Characteristics of the Enterococcus Phage vB_EfS_SE, and the Properties of Its Chimeric Endolysins Harboring a PlySE-Carbohydrate-Binding Domain and a Synthetic Enzymatic Domain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Phage Isolation
2.3. Production of Preparative Quantities of Phage, Purification, Titer Determination and Storage
2.4. Determination of Phage Host Range
2.5. Phage DNA Extraction, Purification, Sequencing and Genome Assembly
2.6. Genome Annotation
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.9. Killing Assay and the Effect of Ca2+ and Mg2+ Salts
2.10. Bacteriophage Thermal and pH Stability
2.11. Cloning of Endolysin Genes
2.12. Expression and Purification of Endolysins
2.13. Bacteriolytic Spectrum of Endolysins
2.14. Turbidimetric Assay of Endolysin Activity
2.15. pH Optimum and Thermal Stability of Endolysins
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Specificity Range
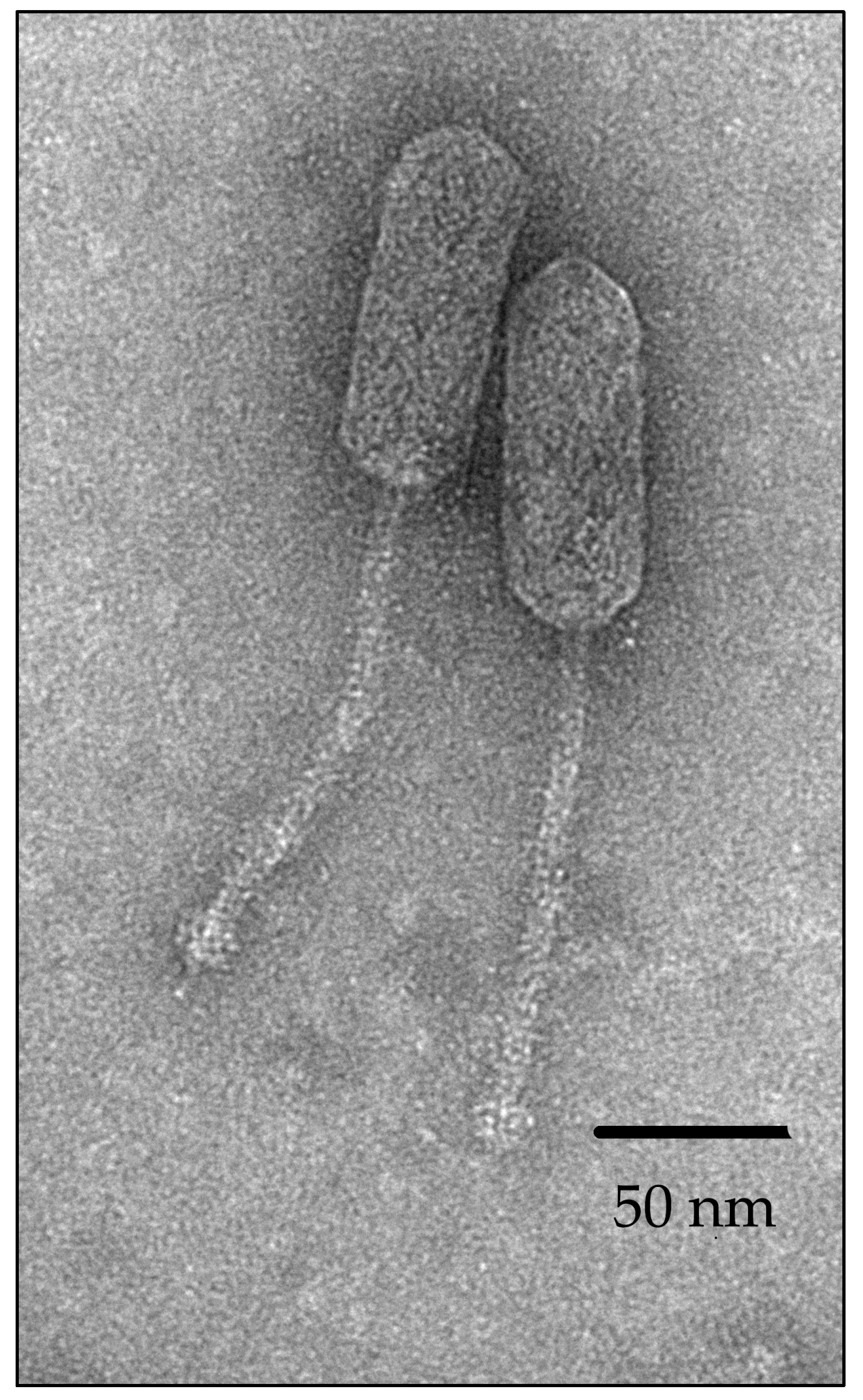
3.2. Plaques and Virion Morphology
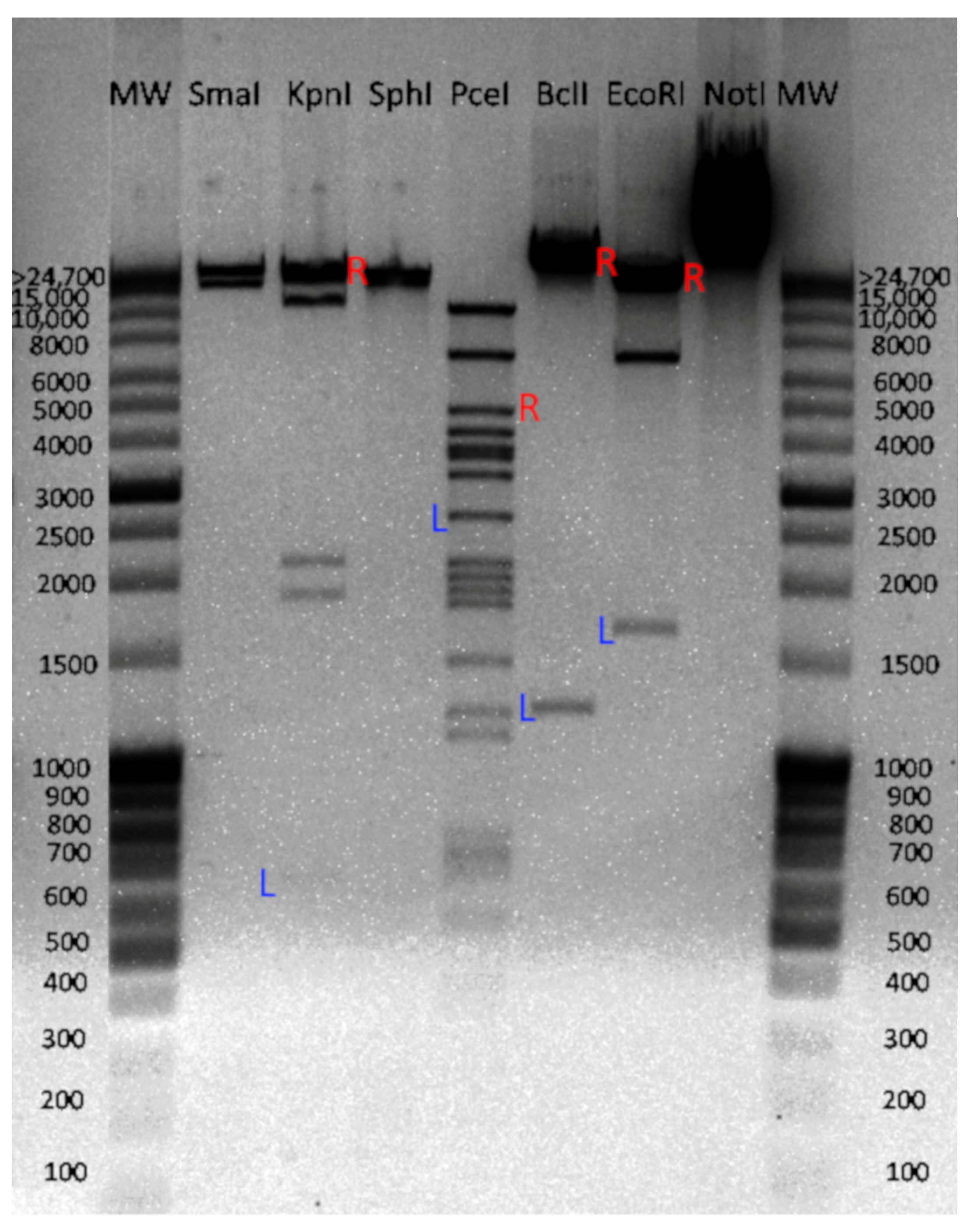
3.3. DNA Packing and Chromosome Organization
3.4. Genome Sequence
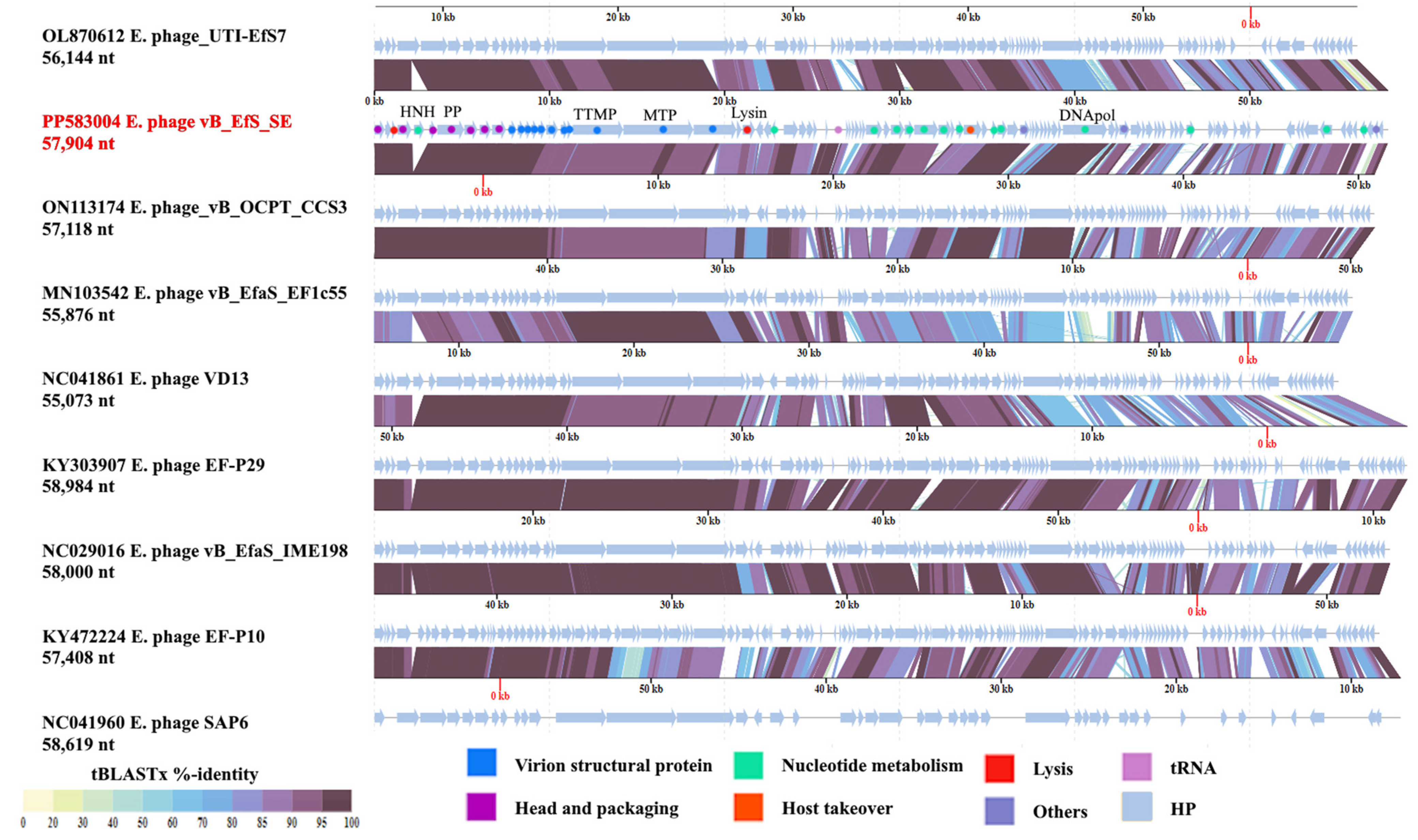
3.5. Genome Organization
3.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
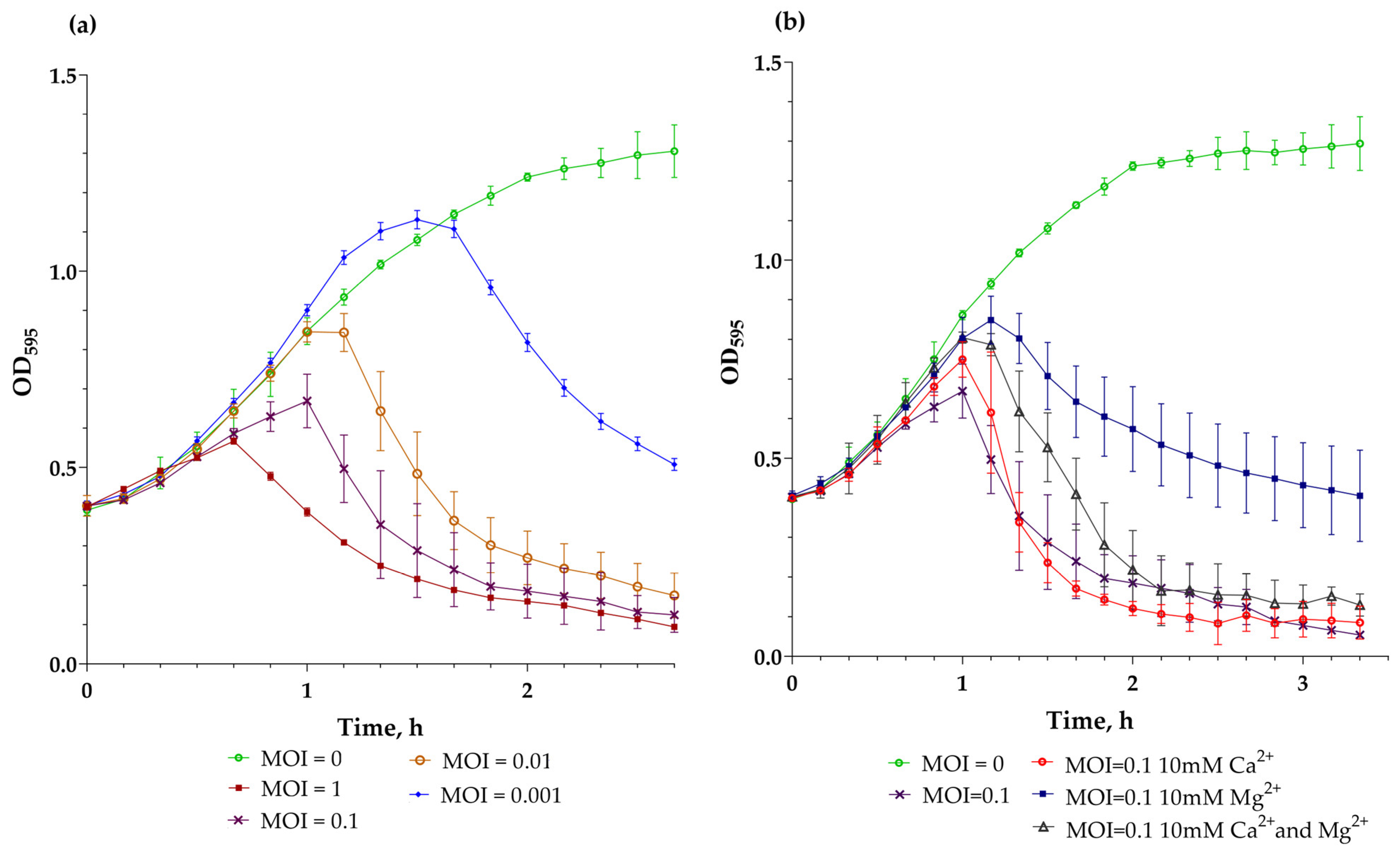
3.7. Killing Assay, Mg2+ and Ca2+ Effects
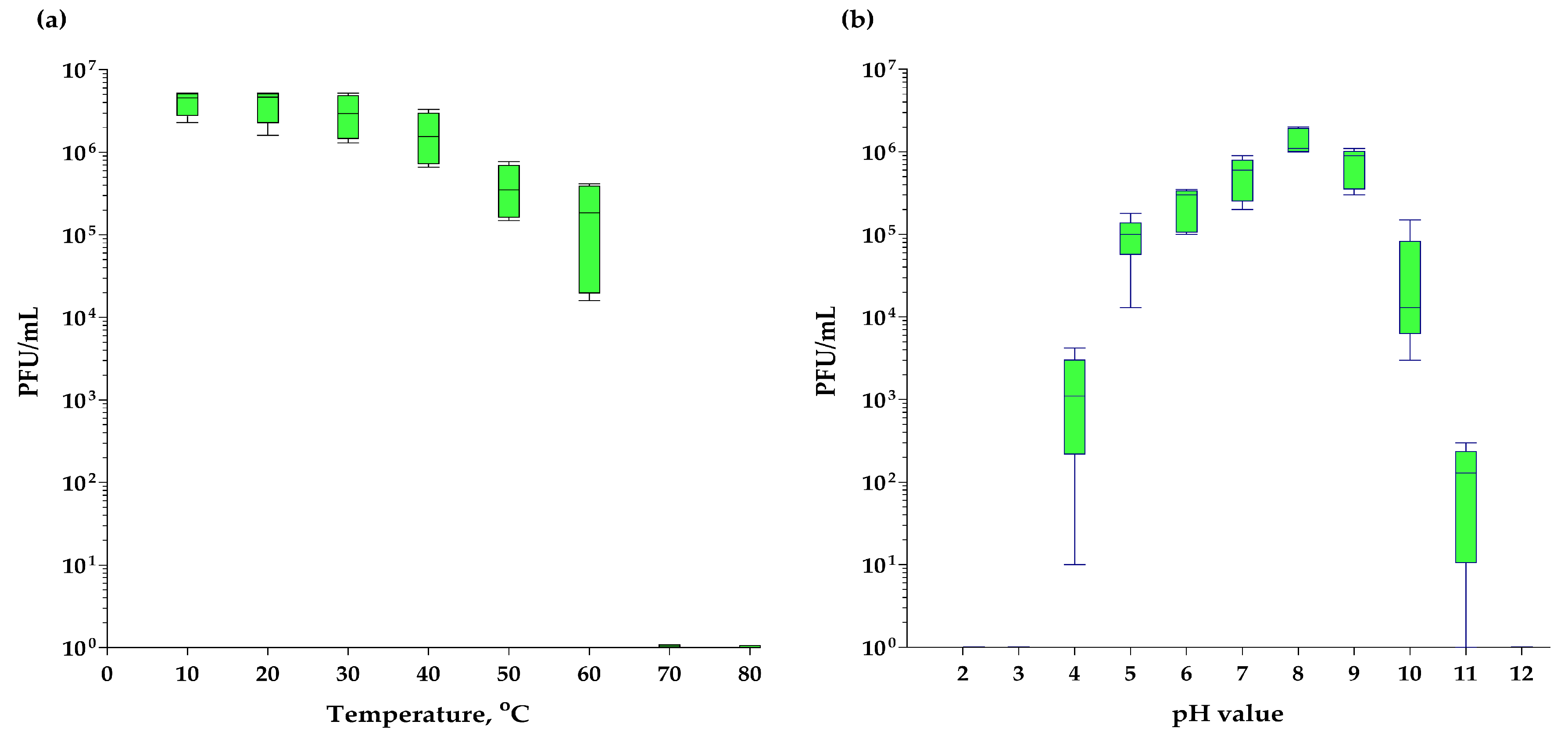
3.8. Thermostability and pH-Stability
3.9. vB_EfS_SE-Phage Endolysin (PlySE), and the Design and Construction of Its Homologs
3.10. The Bacteriolytic Spectrum of PlySE Endolysin and Its Homologs
3.11. pH-Range of Endolysins Activity
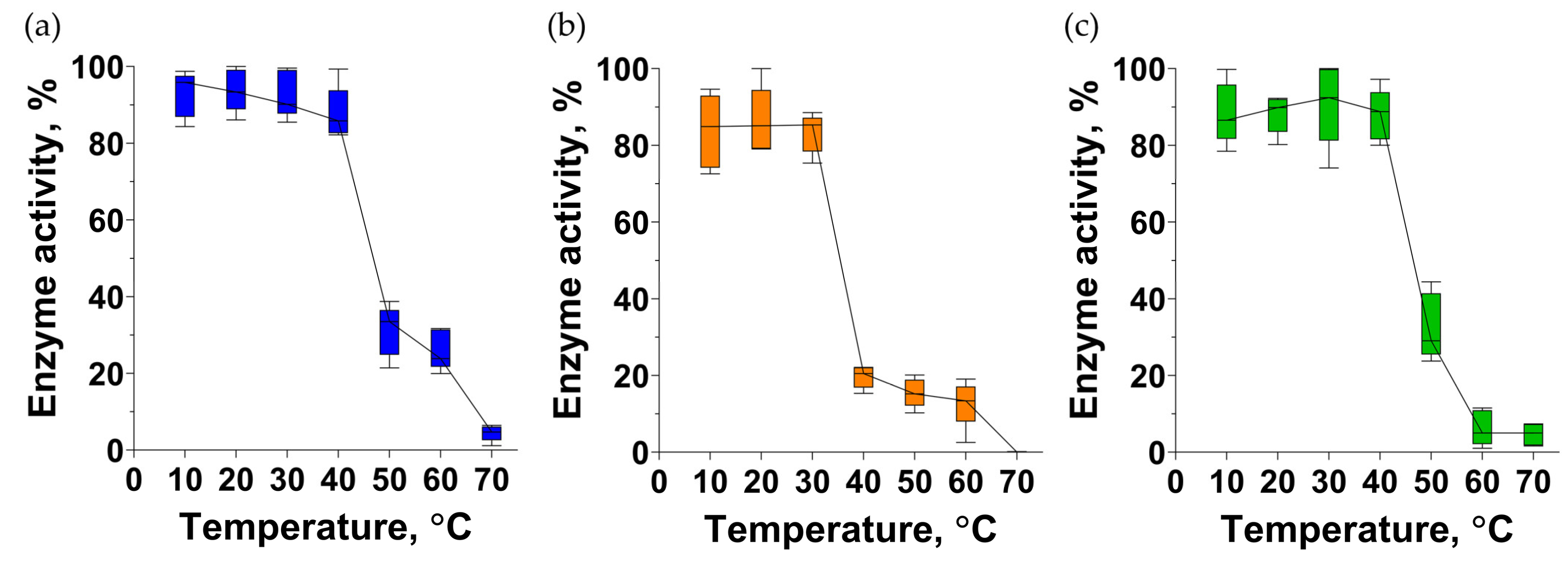
3.12. Endolysins Thermostability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gilmore, M.S.; Clewell, D.B.; Ike, Y.; Shankar, N. (Eds.) Enterococci: From Commensals to Leading Causes of Drug Resistant Infection; Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary: Boston, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bittencourt De Marques, E.; Suzart, S. Occurrence of Virulence-Associated Genes in Clinical Enterococcus Faecalis Strains Isolated in Londrina, Brazil. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiti, T.K.; Nagarathna, S.; Veena Kumari, H.B.; Shukla, D.P. A Series of Enterococcal Brain Abscesses. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2015, 6, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sood, S.; Malhotra, M.; Das, B.K.; Kapil, A. Enterococcal Infections & Antimicrobial Resistance. Indian J. Med. Res. 2008, 128, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; ISBN 978-92-4-009346-1. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. 2023 Antibacterial Agents in Clinical and Preclinical Development an Overview and Analysis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; ISBN 978-92-4-009400-0. [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti, V.A. Bacteriophage Endolysins: A Novel Anti-Infective to Control Gram-Positive Pathogens. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 300, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorynina, A.V.; Piligrimova, E.G.; Kazantseva, O.A.; Kulyabin, V.A.; Baicher, S.D.; Ryabova, N.A.; Shadrin, A.M. Bacillus-Infecting Bacteriophage Izhevsk Harbors Thermostable Endolysin with Broad Range Specificity. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; CSHL Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-0-87969-576-7. [Google Scholar]
- Cock, P.J.A.; Antao, T.; Chang, J.T.; Chapman, B.A.; Cox, C.J.; Dalke, A.; Friedberg, I.; Hamelryck, T.; Kauff, F.; Wilczynski, B.; et al. Biopython: Freely Available Python Tools for Computational Molecular Biology and Bioinformatics. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1422–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.; Biggins, L.; Inglesfield, S.; Carr, H.; Montgomery, J. FastQC 2024. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Schultz, M.B.; Zobel, J.; Holt, K.E. Bandage: Interactive Visualization of de Novo Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3350–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, I.; Stephen, G.; Bayer, M.; Cock, P.J.A.; Pritchard, L.; Cardle, L.; Shaw, P.D.; Marshall, D. Using Tablet for Visual Exploration of Second-Generation Sequencing Data. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouras, G.; Nepal, R.; Houtak, G.; Psaltis, A.J.; Wormald, P.-J.; Vreugde, S. Pharokka: A Fast Scalable Bacteriophage Annotation Tool. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btac776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzikov, R.M.; Kazantseva, O.A.; Piligrimova, E.G.; Ryabova, N.A.; Shadrin, A.M. Bacteriolytic Potential of Enterococcus Phage iF6 Isolated from “Sextaphag®” Therapeutic Phage Cocktail and Properties of Its Endolysins, Gp82 and Gp84. Viruses 2023, 15, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Li, K.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Gu, L.; Xun, L. T5 Exonuclease-Dependent Assembly Offers a Low-Cost Method for Efficient Cloning and Site-Directed Mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Zhen, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, F.; Fan, C.; Perčulija, V.; Tong, Y.; Mi, Z.; Ouyang, S. Structural and Functional Insights into a Novel Two-Component Endolysin Encoded by a Single Gene in Enterococcus Faecalis Phage. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Kuronishi, M.; Uehara, H.; Ogata, H.; Goto, S. ViPTree: The Viral Proteomic Tree Server. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2379–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meile, S.; Du, J.; Staubli, S.; Grossmann, S.; Koliwer-Brandl, H.; Piffaretti, P.; Leitner, L.; Matter, C.I.; Baggenstos, J.; Hunold, L.; et al. Engineered Reporter Phages for Detection of Escherichia Coli, Enterococcus, and Klebsiella in Urine. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraru, C.; Varsani, A.; Kropinski, A.M. VIRIDIC—A Novel Tool to Calculate the Intergenomic Similarities of Prokaryote-Infecting Viruses. Viruses 2020, 12, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Chen, Y.; Sun, E.; Hua, L.; Peng, Z.; Wu, B. Characterization of a Lytic Bacteriophage vB_EfaS_PHB08 Harboring Endolysin Lys08 against Enterococcus Faecalis Biofilms. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Mi, Z.; Yin, X.; Fan, H.; An, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Tong, Y. Characterization of Enterococcus Faecalis Phage IME-EF1 and Its Endolysin. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Im, J.; Na, H.; Ryu, S.; Yun, C.-H.; Han, S.H. The Novel Enterococcus Phage vB_EfaS_HEf13 Has Broad Lytic Activity Against Clinical Isolates of Enterococcus Faecalis. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Telbany, M.; Lin, C.-Y.; Abdelaziz, M.N.; Maung, A.T.; El-Shibiny, A.; Mohammadi, T.N.; Zayda, M.; Wang, C.; Zar Chi Lwin, S.; Zhao, J.; et al. Potential Application of Phage vB_EfKS5 to Control Enterococcus Faecalis and Its Biofilm in Food. AMB Exp. 2023, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Liang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, L.; Gong, P.; Cai, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Ge, J.; Ji, Y.; et al. The Bacteriophage EF-P29 Efficiently Protects against Lethal Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus Faecalis and Alleviates Gut Microbiota Imbalance in a Murine Bacteremia Model. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkachev, P.V.; Pchelin, I.M.; Azarov, D.V.; Gorshkov, A.N.; Shamova, O.V.; Dmitriev, A.V.; Goncharov, A.E. Two Novel Lytic Bacteriophages Infecting Enterococcus Spp. Are Promising Candidates for Targeted Antibacterial Therapy. Viruses 2022, 14, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Dou, J.; Lin, Z.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Wen, G.; Shao, H.; Cheng, G.; et al. Virulent Phage vB_EfaS_WH1 Removes Enterococcus Faecalis Biofilm and Inhibits Its Growth on the Surface of Chicken Meat. Viruses 2023, 15, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Guo, W.; Lu, J.; Pan, W.; Song, F.; Wang, P. Enterococcus Faecalis Bacteriophage vB_EfaS_efap05-1 Targets the Surface Polysaccharide and ComEA Protein as the Receptors. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 866382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkson, J.D.; Wate, C.E.; Allen, G.B.; Schubert, A.M.; Dunbar, K.E.; Coryell, M.P.; Sava, R.L.; Gao, Y.; Hastie, J.L.; Smith, E.M.; et al. Phage-Specific Immunity Impairs Efficacy of Bacteriophage Targeting Vancomycin Resistant Enterococcus in a Murine Model. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lallo, G.; Falconi, M.; Iacovelli, F.; Frezza, D.; D’Addabbo, P. Analysis of Four New Enterococcus Faecalis Phages and Modeling of a Hyaluronidase Catalytic Domain from Saphexavirus. Ther. Appl. Res. 2021, 2, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Hu, L.; Gong, P.; Zhang, L.; Cai, R.; Zhang, H.; Ge, J.; et al. Endolysin LysEF-P10 Shows Potential as an Alternative Treatment Strategy for Multidrug-Resistant Enterococcus Faecalis Infections. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, S.M.; Rowley, D.T.; Young, C.; Franks, A.; Hyman, P.; Donovan, D.M. The Endolysin from the Enterococcus Faecalis Bacteriophage VD13 and Conditions Stimulating Its Lytic Activity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363, fnw216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Lv, Y.; Zheng, W.; Mi, Z.; Pei, G.; An, X.; Xu, X.; Han, C.; Liu, J.; et al. Characterization and Complete Genome Sequence Analysis of Novel Bacteriophage IME-EFm1 Infecting Enterococcus Faecium. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2565–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| # | Species | Strain | vB_EfS_SE | PlySE | PlyIME-SE | PlyShip-SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | E. avium | VKM B-1673 | + | + | + | + |
| 2 | E. durans | VKM B-603 | - | - | - | - |
| 3 | VKPM B-8257 | - | - | - | - | |
| 4 | VKPM B-11854 | - | - | - | - | |
| 5 | E. faecalis | VKPM B-12629 | + | + | + | + |
| 6 | VKPM B-4426 | - | - | - | - | |
| 7 | VKPM B-4053 | - | - | - | - | |
| 8 | E. faecium | FS86 | - | - | - | - |
| 9 | VKPM B-2579 | - | - | - | - | |
| 10 | VKPM B-2990 | - | - | - | - | |
| 11 | VKPM B-3490 | - | - | - | - | |
| 12 | VKPM B-3491 | - | - | - | - | |
| 13 | VKPM B-4054 | + | + | + | + | |
| 14 | VKPM B-4489 | - | - | - | - | |
| 15 | VKPM B-4991 | - | - | - | - | |
| 16 | VKPM B-5000 | - | - | - | - | |
| 17 | VKPM B-8551 | - | - | - | - | |
| 18 | VKPM B-12648 | - | - | - | - | |
| 19 | E. hirae | VKPM B-12152 | + | + | + | + |
| 20 | E. sp. | VKM B-1578 | - | - | - | - |
| 21 | VKM B-1944 | - | - | - | - | |
| 22 | VKPM B-3371 | - | - | - | - | |
| 23 | VKPM B-8711 | - | - | - | - | |
| 24 | VKPM B-8712 | - | - | - | - | |
| 25 | VKPM B-8713 | - | - | - | - | |
| 26 | E. thailandicus | VKPM B-10684 | - | - | - | - |
| E. coli | XL1 Blue | - | - | - | - | |
| B. cereus | B370 | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buzikov, R.M.; Kulyabin, V.A.; Koposova, O.N.; Arlyapov, V.A.; Shadrin, A.M. Characteristics of the Enterococcus Phage vB_EfS_SE, and the Properties of Its Chimeric Endolysins Harboring a PlySE-Carbohydrate-Binding Domain and a Synthetic Enzymatic Domain. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16101312
Buzikov RM, Kulyabin VA, Koposova ON, Arlyapov VA, Shadrin AM. Characteristics of the Enterococcus Phage vB_EfS_SE, and the Properties of Its Chimeric Endolysins Harboring a PlySE-Carbohydrate-Binding Domain and a Synthetic Enzymatic Domain. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(10):1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16101312
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuzikov, Rustam M., Vladislav A. Kulyabin, Olga N. Koposova, Vyacheslav A. Arlyapov, and Andrey M. Shadrin. 2024. "Characteristics of the Enterococcus Phage vB_EfS_SE, and the Properties of Its Chimeric Endolysins Harboring a PlySE-Carbohydrate-Binding Domain and a Synthetic Enzymatic Domain" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 10: 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16101312
APA StyleBuzikov, R. M., Kulyabin, V. A., Koposova, O. N., Arlyapov, V. A., & Shadrin, A. M. (2024). Characteristics of the Enterococcus Phage vB_EfS_SE, and the Properties of Its Chimeric Endolysins Harboring a PlySE-Carbohydrate-Binding Domain and a Synthetic Enzymatic Domain. Pharmaceutics, 16(10), 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16101312









