Effect of Particle Size on Physical Properties, Dissolution, In Vitro Antioxidant Activity, and In Vivo Hepatoprotective Properties of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg Powders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Chemical Reagents
2.3. Preparation of Samples with Different Particle Sizes
2.4. Determination of the Physical Properties of Samples of Different Particle Sizes
2.4.1. Measurement of the Particle Size Distribution
2.4.2. Measurement of the Angle of Repose
2.4.3. Measurement of the Slip Angle
2.4.4. Measurement of Bulk Density
2.4.5. Measurement of the Tap Density
2.4.6. Identification of Microscopic Features
2.5. Determination of the Bioactive Ingredients
2.5.1. Determination of Total Flavonoid Content
2.5.2. Determination of Total Polysaccharide Content
2.5.3. Determination of the Kaempferol-3-O-Rutinoside and Rutin Content
2.6. Dissolution In Vitro
2.7. Antioxidant Activities
2.8. Liver Protection Performance
2.8.1. Animals and Groups
2.8.2. Determination of AST and ALT Activities
2.8.3. Determination of SOD, CAT, and GSH Activities in the Liver
2.8.4. Liver Histopathological Examination of the Mice
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physical Properties of Three Leaf Green Powders with Different Particle Sizes
3.2. Microscopic Characteristics of Different Particle Sizes of TDG Powders
3.3. Results of Bioactive Ingredients Content
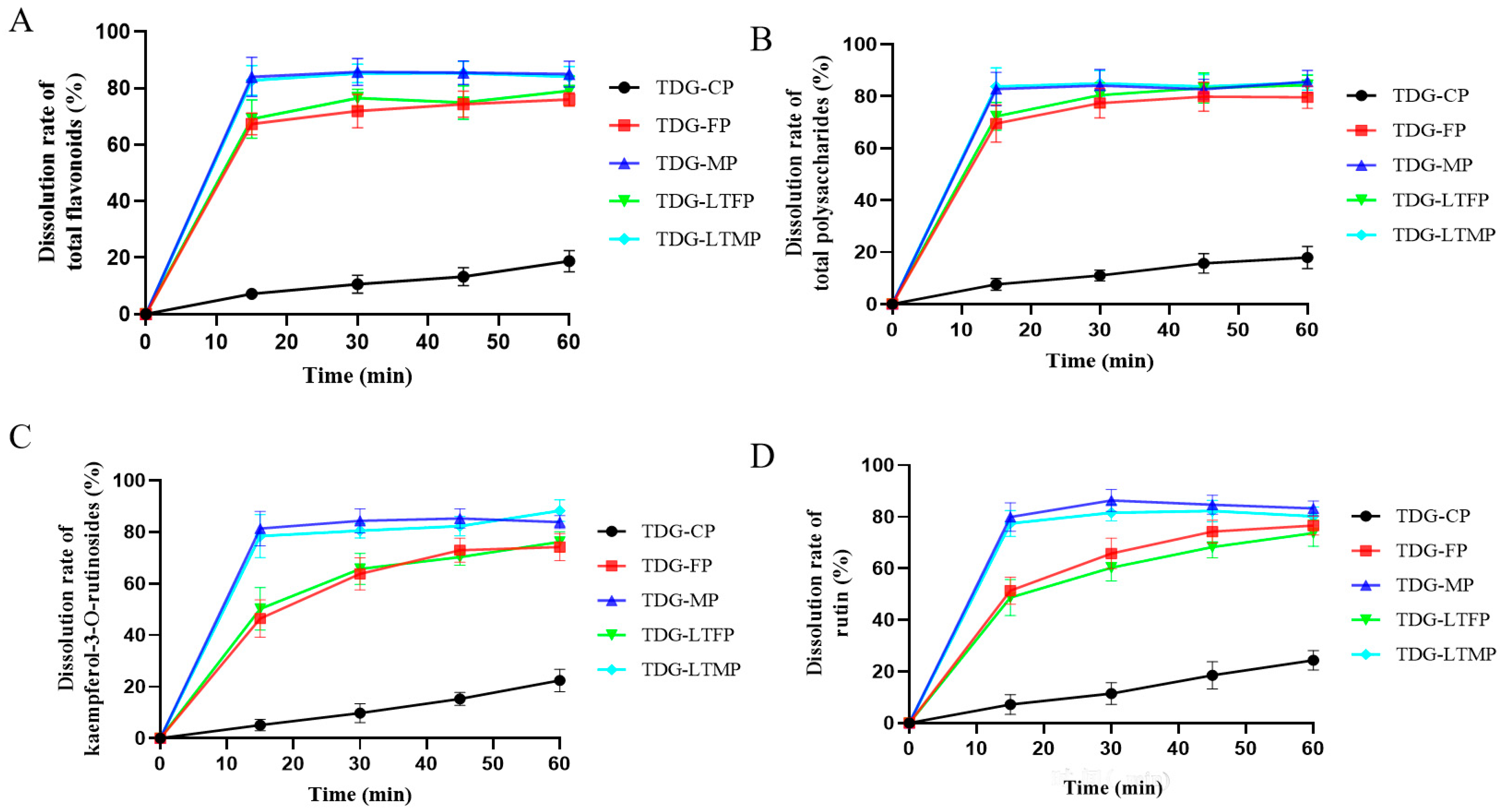
3.4. Effects of TDG Powders with Different Particle Sizes on In Vitro Dissolution
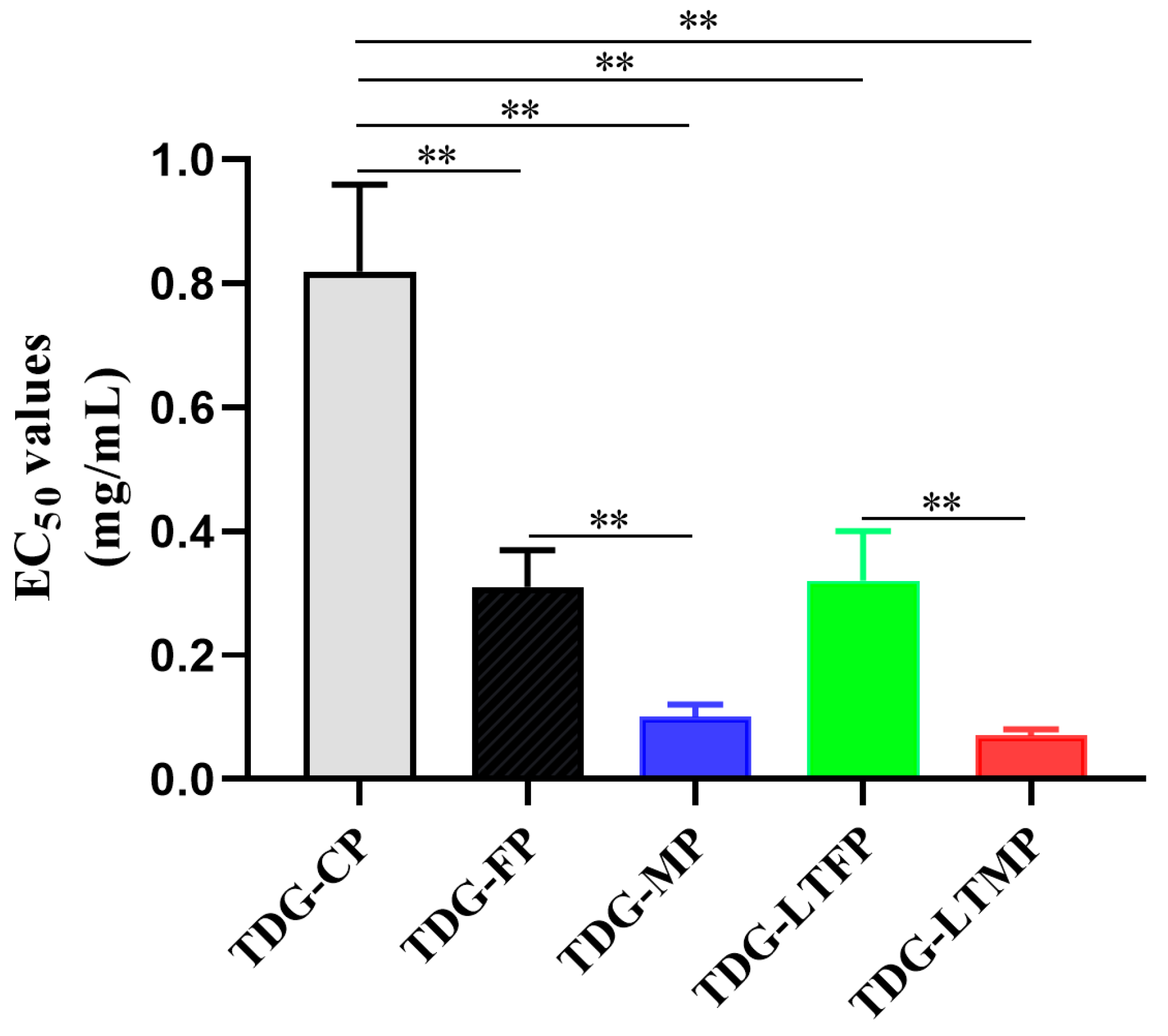
3.5. Effects of TDG Powders with Different Particle Sizes on Antioxidant Activities
3.6. Effects of TDG Powders with Different Particle Sizes on Serum AST and ALT Activities
3.7. Effects of TDG Powders with Different Particle Sizes on Liver Morphology
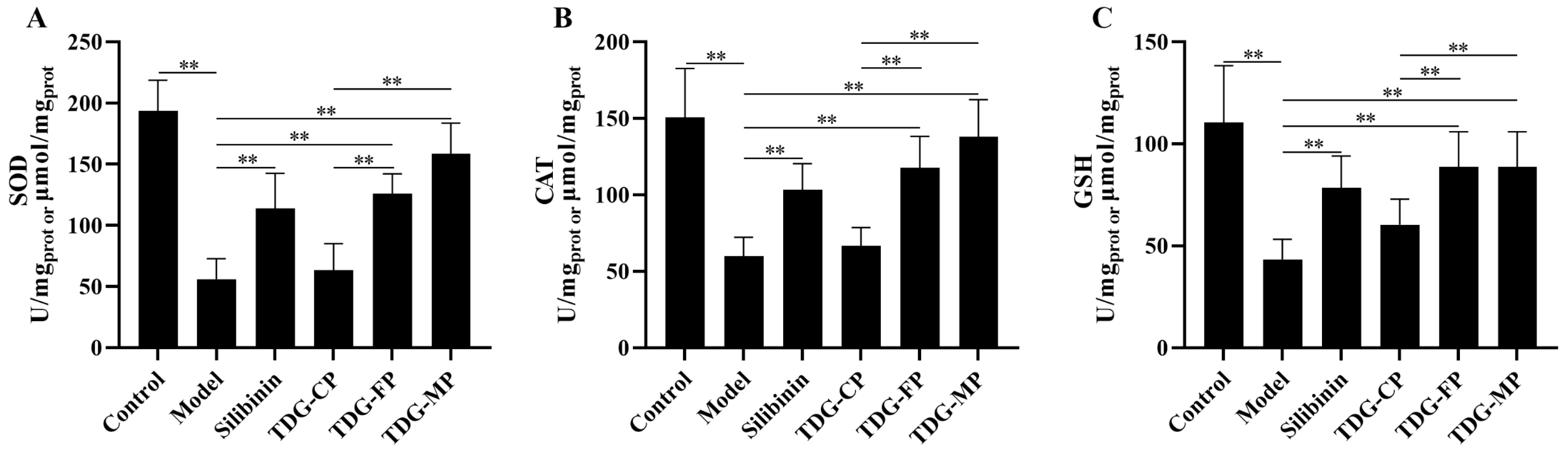
3.8. Effects of TDG Powders with Different Particle Sizes on Liver SOD, CAT, and GSH Activities
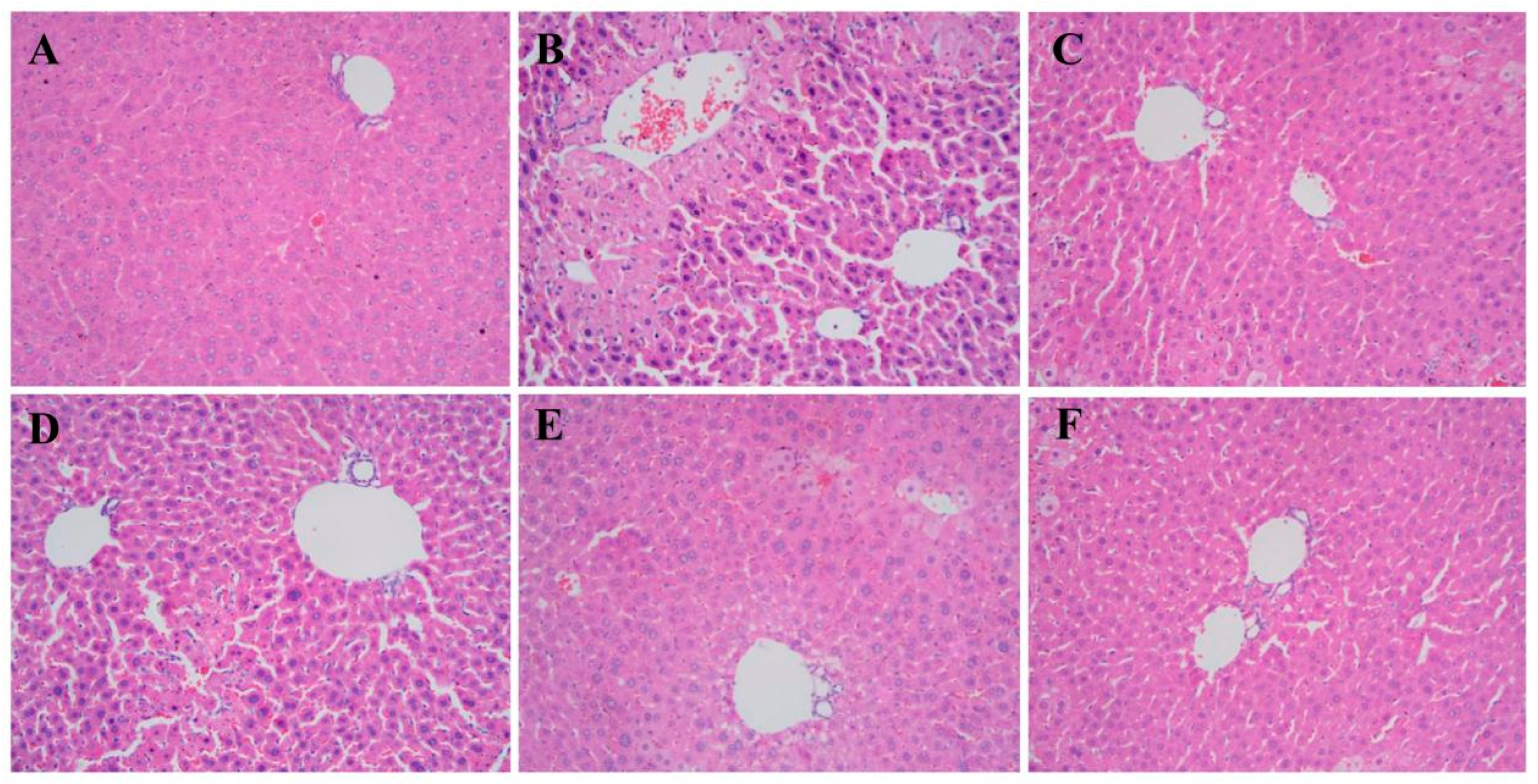
3.9. Effects of TDG Powders with Different Particle Sizes on Liver Histopathology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, Z.; Ye, W.; Feng, L. Bioactives and metabolites of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum root extract alleviate DSS-induced ulcerative colitis by targeting the SYK protein in the B cell receptor signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 322, 117563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.L.; Xu, Z.J.; Cao, Y.F.; Wang, F.; Chu, C.; Zhang, C.; Tao, Y.; Wang, P. HPLC fingerprinting-based multivariate analysis of chemical components in Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg: Correlation to their antioxidant and neuraminidase inhibition activities. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 205, 114314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Z.; Yang, L.; Lv, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Fang, C.; Zhu, B.; Zhou, F.; Ding, Z. A glucuronogalactomannan isolated from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg: Structure and immunomodulatory activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 333, 121922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J. Antioxidant Activity In Vitro Guided Screening and Identification of Flavonoids Antioxidants in the Extract from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 2021, 7195125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Lv, Y.; Mao, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, B.; Yu, Y.; Ding, Z.; Zhou, F. Polysaccharides from Tetrastigma Hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg ameliorated inflammatory bowel disease by rebuilding the intestinal mucosal barrier and inhibiting inflammation through the SCFA-GPR41/43 signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 250, 126167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Xu, X.; Ying, J.; Cao, G.; Wu, X. The Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Quality Control of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels & Gilg in China: A Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 550497. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Gu, Y.; Liu, S.; Jiang, L.; Han, M.; Geng, D. Flavonoids metabolism and physiological response to ultraviolet treatments in Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 926197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhai, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Sun, C.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lu, J.; Kai, G. Total flavonoids of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg inhibits colorectal tumor growth by modulating gut microbiota and metabolites. Food Chem. 2023, 410, 135361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Wang, S.; Kang, C.Z.; Lv, C.G.; Zhou, L.; Huang, L.Q.; Guo, L.P. Pharmacodynamic material basis of traditional Chinese medicine based on biomacromolecules: A review. Plant Methods 2020, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, W.; Huang, S.; Guo, C.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wen, A.; et al. Investigation of the Multi-Target Mechanism of Guanxin-Shutong Capsule in Cerebrovascular Diseases: A Systems Pharmacology and Experimental Assessment. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 650770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, T.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, T.C.; Li, K.; Liu, J.; Zhou, P. Effects of particle size reduction combined with beta-cyclodextrin on the in vitro dissolution and in vivo relative bioavailability of ginsenosides in Panax ginseng. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 10882–10894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, L.; Xu, M.; Tao, X.; Ai, R.; Tang, X. Improvement of dissolution and bioavailability of Ginsenosides by hot melt extrusion and cogrinding. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingale, E.; Bonaccorso, A.; Carbone, C.; Musumeci, T.; Pignatello, R. Drug Nanocrystals: Focus on Brain Delivery from Therapeutic to Diagnostic Applications. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crescenti, A.; Caimari, A.; Alcaide-Hidalgo, J.M.; Marine-Casado, R.; Valls, R.M.; Companys, J.; Salamanca, P.; Calderon-Perez, L.; Pla-Paga, L.; Pedret, A.; et al. Hesperidin Bioavailability Is Increased by the Presence of 2S-Diastereoisomer and Micronization—A Randomized, Crossover and Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fertaki, S.; Bagourakis, G.; Orkoula, M.; Kontoyannis, C. Measuring Bismuth Oxide Particle Size and Morphology in Film-Coated Tablets. Molecules 2022, 27, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Begum, N.; Xia, P.; Liu, J.; Liang, Z. Effects of Different Processing Methods Based on Different Drying Conditions on the Active Ingredients of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Molecules 2022, 27, 4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, H.; Cai, X.; Wu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, L. Preparation and Characterization of Instant Casein Phosphopeptide by Supercritical Fluid Assisted Atomization. Foods 2021, 10, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.K.; McGowan, C.P.; Lin, D.C. Comparison between the kinematics for kangaroo rat hopping on a solid versus sand surface. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2022, 9, 211491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, F.; Sun, Y.; Yu, X.; Xiao, Z.; Fang, R.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Du, L.; Jin, Y. Inhalable Jojoba Oil Dry Nanoemulsion Powders for the Treatment of Lipopolysaccharide- or H2O2-Induced Acute Lung Injury. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Qiu, M.; Qu, Y.; Yuan, W. The Optimization of Extraction Process, Antioxidant, Whitening and Antibacterial Effects of Fengdan Peony Flavonoids. Molecules 2022, 27, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruksiriwanich, W.; Khantham, C.; Muangsanguan, A.; Chittasupho, C.; Rachtanapun, P.; Jantanasakulwong, K.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Sommano, S.R.; Sringarm, K.; Ferrer, E.; et al. Phytochemical Constitution, Anti-Inflammation, Anti-Androgen, and Hair Growth-Promoting Potential of Shallot (Allium ascalonicum L.) Extract. Plants 2022, 11, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, K.; Liu, H.; Xu, D.; Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Huang, J.; Yao, H.; et al. Improved solubility, dissolution rate, and oral bioavailability of main biflavonoids from Selaginella doederleinii extract by amorphous solid dispersion. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Xie, G.; Ding, Y.; Ma, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Z.; Sun, J.; Shang, J. Chemometric Discrimination of Cichorium glandulosum Boiss. et Huet and Cichorium intybus L. via Their Metabolic Profiling, Antioxidative, and Hypoglycemic Activities. Foods 2023, 12, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Gao, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, J.; Zhang, X.; Gong, X.; Hao, Z. Mori fructus aqueous extracts attenuates liver injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via the Nrf2 pathway. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markelic, M.; Mojic, M.; Bovan, D.; Jelaca, S.; Jovic, Z.; Puric, M.; Koruga, D.; Mijatovic, S.; Maksimovic-Ivanic, D. Melanoma Cell Reprogramming and Awakening of Antitumor Immunity as a Fingerprint of Hyper-Harmonized Hydroxylated Fullerene Water Complex (3HFWC) and Hyperpolarized Light Application In Vivo. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yao, P.F.; Sun, P.Y.; Liang, W.; Chen, X.J. Key quality factors for Chinese herbal medicines entering the EU market. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Cao, X.P.; Wei, J.J.; Song, L.; Liao, F.J.; Zheng, G.Q.; Lin, Y. Chuanxiong chadiao powder, a famous Chinese herbal prescription, for headache: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complement. Ther. Med. 2015, 23, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.E.; Ryu, J.; Kim, J.T.; Suh, S.; Hong, G.P.; Ko, S. Physicochemical and in vitro digestion characteristics of size-different red ginseng powders. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, R.; Hayashi, T.; Motoyama, K.; Tahara, K.; Takeuchi, H. Hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin Enhances Oral Absorption of Silymarin Nanoparticles Prepared Using PureNano Continuous Crystallizer. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, M.; Liu, G. Application of Nanomicelles in Enhancing Bioavailability and Biological Efficacy of Bioactive Nutrients. Polymers 2022, 14, 3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra-Leos, M.Z.; Roman-Aguirre, M.; Toxqui-Teran, A.; Espinosa-Solis, V.; Franco-Vega, A.; Leyva-Porras, C. Blends of Carbohydrate Polymers for the Co-Microencapsulation of Bacillus clausii and Quercetin as Active Ingredients of a Functional Food. Polymers 2022, 14, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szelag-Pieniek, S.; Oswald, S.; Post, M.; Lapczuk-Romanska, J.; Drozdzik, M.; Kurzawski, M. Hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes and drug transporters in Wilson’s disease patients with liver failure. Pharmacol. Rep. 2021, 73, 1427–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziamajidi, N.; Khajvand-Abedini, M.; Daei, S.; Abbasalipourkabir, R.; Nourian, A. Ameliorative Effects of Vitamins A, C, and E on Sperm Parameters, Testis Histopathology, and Oxidative Stress Status in Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle-Treated Rats. Biomed Res. Int. 2023, 2023, 4371611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Valderrama, L.; Posadas-Rodriguez, J.; Bonilla-Jaime, H.; Tarrago-Castellanos, M.; Gonzalez-Marquez, H.; Arrieta-Cruz, I.; Gonzalez-Nunez, L.; Salame-Mendez, A.; Rodriguez-Tobon, A.; Morales-Mendez, J.G.; et al. Sperm Dysfunction in the Testes and Epididymides due to Overweight and Obesity Is Not Caused by Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2022, 2022, 3734572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, A.; Jaeschke, H. Oxidative stress and acute hepatic injury. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 7, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okiljević, B.; Martić, N.; Govedarica, S.; Andrejić Višnjić, B.; Bosanac, M.; Baljak, J.; Pavlić, B.; Milanović, I.; Rašković, A. Cardioprotective and Hepatoprotective Potential of Silymarin in Paracetamol-Induced Oxidative Stress. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Guo, L.; Lin, Z.; Peng, X.; Qiu, B. Polysaccharides from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg: Extraction optimization, structural characterizations, antioxidant and antihyperlipidemic activities in hyperlipidemic mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| TDG Powders | Crushing Methods |
|---|---|
| Coarse powders (TDG-CP) | The TDG decoction slices were mashed in a mortar and filtered through a 40-mesh sieve. |
| Fine powders (TDG-FP) | The TDG decoction slices were crushed with a Chinese medicine pulverizer for 1 min and filtered through a 120-mesh sieve. |
| Micro powders (TDG-MP) | First, the TDG decoction slices were crushed with a mortar, the powders were passed through a 120-mesh sieve, and then the powders were added to the fully automatic rapid grinding instrument (JX-2GL, Shanghai Jingxin Industrial Development Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) with a grinding power of 60 Hz. They were ground a total of 3 times, with a grinding time of 30 s, and a grinding interval of 15 s. |
| Low temperature fine powders (TDG-LTFP) | The TDG decoction slices were crushed with a Chinese medicine pulverizer for 1 min after being soaked in liquid nitrogen for 10 min and then filtered through a 120-mesh sieve. |
| Low temperature micro powders (TDG-LTMP) | First, the TDG decoction slices were crushed with a mortar and filtered through a 120-mesh sieve, then the powders were added to the fully automatic rapid grinding instrument with a grinding power of 60 Hz. They were ground a total of 3 times, with a grinding time of 30 s and a grinding interval of 15 s after being soaked in liquid nitrogen for 10 min. |
| Time (min) | A (%) | B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0~30 | 95~90 | 5~10 |
| 30~70 | 90~78 | 10~22 |
| 70~85 | 78~65 | 22~35 |
| 85~95 | 65~20 | 35~80 |
| 95~100 | 20~20 | 80~80 |
| Sample | TDG-CP | TDG-FP | TDG-SP | TDG-LTFP | TDG-LTSP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D90 (μm) | 742.81 ± 24.32 | 379.24 ± 18.63 | 176.74 ± 4.77 | 411.87 ± 11.35 | 161.13 ± 6.72 |
| D50 (μm) | 329.61 ± 12.90 | 123.57 ± 7.26 | 16.20 ± 1.14 | 136.72 ± 4.75 | 14.36 ± 0.98 |
| D10 (μm) | 32.88 ± 3.59 | 15.42 ± 0.65 | 4.38 ± 0.21 | 16.15 ± 3.27 | 5.12 ± 0.33 |
| Span | 1.176 | 1.949 | 3.585 | 2.909 | 3.602 |
| Angle of repose (°) | 25.79 ± 1.03 | 29.25 ± 0.58 | 32.60 ± 0.48 | 29.14 ± 0.60 | 32.81 ± 0.69 |
| Angle of slide (°) | 32.02 ± 0.45 | 40.11 ± 0.50 | 53.01 ± 0.64 | 40.69 ± 0.76 | 53.53 ± 0.42 |
| Bulk density (g/mL) | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 0.47 ± 0.01 | 0.70 ± 0.01 | 0.48 ± 0.01 | 0.69 ± 0.01 |
| Tap density (g/mL) | 0.47 ± 0.01 | 0.49 ± 0.01 | 1.01 ± 0.01 | 0.48 ± 0.01 | 1.02 ± 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Tong, Z.; Luan, F.; Jiang, B.; Pu, F.; Xie, Z.; Wang, P.; Xu, Z. Effect of Particle Size on Physical Properties, Dissolution, In Vitro Antioxidant Activity, and In Vivo Hepatoprotective Properties of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg Powders. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16111352
Zhang Z, Chen Y, Wang S, Tong Z, Luan F, Jiang B, Pu F, Xie Z, Wang P, Xu Z. Effect of Particle Size on Physical Properties, Dissolution, In Vitro Antioxidant Activity, and In Vivo Hepatoprotective Properties of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg Powders. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(11):1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16111352
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhiwen, Yun Chen, Shaoxian Wang, Zheren Tong, Fujia Luan, Binghong Jiang, Faxiang Pu, Zhangfu Xie, Ping Wang, and Zijin Xu. 2024. "Effect of Particle Size on Physical Properties, Dissolution, In Vitro Antioxidant Activity, and In Vivo Hepatoprotective Properties of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg Powders" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 11: 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16111352
APA StyleZhang, Z., Chen, Y., Wang, S., Tong, Z., Luan, F., Jiang, B., Pu, F., Xie, Z., Wang, P., & Xu, Z. (2024). Effect of Particle Size on Physical Properties, Dissolution, In Vitro Antioxidant Activity, and In Vivo Hepatoprotective Properties of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg Powders. Pharmaceutics, 16(11), 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16111352





