Biocompatible Snowman-like Dimer Nanoparticles for Improved Cellular Uptake in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
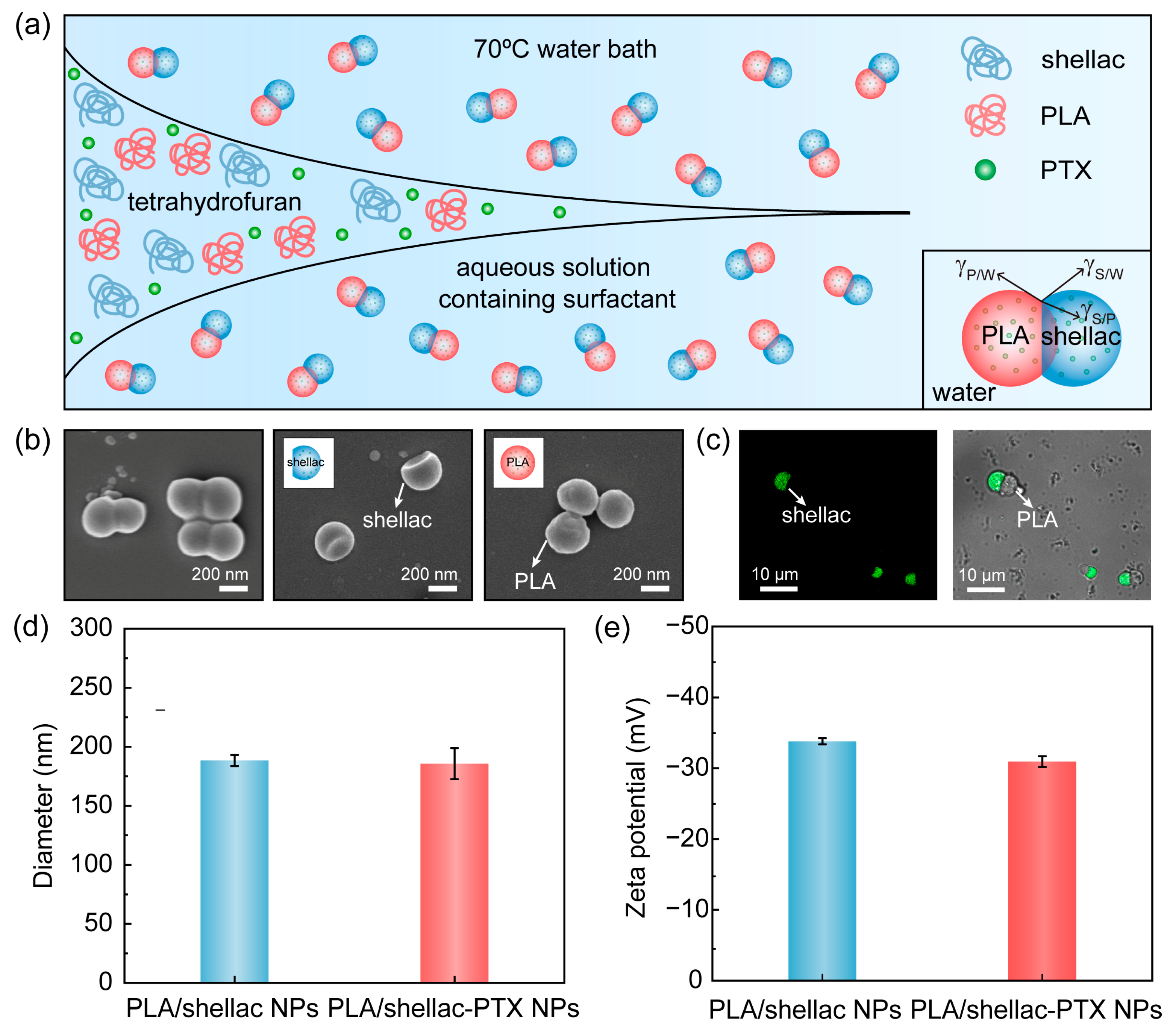
2.1. Preparation of Drug-Loaded PLA/Shellac Dimer Nanoparticles (NPs)
2.2. Characterization of PLA/Shellac Dimer NPs
2.3. Drug Loading Capacity of PLA/Shellac Dimer NPs
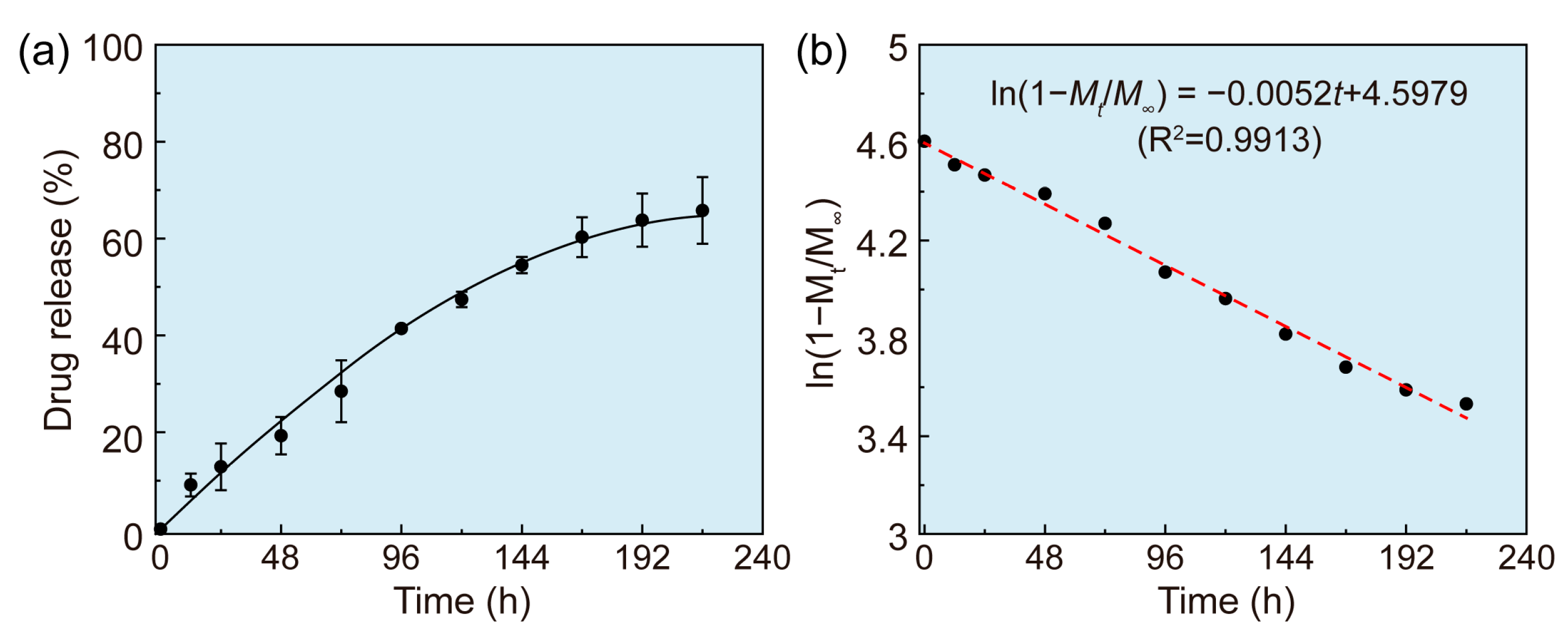
2.4. In Vitro Drug Release of Drug-Loaded PLA/Shellac Dimer NPs
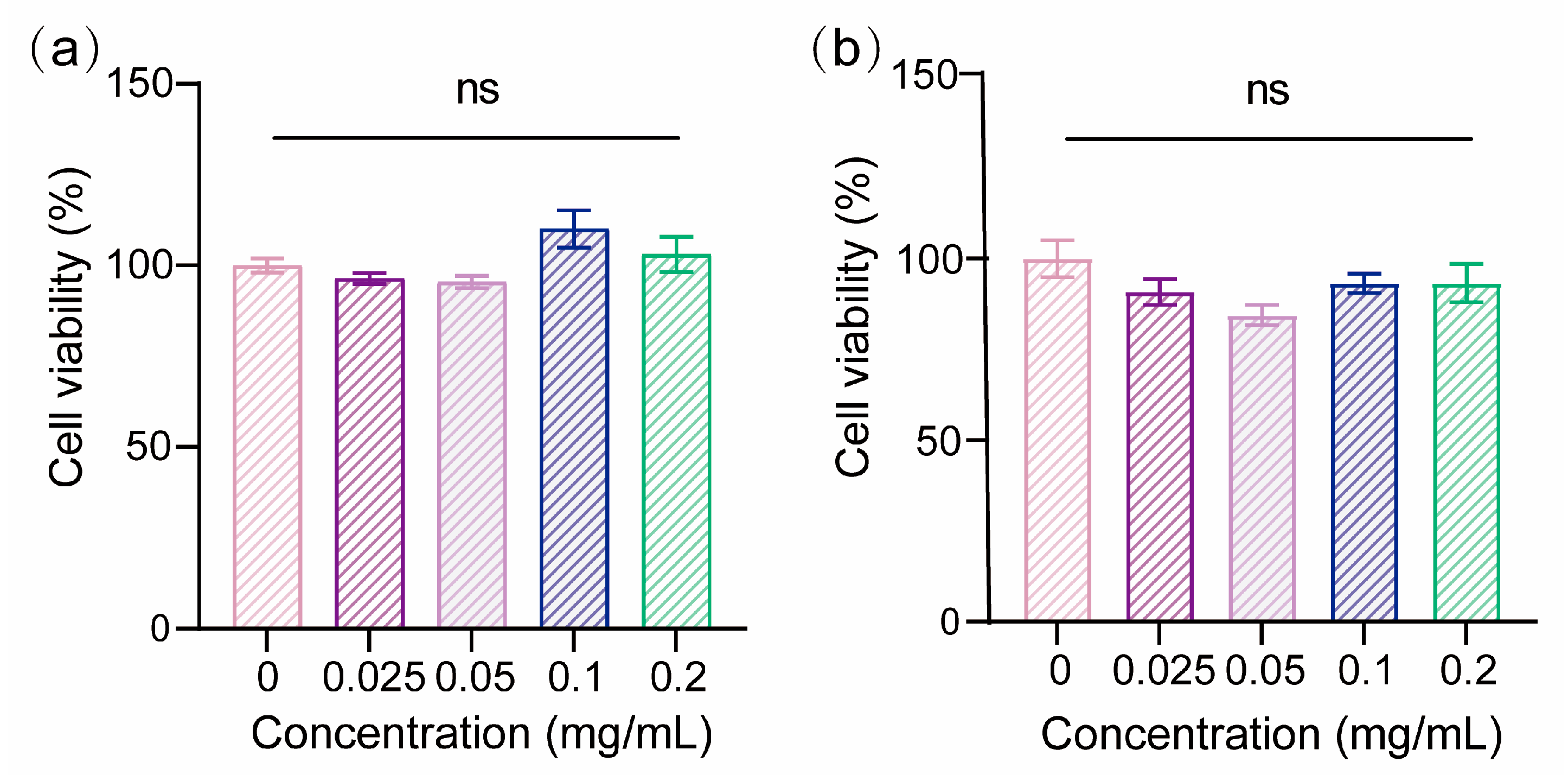
2.5. Biocompatibility of PLA/Shellac Dimer NPs
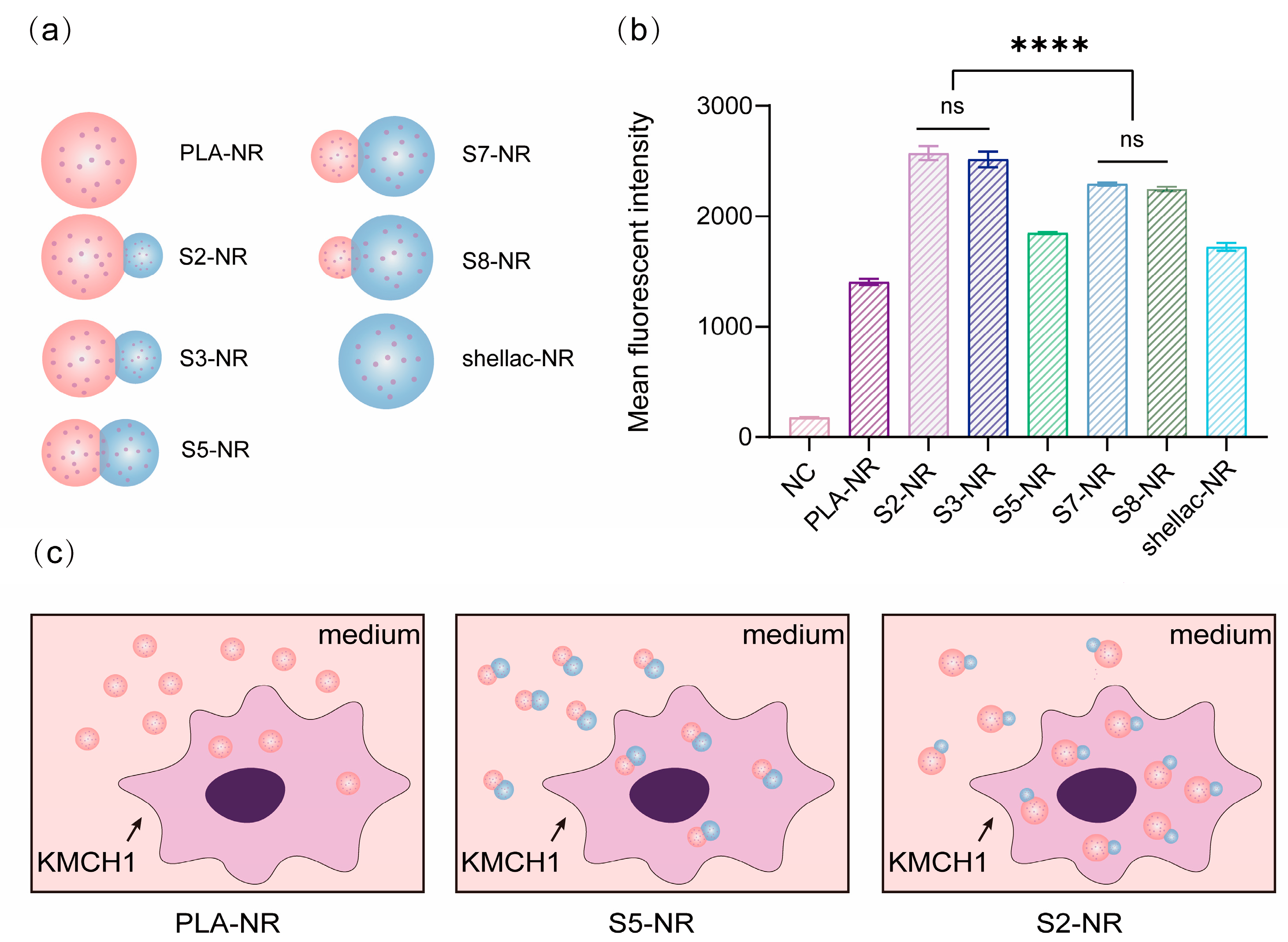
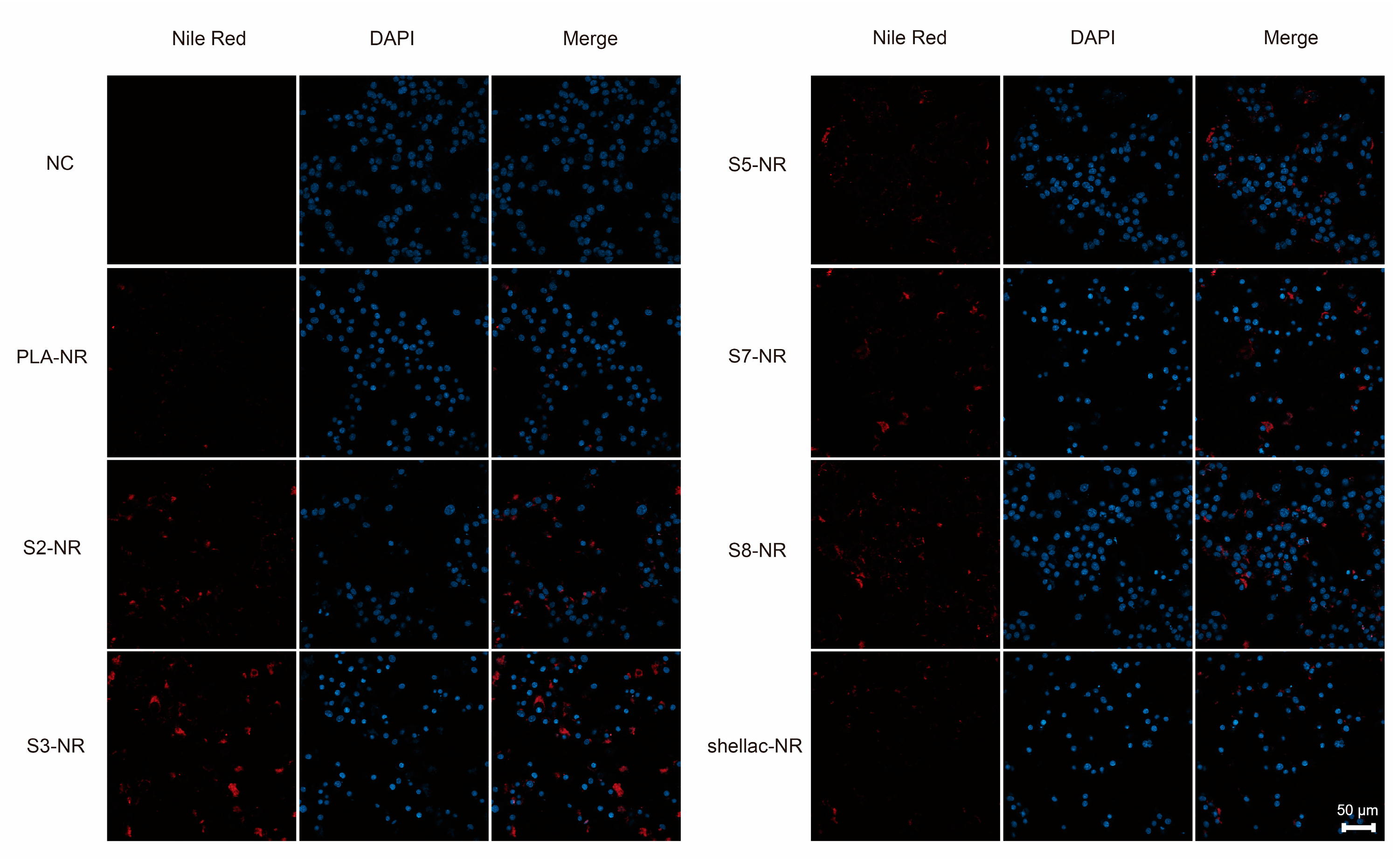
2.6. Cellular Uptake of NR-Loaded PLA/Shellac Dimer NPs
2.7. Cytotoxicity of Paclitaxel (PTX)-Loaded PLA/Shellac Dimer NPs
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
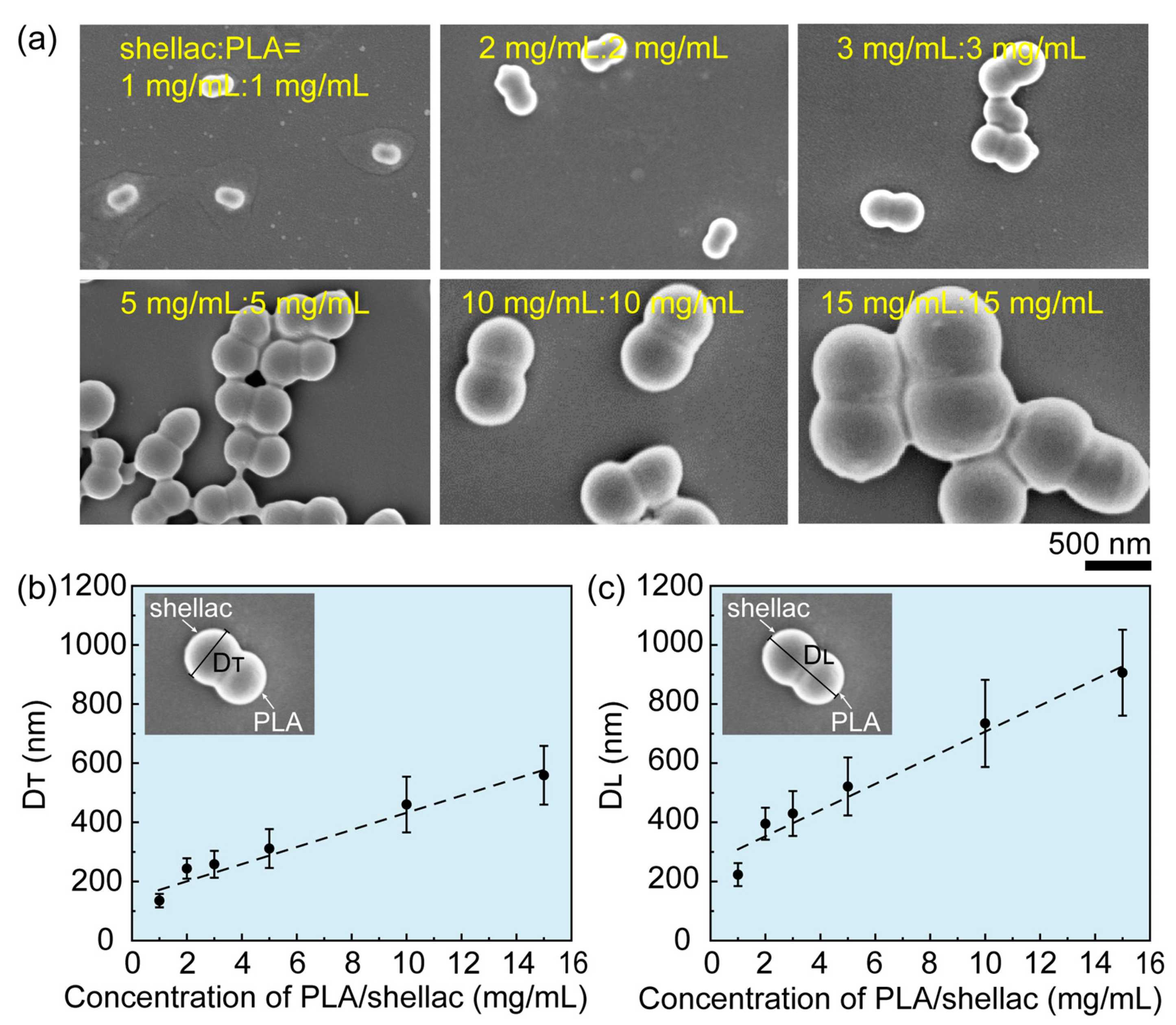
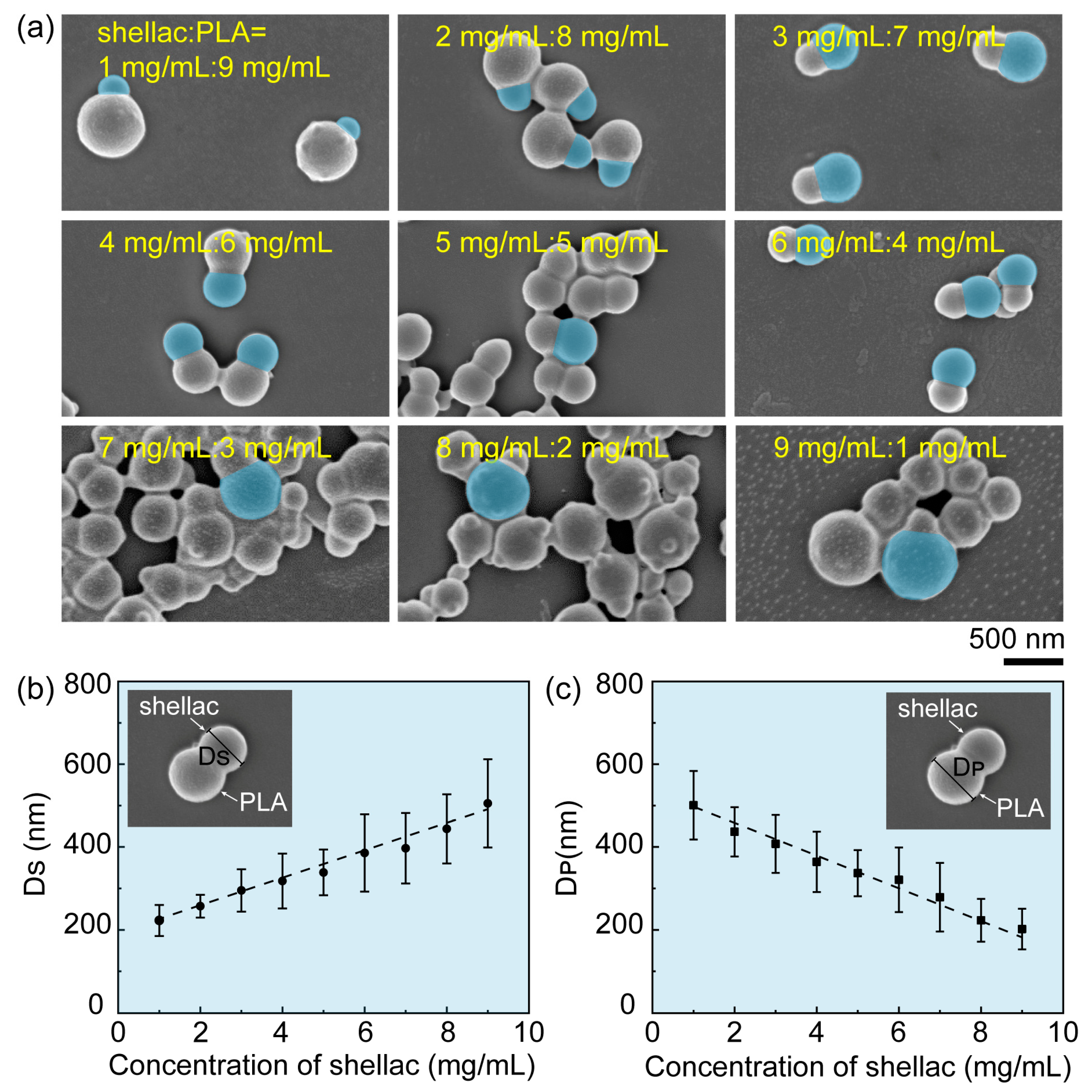
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of PTX-Loaded PLA/Shellac Dimer NPs
3.2. Biocompatibility and Cellular Uptake of PLA/Shellac Dimer NPs
3.3. Anti-Tumor Effects of PTX-Loaded PLA/Shellac Dimer NPs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Yang, T.; Wu, M.; Shen, F. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis and surgical management. Cancer Lett. 2016, 379, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, K.; Li, J.; Mu, X.; Gao, H.; Xu, X. Nanoparticle-mediated therapeutic management in cholangiocarcinoma drug targeting: Current progress and future prospects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 158, 114135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massa, A.; Peraldo-Neia, C.; Vita, F.; Varamo, C.; Basiricò, M.; Raggi, C.; Bernabei, P.; Erriquez, J.; Sarotto, I.; Leone, F.; et al. Paclitaxel Restores Sensitivity to Chemotherapy in Preclinical Models of Multidrug-Resistant Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 771418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadamuro, M.; Spagnuolo, G.; Sambado, L.; Indraccolo, S.; Nardo, G.; Rosato, A.; Brivio, S.; Caslini, C.; Stecca, T.; Massani, M.; et al. Low-Dose Paclitaxel Reduces S100A4 Nuclear Import to Inhibit Invasion and Hematogenous Metastasis of Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4775–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, G.; Song, T.; Zhang, T.; Li, Q. Systemic treatment of advanced or recurrent biliary tract cancer. Biosci. Trends 2020, 14, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Bakar, N.F.; Tan, H.L.; Lim, Y.P.; Adrus, N.; Abdullah, J. Chapter 33—Environmental impact of quantum dots. In Graphene, Nanotubes and Quantum Dots-Based Nanotechnology; Al-Douri, Y., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2022; pp. 837–867. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Sun, H.; Li, X.; Sheng, H.; Zhu, L. Strategies for Solubility and Bioavailability Enhancement and Toxicity Reduction of Norcantharidin. Molecules 2022, 27, 7740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Ruan, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, C.X.; Chen, D.; Shan, J. Nanocarrier-Based Tumor-Targeting Drug Delivery Systems for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatments: Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy and Reduced Drug Toxicity. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2022, 18, 660–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Z.; Yang, L.; Yan, X.; Wang, D.; Hua, Y.; Shi, W.; Lin, J.; Meng, Z. Effect and Mechanism of the Lenvatinib@H-MnO(2)-FA Drug Delivery System in Targeting Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Hang, Y.; Jaramillo, L.; Wehrkamp, C.J.; Phillippi, M.A.; Mohr, A.M.; Chen, Y.; Talmon, G.A.; et al. Cholangiocarcinoma therapy with nanoparticles that combine downregulation of MicroRNA-210 with inhibition of cancer cell invasiveness. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4305–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, A.B. The effect of particle shape on cellular interaction and drug delivery applications of micro- and nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunshine, J.C.; Perica, K.; Schneck, J.P.; Green, J.J. Particle shape dependence of CD8+ T cell activation by artificial antigen presenting cells. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, A.; Tang, P.S.; Chan, W.C. The effect of nanoparticle size, shape, and surface chemistry on biological systems. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, S.E.; Ropp, P.A.; Pohlhaus, P.D.; Luft, J.C.; Madden, V.J.; Napier, M.E.; DeSimone, J.M. The effect of particle design on cellular internalization pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11613–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Taheri-Ledari, R.; Ganjali, F.; Mirmohammadi, S.S.; Qazi, F.S.; Saeidirad, M.; KashtiAray, A.; Zarei-Shokat, S.; Tian, Y.; Maleki, A. Effects of morphology and size of nanoscale drug carriers on cellular uptake and internalization process: A review. RSC Adv. 2022, 13, 80–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbaraju, P.L.; Meka, A.K.; Song, H.; Yang, Y.; Jambhrunkar, M.; Zhang, J.; Xu, C.; Yu, M.; Yu, C. Asymmetric Silica Nanoparticles with Tunable Head-Tail Structures Enhance Hemocompatibility and Maturation of Immune Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 6321–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, J.L.; Herlihy, K.P.; Napier, M.E.; DeSimone, J.M. PRINT: A Novel Platform Toward Shape and Size Specific Nanoparticle Theranostics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Nie, Z.; Seo, M.; Lewis, P.; Kumacheva, E.; Stone, H.A.; Garstecki, P.; Weibel, D.B.; Gitlin, I.; Whitesides, G.M. Generation of Monodisperse Particles by Using Microfluidics: Control over Size, Shape, and Composition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Shen, D.; Li, W.; Wang, G. Self-Assembly of Copolymers Containing Crystallizable Blocks: Strategi es and Applications. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2022, 43, e2200071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sportelli, M.C.; Izzi, M.; Volpe, A.; Clemente, M.; Picca, R.A.; Ancona, A.; Lugarà, P.M.; Palazzo, G.; Cioffi, N. The Pros and Cons of the Use of Laser Ablation Synthesis for the Production of Silver Nano-Antimicrobials. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Cruz-Lopes, L.; Esteves, B.; Evtuguin, D. Nanotechnology Applied to Cellulosic Materials. Materials 2023, 16, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Yan, X.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, L.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Chen, D.; Yang, Z.; Weitz, D. Pickering emulsions stabilized by colloidal surfactants: Role of solid particles. Particuology 2021, 64, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzi, B.; Albino, M.; Gabbani, A.; Omelyanchik, A.; Kozenkova, E.; Petrecca, M.; Innocenti, C.; Balica, E.; Lavacchi, A.; Scavone, F.; et al. Star-Shaped Magnetic-Plasmonic Au@Fe3O4 Nano-Heterostructures for Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 29087–29098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.; Qiao, S.-Z. A mesoporous organosilica nano-bowl with high DNA loading capacity—A potential gene delivery carrier. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17446–17450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud Aghdami, K.; Rahnama, A.; Ertorer, E.; Herman, P.R. Laser nano-filament explosion for enabling open-grating sensing in opt ical fibre. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Wu, B.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, C.-X.; Hai, M.; Weitz, D.A.; Chen, D. Diverse Particle Carriers Prepared by Co-Precipitation and Phase Separation: Formation and Applications. ChemPlusChem 2021, 86, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Yang, C.; Wang, F.; Wu, B.; Shao, B.; Li, Z.; Chen, D.; Yang, Z.; Liu, K. Biocompatible and pH-Responsive Colloidal Surfactants with Tunable Shape for Controlled Interfacial Curvature. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2020, 59, 9365–9369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhvi, M.S.; Zinjarde, S.S.; Gokhale, D.V. Polylactic acid: Synthesis and biomedical applications. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 1612–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thombare, N.; Kumar, S.; Kumari, U.; Sakare, P.; Yogi, R.K.; Prasad, N.; Sharma, K.K. Shellac as a multifunctional biopolymer: A review on properties, applications and future potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 215, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, W.F.; Sun, H.B. Multifunctional superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Design, synthesis and biomedical photonic applications. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 7664–7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Chen, R.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.X.; Chen, Q.; Hai, M.; Chen, D.; Yang, Z.; Weitz, D.A. Controlled co-precipitation of biocompatible colorant-loaded nanoparticles by microfluidics for natural color drinks. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 2089–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yang, C.; Li, B.; Feng, L.; Hai, M.; Zhao, C.-X.; Chen, D.; Liu, K.; Weitz, D.A. Active Encapsulation in Biocompatible Nanocapsules. Small 2020, 16, 2002716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanoiu, G.; Carey, E.; Patil, S.R.; Engelskirchen, S.; Stubenrauch, C. Partition coefficients of nonionic surfactants in water/n-alkane systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 355, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, X.Q.; Ju, X.J.; Zhang, L.; Cai, Q.W.; Liu, Y.Q.; Peng, H.Y.; Xie, R.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Chu, L.Y. Novel Multifunctional Stimuli-Responsive Nanoparticles for Synergetic Chemo-Photothermal Therapy of Tumors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 28802–28817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Li, B.; Du, J.; Wang, Y. Regulation the morphology of cationized gold nanoparticles for effective gene delivery. Colloids Surf. B 2017, 157, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, S.; Auth, T.; Gompper, G. Shape and Orientation Matter for the Cellular Uptake of Nonspherical Particles. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaz, S.; Forbes, B.; Raimi-Abraham, B.T. Exploiting Endocytosis for Non-Spherical Nanoparticle Cellular Uptake. Nanomanufacturing 2022, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.M.; Cheng, C.T.; Wu, R.C.; Chung, Y.H.; Chiang, K.C.; Yeh, T.S.; Liu, C.Y.; Chen, M.H.; Chen, M.H.; Yeh, C.N. Nab-paclitaxel is effective against intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma via disruption of desmoplastic stroma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, C.; Simões, S.; Gaspar, R. Paclitaxel-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: Preparation, physicochemical characterization and in vitro anti-tumoral activity. J. Control. Release 2002, 83, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, R.; Pu, X.; Liu, R.; Dai, X.; Ye, F.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, P.; Ruan, J.; Chen, D. Biocompatible Snowman-like Dimer Nanoparticles for Improved Cellular Uptake in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15082132
Chen R, Pu X, Liu R, Dai X, Ye F, Zhao C, Zhao P, Ruan J, Chen D. Biocompatible Snowman-like Dimer Nanoparticles for Improved Cellular Uptake in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(8):2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15082132
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ruyin, Xingqun Pu, Rongrong Liu, Xiaomeng Dai, Fangfu Ye, Chunxia Zhao, Peng Zhao, Jian Ruan, and Dong Chen. 2023. "Biocompatible Snowman-like Dimer Nanoparticles for Improved Cellular Uptake in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 8: 2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15082132
APA StyleChen, R., Pu, X., Liu, R., Dai, X., Ye, F., Zhao, C., Zhao, P., Ruan, J., & Chen, D. (2023). Biocompatible Snowman-like Dimer Nanoparticles for Improved Cellular Uptake in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Pharmaceutics, 15(8), 2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15082132








