Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer with a Neurotensin–Bombesin Radioligand Combination—First Preclinical Results
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Radioligands
2.1.1. Peptides and Protease Inhibitors
2.1.2. Radiolabeling–Quality Control
2.2. Cell Studies
2.2.1. Cell Culture
2.2.2. Uptake/Internalization of [99mTc]Tc-DT11 in PC-3 Cells
2.2.3. Uptake/Internalization of [99mTc]Tc-DT11+[99mTc]Tc-DB7 in PC-3 Cells
2.3. Animal Studies
2.3.1. Metabolic Stability in Mice
2.3.2. Biodistribution of [99mTc]Tc-DT11 in PC-3 Tumor-Bearing Mice
2.3.3. Biodistribution of [99mTc]Tc-DT11+[99mTc]Tc-DB7 in PC-3 Tumor-Bearing Mice
2.3.4. SPECT/CT of [99mTc]Tc-DT11+[99mTc]Tc-DB7 in PC-3 Tumor-Bearing Mice
3. Results
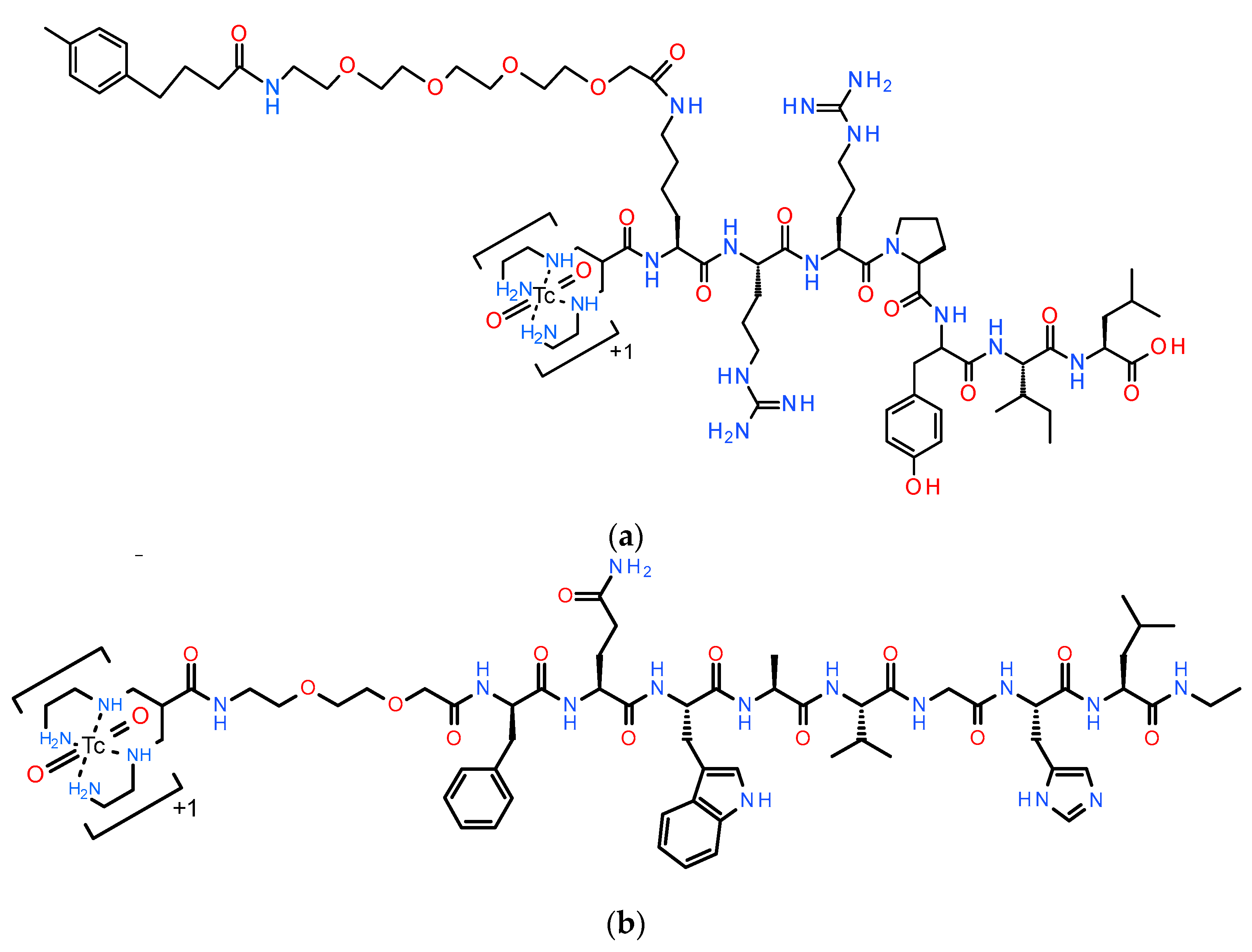
3.1. Ligands and Radioligands
3.2. In Vitro Assays in PC-3 Cells
3.3. Metabolic Stability
3.4. Biodistribution in PC-3 Tumor-Bearing Mice
3.4.1. Biodistribution of [99mTc]Tc-DT11
3.4.2. Biodistribution of [99mTc]Tc-DT11+[99mTc]Tc-DB7 in PC-3 Tumor-Bearing Mice
3.4.3. SPECT/CT of [99mTc]Tc-DT11+[99mTc]Tc-DB7 in PC-3 Tumor-Bearing Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reubi, J.C. Peptide receptors as molecular targets for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 389–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamberts, S.W.J.; Hofland, L.J. ANNIVERSARY REVIEW: Octreotide, 40 years later. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 181, R173–R183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stueven, A.K.; Kayser, A.; Wetz, C.; Amthauer, H.; Wree, A.; Tacke, F.; Wiedenmann, B.; Roderburg, C.; Jann, H. Somatostatin analogues in the treatment of neuroendocrine tumors: Past, present and future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennrich, U.; Kopka, K. Lutathera®: The first FDA- and EMA-approved radiopharmaceutical for peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Parihar, A.S.; Bodei, L.; Hope, T.A.; Mallak, N.; Millo, C.; Prasad, K.; Wilson, D.; Zukotynski, K.; Mittra, E. Somatostatin receptor imaging and theranostics: Current practice and future prospects. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgouros, G.; Bodei, L.; McDevitt, M.R.; Nedrow, J.R. Radiopharmaceutical therapy in cancer: Clinical advances and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 589–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansi, R.; Nock, B.A.; Dalm, S.U.; Busstra, M.B.; van Weerden, W.M.; Maina, T. Radiolabeled bombesin analogs. Cancers 2021, 13, 5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatalic, K.L.; Kwekkeboom, D.J.; de Jong, M. Radiopeptides for imaging and therapy: A radiant future. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 1809–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nock, B.A.; Kanellopoulos, P.; Joosten, L.; Mansi, R.; Maina, T. Peptide Radioligands in cancer theranostics: Agonists and antagonists. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reubi, J.C.; Waser, B. Concomitant expression of several peptide receptors in neuroendocrine tumours: Molecular basis for in vivo multireceptor tumour targeting. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2003, 30, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reubi, J.C.; Fleischmann, A.; Waser, B.; Rehmann, R. Concomitant vascular GRP-receptor and VEGF-receptor expression in human tumors: Molecular basis for dual targeting of tumoral vasculature. Peptides 2011, 32, 1457–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reubi, J.C.; Schär, J.C.; Waser, B.; Wenger, S.; Heppeler, A.; Schmitt, J.S.; Mäcke, H.R. Affinity profiles for human somatostatin receptor subtypes SST1-SST5 of somatostatin radiotracers selected for scintigraphic and radiotherapeutic use. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2000, 27, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reubi, J.C.; Waser, B.; Foekens, J.A.; Klijn, J.G.; Lamberts, S.W.; Laissue, J. Somatostatin receptor incidence and distribution in breast cancer using receptor autoradiography: Relationship to EGF receptors. Int. J. Cancer 1990, 46, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reubi, C.; Gugger, M.; Waser, B. Co-expressed peptide receptors in breast cancer as a molecular basis for in vivo multireceptor tumour targeting. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2002, 29, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reubi, J.C.; Waser, B.; Schaer, J.C.; Markwalder, R. Somatostatin receptors in human prostate and prostate cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 80, 2806–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markwalder, R.; Reubi, J.C. Gastrin-releasing peptide receptors in the human prostate: Relation to neoplastic transformation. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.; Song, H.; Davidzon, G.A.; Moradi, F.; Liang, T.; Loening, A.; Vasanawala, S.; Iagaru, A. Prospective Comparison of 68Ga-NeoB and 68Ga-PSMA-R2 PET/MRI in patients with biochemically recurrent prostate cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2024, 65, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reubi, J.C.; Maecke, H.R. Approaches to multireceptor targeting: Hybrid radioligands, radioligand cocktails, and sequential radioligand applications. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 10S–16S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushnell, D.L.; Madsen, M.T.; O’Cdorisio, T.; Menda, Y.; Muzahir, S.; Ryan, R.; O’Dorisio, M.S. Feasibility and advantage of adding 131I-MIBG to 90Y-DOTATOC for treatment of patients with advanced stage neuroendocrine tumors. EJNMMI Res. 2014, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jin, Z.H.; Tsuji, A.B.; Degardin, M.; Sugyo, A.; Yoshii, Y.; Nagatsu, K.; Zhang, M.R.; Fujibayashi, Y.; Dumy, P.; Boturyn, D.; et al. Uniform intratumoral distribution of radioactivity produced using two different radioagents, 64Cu-cyclam-RAFT-c(-RGDfK-)4 and 64Cu-ATSM, improves therapeutic efficacy in a small animal tumor model. EJNMMI Res. 2018, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mao, F.; Niu, G.; Peng, L.; Lang, L.; Li, F.; Ying, H.; Wu, H.; Pan, B.; Zhu, Z.; et al. 68Ga-BBN-RGD PET/CT for GRPR and integrin alphavbeta3 imaging in patients with breast cancer. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eder, M.; Schafer, M.; Bauder-Wust, U.; Haberkorn, U.; Eisenhut, M.; Kopka, K. Preclinical evaluation of a bispecific low-molecular heterodimer targeting both PSMA and GRPR for improved PET imaging and therapy of prostate cancer. Prostate 2014, 74, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liolios, C.; Schäfer, M.; Haberkorn, U.; Eder, M.; Kopka, K. Novel bispecific PSMA/GRPr targeting radioligands with optimized pharmacokinetics for improved PET imaging of prostate cancer. Bioconjug. Chem. 2016, 27, 737–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judmann, B.; Braun, D.; Wangler, B.; Schirrmacher, R.; Fricker, G.; Wangler, C. Current state of radiolabeled heterobivalent peptidic ligands in tumor imaging and therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nock, B.A.; Maina, T.; Krenning, E.P.; de Jong, M. “To serve and protect”: Enzyme inhibitors as radiopeptide escorts promote tumor targeting. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nock, B.A.; Kaloudi, A.; Lymperis, E.; Giarika, A.; Kulkarni, H.R.; Klette, I.; Singh, A.; Krenning, E.P.; de Jong, M.; Maina, T.; et al. Theranostic perspectives in prostate cancer with the gastrin-releasing peptide receptor antagonist NeoBOMB1: Preclinical and first clinical results. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.M.; Severns, V.; Brown, D.C.; Bisoffi, M.; Sillerud, L.O. Prostate cancer targeting motifs: Expression of alphanubeta3, neurotensin receptor 1, prostate specific membrane antigen, and prostate stem cell antigen in human prostate cancer cell lines and xenografts. Prostate 2012, 72, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, H.; Wu, X.; Li, L.; Wu, H.; Tian, R. New frontiers in molecular imaging using peptide-based radiopharmaceuticals for prostate cancer. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 583309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, S.; Qiu, S.; Fiorentino, F.; Simillis, C.; Rasheed, S.; Tekkis, P.; Kontovounisios, C. The role of neurotensin and its receptors in non-gastrointestinal cancers: A review. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgat, C.; Chastel, A.; Molinie, V.; Schollhammer, R.; Macgrogan, G.; Velasco, V.; Malavaud, B.; Fernandez, P.; Hindie, E. Neurotensin receptor-1 expression in human prostate cancer: A pilot study on primary tumors and lymph node metastases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Tan, H.; Tang, Y.; Smith, E.; Wu, Z.; Liao, W.; Hu, S.; Li, Z. Evaluation of neurotensin receptor 1 as potential biomarker for prostate cancer theranostic use. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2199–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Giglio, B.; Ma, X.; Jiang, G.; Yuan, H.; Wu, Z.; Li, Z. Imaging neurotensin receptor in prostate cancer with 64Cu-labeled neurotensin analogs. Mol. Imaging 2017, 16, 1536012117711369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, S.L.; Burns, J.E.; Maitland, N.J. Altered expression of neurotensin receptors is associated with the differentiation state of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körner, M.; Waser, B.; Rehmann, R.; Reubi, J.C. Early over-expression of GRP receptors in prostatic carcinogenesis. Prostate 2014, 74, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamimoto, R.; Hancock, S.; Schneider, B.; Chin, F.T.; Jamali, M.; Loening, A.; Vasanawala, S.; Gambhir, S.S.; Iagaru, A. Pilot comparison of 68Ga-RM2 PET and 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET in patients with biochemically recurrent prostate cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellopoulos, P.; Lymperis, E.; Kaloudi, A.; de Jong, M.; Krenning, E.P.; Nock, B.A.; Maina, T. [99mTc]Tc-DB1 Mimics with different-length PEG spacers: Preclinical comparison in GRPR-positive models. Molecules 2020, 25, 3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roques, B.P.; Noble, F.; Dauge, V.; Fournie-Zaluski, M.C.; Beaumont, A. Neutral endopeptidase 24.11: Structure, inhibition, and experimental and clinical pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 1993, 45, 87–146. [Google Scholar]
- Roques, B.P. Zinc metallopeptidases: Active site structure and design of selective and mixed inhibitors: New approaches in the search for analgesics and anti-hypertensives. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1993, 21 Pt 3, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, H.; Aoyagi, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Umezawa, H. Letter: A thermolysin inhibitor produced by Actinomycetes: Phosphoramidon. J. Antibiot. 1973, 26, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oefner, C.; D’Arcy, A.; Hennig, M.; Winkler, F.K.; Dale, G.E. Structure of human neutral endopeptidase (Neprilysin) complexed with phosphoramidon. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 296, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studdy, P.R.; Lapworth, R.; Bird, R. Angiotensin-converting enzyme and its clinical significance—A review. J. Clin. Pathol. 1983, 36, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdös, E.G.; Skidgel, R.A. The angiotensin I-converting enzyme. Lab. Investig. 1987, 56, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checler, F.; Vincent, J.P.; Kitabgi, P. Degradation of neurotensin by rat brain synaptic membranes: Involvement of a thermolysin-like metalloendopeptidase (enkephalinase), angiotensin-converting enzyme, and other unidentified peptidases. J. Neurochem. 1983, 41, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skidgel, R.A.; Engelbrecht, S.; Johnson, A.R.; Erdös, E.G. Hydrolysis of substance P and neurotensin by converting enzyme and neutral endopeptidase. Peptides 1984, 5, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitabgi, P.; De Nadai, F.; Rovere, C.; Bidard, J.N. Biosynthesis, maturation, release, and degradation of neurotensin and neuromedin N. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1992, 668, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellopoulos, P.; Nock, B.A.; Krenning, E.P.; Maina, T. Toward stability enhancement of NTS1R-targeted radioligands: Structural interventions on [99mTc]Tc-DT1. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanellopoulos, P.; Nock, B.A.; Rouchota, M.; Loudos, G.; Krenning, E.P.; Maina, T. Side-chain modified [99mTc]Tc-DT1 mimics: A comparative study in NTS1R-positive models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, J.J.; Packer, M.; Solomon, S.D. Neprilysin inhibition for heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2336–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiering, N.; D’Arcy, A.; Villard, F.; Ramage, P.; Logel, C.; Cumin, F.; Ksander, G.M.; Wiesmann, C.; Karki, R.G.; Mogi, M. Structure of neprilysin in complex with the active metabolite of sacubitril. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayalasomayajula, S.; Langenickel, T.; Pal, P.; Boggarapu, S.; Sunkara, G. Clinical pharmacokinetics of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696): A novel angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 1461–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ayalasomayajula, S.; Pan, W.; Yang, F.; Yuan, Y.; Langenickel, T.; Hinder, M.; Kalluri, S.; Pal, P.; Sunkara, G. Pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) after single-dose administration in healthy Chinese subjects. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 42, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Noe, A.; Chandra, P.; Al-Fayoumi, S.; Ligueros-Saylan, M.; Sarangapani, R.; Maahs, S.; Ksander, G.; Rigel, D.F.; Jeng, A.Y.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of LCZ696, a novel dual-acting angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNi). J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 50, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reile, H.; Armatis, P.E.; Schally, A.V. Characterization of high-affinity receptors for bombesin/gastrin releasing peptide on the human prostate cancer cell lines PC-3 and DU-145: Internalization of receptor bound 125I-(Tyr4) bombesin by tumor cells. Prostate 1994, 25, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, P.; Ramos-Alvarez, I.; Moody, T.W.; Jensen, R.T. Bombesin related peptides/receptors and their promising therapeutic roles in cancer imaging, targeting and treatment. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 1055–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitabgi, P. Targeting neurotensin receptors with agonists and antagonists for therapeutic purposes. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev. 2002, 5, 764–776. [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann, A.; Laderach, U.; Friess, H.; Buechler, M.W.; Reubi, J.C. Bombesin receptors in distinct tissue compartments of human pancreatic diseases. Lab. Investig. 2000, 80, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Mixture 1 | +[Tyr4]BBN 2 | +NT 3 | +[Tyr4]BBN + NT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| total/block | membrane-bound | 7.04 ± 0.55 | 1.63 ± 0.13 | 7.91 ± 0.39 | 1.50 ± 0.10 |
| internalized | 3.70 ± 0.33 | 2.73 ± 0.46 | 2.26 ± 0.13 | 1.17 ± 0.15 | |
| sum | 10.74 ± 0.61 | 4.36 ± 0.51 | 10.16 ± 0.45 | 2.67 ± 0.21 | |
| specific | membrane-bound | 5.54 ± 0.52 4 | 0.19 ± 0.15 5 | 6.40 ± 0.34 6 | - |
| internalized | 2.54 ± 0.32 | 1.68 ± 0.49 | 1.09 ± 0.26 | - | |
| sum | 8.08 ± 0.62 | 1.87 ± 0.56 | 7.49 ± 0.46 | - | |
| [99mTc]Tc-DT11 * | [99mTc]Tc-DB7 | |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 56.56 ± 5.19% | 70.6 ± 1.1% * |
| Entresto® | 76.98 ± 3.31% | 93.7 ± 2.2% |
| PA | - | 94.5 ± 1.1% * |
| Organs/Tissues | Block (n = 3) 1,2 | Controls (n = 4) 1 | Entresto® (n = 4) 1,3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood | 0.52 ± 0.13 | 1.05 ± 0.30 | 0.53 ± 0.17 |
| Liver | 1.73 ± 0.13 | 1.39 ± 0.38 | 1.37 ± 0.24 |
| Heart | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 0.39 ± 0.18 | 0.17 ± 0.13 |
| Kidneys | 0.23 ± 0.17 | 2.87 ± 0.37 | 3.21 ± 0.62 |
| Stomach | 0.35 ± 0.20 | 0.38 ± 0.16 | 0.52 ± 0.20 |
| Intestines | 1.62 ± 0.52 | 1.91 ± 0.30 | 2.79 ± 0.62 |
| Spleen | 0.99 ± 0.30 | 0.89 ± 0.23 | 1.27 ± 0.39 |
| Muscle | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.16 ± 0.09 | 0.12 ± 0.03 |
| Lungs | 0.76 ± 0.15 | 1.03 ± 0.42 | 1.02 ± 1.17 |
| Pancreas | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.26 ± 0.09 | 0.21 ± 0.03 |
| PC-3 Tumor | 1.56 ± 0.43 | 4.23 ± 0.58 | 5.88 ± 1.47 |
| Organs/Tissues | Controls | Entresto® 1 | Block 1 2 | Block 2 3 | Block 3 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood | 1.01 ± 0.29 | 0.72 ± 0.13 | 1.08 ± 0.13 | 1.64 ± 0.52 | 1.41 ± 0.92 |
| Liver | 1.27 ± 0.18 | 1.09 ± 0.15 | 1.37 ± 0.08 | 1.81 ± 0.45 | 1.88 ± 0.44 |
| Heart | 0.44 ± 0.11 | 0.30 ± 0.12 | 0.39 ± 0.13 | 0.52 ± 0.19 | 0.63 ± 0.53 |
| Kidneys | 2.69 ± 0.25 | 2.83 ± 0.53 | 2.78 ± 0.30 | 2.93 ± 0.62 | 3.12 ± 0.97 |
| Stomach | 0.58 ± 0.19 | 0.51 ± 0.22 | 0.52 ± 0.12 | 0.67 ± 0.30 | 0.71 ± 0.13 |
| Intestines | 1.68 ± 0.13 | 1.98 ± 0.35 | 1.40 ± 0.17 | 1.96 ± 0.08 | 1.71 ± 0.36 |
| Spleen | 0.67 ± 0.12 | 0.73 ± 0.10 | 0.76 ± 0.07 | 0.98 ± 0.20 | 0.80 ± 0.17 |
| Muscle | 0.14 ± 0.04 | 0.12 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.02 | 0.22 ± 0.10 | 0.18 ± 0.11 |
| Lungs | 0.80 ± 0.15 | 0.93 ± 0.17 | 0.89 ± 0.10 | 1.33 ± 0.35 | 1.65 ± 1.02 |
| Pancreas | 0.55 ± 0.08 | 0.77 ± 0.09 | 0.60 ± 0.03 | 0.50 ± 0.10 | 0.45 ± 0.10 |
| PC-3 Tumor | 7.70 ± 0.89 | 11.57 ± 1.92 | 7.28 ± 1.00 | 3.57 ± 0.44 | 2.05 ± 0.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bibika, M.; Kanellopoulos, P.; Rouchota, M.; Loudos, G.; Nock, B.A.; Krenning, E.P.; Maina, T. Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer with a Neurotensin–Bombesin Radioligand Combination—First Preclinical Results. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16091223
Bibika M, Kanellopoulos P, Rouchota M, Loudos G, Nock BA, Krenning EP, Maina T. Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer with a Neurotensin–Bombesin Radioligand Combination—First Preclinical Results. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(9):1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16091223
Chicago/Turabian StyleBibika, Maria, Panagiotis Kanellopoulos, Maritina Rouchota, George Loudos, Berthold A. Nock, Eric P. Krenning, and Theodosia Maina. 2024. "Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer with a Neurotensin–Bombesin Radioligand Combination—First Preclinical Results" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 9: 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16091223
APA StyleBibika, M., Kanellopoulos, P., Rouchota, M., Loudos, G., Nock, B. A., Krenning, E. P., & Maina, T. (2024). Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer with a Neurotensin–Bombesin Radioligand Combination—First Preclinical Results. Pharmaceutics, 16(9), 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16091223






