Endosomal pH, Redox Dual-Sensitive Prodrug Micelles Based on Hyaluronic Acid for Intracellular Camptothecin Delivery and Active Tumor Targeting in Cancer Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
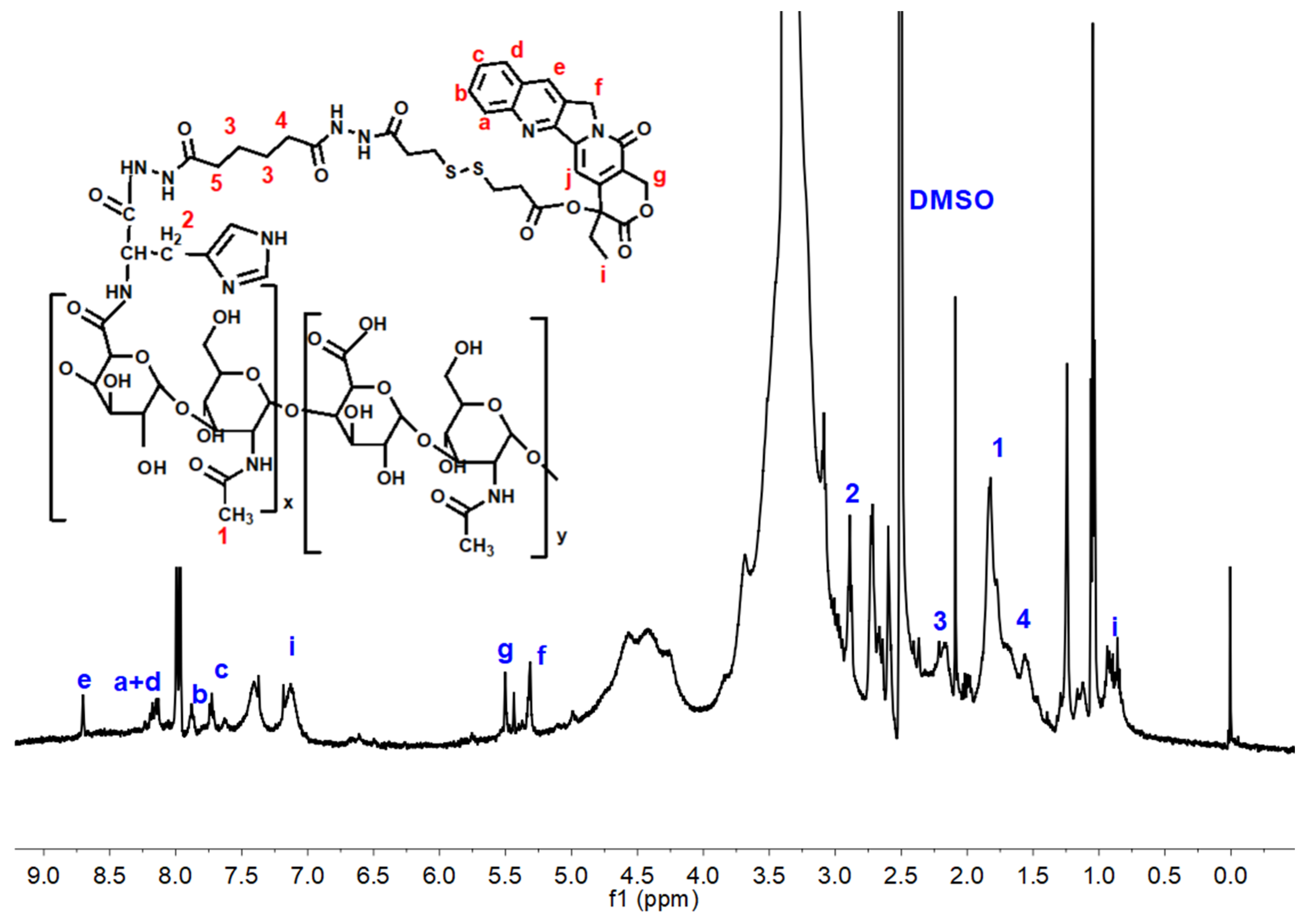
2.1. Polymer Synthesis
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of HHSC Micelles and HC Micelles
2.3. Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC) of HHSC Conjugates
2.4. In Vitro Stability of HHSC Micelles
2.5. In Vitro Drug Release Behavior of HHSC Micelles
2.6. Endosomal Escape of HHSC Micelles
2.7. Intracellular Localization of HHSC Micelles
2.8. In Vitro Cellular Uptake of HHSC Micelles
2.9. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assays of HHSC Micelles
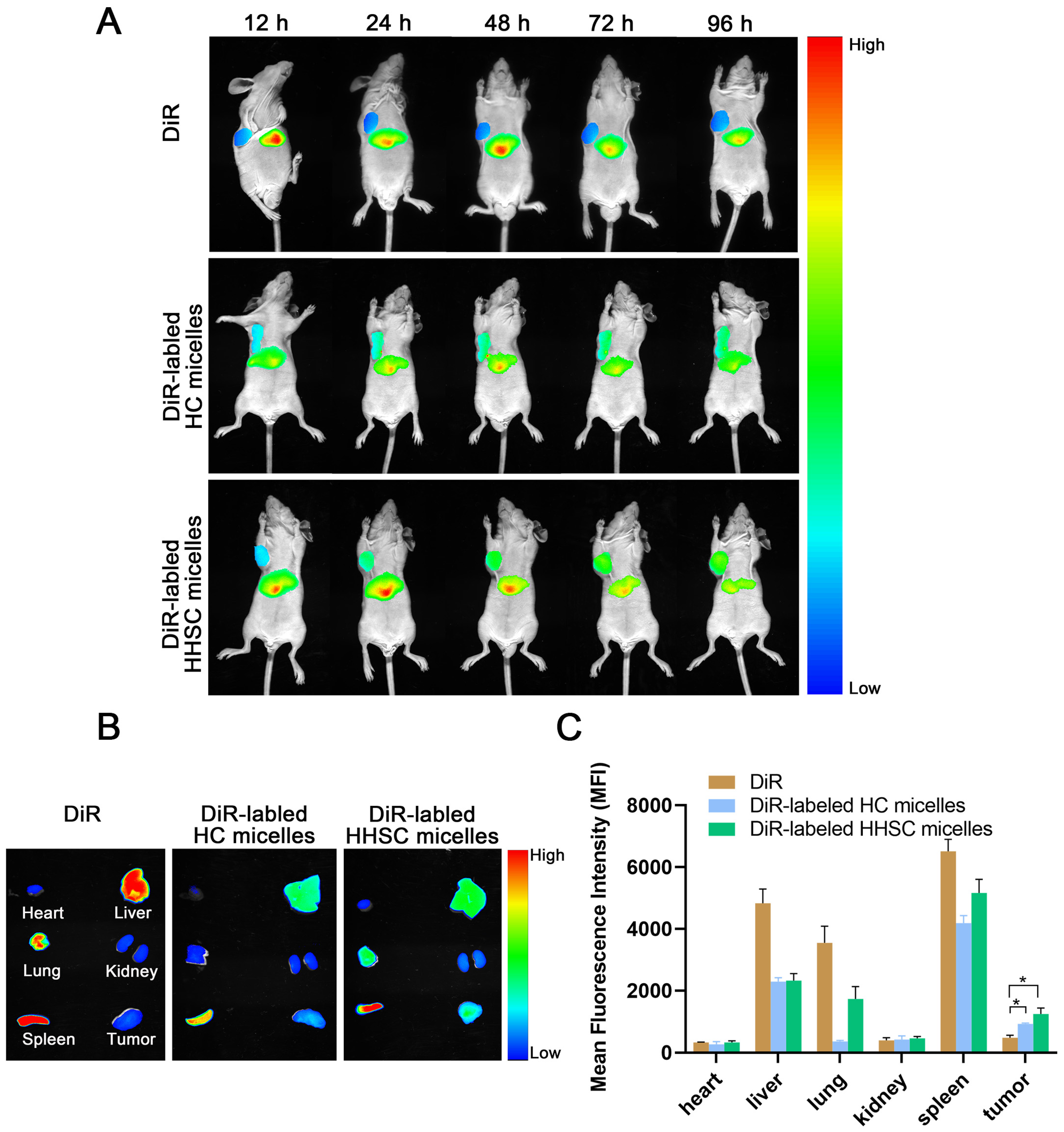
2.10. In Vivo Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging
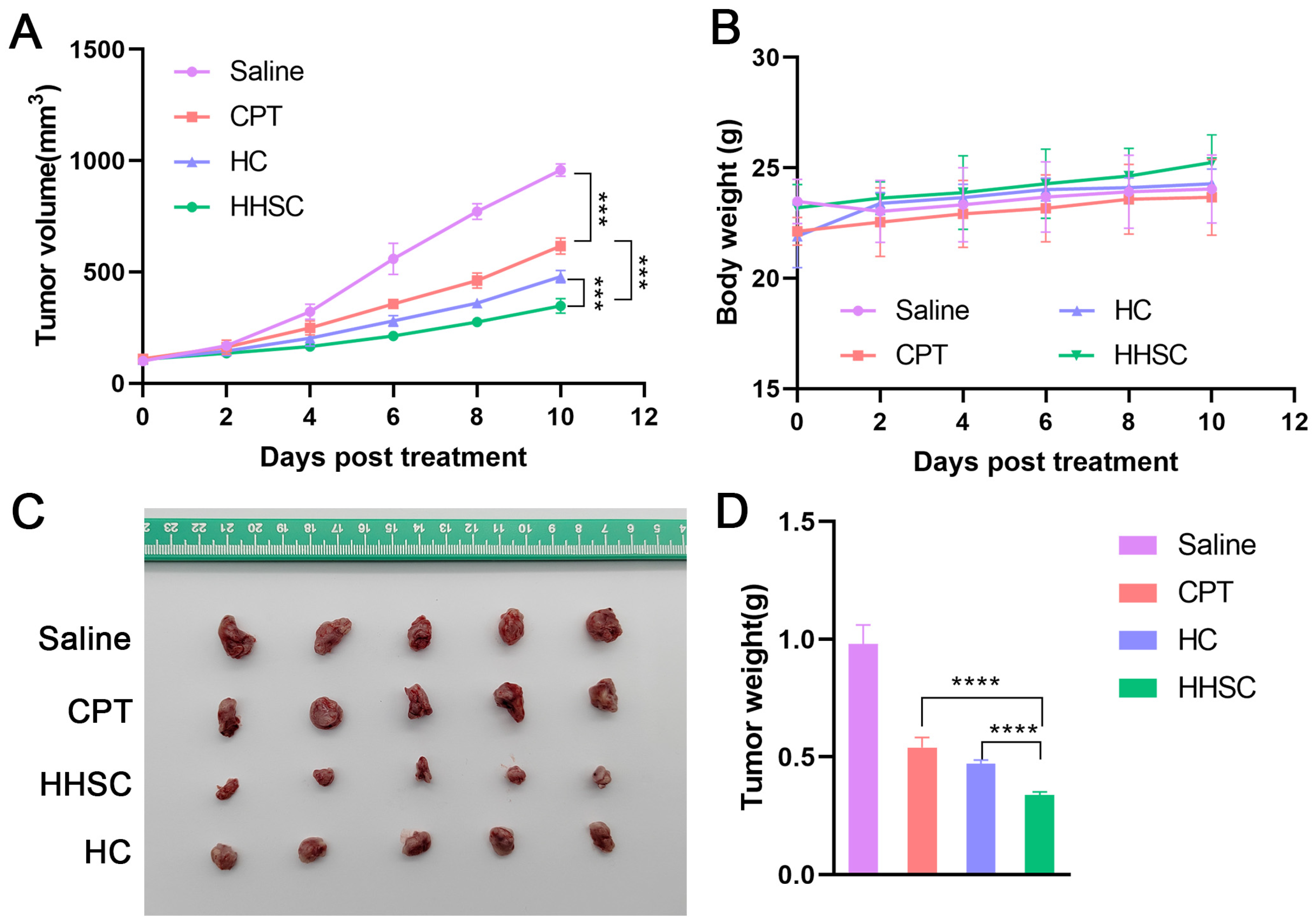
2.11. In Vivo Antitumor Efficacy Study
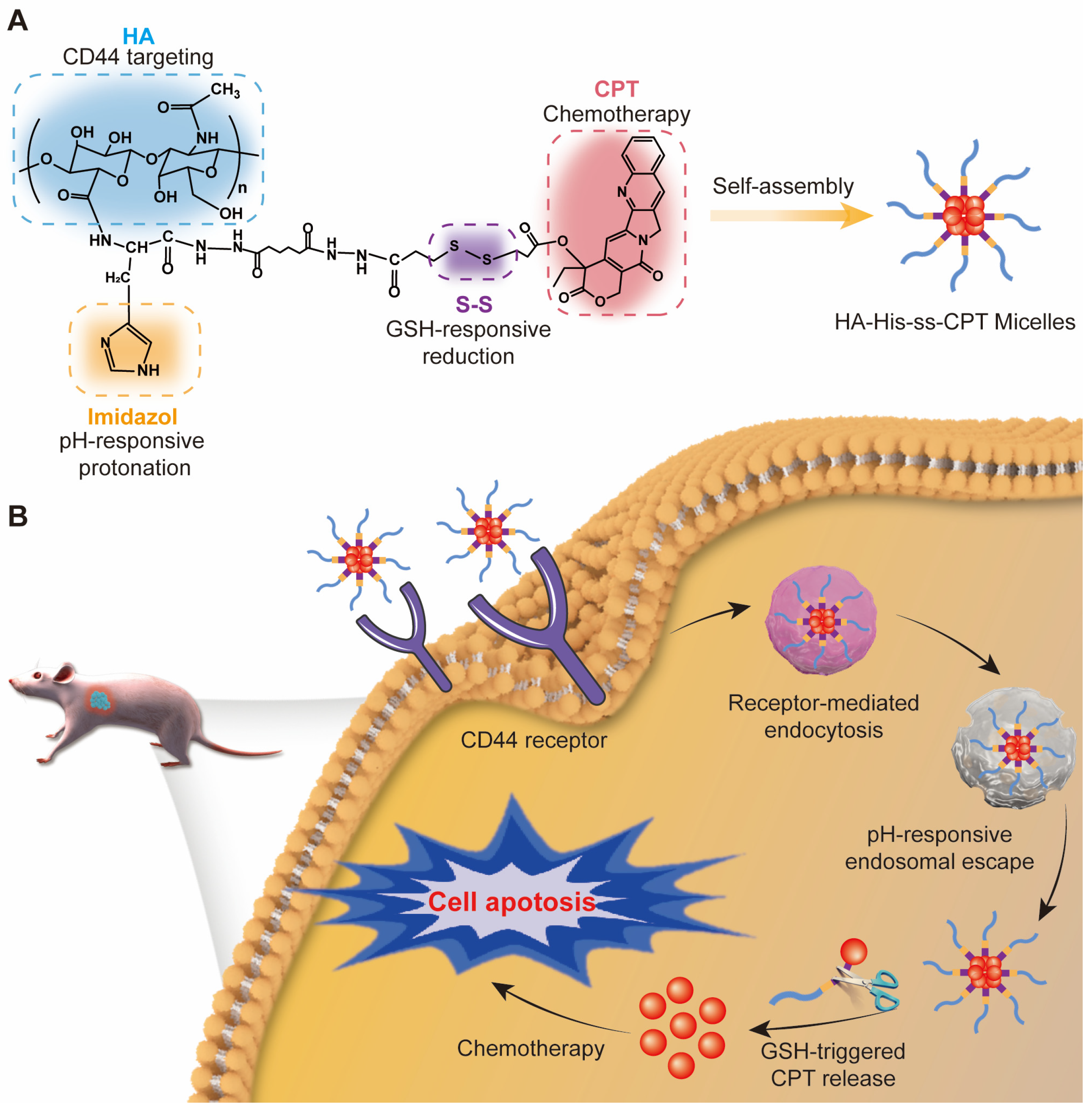
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of HHSC
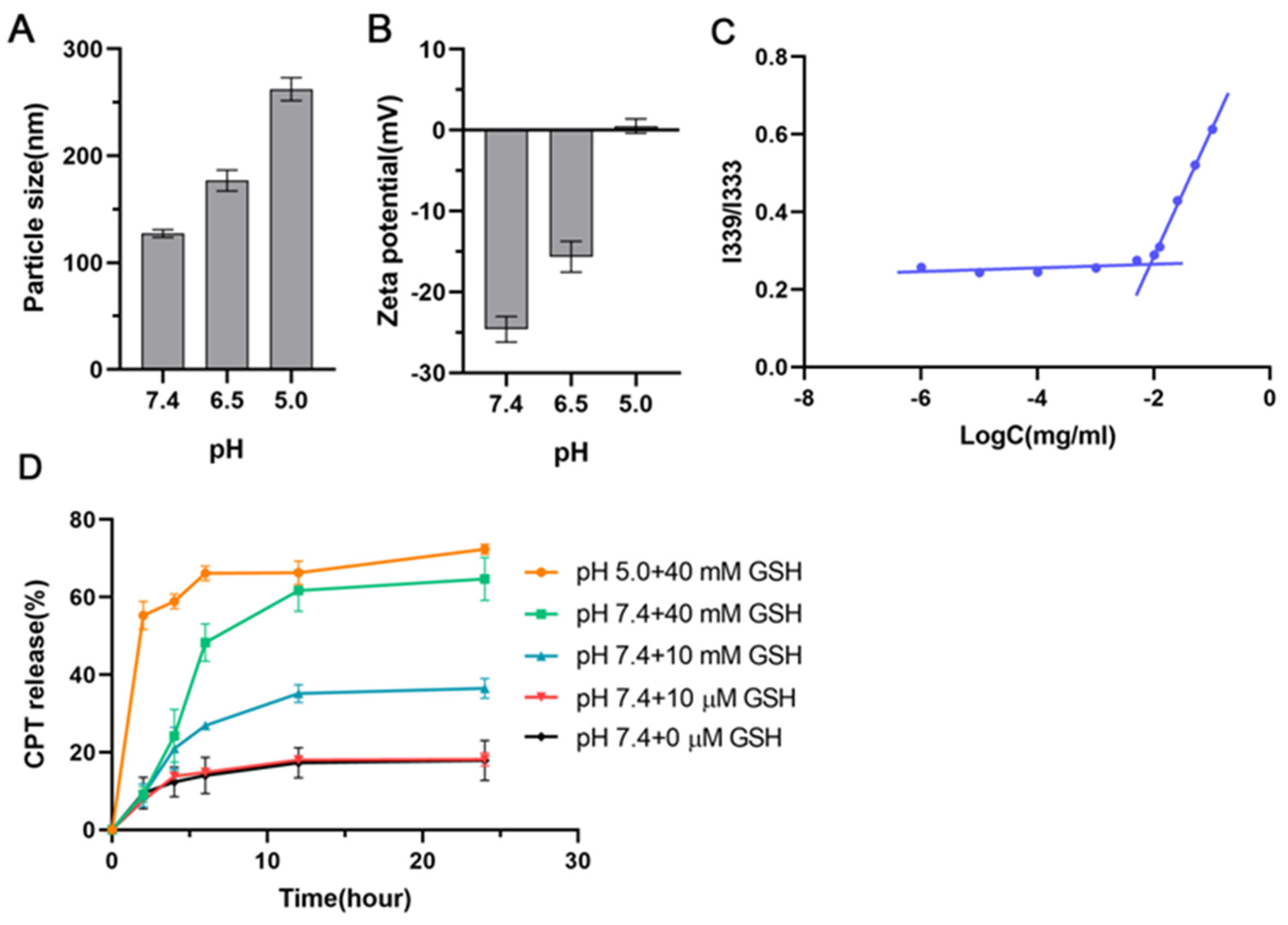
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of HHSC and HC Micelles
3.3. Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC) of HHSC Conjugates
3.4. In Vitro Stability of HHSC Micelles
3.5. In Vitro Drug Release Behavior of HHSC Micelles
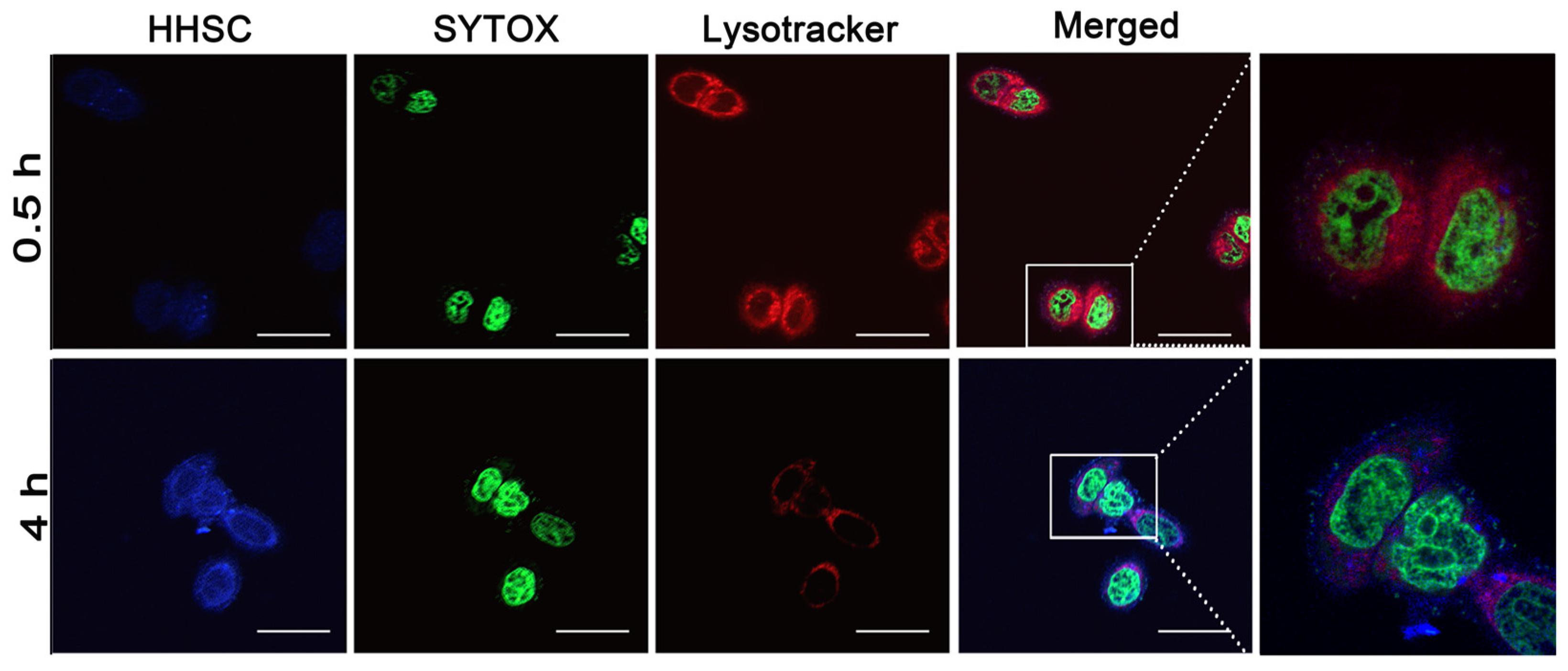
3.6. Endosomal Escape of HHSC Micelles
3.7. Intracellular Localization of HHSC Micelles
3.8. In Vitro Cellular Uptake of HHSC Micelles
3.9. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assays of HHSC Micelles
3.10. In Vivo Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging
3.11. In Vivo Antitumor Efficacy Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aghebati-Maleki, A.; Dolati, S.; Ahmadi, M.; Baghbanzhadeh, A.; Asadi, M.; Fotouhi, A.; Yousefi, M.; Aghebati-Maleki, L. Nanoparticles and cancer therapy: Perspectives for application of nanoparticles in the treatment of cancers. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 1962–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsink, M.; Parente, L.; Silva, F.; Abrantes, A.; Ramos, A.; Primo, I.; Willemen, N.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Severino, P.; Souto, E.B. Nanotherapeutics and Nanotheragnostics for Cancers: Properties, Pharmacokinetics, Biopharmaceutics, and Biosafety. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J. The Enhanced Permeability and Retention (EPR) Effect: The Significance of the Concept and Methods to Enhance Its Application. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, L.J.; Zhang, C.J.; Deng, K.; Ao, Y.W.; Mei, H.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C.X.; Yu, H.; Huang, S.W. Effect of Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) Surface Density on the Fate and Antitumor Efficacy of Redox-Sensitive Hybrid Nanoparticles. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 3975–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi-Soflou, R.; Karkhaneh, A. Redox-Sensitive multifunctional hyaluronic acid-based nanomicelles with Fine-controlled anticancer drug release. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 629, 122402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Zhu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, K.; Li, C.Y.; Cheng, H. Engineering long-circulating nanomaterial delivery systems. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 66, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.H.; Guo, Z.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, X.; Lin, L.; Zhao, D.; Chen, M. Linear-like polypeptide-based micelle with pH-sensitive detachable PEG to deliver dimeric camptothecin for cancer therapy. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 18, 100773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qhattal, H.S.; Hye, T.; Alali, A.; Liu, X. Hyaluronan polymer length, grafting density, and surface poly(ethylene glycol) coating influence in vivo circulation and tumor targeting of hyaluronan-grafted liposomes. ACS Nano. 2014, 8, 5423–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, X.; Hu, M.; Dong, M.; Yang, Z.; Zhan, X.; Chang, X.; Lu, J.; Chen, X. Folic Acid Decorated Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework (ZIF-8) Loaded with Baicalin as a Nano-Drug Delivery System for Breast Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 2021, 16, 8337–8352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzoca, A.; Lucarini, G.; Tognoni, E.; Tognarelli, S.; Ricotti, L.; Gherardini, L.; Pelosi, G.; Pellegrino, M.; Menciassi, A.; Grimaldi, S.; et al. Erythro-Magneto-HA-Virosome: A Bio-Inspired Drug Delivery System for Active Targeting of Drugs in the Lungs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, D.M.; Sharkey, R.M. Antibody-drug conjugates targeting TROP-2 and incorporating SN-38: A case study of anti-TROP-2 sacituzumab govitecan. MAbs 2019, 11, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Qi, G.; Zhang, M.; Hao, L. pH-Responsive Drug Delivery and Imaging Study of Hybrid Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Molecules 2022, 27, 6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, L.; Tang, L.; Xie, J.; Gao, Y.; Yu, C.; Shang, K.; Han, H.; Liu, C.; Lu, Y. Glutathione-Responsive Nanoparticles of Camptothecin Prodrug for Cancer Therapy. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2205246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Cui, L.; Xu, J.; Xian, S.; Meng, F.; Zhan, C.; Wang, H. De novo engineering of both an omega-3 fatty acid-derived nanocarrier host and a prodrug guest to potentiate drug efficacy against colorectal malignancies. Biomaterials 2022, 290, 121814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Mu, J.; Jacobson, O.; Wang, Z.; He, L.; Zhang, F.; Yang, W.; Lin, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, Y.; et al. Reactive Oxygen Species Activatable Heterodimeric Prodrug as Tumor-Selective Nanotheranostics. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 16875–16886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.C.; Yang, X.Z.; Luo, C.M.; Wen, L.F.; Liu, J.Y.; Lin, Z. A promising strategy for synergistic cancer therapy by integrating a photosensitizer into a hypoxia-activated prodrug. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 243, 114749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Xie, S.; Zhou, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, P.; Jiang, R.; Hang, L.; Jiang, G. All-In-One Second Near-Infrared Light-Responsive Drug Delivery System for Synergistic Chemo-Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 3841–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farjadian, F.; Rezaeifard, S.; Naeimi, M.; Ghasemi, S.; Mohammadi-Samani, S.; Welland, M.E.; Tayebi, L. Temperature and pH-responsive nano-hydrogel drug delivery system based on lysine-modified poly (vinylcaprolactam). Int. J. Nanomedicine. 2019, 14, 6901–6915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, S.; Nair, A.B.; Shah, J.; Sreeharsha, N.; Gupta, S.; Shinu, P. Emerging role of hydrogels in drug delivery systems, tissue engineering and wound management. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, F.; Fang, Z.; Li, L.; Wan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, X. pH-triggered “PEG” sheddable and folic acid-targeted nanoparticles for docetaxel delivery in breast cancer treatment. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 644, 123293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Qiao, Z.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, R. A small molecule nanodrug consisting of pH-sensitive ortho ester-dasatinib conjugate for cancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 163, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswanadh, M.K.; Agrawal, N.; Azad, S.; Jha, A.; Poddar, S.; Mahto, S.K.; Muthu, M.S. Novel redox-sensitive thiolated TPGS based nanoparticles for EGFR targeted lung cancer therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 602, 120652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Sun, K.; Sun, J. Combination prostate cancer therapy: Prostate-specific membranes antigen targeted, pH-sensitive nanoparticles loaded with doxorubicin and tanshinone. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; He, W.; Du, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Redox-sensitive irinotecan liposomes with active ultra-high loading and enhanced intracellular drug release. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 206, 111967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, M.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Tong, Y.; Hu, C.; Gu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yin, T. Redox-sensitive hyaluronic acid-cholesterol nanovehicles potentiate efficient transmembrane internalization and controlled release for penetrated “full-line” inhibition of pre-metastatic initiation. J. Control Release 2021, 336, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaiwa, N.; Maarouf, N.R.; Darwish, M.H.; Alhamad, D.W.M.; Sebastian, A.; Hamad, M.; Omar, H.A.; Orive, G.; Al-Tel, T.H. Camptothecin’s journey from discovery to WHO Essential Medicine: Fifty years of promise. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 223, 113639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murjan, S.; Saeedi, S.; Nabid, M.R. Dual Redox/pH-Sensitive Micelles Self-Assembled From Star-Like Amphiphilic Copolymers Based On Sucrose For Controlled Doxorubicin Delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 2196–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Yao, B.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; He, P.; Vasilatos, S.N.; Ren, X.; Bian, W.; Yao, C. Transferrin receptor-targeted redox/pH-sensitive podophyllotoxin prodrug micelles for multidrug-resistant breast cancer therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 5814–5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjama, M.; Mehnath, S.; Rajan, M.; Jeyaraj, M. Engineered Hyaluronic Acid-Based Smart Nanoconjugates for Enhanced Intracellular Drug Delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, Q.N.; Li, Y.; Jang, M.S.; Huynh, D.P.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, D.S. Redox-and pH-Sensitive Polymeric Micelles Based on Poly(β-amino ester)-Grafted Disulfide Methylene Oxide Poly(ethylene glycol) for Anticancer Drug Delivery. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 4046–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yu, J.; Guo, Z.; Jiang, H.; Wang, C. Camptothecin-based prodrug nanomedicines for cancer therapy. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 17658–17697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Sala, F.; Fabozzi, A.; di Gennaro, M.; Nuzzo, S.; Makvandi, P.; Solimando, N.; Pagliuca, M.; Borzacchiello, A. Advances in Hyaluronic-Acid-Based (Nano)Devices for Cancer Therapy. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, e2100304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Huai, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gan, Y.; Wang, G.; Gu, X.; Li, J. Intracellular delivery and antitumor effects of a redox-responsive polymeric paclitaxel conjugate based on hyaluronic acid. Acta Biomater. 2015, 26, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, V.B.; Sharma, C.P. Folate mediated histidine derivative of quaternised chitosan as a gene delivery vector. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 389, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.L.; Liu, C.G.; Wang, X.L.; Huang, Z.H. Preparation and characterization of nanoparticles based on histidine-hyaluronic acid conjugates as doxorubicin carriers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Khan, J.M.; Paray, B.A.; Rashid, K.; Parvez, A. Endolysosomal trapping of therapeutics and endosomal escape strategies. Drug Discov. Today. 2024, 29, 104070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.S.; Gonçalves, C.; Sandrin, P.; Pichon, C.; Midoux, P.; Chaudhuri, A. On the gene delivery efficacies of pH-sensitive cationic lipids via endosomal protonation: A chemical biology investigation. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.S.; Hu, J.; Na, K.; Bae, Y.H. Role of polymeric endosomolytic agents in gene transfection: A comparative study of poly(L-lysine) grafted with monomeric L-histidine analogue and poly(L-histidine). Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 3577–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Hong, W.; Huang, Y. CD44 Receptor Targeting and Endosomal pH-Sensitive Dual Functional Hyaluronic Acid Micelles for Intracellular Paclitaxel Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 4209–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Kirker, K.R.; Prestwich, G.D. Cross-linked hyaluronic acid hydrogel films: New biomaterials for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2000, 69, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; He, N.; Chen, M.; Zhao, L.; Li, X. Tunable conjugation densities of camptothecin on hyaluronic acid for tumor targeting and reduction-triggered release. Acta Biomater. 2016, 43, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajan, G.; Ray, A.; Malugin, A.; Ghandehari, H. PAMAM-camptothecin conjugate inhibits proliferation and induces nuclear fragmentation in colorectal carcinoma cells. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 2307–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Verma, A.; Singh, J.; Teja, B.V.; Mittapelly, N.; Pandey, G.; Urandur, S.; Shukla, R.P.; Konwar, R.; Mishra, P.R. Vitamin B6 Tethered Endosomal pH Responsive Lipid Nanoparticles for Triggered Intracellular Release of Doxorubicin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 30407–30421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Yang, J.; Ma, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X. Dual sensitive and temporally controlled camptothecin prodrug liposomes codelivery of siRNA for high efficiency tumor therapy. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 9731–9745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Huang, Z.; Chen, H.; Yan, L.; Li, J.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, Y. Redox-sensitive lipophilic prodrugs: Delivering unstable chemotherapeutant for improved cancer therapy. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 1068–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beretta, G.L.; Zunino, F. Relevance of extracellular and intracellular interactions of camptothecins as determinants of antitumor activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatangelo, G.; Vindigni, V.; Avruscio, G.; Pandis, L.; Brun, P. Hyaluronic Acid: Redefining Its Role. Cells 2020, 9, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yuan, J.; Luo, X.; Chen, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X. Folate-decorated and reduction-sensitive micelles assembled from amphiphilic polymer-camptothecin conjugates for intracellular drug delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 4258–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Li, W.; Yin, H.; Wang, H.; Ke, X. Endosomal pH, Redox Dual-Sensitive Prodrug Micelles Based on Hyaluronic Acid for Intracellular Camptothecin Delivery and Active Tumor Targeting in Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16101327
Zhang H, Li L, Li W, Yin H, Wang H, Ke X. Endosomal pH, Redox Dual-Sensitive Prodrug Micelles Based on Hyaluronic Acid for Intracellular Camptothecin Delivery and Active Tumor Targeting in Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(10):1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16101327
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huiping, Liang Li, Wei Li, Hongxia Yin, Huiyun Wang, and Xue Ke. 2024. "Endosomal pH, Redox Dual-Sensitive Prodrug Micelles Based on Hyaluronic Acid for Intracellular Camptothecin Delivery and Active Tumor Targeting in Cancer Therapy" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 10: 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16101327
APA StyleZhang, H., Li, L., Li, W., Yin, H., Wang, H., & Ke, X. (2024). Endosomal pH, Redox Dual-Sensitive Prodrug Micelles Based on Hyaluronic Acid for Intracellular Camptothecin Delivery and Active Tumor Targeting in Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics, 16(10), 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16101327






