Lung Inflammation Resolution by RvD1 and RvD2 in a Receptor-Dependent Manner
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Animals
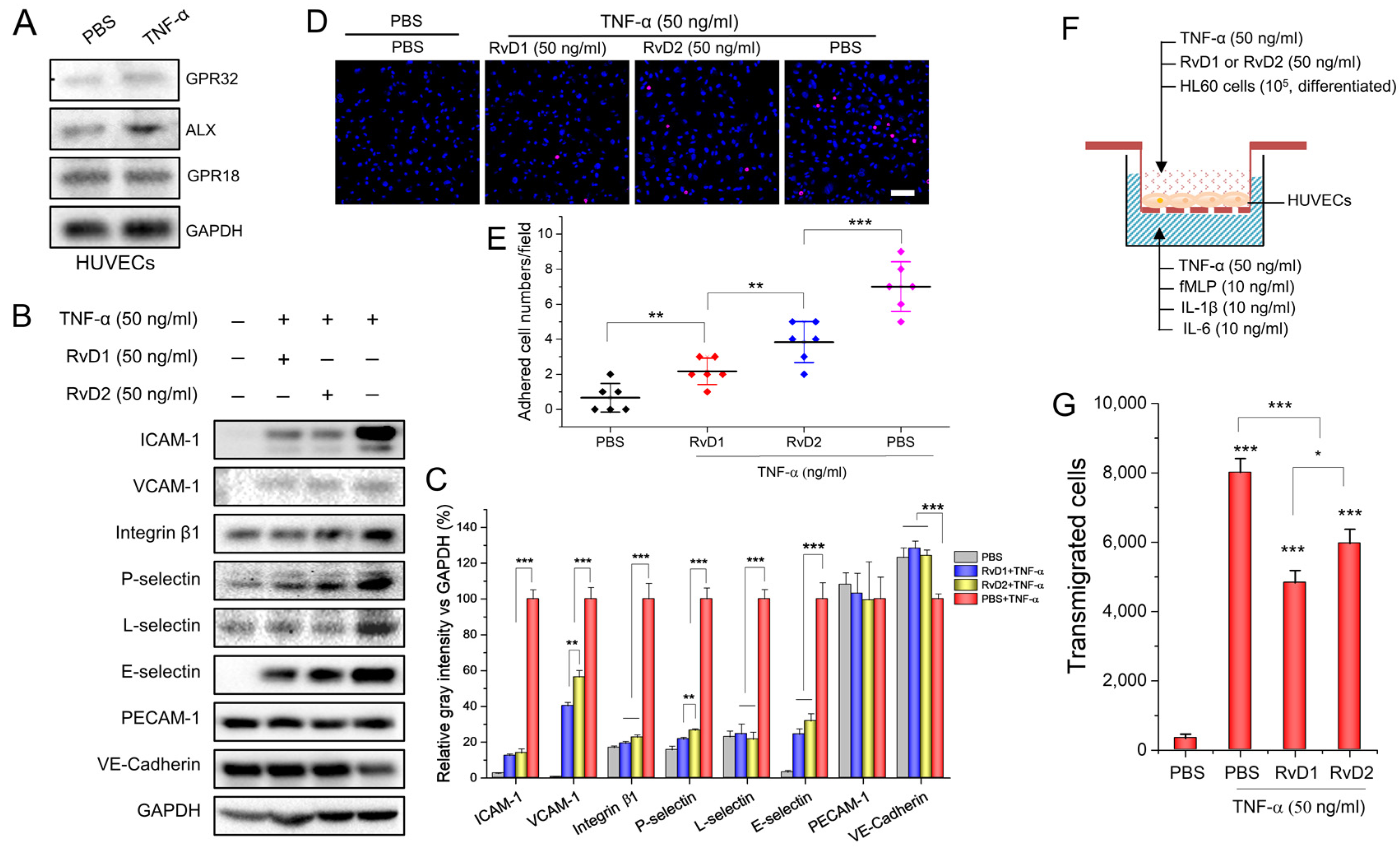
2.4. Cell Surface Marker Detection via Western Blotting
2.5. In Vitro Adhesion Assay
2.6. Transmigration
2.7. Cell Surface Molecules Detected by Flow Cytometry
2.8. Neutrophil Apoptosis
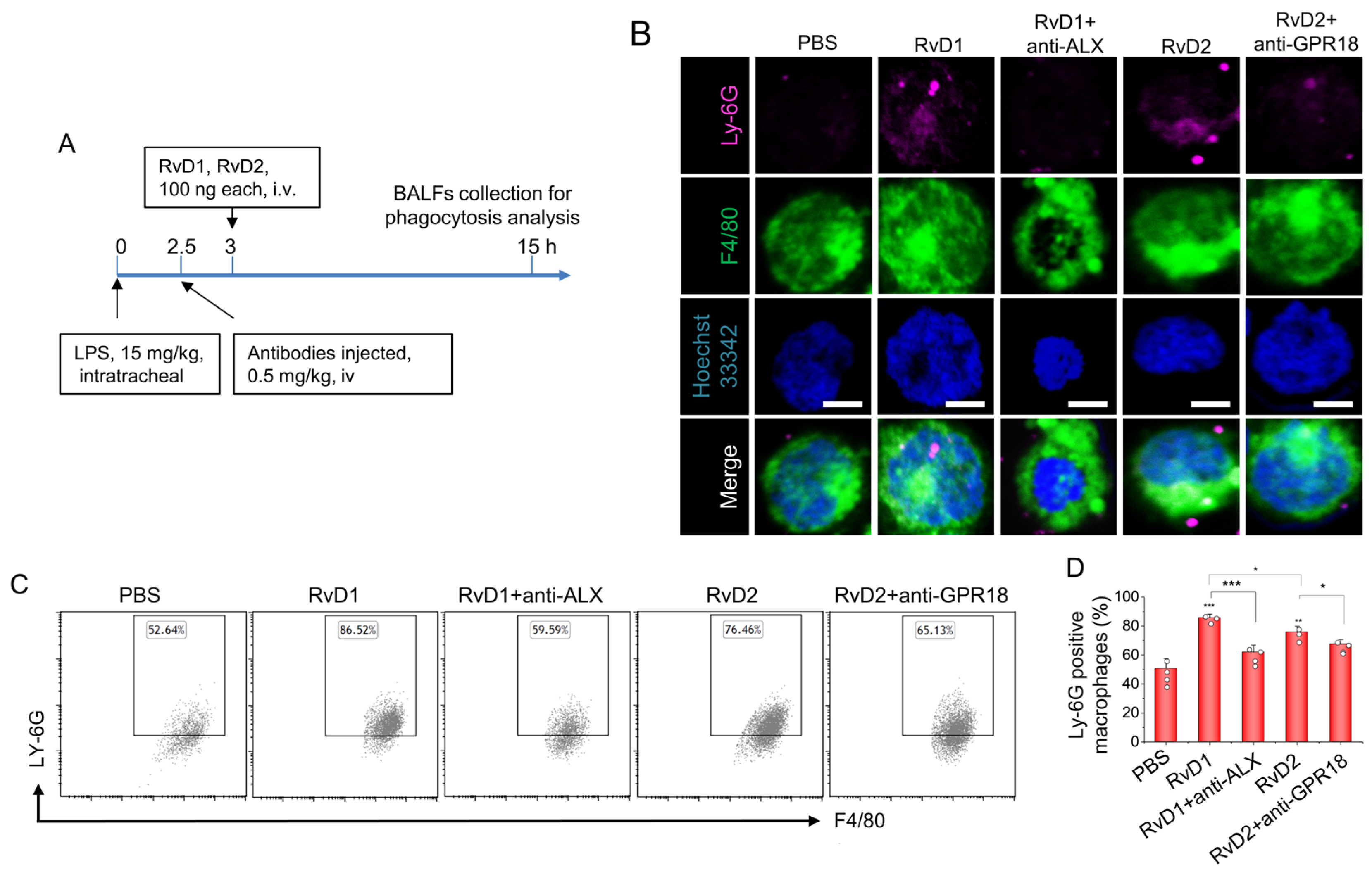
2.9. In Vivo Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Neutrophils via Macrophages
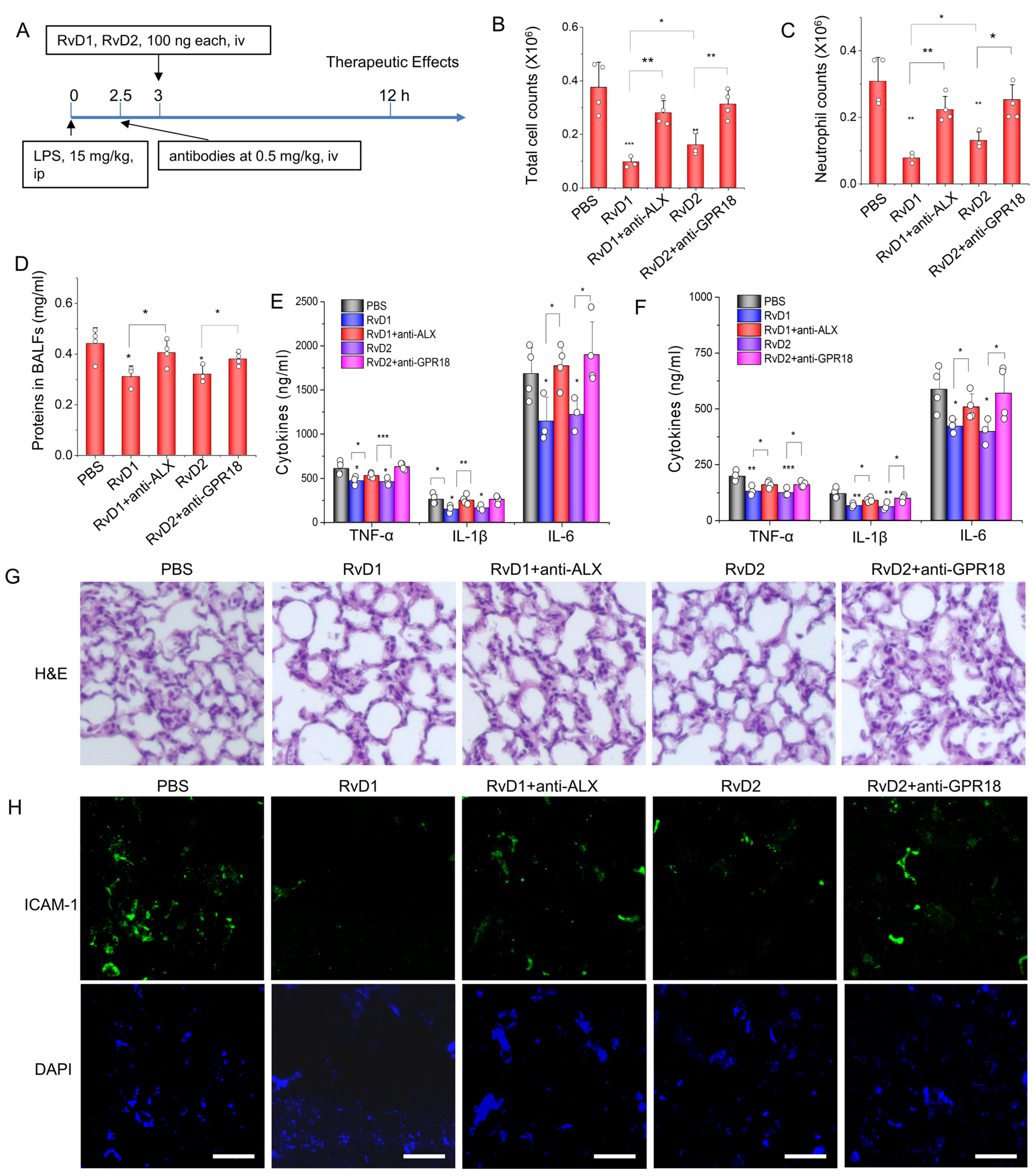
2.10. Acute Lung Inflammation Model and Its Therapy
2.11. Histology and Immunofluorescence
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. RvD1 or RvD2 Inhibits Leukocyte Adhering and Transmigration via Downregulating the Adherent Molecules of HUVECs
3.2. RvD1 or RvD2 Downregulates the Adhesion Proteins of Neutrophils and Promotes Neutrophil Apoptosis
3.3. RvD1 or RvD2 Prevent Inflammation in an Acute Lung Inflammatory Model via Their Receptors
3.4. RvD1 or RvD2 Enhance the Phagocytosis of Macrophages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Serhan, C.N. Pro-resolving lipid mediators are leads for resolution physiology. Nature 2014, 510, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilroy, D.W.; Lawrence, T.; Perretti, M.; Rossi, A.G. Inflammatory Resolution: New opportunities for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Gao, J.; Wang, Z. Liposomal Formulations Enhance the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Eicosapentaenoic Acid in HL60 Cells. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thau-Zuchman, O.; Ingram, R.; Harvey, G.G.; Cooke, T.; Palmas, F.; Pallier, P.N.; Brook, J.; Priestley, J.V.; Dalli, J.; Tremoleda, J.L.; et al. A Single Injection of Docosahexaenoic Acid Induces a Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediator Profile in the Injured Tissue and a Long-Lasting Reduction in Neurological Deficit after Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice. J. Neurotrauma 2020, 37, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvall, M.G.; Levy, B.D. DHA- and EPA-derived resolvins, protectins, and maresins in airway inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 785, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norling, L.V.; Headland, S.E.; Dalli, J.; Arnardottir, H.H.; Haworth, O.; Jones, H.R.; Irimia, D.; Serhan, C.N.; Perretti, M. Proresolving and cartilage-protective actions of resolvin D1 in inflammatory arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 1, e85922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, S.; Recchiuti, A.; Chiang, N.; Yacoubian, S.; Lee, C.-H.; Yang, R.; Petasis, N.A.; Serhan, C.N. Resolvin D1 binds human phagocytes with evidence for proresolving receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1660–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spite, M.; Norling, L.V.; Summers, L.; Yang, R.; Cooper, D.; Petasis, N.A.; Flower, R.J.; Perretti, M.; Serhan, C.N. Resolvin D2 is a potent regulator of leukocytes and controls microbial sepsis. Nature 2009, 461, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, N.; Dalli, J.; Colas, R.A.; Serhan, C.N. Identification of resolvin D2 receptor mediating resolution of infections and organ protection. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norling, L.V.; Dalli, J.; Flower, R.J.; Serhan, C.N.; Perretti, M. Resolvin d1 limits polymorphonuclear leukocyte recruitment to inflammatory loci: Receptor-dependent actions. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 1970–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Gao, J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Hayworth, C.; Frank, M.; Wang, Z. Neutrophil Membrane-Derived Nanovesicles Alleviate Inflammation To Protect Mouse Brain Injury from Ischemic Stroke. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1272–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Dong, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z. Human neutrophil membrane-derived nanovesicles as a drug delivery platform for improved therapy of infectious diseases. Acta Biomater. 2021, 123, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, N.; de la Rosa, X.; Libreros, S.; Serhan, C.N. Novel Resolvin D2 Receptor Axis in Infectious Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Wang, S.; Dong, X.; Leanse, L.G.; Dai, T.; Wang, Z. Co-delivery of resolvin D1 and antibiotics with nanovesicles to lungs resolves inflammation and clears bacteria in mice. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basil, M.C.; Levy, B.D. Specialized pro-resolving mediators: Endogenous regulators of infection and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Gao, J. Activating transcription factor 3 inhibits endometrial carcinoma aggressiveness via JunB suppression. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, J.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. A facile approach for development of a vaccine made of bacterial double-layered membrane vesicles (DMVs). Biomaterials 2018, 187, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Chu, D.; Wang, Z. Cell membrane-formed nanovesicles for disease-targeted delivery. J. Control. Release 2016, 224, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z. High yield, scalable and remotely drug-loaded neutrophil-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) for anti-inflammation therapy. Biomaterials 2017, 135, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Learoyd, J.; Duan, Y.; Leff, A.R.; Zhu, X. Hematopoietic Pyk2 regulates migration of differentiated HL-60 cells. J. Inflamm. 2010, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.H.; O’Driscoll, K.; Sosne, G.; Weinstein, I.B.; E Cayre, Y. 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-induced regulation of protein kinase C gene expression during HL-60 cell differentiation. Cell Growth Differ. 1991, 2, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kasuga, K.; Yang, R.; Porter, T.F.; Agrawal, N.; Petasis, N.A.; Irimia, D.; Toner, M.; Serhan, C.N. Rapid Appearance of Resolvin Precursors in Inflammatory Exudates: Novel Mechanisms in Resolution. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 8677–8687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naccache, P.H. Signals for actin polymerization in neutrophils. Biomed. Pharmacother. 1987, 41, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arnardottir, H.; Thul, S.; Pawelzik, S.C.; Karadimou, G.; Artiach, G.; Gallina, A.L.; Mysdotter, V.; Carracedo, M.; Tarnawski, L.; Caravaca, A.S.; et al. The resolvin d1 receptor gpr32 transduces inflammation resolution and atheroprotection. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e142883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kebir, D.; Filep, J.G. Role of Neutrophil Apoptosis in the Resolution of Inflammation. Sci. World J. 2010, 10, 1731–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.; Gao, J.; Wang, Z. Neutrophil-Mediated Delivery of Therapeutic Nanoparticles across Blood Vessel Barrier for Treatment of Inflammation and Infection. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11800–11811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N.; Hong, S.; Gronert, K.; Colgan, S.P.; Devchand, P.R.; Mirick, G.; Moussignac, R.L. Resolvins: A family of bioactive products of omega-3 fatty acid transformation circuits initiated by aspirin treatment that counter proinflammation signals. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merched, A.J.; Ko, K.; Gotlinger, K.H.; Serhan, C.N.; Chan, L. Atherosclerosis: Evidence for impairment of resolution of vascular inflammation governed by specific lipid mediators. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 3595–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N. Resolution Phase of Inflammation: Novel Endogenous Anti-Inflammatory and Proresolving Lipid Mediators and Pathways. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 101–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Nanoparticle Targeting of Neutrophils for Improved Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Health Mater. 2016, 5, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Chu, D.; Wang, Z. Leukocyte-mediated Delivery of Nanotherapeutics in Inflammatory and Tumor Sites. Theranostics 2017, 7, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Chu, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, P.; Huang, H.; Malik, A.B.; Chatterjee, D.K.; Diagaradjane, P.; Krishnan, S.; Fujimoto, I.; et al. Neutrophil-mediated delivery of nanotherapeutics across blood vessel barrier. Ther. Deliv. 2018, 9, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Gao, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z. Nanomedicine for ischemic stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, C.Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, Z. Targeting of Nanotherapeutics to Infection Sites for Antimicrobial Therapy. Adv. Ther. 2019, 2, 1900095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Dong, X.; Wang, Z. Generation, purification and engineering of extracellular vesicles and their biomedical applications. Methods 2019, 177, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z. Engineering bacterial membrane nanovesicles for improved therapies in infectious diseases and cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 186, 114340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z. Remote Co-loading of amphipathic acid drugs in neutrophil nanovesicles infilled with cholesterol mitigates lung bacterial infection and inflammation. Biomaterials 2023, 296, 122071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, S.; Dong, X.; Wang, Z. RGD-expressed bacterial membrane-derived nanovesicles enhance cancer therapy via multiple tumorous targeting. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3301–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gc, J.B.; Szlenk, C.T.; Gao, J.; Dong, X.; Wang, Z.; Natesan, S. Molecular Dynamics Simulations Provide Insight into the Loading Efficiency of Proresolving Lipid Mediators Resolvin D1 and D2 in Cell Membrane-Derived Nanovesicles. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 2155–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Cho, J.; Malik, A.B. Prevention of vascular inflammation by nanoparticle targeting of adherent neutrophils. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-W.; Wang, Q.; Mei, H.-X.; Zheng, S.-X.; Ali, A.M.; Wu, Q.-X.; Ye, Y.; Xu, H.-R.; Xiang, S.-Y.; Jin, S.-W. RvD1 ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury via the suppression of neutrophil infiltration by reducing CXCL2 expression and release from resident alveolar macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 76, 105877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas-Hernández, A.; Espinoza-Pérez, C.; Vivar, R.; Espitia-Corredor, J.; Lillo, J.; Parra-Flores, P.; Sánchez-Ferrer, C.F.; Peiró, C.; Díaz-Araya, G. Resolvin D1 and E1 promote resolution of inflammation in rat cardiac fibroblast in vitro. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, F.; Parisi, M.; Ammendola, R. Distinct Signaling Cascades Elicited by Different Formyl Peptide Receptor 2 (FPR2) Agonists. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 7193–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.-Y.; Liu, Z.-H.; Zhu, Q.; Wen, S.; Yang, C.-X.; Fu, Z.-J.; Sun, T. Resolvin D2 Relieving Radicular Pain is Associated with Regulation of Inflammatory Mediators, Akt/GSK-3β Signal Pathway and GPR18. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 2384–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, J.; Senchenkova, E.Y.; Vital, S.A.; Al-Yafeai, Z.; Kaur, G.; Sparkenbaugh, E.M.; Orr, A.W.; Pawlinski, R.; Hebbel, R.P.; Granger, D.N.; et al. Targeting the anxa1/fpr2/alx pathway regulates neutrophil function, promoting thromboinflammation resolution in sickle cell disease. Blood 2021, 137, 1538–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z. Lung Inflammation Resolution by RvD1 and RvD2 in a Receptor-Dependent Manner. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051527
Gao J, Su Y, Wang Z. Lung Inflammation Resolution by RvD1 and RvD2 in a Receptor-Dependent Manner. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(5):1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051527
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Jin, Yujie Su, and Zhenjia Wang. 2023. "Lung Inflammation Resolution by RvD1 and RvD2 in a Receptor-Dependent Manner" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 5: 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051527
APA StyleGao, J., Su, Y., & Wang, Z. (2023). Lung Inflammation Resolution by RvD1 and RvD2 in a Receptor-Dependent Manner. Pharmaceutics, 15(5), 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051527





