A Meta-Analysis Methodology in Stan to Estimate Population Pharmacokinetic Parameters from Multiple Aggregate Concentration–Time Datasets: Application to Gevokizumab mPBPK Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Data of Gevokizumab
2.2. Simulation Study
2.3. Second-Generation mPBPK Model for Gevokizumab
2.4. Application to the Real Datasets of Gevokizumab
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Gevokizumab’s Simulation Study
3.2. Application to the Real Datasets of Gevokizumab
3.2.1. Dosage Group of 7 mg
3.2.2. Five Dosage Groups
3.3. Application of the Method to a Variety of Drugs and PK Models
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cavelti-Weder, C.; Babians-Brunner, A.; Keller, C.; Stahel, M.A.; Kurz-Levin, M.; Zayed, H.; Solinger, A.M.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; Dinarello, C.A.; Donath, M.Y. Effects of gevokizumab on glycemia and inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issafras, H.; Corbin, J.A.; Goldfine, I.D.; Roell, M.K. Detailed mechanistic analysis of gevokizumab, an allosteric anti-IL-1β antibody with differential receptor-modulating properties. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 348, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roell, M.K.; Issafras, H.; Bauer, R.J.; Michelson, K.S.; Mendoza, N.; Vanegas, S.I.; Gross, L.M.; Larsen, P.D.; Bedinger, D.H.; Bohmann, D.J.; et al. Kinetic approach to pathway attenuation using XOMA 052, a regulatory therapeutic antibody that modulates interleukin-1beta activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 20607–20614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT03798626 (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- Petrella, B.L.; Vincenti, M.P. Interleukin-1β mediates metalloproteinase-dependent renal cell carcinoma tumor cell invasion through the activation of CCAAT enhancer binding protein β. Cancer Med. 2012, 1, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronov, E.; Apte, R.N. IL-1 in Colon Inflammation, Colon Carcinogenesis and Invasiveness of Colon Cancer. Cancer Microenviron. 2015, 8, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Lan, C.; Pei, H.; Zhu, Z. Expression of interleukin 1β in gastric cancer tissue and its effects on gastric cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 9, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwanji, R.; O’Brien, N.A.; Choi, J.E.; Nguyen, B.; Laszewski, T.; Grauel, A.L.; Yan, Z.; Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Ruddy, D.A.; et al. Targeting the IL1β Pathway for Cancer Immunotherapy Remodels the Tumor Microenvironment and Enhances Antitumor Immune Responses. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2023, 11, 777–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knickelbein, J.E.; Tucker, W.R.; Bhatt, N.; Armbrust, K.; Valent, D.; Obiyor, D.; Nussenblatt, R.B.; Sen, H.N. Gevokizumab in the Treatment of Autoimmune Non-necrotizing Anterior Scleritis: Results of a Phase I/II Clinical Trial. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 172, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Balthasar, J.P.; Jusko, W.J. Second-generation minimal physiologically-based pharmacokinetic model for monoclonal antibodies. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 2013, 40, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Jusko, W.J. Applications of minimal physiologically-based pharmacokinetic models. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 2012, 39, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsamandouras, N.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A.; Aarons, L. Combining the ‘bottom up’ and ‘top down’ approaches in pharmacokinetic modelling: Fitting PBPK models to observed clinical data. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 79, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelman, A.; Bois, F.; Jiang, J. Physiological Pharmacokinetic Analysis Using Population Modeling and Informative Prior Distributions. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1996, 91, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakefield, J. The Bayesian Analysis of Population Pharmacokinetic Models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1996, 91, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.; Gelman, A.; Jones, G.; Meng, X.-L. (Eds.) Handbook of Markov Chain Monte Carlo, 1st ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt, M. Diagnosing Suboptimal Cotangent Disintegrations in Hamiltonian Monte Carlo. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1604.00695. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, B.; Gelman, A.; Hoffman, M.D.; Lee, D.; Goodrich, B.; Betancourt, M.; Brubaker, M.; Guo, J.; Li, P.; Riddell, A. Stan: A Probabilistic Programming Language. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 76, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, M.D.; Gelman, A. The No-U-turn sampler: Adaptively setting path lengths in Hamiltonian Monte Carlo. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 15, 1593–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, S.; Gelman, A.; Lee, D.; Betancourt, M.; Vehtari, A.; Racine-Poon, A. Bayesian aggregation of average data: An application in drug development. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2018, 12, 1583–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiros, P.; Bois, F.Y.; Dokoumetzidis, A.; Tsiliki, G.; Sarimveis, H. Population pharmacokinetic reanalysis of a Diazepam PBPK model: A comparison of Stan and GNU MCSim. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 2019, 46, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CRAN.R. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/deSolve/deSolve.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- Margossian, C.; Gillespie, B. Differential Equations Based Models in Stan; StanCon: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stan. Available online: http://mc-stan.org (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- McKay, M.D.; Beckman, R.J.; Conover, W.J. A Comparison of Three Methods for Selecting Values of Input Variables in the Analysis of Output from a Computer Code. Technometrics 1979, 21, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CRAN.R. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/lhs/lhs.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- Kaikousidis, C.; Bies, R.R.; Dokoumetzidis, A. Simulating realistic patient profiles from pharmacokinetic models by a machine learning postprocessing correction of residual variability. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Gelman, A.; Rubin, D.B. Inference from Iterative Simulation Using Multiple Sequences. Statist. Sci. 1992, 7, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehtari, A.; Gelman, A.; Simpson, D.P.; Carpenter, B.; Burkner, P. Rank-Normalization, Folding, and Localization: An Improved Rˆ for Assessing Convergence of MCMC (with Discussion). Bayesian Anal. 2019, 16, 667–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


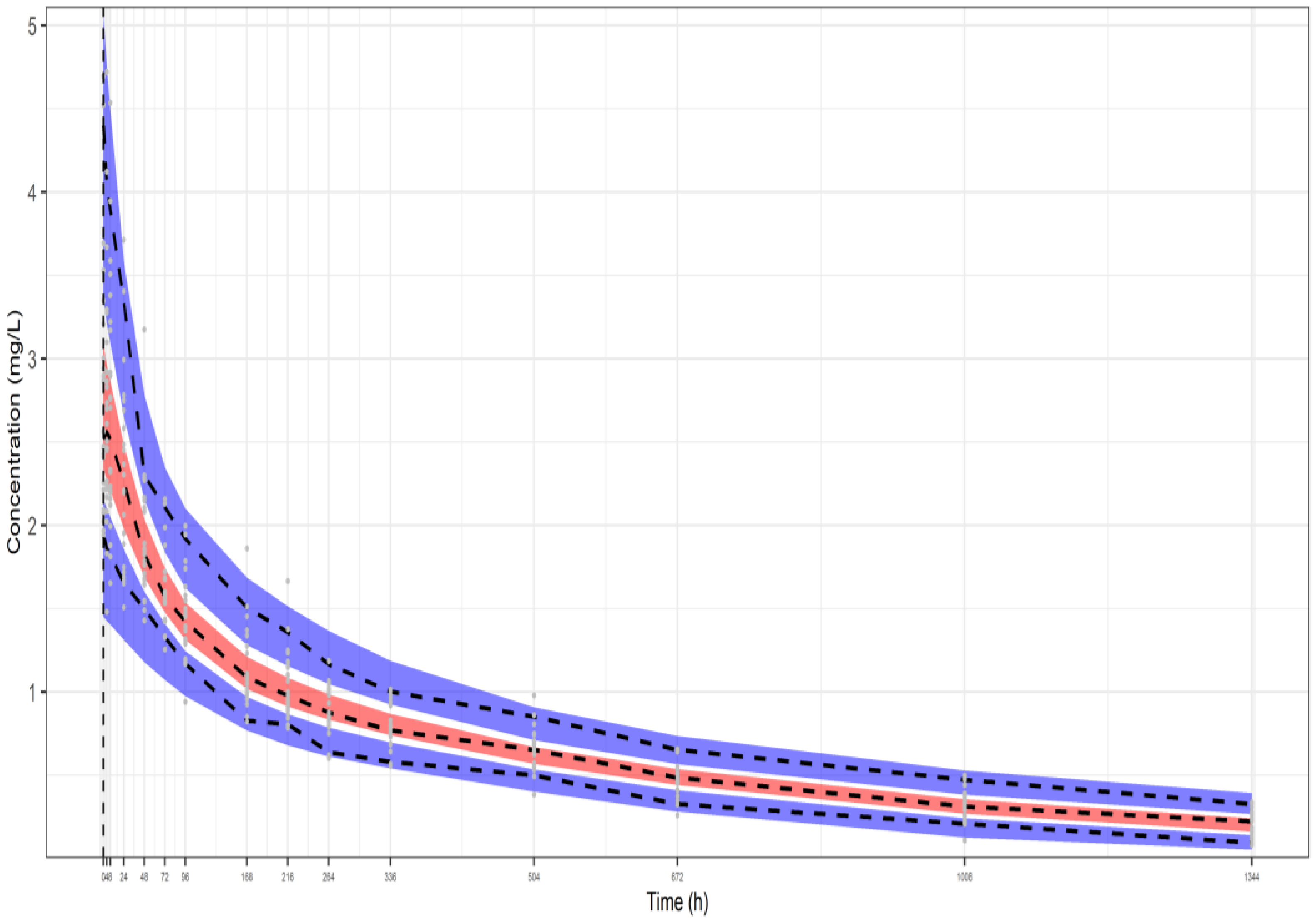
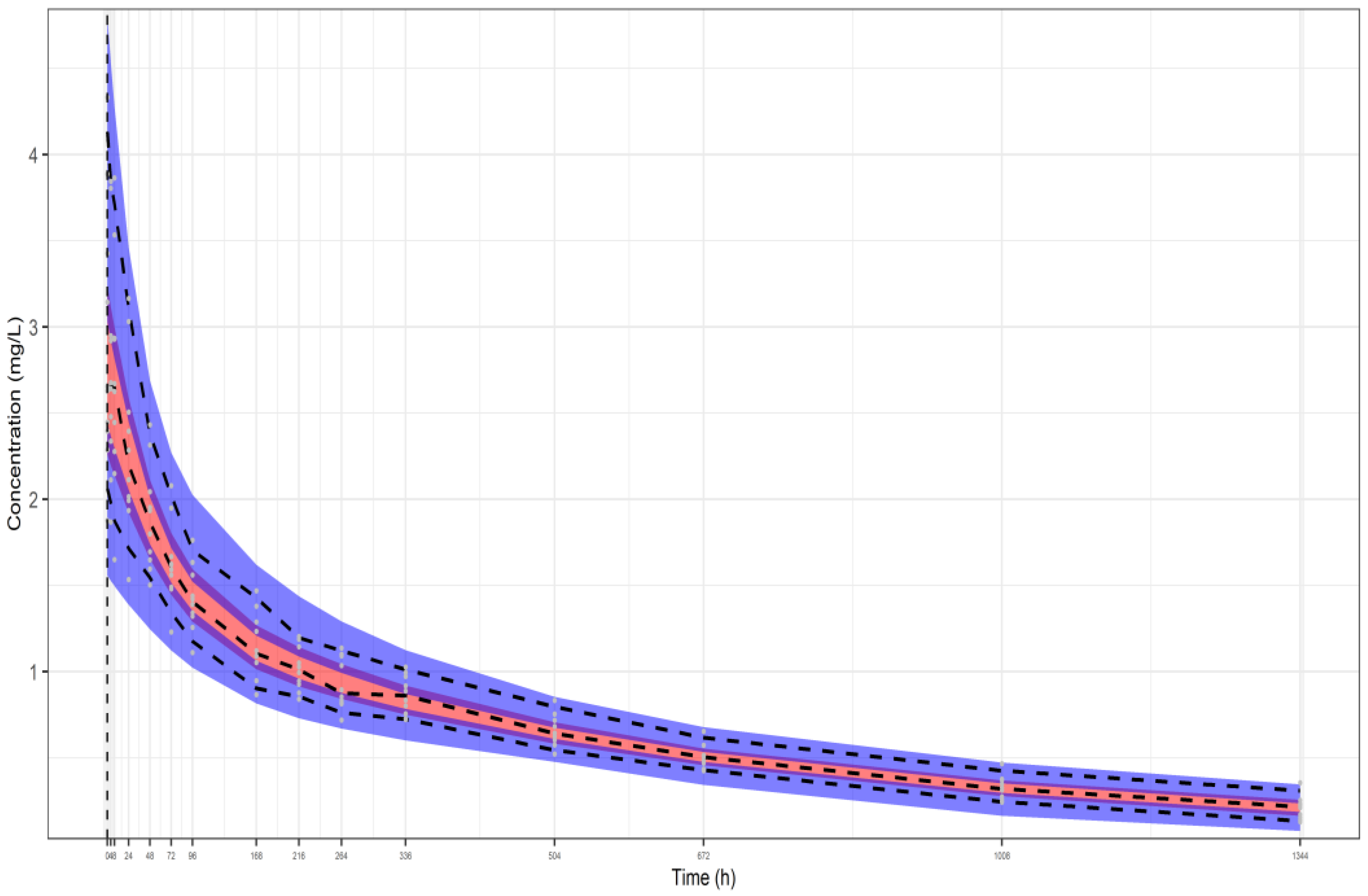
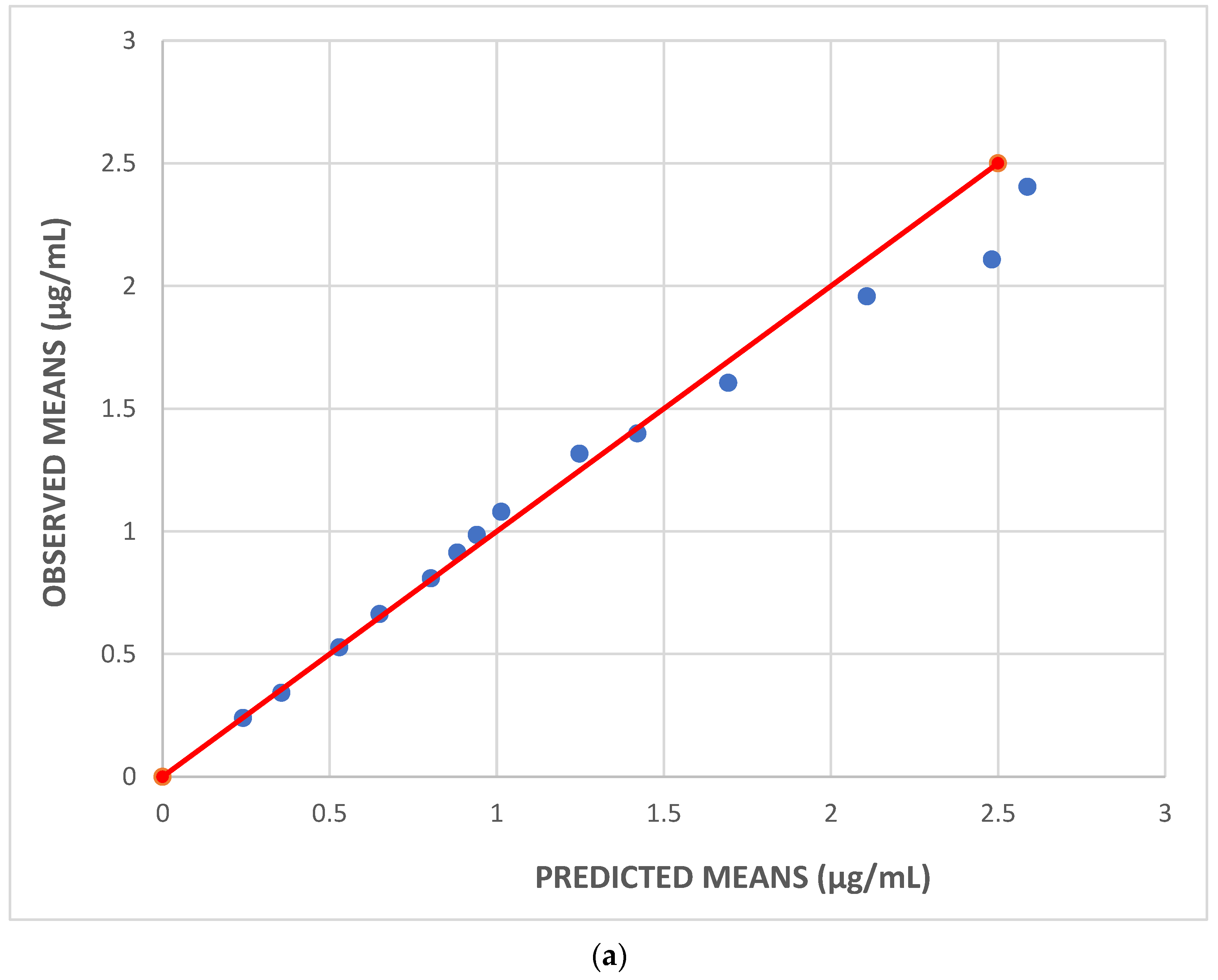

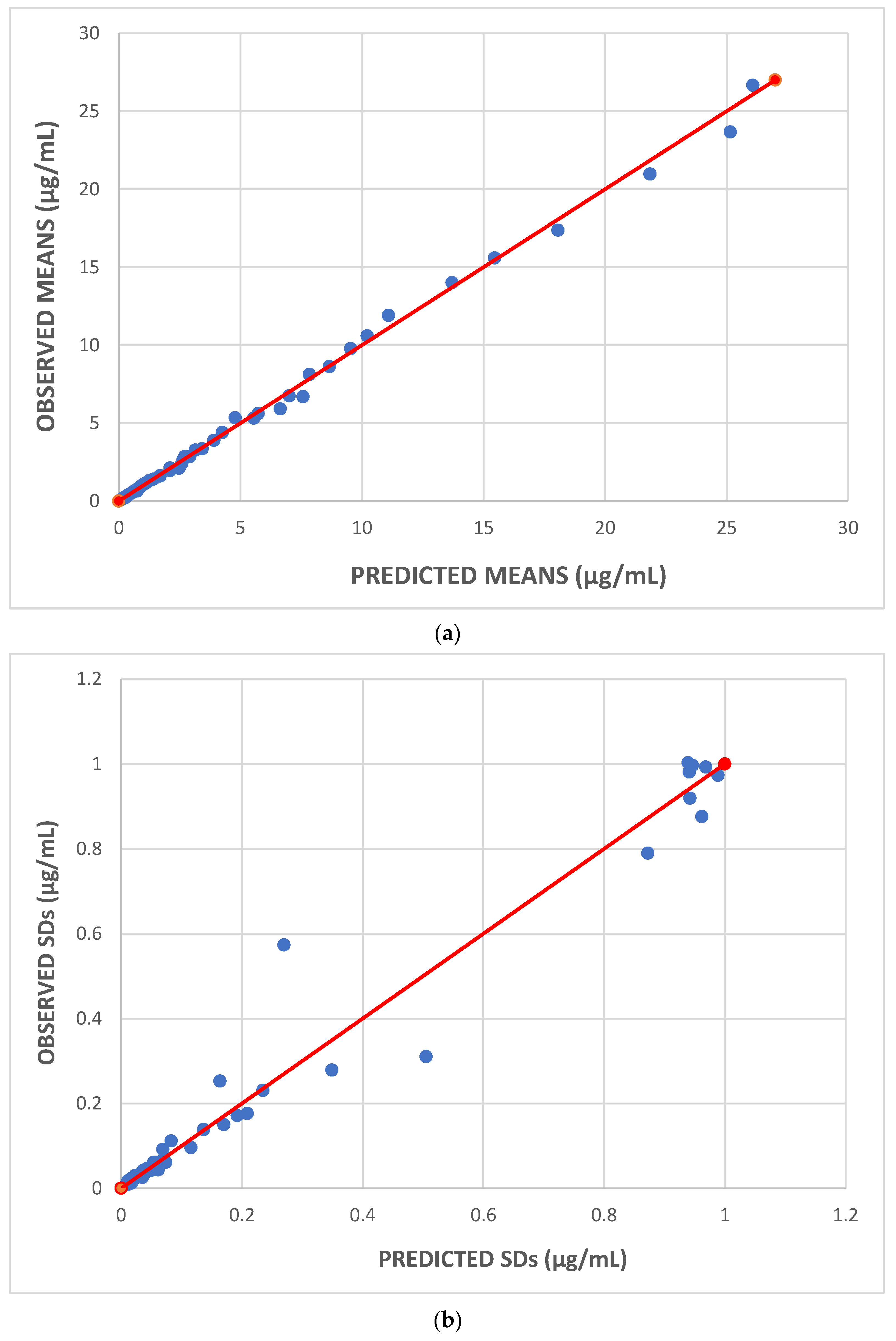
| Parameters | Dataset I | Dataset II | Dataset III |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 24 | 24 | 10 |
| rv (%) | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Dose (mg) | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| CLp (L/h) | 0.00668 | 0.00668 | 0.00668 |
| rc1 | 0.931 | 0.931 | 0.931 |
| rc2 | 0.837 | 0.837 | 0.837 |
| (%) | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| (%) | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Dataset I (rv = 5%, N = 24) | Dataset II (rv = 10%, N = 24) | Dataset III (rv = 5%, N = 10) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean PopPK parameters | |||
| rc1 | |||
| %RBIAS | 0.05727019 | 0.3271362 | −0.007274277 |
| %RMSE | 1.227154 | 1.588526 | 2.048936 |
| %RAE | 0.924102 | 1.293161 | 1.535167 |
| rc2 | |||
| %RBIAS | −0.08333982 | −0.2648748 | −0.5783198 |
| %RMSE | 1.627635 | 2.211325 | 2.688598 |
| %RAE | 1.278485 | 1.754442 | 2.116847 |
| CLp | |||
| %RBIAS | −0.01624675 | −0.4528178 | 0.07686021 |
| %RMSE | 0.5339084 | 1.005213 | 0.8498672 |
| %RAE | 0.4371228 | 0.805272 | 0.6663747 |
| IIV terms | |||
| ωCLp | |||
| %RBIAS | 0.7168948 | 9.489459 | −0.341962 |
| %RMSE | 5.340278 | 12.17255 | 9.716216 |
| %RAE | 4.408732 | 10.12623 | 7.257112 |
| ωV | |||
| %RBIAS | 5.636213 | 20.4582 | 4.685937 |
| %RMSE | 8.651427 | 22.61808 | 12.41132 |
| %RAE | 6.85914 | 20.4582 | 9.153764 |
| Parameter | Mean | SE_mean | SD | 2.5% | 50% | 97.5% | Neff |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sigma_1 | 0.0758 | 0.0004 | 0.019 | 0.049 | 0.072 | 0.123 | 1989.956 |
| sigma_2 | 0.2316 | 0.0012 | 0.056 | 0.151 | 0.222 | 0.370 | 2133.417 |
| CLp_mean | 0.0065 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 1157.409 |
| rc1_mean | 0.9584 | 0.0011 | 0.033 | 0.877 | 0.966 | 0.999 | 967.447 |
| rc2_mean | 0.7645 | 0.0008 | 0.031 | 0.709 | 0.762 | 0.830 | 1415.577 |
| ωCLp | 0.0775 | 0.0002 | 0.010 | 0.059 | 0.077 | 0.100 | 2162.507 |
| ωV | 0.0699 | 0.0001 | 0.007 | 0.057 | 0.070 | 0.084 | 2994.706 |
| Parameter | Mean | SE_Mean | SD | 2.5% | 50% | 97.5% | Neff |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sigma_1 | 0.0734 | 0.0001 | 0.007 | 0.061 | 0.073 | 0.089 | 3739.926 |
| sigma_2 | 0.2706 | 0.0005 | 0.033 | 0.215 | 0.268 | 0.343 | 4736.458 |
| CLp_mean | 0.0064 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 910.859 |
| rc1_mean | 0.9504 | 0.0006 | 0.025 | 0.895 | 0.954 | 0.990 | 1680.591 |
| rc2_mean | 0.7674 | 0.0013 | 0.058 | 0.647 | 0.767 | 0.896 | 2126.448 |
| γCLp | 0.1254 | 0.0029 | 0.101 | 0.029 | 0.102 | 0.368 | 1191.566 |
| γrc1 | 0.0338 | 0.0008 | 0.037 | 0.003 | 0.023 | 0.130 | 2152.609 |
| γrc2 | 0.1810 | 0.0029 | 0.125 | 0.054 | 0.148 | 0.496 | 1872.394 |
| ωCLp [1] | 0.1813 | 0.0020 | 0.109 | 0.010 | 0.176 | 0.401 | 2872.073 |
| ωCLp [2] | 0.1138 | 0.0010 | 0.049 | 0.011 | 0.118 | 0.201 | 2430.177 |
| ωCLp [3] | 0.0798 | 0.0002 | 0.012 | 0.059 | 0.079 | 0.104 | 5461.348 |
| ωCLp [4] | 0.0374 | 0.0002 | 0.009 | 0.022 | 0.037 | 0.056 | 2932.790 |
| ωCLp [5] | 0.2002 | 0.0004 | 0.028 | 0.147 | 0.199 | 0.258 | 3961.537 |
| ωV [1] | 0.1676 | 0.0003 | 0.021 | 0.123 | 0.168 | 0.207 | 4222.692 |
| ωV [2] | 0.3213 | 0.0027 | 0.111 | 0.060 | 0.332 | 0.505 | 1657.621 |
| ωV [3] | 0.0733 | 0.0001 | 0.008 | 0.058 | 0.073 | 0.090 | 3424.664 |
| ωV [4] | 0.0960 | 0.0001 | 0.010 | 0.078 | 0.096 | 0.117 | 5452.132 |
| ωV [5] | 0.1000 | 0.0010 | 0.045 | 0.008 | 0.105 | 0.181 | 1906.016 |
| log_CLp [1] | −5.0572 | 0.0013 | 0.068 | −5.205 | −5.056 | −4.928 | 2925.386 |
| log_CLp [2] | −4.9818 | 0.0009 | 0.040 | −5.060 | −4.981 | −4.903 | 2007.067 |
| log_CLp [3] | −5.0418 | 0.0005 | 0.030 | −5.101 | −5.041 | −4.985 | 4136.353 |
| log_CLp [4] | −5.1067 | 0.0004 | 0.028 | −5.162 | −5.106 | −5.054 | 4340.950 |
| log_CLp [5] | −5.1280 | 0.0006 | 0.033 | −5.197 | −5.127 | −5.065 | 3607.724 |
| log_rc1 [1] | −0.0588 | 0.0008 | 0.037 | −0.152 | −0.052 | −0.007 | 1944.272 |
| log_rc1 [2] | −0.0528 | 0.0007 | 0.030 | −0.123 | −0.049 | −0.007 | 1890.579 |
| log_rc1 [3] | −0.0441 | 0.0006 | 0.026 | −0.103 | −0.041 | −0.004 | 1731.245 |
| log_rc1 [4] | −0.0489 | 0.0006 | 0.026 | −0.106 | −0.046 | −0.006 | 1789.105 |
| log_rc1 [5] | −0.0513 | 0.0006 | 0.028 | −0.115 | −0.047 | −0.007 | 2002.731 |
| log_rc2 [1] | −0.4421 | 0.0011 | 0.055 | −0.544 | −0.444 | −0.326 | 2731.710 |
| log_rc2 [2] | −0.2947 | 0.0009 | 0.043 | −0.378 | −0.295 | −0.210 | 2546.313 |
| log_rc2 [3] | −0.2639 | 0.0007 | 0.035 | −0.330 | −0.266 | −0.194 | 2263.931 |
| log_rc2 [4] | −0.1878 | 0.0006 | 0.031 | −0.245 | −0.189 | −0.123 | 2316.835 |
| log_rc2 [5] | −0.2086 | 0.0007 | 0.035 | −0.273 | −0.210 | −0.140 | 2365.040 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karakitsios, E.; Dokoumetzidis, A. A Meta-Analysis Methodology in Stan to Estimate Population Pharmacokinetic Parameters from Multiple Aggregate Concentration–Time Datasets: Application to Gevokizumab mPBPK Model. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16091129
Karakitsios E, Dokoumetzidis A. A Meta-Analysis Methodology in Stan to Estimate Population Pharmacokinetic Parameters from Multiple Aggregate Concentration–Time Datasets: Application to Gevokizumab mPBPK Model. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(9):1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16091129
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarakitsios, Evangelos, and Aristides Dokoumetzidis. 2024. "A Meta-Analysis Methodology in Stan to Estimate Population Pharmacokinetic Parameters from Multiple Aggregate Concentration–Time Datasets: Application to Gevokizumab mPBPK Model" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 9: 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16091129
APA StyleKarakitsios, E., & Dokoumetzidis, A. (2024). A Meta-Analysis Methodology in Stan to Estimate Population Pharmacokinetic Parameters from Multiple Aggregate Concentration–Time Datasets: Application to Gevokizumab mPBPK Model. Pharmaceutics, 16(9), 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16091129







