Molecularly Imprinted Carriers for Diagnostics and Therapy—A Critical Appraisal
Abstract
1. Introduction
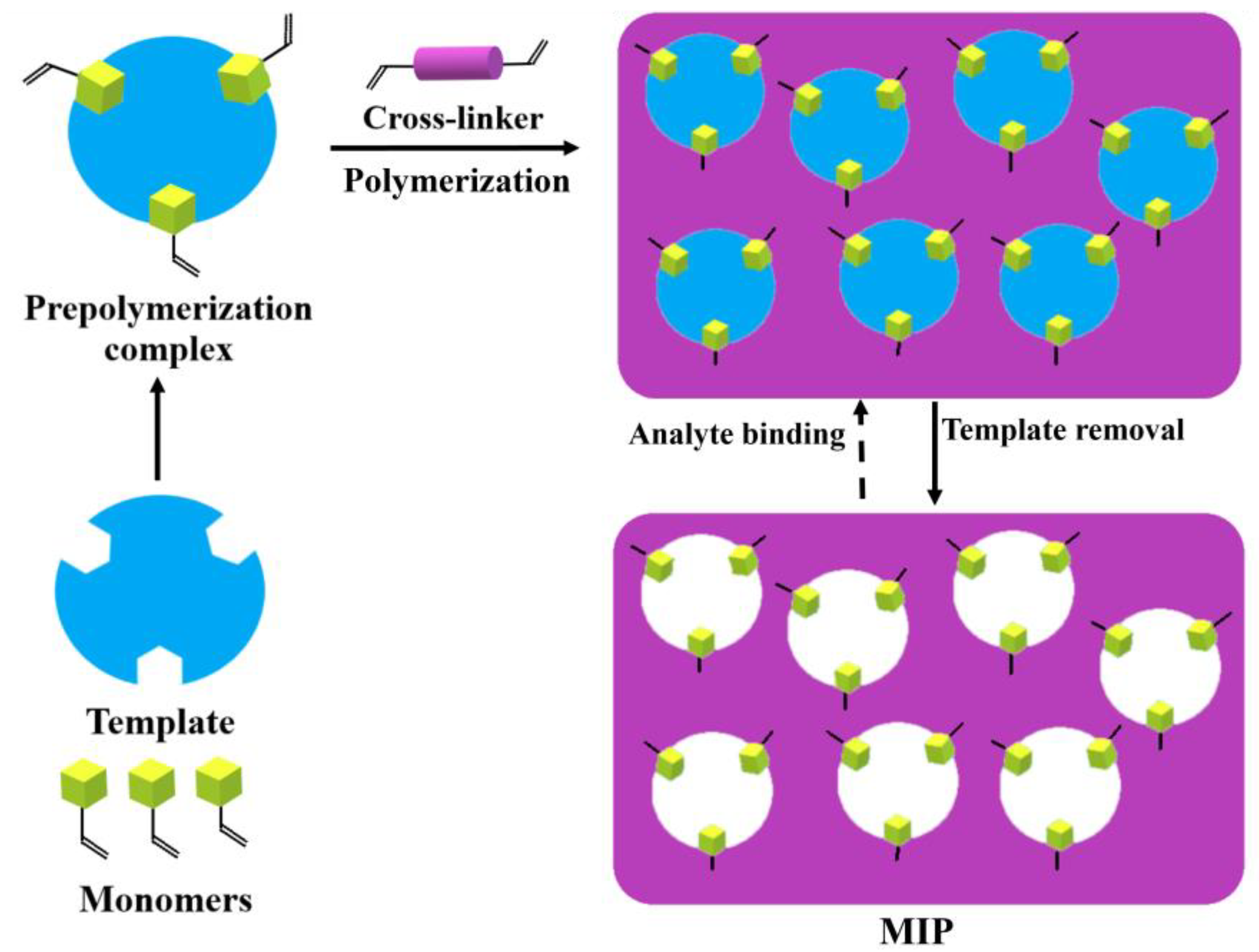
2. Concept of Molecular Imprinting and Its Potential in Therapy
3. Construction Strategies of MIPs for Diagnostics and Therapy
3.1. Targeting Approaches
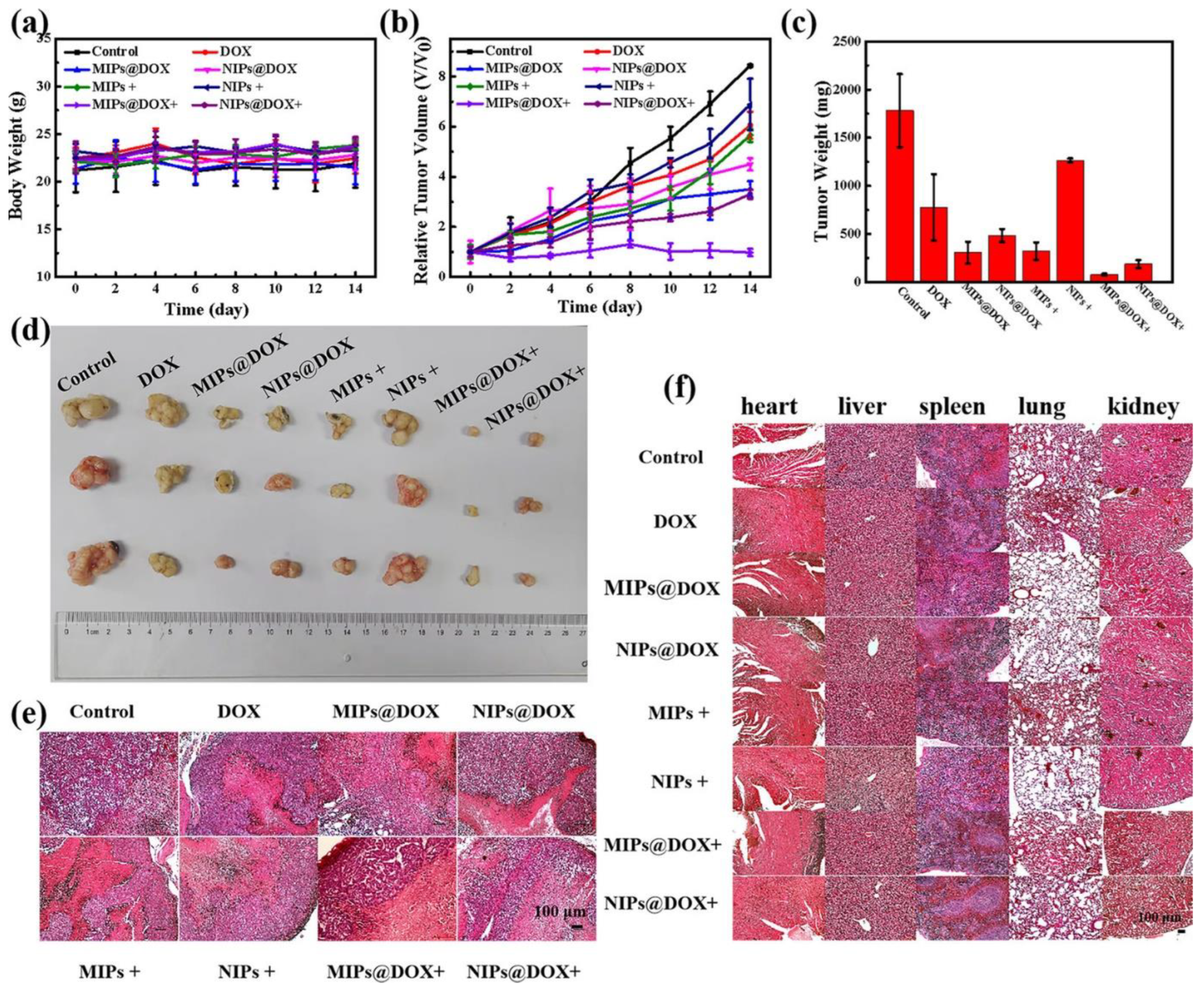
3.1.1. MIPs for Active Targeting
3.1.2. MIPs for Passive Targeting
3.2. Theranostic Approaches
4. Frontiers and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, M.; Shen, A.; Ding, J.; Geng, M. Molecularly Targeted Cancer Therapy: Some Lessons from the Past Decade. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van’t Veer, L.J.; Bernards, R. Enabling Personalized Cancer Medicine through Analysis of Gene-Expression Patterns. Nature 2008, 452, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Otte, A.; Park, K. Evolution of Drug Delivery Systems: From 1950 to 2020 and Beyond. J. Control. Rel. 2022, 342, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrhardt, J.D., Jr.; Güleç, S. A Review of the History of Radioactive Iodine Theranostics: The Origin of Nuclear Ontology. Mol. Imaging Radionucl. Ther. 2020, 29, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setua, S.; Jaggi, M.; Yallapu, M.M.; Chauhan, S.C.; Danilushkina, A.; Lee, H.; Choi, I.S.; Fakhrullin, R.; Esposti, L.D.; Tampieri, A.; et al. Targeted and Theranostic Applications for Nanotechnologies in Medicine. In Nanotechnologies in Preventive and Regenerative Medicine, 1st ed.; Uskoković, V., Uskoković, D.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 399–511. [Google Scholar]
- Shete, M.B.; Patil, T.S.; Deshpande, A.S.; Saraogi, G.; Vasdev, N.; Deshpande, M.; Rajpoot, K.; Tekade, R.K. Current Trends in Theranostic Nanomedicines. J. Drug. Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 71, 103280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, S.; Imam, S.S.; Rizwanullah, M.; Akhter, S.; Mahdi, W.; Kazi, M.; Ahmad, J. Progress of Cancer Nanotechnology as Diagnostics, Therapeutics, and Theranostics Nanomedicine: Preclinical Promise and Translational Challenges. Pharmaceutics 2020, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Gao, Y.; Meng, F.; Luo, L. Recent Progress of Nanotechnology-Based Theranostic Systems in Cancer Treatments. Cancer Biol. Med. 2021, 18, 336–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shende, P.; Gandhi, S. Current Strategies of Radiopharmaceuticals in Theranostic Applications. J. Drug. Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Dilnawaz, F.; Sahoo, S.K. Challenges of Moving Theranostic Nanomedicine into the Clinic. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshady, R.; Mosbach, K. Synthesis of Substrate-Selective Polymers by Host-Guest Polymerization. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1981, 182, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, G.; Sarhan, A. Über die Anwendung von enzymanalog gebauten Polymeren zur Racemattrennung. Angew. Chem. 1972, 84, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Concheiro, A. Handbook of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers, 1st ed.; Smithers Rapra: Shrewsbury, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, L.; Yang, L.-L.; Li, Y.-J.; Jiang, Z.-F.; Li, Q.-Y.; Ma, R.-R.; He, J.-Y.; Zhou, L.-D.; Zhang, Q.-H.; Yuan, C.-S. Investigating Two Distinct Dummy Templates Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Paclitaxel Adsorbent in Synthesis System and Releaser in Biological Samples. Microchem. J. 2021, 165, 106042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Qin, Y.-T.; He, X.-W.; Li, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-K. Epitope Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for Chemo-/Photodynamic Synergistic Cancer Therapy Guided by Targeted Fluorescence Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 13360–13370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.-T.; Peng, H.; He, X.-W.; Li, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-K. Highly Effective Drug Delivery and Cell Imaging Using Fluorescent Double-Imprinted Nanoparticles by Targeting Recognition of the Epitope of Membrane Protein. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12696–12703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfarotta, F.; Lezina, L.; Guerreiro, A.; Czulak, J.; Petukhov, A.; Daks, A.; Smolinska-Kempisty, K.; Poma, A.; Piletsky, S.; Barlev, N.A. Specific Drug Delivery to Cancer Cells with Double-Imprinted Nanoparticles against Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 4641–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Shi, H.; Han, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, R.; Men, J. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers by the Surface Imprinting Technique. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 145, 110231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BelBruno, J.J. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczura, M.; Luliński, P.; Sobiech, M. Imprinting Technology for Effective Sorbent Fabrication: Current State-of-Art and Future Prospects. Materials 2021, 14, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Samukaite-Bubniene, U.; Ratautaite, V.; Bechelany, M.; Ramanavicius, A. Electrochemical Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Sensors for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications (Review). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 215, 114739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahhoseini, F.; Azizi, A.; Bottaro, C.S. A Critical Evaluation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP) Coatings in Solid Phase Microextraction Devices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 156, 116695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobiech, M.; Luliński, P.; Wieczorek, P.P.; Marć, M. Quantum and Carbon Dots Conjugated Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Advanced Nanomaterials for Selective Recognition of Analytes in Environmental, Food and Biomedical Applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 142, 116306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Qi, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, L.; Wan, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q. Ultrasensitive, Label-Free Voltammetric Determination of Norfloxacin Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers and Au Nanoparticle-Functionalized Black Phosphorus Nanosheet Nanocomposite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wu, J.; Qi, X.; Wan, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L. Molecularly Imprinted Polypyrrole Film-Coated Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene):Polystyrene Sulfonate-Functionalized Black Phosphorene for the Selective and Robust Detection of Norfloxacin. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 26, 101043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellergren, B.; Allender, C. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: A Bridge to Advanced Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luliński, P. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based Drug Delivery Devices: A Way to Application in Modern Pharmacotherapy. A Review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2017, 76, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuwahatu, C.A.; Yeung, C.C.; Lam, Y.W.; Roy, V.A.L. The Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Essentials: Curation of Anticancer, Ophthalmic, and Projected Gene Therapy Drug Delivery Systems. J. Control. Rel. 2018, 287, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhang, L.; Bai, S.; Yang, H.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Advances of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIP) and the Application in Drug Delivery. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 143, 110179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Hiratani, H.; Gómez-Amoza, J.L.; Martínez-Pacheco, R.; Souto, C.; Concheiro, A. Soft Contact Lenses Capable of Sustained Delivery of Timolol. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 2182–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Xue, C.; Shao, K.; Xiang, L.; Zhao, X.; Chen, C.; Pan, J.; Lin, D. Photonic Crystal-Embedded Molecularly Imprinted Contact Lenses for Controlled Drug Release. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2022, 5, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raesian, P.; Rad, M.S.; Khodaverdi, E.; Motamedshariaty, V.S.; Mohajeri, S.A. Preparation and Characterization of Fluorometholone Molecular Imprinted Soft Contact Lenses as Ocular Controlled Drug Delivery Systems. J. Drug. Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruela, A.L.M.; Figueiredo, E.C.; Pereira, G.R. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Nicotine Transdermal Delivery Systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 248, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-P.; Wang, X.-L.; Pang, Q.-Q.; Huang, Y.-P.; Tang, L.; Chen, M.; Liu, Z.-S. Solvent-Responsive Floating Liquid Crystalline-Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Gastroretentive Controlled Drug Release System. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.E.; Park, K.; Peppas, N.A. Molecular Imprinting within Hydrogels. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, S.; Saha, J.; Pass, S.; Byrne, M. Transport and Structural Analysis of Molecular Imprinted Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, M.S.; Viveiros, R.; Morgado, P.I.; Aguiar-Ricardo, A.; Correia, I.J.; Casimiro, T. Development of 2-(Dimethylamino)Ethyl Methacrylate-Based Molecular Recognition Devices for Controlled Drug Delivery Using Supercritical Fluid Technology. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 416, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Kawamura, A.; Miyata, T. Conformationally Regulated Molecular Binding and Release of Molecularly Imprinted Polypeptide Hydrogels That Undergo Helix–Coil Transition. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 2136–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanbakht, S.; Saboury, A.; Shaabani, A.; Mohammadi, R.; Ghorbani, M. Doxorubicin Imprinted Photoluminescent Polymer as a pH-Responsive Nanocarrier. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 4168–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.-B.; Xiao, N.-N.; He, X.-W.; Li, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-K. Preparation of Dual-Template Epitope Imprinted Polymers for Targeted Fluorescence Imaging and Targeted Drug Delivery to Pancreatic Cancer BxPC-3 Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 32431–32440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y. Temperature and Magnetism Bi-Responsive Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Preparation, Adsorption Mechanism and Properties as Drug Delivery System for Sustained Release of 5-Fluorouracil. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2016, 61, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yang, K.; Deng, N.; Min, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Thermoresponsive Epitope Surface-Imprinted Nanoparticles for Specific Capture and Release of Target Protein from Human Plasma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5747–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Xu, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Z. Redox-Responsive Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles for Targeted Intracellular Delivery of Protein toward Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18214–18225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, A.; Kitayama, Y.; Kiguchi, K.; Yamada, T.; Akasaka, H.; Sasaki, R.; Takeuchi, T. Gold Nanoparticle-Incorporated Molecularly Imprinted Microgels as Radiation Sensitizers in Pancreatic Cancer. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, O.I.; Francomano, F.; Dattilo, M.; Patitucci, F.; Prete, S.; Amone, F.; Puoci, F. The Evolution of Molecular Recognition: From Antibodies to Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) as Artificial Counterpart. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haupt, K.; Medina Rangel, P.X.; Tse Sun Bui, B. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Antibody Mimics for Bioimaging and Therapy. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 9554–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bărăian, A.-I.; Iacob, B.-C.; Bodoki, A.E.; Bodoki, E. In Vivo Applications of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Drug Delivery: A Pharmaceutical Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Poma, A. Advances in Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Drug Delivery Systems. Molecules 2021, 26, 3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Q.; Liao, Q.; Zhao, Y. CD59: A Promising Target for Tumor Immunotherapy. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.-T.; Feng, Y.-S.; Ma, Y.-J.; He, X.-W.; Li, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-K. Tumor-Sensitive Biodegradable Nanoparticles of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Stabilized Fluorescent Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 for Targeted Imaging and Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24585–24598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Ye, Z.-H.; Huang, M.-Y.; Lu, J.-J. Regulation of CD47 Expression in Cancer Cells. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-Y.; Su, Z.-C.; He, X.-W.; Li, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-K. H2O2 Self-Supplying Degradable Epitope Imprinted Polymers for Targeted Fluorescence Imaging and Chemodynamic Therapy. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 12553–12564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jiang, P.; Jiang, F.; Liu, Y. Recent Advances in Nanomaterial-Based Nanoplatforms for Chemodynamic Cancer Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, C.G.; Karlsson, W.K.; Pommergaard, H.-C.; Burcharth, J.; Rosenberg, J. The Diagnostic Accuracy of Carcinoembryonic Antigen to Detect Colorectal Cancer Recurrence—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Surg. 2016, 25, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Teng, F.; Wang, Y.; Su, L.; Leng, Q.; Jiang, H. Drug-Loaded Dual Targeting Graphene Oxide-Based Molecularly Imprinted Composite and Recognition of Carcino-Embryonic Antigen. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 10980–10988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkley, J.; Scott, E. Targeting Aberrant Sialylation to Treat Cancer. Medicines 2019, 6, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Cui, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, L. Preparation of Sialic Acid-Imprinted Fluorescent Conjugated Nanoparticles and Their Application for Targeted Cancer Cell Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3006–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, U.; Maeda, H.; Jain, R.K.; Sevick-Muraca, E.M.; Zamboni, W.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Barry, S.T.; Gabizon, A.; Grodzinski, P.; Blakey, D.C. Challenges and Key Considerations of the Enhanced Permeability and Retention Effect for Nanomedicine Drug Delivery in Oncology. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2412–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, R.; Zaloga, J.; Unterweger, H.; Lyer, S.; Friedrich, R.P.; Janko, C.; Pöttler, M.; Dürr, S.; Alexiou, C. Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery for Cancer Therapy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 468, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Ding, L.; Ding, J. Recent Advances of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Materials: From Materials Design to Complex Sample Pretreatment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 147, 116514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerantzaki, M.; Michel, A.; Petit, L.; Garnier, M.; Ménager, C.; Griffete, N. Biotinylated Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for Cancer Cell Targeting and Controlled Drug Delivery. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 5642–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boitard, C.; Curcio, A.; Rollet, A.-L.; Wilhelm, C.; Ménager, C.; Griffete, N. Biological Fate of Magnetic Protein-Specific Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Toxicity and Degradation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 35556–35565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lei, S.; Zeng, K.; Wang, M.; Asif, A.; Ge, X. Catalase-Imprinted Fe3O4/Fe@fibrous SiO2/Polydopamine Nanoparticles: An Integrated Nanoplatform of Magnetic Targeting, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, and Dual-Mode Cancer Therapy. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 2351–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, O.I.; Morelli, C.; Puoci, F.; Saturnino, C.; Caruso, A.; Sisci, D.; Trombino, G.E.; Picci, N.; Sinicropi, M.S. Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MMIPs) for Carbazole Derivative Release in Targeted Cancer Therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 6619–6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, O.I.; Ruffo, M.; Malivindi, R.; Vattimo, A.F.; Pezzi, V.; Puoci, F. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) as Theranostic Systems for Sunitinib Controlled Release and Self-Monitoring in Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-Y.; Cao, P.-P.; He, Z.-Y.; He, X.-W.; Li, W.-Y.; Li, Y.-H.; Zhang, Y.-K. Targeted Imaging and Targeted Therapy of Breast Cancer Cells via Fluorescent Double Template-Imprinted Polymer Coated Silicon Nanoparticles by an Epitope Approach. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 17018–17030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z. Targeted Cancer Imaging and Photothermal Therapy via Monosaccharide-Imprinted Gold Nanorods. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 6716–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Deng, C.; Liu, S.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, C.; Lu, W. Active Targeting of Tumors through Conformational Epitope Imprinting. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 5246–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, R.; Huang, H.; Zhu, Q. Vinblastine-Loaded Nanoparticles with Enhanced Tumor-Targeting Efficiency and Decreasing Toxicity: Developed by One-Step Molecular Imprinting Process. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 2675–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Zhu, S.; Amin, F.R.; Hussain, D.; Du, Z.; Hu, L. Molecular Imprinting of Glycoproteins: From Preparation to Cancer Theranostics. Theranostics 2022, 12, 2406–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.-D.; Paudel, R.; Liu, J.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Zhou, S.-K. MRI Contrast Agents: Classification and Application (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, L.E.; Ross, R.D.; Tilley, J.M.; Vargo-Gogola, T.; Roeder, R.K. Gold Nanoparticles as Contrast Agents in X-Ray Imaging and Computed Tomography. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 321–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodoki, A.E.; Iacob, B.-C.; Bodoki, E. Perspectives of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Cancer Therapy. Polymers 2019, 11, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Thomas, J.; Li, J.-A.; Chen, J.-R.; Wang, T.-L.; Lin, H.-Y. Synthesis of Multifunctional Nanoparticles for the Combination of Photodynamic Therapy and Immunotherapy. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitayama, Y.; Yamada, T.; Kiguchi, K.; Yoshida, A.; Hayashi, S.; Akasaka, H.; Igarashi, K.; Nishimura, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Sasaki, R.; et al. In Vivo Stealthified Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanogels Incorporated with Gold Nanoparticles for Radiation Therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 6784–6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Lin, H.-Y.; Thomas, J.L.; Yu, J.-X.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chang, Y.-H.; Lee, M.-H.; Wang, T.-L. Embedded Upconversion Nanoparticles in Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Photodynamic Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse Sum Bui, B.; Haupt, K. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Hydrogel Nanoparticles: Synthetic Antibodies for Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. ChemBioChem 2022, 23, e202100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharatape, A.; Salehi, R. Recent Progress in Theranostic Applications of Hybrid Gold Nanoparticles. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 138, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, N.; Kitayama, Y.; Igarashi, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Takano, E.; Sunayama, H.; Takeuchi, T. Fc Domain-Imprinted Stealth Nanogels Capable of Orientational Control of Immunoglobulin G Adsorbed In Vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 16074–16081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, A.S.; Ramos, M.P.; Herrero, R.; Vilariño, J.M.L. Design, Synthesis and HR – MAS NMR Characterization of Molecular Imprinted Polymers with Emerging Contaminants Templates. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 257, 117860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-González, J.; Peña-Gallego, Á.; Sanmartín, J.; Bermejo, A.M.; Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A. NMR Spectroscopy for Assessing Cocaine-Functional Monomer Interactions When Preparing Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marć, M.; Kupka, T.; Wieczorek, P.P.; Namieśnik, J. Computational Modeling of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as a Green Approach to the Development of Novel Analytical Sorbents. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golker, K.; Olsson, G.D.; Nicholls, I.A. The Influence of a Methyl Substituent on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Morphology and Recognition—Acrylic Acid versus Methacrylic Acid. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 92, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golker, K.; Nicholls, I.A. The Effect of Crosslinking Density on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Morphology and Recognition. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 75, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klejn, D.; Luliński, P.; Maciejewska, D. Molecularly Imprinted Solid Phase Extraction in an Efficient Analytical Protocol for Indole-3-Methanol Determination in Artificial Gastric Juice. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 108801–108809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, A.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Y.; Du, S. Molecularly Imprinted Layer-Coated Hollow Polysaccharide Microcapsules toward Gate-Controlled Release of Water-Soluble Drugs. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 26063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.; Kang, H.; Zhang, L.; Guan, L.; Tian, D. Preparation and Properties of Thermosensitive Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based on Konjac Glucomannan and Its Controlled Recognition and Delivery of 5-Fluorouracil. J. Drug. Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 101977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, E.; Abdouss, M.; Leblanc, R.M.; Ezzati, N.; Wilson, J.N.; Azodi-Deilami, S. In Vitro/In Vivo Study of Novel Anti-Cancer, Biodegradable Cross-Linked Tannic Acid for Fabrication of 5-Fluorouracil-Targeting Drug Delivery Nano-Device Based on a Molecular Imprinted Polymer. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 37308–37318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, E.; Abdouss, M.; Leblanc, R.M.; Ezzati, N.; Wilson, J.N.; Kordestani, D. Synthesis, Characterization and in Vivo Drug Delivery Study of a Biodegradable Nano-Structured Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based on Cross-Linker of Fructose. Polymer 2016, 97, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Sajid, M.; Manzoor, S.; Ahmad, M.M.; Khan, M.I.; Elboughdiri, N.; Kashif, M.; Shanableh, A.; Rajhi, W.; Mersni, W.; et al. Biodegradable Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Anticancer Drug Carrier for the Targeted Delivery of Docetaxel. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 28516–28524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Liu, S.; Song, Y.; Jiang, H. Biodegradable Magnesium Ion-Doped Silica-Based Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles for Targeting Tumor Cells to Drugs Controlled Release and Recognition Mechanism Research. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2022, 217, 112665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-S.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, B.S. Biodegradable Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on Poly(ε-Caprolactone). Biotechnol. Bioprocess. Eng. 2007, 12, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, M.; Bertero, A.; Bifone, A. Molecularly Imprinted Biodegradable Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Song, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, L.; Sun, R. Dual Responsive Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on UiO-66-DOX for Selective Targeting Tumor Cells and Controlled Drug Release. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 171, 111219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-P.; Tang, S.-H.; Mo, C.-E.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y.-P.; Liu, Z.-S. Synergistic Effect of Liquid Crystal and Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane to Prepare Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Paclitaxel Delivery. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 98, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eifler, A.C.; Thaxton, C.S. Nanoparticle Therapeutics: FDA Approval, Clinical Trials, Regulatory Pathways, and Case Study. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 726, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobo, D.; Robinson, K.J.; Islam, J.; Thurecht, K.J.; Corrie, S.R. Nanoparticle-Based Medicines: A Review of FDA-Approved Materials and Clinical Trials to Date. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2373–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etheridge, M.L.; Campbell, S.A.; Erdman, A.G.; Haynes, C.L.; Wolf, S.M.; McCullough, J. The Big Picture on Nanomedicine: The State of Investigational and Approved Nanomedicine Products. Nanomedicine Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2013, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Fu, P.P.; Yu, H.; Ray, P.C. Theranostic Nanomedicine for Cancer Detection and Treatment. J. Food Drug. Anal. 2014, 22, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Li, Y.; Gao, S.; Lv, Y. Selective Recognition of Tumor Cells by Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 2483–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Type of Formulation | Therapeutic Method | Diagnostic Method | Targeting Approach | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| zeolitic nanoparticles as drug carriers | chemotherapy (doxorubicin) | fluorescence imaging | active targeting to CD59 | [50] |
| Fe3O4/Fe nanorods | photothermal and radical therapy | MR imaging | magnetic-guided | [63] |
| core-shell nanoparticles as drug carriers | chemo- (doxorubicin) and photodynamic therapy | MR and fluorescence imaging | active targeting to CD59 | [15] |
| gold nanorods | photothermal therapy | fluorescence imaging | active targeting to sialic acid | [67] |
| polymeric nanoparticles as drug carriers | chemotherapy (vinblastine) | fluorescence imaging | active targeting to folate | [69] |
| magnetic MIPs as drug carriers | chemotherapy (9H-carbazole derivative) | MR imaging (not considered in the paper) | magnetic-guided | [64] |
| graphene oxide-based composite | chemotherapy (doxorubicin) | MR imaging (not considered in the paper) | magnetic-guided and active targeting to carcinoembryonic antigen | [55] |
| magnetic nanoparticles | photodynamic and immunotherapy | MR imaging (not considered in the paper) | active targeting to programmed death-ligand 1 protein | [74] |
| silica nanoparticles-based composite | chemodynamic therapy | fluorescence imaging | active targeting to CD47 | [52] |
| Au-embedded nanogels | X-ray radiotherapy | computed tomography (not considered in the paper) | passive targeting through enhanced permeability and retention effect | [75] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balcer, E.; Sobiech, M.; Luliński, P. Molecularly Imprinted Carriers for Diagnostics and Therapy—A Critical Appraisal. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061647
Balcer E, Sobiech M, Luliński P. Molecularly Imprinted Carriers for Diagnostics and Therapy—A Critical Appraisal. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(6):1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061647
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalcer, Emilia, Monika Sobiech, and Piotr Luliński. 2023. "Molecularly Imprinted Carriers for Diagnostics and Therapy—A Critical Appraisal" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 6: 1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061647
APA StyleBalcer, E., Sobiech, M., & Luliński, P. (2023). Molecularly Imprinted Carriers for Diagnostics and Therapy—A Critical Appraisal. Pharmaceutics, 15(6), 1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061647







