Advancing Lung Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Review of Photodynamic Therapy and Nanoparticle Applications
Abstract
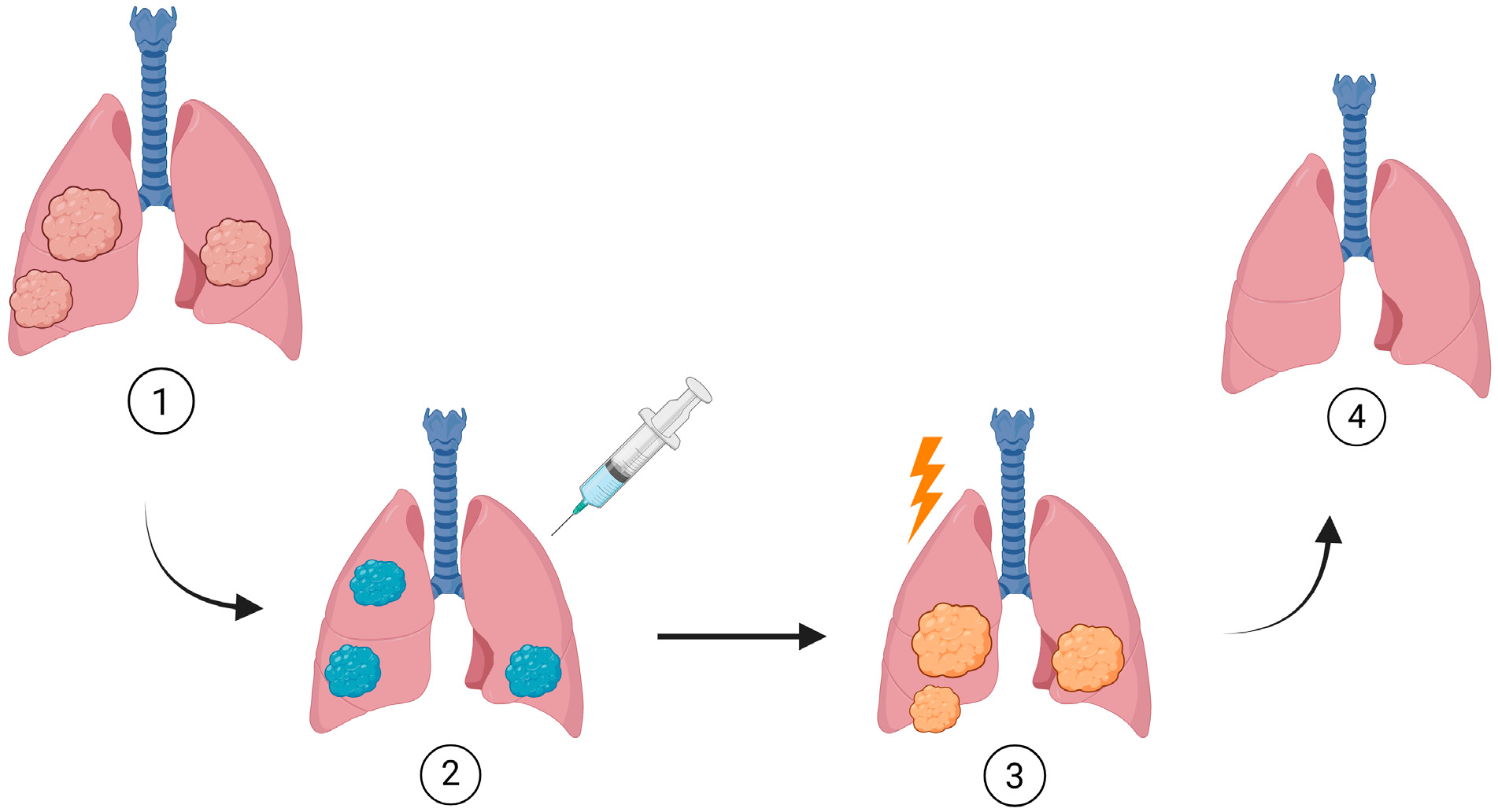
1. Introduction
2. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Photodynamic Therapy
3. Advances in Photosensitizer Development and Formulation Strategies
4. Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy in Lung Cancer Through Nanoparticle Technologies
4.1. Organic Nanoparticles
4.2. Polymeric Nanoparticles
4.3. Porphyrin-Based Nanoparticles
4.4. Inorganic Nanoparticles
4.5. Metal-Based Nanoparticles
4.6. Metal Oxide Nanoparticles
4.7. Meosoporous Silica Nanoparticles
4.8. Quantum Dots (QDs)
4.9. Biomimetic Nanoparticles
4.10. Microfluidic and Organ-on-Chip Platforms
5. Overcoming Inherent Limitations of PDT
5.1. Oxygen-Generating Nanoparticles
5.2. Regulating the Tumor Microenvironment (TME) to Increase Oxygen
5.3. NIR-Activated Nanoparticles
5.4. Novel Light Delivery Systems and Alternative Energy Sources for Deep Activation
5.5. X-Ray-Activated Photodynamic Therapy (X-PDT)
5.6. Cerenkov Radiation-Activated PDT
6. The Role of the Tumor Microenvironment (TME) in Nanoparticle-Ehanced PDT
6.1. pH-Responsive Nanoparticles
6.2. Enzyme-Responsive Nanoparticles
6.3. Immune Cell Infiltration Modulation
6.4. Extracellular Matrix Degradation
7. Clinical Insights and Therapeutic Outcomes of PDT and Nanoparticle-Enhanced PDT
8. Synergistic Combination Therapies with Nanoparticle-Enhanced PDT
8.1. Combination with Chemotherapy
8.2. Combination with Immunotherapy
8.3. Potential Synergies with Targeted Therapy, Radiation Therapy, and Gene Therapy
9. Challenges and Future Directions for Clinical Translation
9.1. Regulatory Considerations and Approval Pathways
9.2. Manufacturing Scalability and Quality Control
9.3. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
9.4. Development of Personalized Treatment Approaches
9.5. Long-Term Safety, Immunogenicity, and Ethical Consideration
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smolarz, B.; Łukasiewicz, H.; Samulak, D.; Piekarska, E.; Kołaciński, R.; Romanowicz, H. Lung Cancer—Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Treatment and Molecular Aspect (Review of Literature). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberg, A.J.; Brock, M.V.; Ford, J.G.; Samet, J.M.; Spivack, S.D. Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Chest 2013, 143, e1S–e29S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrella, F.; Rizzo, S.; Attili, I.; Passaro, A.; Zilli, T.; Martucci, F.; Bonomo, L.; Del Grande, F.; Casiraghi, M.; De Marinis, F.; et al. Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An Overview of Treatment Options. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 3160–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawrocki, S.; Krzakowski, M.; Wasilewska-Tesluk, E.; Kowalski, D.; Rucinska, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Sowa, A. Concurrent Chemotherapy and Short Course Radiotherapy in Patients with Stage IIIA to IIIB Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Not Eligible for Radical Treatment: Results of a Randomized Phase II Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albain, K.S.; Swann, R.S.; Rusch, V.R.; Turrisi, A.T.; Shepherd, F.A.; Smith, C.; Chen, Y.; Livingston, R.B.; Feins, R.; Gandara, D.R.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Chemotherapy with or without Surgical Resection for Stage III Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lancet 2009, 374, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahayneh, K.; Idkedek, M.; Abu Akar, F. NSCLC: Current Evidence on Its Pathogenesis, Integrated Treatment, and Future Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araghi, M.; Mannani, R.; Heidarnejad Maleki, A.; Hamidi, A.; Rostami, S.; Safa, S.H.; Faramarzi, F.; Khorasani, S.; Alimohammadi, M.; Tahmasebi, S.; et al. Recent Advances in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Targeted Therapy; An Update Review. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinis, P.; Berg, K.; Cengel, K.A.; Foster, T.H.; Girotti, A.W.; Gollnick, S.O.; Hahn, S.M.; Hamblin, M.R.; Juzeniene, A.; Kessel, D.; et al. Photodynamic Therapy Of Cancer: An Update. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 250–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, A.; Pace, G.P.; Concioli, M. Photodynamic Effect of Haematoporphyrin on Blood Microcirculation. J. Pathol. Bacteriol. 1963, 86, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.A.; Correia, J.H. Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy: A Review of Combined Energy Sources. Cells 2022, 11, 3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailioaie, L.M.; Ailioaie, C.; Litscher, G. Fighting Cancer with Photodynamic Therapy and Nanotechnologies: Current Challenges and Future Directions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jamal, A.N.; Al-Hussainy, A.F.; Mohammed, B.A.; Abbas, H.H.; Kadhim, I.M.; Ward, Z.H.; Mahapatra, D.K.; Joseph, T.M.; Kianfar, E.; Thomas, S. Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) in Drug Delivery: Nano-Innovations Enhancing Treatment Outcomes. Health Sci. Rev. 2025, 14, 100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, C.; Jin, B.; Sun, T.; Sun, K.; Wang, S.; Fan, Z. Advances in Smart Nanotechnology-Supported Photodynamic Therapy for Cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.; Khan, N.; Geetha, M.; Veettil, R.P.; Kasote, D.M.; Hasan, A.; Sadasivuni, K.K. Therapeutic Applications of Nanobots and Nanocarriers in Cancer Treatment. Anal. Sci. 2025, 41, 1305–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udrea, A.M.; Smarandache, A.; Dinache, A.; Mares, C.; Nistorescu, S.; Avram, S.; Staicu, A. Photosensitizers-Loaded Nanocarriers for Enhancement of Photodynamic Therapy in Melanoma Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Xie, Q.; Sun, Y. Advances in Nanomaterial-Based Targeted Drug Delivery Systems. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1177151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, J.H.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Pimenta, S.; Dong, T.; Yang, Z. Photodynamic Therapy Review: Principles, Photosensitizers, Applications, and Future Directions. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calixto, G.M.F.; Bernegossi, J.; De Freitas, L.M.; Fontana, C.R.; Chorilli, M. Nanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer: A Review. Molecules 2016, 21, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, P.; Erdem, S.S.; Hamblin, M.R. Photodynamic Therapy: One Step Ahead with Self-Assembled Nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 1937–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allamyradov, Y.; ben Yosef, J.; Annamuradov, B.; Ateyeh, M.; Street, C.; Whipple, H.; Er, A.O. Photodynamic Therapy Review: Past, Present, Future, Opportunities and Challenges. Photochem 2024, 4, 434–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwajembola, A.M.; Cleanclay, W.D.; Onyia, A.F.; Chikere, B.N.; Zakari, S.; Ndifreke, E.; De Campos, O.C. Photosensitizers in Photodynamic Therapy: An Advancement in Cancer Treatment. Results Chem. 2024, 10, 101715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.P.; Ayaru, L.; Ackroyd, R.; Mitton, D.; Fullarton, G.; Zammit, M.; Grzebieniak, Z.; Messmann, H.; Ortner, M.-A.; Gao, L.; et al. The Pharmacokinetics and Safety of Porfimer after Repeated Administration 30–45 Days Apart to Patients Undergoing Photodynamic Therapy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 32, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-J.; Wang, K.-P.; Mo, J.-G.; Xiong, L.; Wen, Y. Photodynamic Therapy Regulates Fate of Cancer Stem Cells through Reactive Oxygen Species. World J. Stem Cells 2020, 12, 562–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikas, V.; Yang, W.; Wilson, B.C.; Zhu, T.C.; Hadfield, R.H. Analysis of Singlet Oxygen Luminescence Generated By Protoporphyrin IX. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomova, K.; Raptova, R.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Reactive Oxygen Species, Toxicity, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants: Chronic Diseases and Aging. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 2499–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.A.; Pérez de la Lastra, J.M.; Plou, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. The Chemistry of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Revisited: Outlining Their Role in Biological Macromolecules (DNA, Lipids and Proteins) and Induced Pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, P.S.; Bhattarai, H.K. Singlet Oxygen, Photodynamic Therapy, and Mechanisms of Cancer Cell Death. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 7211485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, J.; Soma, Y.; Matsuda, Y. Biological Action of Singlet Molecular Oxygen from the Standpoint of Cell Signaling, Injury and Death. Molecules 2023, 28, 4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, L.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; Chen, X. Apoptosis of HeLa Cells Induced by a New Targeting Photosensitizer-Based PDT via a Mitochondrial Pathway and ER Stress. Onco Targets Ther. 2015, 8, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroz, P.; Yaroslavsky, A.; Kharkwal, G.B.; Hamblin, M.R. Cell Death Pathways in Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer. Cancers 2011, 3, 2516–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, V.; Furci, F.; Minciullo, P.L.; Casciaro, M.; Allegra, A.; Gangemi, S. Photodynamic Therapy in Cancer: Insights into Cellular and Molecular Pathways. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benov, L. Photodynamic Therapy: Current Status and Future Directions. Med. Princ. Pract. 2014, 24, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Yuan, Z.; Zhou, M. Targeted Photodynamic Therapy: Enhancing Efficacy through Specific Organelle Engagement. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1667812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźnicki, P.; Bartusik-Aebisher, D.; Przygórzewska, A.; Aebisher, D. Molecular Mechanisms of the Effects of Photodynamic Therapy on the Brain: A Review of the Literature. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2025, 52, 104536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunaydin, G.; Gedik, M.E.; Ayan, S. Photodynamic Therapy—Current Limitations and Novel Approaches. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 691697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Shen, X.; He, Z.; Lu, Y. The Role of Photodynamic Therapy in Triggering Cell Death and Facilitating Antitumor Immunology. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 863107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warszyńska, M.; Repetowski, P.; Dąbrowski, J.M. Photodynamic Therapy Combined with Immunotherapy: Recent Advances and Future Research Directions. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 495, 215350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, U.; Sarkar, T.; Mukherjee, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Dutta, A.; Dutta, S.; Nayak, D.; Kaushik, S.; Das, T.; Sa, G. Tumor-Associated Macrophages: An Effective Player of the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1295257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, W.; Sun, T.; Peng, N.; Wang, Z.; Chen, D.; Qiu, H.; Zhao, H. Photodynamic Therapy-Induced Anti-Tumor Immunity: Influence Factors and Synergistic Enhancement Strategies. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruppathi, J.; Vijayan, V.; Park, I.-K.; Lee, S.E.; Rhee, J.H. Enhancing Cancer Immunotherapy with Photodynamic Therapy and Nanoparticle: Making Tumor Microenvironment Hotter to Make Immunotherapeutic Work Better. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1375767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, A.; Khan, S.; Chatterjee, T.; Ghosh, M. Unleashing the Power of Porphyrin Photosensitizers: Illuminating Breakthroughs in Photodynamic Therapy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2023, 248, 112796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Wu, C.; Pan, X.; Huang, Z.; Lu, C.; Quan, G. Photodynamic Therapy for Cancer: Mechanisms, Photosensitizers, Nanocarriers, and Clinical Studies. MedComm 2024, 5, e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rethi, L.; Mutalik, C.; Anurogo, D.; Lu, L.-S.; Chu, H.-Y.; Yougbaré, S.; Kuo, T.-R.; Cheng, T.-M.; Chen, F.-L. Lipid-Based Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery Systems in Breast Cancer Therapy. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, K.M.; Sharma, G.; Singh, A.P.; Siddiqui, J.A. Nanomedicine in Cancer Therapeutics: Current Perspectives from Bench to Bedside. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmina, N.S.; Fedotova, E.A.; Jankovic, P.; Gribova, G.P.; Nyuchev, A.V.; Fedorov, A.Y.; Otvagin, V.F. Enhancing Precision in Photodynamic Therapy: Innovations in Light-Driven and Bioorthogonal Activation. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, J.; Dou, D.; Yang, L. Porphyrin Photosensitizers in Photodynamic Therapy and Its Applications. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 81591–81603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siriwardane, D.A.; Jiang, W.; Mudalige, T. Profiling In-Vitro Release of Verteporfin from VISUDYNE® Liposomal Formulation and Investigating Verteporfin Binding to Human Serum Albumin. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 646, 123449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, Y.; Murayama, Y.; Takamatsu, T.; Otsuji, E.; Tanaka, H. 5-Aminolevulinic Acid-Induced Protoporphyrin IX Fluorescence Imaging for Tumor Detection: Recent Advances and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senge, M.O.; Brandt, J.C. Temoporfin (Foscan®, 5,10,15,20-Tetra(m-Hydroxyphenyl)Chlorin)—A Second-Generation Photosensitizer. Photochem. Photobiol. 2011, 87, 1240–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chornovolenko, K.; Koczorowski, T. Phthalocyanines Conjugated with Small Biologically Active Compounds for the Advanced Photodynamic Therapy: A Review. Molecules 2025, 30, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, J.; Mende, L.K.; Kuthati, Y. A Review of the Efficacy of Nanomaterial-Based Natural Photosensitizers to Overcome Multidrug Resistance in Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajith, S.; Almomani, F.; Elhissi, A.; Husseini, G.A. Nanoparticle-Based Materials in Anticancer Drug Delivery: Current and Future Prospects. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, M.; Eslami, M.; Sahandi-Zangabad, P.; Mirab, F.; Farajisafiloo, N.; Shafaei, Z.; Ghosh, D.; Bozorgomid, M.; Dashkhaneh, F.; Hamblin, M.R. pH-Sensitive Stimulus-Responsive Nanocarriers for Targeted Delivery of Therapeutic Agents. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 8, 696–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Liao, J.; Ma, Y.; Sarwar, M.T.; Yang, H. Advances in Targeted Therapy for Tumor with Nanocarriers: A Review. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 31, 101583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shao, A. Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy and Its Role in Overcoming Drug Resistance. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-López, E.; Guerra, M.; Dias-Ferreira, J.; Lopez-Machado, A.; Ettcheto, M.; Cano, A.; Espina, M.; Camins, A.; Garcia, M.L.; Souto, E.B. Current Applications of Nanoemulsions in Cancer Therapeutics. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, D.; Pan, Y.; Chen, B. Human Serum Albumin Based Nanodrug Delivery Systems: Recent Advances and Future Perspective. Polymers 2023, 15, 3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Shen, B.; Raza, M.A.; Yang, Z.; Amjad, M.N.; Din, G.u.; Yue, L.; Kousar, A.; Kanwal, Q.; Hu, Y. Albumin: A Review of Market Trends, Purification Methods, and Biomedical Innovations. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Staudinger, J.N.; Mindt, T.L.; Gasser, G. Theranostics with Photodynamic Therapy for Personalized Medicine: To See and to Treat. Theranostics 2023, 13, 5501–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhan, B.; Du, Y.; Liu, N.; Liu, S.; Li, X. Targeted Cancer Treatment Using Folic Acid-Functionalized Carbohydrate Polymers: A New Era in Nanomedicine. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 235, 121704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehelgerdi, M.; Chehelgerdi, M.; Allela, O.Q.B.; Pecho, R.D.C.; Jayasankar, N.; Rao, D.P.; Thamaraikani, T.; Vasanthan, M.; Viktor, P.; Lakshmaiya, N.; et al. Progressing Nanotechnology to Improve Targeted Cancer Treatment: Overcoming Hurdles in Its Clinical Implementation. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lin, M.; Wang, W.; Shen, Z.; Wu, Z.-S. DNA Tetrahedral Nanostructures for the Biomedical Application and Spatial Orientation of Biomolecules. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 33, 279–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, T.M.; Kar Mahapatra, D.; Esmaeili, A.; Piszczyk, Ł.; Hasanin, M.S.; Kattali, M.; Haponiuk, J.; Thomas, S. Nanoparticles: Taking a Unique Position in Medicine. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurul, F.; Turkmen, H.; Cetin, A.E.; Topkaya, S.N. Nanomedicine: How Nanomaterials Are Transforming Drug Delivery, Bio-Imaging, and Diagnosis. Next Nanotechnol. 2025, 7, 100129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, L.; Ju, Z.; Skonieczna, M.; Zhou, P.; Huang, R. Nanoparticles-induced Potential Toxicity on Human Health: Applications, Toxicity Mechanisms, and Evaluation Models. MedComm 2023, 4, e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazak, R.; Houri, M.; Achy, S.E.; Hussein, W.; Refaat, T. Passive Targeting of Nanoparticles to Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 2, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagena, I.-A.; Malapani, C.; Gatou, M.-A.; Lagopati, N.; Pavlatou, E.A. Enhancement of EPR Effect for Passive Tumor Targeting: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. The Enhanced Permeability and Retention (EPR) Effect: The Significance of the Concept and Methods to Enhance Its Application. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golombek, S.K.; May, J.-N.; Theek, B.; Appold, L.; Drude, N.; Kiessling, F.; Lammers, T. Tumor Targeting via EPR: Strategies to Enhance Patient Responses. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 130, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, N.; Wu, J.; Xu, X.; Kamaly, N.; Farokhzad, O.C. Cancer Nanotechnology: The Impact of Passive and Active Targeting in the Era of Modern Cancer Biology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 66, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Yu, Z. Application of Nanoparticles in the Treatment of Lung Cancer with Emphasis on Receptors. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 781425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagianni, A.; Alexandratou, E.; Terrones, M.; Kordatos, K.V. Carbon-Based Nanomaterials in Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer. Carbon 2025, 238, 119986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Hu, S.; Teng, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, K.; Xu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, X. Current Advance of Nanotechnology in Diagnosis and Treatment for Malignant Tumors. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curcio, M.; Vittorio, O.; Bell, J.L.; Iemma, F.; Nicoletta, F.P.; Cirillo, G. Hyaluronic Acid within Self-Assembling Nanoparticles: Endless Possibilities for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Shi, Z.; Ou, M.; Li, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, W.; Huang, Q.; Li, M.; Chen, C.; Zeng, X.; et al. Dextran-Based Micelles for Combinational Chemo-Photodynamic Therapy of Tumors via In Vivo Chemiluminescence. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 319, 121192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geszke-Moritz, M.; Moritz, M. Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Comprehensive Overview, Perspectives and Challenges. Polymers 2024, 16, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, S.; Jing, D.; Liu, N.; Luo, X. The Construction of Elastin-like Polypeptides and Their Applications in Drug Delivery System and Tissue Repair. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, S.; Patel, M. Bio-Nanocarriers for Lung Cancer Management: Befriending the Barriers. Nanomicro Lett. 2021, 13, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobdeedamrong, A.; Yoo, H.J.; Jung, H.; Pechyen, C.; Natphopsuk, S.; Thongnuek, P.; Jeong, S.; Lee, J.; Yang, S.-G. Cholesterol-Conjugated Polyion Complex Nanoparticles for Combination Delivery of Hydrophobic Paclitaxel and Hydrophilic miR-34a for Colon Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglo, Y.; Liang, B.J.; Robey, R.W.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Gottesman, M.M.; Huang, H.-C. Porphyrin-Lipid Assemblies and Nanovesicles Overcome ABC Transporter-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy Resistance in Cancer Cells. Cancer Lett. 2019, 457, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Luo, Z.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Cheng, K.; Xue, Y.; Liu, G.; Luo, X.; Wu, F. Self-Assembled Porphyrin Polymer Nanoparticles with NIR-II Emission and Highly Efficient Photothermal Performance in Cancer Therapy. Mater. Today Bio 2021, 13, 100198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Colombani-Garay, D.; Huang, L.; Duan, C.; Han, G. Tailoring Nanoparticles Based on Boron Dipyrromethene for Cancer Imaging and Therapy. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol 2020, 12, e1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harish, V.; Ansari, M.M.; Tewari, D.; Gaur, M.; Yadav, A.B.; García-Betancourt, M.-L.; Abdel-Haleem, F.M.; Bechelany, M.; Barhoum, A. Nanoparticle and Nanostructure Synthesis and Controlled Growth Methods. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinukonda, A.; Bolledla, N.; Jadi, R.K.; Chinthala, R.; Devadasu, V.R. Synthesis of Nanoparticles Using Advanced Techniques. Next Nanotechnol. 2025, 8, 100169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, H.; Akdaşçi, E.; Eker, F.; Bechelany, M.; Karav, S. Gold Nanoparticles: Multifunctional Properties, Synthesis, and Future Prospects. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Barroso, L.G.; Lanzagorta Garcia, E.; Mojicevic, M.; Huerta, M.; Pogue, R.; Devine, D.M.; Brennan-Fournet, M. Triangular Silver Nanoparticles Synthesis: Investigating Potential Application in Materials and Biosensing. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klębowski, B.; Depciuch, J.; Parlińska-Wojtan, M.; Baran, J. Applications of Noble Metal-Based Nanoparticles in Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Martín, M.J.; Otarola, J.; Vakarelska, E.; Simeonov, V.; Lassalle, V.; Nedyalkova, M. Biomedical Applications of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Current Insights Progress and Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiao, J.; Wong, K.; Wang, J. 68Ga-Labeled Magnetic-Nir Persistent Luminescent Hybrid Mesoporous Nanoparticles for Multimodal Imaging-Guided Chemotherapy and Photodynamic Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 9667–9680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corato, R.D.; Béalle, G.; Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Espinosa, A.; Clément, O.; Silva, A.; Ménager, C.; Wilhelm, C. Combining Magnetic Hyperthermia and Photodynamic Therapy for Tumor Ablation with Photoresponsive Magnetic Liposomes. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 2904–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, D.; Park, W.; Park, S.; Lü, Y.; Kim, K.S.; Hackett, M.; Kim, B.H.; Yim, H.; Jeon, Y.S.; Na, K.; et al. Multifunctional Tumor pH-Sensitive Self-Assembled Nanoparticles for Bimodal Imaging and Treatment of Resistant Heterogeneous Tumors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5647–5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Weng, L.; Liu, T.; Sun, S.; Yao, Y.; Chen, X. Cascade Nanoreactor Employs Mitochondrial-Directed Chemodynamic and Δ-ALA-Mediated Photodynamic Synergy for Deep-Seated Oral Cancer Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2304639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Dong, X.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, X. Hybrid Nanomaterials-Based Biomedical Phototheranostic Platforms. Prog. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 3, 032001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Dong, H.; Ge, J.; Chen, D.; Sun, L.; Li, S.; Wang, C.; Yan, C.; Wang, P.; Shu, C. Multifunctional Upconversion–Nanoparticles–Trismethylpyridylporphyrin–Fullerene Nanocomposite: A Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Theranostic Platform for Imaging-Guided Photodynamic Therapy. NPG Asia Mater. 2015, 7, e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidolin, K.; Ding, L.; Chen, J.; Wilson, B.C.; Zheng, G. Porphyrin-Lipid Nanovesicles (Porphysomes) Are Effective Photosensitizers for Photodynamic Therapy. Nanophotonics 2021, 10, 3161–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro-Flores, G.; Ancira-Cortez, A.; Ocampo-García, B.; Meléndez-Alafort, L. Molecularly Targeted Lanthanide Nanoparticles for Cancer Theranostic Applications. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Chen, M.; Bhattarai, P.; Hameed, S.; Tang, Y.; Dai, Z. Complementing Cancer Photodynamic Therapy with Ferroptosis Through Iron Oxide Loaded Porphyrin-Grafted Lipid Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 20164–20180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, C.C.; Bergholt, M.S.; Nagelkerke, A.; Thin, M.Z.; Pence, I.J.; Kauscher, U.; Kalber, T.L.; Stuckey, D.J.; Stevens, M.M. Integrated Photodynamic Raman Theranostic System for Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment, and Post-Treatment Molecular Monitoring. Theranostics 2021, 11, 2006–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, N.; Khan, Y.; Yadav, S.; Saini, K.; Maity, D. Application of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles in Different Carcinomas. J. Nanotheranostics 2024, 5, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, J.W.; Martinez, E.; Louka, P.; Wingett, D.G. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Selective Destruction of Tumor Cells and Potential for Drug Delivery Applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkő, F.; Kristó, K.; Sovány, T. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhamoorthy, M.; Asaithambi, P.; Ramkumar, V.; Elangovan, N.; Perumal, I.; Kim, S.C. A Review on the Recent Advancements of Polymer-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Under Stimuli-Trigger. Polymers 2025, 17, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niroumand, U.; Firouzabadi, N.; Goshtasbi, G.; Hassani, B.; Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. The Effect of Size, Morphology and Surface Properties of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles on Pharmacokinetic Aspects and Potential Toxicity Concerns. Front. Mater. 2023, 10, 1189463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Gao, Y.; Yan, F. Semiconductor Quantum Dots for Biomedicial Applications. Sensors 2011, 11, 11736–11751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimona, M.A.; Rimon, M.I.H.; Zohura, F.T.; Sony, J.M.; Rim, S.I.; Arup, M.M.R.; Mobarak, M.H. Quantum Dot Nanomaterials: Empowering Advances in Optoelectronic Devices. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2025, 21, 100704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, M.; He, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q. CoFe2O4-Quantum Dots for Synergistic Photothermal/Photodynamic Therapy of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Via Triggering Apoptosis by Regulating PI3K/AKT Pathway. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhobongo, B.; Chandran, R.; Abrahamse, H. The Role of Melanoma Cell-Derived Exosomes (MTEX) and Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) Within a Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, A.; Kushwaha, R.; Kumar, A.; Huang, H.; Banerjee, S. Engineered Exosomes as a Photosensitizer Delivery Platform for Cancer Photodynamic Therapy. Chemmedchem 2022, 17, e202200119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, A.; Martínez-Arroyo, O.; Forner, M.J.; Cortés, R. Exosomes as Drug Delivery Systems: Endogenous Nanovehicles for Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Pharmaceutics 2020, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Duo, Y.; Suo, M.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, L.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, L.; Tang, B.Z. Tumor-Exocytosed Exosome/Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogen Hybrid Nanovesicles Facilitate Efficient Tumor Penetration and Photodynamic Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 13836–13843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, S.E.; Ando, H.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Shimizu, T.; Ukawa, M.; Okuhira, K.; Ishima, Y.; Mahdy, M.A.; Ghazy, F.S.; Ishida, T. A Novel Strategy to Increase the Yield of Exosomes (Extracellular Vesicles) for an Expansion of Basic Research. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, P.; Shi, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Cheng, H.; Dai, Q.; Gao, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Functional Nanovesicles Displaying Anti-Pd-L1 Antibodies for Programmed Photoimmunotherapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, M.; Zhang, F.; Xuanyuan, T.; Liu, X.; Yu, D.; Liu, W. An Integrated Microfluidic Biomimetic Tumor-on-a-Chip for Wide-Range Screening of Chemotherapy and Photodynamic Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, e01105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cuzzucoli, F.; Escobar, A.; Lu, S.; Liang, L.; Wang, S. Tumor-on-a-Chip Platforms for Assessing Nanoparticle-Based Cancer Therapy. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 332001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.; Zheng, S.; Liu, X.; Kamei, K. Tumor-on-a-Chip Model for Advancement of Anti-Cancer Nano Drug Delivery System. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervantonakis, I.K.; Arvanitis, C.D. Controlled Drug Release and Chemotherapy Response in a Novel Acoustofluidic 3D Tumor Platform. Small 2016, 12, 2616–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achyuta, A.K.H.; Conway, A.J.; Crouse, R.B.; Bannister, E.C.; Lee, R.N.; Katnik, C.; Behensky, A.A.; Cuevas, J.; Sundaram, S. A Modular Approach to Create a Neurovascular Unit-on-a-Chip. Lab. Chip 2013, 13, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Ivask, A.; Guo, K.; McCormick, S.; Lombi, E.; Priest, C.; Voelcker, N.H. Crossed Flow Microfluidics for High Throughput Screening of Bioactive Chemical–Cell Interactions. Lab. Chip 2017, 17, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ingram, P.; Yoon, E. High-Throughput Cancer Cell Sphere Formation for Characterizing the Efficacy of Photo Dynamic Therapy in 3D Cell Cultures. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheiri, S.; Chen, Z.; Yakavets, I.; Rakhshani, F.; Young, E.W.K.; Kumacheva, E. Integrating Spheroid-on-a-chip with Tubeless Rocker Platform: A High-throughput Biological Screening Platform. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 18, e2200621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaramiri, A.; Asalh, R.A.; Asalh, M.A.; AlSawaftah, N.; Abuwatfa, W.H.; Husseini, G.A. A Comprehensive Review of Smart Thermosensitive Nanocarriers for Precision Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallatah, M.M.; Alradwan, I.; Alfayez, N.; Aodah, A.H.; Alkhrayef, M.; Majrashi, M.; Jamous, Y.F. Nanoparticles for Cancer Immunotherapy: Innovations and Challenges. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornesello, A.L.; Tagliamonte, M.; Tornesello, M.L.; Buonaguro, F.M.; Buonaguro, L. Nanoparticles to Improve the Efficacy of Peptide-Based Cancer Vaccines. Cancers 2020, 12, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabit, H.; Pawlik, T.M.; Radwan, F.; Abdel-Hakeem, M.; Abdel-Ghany, S.; Wadan, A.-H.S.; Elzawahri, M.; El-Hashash, A.; Arneth, B. Precision Nanomedicine: Navigating the Tumor Microenvironment for Enhanced Cancer Immunotherapy and Targeted Drug Delivery. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.G.; Surendran, S.P.; Jeong, Y.Y. Tumor Microenvironment-Stimuli Responsive Nanoparticles for Anticancer Therapy. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 610533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Cao, Y.; Cao, M.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Gong, T. Nanomedicine in Cancer Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, S.; Bakhshali, R.; Bolandi, S.; Zahed, Z.; Mojtaba Zadeh, S.S.; Kaveh Zenjanab, M.; Jahanban Esfahlan, R. For and against Tumor Microenvironment: Nanoparticle-Based Strategies for Active Cancer Therapy. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 31, 101626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Song, J.; Nie, L.; Chen, X. Reactive Oxygen Species Generating Systems Meeting Challenges of Photodynamic Cancer Therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6597–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, N.M.; Gnanasammandhan, M.K.; Zhang, J.; Ho, P.C.; Mahendran, R.; Zhang, Y. In Vivo Photodynamic Therapy Using Upconversion Nanoparticles as Remote-Controlled Nanotransducers. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1580–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamkaew, A.; Cheng, L.; Goel, S.; Valdovinos, H.F.; Barnhart, T.E.; Liu, Z.; Cai, W. Cerenkov Radiation Induced Photodynamic Therapy Using Chlorin E6-Loaded Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 26630–26637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.M.; Darafsheh, A. Light Sources and Dosimetry Techniques for Photodynamic Therapy. Photochem. Photobiol. 2020, 96, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendsøe, N. Photodynamic Therapy: Superficial and Interstitial Illumination. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 041502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Minzioni, P.; Hui, J.; Yun, S.-H.; Yetisen, A.K. Fiber Optic Devices for Diagnostics and Therapy in Photomedicine. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2024, 12, 2400478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Care, A.; Zhang, R.; Lu, Y.; Packer, N.H.; Sunna, A.; Qian, Y.; Zvyagin, A.V. Facile Assembly of Functional Upconversion Nanoparticles for Targeted Cancer Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11945–11953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.S.; Khot, M.I.; Woo, H.-M.; Hong, S.; Baek, D.; Maisey, T.; Daniels, B.; Coletta, P.L.; Yoon, B.-J.; Jayne, D.; et al. AI-Enabled, Implantable, Multichannel Wireless Telemetry for Photodynamic Therapy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, A.; Yang, F.; Tian, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ho, J.S. In Vivo Wireless Photonic Photodynamic Therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.K.; Zhu, T.C. Reconstruction of In-Vivo Optical Properties for Human Prostate Using Interstitial Diffuse Optical Tomography. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 11665–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempstead, J.; Jones, D.P.; Ziouche, A.; Cramer, G.M.; Rizvi, I.; Arnason, S.B.; Hasan, T.; Celli, J.P. Low-Cost Photodynamic Therapy Devices for Global Health Settings: Characterization of Battery-Powered LED Performance and Smartphone Imaging in 3D Tumor Models. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Halls, S.; Dickey, D.J.; Tulip, J.; Moore, R.B. Fractionated Versus Standard Continuous Light Delivery in Interstitial Photodynamic Therapy of Dunning Prostate Carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 7496–7505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, X.; Gao, M.; Xia, D.; Cheng, H. Engineering Tumor-Oxygenated Nanomaterials: Advancing Photodynamic Therapy for Cancer Treatment. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1383930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, L.; Huang, M.; Zeng, S.; Zheng, J.; Peng, S.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Li, S. Innovative Strategies for Photodynamic Therapy against Hypoxic Tumor. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 18, 100775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; He, L.; Xu, J.; Fang, Q.; Yang, L.; Xue, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, R. Oxygen-Producing Catalase-Based Prodrug Nanoparticles Overcoming Resistance in Hypoxia-Mediated Chemo-Photodynamic Therapy. Acta Biomater. 2020, 112, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, S.; Yu, H.; Cao, W.; Chen, W.; Wei, H.; Guo, H. O2-Generating MnO2 Nanoparticles for Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy of Bladder Cancer by Ameliorating Hypoxia. Theranostics 2018, 8, 990–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, C.; Su, K.; Zhao, D.; Lu, A.; Zhong, C. Nanomaterials for Tumor Hypoxia Relief to Improve the Efficacy of ROS-Generated Cancer Therapy. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 649158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Guo, T.; Zhang, C.; Ou, S.; Long, Y.; Hu, Z. Recent Advances in Strategies for Addressing Hypoxia in Tumor Photodynamic Therapy. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.-W.; Li, B.; Li, C.-X.; Fan, J.-X.; Lei, Q.; Li, C.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.-Z. Carbon-Dot-Decorated Carbon Nitride Nanoparticles for Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy against Hypoxic Tumor via Water Splitting. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8715–8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, M.; Fortuni, B.; Mulvaney, P.; Hofkens, J.; Uji-i, H.; Rocha, S.; Hutchison, J.A. Nanoparticle-Mediated Thermal Cancer Therapies: Strategies to Improve Clinical Translatability. J. Control. Release 2024, 372, 751–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Tan, W.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Chen, H.; Zou, J.; Ye, Y.; Wang, T.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; et al. Materials Design of Gas-Releasing Nanoplatforms: Strategies for Precision Delivery in Oral Healthcare. Mater. Des. 2025, 258, 114704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, K.; Fang, R.; Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Ma, J.; Wang, H.; Ding, M.; Wang, X.; Song, Y.; et al. Nanotechnological Strategies to Increase the Oxygen Content of the Tumor. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1140362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamkaew, A.; Chen, F.; Zhan, Y.; Majewski, R.L.; Cai, W. Scintillating Nanoparticles as Energy Mediators for Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 3918–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Cao, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Q. Advanced Near-Infrared Light for Monitoring and Modulating the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Cell Functions in Living Systems. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almadani, I.F.; Almadani, M.F.; AlSawaftah, N.; Abuwatfa, W.H.; Husseini, G.A. Nanocarriers Responsive to Light—A Review. Micro 2024, 4, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Peng, S.; Wang, X.; Cai, R. Near-Infrared Photoactivated Nanomedicines for Photothermal Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Nano Today 2021, 37, 101073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algorri, J.F.; Ochoa, M.; Roldán-Varona, P.; Rodríguez-Cobo, L.; López-Higuera, J.M. Light Technology for Efficient and Effective Photodynamic Therapy: A Critical Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Zhou, J.; Samaddar, S.; Song, S.H.; Elzey, B.D.; Thompson, D.H.; Ziaie, B. An Implantable Ultrasonically-Powered Micro-Light-Source (µLight) for Photodynamic Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souris, J.S.; Leoni, L.; Zhang, H.J.; Pan, A.; Tanios, E.; Tsai, H.-M.; Balyasnikova, I.V.; Bissonnette, M.; Chen, C.-T. X-Ray Activated Nanoplatforms for Deep Tissue Photodynamic Therapy. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, A.K.; Zhang, R.; Andreozzi, J.M.; Gladstone, D.J.; Pogue, B.W. Cherenkov Radiation Fluence Estimates in Tissue for Molecular Imaging and Therapy Applications. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 6701–6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Sheng, S.; Lun, M.C.; Tsai, S.-M.; Chin, W.-C.; Hoglund, R.; Li, C. Photodynamic Therapy Excited by Cerenkov Radiation from Cesium-137 Irradiator: In Vitro Studies. Clin. Oncol. Res. 2020, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; Lang, J.; Yang, Y. Cherenkov Luminescence in Tumor Diagnosis and Treatment: A Review. Photonics 2022, 9, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, F.X.C.; Mu, J.; Li, J.; Yao, H.; Chen, K. Role of Tumor Microenvironment in Cancer Progression and Therapeutic Strategy. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 11149–11165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabit, H.; Arneth, B.; Abdel-Ghany, S.; Madyan, E.F.; Ghaleb, A.H.; Selvaraj, P.; Shin, D.M.; Bommireddy, R.; Elhashash, A. Beyond Cancer Cells: How the Tumor Microenvironment Drives Cancer Progression. Cells 2024, 13, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torna, S.; Gkretsi, V.; Stylianou, A. Photodynamic Therapy and Tumor Microenvironment-Targeting Strategies: A Novel Synergy at the Frontier of Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, B. Extracellular Matrix Stiffness: Mechanisms in Tumor Progression and Therapeutic Potential in Cancer. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2025, 14, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worsley, C.M.; Veale, R.B.; Mayne, E.S. The Acidic Tumour Microenvironment: Manipulating the Immune Response to Elicit Escape. Hum. Immunol. 2022, 83, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmudi, H.; Adili-Aghdam, M.A.; Shahpouri, M.; Jaymand, M.; Amoozgar, Z.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R. Tumor Microenvironment Penetrating Chitosan Nanoparticles for Elimination of Cancer Relapse and Minimal Residual Disease. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1054029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Huang, Y.; Chen, D.; Qiu, F.; Ma, C.; Jin, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Z. pH-Responsive Aerobic Nanoparticles for Effective Photodynamic Therapy. Theranostics 2017, 7, 4537–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, R.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Lv, C.; Liu, Y. pH- and Enzyme-Triggered Drug Release as an Important Process in the Design of Anti-Tumor Drug Delivery Systems. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, F.; Chen, W.; Gong, T.; Zhou, Y.; Dai, X.; Leung, W.; Xu, C. Enzyme-Responsive Materials as Carriers for Improving Photodynamic Therapy. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 763057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Xue, M.; Feng, D. Tumor Microenvironment-Responsive Nanoparticles: Promising Cancer PTT Carriers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2025, 20, 7987–8001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroz, P.; Hashmi, J.T.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Lange, N.; Hamblin, M.R. Stimulation of Anti-Tumor Immunity by Photodynamic Therapy. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 7, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nady, D.S.; Hassan, A.; Amin, M.U.; Bakowsky, U.; Fahmy, S.A. Recent Innovations of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Combined with Photodynamic Therapy for Improving Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koohi Moftakhari Esfahani, M.; Alavi, S.E.; Cabot, P.J.; Islam, N.; Izake, E.L. Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy and Delivery of Repurposed Anthelmintics for Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Nam, J.; Hong, H.; Xu, Y.; Moon, J.J. Positron Emission Tomography-Guided Photodynamic Therapy with Biodegradable Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 12148–12161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parveen, S.; Konde, D.V.; Paikray, S.K.; Tripathy, N.S.; Sahoo, L.; Samal, H.B.; Dilnawaz, F. Nanoimmunotherapy: The Smart Trooper for Cancer Therapy. Explor. Target. Antitumor Ther. 2025, 6, 1002308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zou, M.; Xu, Y.; Lin, P.; Lei, C.; Xia, X. Nano Drug Delivery System for Tumor Immunotherapy: Next-Generation Therapeutics. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 864301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Yong, T.; Gan, L.; Yang, X. Boosting Antitumor Efficacy of Nanoparticles by Modulating Tumor Mechanical Microenvironment. eBioMedicine 2024, 105, 105200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhou, P.; Chen, K.; Tang, W.; Xia, Q.; Ma, J. Bronchoscopy-Guided Intervention Therapy with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Support for Advanced Cancer Metastasis to the Central Airway. Medicine 2020, 99, e19488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermes, A.; Heigener, D.F.; Gatzemeier, U.; Schätz, J.; Reck, M. Efficacy and Safety of Bronchoscopic Laser Therapy in Patients with Tracheal and Bronchial Obstruction: A Retrospective Single Institution Report. Clin. Respir. J. 2011, 6, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, G.; Bithigoffer, C.; Righini, C.A.; Arbib, F.; Lantuéjoul, S.; Jankowski, A. Imaging of Tumors of the Trachea and Central Bronchi. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2010, 20, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crous, A.; Abrahamse, H. Photodynamic Therapy of Lung Cancer, Where Are We? Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 932098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Harris, K.; Dhillon, S.S. Role of Bronchoscopy in Management of Central Squamous Cell Lung Carcinoma in Situ. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, C.B.; Friedberg, J.S.; Glatstein, E.; Stevenson, J.P.; Sterman, D.H.; Hahn, S.M.; Cengel, K.A. Photodynamic Therapy for the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2012, 4, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Liao, K.S.; Hsieh, Y.-S. Bronchoscopic Light Delivery Method for Peripheral Lung Cancer Photodynamic Therapy. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 3611–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudzik, T.; Domański, I.; Makuch, S. The Impact of Photodynamic Therapy on Immune System in Cancer—An Update. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1335920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghissi, K.; Dixon, K.; Thorpe, J.A.C.; Stringer, M.; Oxtoby, C. Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) in Early Central Lung Cancer: A Treatment Option for Patients Ineligible for Surgical Resection. Thorax 2007, 62, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Jin, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, G. Clinical Practice of Photodynamic Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Different Scenarios: Who Is the Better Candidate? Respiration 2024, 103, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaydin, G.; Gedik, M.E.; Ayan, S. Photodynamic Therapy for the Treatment and Diagnosis of Cancer—A Review of the Current Clinical Status. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 686303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafirstein, G.; Battoo, A.; Harris, K.; Baumann, H.; Gollnick, S.O.; Lindenmann, J.; Nwogu, C.E. Photodynamic Therapy of Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Narrative Review and Future Directions. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Zhou, H.; Liu, C. Advancements in Nanocarrier Delivery Systems for Photodynamic Therapy in Lung Cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2025, 20, 6853–6874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, E.D.; Faiz, S.A.; Qdaisat, A.; Abdeldaem, K.; Dagher, J.; Chaftari, P.; Yeung, S.-C.J. Hemoptysis in Cancer Patients. Cancers 2023, 15, 4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebisher, D.; Czech, S.; Dynarowicz, K.; Misiołek, M.; Komosińska-Vassev, K.; Kawczyk-Krupka, A.; Bartusik-Aebisher, D. Photodynamic Therapy: Past, Current, and Future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M.; Li, M.; Zhang, M.; Wu, J.-L.; Choi, M.M.; Bian, W. Mesoporous Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Effective for Combined Chemo/Photo Therapy Against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. IJN 2024, 19, 7493–7508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.-E.; Cho, H.-J.; Jheon, S. Anticancer Efficacy of Photodynamic Therapy with Lung Cancer-Targeted Nanoparticles. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 118, 54865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-E.; Cho, H.-J.; Yi, E.; Kim, D.-D.; Jheon, S. Hypocrellin B and Paclitaxel-Encapsulated Hyaluronic Acid-Ceramide Nanoparticles for Targeted Photodynamic Therapy in Lung Cancer. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2016, 158, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, B.; Ni, J.; Xiang, Y.; He, Z. Combined Chemo- and Photothermal Therapies of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Polydopamine/Au Hollow Nanospheres Loaded with Doxorubicin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 9597–9612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.R.; Šácha, P. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy: What Lies beyond Monoclonal Antibodies? Med. Oncol. 2025, 42, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, Y.; Shen, D.; Zhang, W.; He, R.; Jiang, M. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy—How to Overcome Drug Resistance? Cancers 2022, 14, 3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Gao, S.; Dong, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, S. Research Progress and Future Perspectives of Prodrug Strategies for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Immunotherapy. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2025, 214, 104905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Hao, D.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Pei, Q.; Sun, T.; Wang, K.; Xie, Z. Porphyrin Cholesterol Conjugates for Enhanced Photodynamic Immunotherapy toward Lung Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 35927–35938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Sun, T.; Hoang, H.H.; Burchfield, J.S.; Hamilton, G.F.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Ferrari, M. Enhancing Cancer Immunotherapy through Nanotechnology-Mediated Tumor Infiltration and Activation of Immune Cells. Semin. Immunol. 2017, 34, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, D.; Ding, R.; Yang, H.; Jia, Y.; Lei, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Xie, F. Synergistic Strategies in Photodynamic Combination Therapy for Cancer: Mechanisms, Nanotechnology, and Clinical Translation. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1607259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, M.N.; Kumar, P.; Faísca, P.; Ferreira, H.A.; Coelho, J.M.P.; Gaspar, M.M.; Reis, C.P. Gold Nanoparticle-Mediated Photothermal Therapy: Expanding the Frontiers of Cancer Treatment and Theragnostics. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 190, 118399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vines, J.B.; Yoon, J.-H.; Ryu, N.-E.; Lim, D.-J.; Park, H. Gold Nanoparticles for Photothermal Cancer Therapy. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinakaran, D.; Wilson, B.C. The Use of Nanomaterials in Advancing Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) for Deep-Seated Tumors and Synergy with Radiotherapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1250804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Qiu, J.-M.; Han, X.-J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Xie, S.-Y.; Xie, N. The Application of Nanoparticles in Delivering Small RNAs for Cancer Therapy. Discov. Oncol. 2024, 15, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, M.; Chota, A.; Abrahamse, H.; George, B.P. Efficacy of Green Synthesized Nanoparticles in Photodynamic Therapy: A Therapeutic Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Yin, D.; Chen, Y.; Di, Y.; Chen, H.; Ma, Y.; Achilefu, S.; Gu, Y. In Vivo Targeted Deep-Tissue Photodynamic Therapy Based on Near-Infrared Light Triggered Upconversion Nanoconstruct. ACS Nano 2012, 7, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crous, A.; Abrahamse, H. Targeted Photodynamic Therapy for Improved Lung Cancer Treatment; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Dai, J.; Han, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhen, S.; Zhao, Z.; Lou, X.; Xia, F. A High Therapeutic Efficacy of Polymeric Prodrug Nano-Assembly for a Combination of Photodynamic Therapy and Chemotherapy. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, C.; Jaipuria, A.; Gupta, N. Inhalable Formulations to Treat Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): Recent Therapies and Developments. Pharmaceutics 2022, 15, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Lin, X.; Lin, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Y. Cancer Cell-Targeted Photosensitizer and Therapeutic Protein Co-Delivery Nanoplatform Based on a Metal–Organic Framework for Enhanced Synergistic Photodynamic and Protein Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 36906–36916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.K.W.; Liang, W.; Chan, H. Pulmonary Delivery of Therapeutic siRNA. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-C.; Lin, H.; Thomas, J.L.; Yu, J.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chang, Y.; Lee, M.; Wang, T.-L. Embedded Upconversion Nanoparticles in Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Photodynamic Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazi, R.N.A.; Hasani, I.W.; Khafaga, D.S.R.; Kabba, S.; Farhan, M.; Aatif, M.; Muteeb, G.; Fahim, Y.A. Nanomedicine: The Effective Role of Nanomaterials in Healthcare from Diagnosis to Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangla, B.; Kumar, P.; Javed, S.; Pathan, T.; Ahsan, W.; Aggarwal, G. Regulating Nanomedicines: Challenges, Opportunities, and the Path Forward. Nanomedicine 2025, 20, 1911–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.; de Matos, M.B.C.; Metselaar, J.M.; Storm, G. Current Trends and Challenges in the Clinical Translation of Nanoparticulate Nanomedicines: Pathways for Translational Development and Commercialization. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, S.; Pizzuti, V.; Paris, F.; Alviano, F.; Bonsi, L.; Zattoni, A.; Reschiglian, P.; Roda, B.; Marassi, V. Emerging Technologies for Quality Control of Cell-Based, Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2024, 246, 116182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Padrela, L. Progress on Drug Nanoparticle Manufacturing: Exploring the Adaptability of Batch Bottom-up Approaches to Continuous Manufacturing. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 111, 107120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukheja, Y.; Pal, K.; Ahuja, A.; Sarkar, A.; Kumar, B.; Kuhad, A.; Chopra, K.; Jain, M. Nanotechnology and Artificial Intelligence in Cancer Treatment. Next Res. 2025, 2, 100179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Dhiman, V.K.; Pandey, M.; Dhiman, V.K.; Sharma, A.; Pandey, H.; Verma, S.K.; Pandey, R. Personalized Medicine: An Alternative for Cancer Treatment. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2024, 42, 100860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayi, S.; Niakan Kalhori, S.R.; Saeedi, S. Effectiveness of Artificial Intelligence for Personalized Medicine in Neoplasms: A Systematic Review. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 7842566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najahi-Missaoui, W.; Arnold, R.D.; Cummings, B.S. Safe Nanoparticles: Are We There Yet? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pondman, K.; Le Gac, S.; Kishore, U. Nanoparticle-Induced Immune Response: Health Risk versus Treatment Opportunity? Immunobiology 2023, 228, 152317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljabali, A.A.; Obeid, M.A.; Bashatwah, R.M.; Serrano-Aroca, Á.; Mishra, V.; Mishra, Y.; El-Tanani, M.; Hromić-Jahjefendić, A.; Kapoor, D.N.; Goyal, R.; et al. Nanomaterials and Their Impact on the Immune System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbesen, M.; Jensen, T.G. Nanomedicine: Techniques, Potentials, and Ethical Implications. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2006, 2006, 51516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.H.; Wong, H.Y.T.; Tsang, P.S.W.; Yau, M.; Tam, S.Y.; Law, L.; Yau, K.; Wong, J.; Farah, F.H.M.; Wong, J. Recent Advancements in Lung Cancer Research: A Narrative Review. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2025, 14, 975–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Han, T.; Xia, H.; Dong, L.; Chen, L.; Lei, L. Advances in Photodynamic Therapy Based on Nanotechnology and Its Application in Skin Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 836397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chai, T.; Nguyen, W.; Liu, J.; Xiao, E.; Ran, X.; Ran, Y.; Du, D.; Chen, W.; Chen, X. Phototherapy in Cancer Treatment: Strategies and Challenges. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.; Malhotra, J.; Kulkarni, P.; Horne, D.; Salgia, R.; Singhal, S.S. Emerging Therapeutic Strategies to Overcome Drug Resistance in Cancer Cells. Cancers 2024, 16, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, Y.; Hossen, M.N.; Wilhelm, S.; Bhattacharya, R.; Mukherjee, P. Nanoparticle Interactions with the Tumor Microenvironment. Bioconjug. Chem. 2019, 30, 2247–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obalola, A.A.; Abrahamse, H.; Dhilip Kumar, S.S. Enhanced Therapeutic Precision Using Dual Drug-Loaded Nanomaterials for Targeted Cancer Photodynamic Therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 184, 117909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Wu, X.; Long, G.; Yu, J.; He, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Ye, Z.; Tian, J. Revolutionizing Cancer Treatment: Nanotechnology-Enabled Photodynamic Therapy and Immunotherapy with Advanced Photosensitizers. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1219785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkune, N.W.; Abrahamse, H. Possible Integration of Artificial Intelligence with Photodynamic Therapy and Diagnosis: A Review. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 101, 106210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Photosensitizer Name | Generation | Wavelength (nm) | Singlet Oxygen Yield | Key Properties | Clinical Use/ Approval | Major Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photofrin II (Porfimer sodium) [46] | 1st | ~630 | Type II | Clinically established; deep but limited penetration; heterogeneous mixture | Lung, esophageal, bladder cancer | Prolonged photosensitivity, non-specific accumulation |
| Verteporfin (Visudyne) [47] | 2nd | ~690 (implied) | Type II | Liposomal formulation, rapid clearance | Age-related macular degeneration; under investigation for cholangiocarcinoma, ovarian cancer | Less photostable, susceptible to self-polymerization/photobleaching |
| 5-aminolevulinic acid [48] | 2nd | ~635 (PpIX) | Type II | Endogenous conversion to PpIX; preferential accumulation in dysplastic tissue | Early-stage skin cancers, actinic keratosis; under investigation for bladder, head and neck cancers | Uneven distribution, limited laser penetration depth |
| Temoporfin (mTHPC, Foscan) [49] | 2nd | ~652 | Type II | Strong absorption; high phototoxicity; long tissue retention | Head and neck, esophageal, gastric, gastrointestinal cancers | Marked photosensitivity; high lipophilicity; risk of off-target phototoxicity |
| Photocyanine [50] | 2nd | ~670 | High | High quantum yield, low dark toxicity, minimal skin phototoxicity | Phase II clinical trials for various cancers including bronchial | Relatively shallow tissue penetration limits effectiveness |
| Category | Practical Points from Current Clinical Practice |
|---|---|
| Best-suited tumor stages | CIS and small T1 lesions; select superficial T2 lesions with limited mucosal involvement |
| Tumor location | Most reliable results in central airways (trachea, main bronchi, lobar bronchi); select peripheral lesions treated with CT-guided or navigational techniques |
| Histology | Strongest evidence for squamous cell carcinoma; certain superficially spreading adenocarcinomas may also be eligible |
| Ideal patient profile | Poor surgical candidates; patients with airway obstruction; those needing airway-preserving treatment rather than resection |
| Photosensitizer protocol | Porfimer sodium 2.0 mg/kg IV; ~48 h interval before illumination to improve tumor uptake and reduce background fluorescence |
| Light delivery | 630 nm wavelength (Photofrin); optical fiber or diffuser tip depending on lesion shape; typical fluence ~200 J/cm2 (diffuser) or ~400 J/cm2 (contact) |
| Illumination timing | Usually 300–500 s per site, adjusted according to tumor size and depth |
| Post-procedure care | Bronchoscopy at 2–3 days for debridement and reassessment; repeat PDT if residual disease is present |
| Follow-up | Surveillance bronchoscopy at 4–6 weeks; imaging for deeper or peripheral lesions |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moise-Crintea, A.; Constantin, A.-M.; Jianu, E.M.; Orlea, I.M.; Manea, M.; Cojocariu, R.O.; Carpa, R.; Borlea, B.-A.; Boznea, C.-M.; Coseriu, R.L.; et al. Advancing Lung Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Review of Photodynamic Therapy and Nanoparticle Applications. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121579
Moise-Crintea A, Constantin A-M, Jianu EM, Orlea IM, Manea M, Cojocariu RO, Carpa R, Borlea B-A, Boznea C-M, Coseriu RL, et al. Advancing Lung Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Review of Photodynamic Therapy and Nanoparticle Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(12):1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121579
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoise-Crintea, Andreea, Anne-Marie Constantin, Elena Mihaela Jianu, Ioana Maria Orlea, Minodora Manea, Roxana Oana Cojocariu, Rahela Carpa, Bogdan-Andrei Borlea, Cristina-Maria Boznea, Razvan Lucian Coseriu, and et al. 2025. "Advancing Lung Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Review of Photodynamic Therapy and Nanoparticle Applications" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 12: 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121579
APA StyleMoise-Crintea, A., Constantin, A.-M., Jianu, E. M., Orlea, I. M., Manea, M., Cojocariu, R. O., Carpa, R., Borlea, B.-A., Boznea, C.-M., Coseriu, R. L., & Sovrea, A. (2025). Advancing Lung Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Review of Photodynamic Therapy and Nanoparticle Applications. Pharmaceutics, 17(12), 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121579







