Encapsulation of Thymol in Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMa)-Based Nanoniosome Enables Enhanced Antibiofilm Activity and Wound Healing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Optimization of Niosomal Formulations
2.3. Synthesis of Niosomal Formulations
2.4. Surface Functionalization of the Optimized Niosomal Formulation
2.5. Physicochemical Characterization of the Synthesized Niosomes
2.5.1. Size, Charge Surface, and Polydispersity Index (PDI)
2.5.2. Morphology
2.5.3. Entrapment Efficacy
2.5.4. In Vitro Drug Release and Kinetic Study
2.5.5. Stability
2.6. Antibacterial Tests
2.6.1. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
2.6.2. Agar Diffusion Method
2.6.3. Time-Kill Assay
2.7. Anti-Biofilm Activity
2.8. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.8.1. Culture of HFF Cell Lines
2.8.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.9. In Vitro Wound Scratch Assay
2.10. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Niosome Fabrication
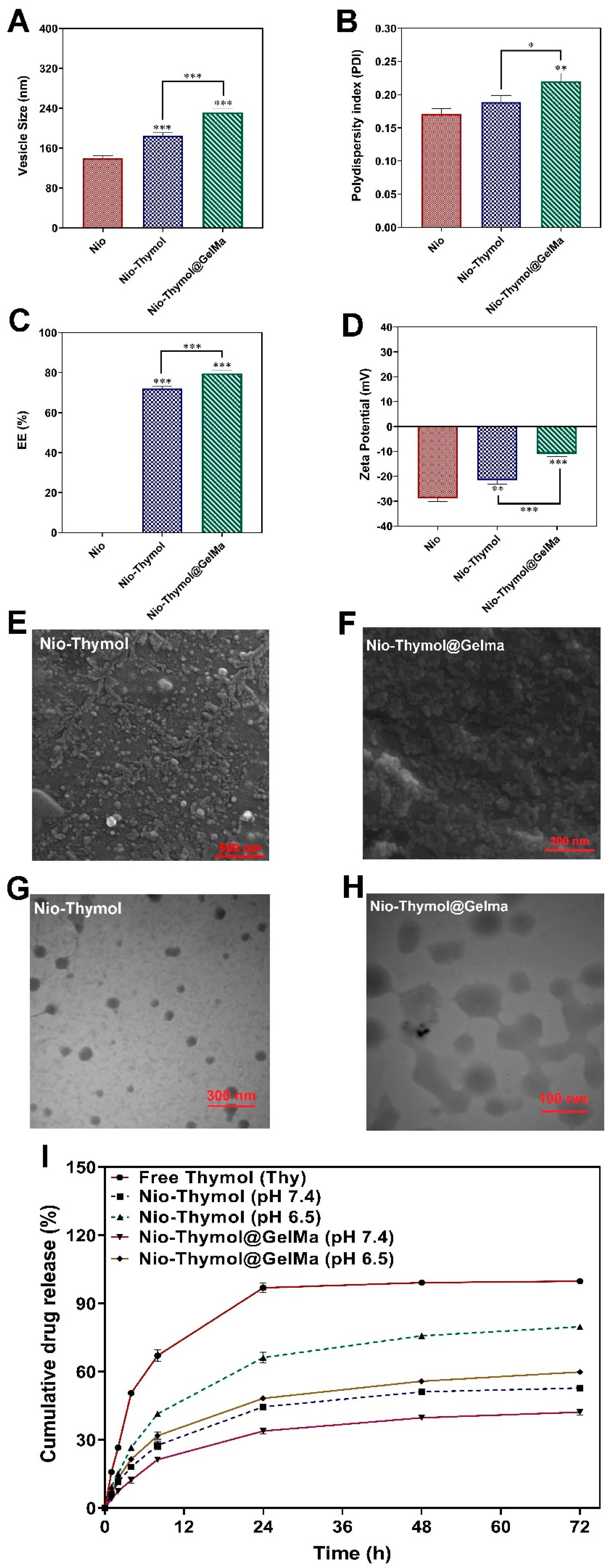
3.2. Characterization of Nio–Thymol and Nio–Thymol@GelMa
3.2.1. Morphology Study
3.2.2. Surface Charge Analysis
3.2.3. In Vitro Release Study
3.2.4. Stability Study
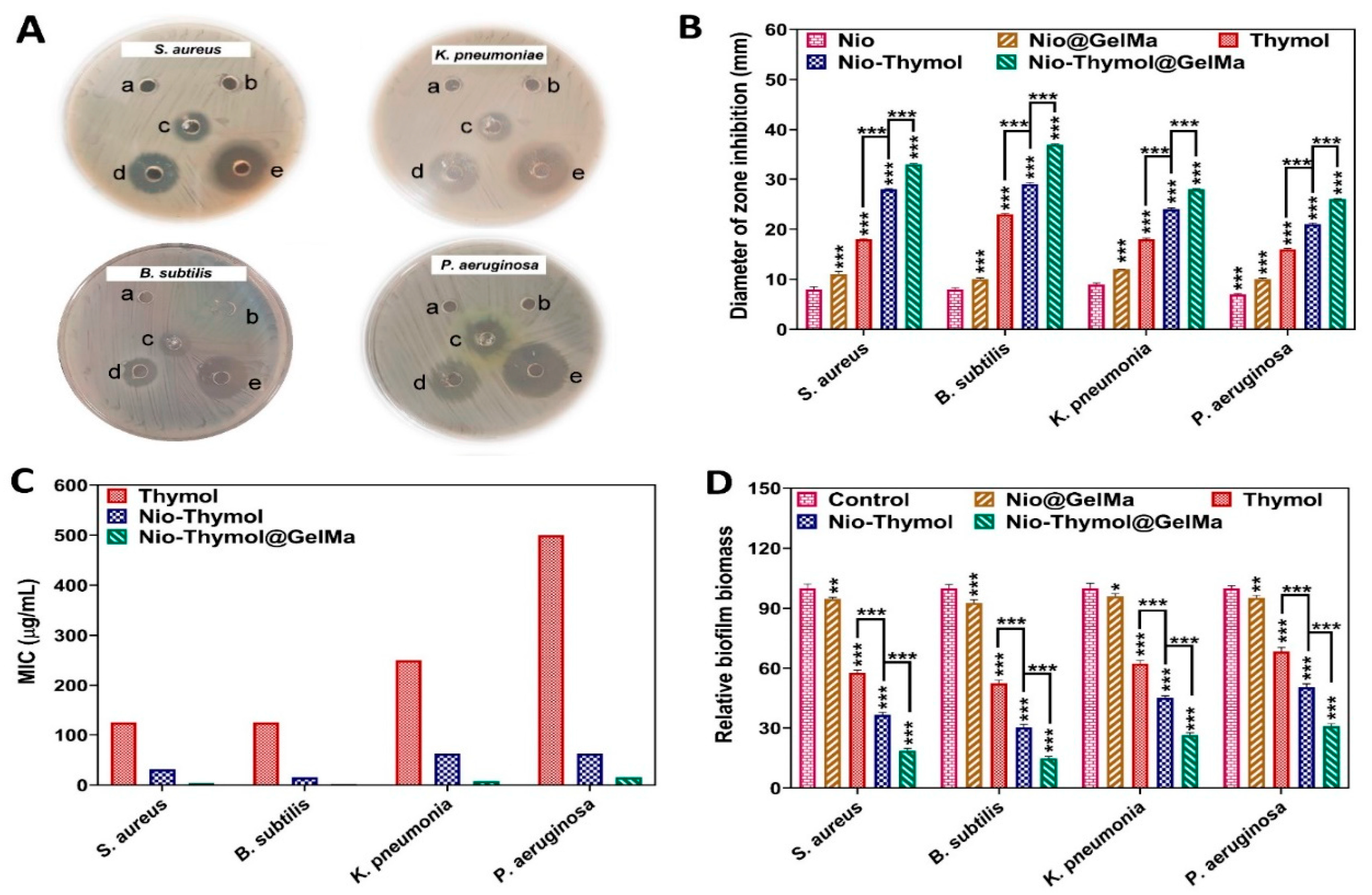
3.3. Antibacterial Assay
3.3.1. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Agar Diffusion Method
3.3.2. Time-Kill Assay
3.3.3. Anti-Biofilm Activity
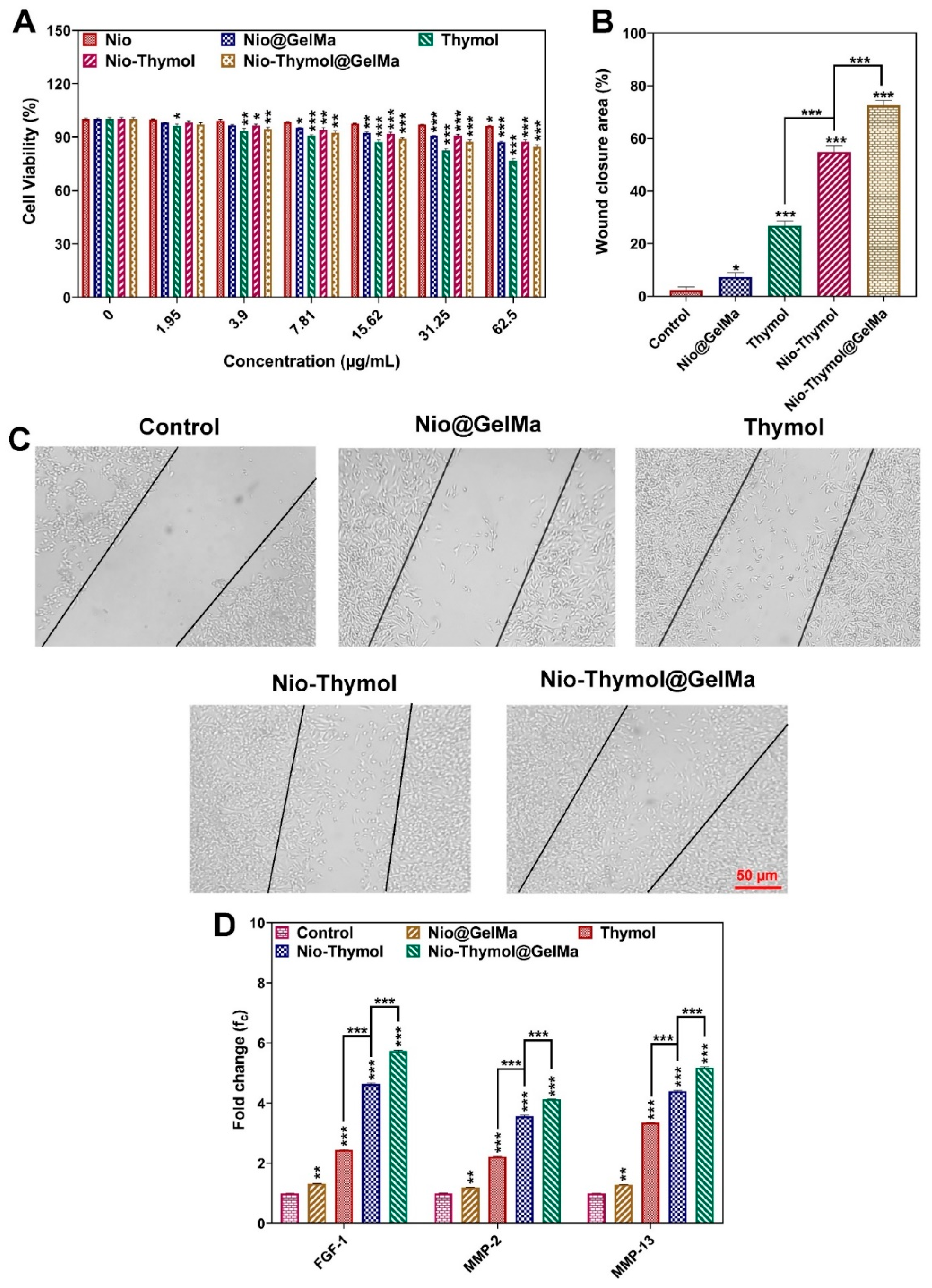
3.4. Wound Healing
3.4.1. Cytotoxicity
3.4.2. In Vitro Cell Migration
3.4.3. Expression of Growth Factors upon Thymol Treatment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bessa, L.J.; Fazii, P.; Di Giulio, M.; Cellini, L. Bacterial isolates from infected wounds and their antibiotic susceptibility pattern: Some remarks about wound infection. Int. Wound J. 2015, 12, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Jubeh, B.; Karaman, R. Resistance of gram-negative bacteria to current antibacterial agents and approaches to resolve it. Molecules 2020, 25, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziato, G. Strategies to overcome antimicrobial resistance (AMR) making use of non-essential target inhibitors: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percival, S.L.; Hill, K.E.; Malic, S.; Thomas, D.W.; Williams, D.W. Antimicrobial tolerance and the significance of persister cells in recalcitrant chronic wound biofilms. Wound Repair Regen. 2011, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, A.; Wright, J.B.; Schultz, G.; Burrell, R.; Nadworny, P. Microbial biofilms and chronic wounds. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; DiPietro, L.A. Factors affecting wound healing. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafloo, R.; Behyari, M.; Imani, R.; Nour, S. A mini-review of Thymol incorporated materials: Applications in antibacterial wound dressing. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 101904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, A.; Orhan, I.E.; Daglia, M.; Barbieri, R.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Nabavi, S.F.; Gortzi, O.; Izadi, M.; Nabavi, S.M. Antibacterial and antifungal activities of thymol: A brief review of the literature. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonetti, A.; Tugnoli, B.; Piva, A.; Grilli, E. Thymol as an Adjuvant to Restore Antibiotic Efficacy and Reduce Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Gene Expression in Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Strains. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachur, K.; Suntres, Z. The antibacterial properties of phenolic isomers, carvacrol and thymol. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3042–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Zhang, M.; Cui, L.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yue, T. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of thymol against Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris vegetative cells and spores. Lwt 2019, 105, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targhi, A.A.; Moammeri, A.; Jamshidifar, E.; Abbaspour, K.; Sadeghi, S.; Lamakani, L.; Akbarzadeh, I. Synergistic effect of curcumin-Cu and curcumin-Ag nanoparticle loaded niosome: Enhanced antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 115, 105116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheorain, J.; Mehra, M.; Thakur, R.; Grewal, S.; Kumari, S. In vitro anti-inflammatory and antioxidant potential of thymol loaded bipolymeric (tragacanth gum/chitosan) nanocarrier. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahrayi, H.; Hosseini, E.; Karimifard, S.; Khayam, N.; Meybodi, S.M.; Amiri, S.; Bourbour, M.; Farasati Far, B.; Akbarzadeh, I.; Bhia, M. Co-delivery of letrozole and cyclophosphamide via folic acid-decorated nanoniosomes for breast cancer therapy: Synergic effect, augmentation of cytotoxicity, and apoptosis gene expression. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrarya, M.; Gharehchelou, B.; Haghighi Poodeh, S.; Jamshidifar, E.; Karimifard, S.; Farasati Far, B.; Akbarzadeh, I.; Seifalian, A. Niosomal formulation for antibacterial applications. J. Drug Target. 2022, 30, 476–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, M.; Khayam, N.; Jamshidifar, E.; Pourseif, T.; Kianian, S.; Mirzaie, A.; Akbarzadeh, I.; Ren, Q. Streptomycin sulfate–loaded niosomes enables increased antimicrobial and anti-biofilm activities. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 745099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghtaderi, M.; Mirzaie, A.; Zabet, N.; Moammeri, A.; Mansoori-Kermani, A.; Akbarzadeh, I.; Eshrati Yeganeh, F.; Chitgarzadeh, A.; Bagheri Kashtali, A.; Ren, Q. Enhanced antibacterial activity of Echinacea angustifolia extract against multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae through niosome encapsulation. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourseif, T.; Ghafelehbashi, R.; Abdihaji, M.; Radan, N.; Kaffash, E.; Heydari, M.; Naseroleslami, M.; Mousavi-Niri, N.; Akbarzadeh, I.; Ren, Q. Chitosan-based nanoniosome for potential wound healing applications: Synergy of controlled drug release and antibacterial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadollahi, M.; Gerashi, E.; Zohrevand, M.; Zarei, M.; Sayedain, S.S.; Alizadeh, R.; Labbaf, S.; Atari, M. Improving mechanical properties and biocompatibility of 3D printed PLA by the addition of PEG and titanium particles, using a novel incorporation method. Bioprinting 2022, 27, e00228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.R.u.; Augustine, R.; Zahid, A.A.; Ahmed, R.; Tariq, M.; Hasan, A. Reduced graphene oxide incorporated GelMA hydrogel promotes angiogenesis for wound healing applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9603–9617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; He, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, G.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, D.; Wang, R.; Tian, W. Tunable mechanical, antibacterial, and cytocompatible hydrogels based on a functionalized dual network of metal coordination bonds and covalent crosslinking. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 6190–6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piri-Gharaghie, T.; Beiranvand, S.; Riahi, A.; Shirin, N.J.; Badmasti, F.; Mirzaie, A.; Elahianfar, Y.; Ghahari, S.; Ghahari, S.; Pasban, K. Fabrication and characterization of thymol-loaded chitosan nanogels: Improved antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities with negligible cytotoxicity. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202100426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, J.B.; Heckler, C.; Tondo, E.C.; Daroit, D.J.; da Silva Malheiros, P. Antimicrobial activity of free and liposome-encapsulated thymol and carvacrol against Salmonella and Staphylococcus aureus adhered to stainless steel. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 252, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcet, I.; Weng, S.; Sáez-Orviz, S.; Rendueles, M.; Díaz, M. Production and characterisation of biodegradable PLA nanoparticles loaded with thymol to improve its antimicrobial effect. J. Food Eng. 2018, 239, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, A.; Atyabi, F.; Khoshayand, M.R.; Mahbod, R.; Cohan, R.A.; Akbarzadeh, I.; Bakhshandeh, H. Design of experiment, preparation, and in vitro biological assessment of human amniotic membrane extract loaded nanoparticles. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2020, 21, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarzadeh, I.; Farid, M.; Javidfar, M.; Zabet, N.; Shokoohian, B.; Arki, M.K.; Shpichka, A.; Noorbazargan, H.; Aghdaei, H.A.; Hossein-Khannazer, N. The optimized formulation of tamoxifen-loaded niosomes efficiently induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in breast cancer cells. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, U.A.; Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Ahmed, O.A.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Tima, S.; Asfour, H.Z.; Al-Rabia, M.W.; Negm, A.A.; Sultan, M.H.; Madkhali, O.A. Intranasal niosomal in situ gel as a promising approach for enhancing flibanserin bioavailability and brain delivery: In vitro optimization and ex vivo/in vivo evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mahallawi, A.M.; Fares, A.R.; Abd-Elsalam, W.H. Enhanced permeation of methotrexate via loading into ultra-permeable niosomal vesicles: Fabrication, statistical optimization, ex vivo studies, and in vivo skin deposition and tolerability. J. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochani, A.K.; Balasubramanian, S.; Girija, A.R.; Raveendran, S.; Borah, A.; Nagaoka, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Maekawa, T.; Kumar, D.S. Dual mode of cancer cell destruction for pancreatic cancer therapy using Hsp90 inhibitor loaded polymeric nano magnetic formulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, J.; Saeedi, M.; Enayatifard, R.; Morteza-Semnani, K.; Hashemi, S.M.H.; Babaei, A.; Rahimnia, S.M.; Rostamkalaei, S.S.; Nokhodchi, A. Curcumin Niosomes (curcusomes) as an alternative to conventional vehicles: A potential for efficient dermal delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 102035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Murthy, P.N.; Nath, L.; Chowdhury, P. Kinetic modeling on drug release from controlled drug delivery systems. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2010, 67, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alemi, A.; Zavar Reza, J.; Haghiralsadat, F.; Zarei Jaliani, H.; Haghi Karamallah, M.; Hosseini, S.A.; Haghi Karamallah, S. Paclitaxel and curcumin coadministration in novel cationic PEGylated niosomal formulations exhibit enhanced synergistic antitumor efficacy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamboj, S.; Saini, V.; Bala, S. Formulation and characterization of drug loaded nonionic surfactant vesicles (niosomes) for oral bioavailability enhancement. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, D.S.; Shaker, M.A.; Hanafy, M.S. Cellular uptake, cytotoxicity and in-vivo evaluation of Tamoxifen citrate loaded niosomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 493, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, S.; Bakhshandeh, H.; Ahangari Cohan, R.; Peirovi, A.; Ehsani, P.; Norouzian, D. Synergistic anti-staphylococcal activity of niosomal recombinant lysostaphin-LL-37. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9777–9792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haney, E.F.; Trimble, M.J.; Hancock, R.E. Microtiter plate assays to assess antibiofilm activity against bacteria. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 2615–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Oh, J. Swelling characterization of photo-cross-linked gelatin methacrylate spherical microgels for bioencapsulation. e-Polymers 2014, 14, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fissan, H.; Ristig, S.; Kaminski, H.; Asbach, C.; Epple, M. Comparison of different characterization methods for nanoparticle dispersions before and after aerosolization. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 7324–7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeiszadeh, M.; Pardakhty, A.; Sharififar, F.; Farsinejad, A.; Mehrabani, M.; Hosseini-Nave, H.; Mehrabani, M. Development, physicochemical characterization, and antimicrobial evaluation of niosomal myrtle essential oil. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 250. [Google Scholar]
- Akbarzadeh, I.; Yaraki, M.T.; Ahmadi, S.; Chiani, M.; Nourouzian, D. Folic acid-functionalized niosomal nanoparticles for selective dual-drug delivery into breast cancer cells: An in-vitro investigation. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 4064–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigata, M.; Meinert, C.; Pahoff, S.; Bock, N.; Hutmacher, D.W. Gelatin methacryloyl hydrogels control the localized delivery of albumin-bound paclitaxel. Polymers 2020, 12, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, M.; Chauhan, S.; Lawrence, S.; Barlow, D. The formation, characterization and stability of non-ionic surfactant vesicles. STP Pharma Sci. 1996, 6, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, K.; Trujillo-de Santiago, G.; Alvarez, M.M.; Tamayol, A.; Annabi, N.; Khademhosseini, A. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials 2015, 73, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satish, J.; Amusa, A.S.; Gopalakrishna, P. In vitro activities of fluoroquinolones entrapped in non-ionic surfactant vesicles against ciprofloxacin-resistant bacteria strains. J. Pharm. Technol. Drug Res. 2012, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.; Chen, X.; Ismail, A.; Aziz, M.; Hamzah, E.; Najafinezhad, A. A new multifunctional monticellite-ciprofloxacin scaffold: Preparation, bioactivity, biocompatibility, and antibacterial properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 222, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-Y.; Jin, X.-Y.; Ma, Y.-H.; Cai, W.-J.; Xiao, W.-Y.; Li, Z.-W.; Qi, X.; Ding, J. Injectable stress relaxation gelatin-based hydrogels with positive surface charge for adsorption of aggrecan and facile cartilage tissue regeneration. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, F.; Akbarzadeh, I.; Nourouzian, D.; Mirzaie, A.; Bakhshandeh, H. Optimization and characterization of tannic acid loaded niosomes for enhanced antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 4768–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhtit, F.; Najar, M.; Agha, D.M.; Melki, R.; Najimi, M.; Sadki, K.; Lewalle, P.; Hamal, A.; Lagneaux, L.; Merimi, M. The biological response of mesenchymal stromal cells to thymol and carvacrol in comparison to their essential oil: An innovative new study. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 134, 110844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.F.; Durço, A.O.; Rabelo, T.K.; Barreto, R.d.S.S.; Guimarães, A.G. Effects of Carvacrol, Thymol and essential oils containing such monoterpenes on wound healing: A systematic review. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavan, R.; Potunuru, U.R.; Nastasijević, B.; Joksić, G.; Dixit, M. Inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by Gentiana lutea root extracts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.-M.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Li, H.-J.; Fang, J.-Y.; Chang, D.-C.; Hung, C.-F. The inhibitory effects of gold nanoparticles on VEGF-A-induced cell migration in choroid-retina endothelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, D.; Zhou, A.; Liu, G. Effects of herbal extract supplementation on growth performance and insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I system in finishing pigs. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2008, 17, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameshk, M.; Sharififar, F.; Mehrabani, M.; Pardakhty, A.; Farsinejad, A.; Mehrabani, M. Proliferation and in vitro wound healing effects of the microniosomes containing Narcissus tazetta L. bulb extract on primary human fibroblasts (HDFs). DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 26, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Run | Levels of Independent Variables | Dependent Variables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Span 60 (mM) | Cholesterol (mM) | Volume Hydration (mL) | Average Size (nm) | PDI | Entrapment Efficiency (EE) (%) | |
| 1 | 3 | 0.5 | 6 | 219 | 0.24 | 70 |
| 2 | 5 | 0.5 | 8 | 194 | 0.25 | 68 |
| 3 | 1 | 1.5 | 6 | 270 | 0.42 | 62 |
| 4 | 3 | 0.5 | 10 | 165 | 0.3 | 67 |
| 5 | 3 | 1.5 | 8 | 190 | 0.24 | 64 |
| 6 | 1 | 0.5 | 8 | 212 | 0.29 | 60 |
| 7 | 3 | 2.5 | 6 | 230 | 0.35 | 53 |
| 8 | 3 | 1.5 | 8 | 183 | 0.25 | 65 |
| 9 | 5 | 1.5 | 6 | 216 | 0.18 | 62 |
| 10 | 1 | 1.5 | 10 | 223 | 0.23 | 47 |
| 11 | 5 | 2.5 | 8 | 205 | 0.21 | 57 |
| 12 | 3 | 2.5 | 10 | 236 | 0.26 | 51 |
| 13 | 1 | 2.5 | 8 | 242 | 0.28 | 45 |
| 14 | 3 | 1.5 | 8 | 199 | 0.23 | 66 |
| 15 | 5 | 1.5 | 10 | 181 | 0.23 | 57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moghtaderi, M.; Bazzazan, S.; Sorourian, G.; Sorourian, M.; Akhavanzanjani, Y.; Noorbazargan, H.; Ren, Q. Encapsulation of Thymol in Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMa)-Based Nanoniosome Enables Enhanced Antibiofilm Activity and Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061699
Moghtaderi M, Bazzazan S, Sorourian G, Sorourian M, Akhavanzanjani Y, Noorbazargan H, Ren Q. Encapsulation of Thymol in Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMa)-Based Nanoniosome Enables Enhanced Antibiofilm Activity and Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(6):1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061699
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoghtaderi, Maryam, Saba Bazzazan, Ghazal Sorourian, Maral Sorourian, Yasaman Akhavanzanjani, Hassan Noorbazargan, and Qun Ren. 2023. "Encapsulation of Thymol in Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMa)-Based Nanoniosome Enables Enhanced Antibiofilm Activity and Wound Healing" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 6: 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061699
APA StyleMoghtaderi, M., Bazzazan, S., Sorourian, G., Sorourian, M., Akhavanzanjani, Y., Noorbazargan, H., & Ren, Q. (2023). Encapsulation of Thymol in Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMa)-Based Nanoniosome Enables Enhanced Antibiofilm Activity and Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics, 15(6), 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061699







