Toward Stability Enhancement of NTS1R-Targeted Radioligands: Structural Interventions on [99mTc]Tc-DT1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Radioligands
2.1.1. Peptides and Protease Inhibitors
2.1.2. Radiolabeling
2.2. Cell Studies
2.2.1. Cell Culture
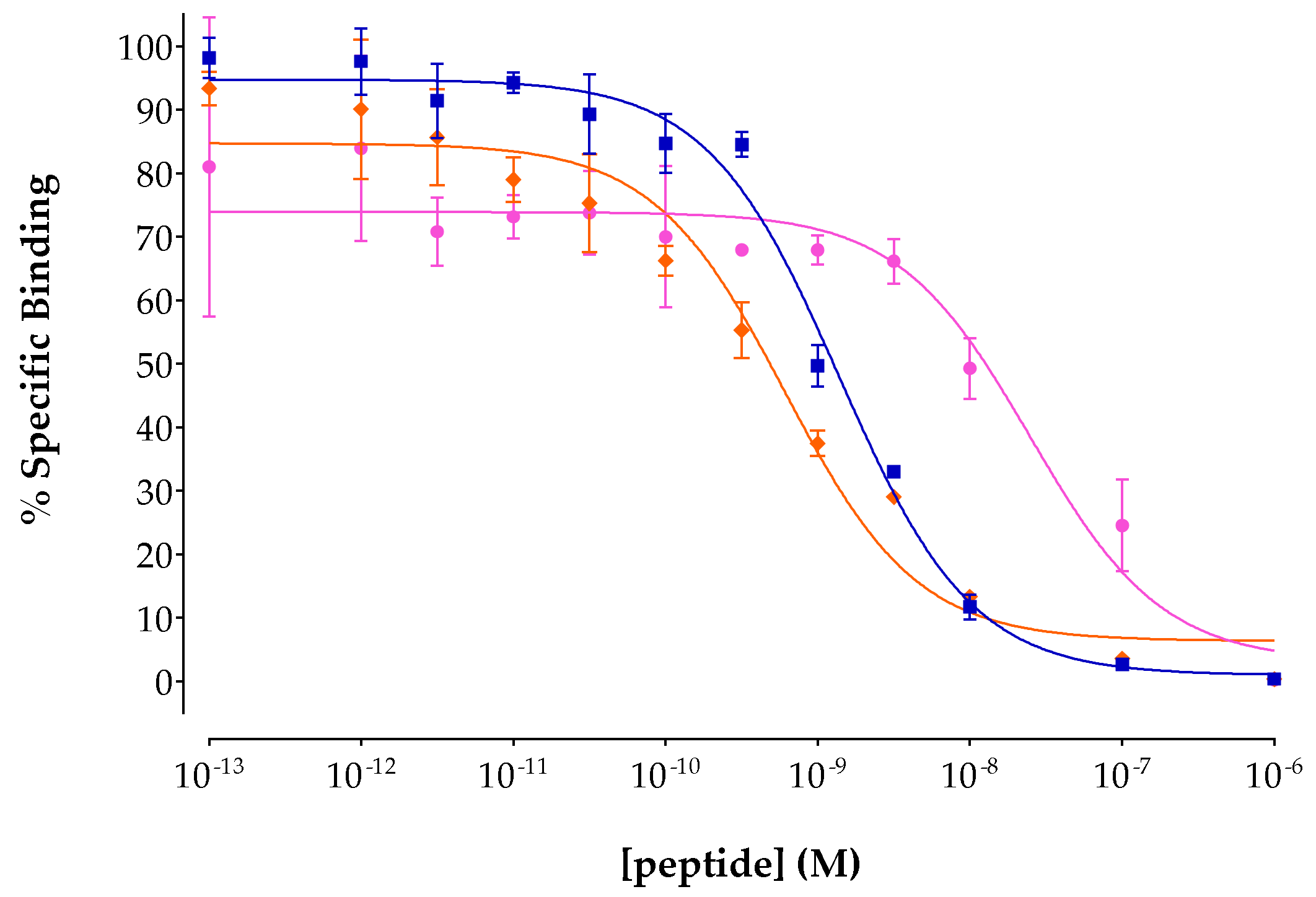
2.2.2. Competition Binding Experiments
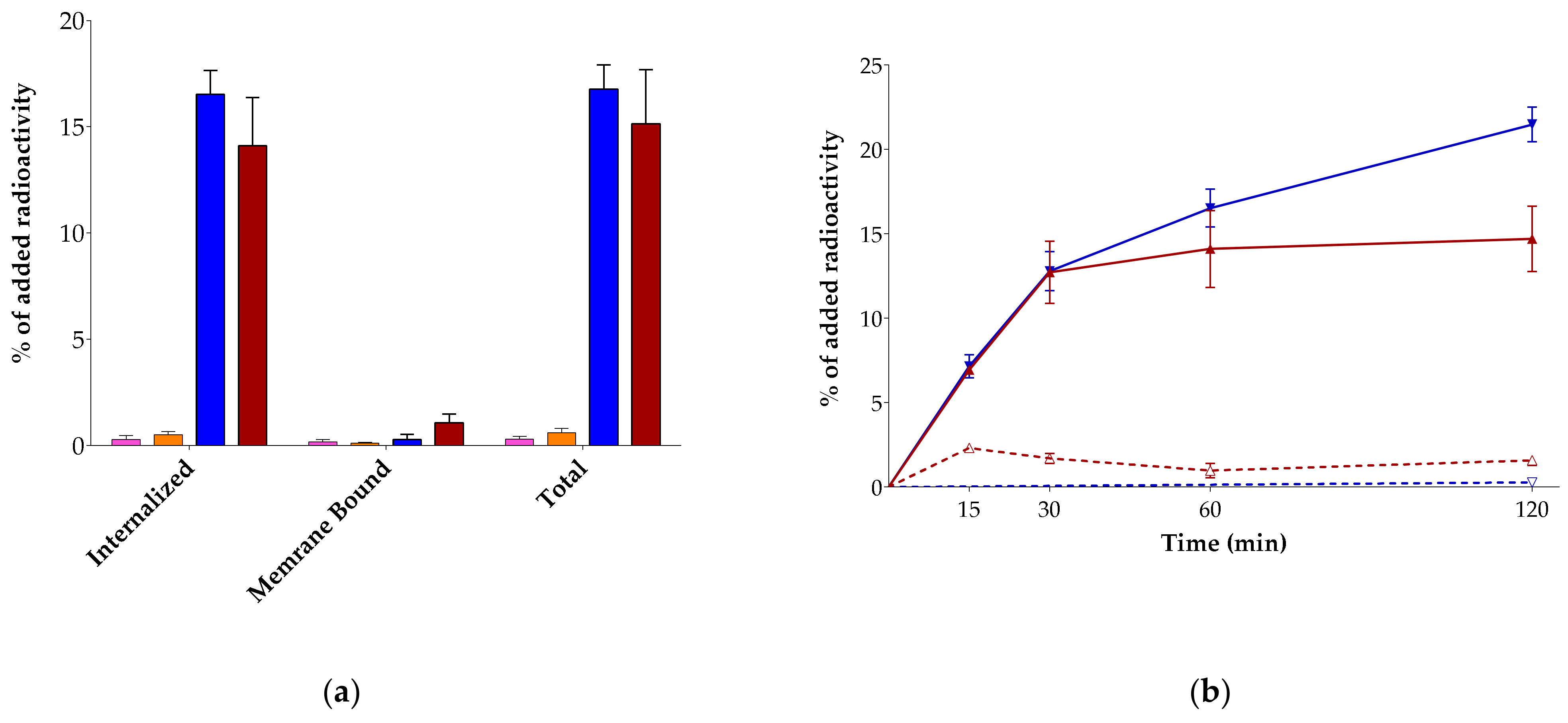
2.2.3. Internalization in AsPC-1 Cells
2.3. Animal Studies
2.3.1. Stability Studies
2.3.2. Biodistribution of [99mTc]Tc-DT9 in SCID Mice Bearing AsPC-1 Xenografts
3. Results
3.1. Ligands and Radioligands
3.2. In Vitro Evaluation
3.2.1. Binding Affinity for the Human NTS1R
3.2.2. Radioligand Internalization in AsPC-1 Cells
3.3. Animal Studies
3.3.1. Radioligand Metabolic Stability in Mice
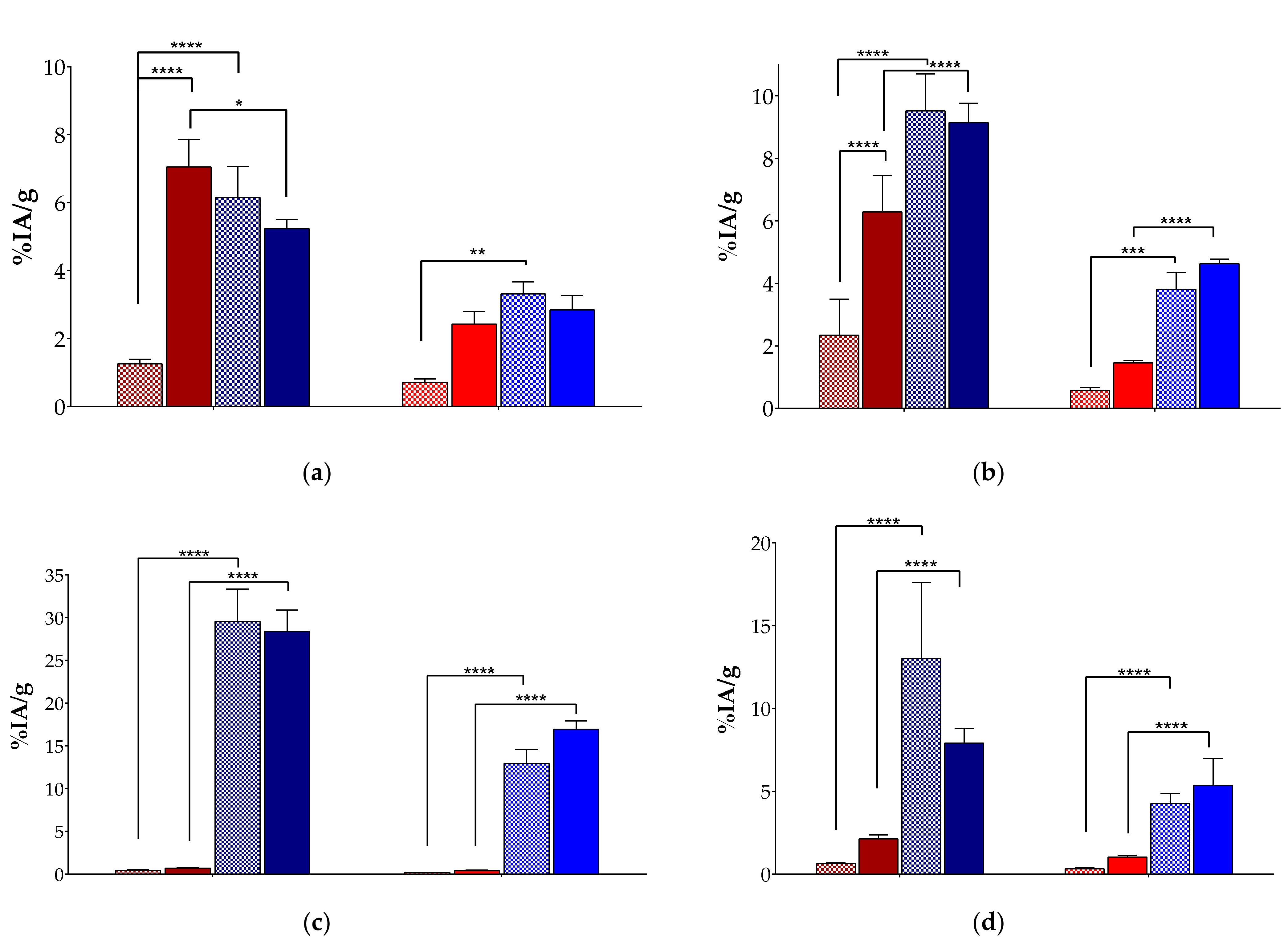
3.3.2. Biodistribution of [99mTc]Tc-DT9 in Mice Bearing AsPC-1 Xenografts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reubi, J.C.; Waser, B.; Friess, H.; Buchler, M.; Laissue, J. Neurotensin receptors: A new marker for human ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Gut 1998, 42, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, M.; Waser, B.; Ströbel, O.; Büchler, M.; Reubi, J.C. Neurotensin receptors in pancreatic ductal carcinomas. EJNMMI Res. 2015, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizuka, J.; Townsend, C.M., Jr.; Thompson, J.C. Neurotensin regulates growth of human pancreatic cancer. Ann. Surg. 1993, 217, 439–445; discussion 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendler, W.P.; Baum, R.P. NTR is the new SSTR? Perspective for neurotensin receptor 1 (NTR)-directed theranostics. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 934–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reubi, J.C.; Waser, B.; Schaer, J.C.; Laissue, J.A. Neurotensin receptors in human neoplasms: High incidence in Ewing’s sarcomas. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 82, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, X.; Guzman, G.; Dobner, P.R.; Kadkol, S.S. Increased neurotensin receptor-1 expression during progression of colonic adenocarcinoma. Peptides 2008, 29, 1609–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgat, C.; Chastel, A.; Molinie, V.; Schollhammer, R.; Macgrogan, G.; Vélasco, V.; Malavaud, B.; Fernandez, P.; Hindié, E. Neurotensin Receptor-1 Expression in Human Prostate Cancer: A Pilot Study on Primary Tumors and Lymph Node Metastases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souaze, F.; Dupouy, S.; Viardot-Foucault, V.; Bruyneel, E.; Attoub, S.; Gespach, C.; Gompel, A.; Forgez, P. Expression of neurotensin and NT1 receptor in human breast cancer: A potential role in tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6243–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitabgi, P. Targeting neurotensin receptors with agonists and antagonists for therapeutic purposes. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Devel. 2002, 5, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Achilefu, S.; Srinivasan, A.; Schmidt, M.A.; Jimenez, H.N.; Bugaj, J.E.; Erion, J.L. Novel bioactive and stable neurotensin peptide analogues capable of delivering radiopharmaceuticals and molecular beacons to tumors. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 3403–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarin, A.; Valverde, I.E.; Mindt, T.L. Structure-activity relationship studies of amino acid substitutions in radiolabeled neurotensin conjugates. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maschauer, S.; Prante, O. Radiopharmaceuticals for imaging and endoradiotherapy of neurotensin receptor-positive tumors. J. Label. Comp. Radiopharm. 2018, 61, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchegger, F.; Bonvin, F.; Kosinski, M.; Schaffland, A.O.; Prior, J.; Reubi, J.C.; Blauenstein, P.; Tourwé, D.; Garcia Garayoa, E.; Bischof Delaloye, A. Radiolabeled neurotensin analog, 99mTc-NT-XI, evaluated in ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients. J. Nucl. Med. 2003, 44, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel, M.; Decristoforo, C.; Woll, E.; Eisterer, W.; Nock, B.; Maina, T.; Moncayo, R.; Virgolini, I. [99mTc]Demotensin VI: Biodistribution and initial clinical results in tumor patients of a pilot/phase I study. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2011, 26, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Visser, M.; Janssen, P.J.J.M.; Srinivasan, A.; Reubi, J.C.; Waser, B.; Erion, J.L.; Schmidt, M.A.; Krenning, E.P.; de Jong, M. Stabilised In-111-labelled DTPA- and DOTA-conjugated neurotensin analogues for imaging and therapy of exocrine pancreatic cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2003, 30, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröberg, A.C.; van Eijck, C.; Verdijsseldonck, M.C.; Melis, M.; Bakker, H.; Krenning, E.P. Use of neurotensin analogue In-111-DTPA-neurotensin (In-111-MP2530) in diagnosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2004, 31 (Suppl. S2), S392. [Google Scholar]
- Schubiger, P.A.; Allemann-Tannahill, L.; Egli, A.; Schibli, R.; Alberto, R.; Carrel-Remy, N.; Willmann, M.; Blauenstein, P.; Tourwe, D. Catabolism of neurotensins. Implications for the design of radiolabeling strategies of peptides. Q. J. Nucl. Med. 1999, 43, 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi, P.; De Nadai, F.; Rovere, C.; Bidard, J.N. Biosynthesis, maturation, release, and degradation of neurotensin and neuromedin n. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1992, 668, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitabgi, P.; Dubuc, I.; Nouel, D.; Costentin, J.; Cuber, J.C.; Fulcrand, H.; Doulut, S.; Rodriguez, M.; Martinez, J. Effects of thiorphan, bestatin and a novel metallopeptidase inhibitor JMV 390-1 on the recovery of neurotensin and neuromedin Ν released from mouse hypothalamus. Neurosci. Lett. 1992, 142, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checler, F.; Vincent, J.P.; Kitabgi, P. Degradation of neurotensin by rat brain synaptic membranes: Involvement of a thermolysin-like metalloendopeptidase (enkephalinase), angiotensin-converting enzyme, and other unidentified peptidases. J. Neurochem. 1983, 41, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skidgel, R.A.; Engelbrecht, S.; Johnson, A.R.; Erdös, E.G. Hydrolysis of substance P and neurotensin by converting enzyme and neutral endopeptidase. Peptides 1984, 5, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nock, B.A.; Nikolopoulou, A.; Reubi, J.C.; Maes, V.; Conrath, P.; Tourwé, D.; Maina, T. Toward stable N4-modified neurotensins for NTS1-receptor-targeted tumor imaging with 99mTc. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 4767–4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maina, T.; Nikolopoulou, A.; Stathopoulou, E.; Galanis, A.S.; Cordopatis, P.; Nock, B.A. [99mTc]Demotensin 5 and 6 in the NTS1-R-targeted imaging of tumours: Synthesis and preclinical results. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2007, 34, 1804–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanellopoulos, P.; Kaloudi, A.; de Jong, M.; Krenning, E.P.; Nock, B.A.; Maina, T. Key-Protease Inhibition Regimens Promote Tumor Targeting of Neurotensin Radioligands. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellopoulos, P.; Nock, B.A.; Krenning, E.P.; Maina, T. Optimizing the profile of [99mTc]Tc-NT(7-13) tracers in pancreatic cancer models by means of protease inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armayor, G.M.; Lopez, L.M. Lisinopril: A new angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. Drug Intell. Clin. Pharm. 1988, 22, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Lindo, E.; Santisteban-Ponce, J.; Chea-Woo, E.; Gutierrez, M. Racecadotril in the treatment of acute watery diarrhea in children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roques, B.P.; Noble, F.; Dauge, V.; Fournie-Zaluski, M.C.; Beaumont, A. Neutral endopeptidase 24.11: Structure, inhibition, and experimental and clinical pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 1993, 45, 87–146. [Google Scholar]
- Schiering, N.; D’Arcy, A.; Villard, F.; Ramage, P.; Logel, C.; Cumin, F.; Ksander, G.M.; Wiesmann, C.; Karki, R.G.; Mogi, M. Structure of neprilysin in complex with the active metabolite of sacubitril. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayalasomayajula, S.; Langenickel, T.; Pal, P.; Boggarapu, S.; Sunkara, G. Clinical pharmacokinetics of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696): A novel angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 1461–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ayalasomayajula, S.; Pan, W.; Yang, F.; Yuan, Y.; Langenickel, T.; Hinder, M.; Kalluri, S.; Pal, P.; Sunkara, G. Pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) after single-dose administration in healthy chinese subjects. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 42, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkema, R.; Schonebaum, L.E.; Fröberg, A.C.; Maina, T.; Nock, B.A.; de Blois, E.; Konijnenberg, M.W.; Koolen, S.L.W.; Peeters, R.P.; Visser, W.E.; et al. PepProtect: Improved detection of cancer and metastases by peptide scanning under the protection of enzyme inhibitors. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49 (Suppl. S1), S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrbach, M.S.; Williams, E.B., Jr.; Rolstad, R.A. Purification and substrate specificity of bovine angiotensin-converting enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kling, R.C.; Burchardt, C.; Einsiedel, J.; Hubner, H.; Gmeiner, P. Structure-based exploration of an allosteric binding pocket in the NTS1 receptor using bitopic NT(8-13) derivatives and molecular dynamics simulations. J. Mol. Model. 2019, 25, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einsiedel, J.; Hubner, H.; Hervet, M.; Harterich, S.; Koschatzky, S.; Gmeiner, P. Peptide backbone modifications on the C-terminal hexapeptide of neurotensin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 2013–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seebach, D.; Lukaszuk, A.; Patora-Komisarska, K.; Podwysocka, D.; Gardiner, J.; Ebert, M.O.; Reubi, J.C.; Cescato, R.; Waser, B.; Gmeiner, P.; et al. On the terminal homologation of physiologically active peptides as a means of increasing stability in human serum--neurotensin, opiorphin, B27-KK10 epitope, NPY. Chem. Biodivers. 2011, 8, 711–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparr, C.; Purkayastha, N.; Yoshinari, T.; Seebach, D.; Maschauer, S.; Prante, O.; Hubner, H.; Gmeiner, P.; Kolesinska, B.; Cescato, R.; et al. Syntheses, receptor bindings, in vitro and in vivo stabilities and biodistributions of DOTA-neurotensin(8-13) derivatives containing beta-amino acid residues—A lesson about the importance of animal experiments. Chem. Biodivers. 2013, 10, 2101–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erak, M.; Bellmann-Sickert, K.; Els-Heindl, S.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. Peptide chemistry toolbox—Transforming natural peptides into peptide therapeutics. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2759–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostelnik, K.B.; Els-Heindl, S.; Kloting, N.; Baumann, S.; von Bergen, M.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. High metabolic in vivo stability and bioavailability of a palmitoylated ghrelin receptor ligand assessed by mass spectrometry. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 3925–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bulaj, G. Converting peptides into drug leads by lipidation. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 1602–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellmann-Sickert, K.; Elling, C.E.; Madsen, A.N.; Little, P.B.; Lundgren, K.; Gerlach, L.O.; Bergmann, R.; Holst, B.; Schwartz, T.W.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. Long-acting lipidated analogue of human pancreatic polypeptide is slowly released into circulation. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 2658–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, A.G.; Norberg, T.; Griffin, D.; Hoeger, C.; Akhtar, M.; Schmidt, K.; Low, W.; Dykert, J.; Richelson, E.; Navarro, V.; et al. Contulakin-G, an O-glycosylated invertebrate neurotensin. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 13752–13759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.R.; White, K.L.; McDougle, D.R.; Zhang, L.; Klein, B.; Scholl, E.A.; Pruess, T.H.; White, H.S.; Bulaj, G. Introduction of lipidization-cationization motifs affords systemically bioavailable neuropeptide Y and neurotensin analogs with anticonvulsant activities. J. Pept. Sci. 2010, 16, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K.; Zhang, L.; Smith, M.D.; Walewska, A.; Vellore, N.A.; Baron, R.; McIntosh, J.M.; White, H.S.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G. A marine analgesic peptide, contulakin-G, and neurotensin are distinct agonists for neurotensin receptors: Uncovering structural determinants of desensitization properties. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidard, J.N.; de Nadai, F.; Rovere, C.; Moinier, D.; Laur, J.; Martinez, J.; Cuber, J.C.; Kitabgi, P. Immunological and biochemical characterization of processing products from the neurotensin/neuromedin N precursor in the rat medullary thyroid carcinoma 6-23 cell line. Biochem. J. 1993, 291 Pt 1, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, L.; Bernhardt, G.; Keller, M. Modifications at Arg and Ile give neurotensin(8-13) derivatives with high stability and retained NTS1 receptor affinity. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschoalin, T.; Carmona, A.K.; Rodrigues, E.G.; Oliveira, V.; Monteiro, H.P.; Juliano, M.A.; Juliano, L.; Travassos, L.R. Characterization of thimet oligopeptidase and neurolysin activities in B16F10-NEX2 tumor cells and their involvement in angiogenesis and tumor growth. Mol. Cancer 2007, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, D.A.; Morano, C.; Russo, L.C.; Castro, L.M.; Cunha, F.M.; Zhang, X.; Sironi, J.; Klitzke, C.F.; Ferro, E.S.; Fricker, L.D. Analysis of intracellular substrates and products of thimet oligopeptidase in human embryonic kidney 293 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 14105–14116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, J. Elevation of serum angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) level in sarcoidosis. Am. J. Med. 1975, 59, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nortier, J.; Pauwels, S.; De Prez, E.; Deschodt-Lanckman, M. Human neutrophil and plasma endopeptidase 24.11: Quantification and respective roles in atrial natriuretic peptide hydrolysis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 25, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ockner, R.K.; Weisiger, R.A.; Gollan, J.L. Hepatic uptake of albumin-bound substances: Albumin receptor concept. Am. J. Physiol. 1983, 245, G13–G18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

 ) or with Lis (darker
) or with Lis (darker  ) or with the Entresto®+Lis combination (darker solid lines
) or with the Entresto®+Lis combination (darker solid lines  ; HPLC system 2); percentages of intact radioligand are summarized in Table 1.
; HPLC system 2); percentages of intact radioligand are summarized in Table 1.
 ) or with Lis (darker
) or with Lis (darker  ) or with the Entresto®+Lis combination (darker solid lines
) or with the Entresto®+Lis combination (darker solid lines  ; HPLC system 2); percentages of intact radioligand are summarized in Table 1.
; HPLC system 2); percentages of intact radioligand are summarized in Table 1.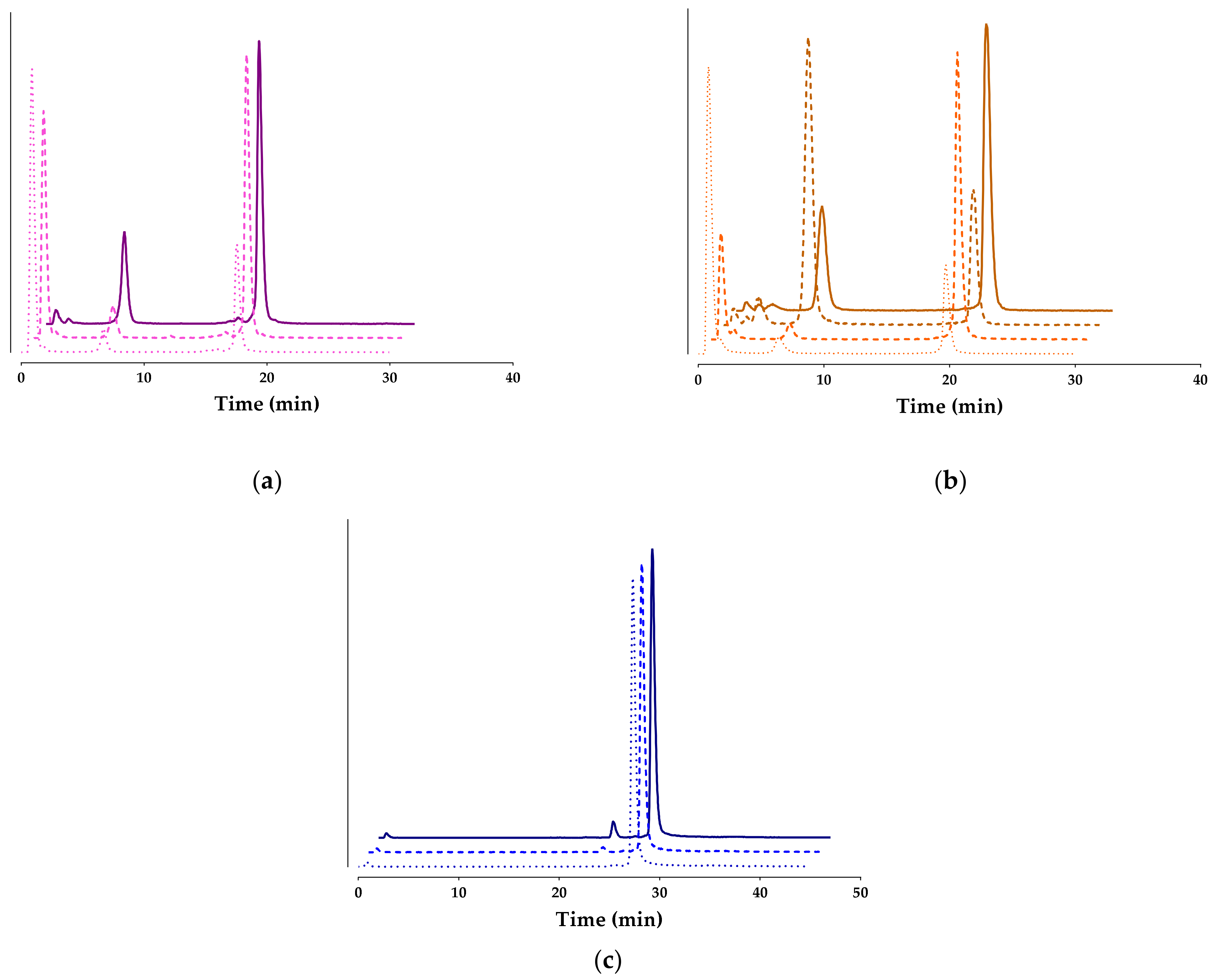
| [99mTc]Tc-DT1 1 | [99mTc]Tc-DT7 | [99mTc]Tc-DT8 | [99mTc]Tc-DT9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.81 ± 0.77 (n = 4) | 26.91 ± 1.91 (n = 3) | 20.68 ± 3.10 (n = 3) | 98.06 ± 1.18 (n = 3) |
| Entresto® | 5.46 ± 3.86 (n = 5) | 56.61 ± 7.92 (n = 6) | 60.72 ± 8.35 (n = 3) | 97.33 ± 1.7 (n = 3) |
| Lis | 18.77 ± 2.54 (n = 3) | - | 28.82 ± 4.59 (n = 3) | - |
| Entresto®+Lis | 63.80 ± 7.51 (n = 3) | 60.27 ± 11.82 (n = 3) | 64.06 ± 4.07 (n = 3) | 93.72 ± 3.7 (n = 3) |
| Organs/Tissues | [99mTc]Tc-DT9 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 h | 24 h | ||||
| Block | Controls | Entresto®+Lis | Controls | Entresto®+Lis | |
| Blood | 4.25 ± 0.37 | 4.63 ± 0.55 | 4.32 ± 0.42 | 0.68 ± 0.18 | 0.70 ± 0.06 |
| Liver | 30.93 ± 4.25 | 29.56 ± 3.77 | 28.42 ± 2.48 | 12.93 ± 1.66 | 16.96 ± 0.94 |
| Heart | 2.79 ± 0.47 | 3.12 ± 0.43 | 2.85 ± 2.48 | 0.64 ± 0.11 | 0.71 ± 0.06 |
| Kidneys | 8.56 ± 0.87 | 9.53 ± 1.18 | 9.15 ± 0.62 | 3.81 ± 0.54 | 4.63 ± 0.15 |
| Stomach | 2.06 ± 0.47 | 3.09 ± 1.06 | 2.27 ± 0.38 | 1.73 ± 0.50 | 1.56 ± 0.31 |
| Intestines | 6.27 ± 0.72 | 13.02 ± 4.60 | 7.90 ± 0.88 | 4.26 ± 0.61 | 5.37 ± 1.61 |
| Spleen | 6.18 ± 1.37 | 6.82 ± 1.11 | 5.47 ± 0.47 | 3.42 ± 0.54 | 4.47 ± 0.83 |
| Muscle | 0.82 ± 0.11 | 0.93 ± 0.13 | 0.81 ± 0.04 | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 0.24 ± 0.01 |
| Lungs | 8.46 ± 1.26 | 8.80 ± 1.42 | 7.61 ± 0.64 | 3.42 ± 0.67 | 3.62 ± 0.94 |
| Pancreas | 1.84 ± 0.41 | 2.10 ± 0.30 | 1.85 ± 0.18 | 0.75 ± 0.17 | 0.80 ± 0.07 |
| AsPC-1 Tumor | 3.68 ± 0.92 | 6.15 ± 0.92 | 5.24 ± 0.27 | 3.32 ± 0.35 | 2.84 ± 0.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanellopoulos, P.; Nock, B.A.; Krenning, E.P.; Maina, T. Toward Stability Enhancement of NTS1R-Targeted Radioligands: Structural Interventions on [99mTc]Tc-DT1. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15082092
Kanellopoulos P, Nock BA, Krenning EP, Maina T. Toward Stability Enhancement of NTS1R-Targeted Radioligands: Structural Interventions on [99mTc]Tc-DT1. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(8):2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15082092
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanellopoulos, Panagiotis, Berthold A. Nock, Eric P. Krenning, and Theodosia Maina. 2023. "Toward Stability Enhancement of NTS1R-Targeted Radioligands: Structural Interventions on [99mTc]Tc-DT1" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 8: 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15082092
APA StyleKanellopoulos, P., Nock, B. A., Krenning, E. P., & Maina, T. (2023). Toward Stability Enhancement of NTS1R-Targeted Radioligands: Structural Interventions on [99mTc]Tc-DT1. Pharmaceutics, 15(8), 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15082092









