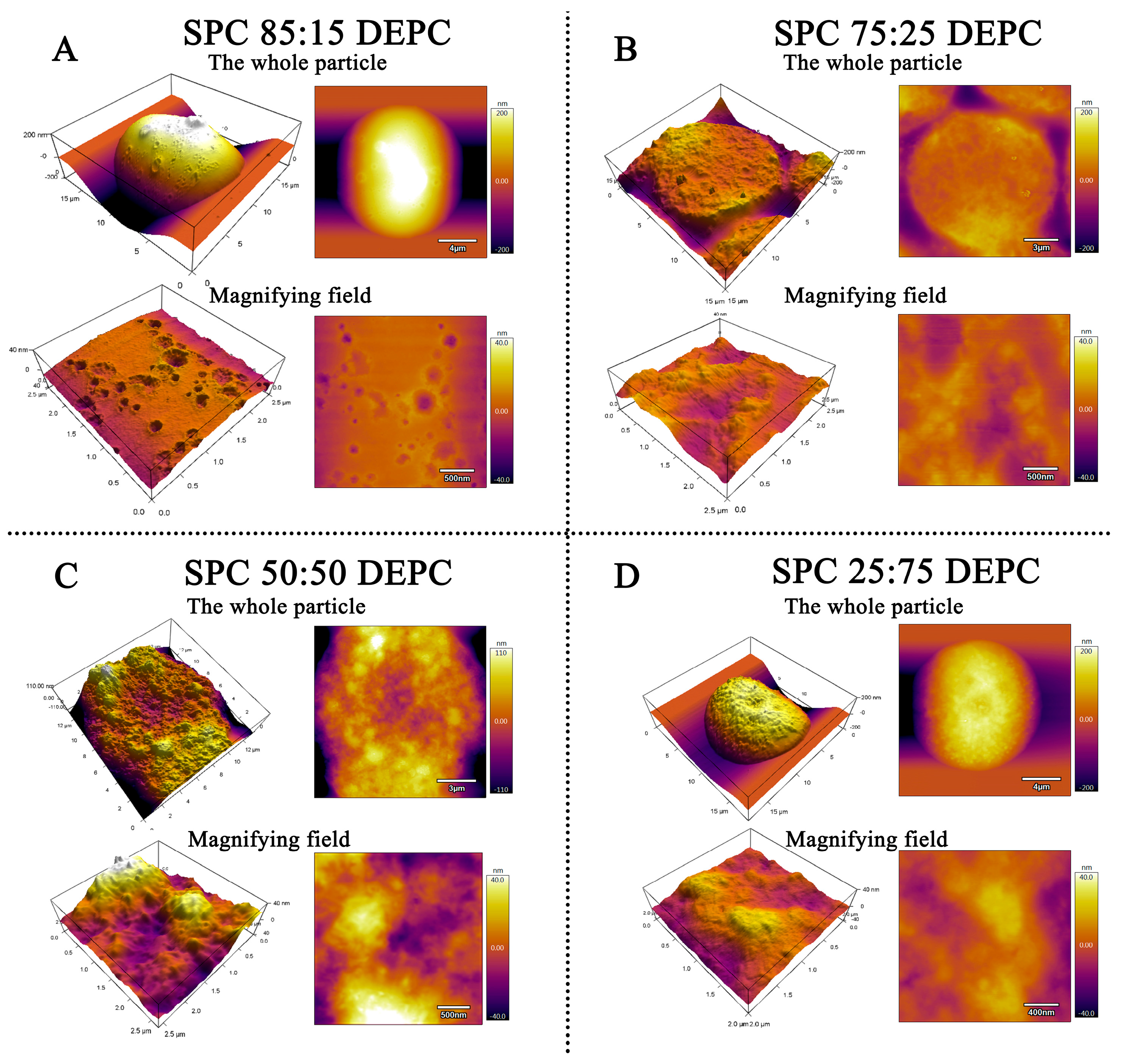
3.3. The Surface Morphology
3.4. Characterization of Aqueous Phase–Particle Interfaces
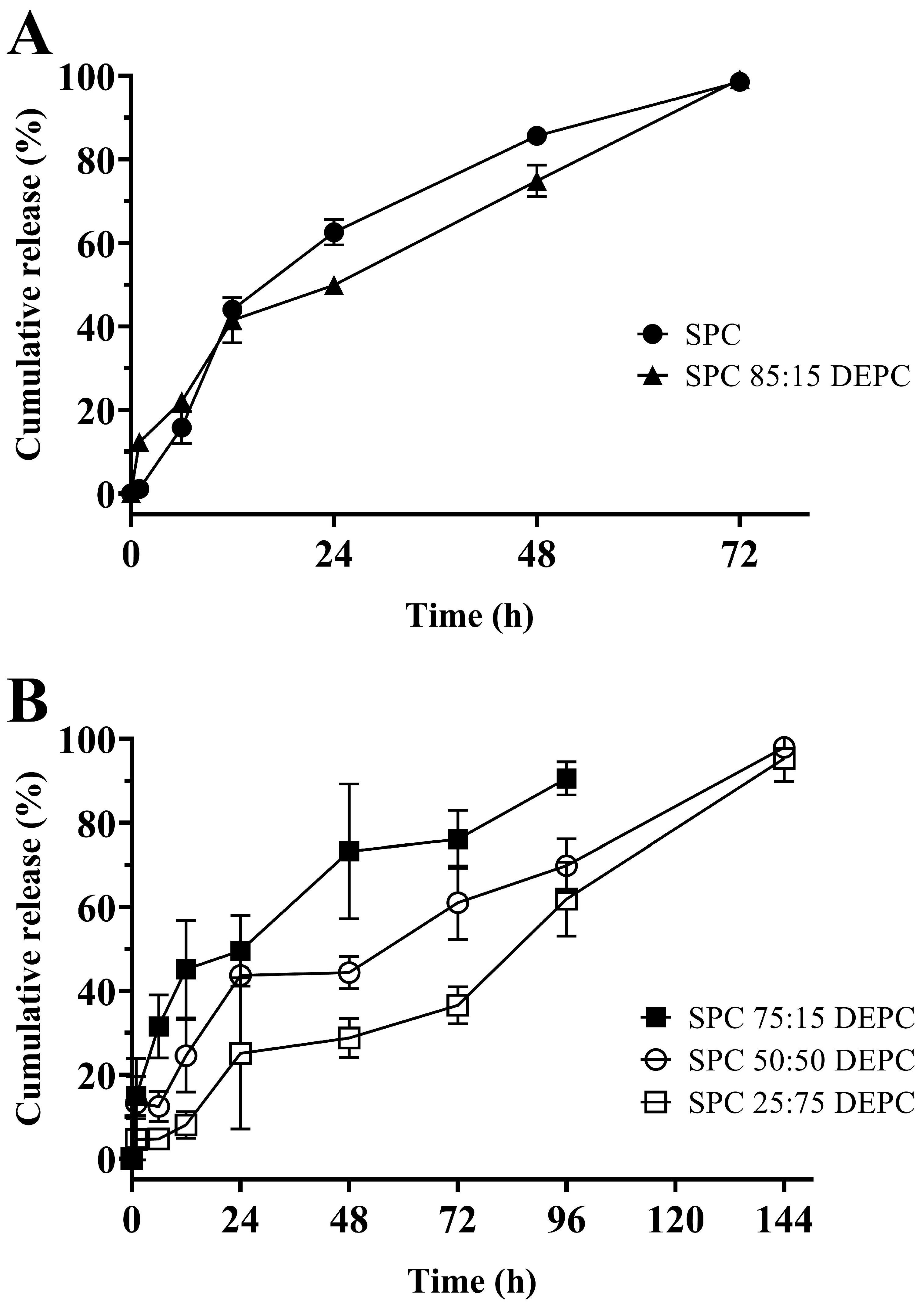
3.5. In Vitro Release of Lir-MVLs Based on Mixed Phospholipids
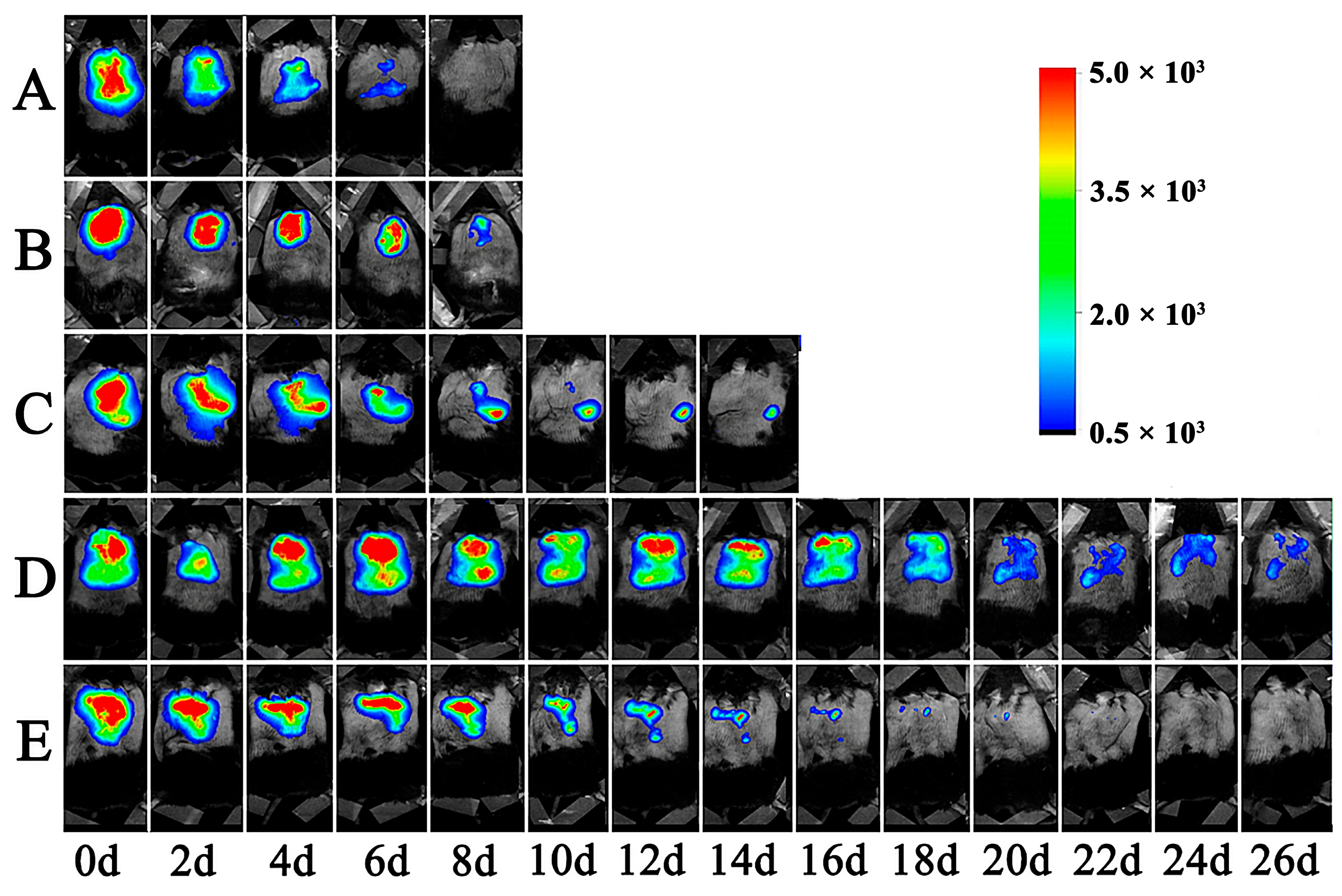
3.6. Hypoglycemic Effect in db/db Diabetes Model Mice
3.7. The Retention of Lir-MVLs at the Local Injection Site in Mice
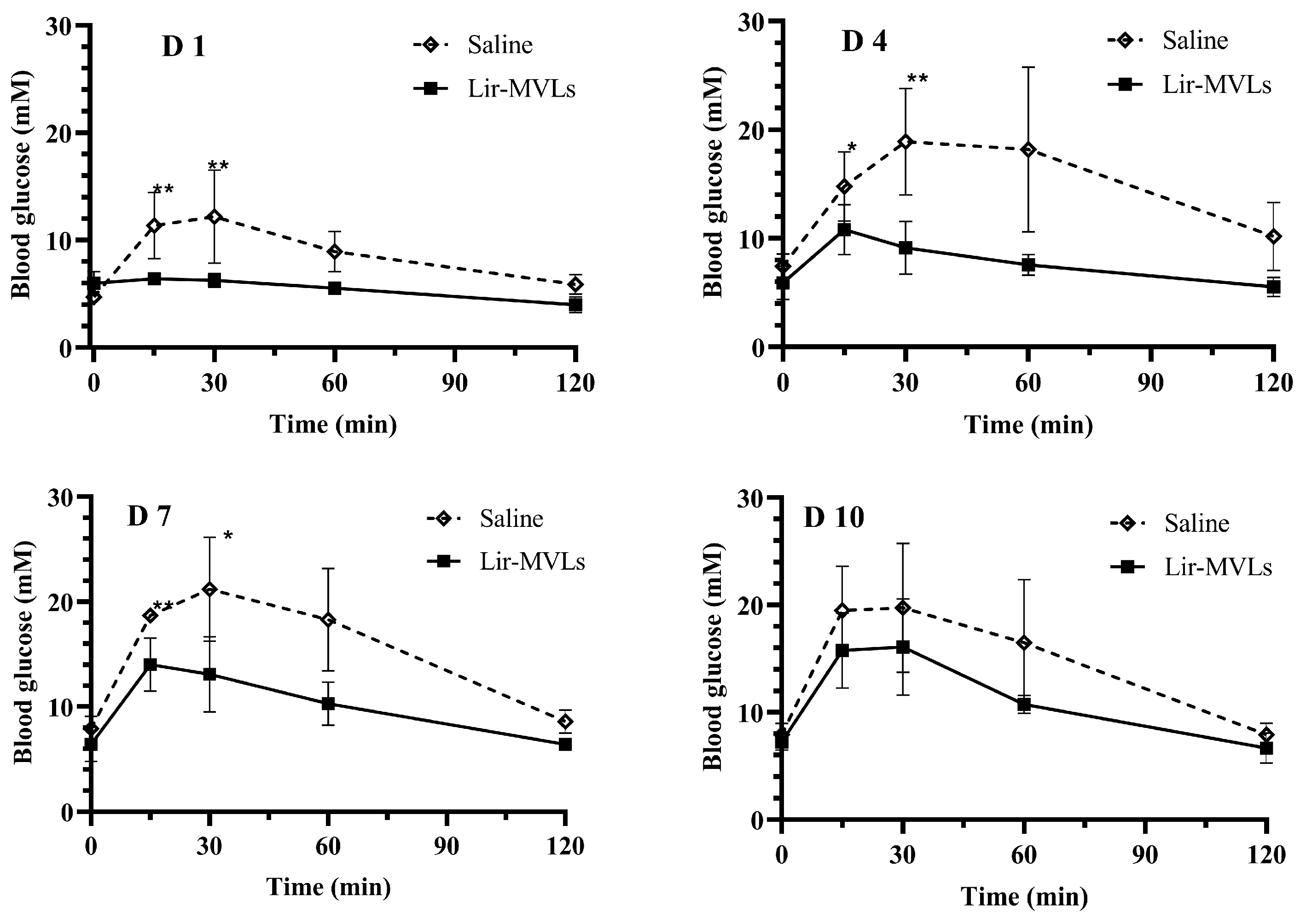
3.8. Postprandial Blood Glucose Control in Healthy Mice
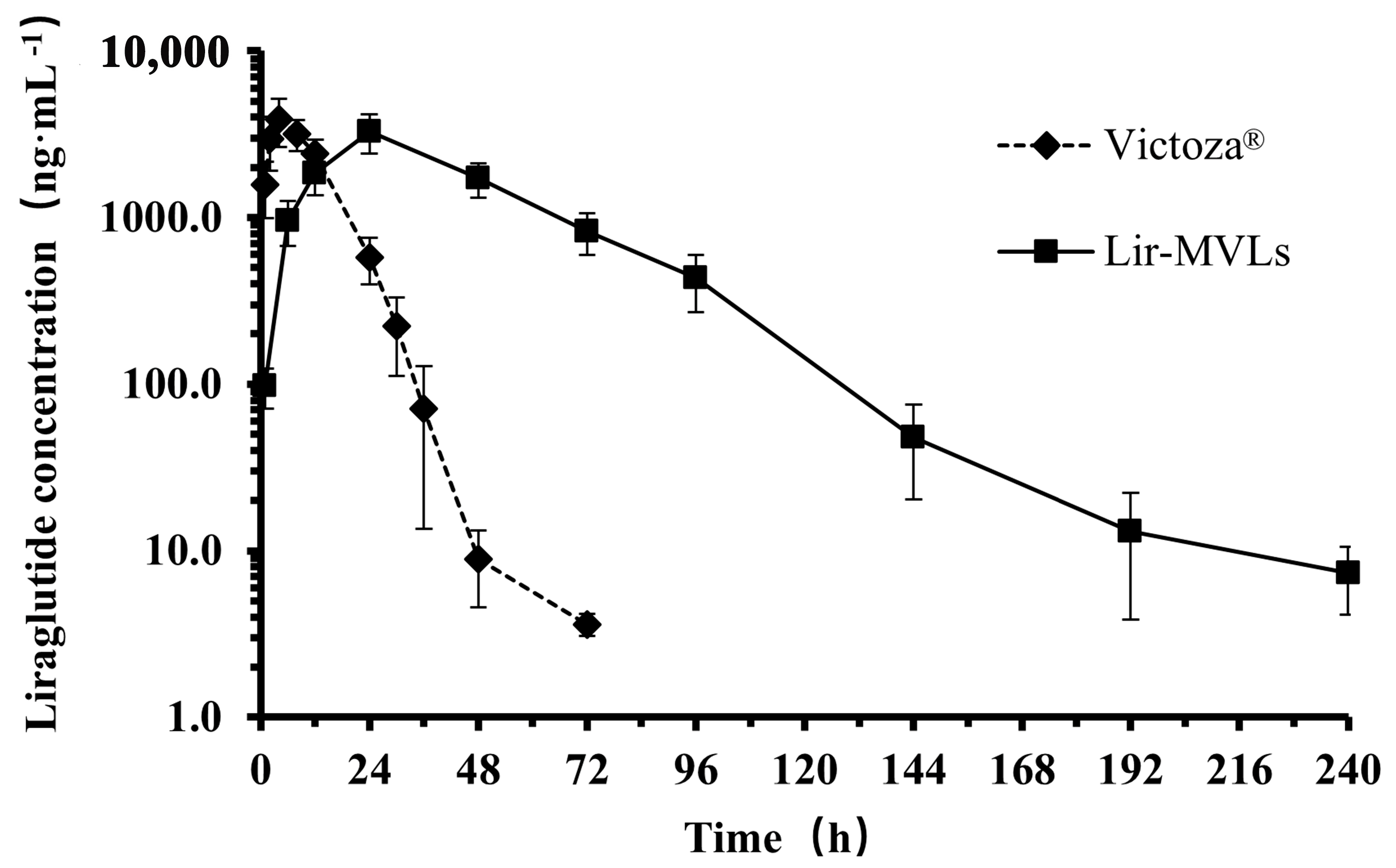
3.9. The Pharmacokinetic Profile in Rats
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ziebarth, J.; da Silva, L.M.; Lorenzett, A.K.P.; Figueiredo, I.D.; Carlstrom, P.F.; Cardoso, F.N.; de Freitas, A.L.F.; Baviera, A.M.; Mainardes, R.M. Oral Delivery of Liraglutide-Loaded Zein/Eudragit-Chitosan Nanoparticles Provides Pharmacokinetic and Glycemic Outcomes Comparable to Its Subcutaneous Injection in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratap-Singh, A.; Guo, Y.; Baldelli, A.; Singh, A. Concept for a unidirectional release mucoadhesive buccal tablet for oral delivery of antidiabetic peptide drugs such as insulin, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1), and their analogs. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlosser, C.S.; Rozek, W.; Mellor, R.D.; Manka, S.W.; Morris, C.J.; Brocchini, S.; Williams, G.R. A lipid-based delivery platform for thermo-responsive delivery of teriparatide. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 667, 124853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, W.; Feng, T.; Liang, Z. Comparison of the efficacy and safety profiles of generic and branded leuprorelin acetate microspheres in patients with prostate cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2024, 28, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; McHugh, K.J. Strategies for overcoming protein and peptide instability in biodegradable drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 199, 114904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Sharma, V.; Bhushan, B.; Malviya, R.; Awasthi, R.; Kulkarni, G.T. Nanocarriers for protein and peptide delivery: Recent advances and progress. J. Res. Pharm. 2021, 25, 99–116. [Google Scholar]
- Butreddy, A.; Gaddam, R.P.; Kommineni, N.; Dudhipala, N.; Voshavar, C. PLGA/PLA-based long-acting injectable depot microspheres in clinical use: Production and characterization overview for protein/peptide delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Ueda, M.; Asayama, S. Inhibition of Aβ Aggregation by Cholesterol-End-Modified PEG Vesicles and Micelles. Pharmaceutics 2024, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, Z.; Eini, M.; Rastegari, A.; Tehrani, M.R. Chitosan as a machine for biomolecule delivery: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 256, 117414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.Z.; Rizwanullah, M.; Ahmad, J.; Alasmary, M.Y.; Akhter, M.H.; Abdel-Wahab, B.A.; Warsi, M.H.; Haque, A. Progress in nanomedicine-based drug delivery in designing of chitosan nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2022, 71, 602–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Xu, H.; Lin, Q.; Chi, J.; Liu, T.; Jin, B.; Ou, J.; Xu, Z.; Peng, T.; Quan, G.; et al. Emerging Trends in Dissolving-Microneedle Technology for Antimicrobial Skin-Infection Therapies. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavda, V.P.; Pandya, A.; Kumar, L.; Raval, N.; Vora, L.K.; Pulakkat, S.; Duo, Y.; Tang, B.Z. Exosome nanovesicles: A potential carrier for therapeutic delivery. Nano Today 2023, 49, 101771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwani, S.; Wasan, E.K.; Badea, I. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Pulmonary Delivery of Biopharmaceuticals: A Review of Opportunities, Challenges, and Delivery Applications. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 3084–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zeng, H.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Wu, C.; Hu, P. Recent Applications of PLGA in Drug Delivery Systems. Polymers 2024, 16, 2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visan, A.I.; Negut, I. Development and applications of PLGA hydrogels for sustained delivery of therapeutic agents. Gels 2024, 10, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, Q.; Zheng, R.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Tong, X.; Wan, Z.; Gong, T. The Advances in Phospholipids-Based Phase Separation Gels for the Sustained Release of Peptides, Proteins, and Chemotherapeutics. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jash, A.; Ubeyitogullari, A.; Rizvi, S.S. Liposomes for oral delivery of protein and peptide-based therapeutics: Challenges, formulation strategies, and advances. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 4773–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drescher, S.; van Hoogevest, P. The phospholipid research center: Current research in phospholipids and their use in drug delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Gangadharappa, H.; Mruthunjaya, K. Phospholipids: Unique carriers for drug delivery systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 39, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghule, T.; Saha, R.N.; Alexander, A.; Singhvi, G. Tailoring the multi-functional properties of phospholipids for simple to complex self-assemblies. J. Control. Release 2022, 349, 460–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, K.; Pani, A.; Chowdhury, T.; Kundu, A.; Thomas, S. Multi-vesicular Liposome and its Applications: A Novel Chemically Modified Approach for Drug Delivery Application. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2024, 24, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantripragada, S. A lipid based depot (DepoFoam® technology) for sustained release drug delivery. Prog. Lipid Res. 2002, 41, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaurasiya, A.; Gorajiya, A.; Panchal, K.; Katke, S.; Singh, A.K. A review on multivesicular liposomes for pharmaceutical applications: Preparation, characterization, and translational challenges. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 1569–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreelaya, P.; Bhattacharya, S. A Mini-review Based on Multivesicular Liposomes: Composition, Design, Preparation, Characteristics, and Therapeutic Importance as DEPOFOAM® Technology. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2023, 24, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Asherman, J.; Stevenson, M.; Brownson, E.; Katre, N.V. DepoFoam™ technology: A vehicle for controlled delivery of protein and peptide drugs. J. Control. Release 2000, 64, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Turker, M.S.; Chi, E.Y.; Sela, S.; Martin, G.M. Preparation of multivesicular liposomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 1983, 728, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorain, B.; Al-Dhubiab, B.E.; Nair, A.; Kesharwani, P.; Pandey, M.; Choudhury, H. Multivesicular liposome: A lipid-based drug delivery system for efficient drug delivery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 4404–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Chang, M.; Lyu, Y.; Dong, N.; Yu, N.; Yin, T.; Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Gou, J.; Tang, X. Intramuscular injection of palmitic acid-conjugated Exendin-4 loaded multivesicular liposomes for long-acting and improving in-situ stability. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2024, 21, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, L.; Tang, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, L. Liraglutide-loaded multivesicular liposome as a sustained-delivery reduces blood glucose in SD rats with diabetes. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3358–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzar, S.M.; Park, E.J.; Seo, Y.; Lee, J.; Baik, S.H.; Hwang, S.J. Preparation and evaluation of intraperitoneal long-acting oxaliplatin-loaded multi-vesicular liposomal depot for colorectal cancer treatment. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, T.; Gao, L.; Quan, D.; Feng, D. Multivesicular liposomes for sustained release of naltrexone hydrochloride: Design, characterization and in vitro/in vivo evaluation. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2013, 18, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Koo, B.; Chen, L.; Petrochenko, P.; Dong, Y.; Choi, S.; Kozak, D.; Oktem, B.; et al. Probing the mechanism of bupivacaine drug release from multivesicular liposomes. J. Control. Release 2019, 294, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Ji, Y.; Xu, S.; Chen, D.Q.; Tu, J. Multivesicular liposome formulations for the sustained delivery of ropivacaine hydrochloride: Preparation, characterization, and pharmacokinetics. Drug Deliv. 2011, 18, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, R.C. Method for Utilizing Neutral Lipids to Modify In Vivo Release from Multivesicular Liposomes. U.S. Patent 5,891,467, 6 April 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Los, K.D.; Garcia, L.D.; Kurz, S.; Kharitonov, V. Multivesicular Liposome Formulations of Tranexamic Acid. U.S. Patent 15/002,243, 21 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Cao, C.; Zhang, G.; Sun, Z. Impact of particle size of multivesicular liposomes on the embolic and therapeutic effects in rabbit VX2 liver tumor. Drug Deliv. 2023, 30, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, S. Liposomes for drug delivery: Review of vesicular composition, factors affecting drug release and drug loading in liposomes. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2023, 51, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Bae, J.; Manna, S.; Smith, W.; Vo, A.; Wang, Y.; Choi, S.; Kozak, D.; Xu, X.; Zheng, J. Confocal laser scanning microscopy to study the effect of manufacturing process on the critical quality attributes of multivesicular liposomes. Microsc. Microanal. 2020, 26, 2284–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Mao, S. Tuning the membrane fluidity of liposomes for desirable in vivo fate with enhanced drug delivery. In Advances in Biomembranes and Lipid Self-Assembly; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 67–106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Yuan, Y.; Xue, J.; Hou, A.; Song, S.; Guan, J.; Zhang, X.; Mao, S. Exploring the influence of microstructure and phospholipid type of liposomes on their interaction with lung. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2024, 198, 114271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z. Investigation on Formulation, Manufacturing Process, and Drug Release of a Bupivacaine Multivesicular Liposomal Formulation (Exparel). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Michigan Library, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2024. Available online: https://deepblue.lib.umich.edu/handle/2027.42/194786 (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Doyen, C.; Larquet, E.; Coureux, P.D.; Frances, O.; Herman, F.; Sablé, S.; Burnouf, J.P.; Sizun, C.; Lescop, E. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: A multifaceted toolbox to probe structure, dynamics, interactions, and real-time in situ release kinetics in peptide-liposome formulations. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 2521–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, R.; Yue, Z.; Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Lin, H. Preparation and characterization of bupivacaine multivesicular liposome: A QbD study about the effects of formulation and process on critical quality attributes. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 598, 120335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Jain, R.K.; Chourasia, M.K.; Jain, A.K.; Chalasani, K.B.; Soni, V.; Jain, A. Design and development of multivesicular liposomal depot delivery system for controlled systemic delivery of acyclovir sodium. AAPS Pharmscitech 2005, 6, E35–E41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahar, P.; Cummings, K.C., III. Liposomal bupivacaine: A review of a new bupivacaine formulation. J. Pain Res. 2012, 5, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Meng, Q.; Chu, Y.; Gu, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Fei, Y.; Fu, J.; Han, J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 loaded phospholipid micelles for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: Improved pharmacokinetic behaviours and prolonged glucose-lowering effects. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 94408–94416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Formulation | EE (%) | D50 (µm) |
|---|---|---|
| SPC | 93.05 ± 0.02 | 28.93 ± 0.08 |
| SPC 85:15 DEPC | 93.04 ± 0.04 | 32.27 ± 0.16 |
| SPC 75:25 DEPC | 95.22 ± 0.05 | 31.15 ± 0.22 |
| SPC 50:50 DEPC | 98.74 ± 0.01 | 29.93 ± 0.23 |
| SPC 25:75 DEPC | 90.02 ± 0.04 | 32.74 ± 2.67 |
| DEPC | 93.10 ± 0.02 | 30.09 ± 0.53 |
| Lir-MVLs | Victoza® | |
|---|---|---|
| AUC0–t (mg·h·mL−1) | 161 ± 32 | 57 ± 10 ** |
| AUC0–∞ (mg·h·mL−1) | 161 ± 32 | 57 ± 10 ** |
| MRT0–t (h) | 44 ± 4 | 10.6 ± 1.3 ** |
| MRT0–∞ (h) | 44 ± 5 | 10.6 ± 1.4 ** |
| Tmax (h) | 24 ± 0 | 4.0 ± 2.4 ** |
| Cmax (ng·mL−1) | 3270 ± 860 | 3810 ± 1020 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Yao, X.; Gao, S.; Xu, T.; Wang, D.; Sha, L.; Yang, L. Sustained Delivery of Liraglutide Using Multivesicular Liposome Based on Mixed Phospholipids. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020203
Zhang R, Yao X, Gao S, Xu T, Wang D, Sha L, Yang L. Sustained Delivery of Liraglutide Using Multivesicular Liposome Based on Mixed Phospholipids. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(2):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020203
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Runpeng, Xinyu Yao, Siqi Gao, Tingting Xu, Da Wang, Luping Sha, and Li Yang. 2025. "Sustained Delivery of Liraglutide Using Multivesicular Liposome Based on Mixed Phospholipids" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 2: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020203
APA StyleZhang, R., Yao, X., Gao, S., Xu, T., Wang, D., Sha, L., & Yang, L. (2025). Sustained Delivery of Liraglutide Using Multivesicular Liposome Based on Mixed Phospholipids. Pharmaceutics, 17(2), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020203





