Medical Management of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Current Approaches and Investigational Drugs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. PAH Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology
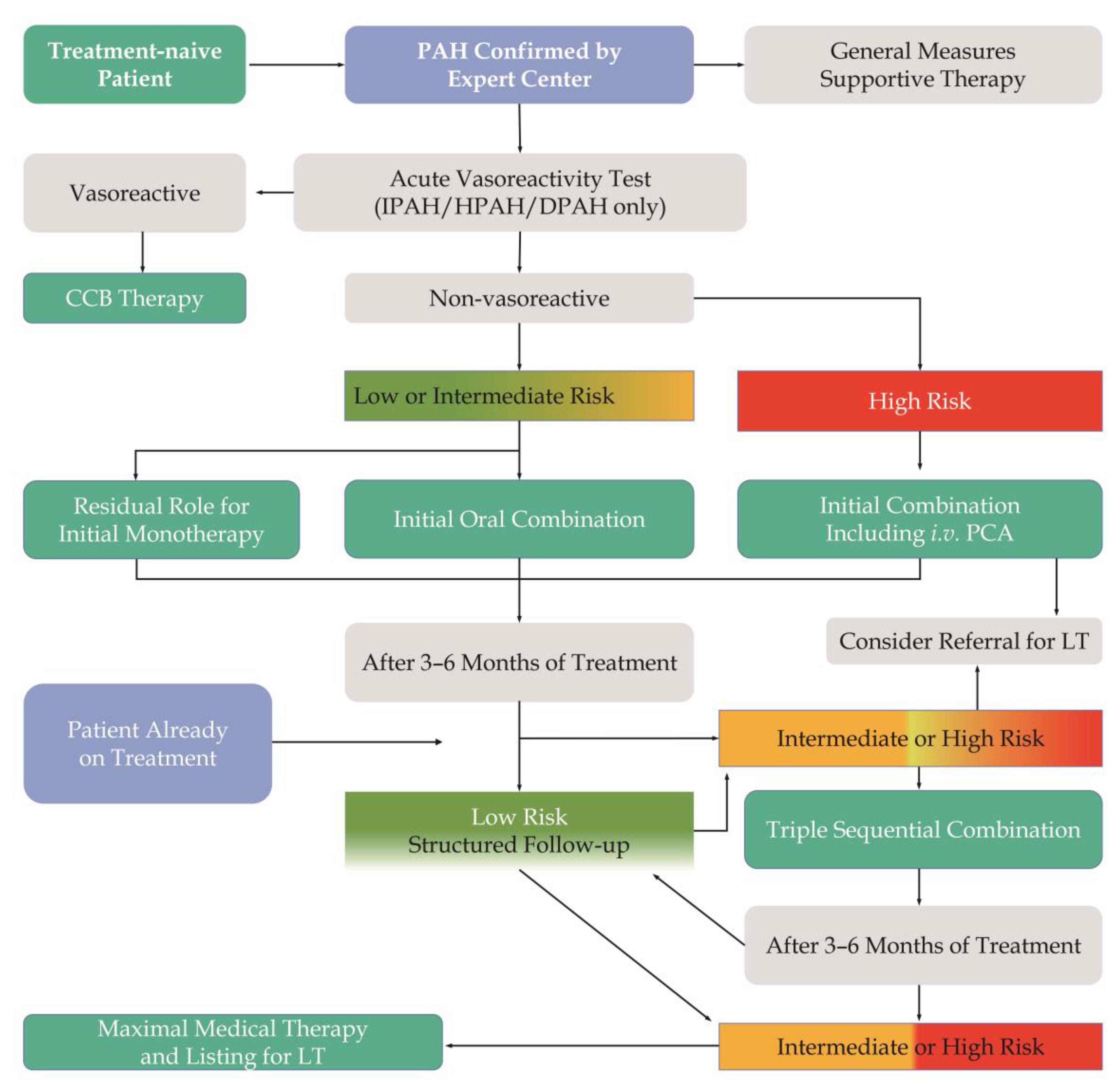
3. PAH Risk Stratification
4. Pharmacological Therapy for PAH
4.1. Inotropes and Vasopressors
4.2. Diuretics
4.3. Anticoagulants
4.4. General Vasodilators
4.5. Treatment of Anemia
4.6. PAH Targeted Therapy
4.6.1. Monotherapy
Endothelin Pathway
Nitric Oxide Pathway
Prostacyclin Pathway
4.6.2. Combination Therapy
Dual Combination Therapy
- 1.
- ERAs Combined with PDE5 Inhibitors
- 2.
- ERAs Combined with Prostacyclin
- 3.
- PDE5 Inhibitors Combined with Prostacyclin
Triple Combination Therapy
- 1.
- Sequential Triple Therapy
- 2.
- Initial Triple Therapy
5. Potential Drugs Being Investigated
6. Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galie, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Beghetti, M.; et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 903–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonneau, G.; Montani, D.; Celermajer, D.S.; Denton, C.P.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Krowka, M.; Williams, P.G.; Souza, R. Haemodynamic definitions and updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2200879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeuffer-Jovic, E.; Weiner, S.; Wilkens, H.; Schmitt, D.; Frantz, S.; Held, M. Impact of the new definition of pulmonary hypertension according to world symposium of pulmonary hypertension 2018 on diagnosis of post-capillary pulmonary hypertension. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 335, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, G.; Zeder, K.; Rosenstock, P.; Avian, A.; Bachmaier, G.; Douschan, P.; Foris, V.; Sassmann, T.; Olschewsk, H. Clinical Impact of the New Definition of Precapillary Pulmonary Hypertension. Chest 2021, 159, 1995–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, J.S.R.; Torbicki, A. Proposed new pulmonary hypertension definition: Is 4 mm(Hg) worth re-writing medical textbooks? Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1900197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, G.; Olschewski, H. Debating the new haemodynamic definition of pulmonary hypertension: Much ado about nothing? Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1901278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, X.; Yan, L.; Li, X.; Duan, A.; An, C.; Ma, X.; et al. Impact of the revised hemodynamic definition on the diagnosis of precapillary pulmonary hypertension: A retrospective single-center study in China. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2021, 11, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.M.; Zhai, Z.G.; Wang, C. The controversy and influence brought by the modification of the diagnostic standard of pulmonary hypertension. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2020, 100, 1684–1687. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, C.; Yang, B. Revising the hemodynamic criteria for pulmonary hypertension: A perspective from China. J. Transl. Intern. Med. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, C.R.; Hamburger, R. The Pulmonary Hypertension Story. Cardiovasc. Innov. Appl. 2018, 3, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonk-Noordegraaf, A.; Haddad, F.; Chin, K.M.; Forfia, P.R.; Kawut, S.M.; Lumens, J.; Naeije, R.; Newman, J.; Oudiz, R.J.; Provencher, S.; et al. Right heart adaptation to pulmonary arterial hypertension: Physiology and pathobiology. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, D22–D33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovitch, M. Molecular pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4306–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houston, B.A.; Brittain, E.L.; Tedford, R.J. Right Ventricular Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1111–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galie, N.; Channick, R.N.; Frantz, R.P.; Grunig, E.; Jing, Z.C.; Moiseeva, O.; Preston, I.R.; Pulido, T.; Safdar, Z.; Tamura, Y.; et al. Risk stratification and medical therapy of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; Sitbon, O.; Yaici, A.; Montani, D.; O’Callaghan, D.S.; Jais, X.; Parent, F.; Savale, L.; Natali, D.; Gunther, S.; et al. Survival in incident and prevalent cohorts of patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 36, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benza, R.L.; Miller, D.P.; Gomberg-Maitland, M.; Frantz, R.P.; Foreman, A.J.; Coffey, C.S.; Frost, A.; Barst, R.J.; Badesch, D.B.; Elliott, C.G.; et al. Predicting survival in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Insights from the Registry to Evaluate Early and Long-Term Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Disease Management (REVEAL). Circulation 2010, 122, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thenappan, T.; Glassner, C.; Gomberg-Maitland, M. Validation of the pulmonary hypertension connection equation for survival prediction in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Chest 2012, 141, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Kramer, T.; Pan, Z.; Eichstaedt, C.A.; Spiesshoefer, J.; Benjamin, N.; Olsson, K.M.; Meyer, K.; Vizza, C.D.; Vonk-Noordegraaf, A.; et al. Mortality in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Prediction by the 2015 European pulmonary hypertension guidelines risk stratification model. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylhammar, D.; Kjellstrom, B.; Hjalmarsson, C.; Jansson, K.; Nisell, M.; Soderberg, S.; Wikstrom, G.; Radegran, G. A comprehensive risk stratification at early follow-up determines prognosis in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 4175–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Pausch, C.; Olsson, K.M.; Huscher, D.; Pittrow, D.; Grunig, E.; Staehler, G.; Vizza, C.D.; Gall, H.; Distler, O.; et al. COMPERA 2.0: A refined four-stratum risk assessment model for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2102311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benza, R.L.; Farber, H.W.; Frost, A.; Grunig, E.; Hoeper, M.M.; Busse, D.; Meier, C.; Nikkho, S.; Ghofrani, H.A. REVEAL risk score in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension receiving riociguat. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2018, 37, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcroix, M.; Staehler, G.; Gall, H.; Grunig, E.; Held, M.; Halank, M.; Klose, H.; Vonk-Noordegraaf, A.; Rosenkranz, S.; Pepke-Zaba, J.; et al. Risk assessment in medically treated chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.Y.; Giorgio, K.; Schmitz, K.; Walker, R.F.; Prins, K.W.; Pritzker, M.R.; Archer, S.L.; Lutsey, P.L.; Thenappan, T. Effect of Chronic Digoxin Use on Mortality and Heart Failure Hospitalization in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e027559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauler, M.; Fares, W.H.; Trow, T.K. Standard nonspecific therapies in the management of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Clin. Chest Med. 2013, 34, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masarone, D.; Kittleson, M.; Pollesello, P.; Tedford, R.J.; Pacileo, G. Use of Levosimendan in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension: What is the Current Evidence? Drugs 2023, 83, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.S.; Andersen, A.; Holmboe, S.; Schultz, J.G.; Ringgaard, S.; Simonsen, U.; Happe, C.; Bogaard, H.J.; Nielsen-Kudsk, J.E. Levosimendan Prevents and Reverts Right Ventricular Failure in Experimental Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharm. 2017, 70, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, C.; Lu, C.; Zeng, Z. The effect of levosimendan on right ventricular function in patients with heart dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Feng, W.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Q.; Luo, X.; Wang, G.; Sun, M.; Yao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Hou, S.; et al. Effect of Levosimendan on Acute Decompensated Right Heart Failure in Patients With Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 778620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Benza, R.L.; Corris, P.; de Perrot, M.; Fadel, E.; Keogh, A.M.; Kuhn, C.; Savale, L.; Klepetko, W. Intensive care, right ventricular support and lung transplantation in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Luo, H.; Li, Y. The role of tolvaptan in pulmonary hypertension: A retrospective study. Medicine 2022, 101, e31587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yan, L.; Liu, Z.; Luo, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Jin, Q.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y. The Effectiveness and Safety of Tolvaptan on Top of Standard Medication in the Treatment of Patients With Right Heart Failure Caused by Pulmonary Hypertension. Chin. Circ. J. 2019, 34, 688–692. [Google Scholar]
- Fuster, V.; Steele, P.M.; Edwards, W.D.; Gersh, B.J.; McGoon, M.D.; Frye, R.L. Primary pulmonary hypertension: Natural history and the importance of thrombosis. Circulation 1984, 70, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, I.R.; Roberts, K.E.; Miller, D.P.; Sen, G.P.; Selej, M.; Benton, W.W.; Hill, N.S.; Farber, H.W. Effect of Warfarin Treatment on Survival of Patients With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) in the Registry to Evaluate Early and Long-Term PAH Disease Management (REVEAL). Circulation 2015, 132, 2403–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.M. Controversy over anticoagulation in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2018, 98, 81–83. [Google Scholar]
- Sedhom, R.; Megaly, M.; Gupta, E.; Amanullah, A. Use of direct oral anticoagulants in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A systematic review. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis. 2022, 53, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; Simonneau, G.; Pittrow, D.; Delcroix, M.; Pepke-Zaba, J.; Langleben, D.; Mielniczuk, L.M.; Escribano Subias, P.; Snijder, R.J.; Barbera, J.A.; et al. Oral anticoagulants (NOAC and VKA) in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2022, 41, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garry, J.D.; Kolaitis, N.A.; Kronmal, R.; Thenappan, T.; Hemnes, A.; Grinnan, D.; Bull, T.; Chakinala, M.M.; Horn, E.; Simon, M.A.; et al. Anticoagulation in pulmonary arterial hypertension—Association with mortality, healthcare utilization, and quality of life: The Pulmonary Hypertension Association Registry (PHAR). J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2022, 41, 1808–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Campen, J.S.; de Boer, K.; van de Veerdonk, M.C.; van der Bruggen, C.E.; Allaart, C.P.; Raijmakers, P.G.; Heymans, M.W.; Marcus, J.T.; Harms, H.J.; Handoko, M.L.; et al. Bisoprolol in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension: An explorative study. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Luo, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Q.; An, C.; Huang, Z.; Jin, Q.; Gao, L.; Yan, L. Prevalence of iron deficiency in different subtypes of pulmonary hypertension. Heart Lung 2018, 47, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiter, G.; Lankhorst, S.; Boonstra, A.; Postmus, P.E.; Zweegman, S.; Westerhof, N.; van der Laarse, W.J.; Vonk-Noordegraaf, A. Iron deficiency is common in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 1386–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, C.J.; Howard, L.S.; Busbridge, M.; Ashby, D.; Kondili, E.; Gibbs, J.S.; Wharton, J.; Wilkins, M.R. Iron deficiency and raised hepcidin in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension: Clinical prevalence, outcomes, and mechanistic insights. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, T.; Wissmuller, M.; Natsina, K.; Gerhardt, F.; Ten Freyhaus, H.; Dumitrescu, D.; Viethen, T.; Hellmich, M.; Baldus, S.; Rosenkranz, S. Ferric carboxymaltose in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension and iron deficiency: A long-term study. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, L.; He, J.; Watson, G.M.J.; Huang, L.; Wharton, J.; Luo, Q.; Kiely, D.G.; Condliffe, R.; Pepke-Zaba, J.; Morrell, N.W.; et al. Supplementation with Iron in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Two Randomized Crossover Trials. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2021, 18, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, L.J.; Badesch, D.B.; Barst, R.J.; Galie, N.; Black, C.M.; Keogh, A.; Pulido, T.; Frost, A.; Roux, S.; Leconte, I.; et al. Bosentan therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galie, N.; Olschewski, H.; Oudiz, R.J.; Torres, F.; Frost, A.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Badesch, D.B.; McGoon, M.D.; McLaughlin, V.V.; Roecker, E.B.; et al. Ambrisentan for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: Results of the ambrisentan in pulmonary arterial hypertension, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, efficacy (ARIES) study 1 and 2. Circulation 2008, 117, 3010–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudiz, R.J.; Galie, N.; Olschewski, H.; Torres, F.; Frost, A.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Badesch, D.B.; McGoon, M.D.; McLaughlin, V.V.; Roecker, E.B.; et al. Long-term ambrisentan therapy for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 1971–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Egan, J.J.; Kawut, S.M.; Flaherty, K.R.; Martinez, F.J.; Nathan, S.D.; Wells, A.U.; Collard, H.R.; et al. Treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with ambrisentan: A parallel, randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, T.; Adzerikho, I.; Channick, R.N.; Delcroix, M.; Galie, N.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Jansa, P.; Jing, Z.C.; Le Brun, F.O.; Mehta, S.; et al. Macitentan and morbidity and mortality in pulmonary arterial hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galie, N.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Torbicki, A.; Barst, R.J.; Rubin, L.J.; Badesch, D.; Fleming, T.; Parpia, T.; Burgess, G.; Branzi, A.; et al. Sildenafil citrate therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 2148–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, L.J.; Badesch, D.B.; Fleming, T.R.; Galie, N.; Simonneau, G.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Oakes, M.; Layton, G.; Serdarevic-Pehar, M.; McLaughlin, V.V.; et al. Long-term treatment with sildenafil citrate in pulmonary arterial hypertension: The SUPER-2 study. Chest 2011, 140, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Q.; Jing, Z.C.; Zhang, J.H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Z.X.; Sun, Y.G.; Pu, J.L.; Yang, Y.J. The efficacy and safety of sildenafil in Chinese patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2009, 32, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.M.; Lu, X.L.; Shan, G.L.; Wu, B.X.; Zhu, X.Y.; Wu, G.H.; Zeng, X.F.; Guo, T.; Liu, Z.H.; Ni, X.H.; et al. Oral sildenafil therapy for Chinese patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: A multicenter study. J. Clin. Pharm. 2012, 52, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galie, N.; Brundage, B.H.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Oudiz, R.J.; Simonneau, G.; Safdar, Z.; Shapiro, S.; White, R.J.; Chan, M.; Beardsworth, A.; et al. Tadalafil therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation 2009, 119, 2894–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudiz, R.J.; Brundage, B.H.; Galie, N.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Simonneau, G.; Botros, F.T.; Chan, M.; Beardsworth, A.; Barst, R.J.; PHIRST Study Group. Tadalafil for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: A double-blind 52-week uncontrolled extension study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, R.P.; Durst, L.; Burger, C.D.; Oudiz, R.J.; Bourge, R.C.; Franco, V.; Waxman, A.B.; McDevitt, S.; Walker, S. Conversion from sildenafil to tadalafil: Results from the sildenafil to tadalafil in pulmonary arterial hypertension (SITAR) study. J. Cardiovasc. Pharm. Ther. 2014, 19, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.C.; Yu, Z.X.; Shen, J.Y.; Wu, B.X.; Xu, K.F.; Zhu, X.Y.; Pan, L.; Zhang, Z.L.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.S.; et al. Vardenafil in pulmonary arterial hypertension: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghofrani, H.A.; Galie, N.; Grimminger, F.; Grunig, E.; Humbert, M.; Jing, Z.C.; Keogh, A.M.; Langleben, D.; Kilama, M.O.; Fritsch, A.; et al. Riociguat for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, L.J.; Galie, N.; Grimminger, F.; Grunig, E.; Humbert, M.; Jing, Z.C.; Keogh, A.; Langleben, D.; Fritsch, A.; Menezes, F.; et al. Riociguat for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: A long-term extension study (PATENT-2). Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghofrani, H.A.; D’Armini, A.M.; Grimminger, F.; Hoeper, M.M.; Jansa, P.; Kim, N.H.; Mayer, E.; Simonneau, G.; Wilkins, M.R.; Fritsch, A.; et al. Riociguat for the treatment of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonneau, G.; D’Armini, A.M.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Grimminger, F.; Hoeper, M.M.; Jansa, P.; Kim, N.H.; Wang, C.; Wilkins, M.R.; Fritsch, A.; et al. Riociguat for the treatment of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A long-term extension study (CHEST-2). Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galie, N.; Muller, K.; Scalise, A.V.; Grunig, E. PATENT PLUS: A blinded, randomised and extension study of riociguat plus sildenafil in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, V.V.; Shillington, A.; Rich, S. Survival in primary pulmonary hypertension: The impact of epoprostenol therapy. Circulation 2002, 106, 1477–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitbon, O.; Humbert, M.; Nunes, H.; Parent, F.; Garcia, G.; Herve, P.; Rainisio, M.; Simonneau, G. Long-term intravenous epoprostenol infusion in primary pulmonary hypertension: Prognostic factors and survival. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 40, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitbon, O.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A. Epoprostenol and pulmonary arterial hypertension: 20 years of clinical experience. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 160055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Schwarze, M.; Ehlerding, S.; Adler-Schuermeyer, A.; Spiekerkoetter, E.; Niedermeyer, J.; Hamm, M.; Fabel, H. Long-term treatment of primary pulmonary hypertension with aerosolized iloprost, a prostacyclin analogue. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1866–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olschewski, H.; Simonneau, G.; Galie, N.; Higenbottam, T.; Naeije, R.; Rubin, L.J.; Nikkho, S.; Speich, R.; Hoeper, M.M.; Behr, J.; et al. Inhaled iloprost for severe pulmonary hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.C.; Jiang, X.; Han, Z.Y.; Xu, X.Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lv, H.; Ma, C.R.; Yang, Y.J.; Pu, J.L. Iloprost for pulmonary vasodilator testing in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 33, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapson, V.F.; Gomberg-Maitland, M.; McLaughlin, V.V.; Benza, R.L.; Widlitz, A.C.; Krichman, A.; Barst, R.J. Safety and efficacy of IV treprostinil for pulmonary arterial hypertension: A prospective, multicenter, open-label, 12-week trial. Chest 2006, 129, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benza, R.L.; Tapson, V.F.; Gomberg-Maitland, M.; Poms, A.; Barst, R.J.; McLaughlin, V.V. One-year experience with intravenous treprostinil for pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2013, 32, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonneau, G.; Barst, R.J.; Galie, N.; Naeije, R.; Rich, S.; Bourge, R.C.; Keogh, A.; Oudiz, R.; Frost, A.; Blackburn, S.D.; et al. Continuous subcutaneous infusion of treprostinil, a prostacyclin analogue, in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barst, R.J.; Galie, N.; Naeije, R.; Simonneau, G.; Jeffs, R.; Arneson, C.; Rubin, L.J. Long-term outcome in pulmonary arterial hypertension patients treated with subcutaneous treprostinil. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomberg-Maitland, M.; Tapson, V.F.; Benza, R.L.; McLaughlin, V.V.; Krichman, A.; Widlitz, A.C.; Barst, R.J. Transition from intravenous epoprostenol to intravenous treprostinil in pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 1586–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, A.; Restrepo-Jaramillo, R.; Thenappan, T.; Ravichandran, A.; Engel, P.; Bajwa, A.; Allen, R.; Feldman, J.; Argula, R.; Smith, P.; et al. Inhaled Treprostinil in Pulmonary Hypertension Due to Interstitial Lung Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, S.D.; Waxman, A.; Rajagopal, S.; Case, A.; Johri, S.; DuBrock, H.; De La Zerda, D.J.; Sahay, S.; King, C.; Melendres-Groves, L.; et al. Inhaled treprostinil and forced vital capacity in patients with interstitial lung disease and associated pulmonary hypertension: A post-hoc analysis of the INCREASE study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, S.D.; Tapson, V.F.; Elwing, J.; Rischard, F.; Mehta, J.; Shapiro, S.; Shen, E.; Deng, C.; Smith, P.; Waxman, A. Efficacy of Inhaled Treprostinil on Multiple Disease Progression Events in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension due to Parenchymal Lung Disease in the INCREASE Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galie, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.L.; Vizza, C.D.; Kneussl, M.; Manes, A.; Sitbon, O.; Torbicki, A.; Delcroix, M.; Naeije, R.; et al. Effects of beraprost sodium, an oral prostacyclin analogue, in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barst, R.J.; McGoon, M.; McLaughlin, V.; Tapson, V.; Rich, S.; Rubin, L.; Wasserman, K.; Oudiz, R.; Shapiro, S.; Robbins, I.M.; et al. Beraprost therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 41, 2119–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitbon, O.; Channick, R.; Chin, K.M.; Frey, A.; Gaine, S.; Galie, N.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Hoeper, M.M.; Lang, I.M.; Preiss, R.; et al. Selexipag for the Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2522–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaine, S.; Chin, K.; Coghlan, G.; Channick, R.; Di Scala, L.; Galie, N.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Lang, I.M.; McLaughlin, V.; Preiss, R.; et al. Selexipag for the treatment of connective tissue disease-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1602493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogo, T.; Shimokawahara, H.; Kinoshita, H.; Sakao, S.; Abe, K.; Matoba, S.; Motoki, H.; Takama, N.; Ako, J.; Ikeda, Y.; et al. Selexipag for the treatment of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 60, 2101694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruenig, E.; Michelakis, E.; Vachiery, J.L.; Vizza, C.D.; Meyer, F.J.; Doelberg, M.; Bach, D.; Dingemanse, J.; Galie, N. Acute hemodynamic effects of single-dose sildenafil when added to established bosentan therapy in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: Results of the COMPASS-1 study. J. Clin. Pharm. 2009, 49, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardi, F.; Manes, A.; Palazzini, M.; Bachetti, C.; Mazzanti, G.; Rinaldi, A.; Albini, A.; Gotti, E.; Monti, E.; Bacchi Reggiani, M.L.; et al. Combining bosentan and sildenafil in pulmonary arterial hypertension patients failing monotherapy: Real-world insights. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galie, N.; Barbera, J.A.; Frost, A.E.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Hoeper, M.M.; McLaughlin, V.V.; Peacock, A.J.; Simonneau, G.; Vachiery, J.L.; Grunig, E.; et al. Initial Use of Ambrisentan plus Tadalafil in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; Barst, R.J.; Robbins, I.M.; Channick, R.N.; Galie, N.; Boonstra, A.; Rubin, L.J.; Horn, E.M.; Manes, A.; Simonneau, G. Combination of bosentan with epoprostenol in pulmonary arterial hypertension: BREATHE-2. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 24, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, V.V.; Oudiz, R.J.; Frost, A.; Tapson, V.F.; Murali, S.; Channick, R.N.; Badesch, D.B.; Barst, R.J.; Hsu, H.H.; Rubin, L.J. Randomized study of adding inhaled iloprost to existing bosentan in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Leuchte, H.; Halank, M.; Wilkens, H.; Meyer, F.J.; Seyfarth, H.J.; Wensel, R.; Ripken, F.; Bremer, H.; Kluge, S.; et al. Combining inhaled iloprost with bosentan in patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, L.; Fang, L.; Chai, Y.; Niu, M.; Yu, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Qu, S.; et al. Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Using Initial Combination Therapy of Bosentan and Iloprost. Respir Care 2017, 62, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, V.V.; Benza, R.L.; Rubin, L.J.; Channick, R.N.; Voswinckel, R.; Tapson, V.F.; Robbins, I.M.; Olschewski, H.; Rubenfire, M.; Seeger, W. Addition of inhaled treprostinil to oral therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 1915–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapson, V.F.; Torres, F.; Kermeen, F.; Keogh, A.M.; Allen, R.P.; Frantz, R.P.; Badesch, D.B.; Frost, A.E.; Shapiro, S.M.; Laliberte, K.; et al. Oral treprostinil for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension in patients on background endothelin receptor antagonist and/or phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor therapy (the FREEDOM-C study): A randomized controlled trial. Chest 2012, 142, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonneau, G.; Rubin, L.J.; Galie, N.; Barst, R.J.; Fleming, T.R.; Frost, A.E.; Engel, P.J.; Kramer, M.R.; Burgess, G.; Collings, L.; et al. Addition of sildenafil to long-term intravenous epoprostenol therapy in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 149, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghofrani, H.A.; Wiedemann, R.; Rose, F.; Olschewski, H.; Schermuly, R.T.; Weissmann, N.; Seeger, W.; Grimminger, F. Combination therapy with oral sildenafil and inhaled iloprost for severe pulmonary hypertension. Ann. Intern. Med. 2002, 136, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghofrani, H.A.; Rose, F.; Schermuly, R.T.; Olschewski, H.; Wiedemann, R.; Kreckel, A.; Weissmann, N.; Ghofrani, S.; Enke, B.; Seeger, W.; et al. Oral sildenafil as long-term adjunct therapy to inhaled iloprost in severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 42, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomberg-Maitland, M.; McLaughlin, V.; Gulati, M.; Rich, S. Efficacy and safety of sildenafil added to treprostinil in pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 96, 1334–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alto, M.; Badagliacca, R.; Lo Giudice, F.; Argiento, P.; Casu, G.; Corda, M.; Correale, M.; Ghio, S.; Greco, A.; Lattanzio, M.; et al. Hemodynamics and risk assessment 2 years after the initiation of upfront ambrisentantadalafil in pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2020, 39, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizza, C.D.; Lang, I.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Benza, R.L.; Rosenkranz, S.; White, R.J.; Adir, Y.; Andreassen, A.K.; Balasubramanian, V.; Bartolome, S.; et al. Aggressive Afterload Lowering to Improve the Right Ventricle: A New Target for Medical Therapy in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, K.M.; Richter, M.J.; Kamp, J.C.; Gall, H.; Heine, A.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Fuge, J.; Ewert, R.; Hoeper, M.M. Intravenous treprostinil as an add-on therapy in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2019, 38, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alto, M.; Constantine, A.; Balint, O.H.; Romeo, E.; Argiento, P.; Ablonczy, L.; Skoro-Sajer, N.; Giannakoulas, G.; Dimopoulos, K. The effects of parenteral prostacyclin therapy as add-on treatment to oral compounds in Eisenmenger syndrome. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1901401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitbon, O.; Jais, X.; Savale, L.; Cottin, V.; Bergot, E.; Macari, E.A.; Bouvaist, H.; Dauphin, C.; Picard, F.; Bulifon, S.; et al. Upfront triple combination therapy in pulmonary arterial hypertension: A pilot study. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 1691–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alto, M.; Badagliacca, R.; Argiento, P.; Romeo, E.; Farro, A.; Papa, S.; Sarubbi, B.; Russo, M.G.; Vizza, C.D.; Golino, P.; et al. Risk Reduction and Right Heart Reverse Remodeling by Upfront Triple Combination Therapy in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Chest 2020, 157, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momoi, M.; Hiraide, T.; Shinya, Y.; Momota, H.; Fukui, S.; Kawakami, M.; Itabashi, Y.; Fukuda, K.; Kataoka, M. Triple oral combination therapy with macitentan, riociguat, and selexipag for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2021, 15, 1753466621995048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, K.M.; Sitbon, O.; Doelberg, M.; Feldman, J.; Gibbs, J.S.R.; Grunig, E.; Hoeper, M.M.; Martin, N.; Mathai, S.C.; McLaughlin, V.V.; et al. Three- Versus Two-Drug Therapy for Patients With Newly Diagnosed Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 78, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucly, A.; Savale, L.; Jais, X.; Bauer, F.; Bergot, E.; Bertoletti, L.; Beurnier, A.; Bourdin, A.; Bouvaist, H.; Bulifon, S.; et al. Association between Initial Treatment Strategy and Long-Term Survival in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshner, M.; Spiekerkoetter, E.; Bogaard, H.; Hansmann, G.; Nikkho, S.; Prins, K.W. Repurposing of medications for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2020, 10, 2045894020941494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condon, D.F.; Agarwal, S.; Chakraborty, A.; Auer, N.; Vazquez, R.; Patel, H.; Zamanian, R.T.; de Jesus Perez, V.A. Novel Mechanisms Targeted by Drug Trials in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Chest 2022, 161, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, L.M.; Yang, P.; Joshi, S.; Augur, Z.M.; Kim, S.S.J.; Bocobo, G.A.; Dinter, T.; Troncone, L.; Chen, P.S.; McNeil, M.E.; et al. ACTRIIA-Fc rebalances activin/GDF versus BMP signaling in pulmonary hypertension. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaz5660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; McLaughlin, V.; Gibbs, J.S.R.; Gomberg-Maitland, M.; Hoeper, M.M.; Preston, I.R.; Souza, R.; Waxman, A.; Escribano Subias, P.; Feldman, J.; et al. Sotatercept for the Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, M.; McLaughlin, V.; Gibbs, J.S.R.; Gomberg-Maitland, M.; Hoeper, M.M.; Preston, I.R.; Souza, R.; Waxman, A.B.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Escribano Subias, P.; et al. Sotatercept for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: PULSAR open-label extension. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2201347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Badesch, D.B.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Gibbs, J.S.R.; Gomberg-Maitland, M.; McLaughlin, V.V.; Preston, I.R.; Souza, R.; Waxman, A.B.; Grunig, E.; et al. Phase 3 Trial of Sotatercept for Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1478–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.A.; Kramer, B.; Shin, Y.J.; Vallar, P.; Boatman, P.D.; Zou, N.; Sage, C.R.; Gharbaoui, T.; Krishnan, A.; Pal, B.; et al. Discovery of 2-(((1r,4r)-4-(((4-Chlorophenyl)(phenyl)carbamoyl)oxy)methyl)cyclohexyl)methoxy)a cetate (Ralinepag): An Orally Active Prostacyclin Receptor Agonist for the Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, F.; Farber, H.; Ristic, A.; McLaughlin, V.; Adams, J.; Zhang, J.; Klassen, P.; Shanahan, W.; Grundy, J.; Hoffmann, I.; et al. Efficacy and safety of ralinepag, a novel oral IP agonist, in PAH patients on mono or dual background therapy: Results from a phase 2 randomised, parallel group, placebo-controlled trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1901030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, J.S.; King, C.D.; Adams, J.W.; Cabell, C.H. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of the selective prostacyclin receptor agonist ralinepag in single and multiple dosing studies of an immediate-release oral formulation in healthy volunteers. Pulm. Circ. 2020, 10, 2045894020922814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, X.; Tian, G.; Yang, R.; Wu, J.; Zou, X.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Wu, C.; et al. Pharmacokinetics-Driven Optimization of 4(3 H)-Pyrimidinones as Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors Leading to TPN171, a Clinical Candidate for the Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 4979–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.; Chen, Q.; Liang, L.; Zou, Y.; Pu, H.; Xin, L.; Song, R.; Li, T.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. A Phase I Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of TPN171H, a Novel Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitor, in Healthy Subjects. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 15, 2947–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.F.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J.H.; Cheng, H.; Odilov, A.; Yang, F.P.; Tian, G.H.; Yao, X.M.; Duan, H.Q.; Yu, C.Y.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, mass balance, and metabolism of [(14)C]TPN171, a novel PDE5 inhibitor, in humans for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2023, 44, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ma, Y.; Li, A.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, W.; Jin, J. Two novel multi-functional magnetic adsorbents for effective removal of hydrophilic and hydrophobic nitroaromatic compounds. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 294, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jing, S. Therapeutic antibody approach for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Int. J. Cardiol. Res. 2021, 1, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Chen, X.; Song, X.; Chen, X.; Ma, W.; Lin, J.; Wu, H.; Hu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Immunotherapy of Endothelin-1 Receptor Type A for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 2567–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Ma, W.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Song, X.; Bai, Z.; Shi, D.; Zheng, J.; Pan, G.; et al. Long-Term Effect of a Vaccine Targeting Endothelin-1 Receptor Type A in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 683436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, W.M.; Oliveira, R.K.F.; Wang, R.S.; Opotowsky, A.R.; Rubins, D.M.; Hainer, J.; Wertheim, B.M.; Alba, G.A.; Choudhary, G.; Tornyos, A.; et al. Network Analysis to Risk Stratify Patients with Exercise Intolerance. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 864–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benincasa, G.; Napoli, C.; Loscalzo, J.; Maron, B.A. Pursuing functional biomarkers in complex disease: Focus on pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. Heart J. 2023, 258, 96–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Group 1 Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) | Group 3 PH associated with lung diseases and/or hypoxia |
|---|---|
| 1.1 Idiopathic | 3.1 Obstructive lung disease or emphysema |
| 1.1.1 Non-responders at vasoreactivity testing | 3.2 Restrictive lung disease |
| 1.1.2 Acute responders at vasoreactivity testing | 3.3 Lung disease with mixed restrictive/obstructive pattern |
| 1.2 Heritable | 3.4 Hypoventilation syndromes |
| 1.3 Associated with drugs and toxins | 3.5 Hypoxia without lung disease |
| 1.4 Associated with: | 3.6 Developmental lung disorders |
| 1.4.1 Connective tissue disease | Group 4 PH associated with pulmonary artery obstructions |
| 1.4.2 HIV infection | |
| 1.4.3 Portal hypertension | |
| 1.4.4 Congenital heart disease | 4.1 Chronic thrombo-embolic PH |
| 1.4.5 Schistosomiasis | 4.2 Other pulmonary artery obstructions |
| 1.5 PAH with features of venous/capillary involvement | Group 5 PH with unclear and/or multifactorial mechanisms |
| 1.6 Persistent PH of the newborn | |
| Group 2 PH associated with left heart disease | |
| 5.1 Hematological disorders | |
| 2.1 Heart failure: | 5.2 Systemic disorders |
| 2.1.1 with preserved ejection fraction | 5.3 Metabolic disorders |
| 2.1.2 with reduced or mildly reduced ejection fraction | 5.4 Chronic renal failure with or without hemodialysis |
| 2.2 Valvular heart disease | 5.5 Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy |
| 2.3 Congenital/acquired cardiovascular conditions leading to post-capillary PH | 5.6 Fibrosing mediastinitis |
| PAH Targeted Drug | Usage | Main Side Effects | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Endothelin Receptor Antagonists | Bosentan | 62.5–125 mg, bid | Elevated transaminase, peripheral edema, anemia |
| Ambrisentan | 5–10 mg, qd | Headache, peripheral edema, anemia | |
| Macitentan | 10 mg, qd | Anemia | |
| Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors | Sildenafil | 20 mg, tid | Headache, blushing, increased menstruation |
| Tadalafil | 20–40 mg, qd | Headache, blushing, muscle soreness | |
| Vardenafil | 5 mg, bid | Headache, blushing, muscle soreness | |
| Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Agonists | Riociguat | 1–2.5 mg, tid | Gastrointestinal symptoms, hypotension, hemoptysis |
| Prostacyclin Analogs | Epoprostenol | Initiated at 2–4 ng/kg/min | Headache, gastrointestinal symptoms, catheter-related infections |
| Iloprost | 10–20 ug once, 6–9 times/d | Headache, flushing, hypotension | |
| Treprostinil | Initiated at 1.25 ng/kg/min, iv/sc | Infusion site pain, headache, diarrhea | |
| Beraprost | 20–80 ug, tid-qid | Headache and flushing | |
| Prostacyclin Receptor Agonists | Selexipag | 200–1600 μg, bid | Headache, diarrhea, vomiting, jaw pain |
| Type | Drug Name | Mechanism/Feature | Phase | Estimated Enrollment | Recruitment Status | Clinical Trial Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endothelin Pathway | GMA301 | Humanized monoclonal antibody against ETA | 1 | 48 | Recruiting | NCT04503733 |
| Prostacyclin Pathway | Ralinepag | Oral selective prostacyclin IP receptor agonist | 2 | 45 | Completed | NCT02279745 |
| 2 | 61 | Completed | NCT02279160 | |||
| 3 | 10 | Active, not recruiting | NCT04084678 | |||
| 3 | 1000 | Enrolling by invitation | NCT03683186 | |||
| 3 | 1000 | Recruiting | NCT03626688 | |||
| Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Stimulator | BAY1237592 | Inhaled soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator | 1 | 38 | Completed | NCT03754660 |
| MK-5475 | 1 | 25 | Completed | NCT03744637 | ||
| 2, 3 | 450 | Recruiting | NCT04732221 | |||
| Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor | Milrinone | Phosphodiesterase type 3 inhibitor | 1 | 40 | Completed | NCT04391478 |
| TPN171H | Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor | 2 | 60 | Completed | NCT04483115 | |
| Udenafil | 2 | 63 | Completed | NCT01553721 | ||
| 2, 3 | 59 | Completed | NCT02304198 | |||
| Vardenafil RT234 | 2 | 14 | Completed | NCT05343637 | ||
| 2b | 86 | Recruiting | NCT04266197 | |||
| TGF-β/BMP Signal | Sotatercept | Activin signaling inhibitor rebalancing anti-proliferative and Pro-Proliferative signaling pathways | 2 | 106 | Completed | NCT03496207 |
| 2 | 21 | Completed | NCT03738150 | |||
| 3 | 324 | Completed | NCT04576988 | |||
| 3 | 662 | Recruiting | NCT04811092 | |||
| 3 | 700 | Recruiting | NCT04796337 | |||
| 3 | 200 | Recruiting | NCT04896008 | |||
| DNA Damage Repair/ Epigenetic Modification | ABI-009 | Albumin-bound mTOR inhibitor | 1/1b | 15 | Completed | NCT02587325 |
| Apabetalone | Selective BET protein inhibitor | Early Phase 1 | 7 | Completed | NCT03655704 | |
| 2 | 72 | Not yet recruiting | NCT04915300 | |||
| Olaparib | Polymerase inhibitors | 1, 2 | 20 | Recruiting | NCT03782818 | |
| Hormone Modulators | Anastrozole | Third-generation aromatase inhibitor | 2 | 18 | Completed | NCT01545336 |
| 2 | 84 | Completed | NCT03229499 | |||
| DHEA | Dehydroepiandrosterone | 2 | 24 | Recruiting | NCT03648385 | |
| 2 | 130 | Recruiting | NCT03617458 | |||
| Fulvestrant | Estrogen receptor antagonist | 2 | 5 | Completed | NCT02911844 | |
| rhACE2 | Recombinant human ACE2 | 2 | 23 | Completed | NCT03177603 | |
| NA | 1899 | Recruiting | NCT01884051 | |||
| Rodatristat Ethyl | Tryptophan hydroxylase 1 inhibitor | 2 | 90 | Recruiting | NCT04712669 | |
| Spironolactone | Aldosterone receptor antagonist | 2 | 70 | Recruiting | NCT01712620 | |
| Tamoxifen | Selective estrogen receptor modulator | 2 | 24 | Recruiting | NCT03528902 | |
| Inflammation and Immunity | Anakinra | IL-1 receptor antagonist | Ib/II | 7 | Completed | NCT03057028 |
| Elafin | Elastase-Specific Protease Inhibitor | 1 | 30 | Completed | NCT03522935 | |
| Rituximab | CD20 monoclonal antibody | 2 | 57 | Completed | NCT01086540 | |
| Satralizumab | Anti-IL-6 receptor antibody | 2 | 24 | Recruiting | NCT05679570 | |
| Sulfasalazine | Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug | 1, 2 | 80 | Recruiting | NCT04528056 | |
| Tacrolimus | Calcineurin inhibitors | 2 | 23 | Completed | NCT01647945 | |
| Metabolic Regulator | Benzbromarone | Non-competitive inhibitor of xanthine oxidase | 2 | 10 | Completed | NCT02790450 |
| Dapagliflozin | SGLT2 inhibitor | 2 | 52 | Recruiting | NCT05179356 | |
| Empagliflozin | 2 | 8 | Not yet recruiting | NCT05493371 | ||
| L-Carnitine | Fatty acid metabolism | 1 | 12 | Active, not recruiting | NCT04908397 | |
| Metformin | AMPK activator | 2 | 130 | Recruiting | NCT03617458 | |
| Trimetazidine | Partial fatty acid oxidation inhibitor | 2 | 25 | Completed | NCT02102672 | |
| Coagulation and Thrombosis | Ifetroban | Thomboxane A2/prostaglandin H2 receptor antagonist | 2 | 34 | Recruiting | NCT02682511 |
| Others | Carvedilol | Non-selective beta-blockers | NA | 30 | Completed | NCT01586156 |
| Famotidine | Histamine-2 receptor antagonist | 2 | 80 | Recruiting | NCT03554291 | |
| Hymecromone | Inhibitor of hyaluronan synthesis | 2 | 16 | Active, not recruiting | NCT05128929 | |
| Imatinib | Tyrosine kinase inhibitors | 1 | 83 | Completed | NCT04903730 | |
| 2, 3 | 462 | Recruiting | NCT05036135 | |||
| 2 | 43 | Recruiting | NCT04416750 | |||
| 3 | 462 | Recruiting | NCT05557942 | |||
| LTP001 | SMURF1 inhibitor | 2 | 44 | Recruiting | NCT05135000 | |
| 2 | 40 | Recruiting | NCT05764265 | |||
| MN-08 | Dual-functional memantine nitrate derivative | 1 | 16 | Not yet recruiting | NCT05660863 | |
| Seralutinib | PDGFR kinase inhibitor | 2 | 86 | Completed | NCT04456998 | |
| 2 | 100 | Recruiting | NCT04816604 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Q.; Chen, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhong, D.; Lin, D.; Guan, L.; Pan, W.; Zhou, D.; Ge, J. Medical Management of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Current Approaches and Investigational Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061579
Jin Q, Chen D, Zhang X, Zhang F, Zhong D, Lin D, Guan L, Pan W, Zhou D, Ge J. Medical Management of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Current Approaches and Investigational Drugs. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(6):1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061579
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Qi, Dandan Chen, Xiaochun Zhang, Feng Zhang, Dongxiang Zhong, Dawei Lin, Lihua Guan, Wenzhi Pan, Daxin Zhou, and Junbo Ge. 2023. "Medical Management of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Current Approaches and Investigational Drugs" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 6: 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061579
APA StyleJin, Q., Chen, D., Zhang, X., Zhang, F., Zhong, D., Lin, D., Guan, L., Pan, W., Zhou, D., & Ge, J. (2023). Medical Management of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Current Approaches and Investigational Drugs. Pharmaceutics, 15(6), 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061579







