Characterization of Surfactant Spheroidal Micelle Structure for Pharmaceutical Applications: A Novel Analytical Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
- ATSAS package [5], which includes various programs (PRIMUS, GNOM,…) for SAXS data analysis and structure modeling, provides information such as distance distribution function, gyration radius, molecular weight, flexibility, etc.
- SASView [7], an open-source software designed for scattering analysis with a focus on user-friendliness and data visualization.
- SCATTER [8], a program for the analysis, modeling, and fitting of 1D and 2D SAXS data of non-ordered, partially ordered, or fully ordered nano- and mesoscale structures.
2. The New Graphical-Analytical Approach
3. Application of the Graphical-Analytical Approach to Micelles
3.1. PS20 Micelles
3.2. DPC Micelles
3.3. VitE-TPGS Micelles
3.4. VitE-TPGS Micelles with Eltrombopag (PSC)
3.5. SDS Micelles
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CMC | Critical Micelle Concentration |
| DPC | Dodecyl phosphocholine |
| Pair Distribution Function | |
| PEG | Polyethylene Glycol |
| PSC | Poorly Soluble Compound |
| PS20 | Polysorbate 20 |
| SAXS | Small-Angle X-ray Scattering |
| SDS | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate |
| VitE-TPGS | D-α-tocopherol polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate |
Appendix A. Derivation of the Analytic Formulae
References
- Ivanović, M.T.; Hermann, M.R.; Wójcik, M.; Pérez, J.; Hub, J.S. Small-Angle X-ray Scattering Curves of Detergent Micelles: Effects of Asymmetry, Shape Fluctuations, Disorder, and Atomic Details. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiras, A.; Domingues, C.; Jarak, I.; Santos, A.I.; Parra, A.; Pais, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Concheiro, A.; Kabanov, A.; Cabral, H.; et al. New Advances in Biomedical Application of Polymeric Micelles. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosig, S.; Cucuzza, S.; Serno, T.; Bechtold-Peters, K.; Buecheler, J.; Zivec, M.; Germershaus, O.; Gallou, F. Not the Usual Suspects: Alternative Surfactants for Biopharmaceuticals. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 34540–34553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Caro, L.; Del Giudice, A.; Morin, M.; Reinle-Schmitt, M.; Grandeury, A.; Gozzo, F.; Giannini, C. Small Angle X-Ray Scattering Data Analysis and Theoretical Modelling for the Size and Shape Characterization of Drug Delivery Systems Based on Vitamin E TPGS Micelles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manalastas-Cantos, K.; Konarev, P.V.; Hajizadeh, N.R.; Kikhney, A.G.; Petoukhov, M.V.; Molodenskiy, D.S.; Panjkovich, A.; Mertens, H.D.T.; Gruzinov, A.; Borges, C.; et al. ATSAS 3.0: Expanded functionality and new tools for small-angle scattering data analysis. J. Appl. Cryst. 2021, 54, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Hammel, M.; Tainer, J.A.; Sali, A. Accurate SAXS profile computation and its assessment by contrast variation experiments. Biophys. J. 2013, 105, 962–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Hammel, M.; Tainer, J.A.; Sali, A. FoXS, FoXSDock and MultiFoXS: Single-state and multi-state structural modeling of proteins and their complexes based on SAXS profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W424–W429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förster, S.; Apostol, L.; Bras, W. Scatter: Software for the analysis of nano- and mesoscale small-angle scattering. J. Appl. Cryst. 2010, 43, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piiadov, V.; de Araujo, E.A.; de Oliveira Neto, M.; Craievich, A.F.; Polikarpov, I. SAXSMoW 2.0: Online calculator of the molecular weight of proteins in dilute solution from experimental SAXS data measured on a relative scale. Protein Sci. 2019, 28, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Neto, M.; de Freitas Fernandes, A.; Piiadov, V.; Craievich, A.F.; de Araújo, E.A.; Polikarpov, I. SAXSMoW 3.0: New advances in the determination of the molecular weight of proteins in dilute solutions from SAXS intensity data on a relative scale. Prot. Sci. 2021, 31, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pambou, E.; Crewe, J.; Yaseen, M.; Padia, F.N.; Rogers, S.; Wang, D.; Xu, H.; Lu, J.R. Structural Features of Micelles of Zwitterionic Dodecylphosphocholine (C12PC) Surfactants Studied by Small-Angle Neutron Scattering. Langmuir 2015, 31, 9781–9789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrit, G.; Grawert, T.W.; Goddeke, H.; Konarev, P.V.; Svergun, D.I.; Nagel, N. Small-angle x-ray scattering investigation of the integration of free fatty acids in polysorbate 20 micelles. Biophys. J. 2023, 122, 3078–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozza, A.; Bonneté, F. Analysis and modeling of SDS and DPC micelle SAXS data for membrane protein solution structure characterization. Data Brief 2023, 47, 10891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svergun, D.I.; Koch, M.H.J. Small-angle scattering studies of biological macromolecules in solution. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2003, 66, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoulis, A. Probability & Statistics; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Le Maire, M.; Champeil, P.; Møller, J.V. Interaction of membrane proteins and lipids with solubilizing detergents. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1508, 86–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putnam, C.D. Guinier peak analysis for visual and automated inspection of small-angle X-ray scattering data. J. Appl. Cryst. 2016, 49, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israelachvili, J.N.; Mitchel, D.J.; Ninham, B.W. Theory of Self-Assembly of Hydrocarbon Amphiphiles into Micelles and Bilayers. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1976, 72, 1525–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanford, C. The Hydrophobic Effect: Formation of Micelles and Biological Membranes, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Glatter, O. Scattering Methods and Their Application in Colloid and Interface Science, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
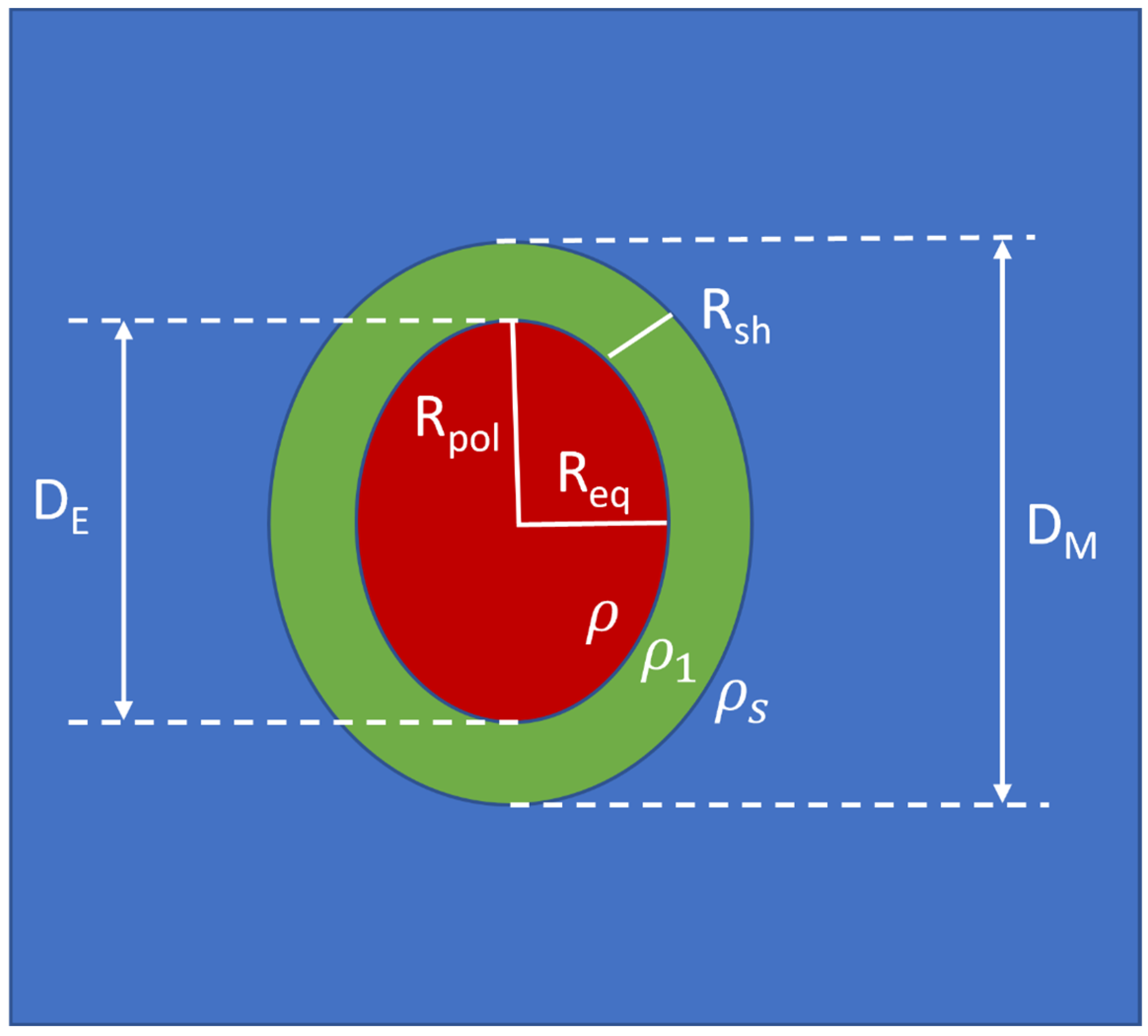



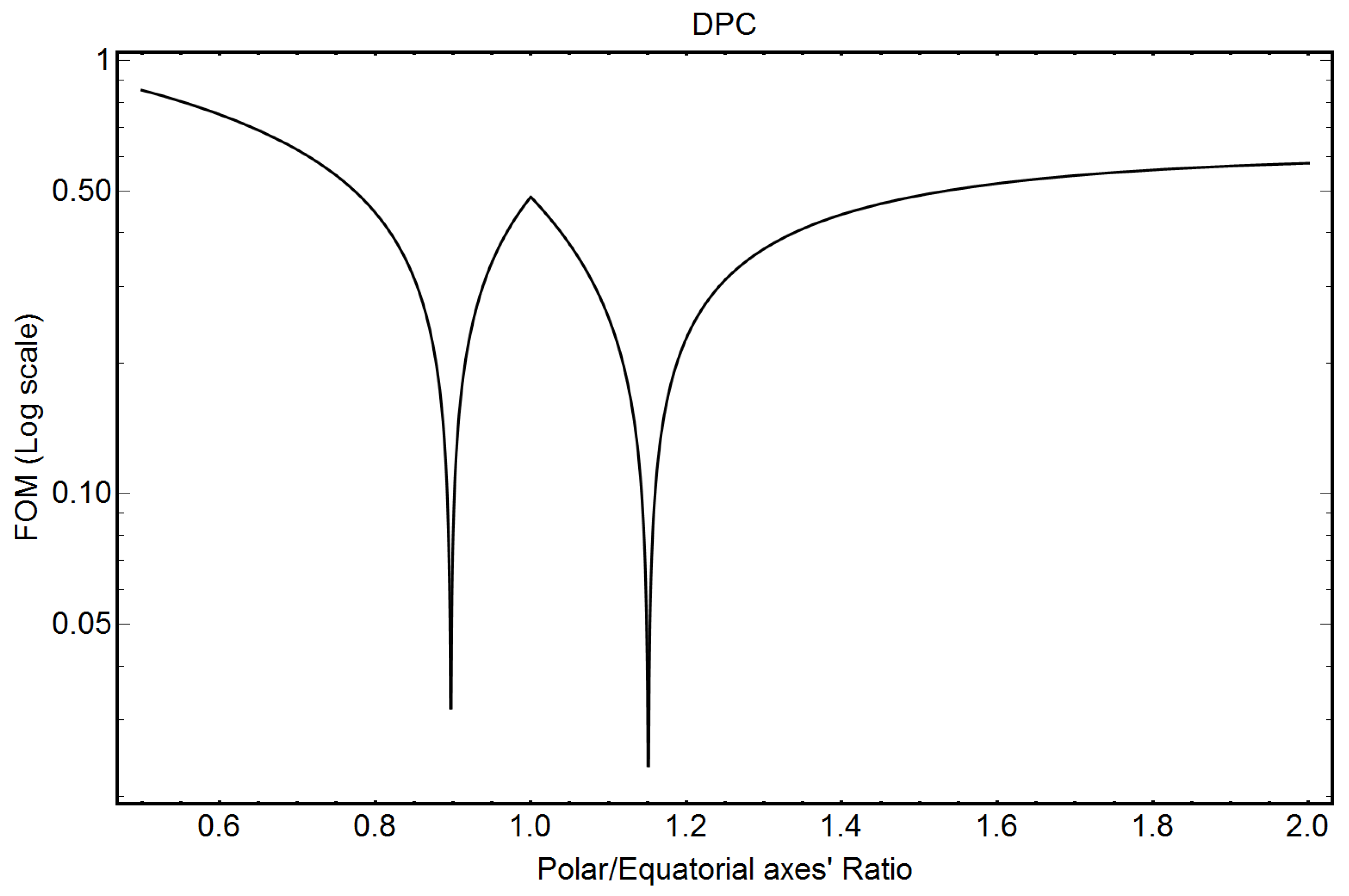



| Compound | Mole Mass (g) | Ne = ne/Molecule | Monomer or Molecule Volume (Å3) | Mole/L | ne/L | Electron Density ρ (ne/Å3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS20 C58H114O26 | 1227.54 | 670 | 1771 | 0.938 | 616.4 × NA | 0.378 |
| Water H2O | 18.016 | 10 | 29.9 | 55.51 | 555.1 × NA | 0.334 |
| Method | Rsh (Å) | DM (Å) | DM/2 − Rsh (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Published [12] | 8.8 ± 0.7 | 86.0 ± 0.5 | 36.8 ± 0.7 (*) |
| Graphical | 9.0 ± 0.5 | 86.0 ± 0.5 | 34.1 ± 0.5 |
| Method | ε | Nagg | (ne/Å3) | (ne/Å3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Published [12] | 1.50 ± 0.06 | 34 | −0.035 ± 0.002 | 0.060 ± 0.004 |
| Published [12] | 1.50 ± 0.06 | 34 | −0.031 ± 0.002 | 0.064 ± 0.003 |
| Analytical | 1.47 ± 0.01 | 35 ± 1 | −0.030 ± 0.002 | 0.050 ± 0.005 |
| Compound | Mole Mass (g) | Ne = ne/Molecule | Monomer or Molecule Volume (Å3) | Mole/L | ne/L | Electron Density ρ (ne/Å3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPC C17H38NO4P | 351.5 | 194 | 548 | 3.03 | 587.9 × NA | 0.354 |
| H2O | 18.016 | 10 | 29.9 | 55.51 | 555.1 × NA | 0.334 |
| Method | Rsh (Å) | DM (Å) | DM/2 − Rsh (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Published [13] | 6.83 ± 0.22 | 58.1 ± 1.2 | 22.21 ± 0.38 |
| Graphical | 6.8 ± 0.5 | 58.0 ± 0.5 | 22.2 ± 0.5 |
| Method | ε | Nagg | (ne/Å3) | (ne/Å3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Published [13] | 1.52 ± 0.014 | 56 | −0.066 ± 0.003 | 0.054 ± 0.004 |
| Analytical | 1.15 ± 0.07 | 57 | −0.043 ± 0.003 | 0.041 ± 0.007 |
| Analytical | 0.90 ± 0.07 | 57 | −0.041 ± 0.003 | 0.038 ± 0.007 |
| Compound | Mole Mass (g) | Ne = ne/Molecule | Monomer or Molecule Volume (Å3) | Mole/L | ne/L | Electron Density ρ (ne/Å3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| vitE-TPGS C33O5H54(CH2CH2O)n n = 0.7 × 22 + 0.3 × 23 | 1513.1 | 827 | 2327 | 0.716 | 592.1 × NA | 0.357 |
| H2O | 18.016 | 10 | 29.9 | 55.51 | 555.1 × NA | 0.334 |
| Method | Rsh (Å) | σ (Å) | DM + σ (*) (Å) | DM − 2Rsh + σ (*) (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Published [4] | 16.8 ± 1.0 | 28.0 ± 0.5 | 119.5 ± 1.0 | 85.9 ± 2.5 |
| Graphical | 16.1 ± 0.5 | 0 | 121.0 ± 1.0 | 88.8 ± 1.5 |
| Method | (ne/Å3) | (ne/Å3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Published [4] | −0.037 ± 0.001 | 0.037 ± 0.001 | 1 (assumed) | 116 ± 1 |
| Analytical | −0.029 ± 0.004 | 0.033 ± 0.002 | 1.41 ± 0.002 | 125 ± 1 |
| Method | Rsh (Å) | σ (Å) | DM + σ (*) (Å) | DM − 2Rsh + σ (*) (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Published [4] | 18.7 ± 1.0 | 29.0 ± 0.5 | 116.5 ± 1.0 | 79.1 ± 2.5 |
| Graphical | 17.7 ± 0.5 | 0 | 116.9 ± 1.0 | 81.5 ± 1.5 |
| Method | (ne/Å3) | (ne/Å3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Published [4] | −0.055 ± 0.001 | 0.045 ± 0.001 | 1 (assumed) | 117 ± 1 |
| Analytical | −0.046 ± 0.002 | 0.043 ± 0.002 | 1.45 ± 0.001 | 123 ± 1 |
| Compound | Mole Mass (g) | Ne = ne/Molecule | Monomer or Molecule Volume (Å3) | Mole/L | ne/L | Electron Density ρ (ne/Å3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDS C12H25SO4Na | 288.4 | 156 | 435.4 | 3.81 | 595.0 × NA | 0.358 |
| H2O | 18.016 | 10 | 29.9 | 55.51 | 555.1 × NA | 0.334 |
| Method | Rsh (Å) | DM (Å) | DM/2 − Rsh (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Published [13] | 4.85 ± 0.17 | 72.07 ± 4.32 | 31.185 ± 1.99 |
| Graphical | 6.6 ± 0.5 | 73.0 ± 0.5 | 29.9 ± 0.5 |
| Method | ε | Nagg | (ne/Å3) | (ne/Å3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Published [13] | 1.75 ± 0.11 | 90, 118 | −0.073 ± 0.006 | 0.138 ± 0.004 |
| Analytical | 1.60 ± 0.07 | 96 ± 1 | −0.082 ± 0.010 | 0.105 ± 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Caro, L.; Stoll, T.; Grandeury, A.; Gozzo, F.; Giannini, C. Characterization of Surfactant Spheroidal Micelle Structure for Pharmaceutical Applications: A Novel Analytical Framework. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050604
De Caro L, Stoll T, Grandeury A, Gozzo F, Giannini C. Characterization of Surfactant Spheroidal Micelle Structure for Pharmaceutical Applications: A Novel Analytical Framework. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(5):604. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050604
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Caro, Liberato, Thibaud Stoll, Arnaud Grandeury, Fabia Gozzo, and Cinzia Giannini. 2024. "Characterization of Surfactant Spheroidal Micelle Structure for Pharmaceutical Applications: A Novel Analytical Framework" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 5: 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050604
APA StyleDe Caro, L., Stoll, T., Grandeury, A., Gozzo, F., & Giannini, C. (2024). Characterization of Surfactant Spheroidal Micelle Structure for Pharmaceutical Applications: A Novel Analytical Framework. Pharmaceutics, 16(5), 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050604






