Novel Drug Targets and Emerging Pharmacotherapies in Neuropathic Pain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Drug Targets in Neuropathic Pain
3. Current Pharmacotherapies in Neuropathic Pain
3.1. Gabapentinoids
3.2. Tricyclic Antidepressants
3.3. Serotonin–Norepinephrine Re-Uptake Inhibitors
3.4. Lidocaine
3.5. Capsaicin
3.6. Second Line Choices for Neuropathic Pain Treatment
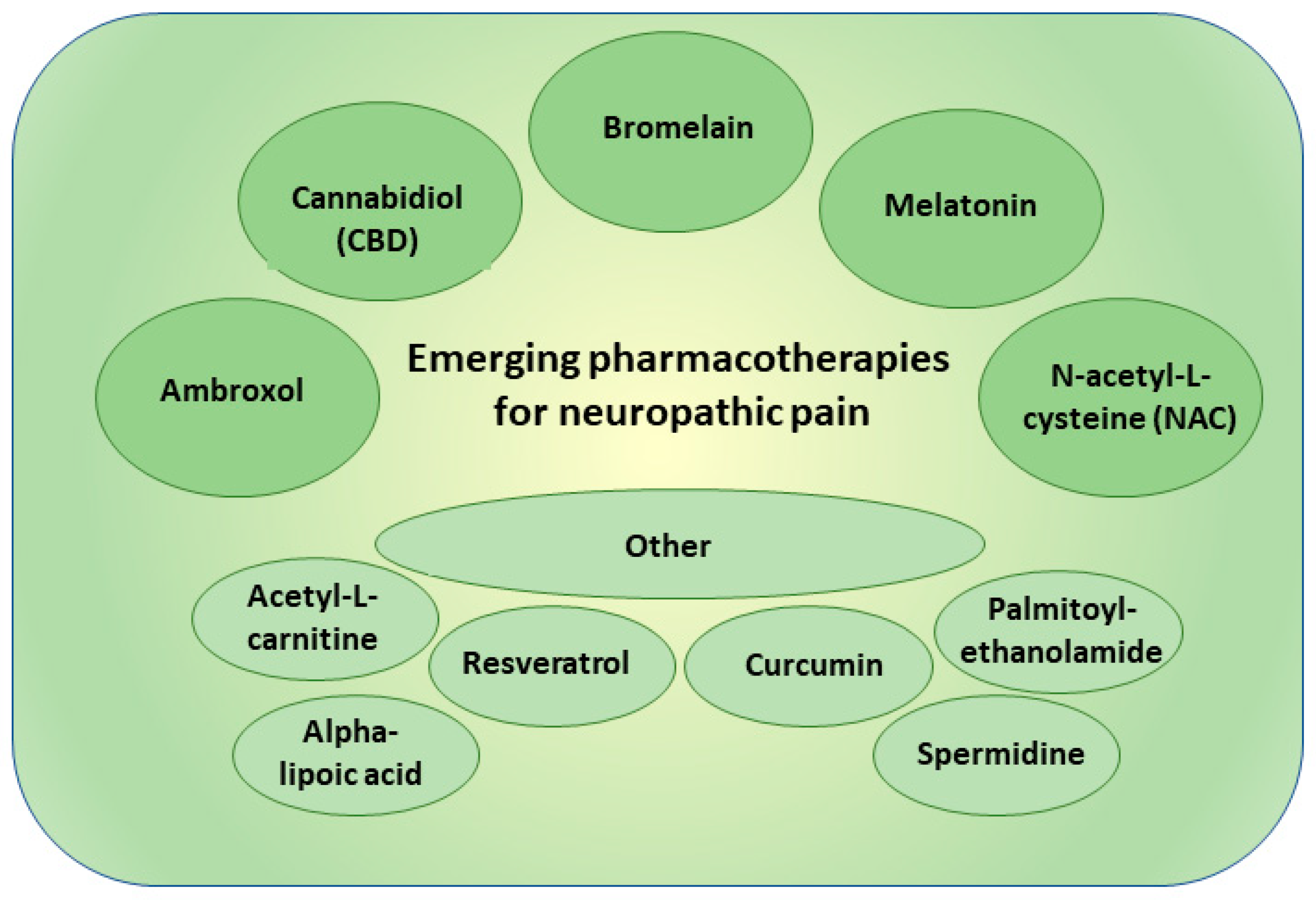
4. New Pharmacotherapies in Neuropathic Pain
4.1. Ambroxol
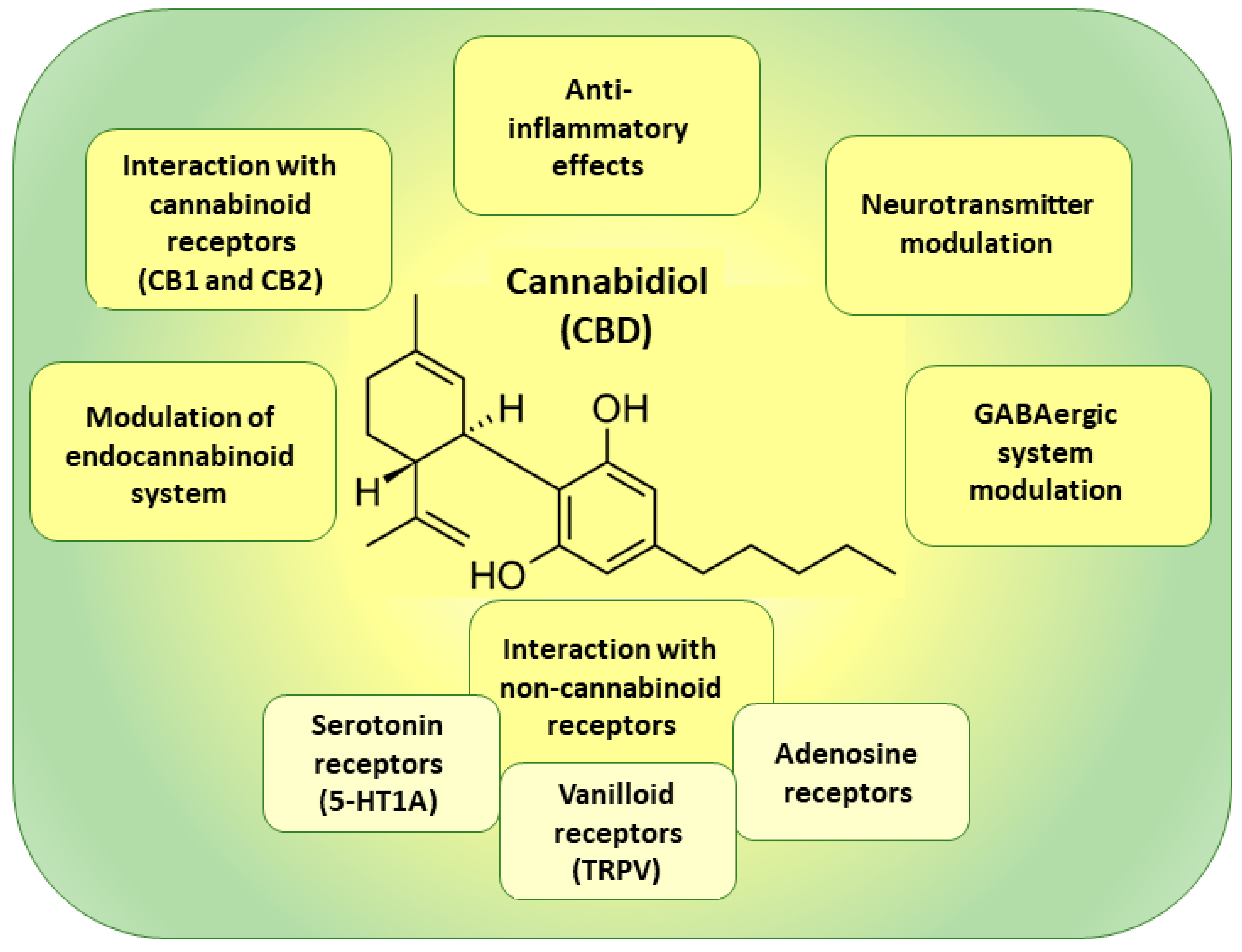
4.2. Cannabidiol
4.3. Bromelain
4.4. Melatonin
4.5. N-acetyl-L-cysteine
4.6. Other Experimental Therapies
5. Further Perspectives in Neuropathic Pain Management
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finnerup, N.B.; Kuner, R.; Jensen, T.S. Neuropathic Pain: From Mechanisms to Treatment. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 259–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzcharles, M.A.; Cohen, S.P.; Clauw, D.J.; Littlejohn, G.; Usui, C.; Häuser, W. Nociplastic pain: Towards an understanding of prevalent pain conditions. Lancet 2021, 397, 2098–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakar, S.; Shim, J.; Jo, S.; Bean, B.P.; Singeç, I.; Woolf, C.J. Developing nociceptor-selective treatments for acute and chronic pain. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabj9837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treede, R.D.; Jensen, T.S.; Campbell, J.N.; Cruccu, G.; Dostrovsky, J.O.; Griffin, J.W.; Hansson, P.; Hughes, R.; Nurmikko, T.; Serra, J. Neuropathic pain: Redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 2008, 70, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP). IASP Terminology. 2023. Available online: https://www.iasp-pain.org/terminology#Nociplasticpain (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- Sacerdote, P.; Franchi, S.; Moretti, S.; Castelli, M.; Procacci, P.; Magnaghi, V.; Panerai, A.E. Cytokine modulation is necessary for efficacious treatment of experimental neuropathic pain. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013, 8, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.J.; Ji, R.R. Targeting astrocyte signaling for chronic pain. Neurotherapeutics 2010, 7, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Zhang, J.; Han, X.; Yu, W.; Gu, X. Potential novel therapeutic strategies for neuropathic pain. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1138798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.; Kersebaum, D.; Lawn, T.; Sachau, J.; Sendel, M.; Vollert, J. Improving neuropathic pain treatment—By rigorous stratification from bench to bedside. J. Neurochem. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truini, A. A Review of Neuropathic Pain: From Diagnostic Tests to Mechanisms. Pain Ther. 2017, 6, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Zou, T.; Sun, S.; Yang, D. Cell therapy for neuropathic pain. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1119223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães Pereira, J.E.; Ferreira Gomes Pereira, L.; Mercante Linhares, R.; Darcy Alves Bersot, C.; Aslanidis, T.; Ashmawi, H.A. Efficacy and Safety of Ketamine in the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Pain Res. 2022, 15, 1011–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamp, J.; Van Velzen, M.; Olofsen, E.; Boon, M.; Dahan, A.; Niesters, M. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations for NMDA-receptor antagonist ketamine in the treatment of chronic neuropathic pain: An update of the most recent literature. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2019, 15, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coluzzi, F.; Rullo, L.; Scerpa, M.S.; Losapio, L.M.; Rocco, M.; Billeci, D.; Candeletti, S.; Romualdi, P. Current and Future Therapeutic Options in Pain Management: Multi-mechanistic Opioids Involving Both MOR and NOP Receptor Activation. CNS Drugs 2022, 36, 617–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, M.C.; Williams, B.R.; Singh, N.; Posa, L.; Freyberg, Z.; Logan, R.W.; Puig, S. Mu-opioid receptor and receptor tyrosine kinase crosstalk: Implications in mechanisms of opioid tolerance, reduced analgesia to neuropathic pain, dependence, and reward. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1059089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.Q. The Downregulation of Opioid Receptors and Neuropathic Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenzi, M.; Milella, M.S.; D’Ottavio, G.; Caprioli, D.; Reverte, I.; Maftei, D. Targeting Chemokines and Chemokine GPCRs to Enhance Strong Opioid Efficacy in Neuropathic Pain. Life 2022, 12, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almogi-Hazan, O.; Or, R. Cannabis, the Endocannabinoid System and Immunity-the Journey from the Bedside to the Bench and Back. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laprairie, R.B.; Bagher, A.M.; Kelly, M.E.; Denovan-Wright, E.M. Cannabidiol is a negative allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4790–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Gong, J.P.; Patel, S.; Perchuk, A.; Meozzi, P.A.; Myers, L.; Mora, Z.; Tagliaferro, P.; Gardner, E.; et al. Discovery of the presence and functional expression of cannabinoid CB2 receptors in brain. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1074, 514–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sickle, M.D.; Duncan, M.; Kingsley, P.J.; Mouihate, A.; Urbani, P.; Mackie, K.; Stella, N.; Makriyannis, A.; Piomelli, D.; Davison, J.S.; et al. Identification and functional characterization of brainstem cannabinoid CB2 receptors. Science 2005, 310, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, C.; Naziroǧlu, M.; Rodríguez, A.B.; Pariente, J.A. Neuropathic Pain: Delving into the Oxidative Origin and the Possible Implication of Transient Receptor Potential Channels. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Logu, F.; Geppetti, P. Ion Channel Pharmacology for Pain Modulation. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2019, 260, 161–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannone, L.F.; De Logu, F.; Geppetti, P.; De Cesaris, F. The role of TRP ion channels in migraine and headache. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 768, 136380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Jo, Y.Y.; Chung, G.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, C.K. Functional Importance of Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) Channels in Neurological Disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 611773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAnally, H.; Bonnet, U.; Kaye, A.D. Gabapentinoid Benefit and Risk Stratification: Mechanisms Over Myth. Pain Ther. 2020, 9, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroianu, G.A.; Aloum, L.; Adem, A. Neuropathic pain: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1072629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macone, A.; Otis, J.A.D. Neuropathic Pain. Semin. Neurol. 2018, 38, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, A.B.; Cui, M.; Booth, R.G.; Canal, C.E. “Selective” serotonin 5-HT(2A) receptor antagonists. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 200, 115028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, S.; Shi, W.; Liu, W.; Chen, Q.Y.; Zhuo, M. Multiple modulatory roles of serotonin in chronic pain and injury-related anxiety. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1122381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satiamurthy, R.; Yaakob, N.S.; Shah, N.M.; Azmi, N.; Omar, M.S. Potential Roles of 5-HT(3) Receptor Antagonists in Reducing Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN). Curr. Mol. Med. 2023, 23, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, P.R.; Vahid-Ansari, F. The 5-HT1A receptor: Signaling to behavior. Biochimie 2019, 161, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haleem, D.J. Targeting Serotonin1A Receptors for Treating Chronic Pain and Depression. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahid-Ansari, F.; Zhang, M.; Zahrai, A.; Albert, P.R. Overcoming Resistance to Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors: Targeting Serotonin, Serotonin-1A Receptors and Adult Neuroplasticity. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, P.; Mozumder, S.; Bej, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Sengupta, J.; Chattopadhyay, A. Structure, dynamics and lipid interactions of serotonin receptors: Excitements and challenges. Biophys. Rev. 2020, 13, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashida, K.I.; Obata, H. Strategies to Treat Chronic Pain and Strengthen Impaired Descending Noradrenergic Inhibitory System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorca-Torralba, M.; Borges, G.; Neto, F.; Mico, J.A.; Berrocoso, E. Noradrenergic Locus Coeruleus pathways in pain modulation. Neuroscience 2016, 338, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraci, F.; Merlo, S.; Drago, F.; Caruso, G.; Parenti, C.; Sortino, M.A. Rescue of Noradrenergic System as a Novel Pharmacological Strategy in the Treatment of Chronic Pain: Focus on Microglia Activation. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, H. Analgesic Mechanisms of Antidepressants for Neuropathic Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Micheli, L.; Crocetti, L.; Giovannoni, M.P.; Vergelli, C.; Ghelardini, C. α2 Adrenoceptor: A Target for Neuropathic Pain Treatment. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K. The Role of ATP Receptors in Pain Signaling. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 2454–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Yang, R.; Li, L.; Xu, X.; Liang, S. Purinergic signaling: A potential therapeutic target for depression and chronic pain. Purinergic Signal. 2023, 19, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.M.; Peyton, L.; Essa, H.; Choi, D.S. Adenosine receptors: Emerging non-opioids targets for pain medications. Neurobiol. Pain 2022, 11, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Wu, J.; Chang, H.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Guo, Y. Adenosine signaling mediate pain transmission in the central nervous system. Purinergic Signal. 2023, 19, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattler, C.; Benndorf, K. Enlightening activation gating in P2X receptors. Purinergic Signal. 2022, 18, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, K.A.; Pradhan, B.; Wen, Z.; Pramanik, A. New paradigms in purinergic receptor ligand discovery. Neuropharmacology 2023, 230, 109503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrenk-Siemens, K.; Rösseler, C.; Lampert, A. Translational Model Systems for Complex Sodium Channel Pathophysiology in Pain. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2018, 246, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St John Smith, E. Advances in understanding nociception and neuropathic pain. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Q.; Jin, Z.; Qin, Y.; Meng, F.; Zhao, G. Review of Voltage-gated Calcium Channel α2δ Subunit Ligands for the Treatment of Chronic Neuropathic Pain and Insight into Structure-activity Relationship (SAR) by Pharmacophore Modeling. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 5097–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppanova, L.; Lacinova, L. Voltage-dependent Ca(V)3.2 and Ca(V)2.2 channels in nociceptive pathways. Pflügers Arch. 2022, 474, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elsayed, A.; Jackson, M.; Gu, S.L.; Fiala, K.; Gu, J. Neuropathic pain and Kv7 voltage-gated potassium channels: The potential role of Kv7 activators in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Mol. Pain 2019, 15, 1744806919864256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemel, B.M.; Ritter, D.M.; Covarrubias, M.; Muqeem, T. A-Type K(V) Channels in Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons: Diversity, Function, and Dysfunction. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.G.; Xu, T.L. Acid-sensing ion channels: A novel therapeutic target for pain and anxiety. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Song, S.; Ezenwukwa, C.C.; Jalali, S.; Sun, B.; Sun, D. Ion channels and transporters in microglial function in physiology and brain diseases. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 142, 104925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, A.E.; Franchi, S.; Panerai, A.E.; Rossi, A.; Sacerdote, P.; Colleoni, M. The soy isoflavone genistein reverses oxidative and inflammatory state, neuropathic pain, neurotrophic and vasculature deficits in diabetes mouse model. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 650, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hingtgen, C.M.; Waite, K.J.; Vasko, M.R. Prostaglandins facilitate peptide release from rat sensory neurons by activating the adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate transduction cascade. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 5411–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page-McCaw, A.; Ewald, A.J.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.R.; Xu, Z.Z.; Wang, X.; Lo, E.H. Matrix metalloprotease regulation of neuropathic pain. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbardar, M.G.; Amin, B.; Mehri, S.; Mirnajafi-Zadeh, S.J.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Rosmarinic acid attenuates development and existing pain in a rat model of neuropathic pain: An evidence of anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects. Phytomedicine 2018, 40, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.; Pan, H.L. Epigenetic Mechanisms of Neural Plasticity in Chronic Neuropathic Pain. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Li, X.; Tang, S.; Song, F.; Li, W.; Xie, G.; Liang, J.; Zhou, J. Epigenetic modifications in neuropathic pain. Mol. Pain 2021, 17, 17448069211056767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, P.; Jia, Y.; Liu, M.; Jiang, J. Non-coding RNA and n6-methyladenosine modification play crucial roles in neuropathic pain. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1002018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meaadi, J.; Obara, I.; Eldabe, S.; Nazar, H. The safety and efficacy of gabapentinoids in the management of neuropathic pain: A systematic review with meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2023, 45, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Shen, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Liu, W.; Jiang, G. A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Comparing the Efficacy and Safety of Pregabalin and Gabapentin in the Treatment of Postherpetic Neuralgia. Pain Ther. 2023, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-Campos, M.S.; Pimenta-Fermisson-Ramos, P.; Díaz-Cambronero, J.I.; Carbonell-Sanchís, R.; López-Briz, E.; Ruíz-García, V. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effectiveness and adverse events of gabapentin and pregabalin for sciatica pain. Aten. Primaria 2022, 54, 102144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanthanna, H.; Gilron, I.; Rajarathinam, M.; AlAmri, R.; Kamath, S.; Thabane, L.; Devereaux, P.J.; Bhandari, M. Benefits and safety of gabapentinoids in chronic low back pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Attal, N.; Haroutounian, S.; McNicol, E.; Baron, R.; Dworkin, R.H.; Gilron, I.; Haanpää, M.; Hansson, P.; Jensen, T.S.; et al. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goins, A.; Patel, K.; Alles, S.R.A. The gabapentinoid drugs and their abuse potential. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 227, 107926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Meng, L.; Han, F. The efficacy of gabapentin combined with opioids for neuropathic cancer pain: A meta-analysis. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, M.; Salvat, E.; Muller, A.; Yalcin, I.; Barrot, M. Antidepressants and gabapentinoids in neuropathic pain: Mechanistic insights. Neuroscience 2016, 338, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindrup, S.H.; Otto, M.; Finnerup, N.B.; Jensen, T.S. Antidepressants in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2005, 96, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Max, M.B.; Lynch, S.A.; Muir, J.; Shoaf, S.E.; Smoller, B.; Dubner, R. Effects of desipramine, amitriptyline, and fluoxetine on pain in diabetic neuropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saarto, T.; Wiffen, P.J. Antidepressants for neuropathic pain. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2007, Cd005454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attal, N. Pharmacological treatments of neuropathic pain: The latest recommendations. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 175, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.C.; Chen, P.P. A review of SSRIs and SNRIs in neuropathic pain. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2010, 11, 2813–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raskin, J.; Pritchett, Y.L.; Wang, F.; D’Souza, D.N.; Waninger, A.L.; Iyengar, S.; Wernicke, J.F. A double-blind, randomized multicenter trial comparing duloxetine with placebo in the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain Med. 2005, 6, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, D.J.; Lu, Y.; Detke, M.J.; Lee, T.C.; Iyengar, S. Duloxetine vs. placebo in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy. Pain 2005, 116, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernicke, J.F.; Pritchett, Y.L.; D’Souza, D.N.; Waninger, A.; Tran, P.; Iyengar, S.; Raskin, J. A randomized controlled trial of duloxetine in diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Neurology 2006, 67, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.M.; Hussain, S.M.; Ekram, A.R. Duloxetine in Painful Diabetic Neuropathy: A Systematic Review. Clin. J. Pain 2016, 32, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornasari, D.; Magni, A.; Pais, P.; Palao, T.; Polati, E.; Sansone, P. Changing the paradigm in postherpetic neuralgia treatment: Lidocaine 700 mg medicated plaster. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 3664–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, V.; Osborn, J.; Chaturvedi, R.; Shah, V.; Chakravarthy, K. Advances in the interventional management of neuropathic pain. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voute, M.; Morel, V.; Pickering, G. Topical Lidocaine for Chronic Pain Treatment. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 4091–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocot-Kępska, M.; Zajączkowska, R.; Mika, J.; Kopsky, D.J.; Wordliczek, J.; Dobrogowski, J.; Przeklasa-Muszyńska, A. Topical Treatments and Their Molecular/Cellular Mechanisms in Patients with Peripheral Neuropathic Pain-Narrative Review. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Patel, A.; Eswani, Z.; Moore, P.; Steib, M.; Lee, C.; Kaye, A.D. Role of Intravenous Lidocaine Infusion in the Treatment of Peripheral Neuropathy. Orthop. Rev. 2021, 13, 25567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, D.E.; Morley-Forster, P.K.; Pirani, Z.; Rohfritsch, C.; Stitt, L. Intravenous lidocaine in the management of chronic peripheral neuropathic pain: A randomized-controlled trial. Can. J. Anaesth. 2019, 66, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bnyan, R.; Khan, I.; Ehtezazi, T.; Saleem, I.; Gordon, S.; O’Neill, F.; Roberts, M. Formulation and optimisation of novel transfersomes for sustained release of local anaesthetic. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 1508–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attal, N.; Gaudé, V.; Brasseur, L.; Dupuy, M.; Guirimand, F.; Parker, F.; Bouhassira, D. Intravenous lidocaine in central pain: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, psychophysical study. Neurology 2000, 54, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Zheng, X.; Li, D.; Chen, H.; Li, L. Comparison of lidocaine and ropivacaine stellate ganglion blockade in treating upper limb postherpetic neuralgia. Medicine 2022, 101, e29394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.J.; Lee, J.H.; Seo, T.B.; Oh, S.H. Lidocaine/multivalent ion complex as a potential strategy for prolonged local anesthesia. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 115, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Wu, H.; Zou, Z. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a novel lidocaine-loaded cubosomal gel for prolonged local anesthesia. J. Biomater. Appl. 2022, 37, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulvi, F.A.; Pillai, L.V.; Patel, K.P.; Desai, A.R.; Shukla, M.R.; Desai, D.T.; Patel, H.P.; Ranch, K.M.; Shah, S.A.; Shah, D.O. Lidocaine tripotassium phosphate complex laden microemulsion for prolonged local anaesthesia: In vitro and in vivo studies. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 185, 110632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chang, S.; Zhang, X.; Hou, T.; Yao, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, X.; Wang, X. Fabrication of a controlled-release delivery system for relieving sciatica nerve pain using an ultrasound-responsive microcapsule. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1072205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, R.; Mayoral, V.; Leijon, G.; Binder, A.; Steigerwald, I.; Serpell, M. Efficacy and safety of 5% lidocaine (lignocaine) medicated plaster in comparison with pregabalin in patients with postherpetic neuralgia and diabetic polyneuropathy: Interim analysis from an open-label, two-stage adaptive, randomized, controlled trial. Clin. Drug Investig. 2009, 29, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, J.; Pew, S.; Wie, C.; Gupta, R.; Freeman, J.; Strand, N. Comprehensive Review of Topical Analgesics for Chronic Pain. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2021, 25, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, K. Biological Activities of Red Pepper (Capsicum annuum) and Its Pungent Principle Capsaicin: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1488–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, E.S.; Cerqueira, A.R.; Soares, A.G.; Costa, S.K. Capsaicin and Its Role in Chronic Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 929, 91–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonezzi, C.; Costantini, A.; Cruccu, G.; Fornasari, D.M.M.; Guardamagna, V.; Palmieri, V.; Polati, E.; Zini, P.; Dickenson, A.H. Capsaicin 8% dermal patch in clinical practice: An expert opinion. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2020, 21, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaccari, L.G.; Aurilio, C.; Coppolino, F.; Pace, M.C.; Passsavanti, M.B.; Pota, V.; Sansone, P. Capsaicin 8% Patch and Chronic Postsurgical Neuropathic Pain. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leavell, Y.; Simpson, D.M. The role of the capsaicin 8% patch in the treatment of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Pain Manag. 2022, 12, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olusanya, A.; Yearsley, A.; Brown, N.; Braun, S.; Hayes, C.; Rose, E.; Connolly, B.; Dicks, M.; Beal, C.; Helmonds, B.; et al. Capsaicin 8% Patch for Spinal Cord Injury Focal Neuropathic Pain, a Randomized Controlled Trial. Pain Med. 2023, 24, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezón-Gutiérrez, L.; Custodio-Cabello, S.; Palka-Kotlowska, M.; Khosravi-Shahi, P. High-Dose 8% Capsaicin Patch in Treatment of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. A Systematic Review. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2020, 60, 1047–1054.e1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosenovic, S.; Jelicic Kadic, A.; Miljanovic, M.; Biocic, M.; Boric, K.; Cavar, M.; Markovina, N.; Vucic, K.; Puljak, L. Interventions for Neuropathic Pain: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. Anesth. Analg. 2017, 125, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, D.; Schultheis, B.C.; Hanes, M.C.; Jolly, S.M.; Chakravarthy, K.V.; Deer, T.R.; Levy, R.M.; Hunter, C.W. A Comprehensive Algorithm for Management of Neuropathic Pain. Pain Med. 2019, 20, S2–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthuraman, A.; Singh, N.; Jaggi, A.S.; Ramesh, M. Drug therapy of neuropathic pain: Current developments and future perspectives. Curr. Drug Targets 2014, 15, 210–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Maher, D.P.; Cohen, S.P. Emerging concepts on the use of ketamine for chronic pain. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 13, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, J.E.; St Pierre, S.; Ellis, E.; Hanukaai, J.S.; Noor, N.; Varrassi, G.; Wells, M.; Kaye, A.D. Ketamine for the Treatment of Chronic Pain: A Comprehensive Review. Health Psychol. Res. 2021, 9, 25535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeng, S.; Hiranita, T.; León, F.; McMahon, L.R.; McCurdy, C.R. Novel Approaches, Drug Candidates, and Targets in Pain Drug Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 6523–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, A.; Della Pasqua, O.; Danhof, M. Challenges in translational drug research in neuropathic and inflammatory pain: The prerequisites for a new paradigm. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 73, 1219–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.; Rice, A.S.C.; Dworkin, R.H. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for neuropathic pain: How do we explain continued widespread use? Pain 2009, 143, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, A.; Bleakley, C.; Hurley, D.A.; Gill, C.; Hannon-Fletcher, M.; Bell, P.; McDonough, S. Herbal medicinal products or preparations for neuropathic pain. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 4, Cd010528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, B.; Pirvulescu, I.; Candido, K.D.; Knezevic, N.N. Herbal Medicine for Pain Management: Efficacy and Drug Interactions. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskell, H.; Derry, S.; Stannard, C.; Moore, R.A. Oxycodone for neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 7, Cd010692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshehri, F.S. Tapentadol: A Review of Experimental Pharmacology Studies, Clinical Trials, and Recent Findings. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2023, 17, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, A. Revisiting Tramadol: A Multi-Modal Agent for Pain Management. CNS Drugs 2019, 33, 481–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, J.; Barbosa, J.; Moreira, R.; Queirós, O.; Carvalho, F.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Comparative pharmacology and toxicology of tramadol and tapentadol. Eur. J. Pain 2018, 22, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisignano, M.; Gribbon, P.; Geisslinger, G. Drug Repurposing to Target Neuroinflammation and Sensory Neuron-Dependent Pain. Drugs 2022, 82, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazan, D.; Klimek, L.; Sperl, A.; Plomer, M.; Kölsch, S. Safety of ambroxol in the treatment of airway diseases in adult patients. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2018, 17, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malerba, M.; Ragnoli, B. Ambroxol in the 21st century: Pharmacological and clinical update. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2008, 4, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.A.; Baron, R.; Dickenson, A.H.; Kern, K.U.; Santarelli, D.M. Ambroxol for neuropathic pain: Hiding in plain sight? Pain 2023, 164, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salat, K.; Gryzlo, B.; Kulig, K. Experimental Drugs for Neuropathic Pain. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 1193–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaida, W.; Klinder, K.; Arndt, K.; Weiser, T. Ambroxol, a Nav1.8-preferring Na+ channel blocker, effectively suppresses pain symptoms in animal models of chronic, neuropathic and inflammatory pain. Neuropharmacology 2005, 49, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furgała, A.; Fijałkowski, Ł.; Nowaczyk, A.; Sałat, R.; Sałat, K. Time-shifted co-administration of sub-analgesic doses of ambroxol and pregabalin attenuates oxaliplatin-induced cold allodynia in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hama, A.T.; Plum, A.W.; Sagen, J. Antinociceptive effect of ambroxol in rats with neuropathic spinal cord injury pain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2010, 97, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, K.U.; Weiser, T. Topical ambroxol for the treatment of neuropathic pain. An initial clinical observation. Schmerz 2015, 29 (Suppl. S3), S89–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maihöfner, C.; Schneider, S.; Bialas, P.; Gockel, H.; Beer, K.G.; Bartels, M.; Kern, K.U. Successful treatment of complex regional pain syndrome with topical ambroxol: A case series. Pain Manag. 2018, 8, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, K.U.; Schwickert-Nieswandt, M.; Maihöfner, C.; Gaul, C. Topical Ambroxol 20% for the Treatment of Classical Trigeminal Neuralgia—A New Option? Initial Clinical Case Observations. Headache 2019, 59, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarberg, B.H.; Barkin, R.L. The future of cannabinoids as analgesic agents: A pharmacologic, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic overview. Am. J. Ther. 2007, 14, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karst, M.; Salim, K.; Burstein, S.; Conrad, I.; Hoy, L.; Schneider, U. Analgesic effect of the synthetic cannabinoid CT-3 on chronic neuropathic pain: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2003, 290, 1757–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atakan, Z. Cannabis, a complex plant: Different compounds and different effects on individuals. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 2, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, N.M.; Mechoulam, R. Cannabinoids in health and disease. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2007, 9, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfait, A.M.; Gallily, R.; Sumariwalla, P.F.; Malik, A.S.; Andreakos, E.; Mechoulam, R.; Feldmann, M. The nonpsychoactive cannabis constituent cannabidiol is an oral anti-arthritic therapeutic in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 9561–9566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, A.J.; Grimaldi, M.; Axelrod, J.; Wink, D. Cannabidiol and (-)Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol are neuroprotective antioxidants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8268–8273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, E.M.; Bolognini, D.; Limebeer, C.L.; Cascio, M.G.; Anavi-Goffer, S.; Fletcher, P.J.; Mechoulam, R.; Pertwee, R.G.; Parker, L.A. Cannabidiol, a non-psychotropic component of cannabis, attenuates vomiting and nausea-like behaviour via indirect agonism of 5-HT(1A) somatodendritic autoreceptors in the dorsal raphe nucleus. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 2620–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.; Pryce, G.; Croxford, J.L.; Brown, P.; Pertwee, R.G.; Huffman, J.W.; Layward, L. Cannabinoids control spasticity and tremor in a multiple sclerosis model. Nature 2000, 404, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbazi, F.; Grandi, V.; Banerjee, A.; Trant, J.F. Cannabinoids and Cannabinoid Receptors: The Story so Far. iScience 2020, 23, 101301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertwee, R.G. The diverse CB1 and CB2 receptor pharmacology of three plant cannabinoids: Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and delta9-tetrahydrocannabivarin. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oláh, A.; Szekanecz, Z.; Bíró, T. Targeting Cannabinoid Signaling in the Immune System: “High”-ly Exciting Questions, Possibilities, and Challenges. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, S. Cannabidiol (CBD) and its analogs: A review of their effects on inflammation. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmes, M.W.; Kaczocha, M.; Berger, W.T.; Leung, K.; Ralph, B.P.; Wang, L.; Sweeney, J.M.; Miyauchi, J.T.; Tsirka, S.E.; Ojima, I.; et al. Fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs) are intracellular carriers for Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 8711–8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petzke, F.; Tölle, T.; Fitzcharles, M.A.; Häuser, W. Cannabis-Based Medicines and Medical Cannabis for Chronic Neuropathic Pain. CNS Drugs 2022, 36, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, R.M.P.; Aguiar, A.F.L.; Paes-Colli, Y.; Trindade, P.M.P.; Ferreira, B.K.; de Melo Reis, R.A.; Sampaio, L.S. Cannabinoid Therapeutics in Chronic Neuropathic Pain: From Animal Research to Human Treatment. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 785176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron-Flores, V.; Diaz-Ruiz, A.; Manzanares, J.; Rios, C.; Burelo, M.; Jardon-Guadarrama, G.; Martínez-Cárdenas, M.; Mata-Bermudez, A. Cannabidiol attenuates hypersensitivity and oxidative stress after traumatic spinal cord injury in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 788, 136855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, R.; Veras, F.; Netto, G.; Elisei, L.; Sorgi, C.; Faccioli, L.; Galdino, G. Cannabidiol prevents chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain by modulating spinal TLR4 via endocannabinoid system activation. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2023, 75, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eeswara, A.; Pacheco-Spiewak, A.; Jergova, S.; Sagen, J. Combined non-psychoactive Cannabis components cannabidiol and β-caryophyllene reduce chronic pain via CB1 interaction in a rat spinal cord injury model. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, R.; Wright, R. A Scoping Review on Clinical Trials of Pain Reduction With Cannabis Administration in Adults. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2020, 12, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainsbury, B.; Bloxham, J.; Pour, M.H.; Padilla, M.; Enciso, R. Efficacy of cannabis-based medications compared to placebo for the treatment of chronic neuropathic pain: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Dent. Anesth. Pain Med. 2021, 21, 479–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippini, G.; Minozzi, S.; Borrelli, F.; Cinquini, M.; Dwan, K. Cannabis and cannabinoids for symptomatic treatment for people with multiple sclerosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 5, Cd013444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arout, C.A.; Haney, M.; Herrmann, E.S.; Bedi, G.; Cooper, Z.D. A placebo-controlled investigation of the analgesic effects, abuse liability, safety and tolerability of a range of oral cannabidiol doses in healthy humans. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 88, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesney, E.; Oliver, D.; Green, A.; Sovi, S.; Wilson, J.; Englund, A.; Freeman, T.P.; McGuire, P. Adverse effects of cannabidiol: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, T.C.; Hayley, A.C.; Downey, L.A.; Parrott, A.C. Cannabis: An Overview of its Adverse Acute and Chronic Effects and its Implications. Curr. Drug Abus. Rev. 2017, 10, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huestis, M.A.; Solimini, R.; Pichini, S.; Pacifici, R.; Carlier, J.; Busardò, F.P. Cannabidiol Adverse Effects and Toxicity. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 974–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.J.; Galettis, P.; Schneider, J. The pharmacokinetics and the pharmacodynamics of cannabinoids. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 2477–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huestis, M.A. Human cannabinoid pharmacokinetics. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 1770–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakare, A.O.; Owoyele, B.V. Antinociceptive and neuroprotective effects of bromelain in chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in Wistar rats. Korean J. Pain 2020, 33, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakare, A.O.; Owoyele, B.V. Bromelain reversed electrolyte imbalance in the chronically constricted sciatic nerve of Wistar rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakare, A.O.; Owoyele, B.V. Bromelain reduced pro-inflammatory mediators as a common pathway that mediate antinociceptive and anti-anxiety effects in sciatic nerve ligated Wistar rats. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desideri, I.; Francolini, G.; Becherini, C.; Terziani, F.; Delli Paoli, C.; Olmetto, E.; Loi, M.; Perna, M.; Meattini, I.; Scotti, V.; et al. Use of an alpha lipoic, methylsulfonylmethane and bromelain dietary supplement (Opera(®)) for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy management, a prospective study. Med. Oncol. 2017, 34, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentieri, A.; Díaz de Barboza, G.; Areco, V.; Peralta López, M.; Tolosa de Talamoni, N. New perspectives in melatonin uses. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 65, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeland, R.; Cardinali, D.P.; Srinivasan, V.; Spence, D.W.; Brown, G.M.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R. Melatonin—A pleiotropic, orchestrating regulator molecule. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 93, 350–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña Castroviejo, D.; López, L.C.; Escames, G.; López, A.; García, J.A.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin-mitochondria interplay in health and disease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J.; Mayo, J.C.; Tan, D.X.; Sainz, R.M.; Alatorre-Jimenez, M.; Qin, L. Melatonin as an antioxidant: Under promises but over delivers. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 61, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, A.; García, J.A.; Escames, G.; Venegas, C.; Ortiz, F.; López, L.C.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Melatonin protects the mitochondria from oxidative damage reducing oxygen consumption, membrane potential, and superoxide anion production. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 46, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, J.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Sainz, R.M.; Mayo, J.C.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin and mitochondrial function. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 765–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Martín, M.; Macías, M.; Escames, G.; León, J.; Khaldy, H.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin, mitochondria, and cellular bioenergetics. J. Pineal Res. 2001, 30, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Labani, N.; Cecon, E.; Jockers, R. Melatonin Target Proteins: Too Many or Not Enough? Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legros, C.; Chesneau, D.; Boutin, J.A.; Barc, C.; Malpaux, B. Melatonin from cerebrospinal fluid but not from blood reaches sheep cerebral tissues under physiological conditions. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2014, 26, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuthati, Y.; Lin, S.H.; Chen, I.J.; Wong, C.S. Melatonin and their analogs as a potential use in the management of Neuropathic pain. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2019, 118, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, V.; Lauterbach, E.C.; Ho, K.Y.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Zakaria, R.; Brzezinski, A. Melatonin in antinociception: Its therapeutic applications. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2012, 10, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambriz-Tututi, M.; Rocha-González, H.I.; Cruz, S.L.; Granados-Soto, V. Melatonin: A hormone that modulates pain. Life Sci. 2009, 84, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, V.; Zakaria, R.; Jeet Singh, H.; Acuna-Castroviejo, D. Melatonin and its agonists in pain modulation and its clinical application. Arch. Ital. Biol. 2012, 150, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posa, L.; De Gregorio, D.; Gobbi, G.; Comai, S. Targeting Melatonin MT2 Receptors: A Novel Pharmacological Avenue for Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 3866–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Omary, F.A. Melatonin: Comprehensive profile. Profiles Drug Subst. Excip. Relat. Methodol. 2013, 38, 159–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.Q.; Guo, Y.; Chu, X.Y. Neuropathic Pain: The Dysfunction of Drp1, Mitochondria, and ROS Homeostasis. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 38, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, C.A. Is melatonin the next “new” therapy to improve sleep and reduce pain? Sleep 2014, 37, 1405–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsani, E.; Buffoli, B.; Bonazza, V.; Reiter, R.J.; Rezzani, R.; Rodella, L.F. Single Administration of Melatonin Modulates the Nitroxidergic System at the Peripheral Level and Reduces Thermal Nociceptive Hypersensitivity in Neuropathic Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.T.; Chen, S.H.; Chang, C.F.; Lin, S.C.; Lue, J.H.; Tsai, Y.J. Melatonin reduces neuropathic pain behavior and glial activation through MT(2) melatonin receptor modulation in a rat model of lysophosphatidylcholine-induced demyelination neuropathy. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 140, 104827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, S.; Kiani, A.; Jalili, C.; Abbaszadeh, F.; Piri, S.; Farzaei, M.H.; Rastegari-Pouyani, M.; Mohammadi-Noori, E.; Khan, H. Intrathecal Administration of Melatonin Ameliorates the Neuroinflammation- Mediated Sensory and Motor Dysfunction in A Rat Model of Compression Spinal Cord Injury. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, T.; Yue, L.P.; Hu, L. Exogenous melatonin alleviates neuropathic pain-induced affective disorders by suppressing NF-κB/ NLRP3 pathway and apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesi, N.; Govoni, S.; Allegri, M. Non-drug pain relievers active on non-opioid pain mechanisms. Pain Pract. 2022, 22, 255–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Berk, M.; Campochiaro, P.A.; Jaeschke, H.; Marenzi, G.; Richeldi, L.; Wen, F.Q.; Nicoletti, F.; Calverley, P.M.A. The Multifaceted Therapeutic Role of N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) in Disorders Characterized by Oxidative Stress. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 1202–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horst, A.; de Souza, J.A.; Santos, M.C.Q.; Riffel, A.P.K.; Kolberg, C.; Partata, W.A. Effects of N-acetylcysteine on spinal cord oxidative stress biomarkers in rats with neuropathic pain. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2017, 50, e6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horst, A.; Kolberg, C.; Moraes, M.S.; Riffel, A.P.; Finamor, I.A.; Belló-Klein, A.; Pavanato, M.A.; Partata, W.A. Effect of N-acetylcysteine on the spinal-cord glutathione system and nitric-oxide metabolites in rats with neuropathic pain. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 569, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabucci, M.; Notartomaso, S.; Zappulla, C.; Fazio, F.; Cannella, M.; Motolese, M.; Battaglia, G.; Bruno, V.; Gradini, R.; Nicoletti, F. N-Acetyl-cysteine causes analgesia by reinforcing the endogenous activation of type-2 metabotropic glutamate receptors. Mol. Pain 2012, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgül, C.; Nazıroğlu, M. TRPM2 channel protective properties of N-acetylcysteine on cytosolic glutathione depletion dependent oxidative stress and Ca2+ influx in rat dorsal root ganglion. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 106, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sözbir, E.; Nazıroğlu, M. Diabetes enhances oxidative stress-induced TRPM2 channel activity and its control by N-acetylcysteine in rat dorsal root ganglion and brain. Metab. Brain Dis. 2016, 31, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notartomaso, S.; Scarselli, P.; Mascio, G.; Liberatore, F.; Mazzon, E.; Mammana, S.; Gugliandolo, A.; Cruccu, G.; Bruno, V.; Nicoletti, F.; et al. N-Acetylcysteine causes analgesia in a mouse model of painful diabetic neuropathy. Mol. Pain 2020, 16, 1744806920904292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xu, L.; Deng, X.; Jiang, C.; Pan, C.; Chen, L.; Han, Y.; Dai, W.; Hu, L.; Zhang, G.; et al. N-acetyl-cysteine attenuates neuropathic pain by suppressing matrix metalloproteinases. Pain 2016, 157, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Fan, T.; Chen, Y.; Huo, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Cai, Y.; Cheung, C.W.; Tang, J.; Cui, J.; et al. CXCR4/CX43 Regulate Diabetic Neuropathic Pain via Intercellular Interactions between Activated Neurons and Dysfunctional Astrocytes during Late Phase of Diabetes in Rats and the Effects of Antioxidant N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 8547563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, N.; Sajedi, F.; Mohammadi, Y.; Mirjalili, M.; Mehrpooya, M. Ameliorative Effects Of N-Acetylcysteine As Adjunct Therapy On Symptoms Of Painful Diabetic Neuropathy. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 3147–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, M.; Pivetta, B.; Gilron, I.; Khan, J.S. Efficacy and Safety of N-Acetylcysteine for the Management of Chronic Pain in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pain Med. 2021, 22, 2896–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, W.; Guimarães, J.O.; Pina, L.T.S.; Serafini, M.R.; Guimarães, A.G. Antinociceptive effect of plant-based natural products in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathies: A systematic review. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1001276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freo, U.; Brugnatelli, V.; Turco, F.; Zanette, G. Analgesic and Antidepressant Effects of the Clinical Glutamate Modulators Acetyl-L-Carnitine and Ketamine. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 584649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Giorgi, V.; Di Lascio, S.; Fornasari, D. Acetyl-L-carnitine in chronic pain: A narrative review. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 173, 105874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolim, L.C.; da Silva, E.M.; Flumignan, R.L.; Abreu, M.M.; Dib, S.A. Acetyl-L-carnitine for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 6, Cd011265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowin, J. Integrative neuromuscular medicine: Neuropathy and neuropathic pain: Consider the alternatives. Muscle Nerve 2019, 60, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.D.M.; Lauria, P.S.S.; Lima, A.A.; Opretzka, L.C.F.; Marcelino, H.R.; Villarreal, C.F. Alpha-Lipoic Acid as an Antioxidant Strategy for Managing Neuropathic Pain. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang-Illievich, K.; Klivinyi, C.; Lasser, C.; Brenna, C.T.A.; Szilagyi, I.S.; Bornemann-Cimenti, H. Palmitoylethanolamide in the Treatment of Chronic Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi-Manesh, H.; Shirooie, S.; Noori, T.; Sheibani, M.; Tavangar, S.M.; Hemmati, S.; Sadeghi, M.A.; Akbarniakhaky, H.; Mohammadi, Z.; Foroutani, L.; et al. Spermidine reduced neuropathic pain in chronic constriction injury-induced peripheral neuropathy in rats. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, C.A.; Noya-Riobó, M.V.; Mazzone, G.L.; Villar, M.J.; Coronel, M.F. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective actions of resveratrol after experimental nervous system insults. Special focus on the molecular mechanisms involved. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 150, 105188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.L.; Castro, L.; Fang, C.Y.; Castro, M.; Sherali, S.; White, S.; Wang, R.; Neugebauer, V. Bioactive compounds for neuropathic pain: An update on preclinical studies and future perspectives. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 104, 108979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, F.; Braun, C.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Rittner, H.; Tian, Y.K.; Cai, X.Y.; Ye, D.W. Role of curcumin in the management of pathological pain. Phytomedicine 2018, 48, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urošević, M.; Nikolić, L.; Gajić, I.; Nikolić, V.; Dinić, A.; Miljković, V. Curcumin: Biological Activities and Modern Pharmaceutical Forms. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roganović, J.; Petrović, N. Clinical Perspectives of Non-Coding RNA in Oral Inflammatory Diseases and Neuropathic Pain: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, C.; Chambel, S.; Ferreira, A.; Cruz, C.D. Involvement of nerve growth factor (NGF) in chronic neuropathic pain—A systematic review. Rev. Neurosci. 2023, 34, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernatoniene, J.; Sciupokas, A.; Kopustinskiene, D.M.; Petrikonis, K. Novel Drug Targets and Emerging Pharmacotherapies in Neuropathic Pain. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071799
Bernatoniene J, Sciupokas A, Kopustinskiene DM, Petrikonis K. Novel Drug Targets and Emerging Pharmacotherapies in Neuropathic Pain. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(7):1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071799
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernatoniene, Jurga, Arunas Sciupokas, Dalia Marija Kopustinskiene, and Kestutis Petrikonis. 2023. "Novel Drug Targets and Emerging Pharmacotherapies in Neuropathic Pain" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 7: 1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071799
APA StyleBernatoniene, J., Sciupokas, A., Kopustinskiene, D. M., & Petrikonis, K. (2023). Novel Drug Targets and Emerging Pharmacotherapies in Neuropathic Pain. Pharmaceutics, 15(7), 1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071799





