Vitamin D Nanoliposomes to Improve Solubility, Stability, and Uptake Across Intestinal Barrier
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Analytical Method
2.3. Preparation of Liposomes (LP), TPGS-Coated Liposomes (LPT), VD-Loaded Liposomes (LP-VD) and VD-Loaded TPGS-Coated Liposomes (LPT-VD)
2.4. Preparation of 6C-Loaded Liposomes (LP-6C) and 6C-Loaded TPGS-Coated Liposomes (LPT-6C)
2.5. Lyophilization Method
2.6. Physical Characterization
2.7. Encapsulation Efficiency (EE%) and Recovery% (R%)
2.8. Stability Studies
2.8.1. Storage Stability Studies
2.8.2. Gastrointestinal Stability
2.9. Dissolution Test
2.10. In Vitro Cellular Study
2.10.1. Cell Culture Conditions
2.10.2. Uptake Study
2.10.3. Cytotoxicity
2.11. LDH Assay
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of Liposomes
3.2. Encapsulation Efficiency (EE%)
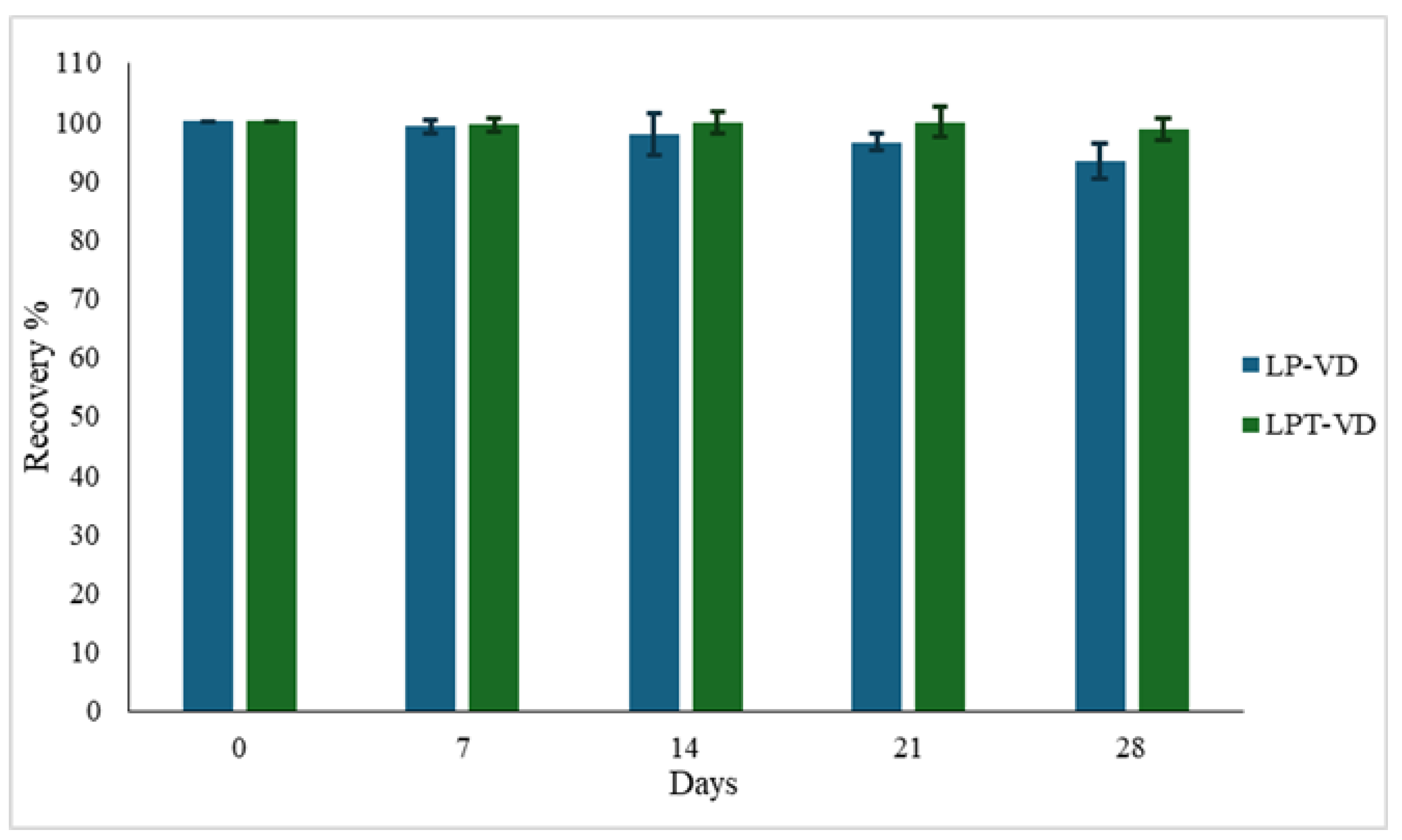
3.3. Storage Stability Studies
3.3.1. Chemical Stability
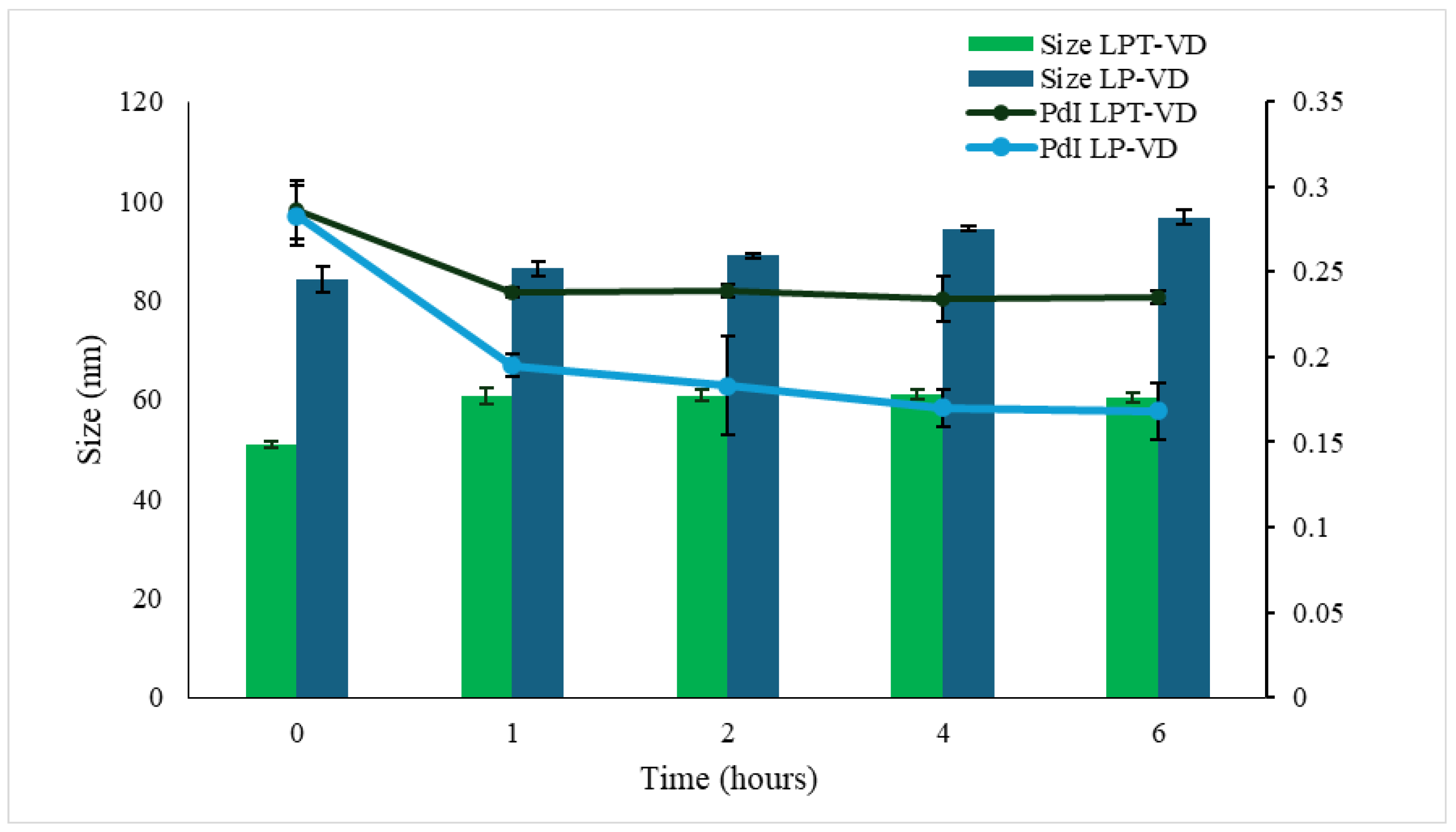
3.3.2. Physical Stability
3.3.3. Gastrointestinal Stability
3.4. Dissolution Test
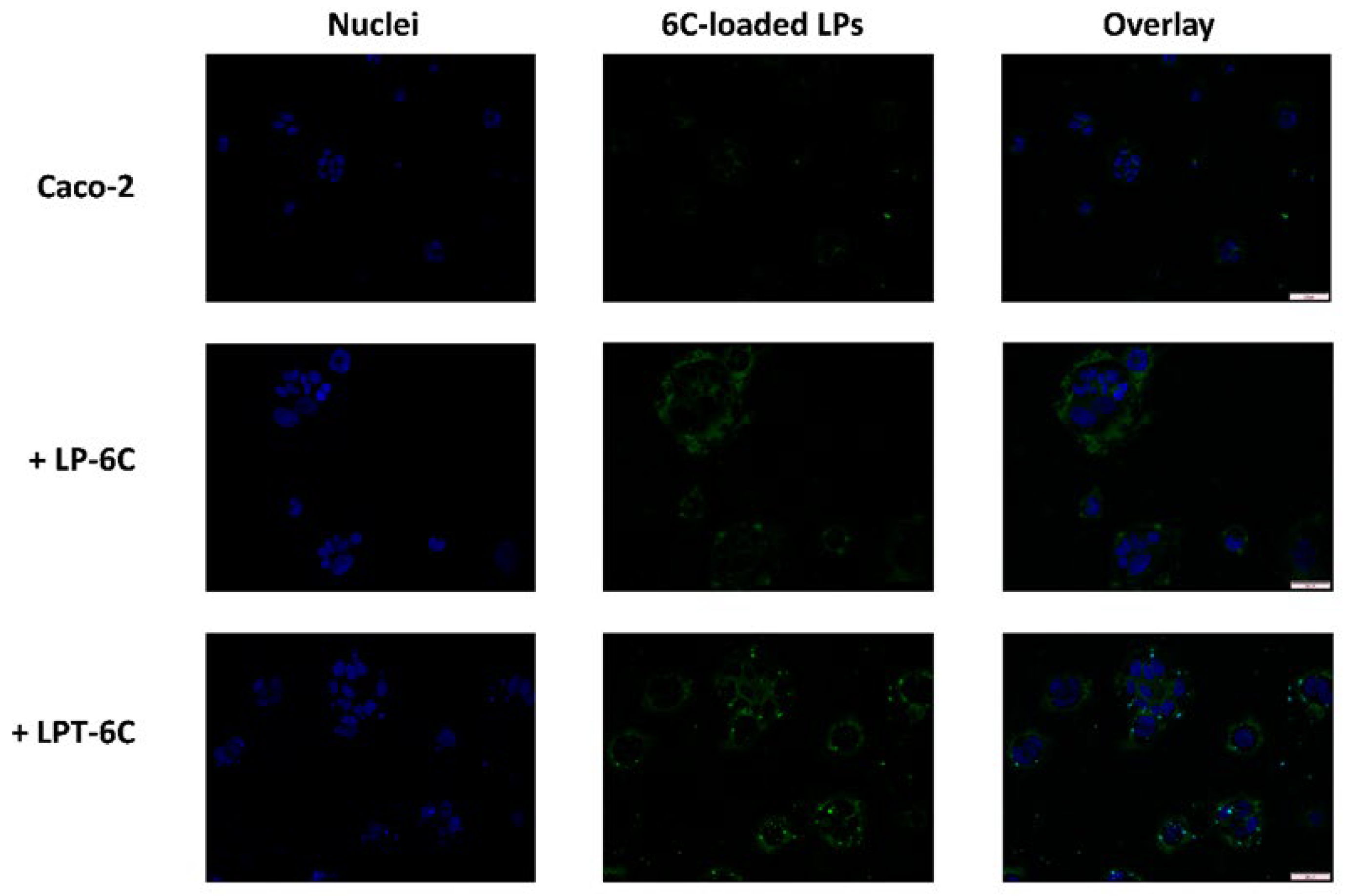
3.5. Cellular Uptake Studies
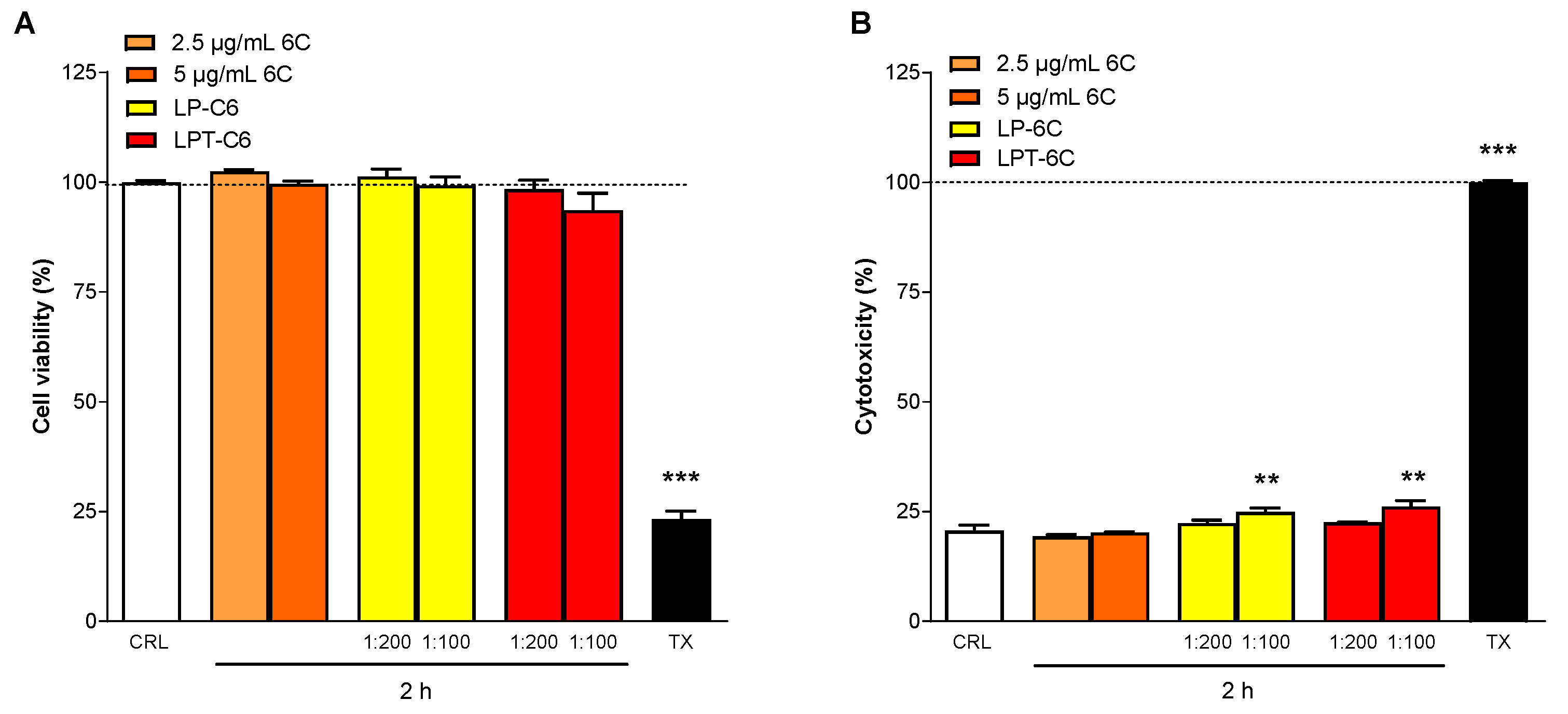
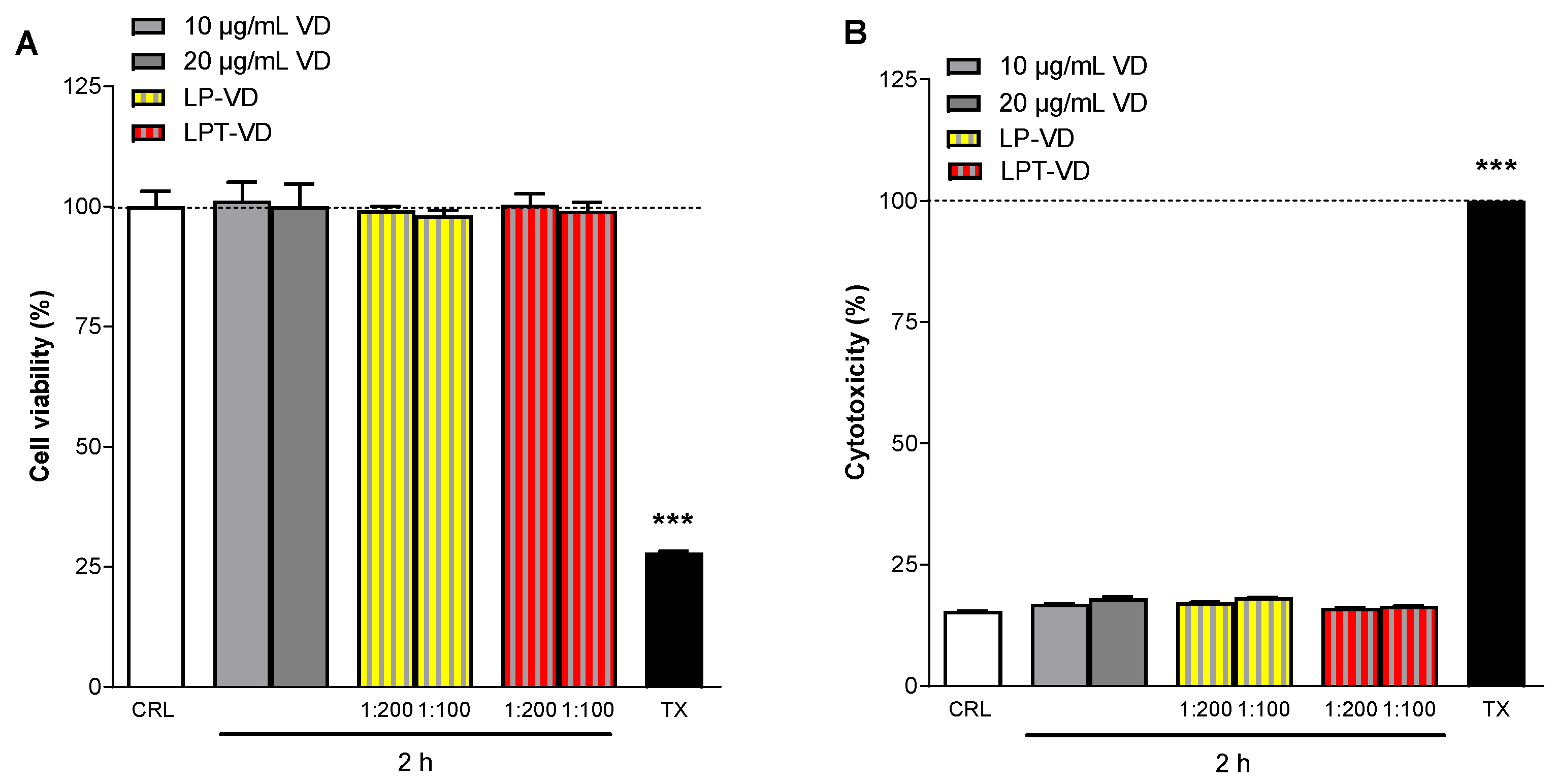
3.6. MTT and LDH Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rebelos, E.; Tentolouris, N.; Jude, E. The Role of Vitamin D in Health and Disease: A Narrative Review on the Mechanisms Linking Vitamin D with Disease and the Effects of Supplementation. Drugs 2023, 83, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee to Review Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin D and Calcium. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D; Ross, A.C., Taylor, C.L., Yaktine, A.L., del Valle, H.B., Eds.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK56070/ (accessed on 4 July 2025).
- Jones, G. 100 YEARS OF VITAMIN D: Historical aspects of vitamin D. Endocr. Connect. 2022, 11, e210594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyles, D.W. Vitamin D: Brain and Behavior. JBMR Plus 2021, 5, e10419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Shi, Y.; Jie, R.; He, J.; Luo, Z.; Li, J. Vitamin D: The crucial neuroprotective factor for nerve cells. Neuroscience 2024, 560, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryabor, G.; Gholijani, N.; Kahmini, F.R. A review of the critical role of vitamin D axis on the immune system. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2023, 132–133, 104866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christakos, S.; Dhawan, P.; Verstuyf, A.; Verlinden, L.; Carmeliet, G. Vitamin D: Metabolism, Molecular Mechanism of Action, and Pleiotropic Effects. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 365–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Sun, Q.; Hui, Y.; Xu, J.; Shi, P.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y. Vitamin D receptor prevents tumour development by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway in human colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaiano, A.; Facchini, B.A.; Iacovino, M.; Santorsola, M.; Facchini, S.; di Mauro, G.; Toscano, E.; Montopoli, M.; di Mauro, A.; Quagliariello, V.; et al. Impact of Vitamin D Levels on Progression-Free Survival and Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, S.; Reeves, A.A.; Lafortune, S. Simulation of physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties of vitamin d3 and its natural derivatives. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.C.; Furlanetto, T.W. Intestinal absorption of vitamin D: A systematic review. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam Shishir, M.R.; Karim, N.; Gowd, V.; Zheng, X.; Chen, W. Liposomal delivery of natural product: A promising approach in health research. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 85, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzuto, G.; Molinari, A. Liposomes as nanomedical devices. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 975–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J. A Review of Liposomes as a Drug Delivery System: Current Status of Approved Products, Regulatory Environments, and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.A.; Trevaskis, N.L. TPGS Decorated Liposomes as Multifunctional Nano-Delivery Systems. Pharm. Res. 2023, 40, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasarri, M.; Ponti, L.; Degl’Innocenti, D.; Bergonzi, M.C. Liposomal Formulation Improves the Bioactivity of Usnic Acid in RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells Reducing its Toxicity. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2024, 21, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergonzi, M.C.; de Stefani, C.; Vasarri, M.; Ivanova Stojcheva, E.; Ramos-Pineda, A.M.; Baldi, F.; Bilia, A.R.; Degl’Innocenti, D. Encapsulation of Olive Leaf Polyphenol-Rich Extract in Polymeric Micelles to Improve Its Intestinal Permeability. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergonzi, M.C.; Vasarri, M.; Marroncini, G.; Barletta, E.; Degl’Innocenti, D. Thymoquinone-loaded soluplus®®-solutol®® HS15 mixed micelles: Preparation, in vitro characterization, and effect on the SH-SY5Y cell migration. Molecules 2020, 25, 4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowka, E.; Stasiak, J.; Lulek, J. Drug delivery systems for vitamin D supplementation and therapy. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzini, V.; D’Ambrosio, M.; Luceri, C.; Cinci, L.; Landucci, E.; Bilia, A.R.; Bergonzi, M.C. Formulation of nanomicelles to improve the solubility and the oral absorption of silymarin. Molecules 2019, 24, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landucci, E.; Mazzantini, C.; Calvani, M.; Pellegrini-Giampietro, D.E.; Bergonzi, M.C. Evaluation of Conventional and Hyaluronic Acid-Coated Thymoquinone Liposomes in an In Vitro Model of Dry Eye. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheli, L.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Mosti, E.; Ghelardini, C.; Bilia, A.R.; Bergonzi, M.C. Antinociceptive Action of Thymoquinone-Loaded Liposomes in an In Vivo Model of Tendinopathy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Y.; Xia, H.; Li, L.; Lee, R.J.; Xie, J.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Teng, L. Liposomal vitamin D3 as an anti-aging agent for the skin. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Hamishehkar, H. Formulation of nanoliposomal vitamin D3 for potential application in beverage fortification. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 4, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Li, W.; Adu-Frimpong, M.; Wang, Q.; Yu, J.; Xu, X. Preparation and Characterization of Syringic Acid–Loaded TPGS Liposome with Enhanced Oral Bioavailability and In Vivo Antioxidant Efficiency. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchi, L.; Piazzini, V.; D’Ambrosio, M.; Luceri, C.; Rocco, F.; Innocenti, M.; Bilia, A.R.; Mulinacci, N.; Bergonzi, M.C. Formulation of phenol-rich extracts from unripe olives (Olea europaea L.) in microemulsion to improve its solubility and permeability. Molecules 2020, 25, 3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briuglia, M.L.; Rotella, C.; McFarlane, A.; Lamprou, D.A. Influence of cholesterol on liposome stability and on in vitro drug release. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2015, 5, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaddah, S.; Khreich, N.; Kaddah, F.; Charcosset, C.; Greige-Gerges, H. Cholesterol modulates the liposome membrane fluidity and permeability for a hydrophilic molecule. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 113, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, E.; Gomes, A.C.; Preto, A.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Design of liposomal formulations for cell targeting. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, L.; Panico, A.M.; Bonina, F. Quantitative determination of hydrophobic compound entrapment in dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine liposomes by differential scanning calorimetry. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 138, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakuša, Ž.T.; Pišlar, M.; Kristl, A.; Roškar, R. Comprehensive stability study of vitamin d3 in aqueous solutions and liquid commercial products. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Ebrahimzadeh, M.A.; Davoodi, D. Stability of vitamin D3 encapsulated in nanoparticles of whey protein isolate. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, M.A.; Xinyu, H.; Jabeen, A.; Ahsan, A.; Seidu, T.A.; Kutoka, P.T.; Wang, B. Enhanced cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of vorinostat through encapsulation in TPGS-modified liposomes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 199, 111523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faassen, F.; Vogel, G.; Spanings, H.; Vromans, H. Caco-2 permeability, P-glycoprotein transport ratios and brain penetration of heterocyclic drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 263, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dintaman, J.M.; Silverman, J.A. Inhibition of P-Glycoprotein by D-α-Tocopheryl Polyethylene Glycol 1000 Succinate (TPGS). Pharm. Res. 1999, 16, 1550–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Formulation | PC | CH | TPGS | VD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LP | 3 | 1 | - | - |
| LPT | 3 | 1 | 3 | - |
| LP-VD | 3 | 1 | - | 0.2 |
| LPT-VD | 3 | 1 | 3 | 0.2 |
| PC:CH:TPGS Ratio | Size (nm) ± SD | PdI ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| 3:1:1 | 83.96 ± 0.40 | 0.22 ± 0.02 |
| 3:1:3 | 59.36 ± 0.70 | 0.26 ± 0.02 |
| 3:3:1 | 135.20 ± 0.26 | 0.22 ± 0.01 |
| Size (nm) ± SD | PdI ± SD | ZP ± SD (mV) | EE% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LP | 69.98 ± 1.90 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | −21.12 ± 3.24 | - |
| LPT | 59.36 ± 0.70 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | −9.50 ± 3.57 | - |
| LP-VD | 85.50 ± 5.70 | 0.24 ± 0.06 | −20.90 ± 4.37 | 95.76 ± 1.26% |
| LPT-VD | 61.70 ± 3.90 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | −9.45 ± 2.99 | 97.54 ± 3.24% |
| Sample | 1 Day | 3 Days | 4 Days | 7 Days | 14 Days | 21 Days | 28 Days |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VD solution | 86.46 ± 4.23 | 40.17 ± 3.4 | 39.28 ± 3.38 | - | - | - | - |
| LP-VD | 99.54 ± 2.42 | 99.85 ± 0.69 | 99.41 ± 3.13 | 98.95 ± 2.47 | 98.20 ± 2.79 | 96.53 ± 0.95 | 94.12 ± 5.25 |
| LPT-VD | 99.90 ± 2.75 | 99.65 ± 2.65 | 99.87 ± 4.49 | 99.35 ± 1.23 | 97.86 ± 1.22 | 96.89 ± 4.84 | 96.69 ± 4.94 |
| LP-VD | LPT-VD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (Days) | Size | PdI | ZP | Size | PdI | ZP |
| 0 | 84.72 ± 5.70 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | −20.22 ± 0.93 | 57.20 ± 0.51 | 0.26 ± 0.00 | −9.6 ± 0.6 |
| 1 | 84.31 ± 3.11 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | −20.54 ± 0.35 | 57.97 ± 0.53 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | −9.9 ± 0.3 |
| 5 | 85.13 ± 4.19 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | −20.38 ± 0.26 | 57.99 ± 0.23 | 0.26 ± 0.00 | −10.0 ± 0.2 |
| 7 | 88.52 ± 6.11 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | −21.43 ± 1.10 | 58.89 ± 0.99 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | −9.92 ± 0.3 |
| 14 | 87.23 ± 2.60 | 0.22 ± 0.25 | −22.24 ± 1.18 | 57.83 ± 0.50 | 0.27 ± 0.00 | −9.74 ± 0.3 |
| 21 | 93.14 ± 2.97 | 0.25 ± 0.00 | −23.80 ± 0.70 | 58.70 ± 0.61 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | −12.2 ± 1.4 |
| 28 | 98.31 ± 3.23 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | −26.42 ± 0.69 | 60.12 ± 0.72 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | −12.9 ± 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Landi, C.; Landucci, E.; Mazzantini, C.; Castellacci, R.; Bergonzi, M.C. Vitamin D Nanoliposomes to Improve Solubility, Stability, and Uptake Across Intestinal Barrier. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101244
Landi C, Landucci E, Mazzantini C, Castellacci R, Bergonzi MC. Vitamin D Nanoliposomes to Improve Solubility, Stability, and Uptake Across Intestinal Barrier. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(10):1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101244
Chicago/Turabian StyleLandi, Cosimo, Elisa Landucci, Costanza Mazzantini, Rebecca Castellacci, and Maria Camilla Bergonzi. 2025. "Vitamin D Nanoliposomes to Improve Solubility, Stability, and Uptake Across Intestinal Barrier" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 10: 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101244
APA StyleLandi, C., Landucci, E., Mazzantini, C., Castellacci, R., & Bergonzi, M. C. (2025). Vitamin D Nanoliposomes to Improve Solubility, Stability, and Uptake Across Intestinal Barrier. Pharmaceutics, 17(10), 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101244










