An Esterase-Responsive SLC7A11 shRNA Delivery System Induced Ferroptosis and Suppressed Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Patients and Specimens
2.2.2. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Analysis
2.2.3. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.2.4. Preparation and Characterization of Polyplexes with Different N/P Ratios
2.2.5. Fabrication and Characterization of the PEF-GPEG-Decorated Lipopolyplexes (G−LPQDEA/shSLC7A11)
2.2.6. Cell Viability Assay
2.2.7. Measurement of Cellular Labile Iron
2.2.8. ROS Analysis
2.2.9. GSH Analysis
2.2.10. Lipid Peroxidation (MDA) Assay
2.2.11. In Vivo Experiments
2.2.12. Biodistribution Study
2.2.13. Western Blotting
2.2.14. RT-qPCR
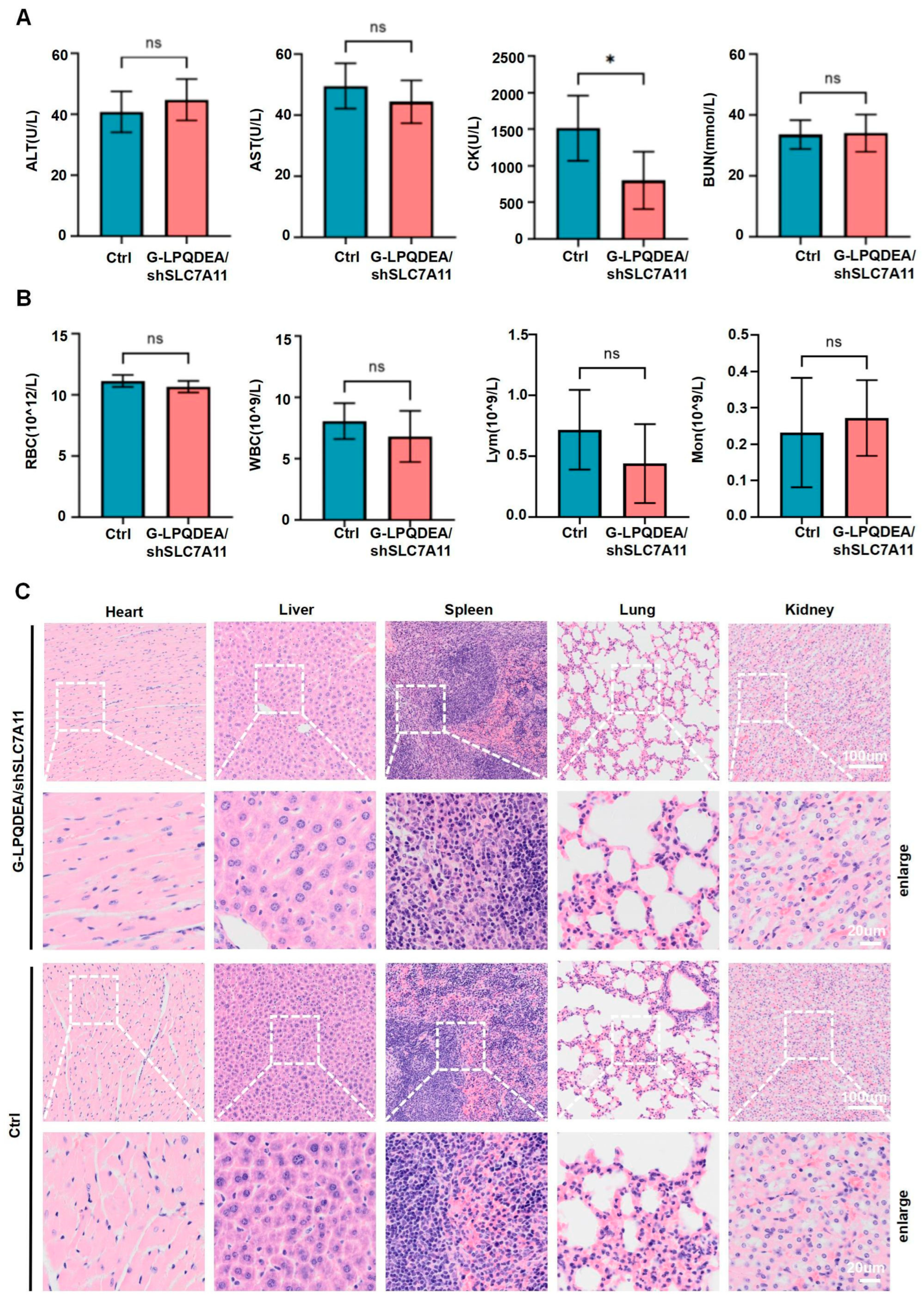
2.2.15. In Vivo Safety Evaluation
2.2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
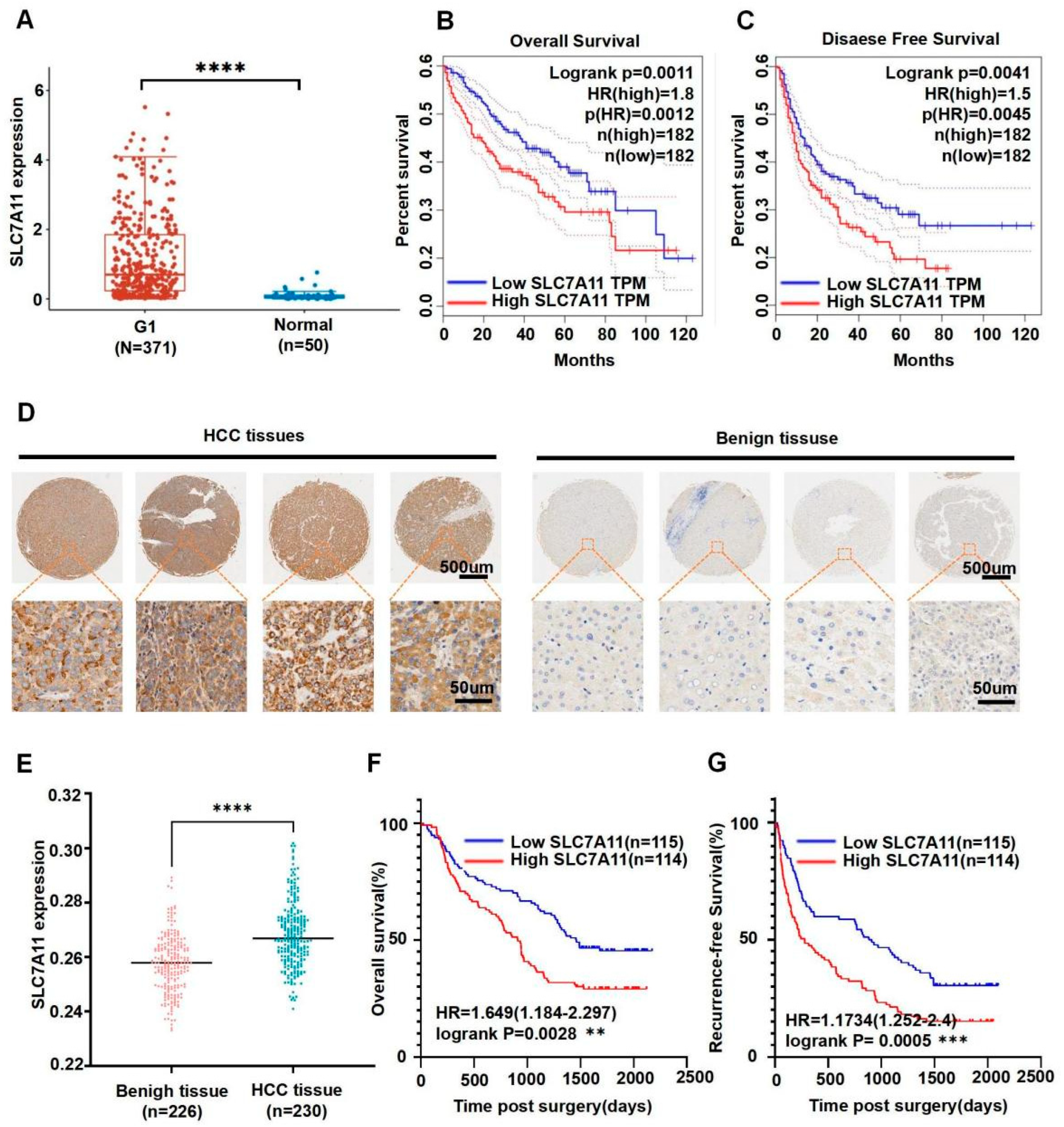
3.1. SLC7A11 Expression Was Associated with Progression and Prognosis of Human HCC
3.2. Construction of Polyplexes
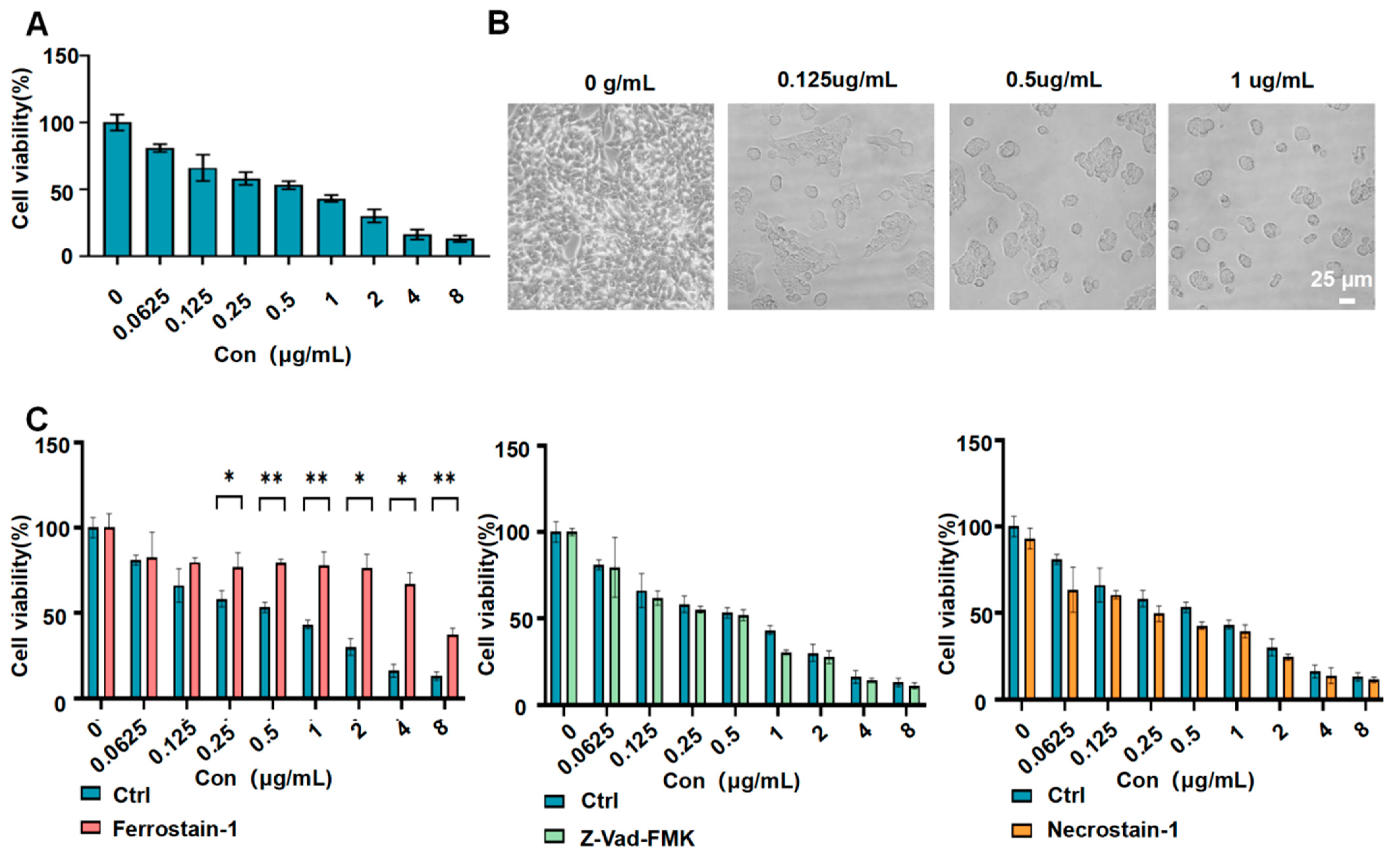
3.3. G−LPQDEA/shSLC7A11 Reduced the Viability of HCC Cell Lines
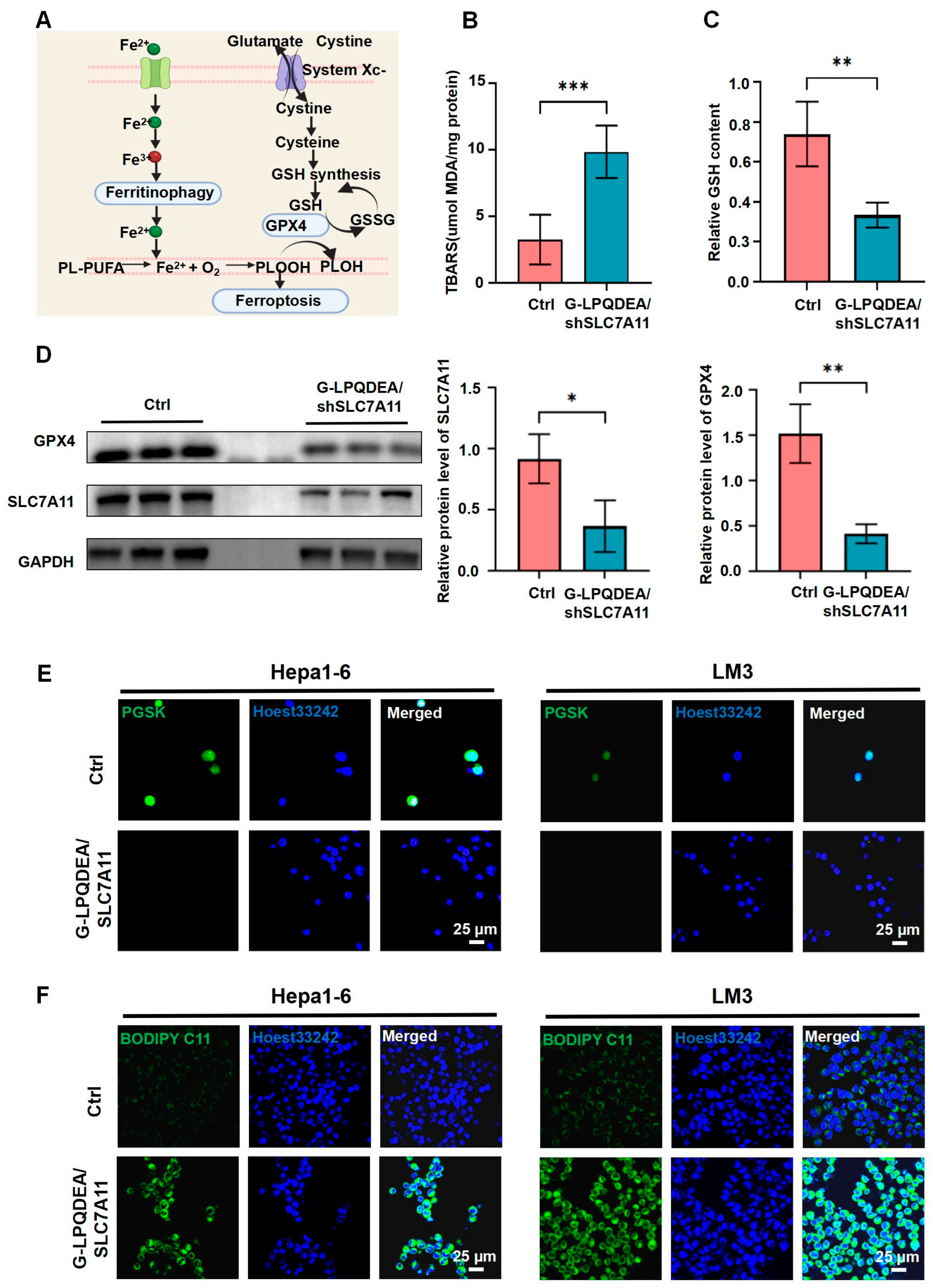
3.4. G−LPQDEA/shSLC7A11 Induced ROS-Mediated Ferroptosis of HCC Cell Lines
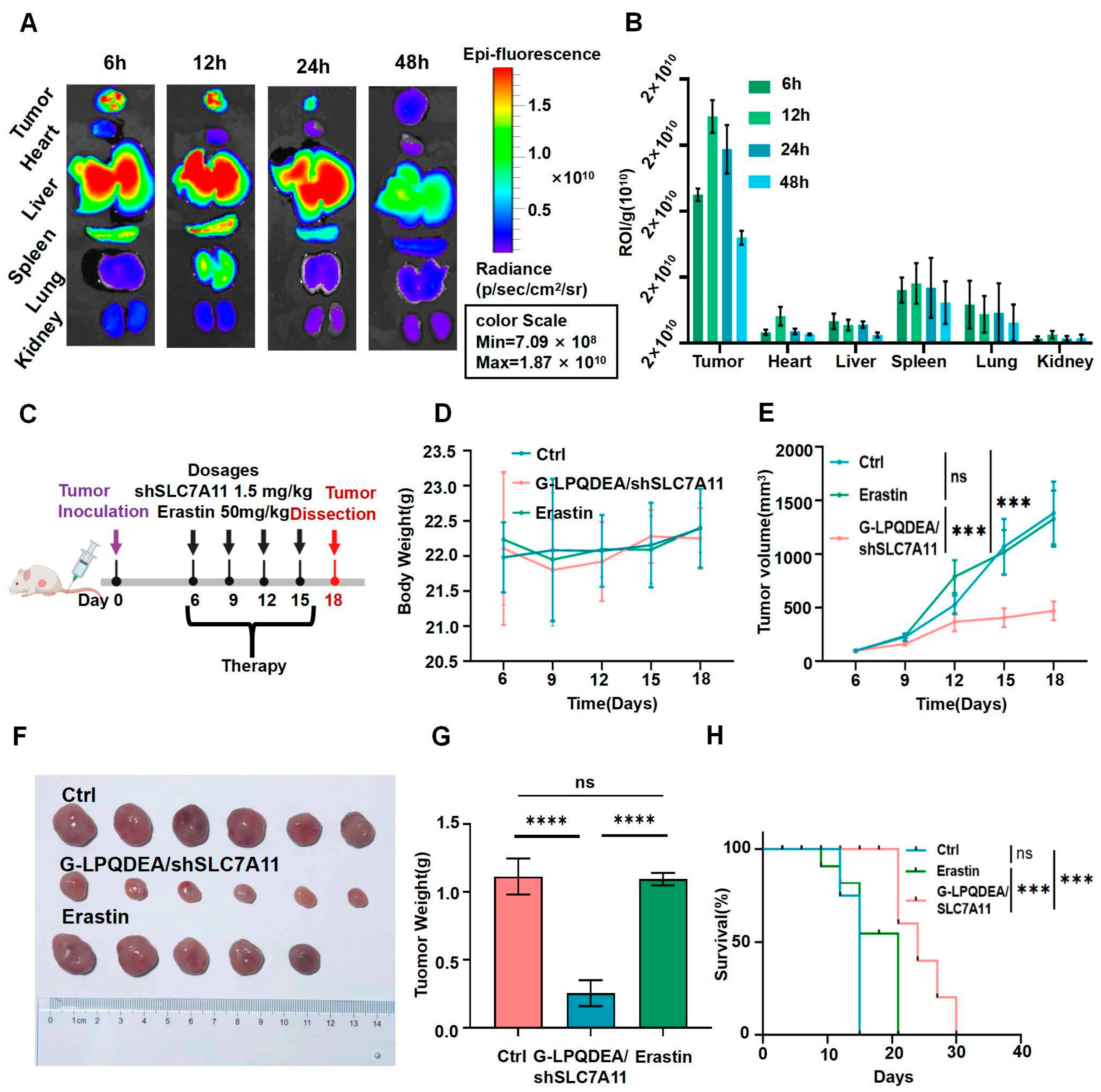
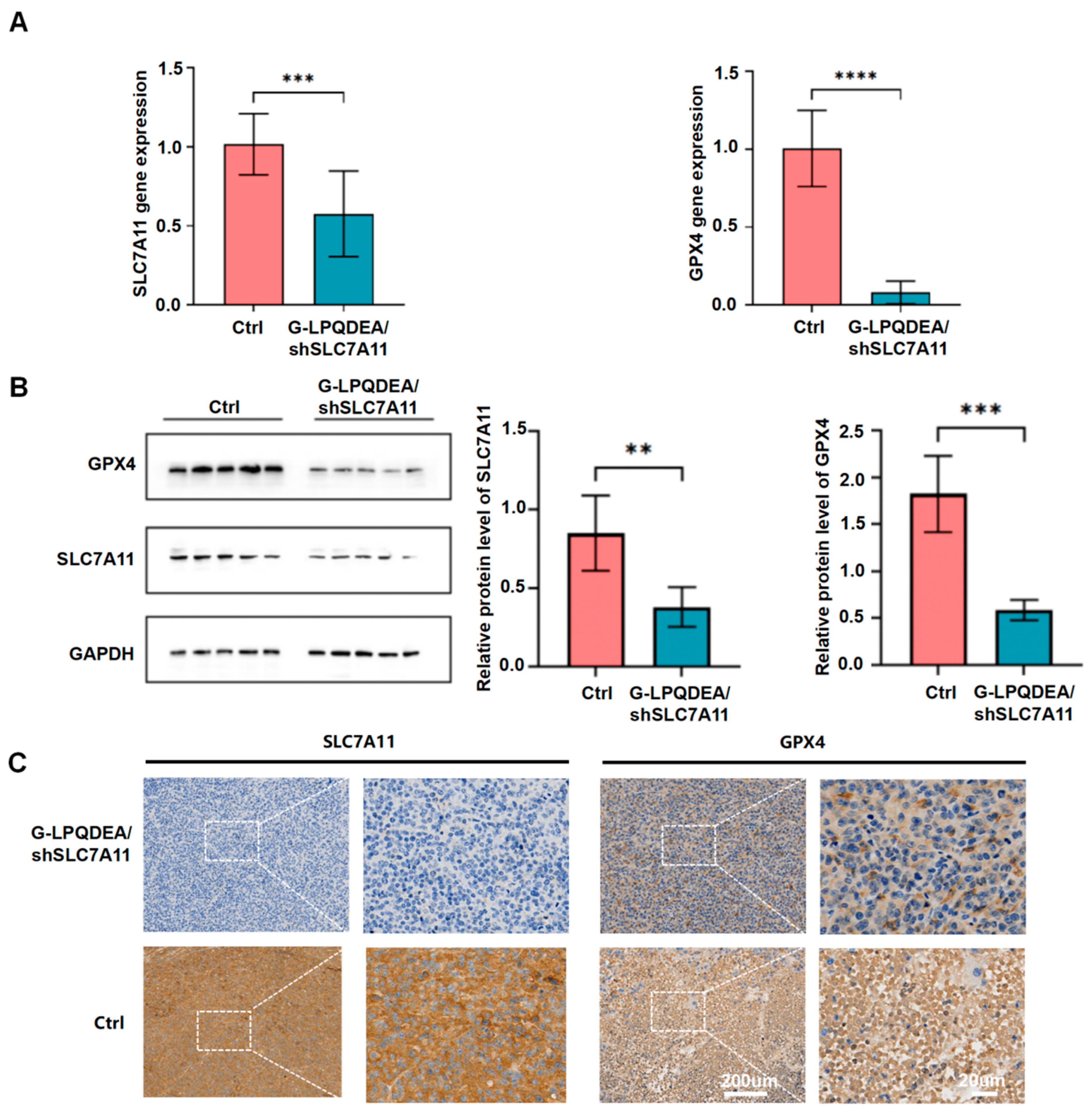
3.5. G−LPQDEA/shSLC7A11 Could Inhibit HCC Growth and Prolong Mouse Survival with Minimal Toxicity
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wen, F.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, P.; Liao, W.; Zhou, K.; Li, Q. Atezolizumab and bevacizumab combination compared with sorafenib as the first-line systemic treatment for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A cost-effectiveness analysis in China and the United States. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Shi, Y.; Lv, Y.; Yuan, S.; Ramirez, C.F.A.; Lieftink, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Dias, M.H.; et al. EGFR activation limits the response of liver cancer to lenvatinib. Nature 2021, 595, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucchetti, A.; Zhong, J.; Berhane, S.; Toyoda, H.; Shi, K.; Tada, T.; Chong, C.C.; Xiang, B.-D.; Li, L.-Q.; Lai, P.B.; et al. The chances of hepatic resection curing hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.J.; Ma, C.; Heinrich, B.; Brown, Z.J.; Sandhu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q.; Agdashian, D.; Rosato, U.; Korangy, F.; et al. Targeting the crosstalk between cytokine-induced killer cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricke, J.; Schinner, R.; Seidensticker, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; van Delden, O.M.; Amthauer, H.; Peynircioglu, B.; Bargellini, I.; Iezzi, R.; De Toni, E.N.; et al. Liver function after combined selective internal radiation therapy or sorafenib monotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donne, R.; Lujambio, A. The liver cancer immune microenvironment: Therapeutic implications for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1773–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Ge, C.; Min, J.; Wang, F. The multifaceted role of ferroptosis in liver disease. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, Z.J.; Tsilimigras, D.I.; Ruff, S.M.; Mohseni, A.; Kamel, I.R.; Cloyd, J.M.; Pawlik, T.M. Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review. JAMA Surg. 2023, 158, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordan, J.D.; Kennedy, E.B.; Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Beg, M.S.; Brower, S.T.; Gade, T.P.; Goff, L.; Gupta, S.; Guy, J.; Harris, W.P. Systemic Therapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 4317–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Jin, S.; Chen, Y.; Guo, R. Ferroptosis in cancer therapy: A novel approach to reversing drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangauer, M.J.; Viswanathan, V.S.; Ryan, M.J.; Bole, D.; Eaton, J.K.; Matov, A.; Galeas, J.; Dhruv, H.D.; Berens, M.E.; Schreiber, S.L.; et al. Drug-tolerant persister cancer cells are vulnerable to GPX4 inhibition. Nature 2017, 551, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Kang, R.; Kroemer, G.; Tang, D. Broadening horizons: The role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, R.; Xie, Y.; Tsai, H.-I.; Zha, H.; Xi, L.; Wang, K.; Cheng, X.; et al. Fe3+-binding transferrin nanovesicles encapsulating sorafenib induce ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomater. Res. 2023, 27, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Hou, W.; Song, X.; Yu, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, X.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Ferroptosis: Process and function. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, B.R.; Angeli, J.P.F.; Bayir, H.; Bush, A.I.; Conrad, M.; Dixon, S.J.; Fulda, S.; Gascón, S.; Hatzios, S.K.; Kagan, V.E.; et al. Ferroptosis: A Regulated Cell Death Nexus Linking Metabolism, Redox Biology, and Disease. Cell 2017, 171, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.; Liu, X.; Feng, L.; Gong, Z.; Koppula, P.; Sirohi, K.; Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Lee, H.; et al. BAP1 links metabolic regulation of ferroptosis to tumour suppression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louandre, C.; Marcq, I.; Bouhlal, H.; Lachaier, E.; Godin, C.; Saidak, Z.; François, C.; Chatelain, D.; Debuysscher, V.; Barbare, J.C.; et al. The retinoblastoma (Rb) protein regulates ferroptosis induced by sorafenib in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356 Pt B, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Niu, X.; Chen, R.; He, W.; Chen, D.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Metallothionein-1G facilitates sorafenib resistance through inhibition of ferroptosis. Hepatology 2016, 64, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, J.L.; Kim, E.H.; Jang, H.; Shin, D. Nrf2 inhibition reverses the resistance of cisplatin-resistant head and neck cancer cells to artesunate-induced ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Duan, X.; Ni, K.; Li, Y.; Chan, C.; Lin, W. Co-delivery of dihydroartemisinin and pyropheophorbide-iron elicits ferroptosis to potentiate cancer immunotherapy. Biomaterials 2022, 280, 121315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Song, J.; Yung, B.C.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, A.; Chen, X. Emerging Strategies of Cancer Therapy Based on Ferroptosis. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1704007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Stockwell, B.R.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qiao, X.; Liu, X.-M.; Shi, S.-H.; Xu, J.-Y. Blocking xCT and PI3K/Akt pathway synergized with DNA damage of Riluzole-Pt(IV) prodrugs for cancer treatment. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 250, 115233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, J.L.; Kim, E.H.; Jang, H.; Shin, D. Aspirin plus sorafenib potentiates cisplatin cytotoxicity in resistant head and neck cancer cells through xCT inhibition. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 104, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Luo, G.; Shi, X.; Long, Y.; Shen, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X. The Xc− inhibitor sulfasalazine improves the anti-cancer effect of pharmacological vitamin C in prostate cancer cells via a glutathione-dependent mechanism. Cell Oncol. 2020, 43, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, L.; Bolli, E.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Franceschi, V.; Macchi, F.; Riccardo, F.; Ruiu, R.; Russo, L.; Quaglino, E.; Donofrio, G.; et al. Immunotargeting of the xCT Cystine/Glutamate Antiporter Potentiates the Efficacy of HER2-Targeted Immunotherapies in Breast Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 1039–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, N.; Liu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Piao, Y.; Miao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, J.; Huang, L.; Shen, Y. Esterase-Activated Charge-Reversal Polymer for Fibroblast-Exempt Cancer Gene Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 10613–10622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, N.; Gao, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y. Enzyme-Responsive Charge-Reversal Polymer-Mediated Effective Gene Therapy for Intraperitoneal Tumors. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 2308–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, N.; Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Guo, M.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhou, H.; Bai, R.; You, M.; et al. Tumor-Associated Macrophage and Tumor-Cell Dually Transfecting Polyplexes for Efficient Interleukin-12 Cancer Gene Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2006189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jyotsana, N.; Ta, K.T.; DelGiorno, K.E. The Role of Cystine/Glutamate Antiporter SLC7A11/xCT in the Pathophysiology of Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 858462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ji, Y.; Hu, N.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Wu, F.; Xu, H.; Tang, Q.; Li, X. Ferroptosis-induced anticancer effect of resveratrol with a biomimetic nano-delivery system in colorectal cancer treatment. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 17, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Mao, C.; Yan, Y.; Koppula, P.; Cheng, W.; Sood, A.K.; et al. Ferroptosis as a mechanism to mediate p53 function in tumor radiosensitivity. Oncogene 2021, 40, 3533–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, B. How erastin assassinates cells by ferroptosis revealed. Protein Cell 2023, 14, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Guo, H.; Wei, X.; Lu, D.; Shu, W.; Song, Y.; Qiu, N.; Xu, X. Current Status and Prospect of Delivery Vehicle Based on Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Liver Diseases. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 2873–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Gong, N.; Li, D.; Deng, Y.; Chen, J.; Luo, D.; Zhou, W.; Xu, K. Identifying hepatocellular carcinoma patients with survival benefits from surgery combined with chemotherapy: Based on machine learning model. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 20, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Mao, X.; Xu, T.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Lin, N.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y. Pien-Tze-Huang prevents hepatocellular carcinoma by inducing ferroptosis via inhibiting SLC7A11-GSH-GPX4 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.; Bai, L.; Zhi, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, C.; Qi, Y.; Gao, W.; He, W.; et al. RBMS1 regulates lung cancer ferroptosis through translational control of SLC7A11. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e152067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, P.; Sharma, P.; Sundaram, S.; Venkatraman, G.; Bera, A.K.; Karunagaran, D. SLC7A11/xCT is a target of miR-5096 and its restoration partially rescues miR-5096-mediated ferroptosis and anti-tumor effects in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2021, 522, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, F.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, T.; Mao, S.; Yan, Y.; et al. PHGDH Inhibits Ferroptosis and Promotes Malignant Progression by Upregulating SLC7A11 in Bladder Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 5459–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Xiang, X.; Xie, C.; Lu, X.; Guo, H.; Sun, Y.; Shi, Z.; Song, H.; Qiu, N.; et al. An Esterase-Responsive SLC7A11 shRNA Delivery System Induced Ferroptosis and Suppressed Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020249
Zhang H, Wang J, Xiang X, Xie C, Lu X, Guo H, Sun Y, Shi Z, Song H, Qiu N, et al. An Esterase-Responsive SLC7A11 shRNA Delivery System Induced Ferroptosis and Suppressed Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(2):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020249
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hui, Jianguo Wang, Xiaonan Xiang, Chang Xie, Xinfeng Lu, Haijun Guo, Yiyang Sun, Zhixiong Shi, Hongliang Song, Nasha Qiu, and et al. 2024. "An Esterase-Responsive SLC7A11 shRNA Delivery System Induced Ferroptosis and Suppressed Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 2: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020249
APA StyleZhang, H., Wang, J., Xiang, X., Xie, C., Lu, X., Guo, H., Sun, Y., Shi, Z., Song, H., Qiu, N., & Xu, X. (2024). An Esterase-Responsive SLC7A11 shRNA Delivery System Induced Ferroptosis and Suppressed Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression. Pharmaceutics, 16(2), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020249





