68Ga-DOTA-D-Alanine-BoroPro Radiotracer for Imaging of the Fibroblast Activation Protein in Malignant and Non-Malignant Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Methodology
2.2. DOTA-iFAP Synthesis
2.3. Chemical Characterization
2.4. Preparation of 68Ga-iFAP
2.5. Radiochemical Purity
2.6. Stability
2.7. Biological Characterization
2.7.1. Cell Culture
2.7.2. Binding Assay
2.7.3. Western Blot Assay
2.7.4. Immunofluorescence
2.7.5. Internalization and Uptake by Cancer Cells
2.7.6. Biodistribution
2.7.7. Infarcted Mouse Model Ex Vivo Imaging
2.7.8. Immunohistochemistry
2.8. Clinical Imaging
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Molecular Docking
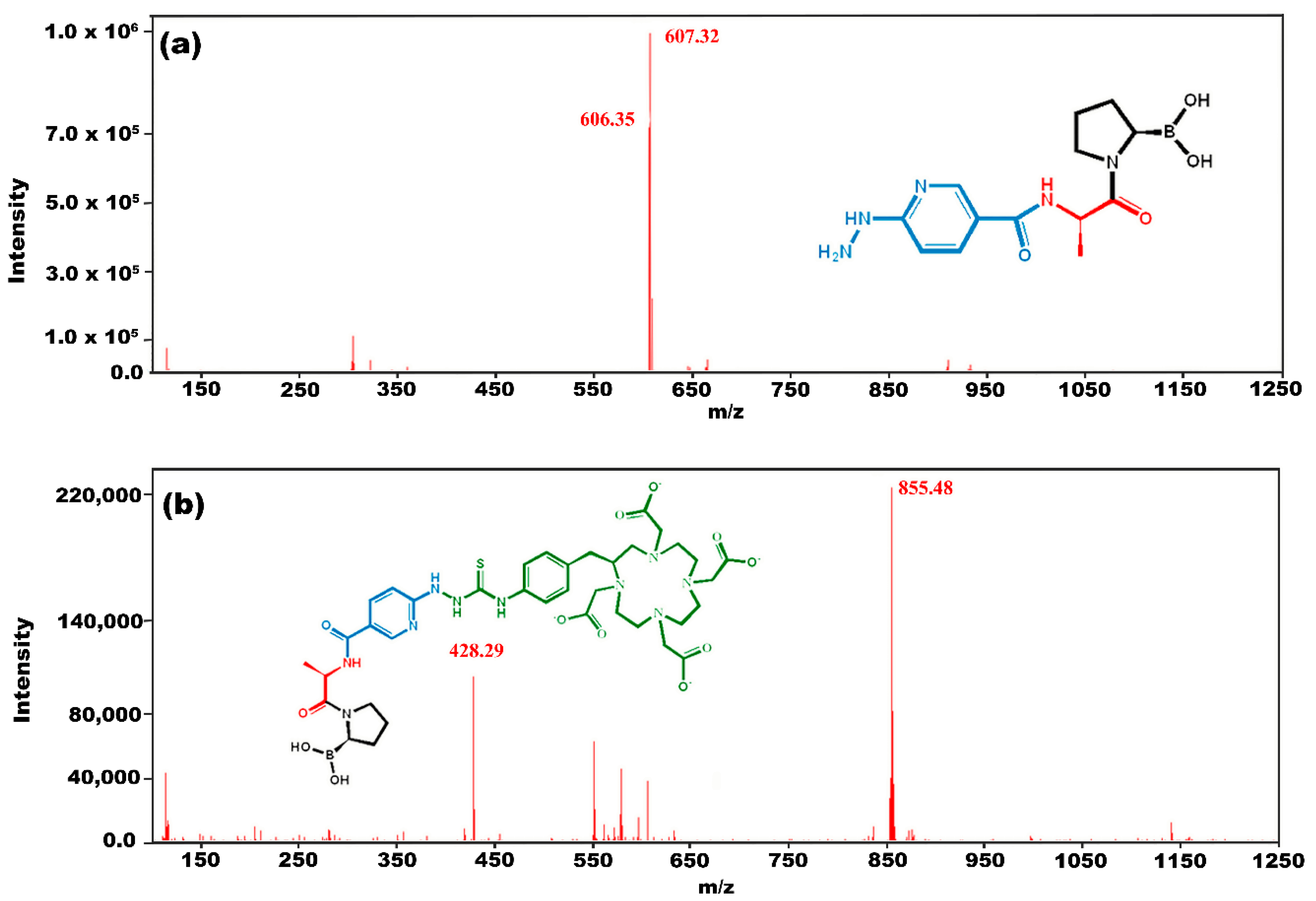
3.2. Chemical Synthesis
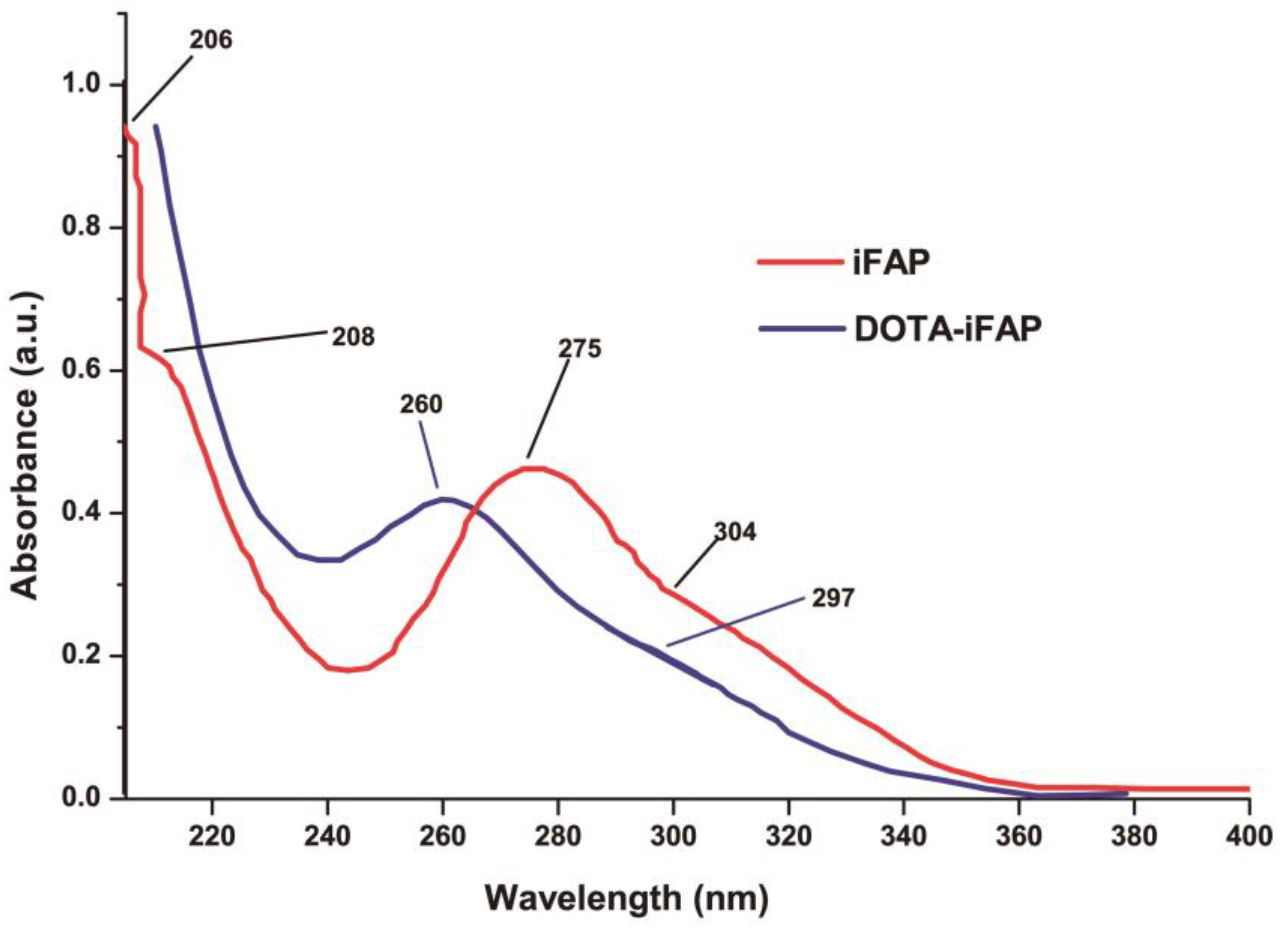
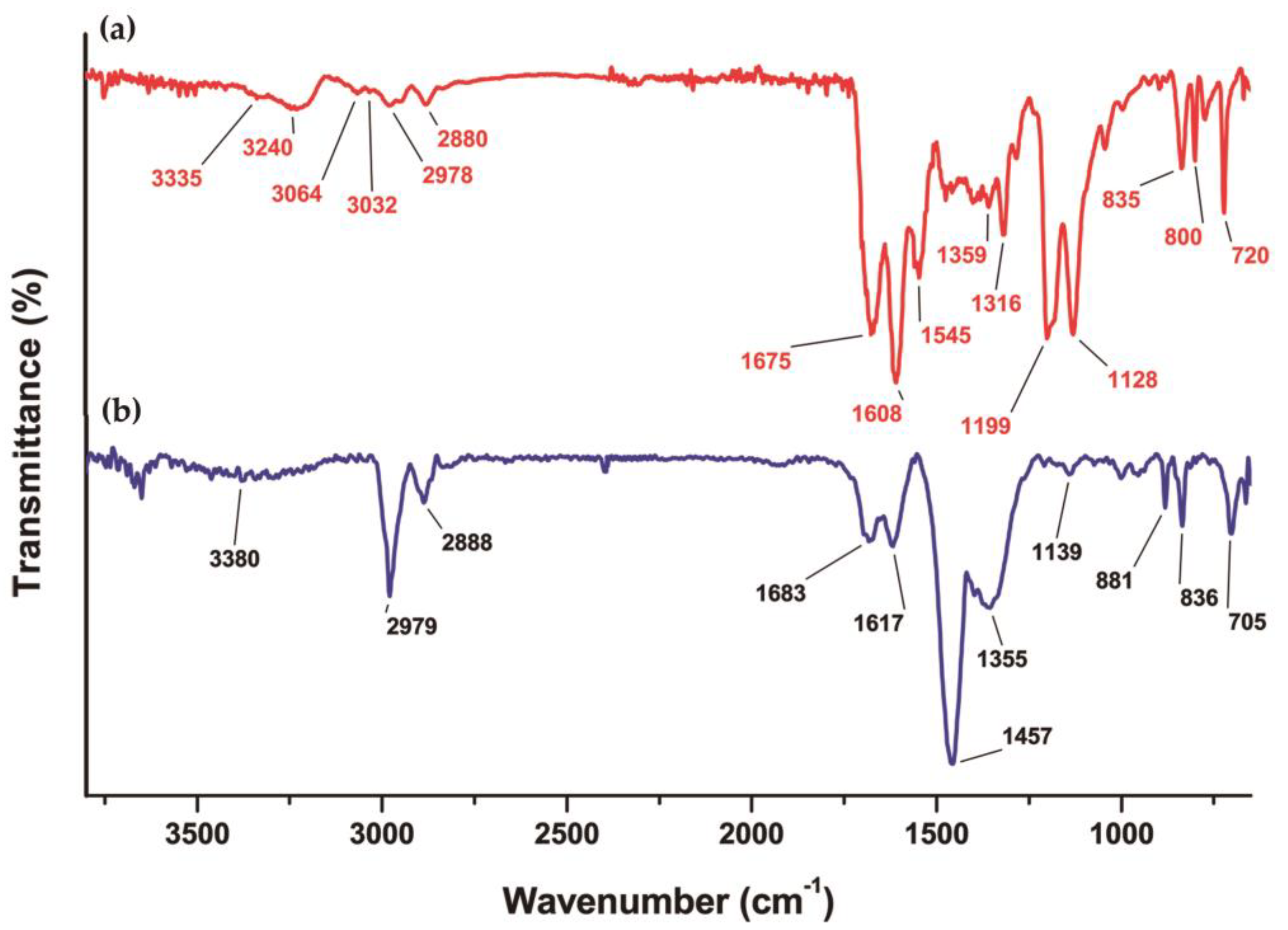
3.3. Chemical Evaluation
3.3.1. DOTA-iFAP
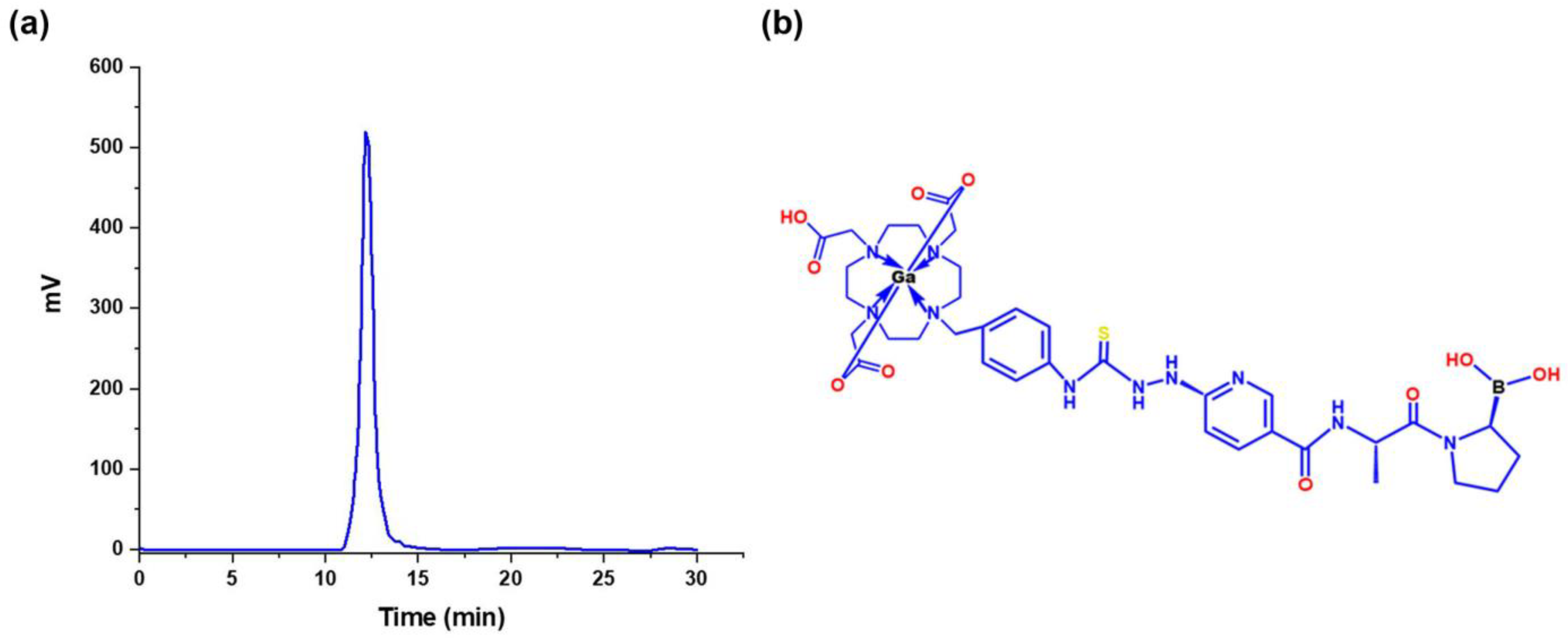
3.3.2. 68Ga-iFAP Radiochemical Purity
3.3.3. 68Ga-iFAP Stability
3.4. Biological Characterization
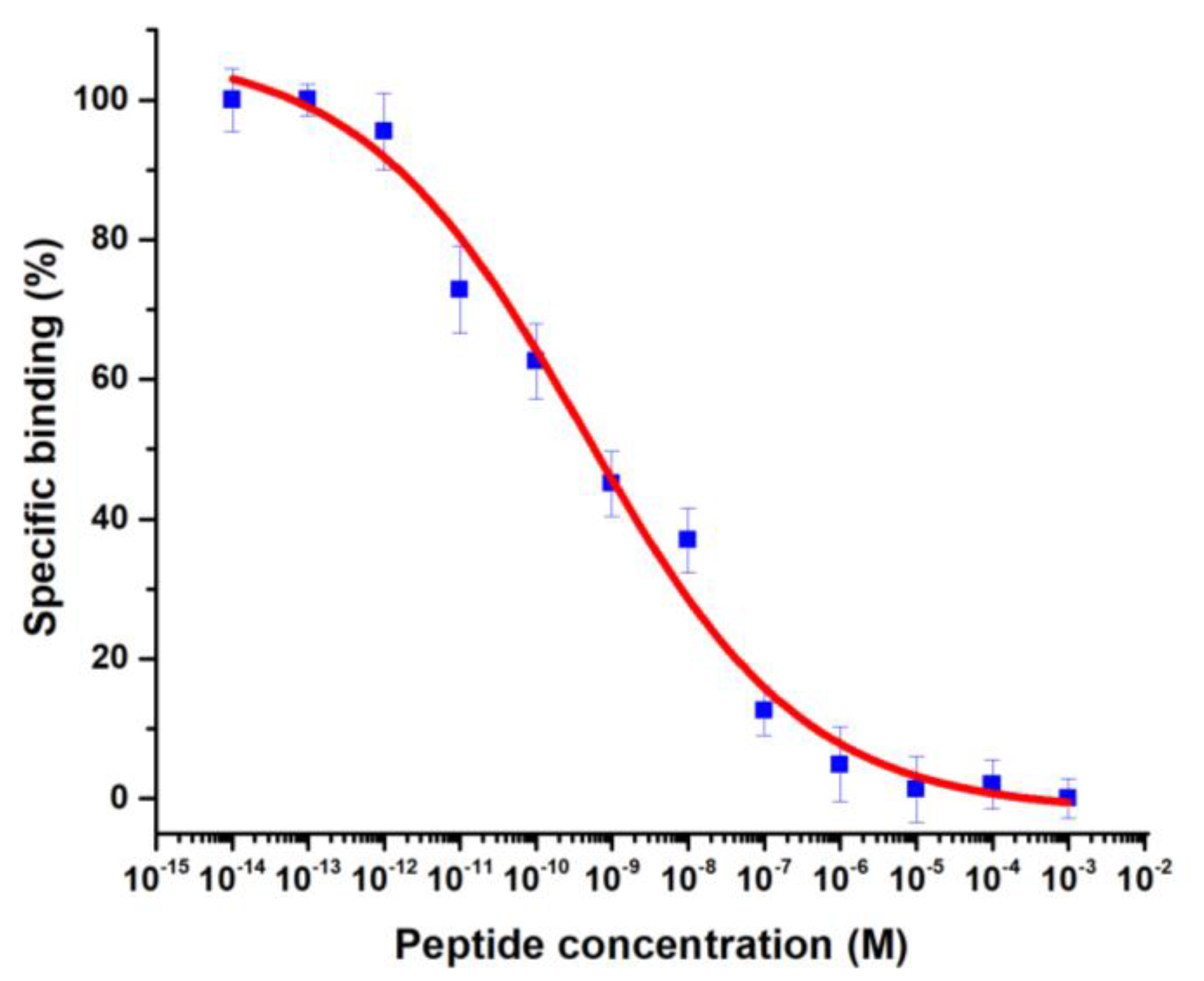
3.4.1. Binding Assay
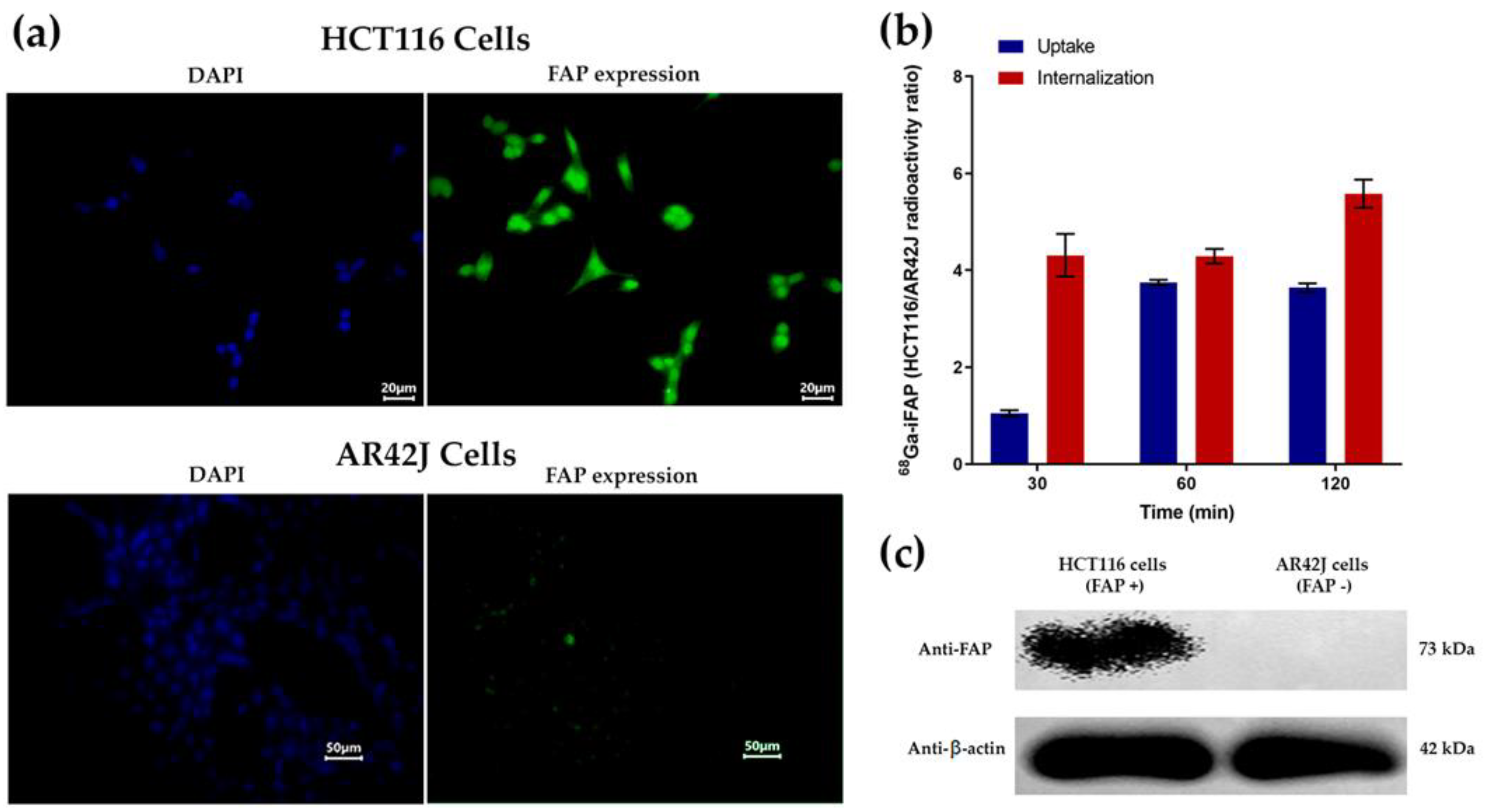
3.4.2. Immunofluorescence, Western Blot, Cellular Uptake, and Internalization
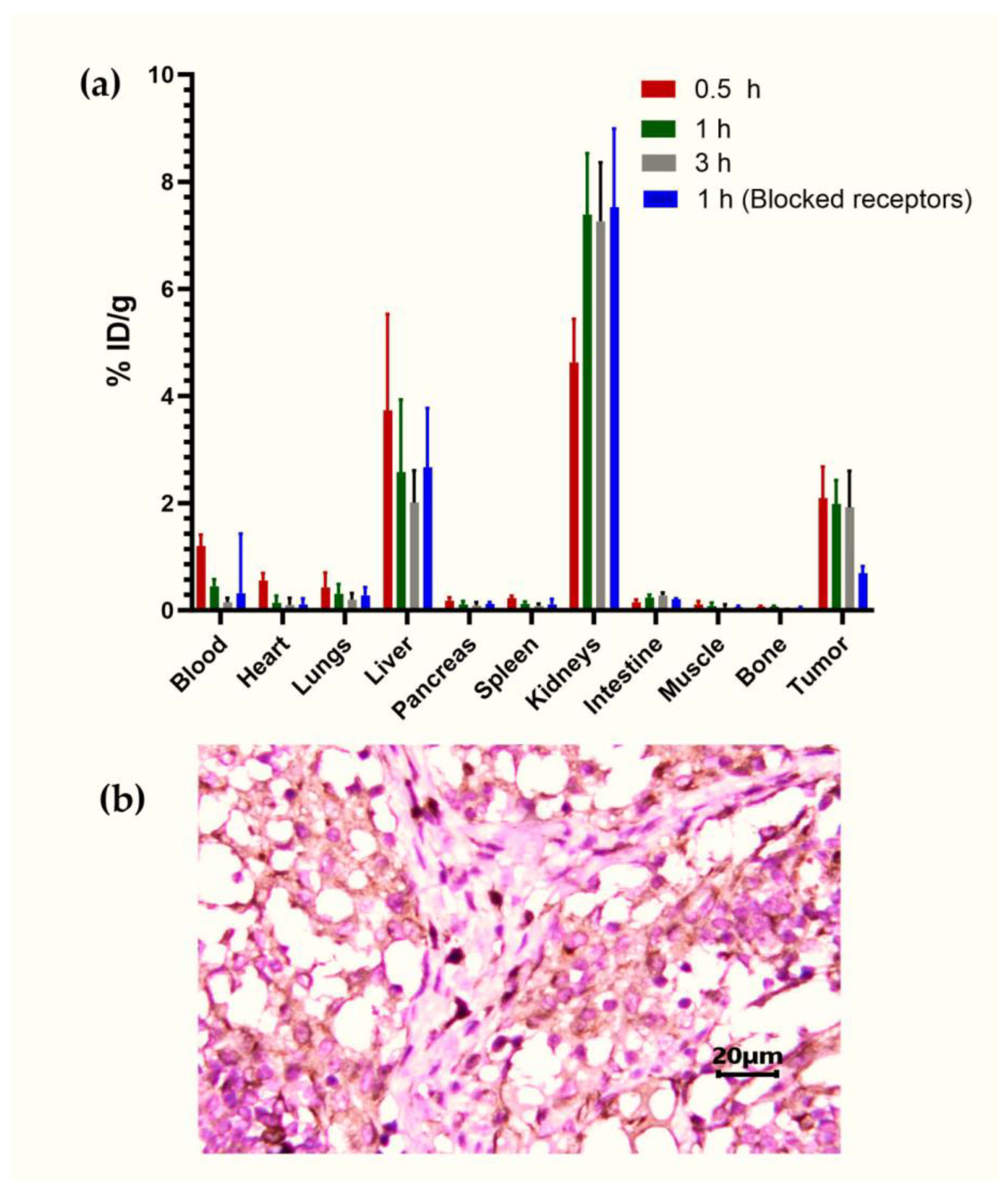
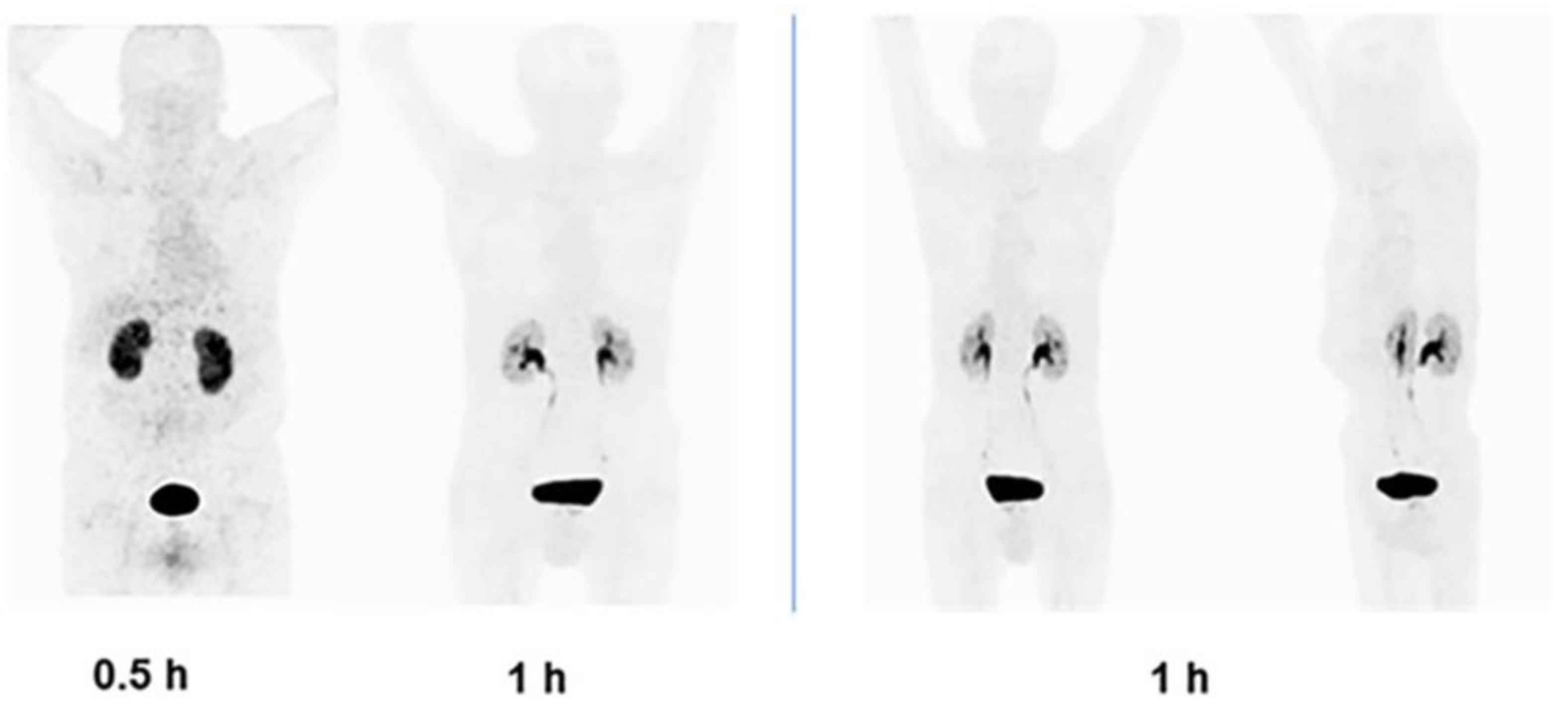
3.4.3. Biodistribution
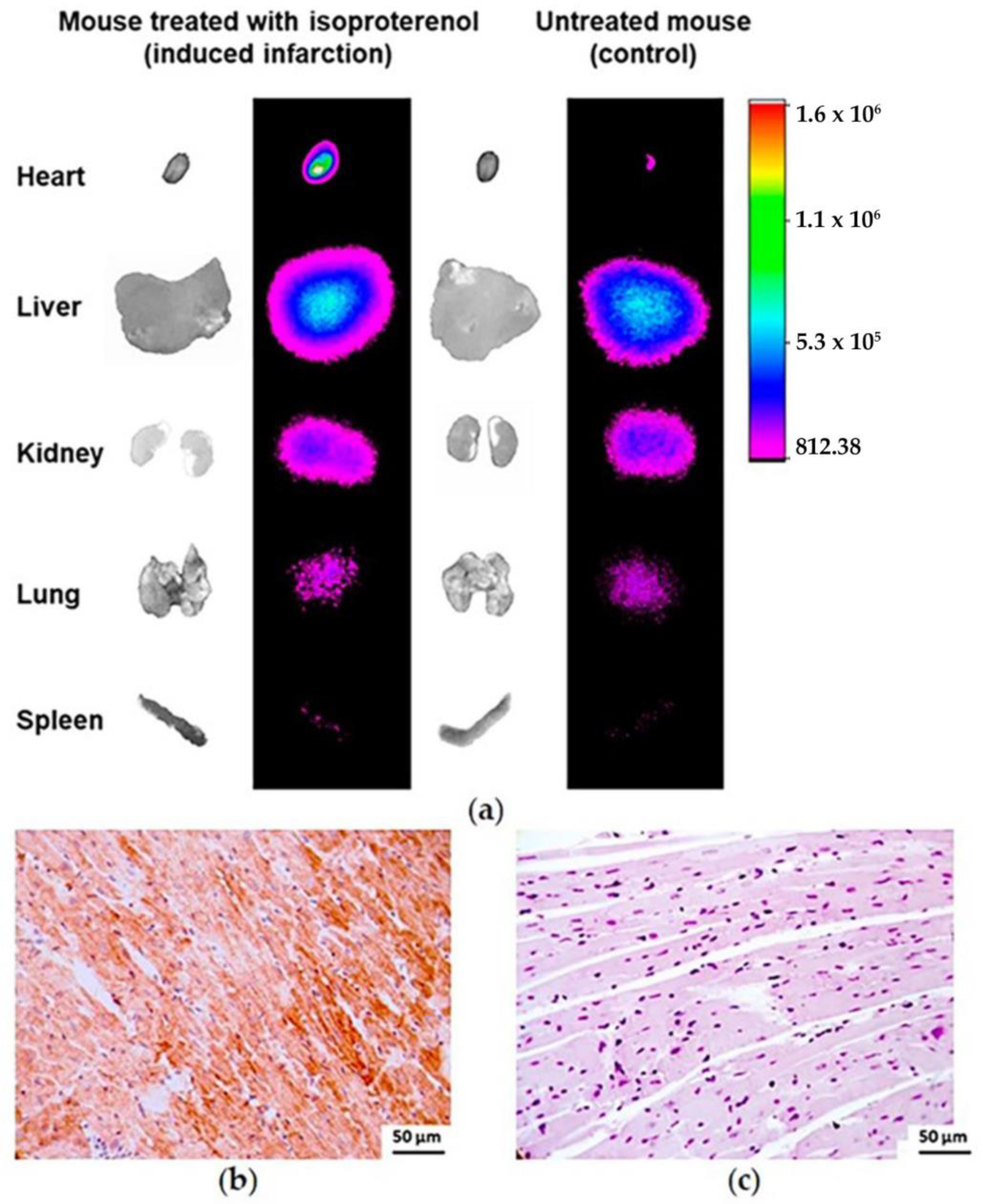
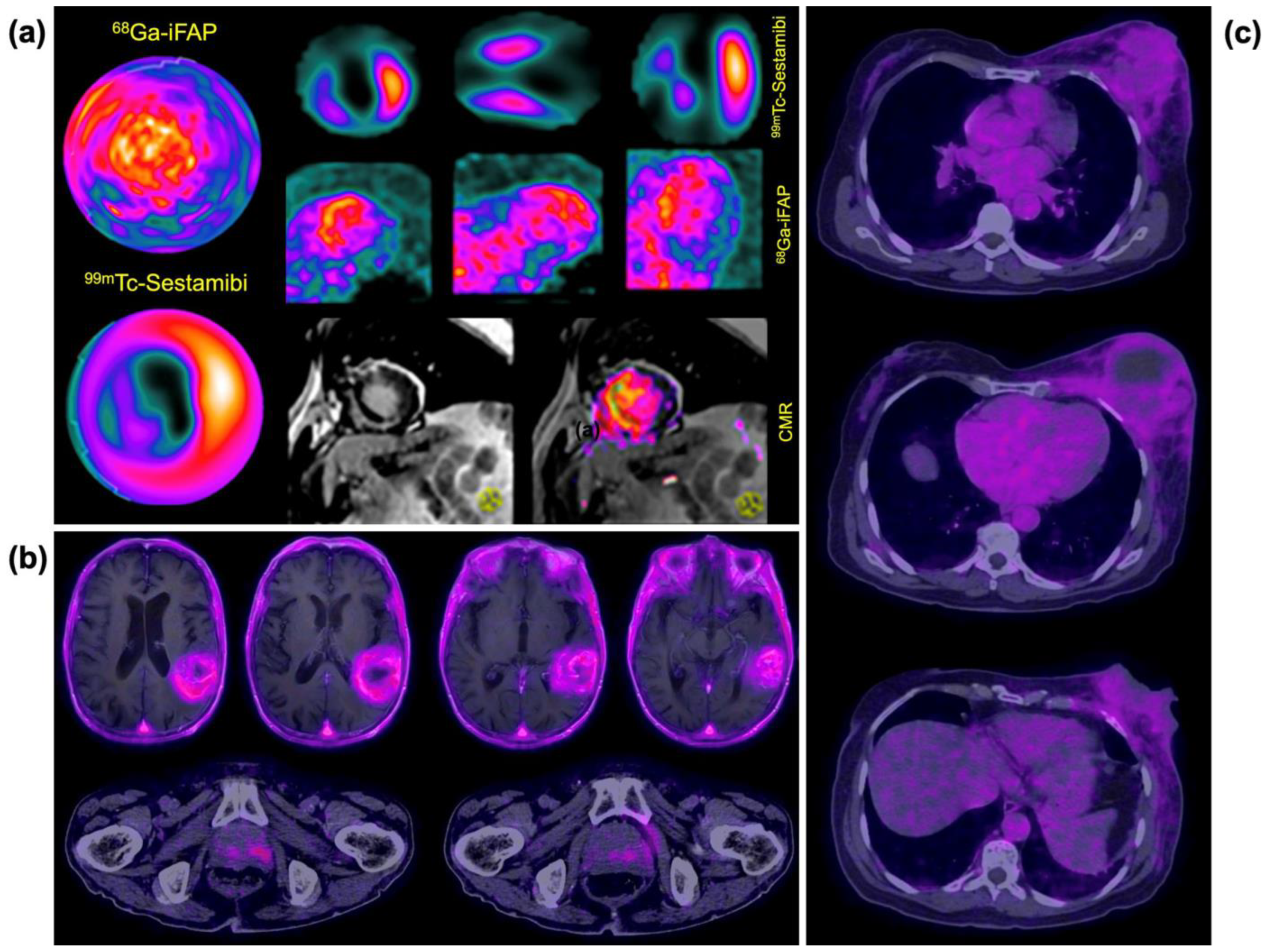
3.4.4. Infarcted Mouse Model Ex Vivo Imaging
3.5. Clinical Imaging
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altmann, A.; Haberkorn, U.; Siveke, J. The latest developments in imaging of fibroblast activation protein. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, A.A.; Weiner, L.M. The role of fibroblast activation protein in health and malignancy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 783–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Younis, M.H.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, W.; Lan, X. Clinical summary of fibroblast activation protein inhibitor-based radiopharmaceuticals: Cancer and beyond. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 2844–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Gao, J.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lv, S.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, C.; Yang, X.; Zhang, R. Fibroblast activation protein-α as a target in the bench-to-bedside diagnosis and treatment of tumors: A narrative review. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 648187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Watabe, T.; Kaneda-Nakashima, K.; Shirakami, Y.; Naka, S.; Ooe, K.; Toyoshima, A.; Nagata, K.; Haberkorn, U.; Kratochwil, C. Fibroblast activation protein targeted therapy using [177 Lu] FAPI-46 compared with [225 Ac] FAPI-46 in a pancreatic cancer model. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, C.; Wang, T.; Fang, D.; Zuo, C.; Yuan, G.; Li, R.; Li, X. SPECT Imaging with Tc-99m-Labeled HYNIC-FAPI-04 to Extend the Differential Time Window in Evaluating Tumor Fibrosis. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo-Benítez, D.; Luna-Gutiérrez, M.; Ferro-Flores, G.; Ocampo-García, B.; Santos-Cuevas, C.; Bravo-Villegas, G.; Morales-Ávila, E.; Cruz-Nova, P.; Díaz-Nieto, L.; García-Quiroz, J. Design, Synthesis and Preclinical Assessment of 99mTc-iFAP for In Vivo Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP) Imaging. Molecules 2022, 27, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, F.F. SPECT/CT and PET/CT, related radiopharmaceuticals, and areas of application and comparison. Saudi Pharm. J. 2022, 31, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Dendl, K.; Cardinale, J.; Kratochwil, C.; Giesel, F.L.; Haberkorn, U. FAPI PET: Fibroblast activation protein inhibitor use in oncologic and nononcologic disease. Radiology 2023, 306, e220749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varasteh, Z.; Mohanta, S.; Robu, S.; Braeuer, M.; Li, Y.; Omidvari, N.; Topping, G.; Sun, T.; Nekolla, S.G.; Richter, A. Molecular imaging of fibroblast activity after myocardial infarction using a 68Ga-labeled fibroblast activation protein inhibitor, FAPI-04. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharmacopoeia of the United Mexican States (Thirteenth Edition), Mexico. 2021. Available online: https://www.farmacopea.org.mx/publicaciones-detalle.php?m=3&pid=12. (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Hu, K.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, L.; Ye, S.; Han, Y.; Huang, S.; Wu, H.; Su, J. Preclinical evaluation and pilot clinical study of [18F] AlF-labeled FAPI-tracer for PET imaging of cancer associated fibroblasts. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, W.; Ren, S.; Kong, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Guan, Y.; Jia, H.; Chen, J.; Lu, L. 68Ga-FAPI-04 versus 18F-FDG PET/CT in the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 693640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poplawski, S.E.; Lai, J.H.; Li, Y.; Jin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sudmeier, J.L.; Sanford, D.G. Identification of selective and potent inhibitors of fibroblast activation protein and prolyl oligopeptidase. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 3467–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, T.; Loktev, A.; Altmann, A.; Giesel, F.; Kratochwil, C.; Debus, J.; Jäger, D.; Mier, W.; Haberkorn, U. Development of quinoline-based theranostic ligands for the targeting of fibroblast activation protein. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, T.; Loktev, A.; Giesel, F.; Kratochwil, C.; Altmann, A.; Haberkorn, U. Targeting of activated fibroblasts for imaging and therapy. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2019, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Pang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, L.; Hao, B.; Wu, J.; Wei, J.; Wu, S.; Zhao, L.; Luo, Z. Comparison of [68 Ga] Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 and [18 F] FDG PET/CT for the diagnosis of primary and metastatic lesions in patients with various types of cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 1820–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Wang, J.; Xi, X.-Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, B.-X.; Li, L.; Hua, C.; Zhao, S.; Su, P.; Chen, M. Fibroblast activation protein imaging in reperfused ST-elevation myocardial infarction: Comparison with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 2786–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmanns, J.; Hoffmann, D.; Habbaba, Y.; Schmitto, J.D.; Sedding, D.; Fraccarollo, D.; Galuppo, P.; Bauersachs, J. Fibroblast activation protein alpha expression identifies activated fibroblasts after myocardial infarction. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2015, 87, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Iyer, R.P.; Jung, M.; Czubryt, M.P.; Lindsey, M.L. Cardiac fibroblast activation post-myocardial infarction: Current knowledge gaps. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notohamiprodjo, S.; Nekolla, S.G.; Robu, S.; Villagran Asiares, A.; Kupatt, C.; Ibrahim, T.; Laugwitz, K.-L.; Makowski, M.R.; Schwaiger, M.; Weber, W.A. Imaging of cardiac fibroblast activation in a patient after acute myocardial infarction using 68 Ga-FAPI-04. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2021, 29, 2254–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Quan, W.; Zhu, T.; Feng, S.; Huang, X.; Meng, H.; Du, R.; Zhu, Z.; Qu, X.; Li, P. [68Ga] Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/MR in patients with acute myocardial infarction: Potential role of predicting left ventricular remodeling. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loktev, A.; Lindner, T.; Burger, E.-M.; Altmann, A.; Giesel, F.; Kratochwil, C.; Debus, J.; Marmé, F.; Jäger, D.; Mier, W. Development of fibroblast activation protein–targeted radiotracers with improved tumor retention. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Zhou, H.; Alhaskawi, A.; Wang, Z.; Lai, J.; Yao, C.; Liu, Z.; Hasan Abdullah Ezzi, S.; Goutham Kota, V.; Hasan Abdulla Hasan Abdulla, M. The Superiority of Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor (FAPI) PET/CT Versus FDG PET/CT in the Diagnosis of Various Malignancies. Cancers 2023, 15, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nader, M.; Valla, D.; Vriamont, C.; Masset, J.; Pacelli, A.; Herrmann, K.; Zarrad, F. [68Ga]/[90Y] FAPI-46: Automated production and analytical validation of a theranostic pair. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2022, 110, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diekmann, J.; Koenig, T.; Thackeray, J.T.; Derlin, T.; Czerner, C.; Neuser, J.; Ross, T.L.; Schäfer, A.; Tillmanns, J.; Bauersachs, J. Cardiac fibroblast activation in patients early after acute myocardial infarction: Integration with MR tissue characterization and subsequent functional outcome. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaei, Z.; Manafi-Farid, R.; Rashidi, B.; Kiani, F.K.; Zarei, A.; Fathi, M.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F. The Prognostic and therapeutic value and clinical implications of fibroblast activation protein-α as a novel biomarker in colorectal cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Ni, Y.; He, R.; Liu, W.; Du, J. Clinical implications of fibroblast activation protein-α in non-small cell lung cancer after curative resection: A new predictor for prognosis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, R.P.; Schuchardt, C.; Singh, A.; Chantadisai, M.; Robiller, F.C.; Zhang, J.; Mueller, D.; Eismant, A.; Almaguel, F.; Zboralski, D. Feasibility, biodistribution, and preliminary dosimetry in peptide-targeted radionuclide therapy of diverse adenocarcinomas using 177Lu-FAP-2286: First-in-humans results. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Gutiérrez, M.; Ocampo-García, B.; Jiménez-Mancilla, N.; Ancira-Cortez, A.; Trujillo-Benítez, D.; Hernández-Jiménez, T.; Ramírez-Nava, G.; Hernández-Ramírez, R.; Santos-Cuevas, C.; Ferro-Flores, G. Targeted Endoradiotherapy with Lu2O3-iPSMA/-iFAP Nanoparticles Activated by Neutron Irradiation: Preclinical Evaluation and First Patient Image. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ligand | Affinity (kcal/mol) | Ki (nM) | Distance Ser624–Boro (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
FAPI-O4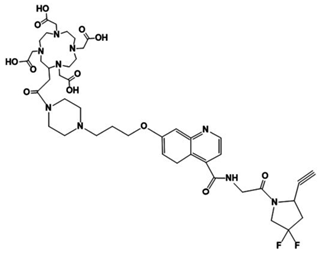 | −10.56 | 18.12 | 4.29 |
DOTA-D-Alanine-BoroPro (DOTA-iFAP)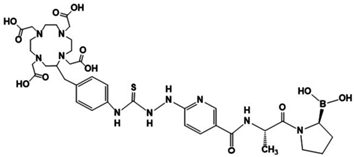 | −10.89 | 18.02 | 4.49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trujillo-Benítez, D.; Luna-Gutiérrez, M.; Aguirre-De Paz, J.G.; Cruz-Nova, P.; Bravo-Villegas, G.; Vargas-Ahumada, J.E.; Vallejo-Armenta, P.; Morales-Avila, E.; Jiménez-Mancilla, N.; Oros-Pantoja, R.; et al. 68Ga-DOTA-D-Alanine-BoroPro Radiotracer for Imaging of the Fibroblast Activation Protein in Malignant and Non-Malignant Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040532
Trujillo-Benítez D, Luna-Gutiérrez M, Aguirre-De Paz JG, Cruz-Nova P, Bravo-Villegas G, Vargas-Ahumada JE, Vallejo-Armenta P, Morales-Avila E, Jiménez-Mancilla N, Oros-Pantoja R, et al. 68Ga-DOTA-D-Alanine-BoroPro Radiotracer for Imaging of the Fibroblast Activation Protein in Malignant and Non-Malignant Diseases. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(4):532. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040532
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrujillo-Benítez, Diana, Myrna Luna-Gutiérrez, José G. Aguirre-De Paz, Pedro Cruz-Nova, Gerardo Bravo-Villegas, Joel E. Vargas-Ahumada, Paola Vallejo-Armenta, Enrique Morales-Avila, Nallely Jiménez-Mancilla, Rigoberto Oros-Pantoja, and et al. 2024. "68Ga-DOTA-D-Alanine-BoroPro Radiotracer for Imaging of the Fibroblast Activation Protein in Malignant and Non-Malignant Diseases" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 4: 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040532
APA StyleTrujillo-Benítez, D., Luna-Gutiérrez, M., Aguirre-De Paz, J. G., Cruz-Nova, P., Bravo-Villegas, G., Vargas-Ahumada, J. E., Vallejo-Armenta, P., Morales-Avila, E., Jiménez-Mancilla, N., Oros-Pantoja, R., Santos-Cuevas, C., Azorín-Vega, E., Ocampo-García, B., & Ferro-Flores, G. (2024). 68Ga-DOTA-D-Alanine-BoroPro Radiotracer for Imaging of the Fibroblast Activation Protein in Malignant and Non-Malignant Diseases. Pharmaceutics, 16(4), 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040532











