Performance Characterisation of the Airvo2TM Nebuliser Adapter in Combination with the Aerogen SoloTM Vibrating Mesh Nebuliser for in Line Aerosol Therapy during High Flow Nasal Oxygen Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. High Flow Nasal Oxygen Therapy System
2.2. Nebuliser
2.3. System Characterisation
2.3.1. Emitted Dose
2.3.2. Tracheal Dose
2.3.3. Droplet Size Characterisation—Mass Median Aerodynamic Diameter (MMAD)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Emitted Dose
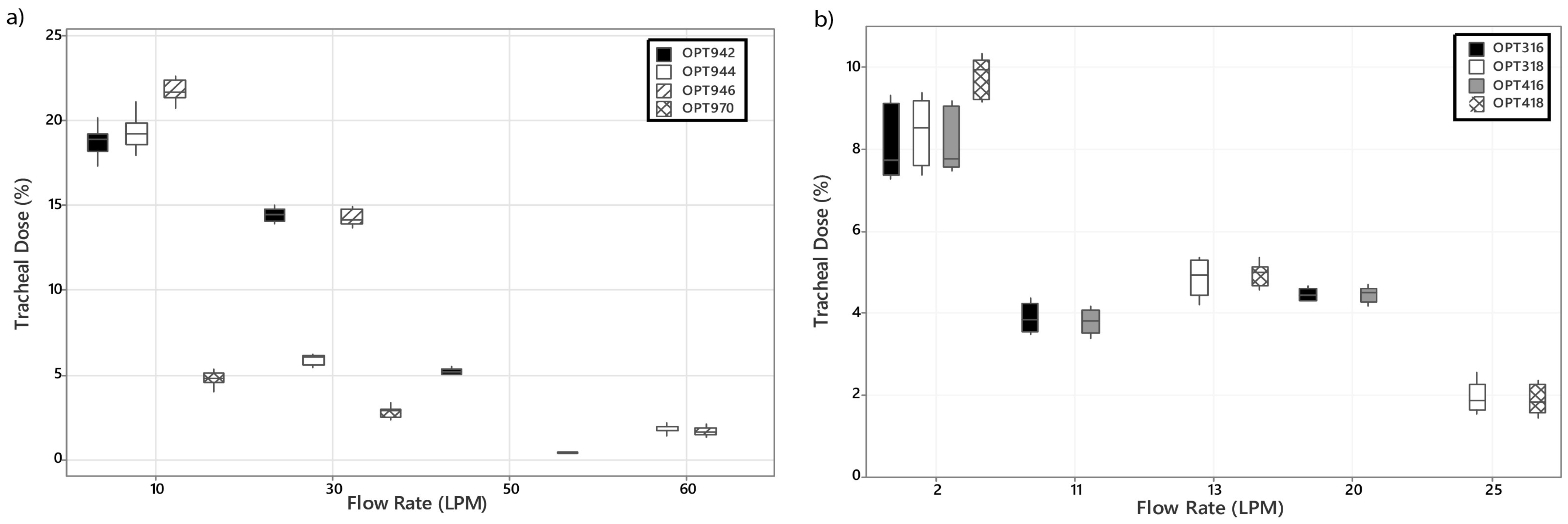
3.2. Tracheal Dose
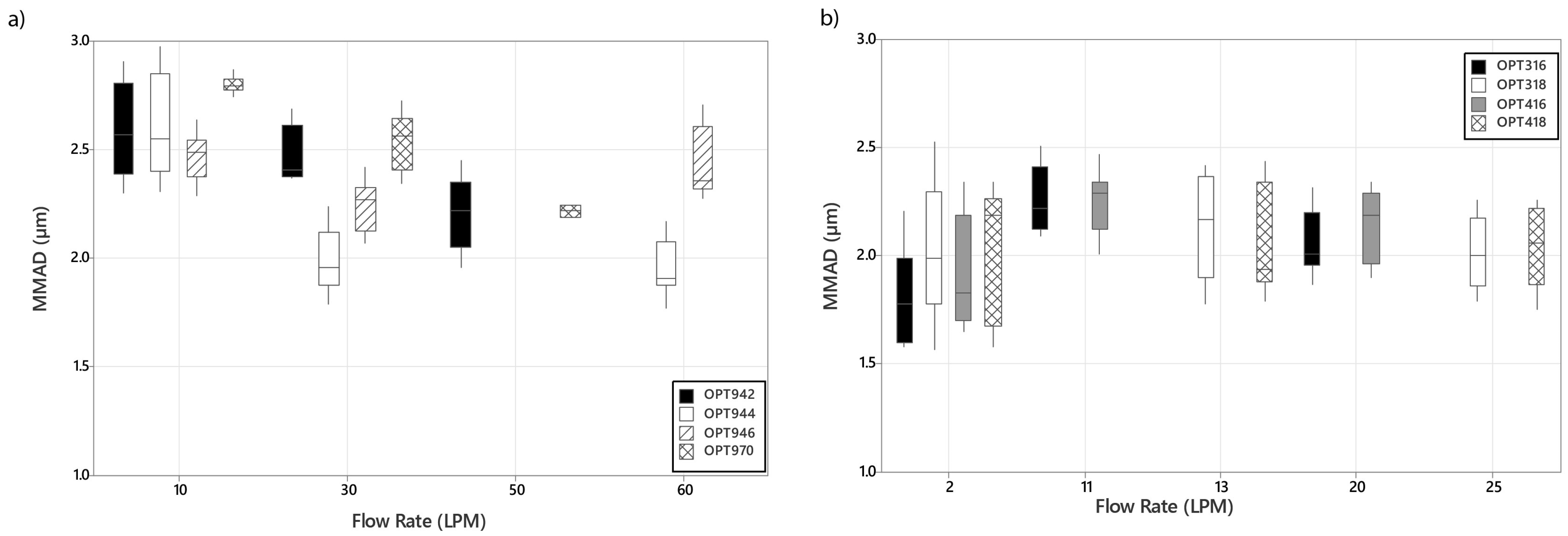
3.3. MMAD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soriano, J.B.; Kendrick, P.J.; Paulson, K.R.; Gupta, V.; Abrams, E.M.; Adedoyin, R.A.; Adhikari, T.B.; Advani, S.M.; Agrawal, A.; Ahmadian, E.; et al. Prevalence and attributable health burden of chronic respiratory diseases, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, J.F.; Spooner, A.J.; Dunster, K.R.; Anstey, C.M.; Corley, M. Nasal high flow oxygen therapy in patients with COPD reduces respiratory rate and tissue carbon dioxide while increasing tidal and end-expiratory lung volumes: A randomised crossover trial Research letter. Thorax 2016, 71, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, C.; Annunziata, A.; Mariniello, D.F.; Allocca, V.; Imitazione, P.; Cauteruccio, R.; Simioli, F.; Fiorentino, G. Aerosol delivery through high-flow nasal therapy: Technical issues and clinical benefits. Front. Med. 2023, 9, 1098427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Batu, W.; You, S.; Tong, Z.; He, H. High-Flow Nasal Cannula: A Promising Oxygen Therapy for Patients with Severe Bronchial Asthma Complicated with Respiratory Failure. Can. Respir. J. 2020, 2020, 2301712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, S.; Valentine, M.; Chua, W.H.; Tatkov, S. Impact of high-and low-flow nebulised saline on airway hydration and mucociliary transport. ERJ Open Res. 2023, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eain, M.M.G.; MacLoughlin, R. In-Line Aerosol Therapy via Nasal Cannula during Adult and Paediatric Normal, Obstructive, and Restrictive Breathing. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Williams, L.; Fink, J.B. The Impact of High-Flow Nasal Cannula Device, Nebulizer Type, and Placement on Trans-Nasal Aerosol Drug Delivery: An In Vitro Study. Respir. Care 2022, 67, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Gong, L.; Fink, J.B. The ratio of nasal cannula gas flow to patient inspiratory flow on trans-nasal pulmonary aerosol delivery for adults: An in vitro study. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golshahi, L.; Longest, P.W.; Azimi, M.; Syed, A.; Hindle, M. Intermittent aerosol delivery to the lungs during high-flow nasal cannula therapy. Respir. Care 2014, 59, 1476–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcane, L.; Vecellio, L.; Delval, G.; Reychler, G.; Reychler, H.; Liistoro, G. Aerosol Delivery Through Tracheostomy Tubes: An in-vitro study. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2013, 26, 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Madney, Y.M.; Fathy, M.; Elberry, A.A.; Rabea, H.; Abdelrahim, M.E.A. Aerosol delivery through an adult high-flow nasal cannula circuit using low-flow oxygen. Respir. Care 2019, 64, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madney, Y.M.; Laz, N.I.; Elberry, A.A.; Rabea, H.; Abdelrahim, M.E.A. Aerosol delivery aspects within a high-flow therapy system in copd patients. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beuvon, C.M.; Coudroy, R.M.; Bardin, J.; Marjanovic, N.; Rault, C.; Bironneau, V.; Drouot, X.; Robert, R.; Thille, A.W.; Frat, J.P. β Agonist Delivery by High-Flow Nasal Cannula During COPD Exacerbation: A Prospective Physiological Study. Respir. Care 2022, 67, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugernier, J.; Hesse, M.; Jumetz, T.; Bialais, E.; Roeseler, J.; Depoortere, V.; Michotte, J.B.; Wittebole, X.; Ehrmann, S.; Laterre, P.F.; et al. Aerosol Delivery with Two Nebulizers Through High-Flow Nasal Cannula: A Randomized Cross-Over Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography-Computed Tomography Study. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2017, 30, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denise Willis, L.; Berlinski, A. Survey of aerosol delivery techniques to spontaneously breathing tracheostomized children. Respir. Care 2012, 57, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Fink, J.B.; MacLoughlin, R.; Dhand, R. A narrative review on trans-nasal pulmonary aerosol delivery. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, G.; Joyce, M.; Sweeney, L.; MacLoughlin, R. In Vitro Determination of the Main Effects in the Design of High-Flow Nasal Therapy Systems with Respect to Aerosol Performance. Pulm. Ther. 2018, 4, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, B.; Eain, M.M.G.; Joyce, M.; Fink, J.B.; MacLoughlin, R. Evaluation of aerosol drug delivery with concurrent low and high flow nasal oxygen. ERJ Open Res. 2022, 8, 00220-02022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, G.; Joyce, M.; Sweeney, L.; MacLoughlin, R. In Vitro Study of the Effect of Breathing Pattern on Aerosol Delivery during High-Flow Nasal Therapy. Pulm. Ther. 2019, 5, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Leime, C.O.; Gao, W.; MacLoughlin, R. Aerosol delivery in models of pediatric high flow nasal oxygen and mechanical ventilation. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2023, 58, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réminiac, F.; Vecellio, L.; Loughlin, R.M.; Le Pennec, D.; Cabrera, M.; Vourc’h, N.H.; Fink, J.B.; Ehrmann, S. Nasal high flow nebulization in infants and toddlers: An in vitro and in vivo scintigraphic study. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2017, 52, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trachsel, D.; Hammer, J. Indications for tracheostomy in children. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2006, 7, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhand, R. Special problems in aerosol delivery: Artificial airways. Respir. Care 2000, 45, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ari, A.; Harwood, R.J.; Sheard, M.M.; Fink, J.B. An in vitro evaluation of aerosol delivery through tracheostomy and endotracheal tubes using different interfaces. Respir. Care 2012, 57, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhamad, B.R.; Fink, J.B.; Harwood, R.J.; Sheard, M.M.; Ari, A. Effect of aerosol devices and administration techniques on drug delivery in a simulated spontaneously breathing pediatric tracheostomy model. Respir. Care 2015, 60, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattinoni, L.; Caironi, P.; Cressoni, M.; Chiumello, D.; Ranieri, V.M.; Quintel, M.; Russo, S.; Patroniti, N.; Cornejo, R.; Bugedo, G. Lung Recruitment in Patients with the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1775–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugis, A.A.; Sheard, M.M.; Fink, J.B.; Harwood, R.J.; Ari, A. Comparison of aerosol delivery by face mask and tracheostomy collar. Respir. Care 2015, 60, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarroel, G.S.; Faúndez, M.; Jalil, Y.F.; Oyarzún, I.J.; Fernandez, T.R.; Barañao, P.I.; Mendez, M.P.; Muñoz, S.R. Factors Associated With Accidental Decannulation in Tracheostomized Children. Respir. Care 2023, 68, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, H.M.; Krijgsman, A.; Verbraak, T.F.M.; Hop, W.C.J.; Jongste, J.C.D. Determining Factors of Aerosol Deposition for Four pMDI-Spacer Combinations in an Infant Upper Airway Model. J. Aerosol. Med. 2004, 17, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO27427; Anaesthetic and Respiratory Equipment—Nebulizing Systems and Components. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/59482.html (accessed on 10 November 2018).
- Pharmacopoeia, E. Inhalation: Aerodynamic assessment of fine particles Fine particle dose and particle size distribution. Connect 2005.
- USP 1601 Products for Nebulisation—Characterisation Tests. 2018. Available online: https://doi.usp.org/USPNF/USPNF_M4347_03_01.html (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Dailey, P.A.; Harwood, R.; Walsh, K.; Fink, J.B.; Thayer, T.; Gagnon, G.; Ari, A. Aerosol delivery through adult high flow nasal cannula with heliox and oxygen. Respir. Care 2017, 62, 1186–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, S.A.; Kesser, K.C.; Geller, D.E.; Selhorst, D.M.; Rendle, J.K.; Hertzog, J.H. Influences of cannula size and flow rate on aerosol drug delivery through the Vapotherm humidified high-flow nasal cannula system. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 14, e250–e256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golshahi, L.; Walenga, R.L.; Longest, P.W.; Hindle, M. Development of a transient flow aerosol mixer-heater system for lung delivery of nasally administered aerosols using a nasal cannula. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Ehrmann, S.; Wu, J.; Xie, L. Bronchodilator Delivery via High-Flow Nasal Cannula: A Randomized Controlled Trial to Compare the Effects of Gas Flows. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.G.; Gentle, M.A.; Tyler, L.M.; Napolitano, N. High-flow nasal cannula in pediatric patients: A survey of clinical practice. Respir. Care 2018, 63, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, T.E.; Saville, A.; Adams, P.S.; Johnston, D.J.; Czachowski, M.R.; Domnina, Y.A.; Lin, J.H.; Weiner, D.J.; Huber, A.S.; Sanchez De Toledo, J.; et al. Deposition studies of aerosol delivery by nasal cannula to infants. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, D.R. Aerosol delivery devices in the treatment of asthma. Respir. Care 2008, 53, 699–723. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, J.; Kline, L.C.; Sherwood, J.K.; Chaudhry, S.; Obenauer-Kutner, L.; Hart, J.L.; Sequeira, J. Influence of the size of micronized active pharmaceutical ingredient on the aerodynamic particle size and stability of a metered dose inhaler. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2004, 30, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhashyam, A.R.; Wolf, M.T.; Marcinkowski, A.L.; Saville, A.; Thomas, K.; Carcillo, J.A.; Corcoran, T.E. Aerosol delivery through nasal cannulas: An in vitro study. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2008, 21, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

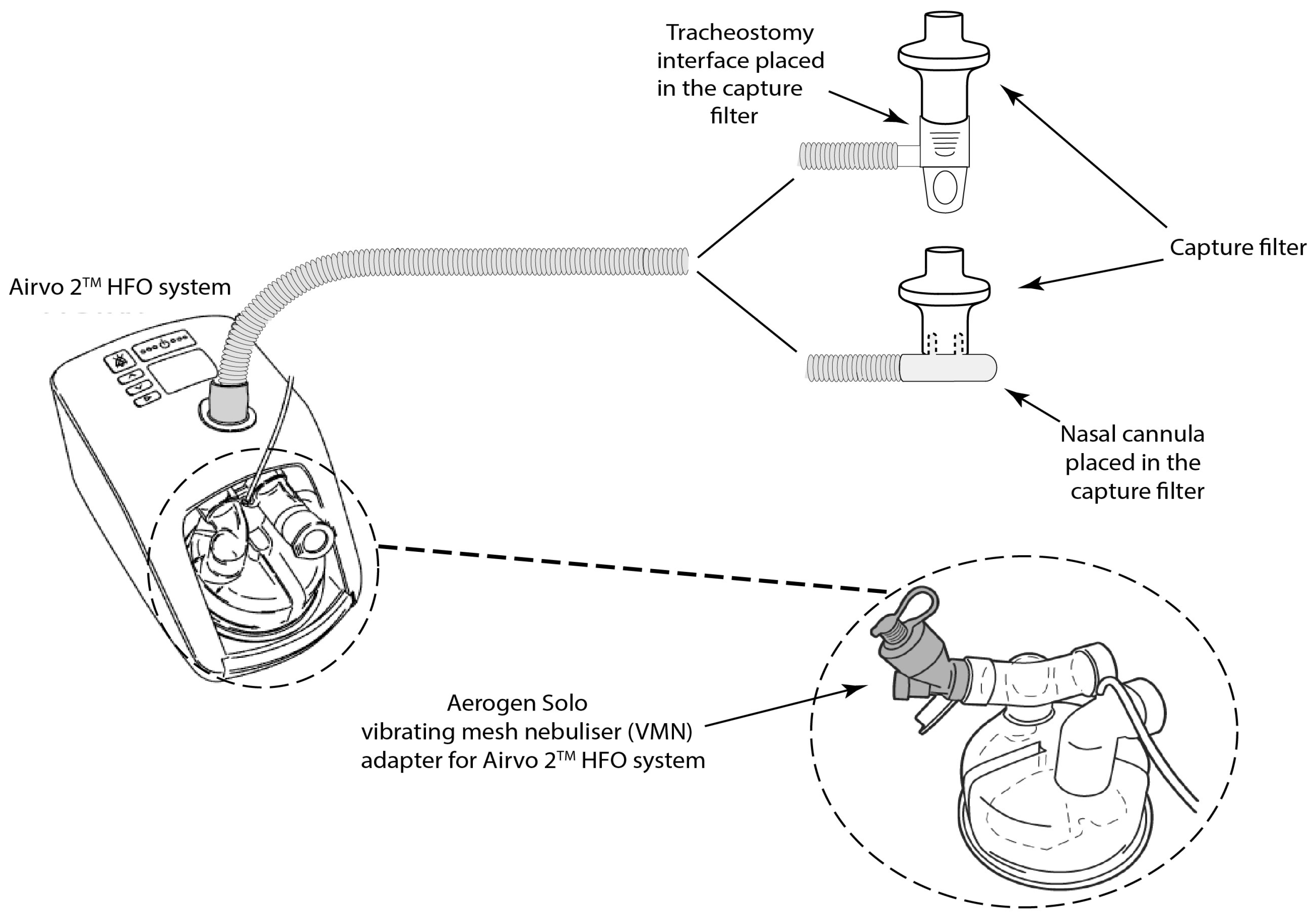
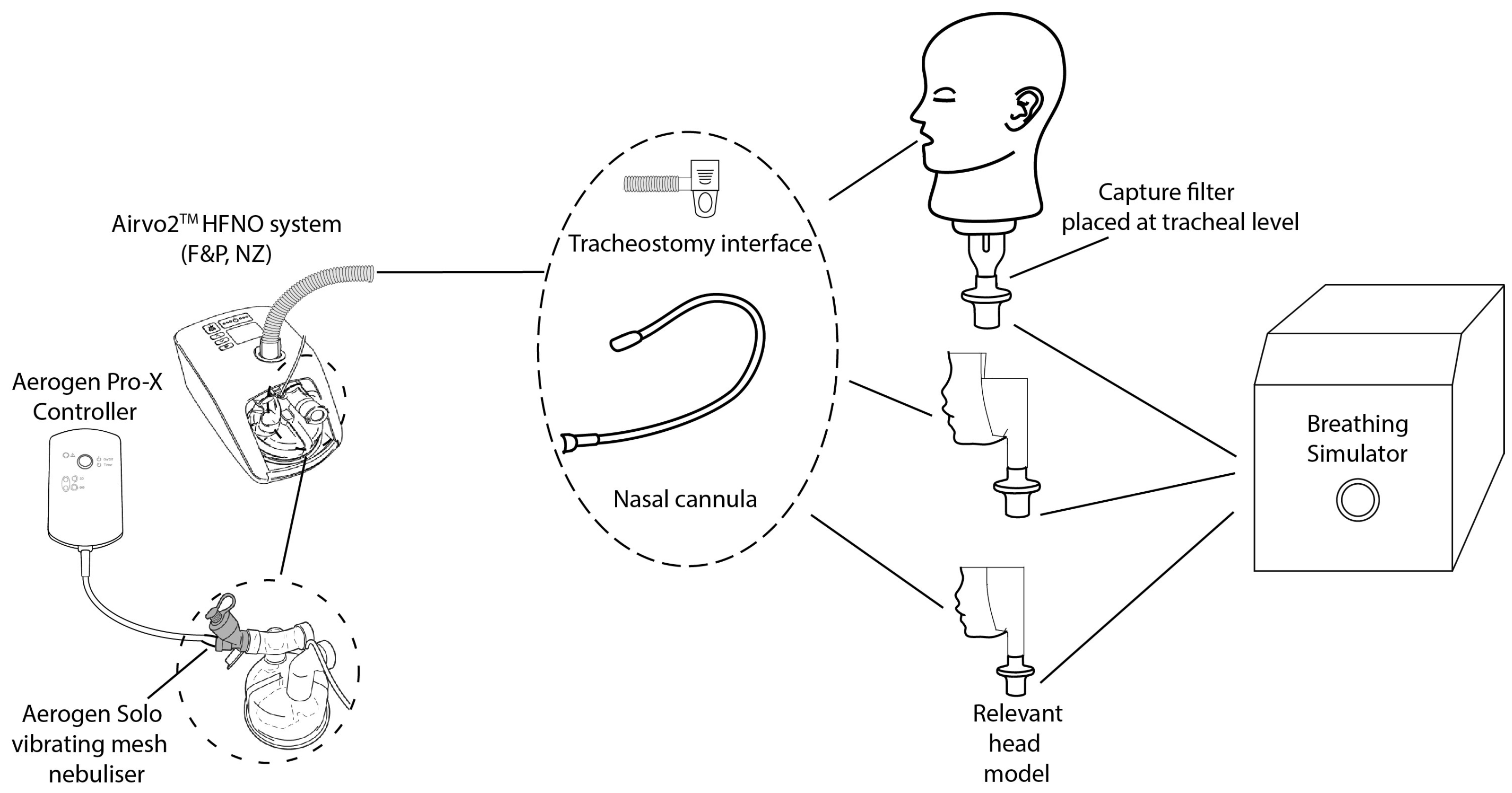

| Cannula Reference | Size | Approved Gas Flow Rate Range (LPM) |
|---|---|---|
| OPT942 | Small Adult Cannula | 10–50 |
| OPT944 | Medium Adult Cannula | 10–60 |
| OPT946 | Large Adult Cannula | 10–60 |
| OPT316 | Infant Nasal Cannula | 2–20 |
| OPT318 | Paediatric Nasal Cannula | 2–25 |
| OPT416 | Infant Nasal Cannula | 2–20 |
| OPT418 | Paediatric Nasal Cannula | 2–25 |
| OPT970 | Tracheostomy Interface | 10–60 |
| Head Model | Paediatric | Adult | Adult | Adult |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas Flow (LPM) | OPT942 * (S) | OPT944 (M) | OPT946 (L) | OPT970 |
| 10 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 30 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 50 | ✓ | Not tested | Not tested | ✓ |
| 60 | Not tested | ✓ | ✓ | Not tested |
| Head Model | Infant | Paediatric | Infant | Paediatric |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas Flow (LPM) | OPT316 | OPT318 | OPT416 | OPT418 |
| 2 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 11 | ✓ | Not tested | ✓ | Not tested |
| 13 | Not tested | ✓ | Not tested | ✓ |
| 20 | ✓ | Not tested | ✓ | Not tested |
| 25 | Not tested | ✓ | Not tested | ✓ |
| Head Model | Tidal Volume (mL) | Breaths per Minute | I/E Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adult | 500 | 15 | 1:1 |
| Paediatric | 155 | 25 | 1:2 |
| Infant | 50 | 30 | 1:3 |
| Gas Flow (LPM) | OPT942 | OPT944 | OPT946 | p-Value | OPT970 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 2.59 ± 0.21 | 2.62 ± 0.24 | 2.47 ± 0.11 | 0.247 | 2.81 ± 0.03 |
| 30 | 2.50 ± 0.13 | 2.00 ± 0.15 | 2.24 ± 0.12 | 0.000 | 2.54 ± 0.15 |
| 50 | 2.21 ± 0.17 | Not tested | Not tested | - | 2.22 ± 0.03 |
| 60 | Not tested | 1.96 ± 0.13 | 2.45 ± 0.16 | 0.000 | Not tested |
| p-value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| Gas Flow (LPM) | OPT316 | OPT416 | p-Value | OPT318 | OPT418 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1.80 ± 0.23 | 1.93 ± 0.26 | 0.089 | 2.02 ± 0.31 | 2.04 ± 0.31 | 0.740 |
| 11 | 2.27 ± 0.16 | 2.24 ± 0.14 | 0.444 | Not tested | - | |
| 13 | Not tested | - | 2.14 ± 0.24 | 2.06 ± 0.25 | 0.119 | |
| 20 | 2.06 ± 0.15 | 2.14 ± 0.17 | 0.091 | Not tested | - | |
| 25 | Not tested | - | 2.01 ± 0.17 | 2.03 ± 0.19 | 0.232 | |
| p-value | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.491 | 0.975 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
MacLoughlin, R.; Mac Giolla Eain, M. Performance Characterisation of the Airvo2TM Nebuliser Adapter in Combination with the Aerogen SoloTM Vibrating Mesh Nebuliser for in Line Aerosol Therapy during High Flow Nasal Oxygen Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040565
MacLoughlin R, Mac Giolla Eain M. Performance Characterisation of the Airvo2TM Nebuliser Adapter in Combination with the Aerogen SoloTM Vibrating Mesh Nebuliser for in Line Aerosol Therapy during High Flow Nasal Oxygen Therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(4):565. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040565
Chicago/Turabian StyleMacLoughlin, Ronan, and Marc Mac Giolla Eain. 2024. "Performance Characterisation of the Airvo2TM Nebuliser Adapter in Combination with the Aerogen SoloTM Vibrating Mesh Nebuliser for in Line Aerosol Therapy during High Flow Nasal Oxygen Therapy" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 4: 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040565
APA StyleMacLoughlin, R., & Mac Giolla Eain, M. (2024). Performance Characterisation of the Airvo2TM Nebuliser Adapter in Combination with the Aerogen SoloTM Vibrating Mesh Nebuliser for in Line Aerosol Therapy during High Flow Nasal Oxygen Therapy. Pharmaceutics, 16(4), 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040565






