Biocontrol Microneedle Patch: A Promising Agent for Protecting Citrus Fruits from Postharvest Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
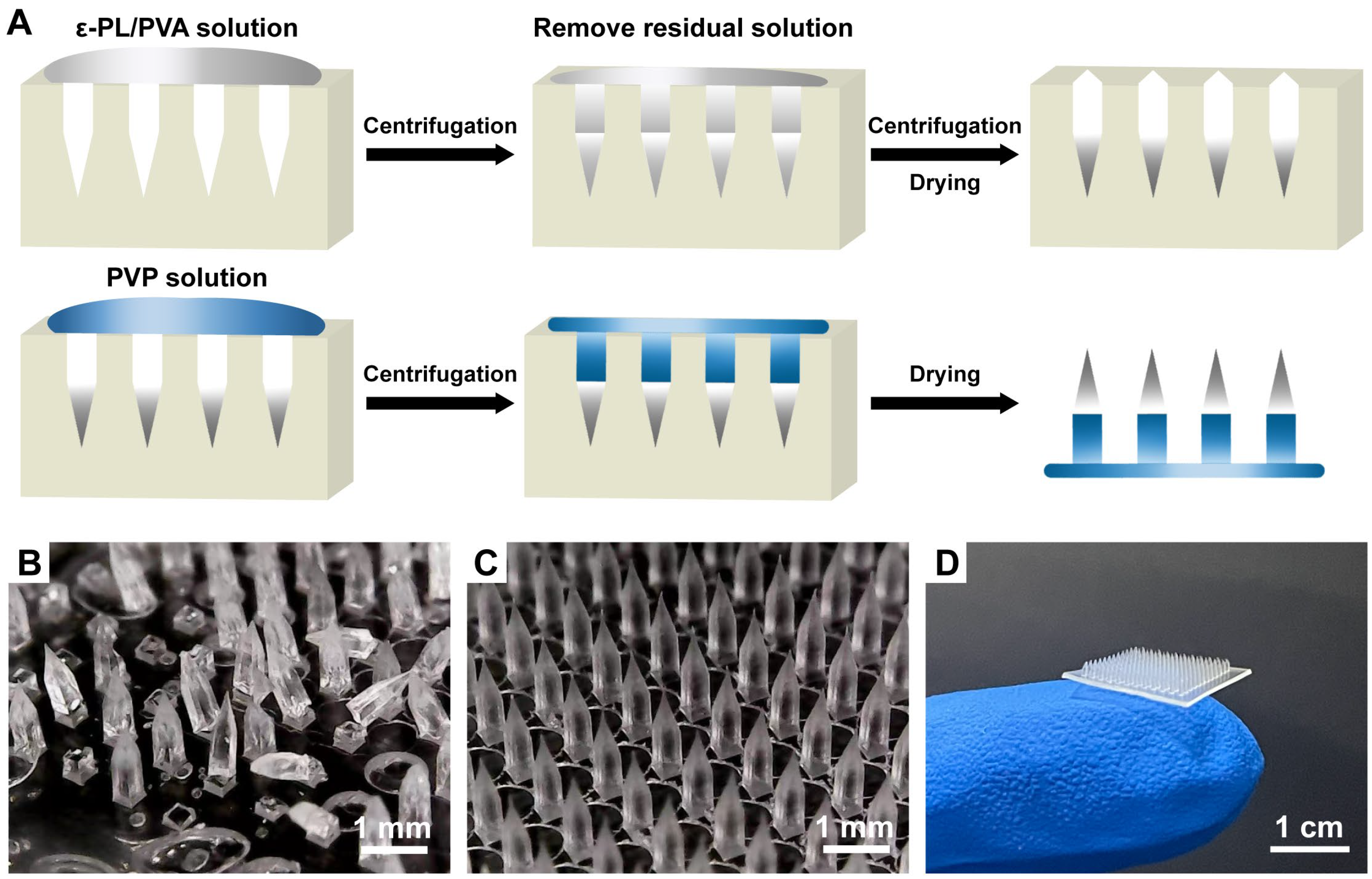
2.2. Fabrication and Imaging Study of Various Microneedles
2.3. Fruit Treatment
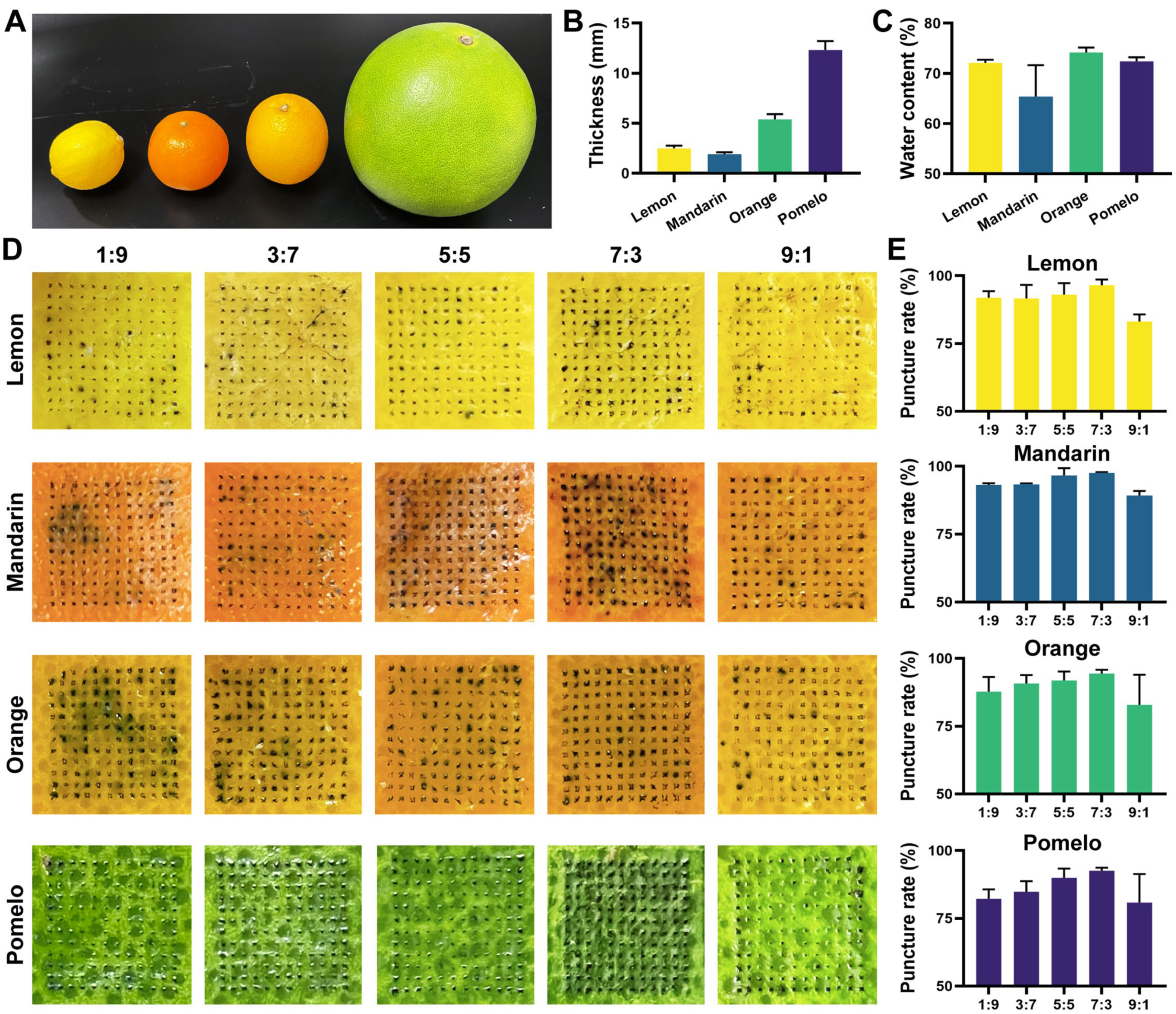
2.4. An Ex Vivo Insertion Test of Various Microneedles in Pericarp
2.5. Determination of the Thickness and Water Content of Various Pericarp
2.6. Drug Loading Amount of BMN
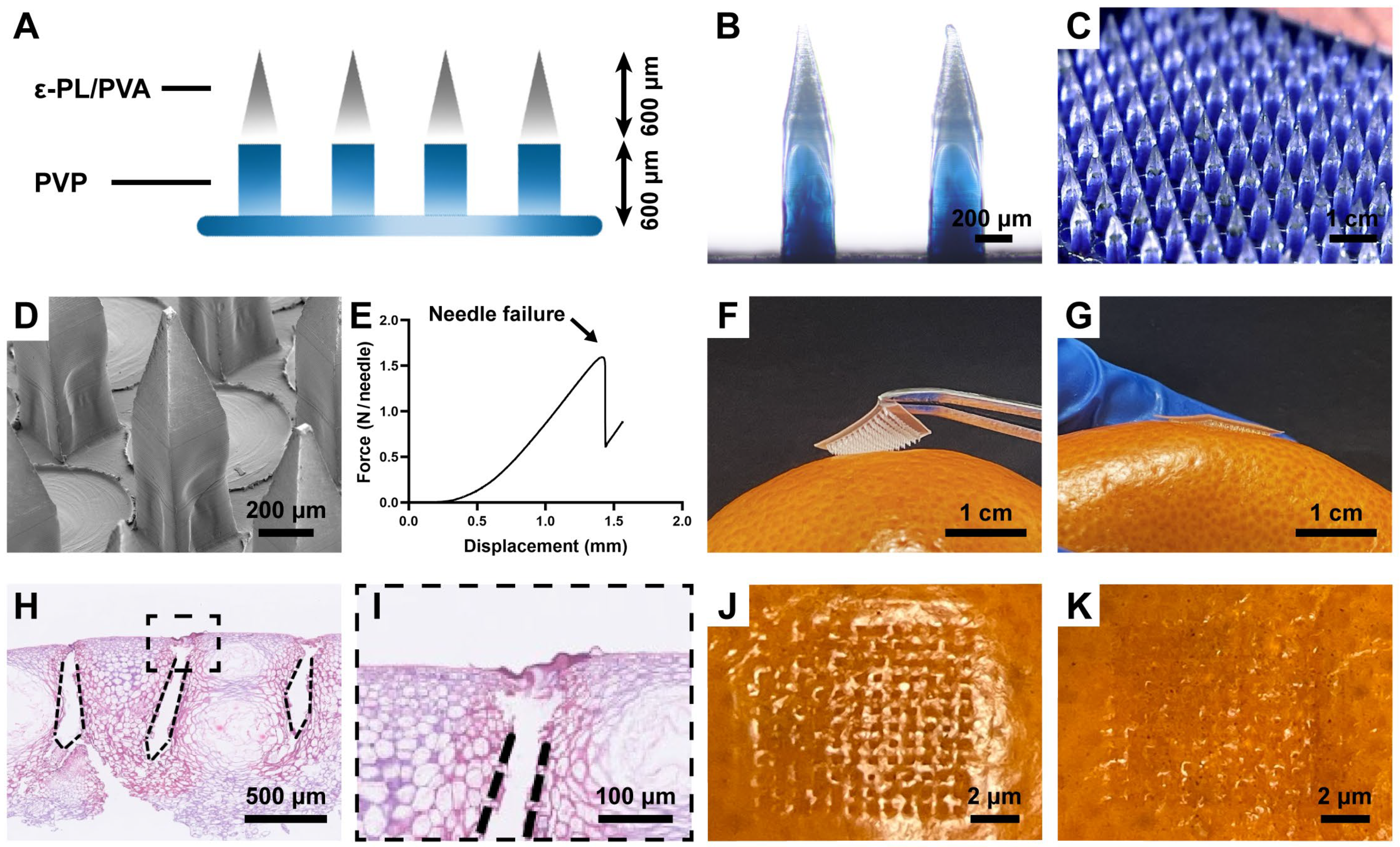
2.7. Microneedle Mechanics
2.8. Pericarp Morphology after Microneedle Insertion
2.9. Dissolution Rate of Microneedle Tip in Pericarp
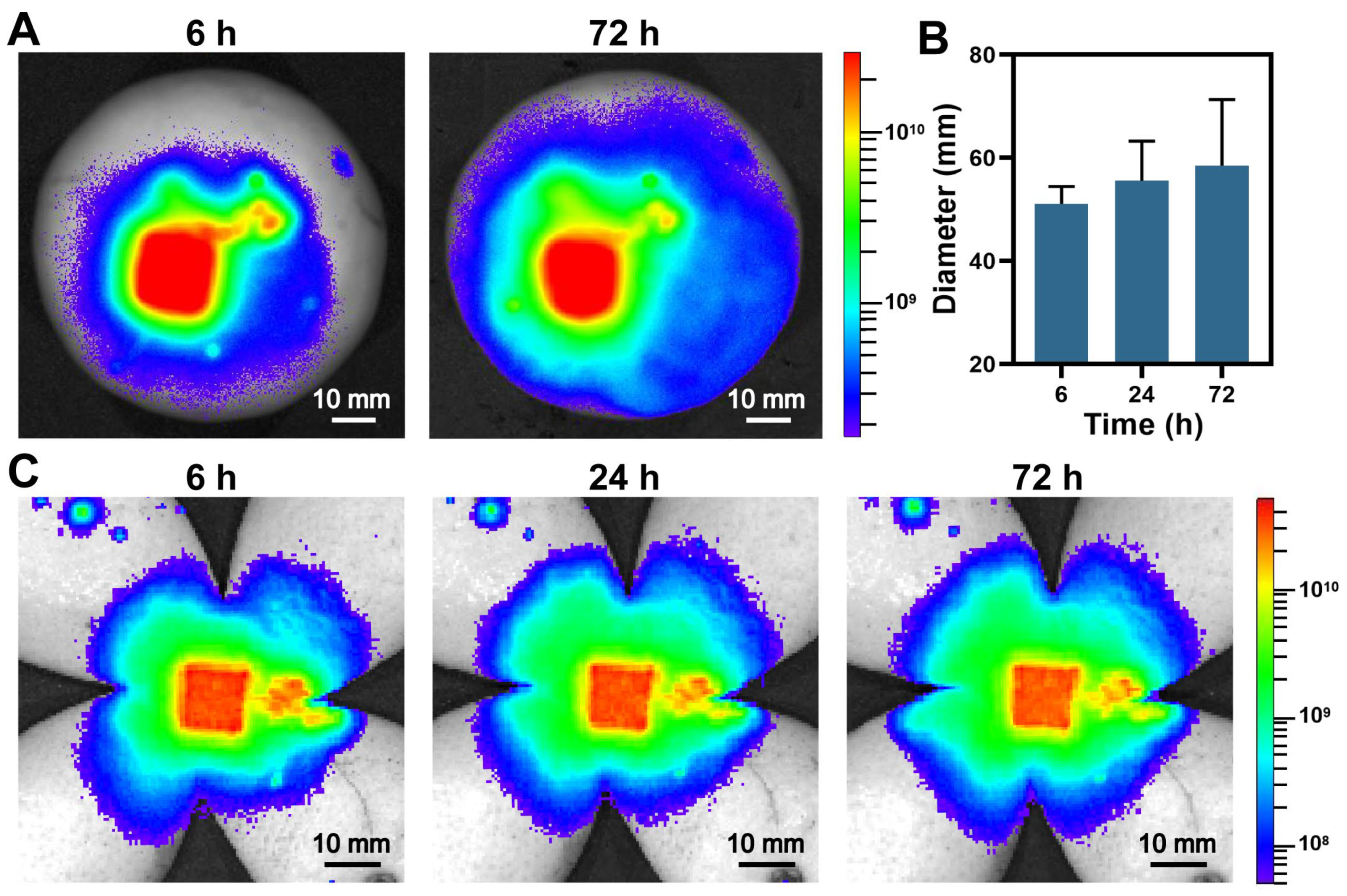
2.10. Study of Drug Distribution after Microneedle Administration
2.11. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
2.12. Fabrication of Microneedles with an Adhesive Label
3. Results and Discussion
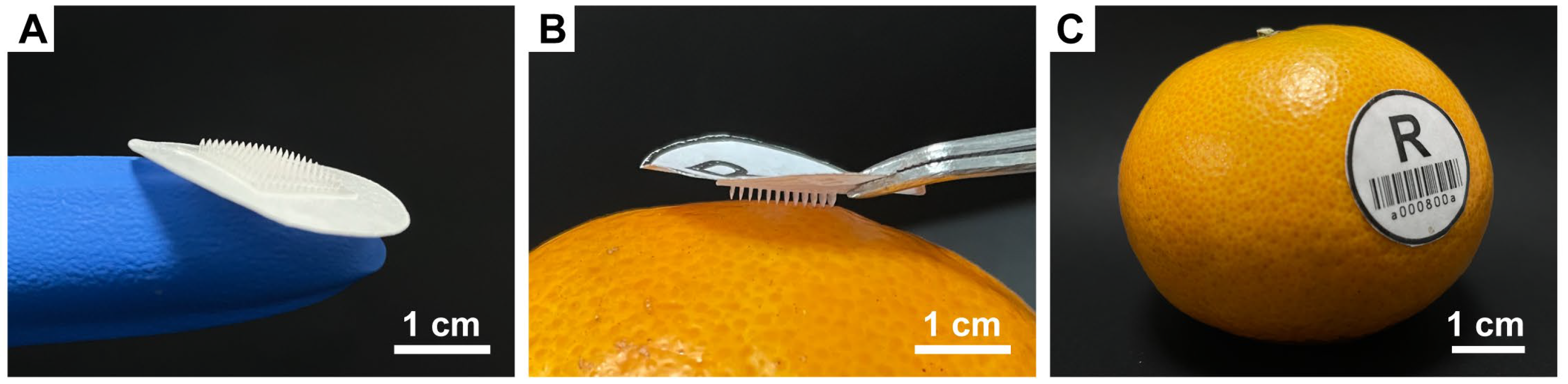
3.1. Preparation of Microneedles Loaded with ε-PL
3.2. Pericarp Insertion Performance and Optimization of Various Microneedles
3.3. Characterization of BMN
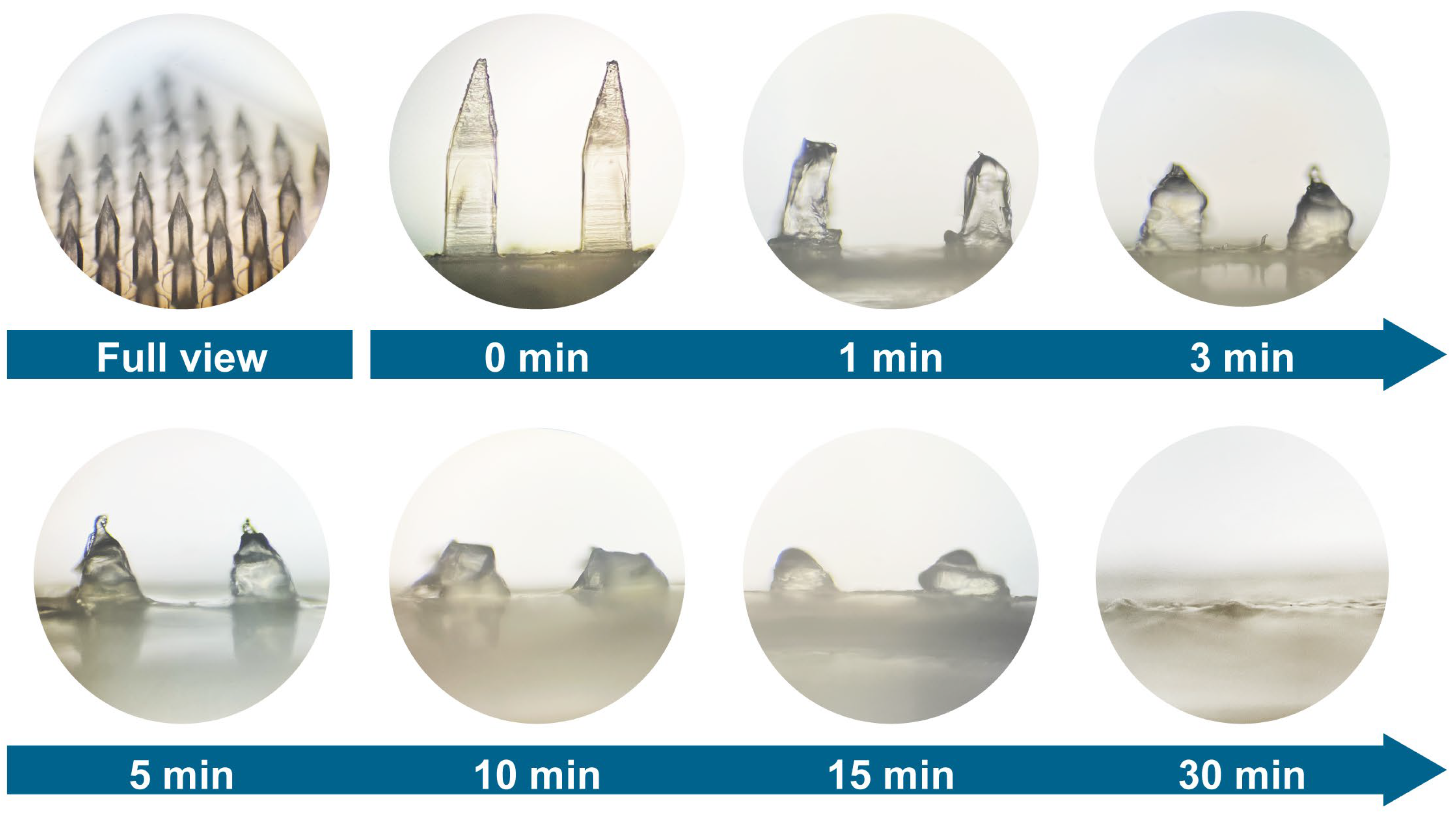
3.4. Dissolution Properties of BMN in Fruit Pericarp
3.5. Antifungal Potential of BMN
3.6. Drug Distribution Study
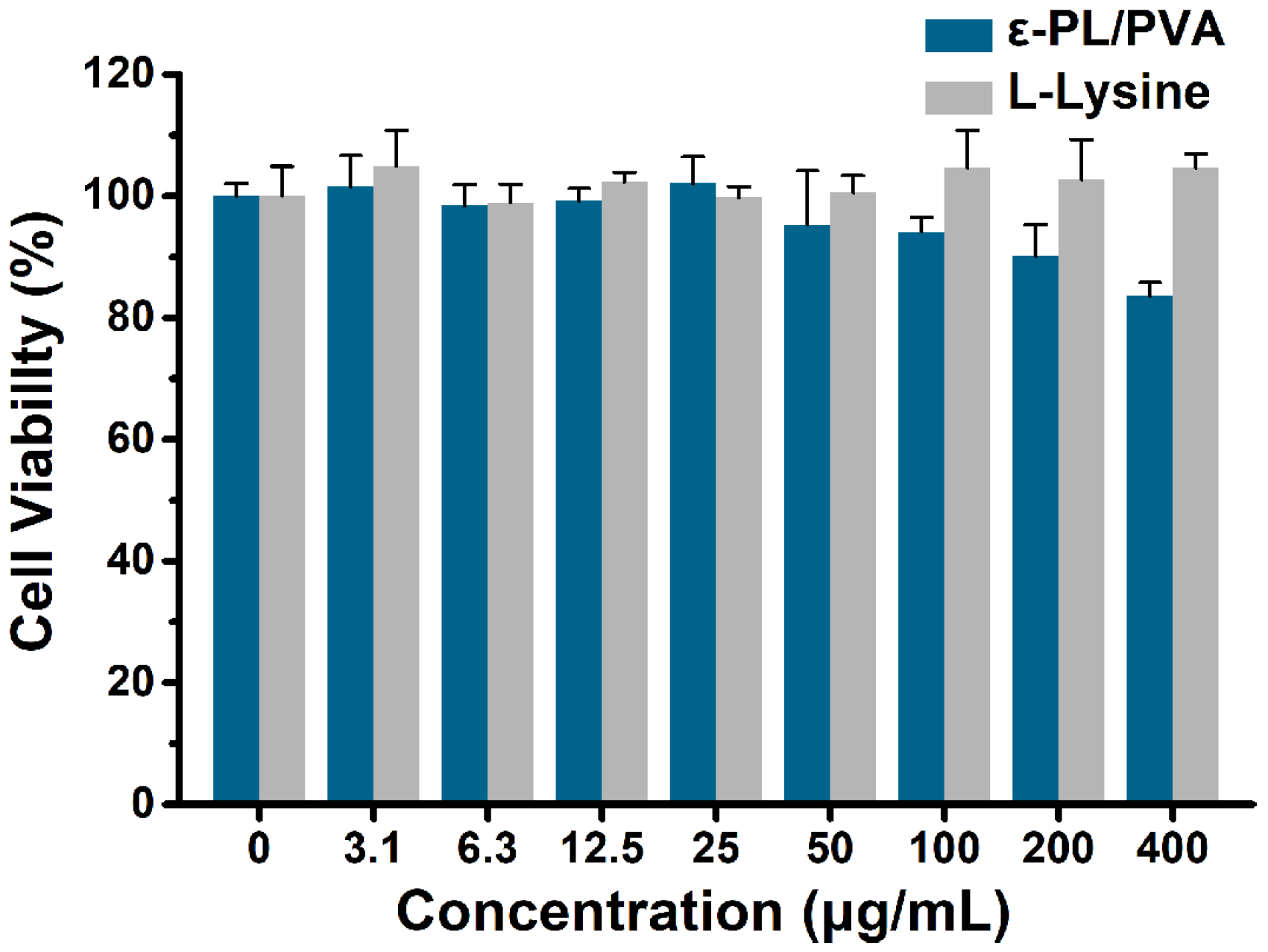
3.7. Cytocompatibility Study
3.8. Adhesive Outer Layer and Its Potential Applications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salem, M.F.; Abd-Elraoof, W.A.; Tayel, A.A.; Alzuaibr, F.M.; Abonama, O.M. Antifungal Application of Biosynthesized Selenium Nanoparticles with Pomegranate Peels and Nanochitosan as Edible Coatings for Citrus Green Mold Protection. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, P.; Dubey, N.K.; Shukla, A.K. Use of some Essential Oils as Post-Harvest Botanical Fungicides in the Management of Grey Mould of Grapes Caused by Botrytis cinerea. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L.; Ngea, G.L.N.; Godana, E.A.; Shi, Y.; Lanhuang, B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, L.N.; Yang, Q.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Zhang, H.Y. Recent Advances in Penicillium expansum Infection Mechanisms and Current Methods in Controlling P. expansum in Postharvest Apples. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, F.X.; Fu, Y.P. Baseline Sensitivity and Fungicidal Action of Propiconazole against Penicillium digitatum. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 172, 104752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Qin, D.K.; Li, W.T.; Wu, F.H.; Li, L.; Liu, X.Q. Inactivation of Penicillium italicum on Kumquat via Plasma-Activated Water and Its Effects on Quality Attributes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 343, 109090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciano-Rosario, D.; Keller, N.P.; Jurick, W.M. Penicillium expansum: Biology, Omics, and Management Tools for a Global Postharvest Pathogen Causing Blue Mould of Pome Fruit. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 21, 1391–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, K.; Liang, Y.; Mengiste, T.; Sharon, A. Killing Softly: A Roadmap of Botrytis cinerea Pathogenicity. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 28, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Saito, S.; Michailides, T.J.; Xiao, C.L. Postharvest Use of Natamycin to Control Alternaria Rot on Blueberry Fruit Caused by Alternaria alternata and A. arborescens. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 172, 111383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Wang, W.J.; Ruan, C.Q.; Deng, L.L.; Yao, S.X.; Zeng, K.F. Involvement of CsWRKY70 in Salicylic Acid-Induced Citrus Fruit Resistance against Penicillium digitatum. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiao, W.X.; Du, Y.M.; Chen, Q.M.; Su, Z.B.; Fu, M.R. Chlorine Dioxide Controls Green Mold Caused by Penicillium digitatum in Citrus Fruits and the Mechanism Involved. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 13897–13905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, U.K. Alternative Management Approaches of Citrus Diseases Caused by Penicillium digitatum (Green Mold) and Penicillium italicum (Blue Mold). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 833328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.M.; Einson, J.E.; Lopez-Pena, C.L.; Song, M.Y.; Xiao, H.; McClements, D.J.; Sela, D.A. Food-Grade Cationic Antimicrobial ε-polylysine Transiently Alters the Gut Microbial Community and Predicted Metagenome Function in CD-1 Mice. NPJ Sci. Food 2017, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.S.; Lu, W.Y.W.; Park, S.H.; Kang, D.H. Control of Foodborne Pathogens on Ready-To-Eat Roast Beef Slurry by Epsilon-polylysine. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Rao, Z.M.; Xu, X.M.; Mao, Z.G.; Chen, X.S. Epsilon-poly-L-lysine: Recent Advances in Biomanufacturing and Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 748976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Sun, S.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, K.T.; Yu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Xin, P.Y.; Chu, J.F.; Zhao, T.M.; Wang, H.Z.; et al. FIS1 Encodes a GA2-oxidase that Regulates Fruit Firmness in Tomato. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Tokunaga, E.; Kobayashi, O.; Hirai, K.; Shibata, N. Current Contributions of Organofluorine Compounds to the Agrochemical Industry. iScience 2020, 23, 101467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Chen, M.L.; Fu, J.T.; Sun, Y.; Lu, C.; Quan, G.L.; Pan, X.; Wu, C.B. Recent Advances in Microneedles-Mediated Transdermal Delivery of Protein and Peptide Drugs. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2326–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Zeng, Y.N.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.Y.; Li, W. Advances in Microneedle Patches for Long-Acting Contraception. Acta Mater. Med. 2023, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.Q.; Xian, D.Y.; Fu, J.T.; Luo, R.; Wang, W.H.; Zheng, Y.W.; He, Q.; Ouyang, Z.; Fang, S.B.; Zhang, W.C.; et al. Four-Armed Host-Defense Peptidomimetics-Augmented Vanadium Carbide MXene-Based Microneedle Array for Efficient Photo-Excited Bacteria-Killing. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 141121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.Y.; Liu, P.; Zhu, J.J.; Lan, J.J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.B.; Zhu, J.T.; Tao, J. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Dissolving Microneedle Patch Loaded with Methotrexate for Improved Treatment of Psoriasis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 43588–43598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Geng, R.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhu, J.T. Advanced Nanocarrier- and Microneedle-Based Transdermal Drug Delivery Strategies for Skin Diseases Treatment. Theranostics 2022, 12, 3372–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaledin, R.; Yiu, C.K.Y.; Zare, E.N.; Niu, L.N.; Vecchione, R.; Chen, G.J.; Gu, Z.; Tay, F.R.; Makvandi, P. Advances in Antimicrobial Microneedle Patches for Combating Infections. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Hu, T.L.; Xu, C.J. A Skin Patch Integrating Swellable Microneedles and Electrochemical Test Strips for Glucose and Alcohol Measurement in Skin Interstitial Fluid. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2022, 10413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.Y.; Liu, H.; Fang, T.S.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, H.Q.; Han, F.; Gao, B.; Li, F.; Xu, F. A Colorimetric Dermal Tattoo Biosensor Fabricated by Microneedle Patch for Multiplexed Detection of Health-Related Biomarkers. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2103030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Zhang, M.Y.; Xu, W.X.; Ling, G.X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, P. Swellable PVA/PVP Hydrogel Microneedle Patches for the Extraction of Interstitial Skin Fluid toward Minimally Invasive Monitoring of Blood Glucose Level. Analyst 2022, 147, 1478–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creighton, R.L.; Woodrow, K.A. Microneedle-Mediated Vaccine Delivery to the Oral Mucosa. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2019, 8, 1801180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolluru, C.; Gomaa, Y.; Prausnitz, M.R. Development of a Thermostable Microneedle Patch for Polio Vaccination. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, J.M.; Dewitt, K.; Scott-Garrard, M.; Chiang, Y.W.; Prausnitz, M.R. Rabies Vaccination in Dogs Using a Dissolving Microneedle Patch. J. Control. Release 2016, 239, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Kim, H.; Park, Y.; Kong, W.H.; Lee, S.W.; Kwok, S.J.J.; Hahn, S.K.; Yun, S.H. Noninvasive Transdermal Vaccination Using Hyaluronan Nanocarriers and Laser Adjuvant. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2512–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, M. Molecular Mass Control Using Polyanionic Cyclodextrin Derivatives for the Epsilon-poly-L-lysine Biosynthesis by Streptomyces. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2009, 45, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Han, Q.; Feng, J.L.; Tian, W.L.; Mo, H.Z. Antibacterial Characteristics and Mechanisms of ɛ-psilon-poly-lysine against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control 2014, 43, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Shettar, A.; Sharma, P.K.; Repka, M.A.; Murthy, S.N. Development of Lysozyme Loaded Microneedles for Dermal Applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 593, 120104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.W.; Yan, Y.L.; Lin, L.M.; He, Q.; Hu, H.H.; Luo, R.; Xian, D.Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Shi, Y.; Zeng, F.P.; et al. Titanium Carbide MXene-based Hybrid Hydrogel for Chemo-Photothermal Combinational Treatment of Localized Bacterial Infection. Acta Biomater. 2022, 142, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.H.; Zhu, C.N.; Long, J.Y.; Lu, C.; Pan, X.; Wu, C.B. PLGA Microsphere-Based Composite Hydrogel for Dual Delivery of Ciprofloxacin and Ginsenoside Rh2 to Treat Staphylococcus aureus-Induced Skin Infections. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.H.; Quan, G.L.; Lu, C.; Pan, X.; Wu, C.B. Dissolving Microneedles Integrated with pH-Responsive Micelles Containing AIEgen with Ultra-Photostability for Enhancing Melanoma Photothermal Therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 5739–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Biodegradable polymer microneedles: Fabrication, Mechanics and Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Control. Release 2005, 104, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillon, C.; Hughes, H.; O’Reilly, N.J.; McLoughlin, P. Formulation and Characterisation of Dissolving Microneedles for the Transdermal Delivery of Therapeutic Peptides. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.M.; Chi, J.Y.; Yan, Y.L.; Luo, R.; Feng, X.Q.; Zheng, Y.W.; Xian, D.Y.; Li, X.; Quan, G.L.; Liu, D.J.; et al. Membrane-Disruptive Peptides/Peptidomimetics-Based Therapeutics: Promising Systems to Combat Bacteria and Cancer in the Drug-Resistant Era. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2609–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Feng, X.Q.; Lin, L.M.; Wang, J.; Chi, J.Y.; Wu, B.Y.; Zhou, G.L.; Yu, F.Y.; Xu, Q.; Liu, D.J.; et al. Virus-Inspired Surface-Nanoengineered Antimicrobial Liposome: A Potential System to Simultaneously Achieve High Activity and Selectivity. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 3207–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.H.; Shi, C.; Cong, Z.H.; Chen, Q.; Bi, Y.F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ma, K.Q.; Liu, S.Q.; Gu, J.W.; Chen, M.Z.; et al. Microbial Metabolite Inspired β-Peptide Polymers Displaying Potent and Selective Antifungal Activity. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2104871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.W.; Zhou, X.J.; Fu, M.R. Inhibiting Effects of Epsilon-poly-lysine (ε-PL) on Pencillium digitatum and Its Involved Mechanism. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2017, 123, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, C.; Li, G.J.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Li, B.Q.; Tian, S.P. The modes of action of epsilon-polylysine (ε-PL) against Botrytis cinerea in jujube fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 147, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.F.; Zhang, L.H.; Liu, M.P.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhao, G.Y.; Zong, W. Effect of Poly-ε-lysine Incorporated into Alginate-Based Edible Coatings on Microbial and Physicochemical Properties of Fresh-Cut Kiwifruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2017, 134, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Routledge, M.N.; Gong, Y.Y.; Godana, E.A.; Dhanasekaran, S.; Yang, Q.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, H.Y. Efficacy of epsilon-poly-L-lysine inhibition of postharvest blue mold in apples and potential mechanisms. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 171, 111346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.Z.; Yang, Q.C.; Zhang, A.C.; Guo, J.; Liu, X.J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Q. Synergistic Effect of the Combined Bio-Fungicides ε-poly-L-lysine and Chitooligosaccharide in Controlling Grey Mould (Botrytis cinerea) in Tomatoes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 276, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Cui, K.B.; Li, Q.Q.; Cao, J.K.; Jiang, W.B. Epsilon-poly-L-lysine (ε-PL) Exhibits Multifaceted Antifungal Mechanisms of Action that Control Postharvest Alternaria Rot. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 348, 109224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.T.; Wang, X.C.; Yang, C.Y.; Huang, R.K.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.J. Microfluidic 3D Printing Polyhydroxyalkanoates-Based Bionicskin for Wound Healing. Mater. Futures 2022, 1, 015401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, L.; Huang, H.; Shi, X.; Wu, J.; Ye, J.; Xu, Q.; Fang, S.; Wu, C.; Luo, R.; Lu, C.; et al. Biocontrol Microneedle Patch: A Promising Agent for Protecting Citrus Fruits from Postharvest Infection. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041219
Jiang L, Huang H, Shi X, Wu J, Ye J, Xu Q, Fang S, Wu C, Luo R, Lu C, et al. Biocontrol Microneedle Patch: A Promising Agent for Protecting Citrus Fruits from Postharvest Infection. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(4):1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041219
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Ling, Huan Huang, Xingyu Shi, Jian Wu, Juexian Ye, Qian Xu, Shaobin Fang, Chuanbin Wu, Rui Luo, Chao Lu, and et al. 2023. "Biocontrol Microneedle Patch: A Promising Agent for Protecting Citrus Fruits from Postharvest Infection" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 4: 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041219
APA StyleJiang, L., Huang, H., Shi, X., Wu, J., Ye, J., Xu, Q., Fang, S., Wu, C., Luo, R., Lu, C., & Liu, D. (2023). Biocontrol Microneedle Patch: A Promising Agent for Protecting Citrus Fruits from Postharvest Infection. Pharmaceutics, 15(4), 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041219






