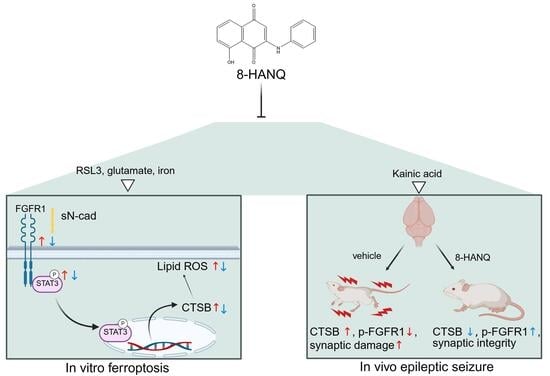
8-Hydroxy-2-Anilino-1,4-Naphthoquinone Prevents Against Ferroptotic Neuronal Death and Kainate-Induced Epileptic Seizures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. NQ-Derived Compounds
2.2.1. 8-HANQ and 5-HANQ
General Chemistry
Synthesis
2.2.2. Other NQ-Derived Compounds
2.3. HT22 Mouse Hippocampal Cell Culture
2.4. Cell Viability Assay
2.5. Lipid ROS Detection with C11-BODIPY581/591
2.6. Ferrous Iron Chelation Assay
2.7. Measurement of Soluble N-Cadherin Release
2.8. Animal Experiments
2.8.1. Animals
2.8.2. Stereotaxic Drug Administration and KA-Induced Seizure Induction
2.8.3. Behavioral Seizure Assessment
2.9. Sample Preparation and Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
2.11. Generative AI Assistance in Manuscript Preparation
3. Results
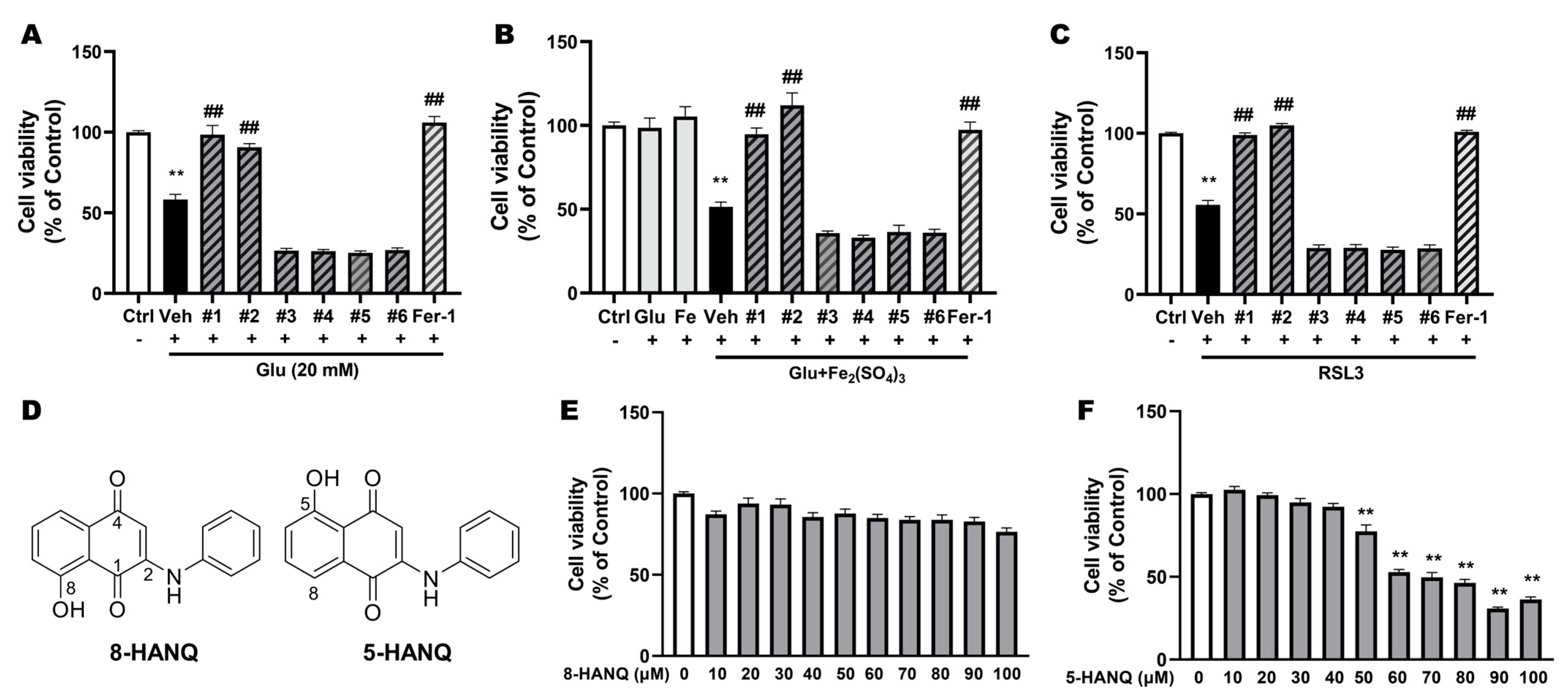
3.1. Selection of Novel NQ Derivatives Preventing Ferroptotic Neuronal Death
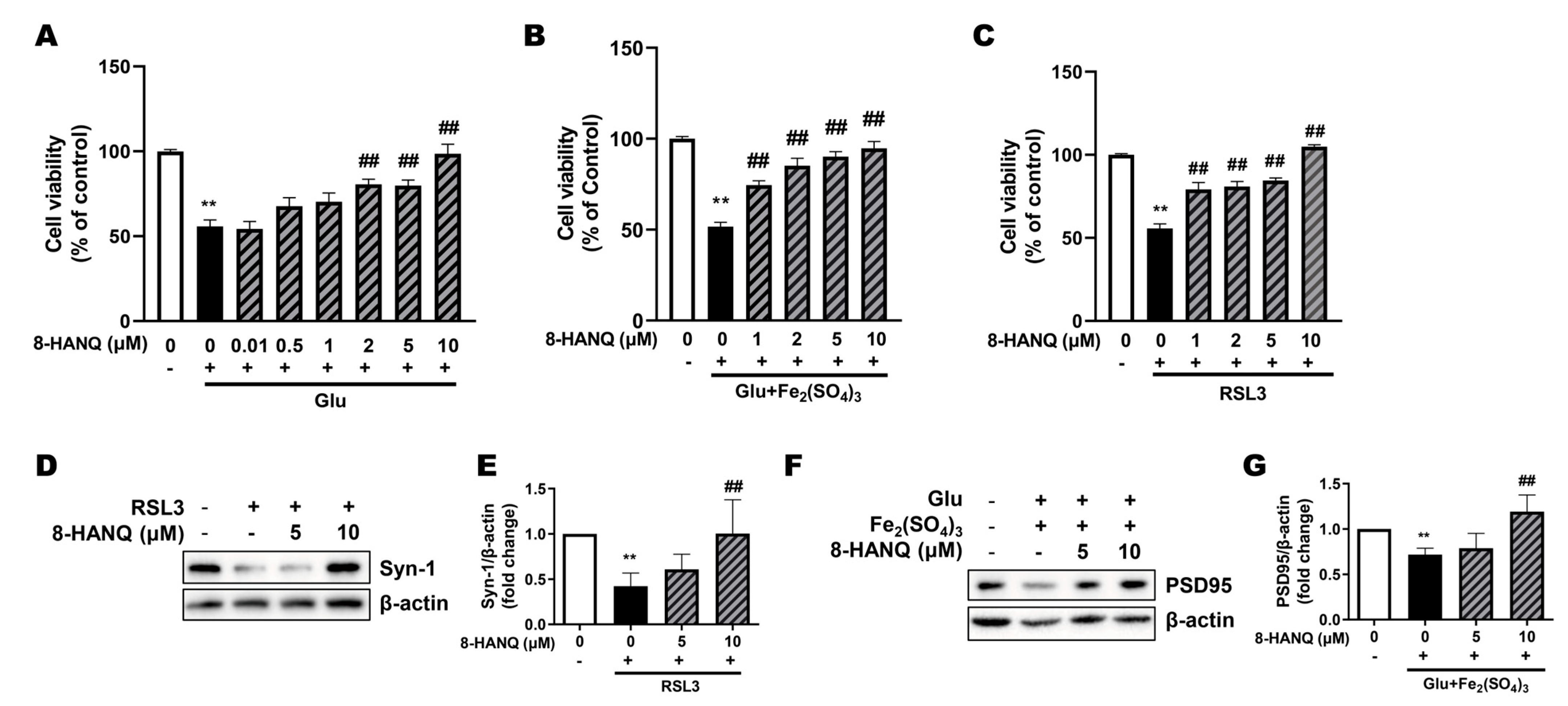
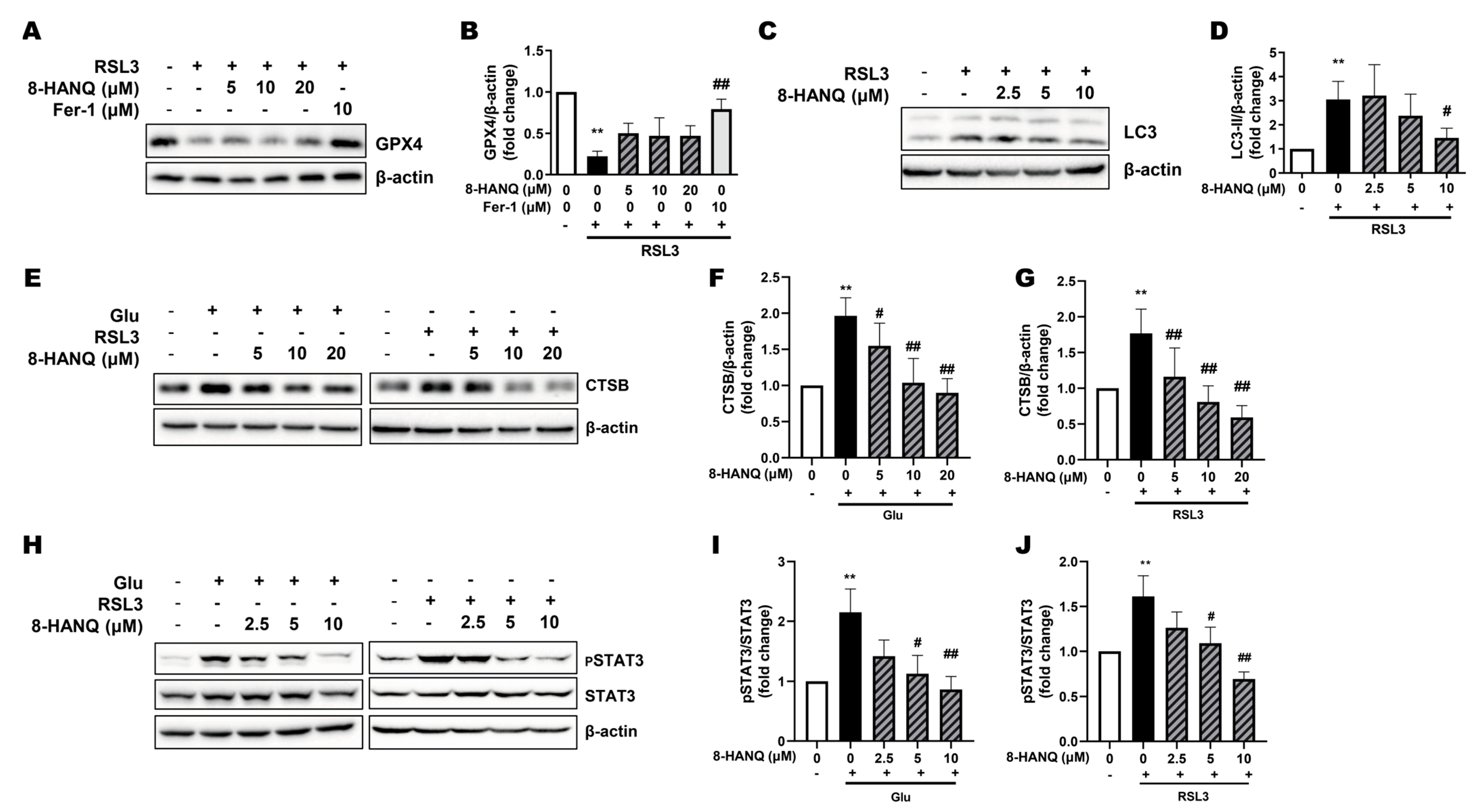
3.2. 8-HANQ Exhibits Dose-Dependent Neuroprotection Against Ferroptotic Neuronal Death and Synaptic Dysregulation in HT22 Cells
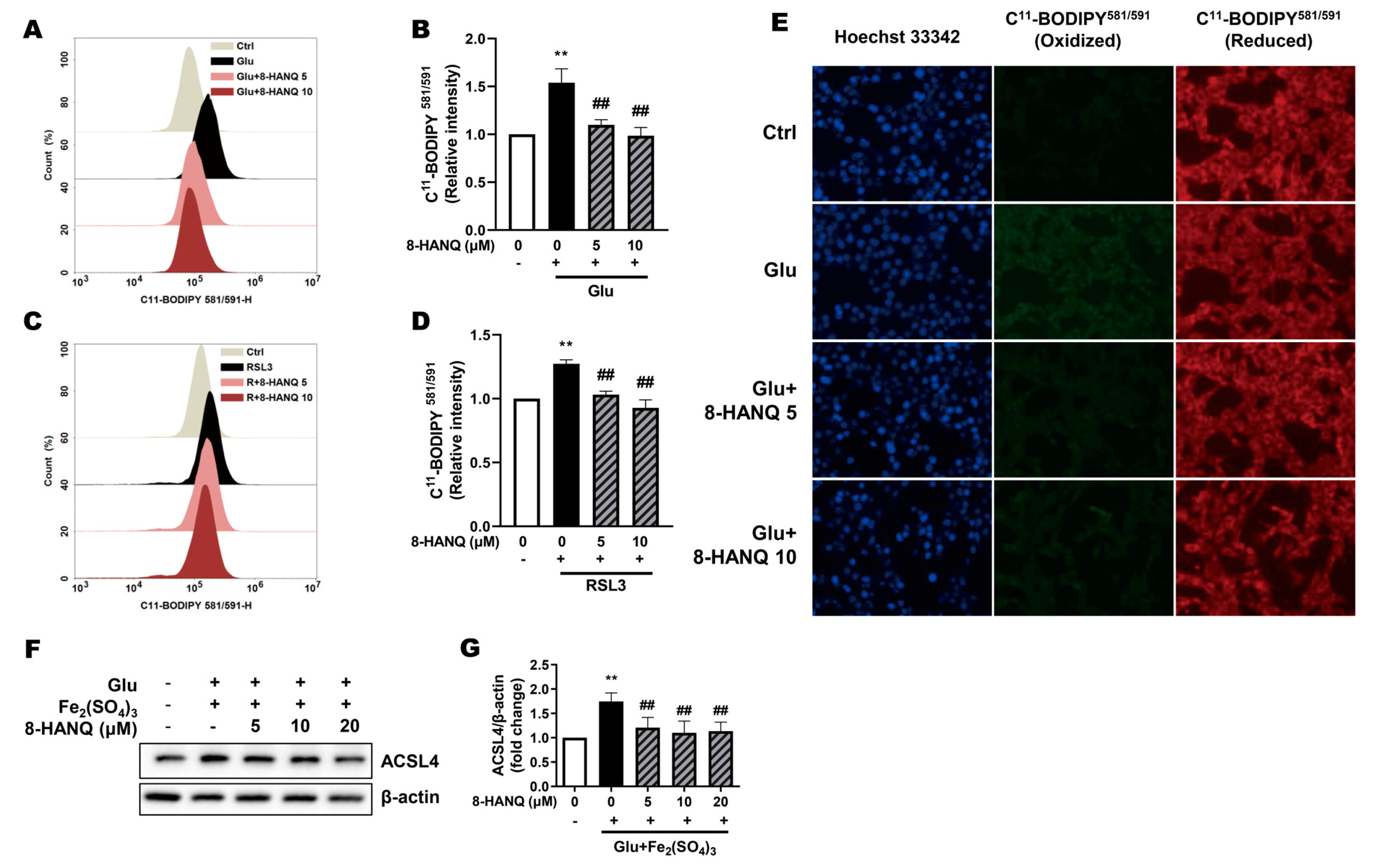
3.3. 8-HANQ Suppresses Lipid ROS Accumulation to Inhibit Ferroptosis
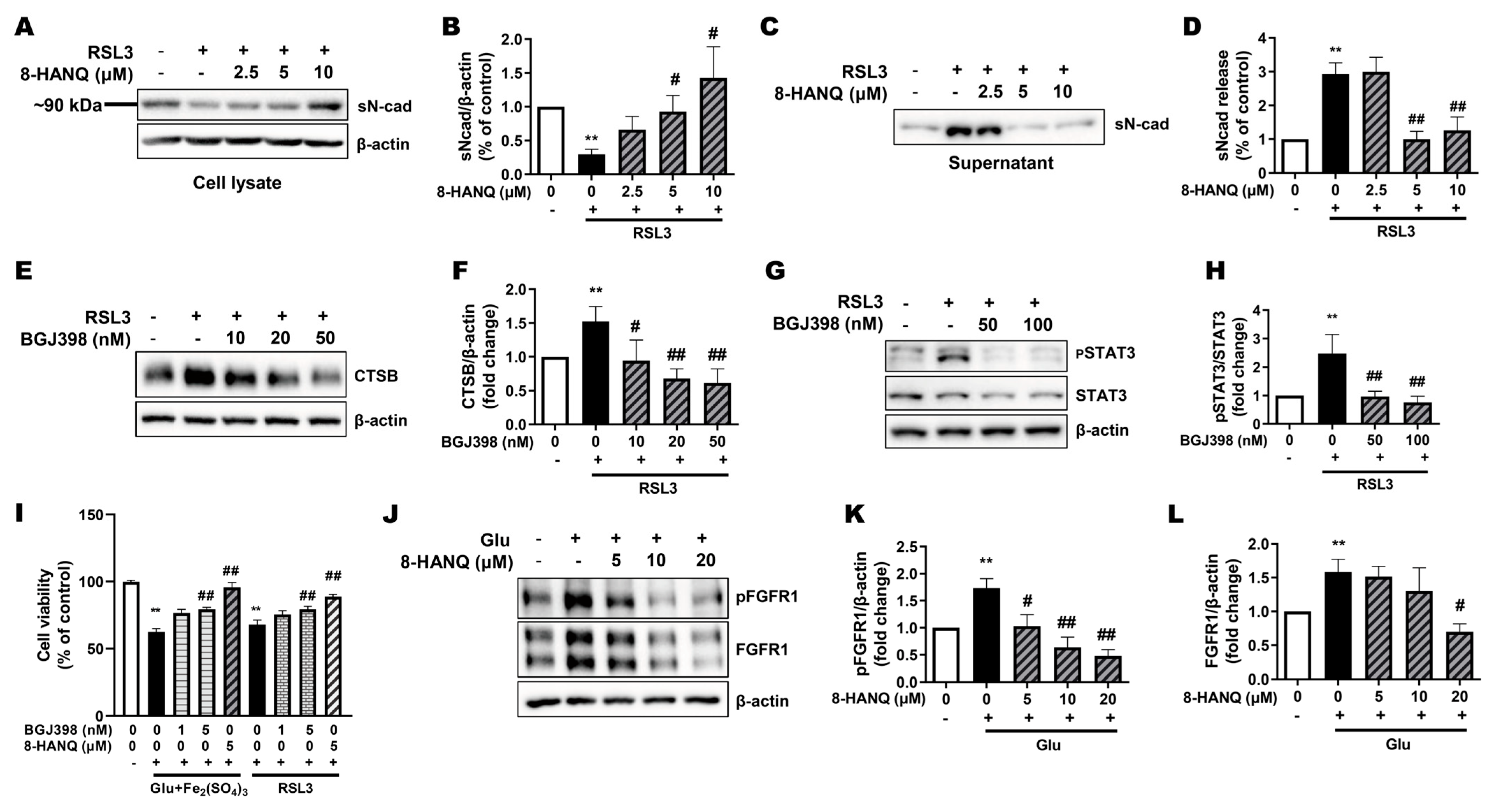
3.4. 8-HANQ Inhibits the STAT3/Cathepsin-B Axis Mediated by Soluble N-Cadherin/FGFR1 Signaling to Attenuate Ferroptosis
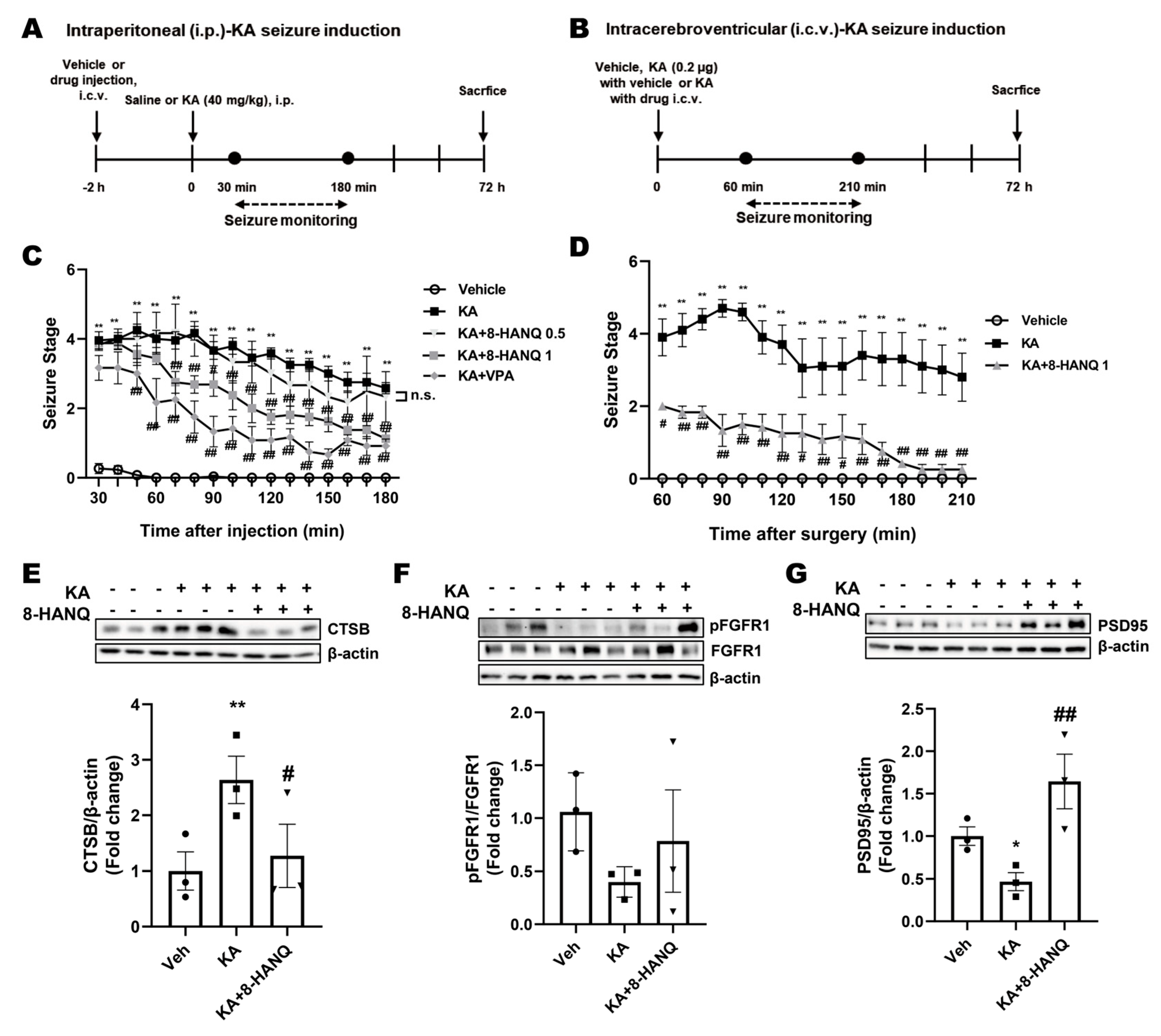
3.5. 8-HANQ Mitigates Seizure Severity and Restores Hippocampal Cathepsin-B, FGFR1, and PSD95 Dysregulation in KA-Induced Epileptic Mice
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5-HANQ | 5-Hydroxy-2-anilino-1,4-naphthoquinone |
| 8-HANQ | 8-Hydroxy-2-anilino-1,4-naphthoquinone |
| ACSL4 | Acyl-CoA Synthetase Long-chain Family Member 4 |
| Aβ | Amyloid β |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| DFO | Deferoxamine |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid |
| FGFR1 | Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 |
| FSP1 | Ferroptosis Suppressor Protein 1 |
| FTH1 | Ferritin Heavy Chain 1 |
| GPX4 | Glutathione Peroxidase 4 |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| HO-1 | Heme Oxygenase-1 |
| HPCAL1 | Hippocalcin-like 1 |
| iron (III) | Iron(III) Sulfate |
| KA | Kainic Acid |
| LC3 | Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 |
| NQ | Naphthoquinone |
| PSD95 | Postsynaptic Density Protein 95 |
| PUFA | Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| RSL3 | RAS-selective lethal 3 |
| STAT3 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 |
References
- Bermejo-Bescos, P.; Martin-Aragon, S.; Jimenez-Aliaga, K.L.; Ortega, A.; Molina, M.T.; Buxaderas, E.; Orellana, G.; Csaky, A.G. In vitro antiamyloidogenic properties of 1,4-naphthoquinones. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 400, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agafonova, I.; Chingizova, E.; Chaikina, E.; Menchinskaya, E.; Kozlovskiy, S.; Likhatskaya, G.; Sabutski, Y.; Polonik, S.; Aminin, D.; Pislyagin, E. Protection Activity of 1,4-Naphthoquinones in Rotenone-Induced Models of Neurotoxicity. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Himes, R.A.; Prosser, L.C.; Christie, C.F.; Watt, E.; Edwards, S.F.; Metcalf, C.S.; West, P.J.; Wilcox, K.S.; Chan, S.S.L.; et al. Discovery of the First Vitamin K Analogue as a Potential Treatment of Pharmacoresistant Seizures. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 5865–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishima, E.; Ito, J.; Wu, Z.; Nakamura, T.; Wahida, A.; Doll, S.; Tonnus, W.; Nepachalovich, P.; Eggenhofer, E.; Aldrovandi, M.; et al. A non-canonical vitamin K cycle is a potent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature 2022, 608, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, M.; Jiang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Du, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Z. Role and mechanism of ferroptosis in neurological diseases. Mol. Metab. 2022, 61, 101502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; Kim, K.J.; Gaschler, M.M.; Patel, M.; Shchepinov, M.S.; Stockwell, B.R. Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E4966–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; SriRamaratnam, R.; Welsch, M.E.; Shimada, K.; Skouta, R.; Viswanathan, V.S.; Cheah, J.H.; Clemons, P.A.; Shamji, A.F.; Clish, C.B.; et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 2014, 156, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, S.; Proneth, B.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Panzilius, E.; Kobayashi, S.; Ingold, I.; Irmler, M.; Beckers, J.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersuker, K.; Hendricks, J.M.; Li, Z.; Magtanong, L.; Ford, B.; Tang, P.H.; Roberts, M.A.; Tong, B.; Maimone, T.J.; Zoncu, R.; et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature 2019, 575, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, S.; Freitas, F.P.; Shah, R.; Aldrovandi, M.; da Silva, M.C.; Ingold, I.; Goya Grocin, A.; Xavier da Silva, T.N.; Panzilius, E.; Scheel, C.H.; et al. FSP1 is a glutathione-independent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature 2019, 575, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Li, H.; Yu, Z.; Cao, C.; Xu, Z.; Peng, L.; Zhang, J.H.; Chen, G. Cathepsin B as a key regulator of ferroptosis in microglia following intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurobiol. Dis. 2024, 194, 106468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagakannan, P.; Islam, M.I.; Conrad, M.; Eftekharpour, E. Cathepsin B is an executioner of ferroptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2021, 1868, 118928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Bai, Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Kang, R.; Tang, D.; Dai, E. Ferroptosis is a lysosomal cell death process. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 1550–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Song, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Yu, C.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, J.; Liao, S.; Klionsky, D.J.; Kroemer, G.; et al. Identification of HPCAL1 as a specific autophagy receptor involved in ferroptosis. Autophagy 2023, 19, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Liao, Z.; Liang, H.; Tong, B.; Song, Y.; Li, G.; Ma, L.; Wang, K.; Feng, X.; Li, S.; et al. Stiff Substrate Induces Nucleus Pulposus Cell Ferroptosis via YAP and N-Cadherin Mediated Mechanotransduction. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, e2300458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neo Shin, N.; Jeon, H.; Jung, Y.; Baek, S.; Lee, S.; Yoo, H.C.; Bae, G.H.; Park, K.; Yang, S.H.; Han, J.M.; et al. Fluorescent 1,4-Naphthoquinones To Visualize Diffuse and Dense-Core Amyloid Plaques in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mouse Brains. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 3031–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, C.-K.; Chae, M.J. Synthesis and antifungal activity of naphthalene-1, 4-diones modified at positions 2, 3, and 5. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2005, 28, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-A.; Jung, S.-H.; Bae, M.K.; Ryu, C.-K.; Lee, J.-Y.; Chung, J.-H.; Kim, H.-J. Pharmacological effects of novel quinone compounds, 6-(fluorinated-phenyl) amino-5, 8-quinolinediones, on inhibition of drug-induced relaxation of rat aorta and their putative action mechanism. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 2000, 34, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, C.K.; Lee, Y.; Park, S.G.; You, H.J.; Lee, R.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, S. 3D-QSAR studies of heterocyclic quinones with inhibitory activity on vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation using pharmacophore-based alignment. Bioorg Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 9772–9779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano-Castell, D.; Currais, A.; Maher, P. Defining a pharmacological inhibitor fingerprint for oxytosis/ferroptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 171, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsch, R.M.; Wurtman, R.J.; Growdon, J.H. Regulation of APP processing. Potential for the therapeutical reduction of brain amyloid burden. Ann. N. Y Acad. Sci. 1996, 777, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusina, E.; Bernard, C.; Williamson, A. The Kainic Acid Models of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. eNeuro 2021, 8, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racine, R.J. Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation: II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1972, 32, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Nelson, C.D.; Li, X.; Winters, C.A.; Azzam, R.; Sousa, A.A.; Leapman, R.D.; Gainer, H.; Sheng, M.; Reese, T.S. PSD-95 is required to sustain the molecular organization of the postsynaptic density. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 6329–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derycke, L.; De Wever, O.; Stove, V.; Vanhoecke, B.; Delanghe, J.; Depypere, H.; Bracke, M. Soluble N-cadherin in human biological fluids. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 2895–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utton, M.A.; Eickholt, B.; Howell, F.V.; Wallis, J.; Doherty, P. Soluble N-cadherin stimulates fibroblast growth factor receptor dependent neurite outgrowth and N-cadherin and the fibroblast growth factor receptor co-cluster in cells. J. Neurochem. 2001, 76, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, H.J.; Choi, J.H.; Park, I.C.; Kim, C.H.; An, S.K.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, J.H. Selective FGFR inhibitor BGJ398 inhibits phosphorylation of AKT and STAT3 and induces cytotoxicity in sphere-cultured ovarian cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudka, A.A.; Sweet, S.M.; Heath, J.K. Signal transducers and activators of transcription-3 binding to the fibroblast growth factor receptor is activated by receptor amplification. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3391–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Ren, L.; Jing, X.; Wang, H. Targeting ferroptosis as novel therapeutic approaches for epilepsy. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1185071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Zhao, W.; Lowe, S.; Bentley, R.; Hu, G.; Mei, H.; Jiang, X.; Sun, C.; Wu, Y.; Yueying, L. Quercetin alleviates kainic acid-induced seizure by inhibiting the Nrf2-mediated ferroptosis pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 191, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhang, K.; Guan, Q.W.; Wang, Z.J.; Chen, K.N.; Mao, X.Y. D-Penicillamine Reveals the Amelioration of Seizure-Induced Neuronal Injury via Inhibiting Aqp11-Dependent Ferroptosis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Zeng, C.; Dong, L.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wu, Y. Inhibition of ferroptosis processes ameliorates cognitive impairment in kainic acid-induced temporal lobe epilepsy in rats. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 875. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, M.; Sasse, V.A.; Wang, Y.; Maulik, M.; Kar, S. Increased levels and activity of cathepsins B and D in kainate-induced toxicity. Neuroscience 2015, 284, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, S.; Lu, L.; Pan, S.S.; Wei, X.Q.; Miao, R.R.; Liu, X.H.; Xue, M.; Lin, X.K.; Xu, H.L. Targeting NQO1/GPX4-mediated ferroptosis by plumbagin suppresses in vitro and in vivo glioma growth. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 127, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Ling, G.; Qiu, J.; Li, J.; Gan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Tang, J.; Mo, L.; Piao, H. Juglone induces ferroptosis in glioblastoma cells by inhibiting the Nrf2-GPX4 axis through the phosphorylation of p38MAPK. Chin. Med. 2024, 19, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, T.G.; Camandola, S.; Arumugam, T.V.; Cutler, R.G.; Telljohann, R.S.; Mughal, M.R.; Moore, T.A.; Luo, W.; Yu, Q.S.; Johnson, D.A.; et al. Plumbagin, a novel Nrf2/ARE activator, protects against cerebral ischemia. J. Neurochem. 2010, 112, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Shi, L.; Li, N.; Feng, S. Juglone promotes spinal cord injury recovery by suppressing pyroptosis and necroptosis through FOS/USP53/ubiquitination. Phytomedicine 2025, 148, 157341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, F.; Lane, D.; Nguyen, T.P.M.; Bush, A.I.; Ayton, S. In defence of ferroptosis. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchaoui, H.; Mahoney-Sanchez, L.; Garcon, G.; Berdeaux, O.; Alleman, L.Y.; Devos, D.; Duce, J.A.; Devedjian, J.C. ACSL4 and the lipoxygenases 15/15B are pivotal for ferroptosis induced by iron and PUFA dyshomeostasis in dopaminergic neurons. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 195, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, F.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Cathepsin B is a mediator of organelle-specific initiation of ferroptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 533, 1464–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Luo, D.; Xing, P.; Ding, W. The Dual Roles of STAT3 in Ferroptosis: Mechanism, Regulation and Therapeutic Potential. J. Inflamm. Res. 2025, 18, 4251–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Jing, X.; Huang, K.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Q.; Tao, E.; Lin, D. Involvement of the STAT3/HIF-1alpha signaling pathway in alpha-synuclein-induced ferroptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2025, 752, 151419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Shi, G.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, C.; Gheyret, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; et al. IL-23 promotes neuronal ferroptosis via IL-23R/STAT3 signaling after traumatic brain injury. Cell Commun. Signal 2025, 23, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, F.; Griffiths, J.I.; Nath, A.; Bild, A.H. Paradoxical cancer cell proliferation after FGFR inhibition through decreased p21 signaling in FGFR1-amplified breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2024, 26, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polish, N.V.; Nesterkina, M.V.; Protunkevych, M.S.; Karkhut, A.I.; Marintsova, N.G.; Polovkovych, S.V.; Ikravchenko, I.A.; Voskoboinik, O.Y.; Kovalenko, S.I.; Karpenko, O.V. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of novel naphthoquinone derivatives containing 1,2,4-triazine and 1,2,4-triazole moieties of methylene blue on the surface of a “core–shell” type catalyst for the Fenton system. Vopr. Khimii I Khimicheskoi Tekhnologii 2021, 138, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosratiyan, N.; Ghasemi-Kasman, M.; Pourghasem, M.; Feizi, F.; Sadeghi, F. Plumbagin Improves Cognitive Function via Attenuating Hippocampal Inflammation in Valproic Acid-Induced Autism Model. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putra, M.; Rao, N.S.; Gardner, C.; Liu, G.; Trommater, J.; Bunney, M.; Gage, M.; Bassuk, A.G.; Hefti, M.; Lee, G.; et al. Enhanced Fyn-tau and NR2B-PSD95 interactions in epileptic foci in experimental models and human epilepsy. Brain Commun. 2024, 6, fcae327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avdic, U.; Ahl, M.; Chugh, D.; Ali, I.; Chary, K.; Sierra, A.; Ekdahl, C.T. Nonconvulsive status epilepticus in rats leads to brain pathology. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Zeng, C.; Luo, C.; Wu, Y. Ferrostatin-1 mitigates cognitive impairment of epileptic rats by inhibiting P38 MAPK activation. Epilepsy Behav. 2020, 103, 106670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lyu, D.; Wang, F.; Shi, S.; Wang, M.; Yang, W.; Huang, H.; Wei, Z.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; et al. Ketamine May Exert Rapid Antidepressant Effects Through Modulation of Neuroplasticity, Autophagy, and Ferroptosis in the Habenular Nucleus. Neuroscience 2022, 506, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.F.; Chiu, W.C.; Chen, J.C.; Chuang, W.C.; Wang, S.J. NRICM101 prevents kainic acid-induced seizures in rats by modulating neuroinflammation and the glutamatergic system. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 140, 112842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradiso, B.; Zucchini, S.; Simonato, M. Implication of fibroblast growth factors in epileptogenesis-associated circuit rearrangements. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2013, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugra, K.; Pollard, H.; Charton, G.; Moreau, J.; Ben-Ari, Y.; Khrestchatisky, M. aFGF, bFGF and flg mRNAs show distinct patterns of induction in the hippocampus following kainate-induced seizures. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1994, 6, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.; Na, E.J.; Heo, Y.; Yu, J.; Kim, H.-J. 8-Hydroxy-2-Anilino-1,4-Naphthoquinone Prevents Against Ferroptotic Neuronal Death and Kainate-Induced Epileptic Seizures. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111415
Lee D, Na EJ, Heo Y, Yu J, Kim H-J. 8-Hydroxy-2-Anilino-1,4-Naphthoquinone Prevents Against Ferroptotic Neuronal Death and Kainate-Induced Epileptic Seizures. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(11):1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111415
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Daseul, Eun Jung Na, Yumi Heo, Jinha Yu, and Hwa-Jung Kim. 2025. "8-Hydroxy-2-Anilino-1,4-Naphthoquinone Prevents Against Ferroptotic Neuronal Death and Kainate-Induced Epileptic Seizures" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 11: 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111415
APA StyleLee, D., Na, E. J., Heo, Y., Yu, J., & Kim, H.-J. (2025). 8-Hydroxy-2-Anilino-1,4-Naphthoquinone Prevents Against Ferroptotic Neuronal Death and Kainate-Induced Epileptic Seizures. Pharmaceutics, 17(11), 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111415