Paclitaxel-Loaded Lipid-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Dual Chemo-Magnetic Hyperthermia Therapy of Melanoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Manganese Ferrite (MnFe2O4) Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNP)
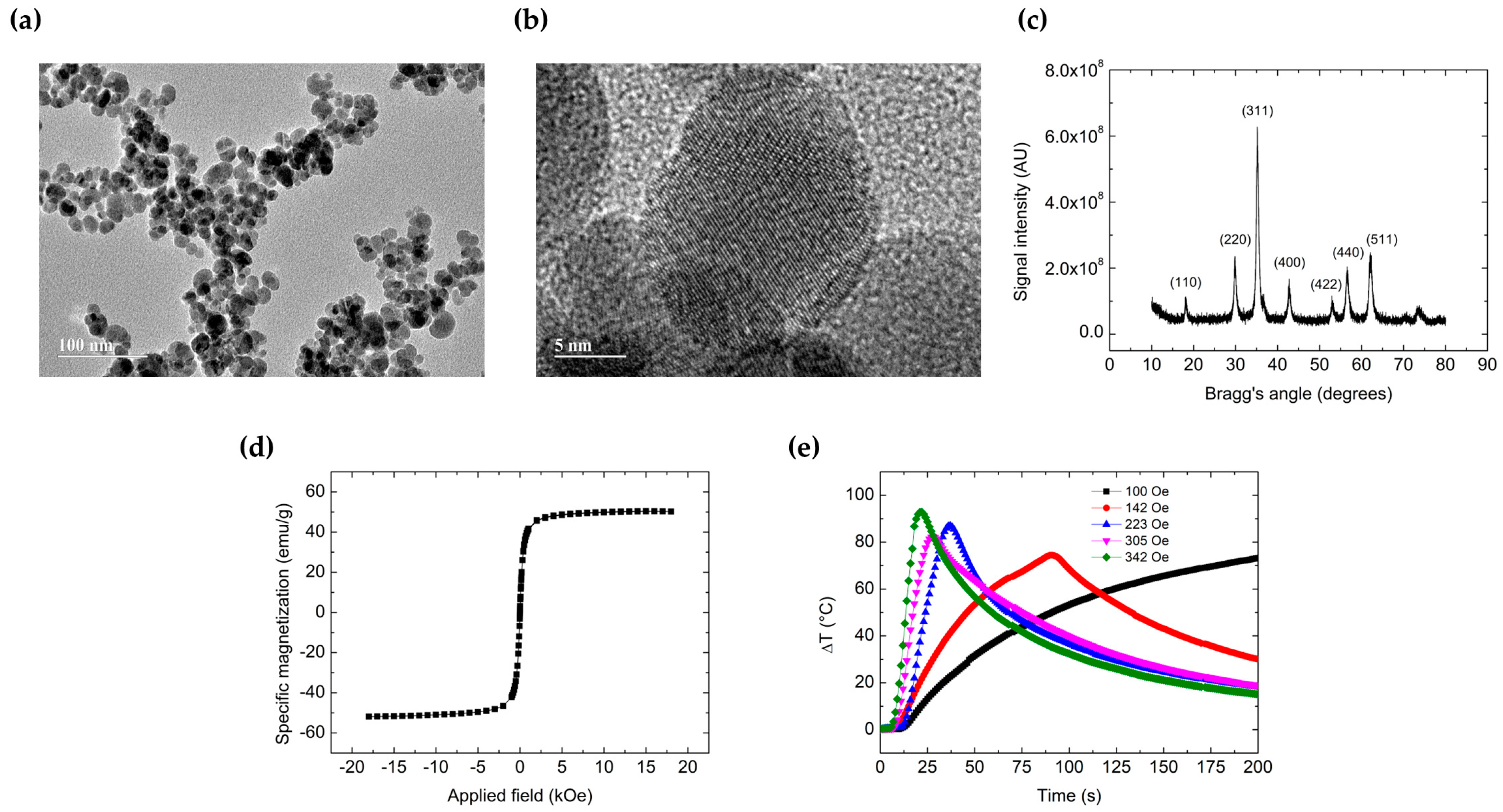
2.3. Characterization of MnFe2O4 MNP
2.4. Preparation of PTX-Loaded Lipid-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles (PTX-LMNP)
2.5. Characterization of PTX-LMNP
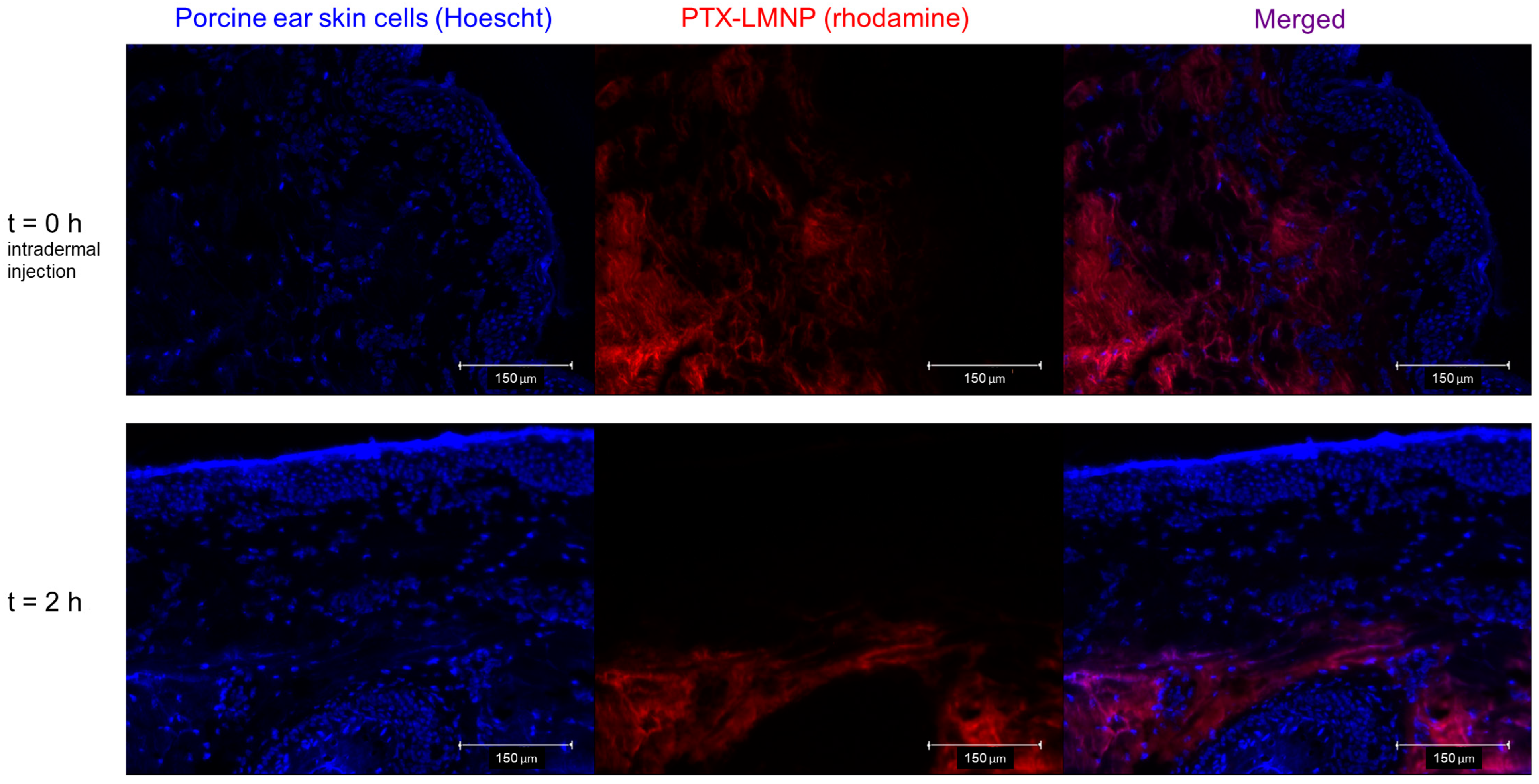
2.6. PTX-LMNP Distribution in Porcine Ear Skin
2.7. PTX-LMNP In Vitro Drug Release Profile
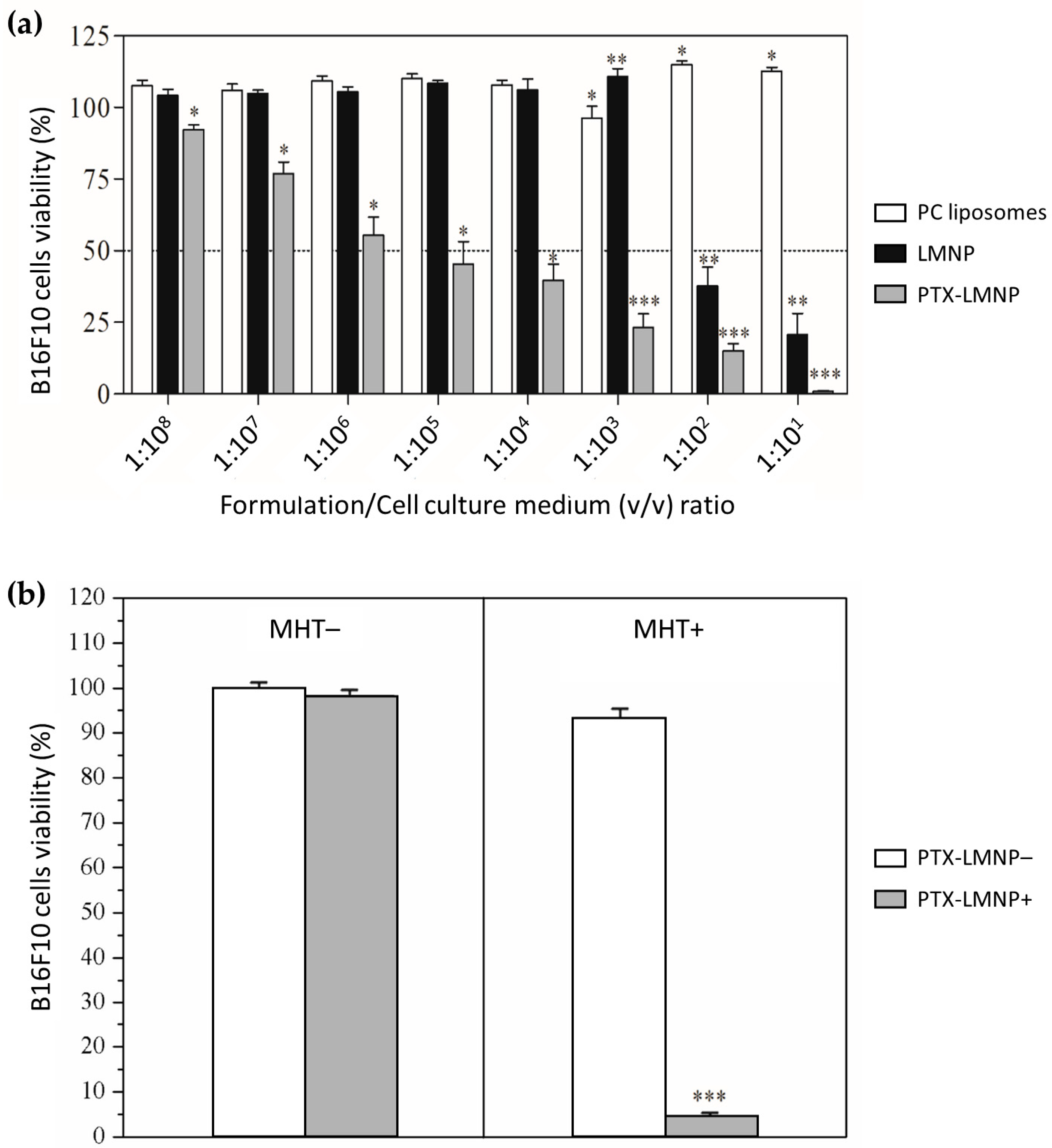
2.8. PTX-LMNP Cytotoxicity against B16F10 Melanoma Cells
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of MnFe2O4 MNP
3.2. Characterization of PTX-LMNP
3.3. PTX-LMNP Distribution in Porcine Ear Skin
3.4. PTX-LMNP In Vitro Drug Release Profile
3.5. PTX-LMNP Cytotoxicity against B16F10 Melanoma Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International World Cancer Research Fund. Skin Cancer Statistics. Available online: https://www.wcrf.org/cancer-trends/skin-cancer-statistics/ (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Lens, M.B.; Dawes, M. Global Perspectives of Contemporary Epidemiological Trends of Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2004, 150, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hersh, E.M.; Del Vecchio, M.; Brown, M.P.; Kefford, R.; Loquai, C.; Testori, A.; Bhatia, S.; Gutzmer, R.; Conry, R.; Haydon, A.; et al. A Randomized, Controlled Phase III Trial of Nab-Paclitaxel versus Dacarbazine in Chemotherapy-Naïve Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 2267–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pflugfelder, A.; Eigentler, T.K.; Keim, U.; Weide, B.; Leiter, U.; Ikenberg, K.; Berneburg, M.; Garbe, C. Effectiveness of Carboplatin and Paclitaxel as First- and Second-Line Treatment in 61 Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, R.D.; Holtan, S.G.; Ingle, J.N.; Croghan, G.A.; Kottschade, L.A.; Creagan, E.T.; Kaur, J.S.; Pitot, H.C.; Markovic, S.N. Combination of Paclitaxel and Carboplatin as Second-Line Therapy for Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. Cancer 2006, 106, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bombelli, F.B.; Webster, C.A.; Moncrieff, M.; Sherwood, V. The Scope of Nanoparticle Therapies for Future Metastatic Melanoma Treatment. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e22–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiff, P.B.; Fant, J.; Horwitz, S.B. Promotion of Microtubule Assembly in Vitro by Taxol. Nature 1979, 277, 665–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, K.H.; Gertsch, J. Anticancer Drugs from Nature-Natural Products as a Unique Source of New Microtubule-Stabilizing Agents. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 327–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-J.; Hong, S.-S.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, J.O.; Lee, M.-K.; Kim, S.H. Development of Paclitaxel-Loaded Liposomal Nanocarrier Stabilized by Triglyceride Incorporation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 4465–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ling, L.; Du, Y.; Yao, C.; Li, X. Reduction Responsive Liposomes Based on Paclitaxel-Ss-Lysophospholipid with High Drug Loading for Intracellular Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 564, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Kumar, D.; Swarnakar, N.K.; Thanki, K. Polyelectrolyte Stabilized Multilayered Liposomes for Oral Delivery of Paclitaxel. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6758–6768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Yan, C.; Liu, K.; Tao, J.; Guo, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, F.; Gu, N. Paclitaxel-Loaded Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Application in Targeting. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Ding, D.; Gong, X.; Keidar, M.; Zhang, W. Paclitaxel-Loaded Core–Shell Magnetic Nanoparticles and Cold Atmospheric Plasma Inhibit Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Growth. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 43462–43471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, R.R.; Carrião, M.S.; Pacheco, M.T.; Branquinho, L.C.; de Souza, A.L.R.; Bakuzis, A.F.; Lima, E.M. Triggered Release of Paclitaxel from Magnetic Solid Lipid Nanoparticles by Magnetic Hyperthermia. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abriata, J.P.; Turatti, R.C.; Luiz, M.T.; Raspantini, G.L.; Tofani, L.B.; do Amaral, R.L.F.; Swiech, K.; Marcato, P.D.; Marchetti, J.M. Development, Characterization and Biological In Vitro Assays of Paclitaxel-Loaded PCL Polymeric Nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 96, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Fu, S.; Peng, Q.; Han, Y.; Xie, J.; Zan, N.; Chen, Y.; Fan, J. Paclitaxel-Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles Combined with Chronomodulated Chemotherapy on Lung Cancer: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 516, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Cho, C.W. Modification of Paclitaxel-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles with 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Enhances Absorption and Reduces Nephrotoxicity Associated with Intravenous Injection. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 5397–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, I.; De, K.; Mukherjee, D.; Dey, G.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Mukherjee, M.; Mandal, M.; Bandyopadhyay, A.K.; Gupta, A.; Ganguly, S.; et al. Paclitaxel-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Modified with Tyr-3-Octreotide for Enhanced Anti-Angiogenic and Anti-Glioma Therapy. Acta Biomater. 2016, 38, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosta, F.V.; Andrade, L.M.; Mendes, L.P.; Anjos, J.L.V.; Alonso, A.; Marreto, R.N.; Lima, E.M.; Taveira, S.F. Paclitaxel-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles for Topical Application: The Influence of Oil Content on Lipid Dynamic Behavior, Stability, and Drug Skin Penetration. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2014, 16, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.M.; Guo, J.; Zhang, L.J.; Wang, Q.S.; Fang, X.L. Pharmacokinetics and Biodistribution of Polymeric Micelles of Paclitaxel with Pluronic P123. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2006, 27, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Huh, K.M.; Lee, J.; Cho, Y.W.; Galinsky, R.E.; Park, K. Hydrotropic Polymeric Micelles for Enhanced Paclitaxel Solubility: In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idris, N.M.; Gnanasammandhan, M.K.; Zhang, J.; Ho, P.C.; Mahendran, R.; Zhang, Y. In Vivo Photodynamic Therapy Using Upconversion Nanoparticles as Remote-Controlled Nanotransducers. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1580–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busetti, A.; Soncin, M.; Jori, G.; Rodgers, M.A.J. High Efficiency of Benzoporphyrin Derivative in the Photodynamic Therapy of Pigmented Malignant Melanoma. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 79, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branquinho, L.C.; Carrião, M.S.; Costa, A.S.; Zufelato, N.; Sousa, M.H.; Miotto, R.; Ivkov, R.; Bakuzis, A.F. Effect of Magnetic Dipolar Interactions on Nanoparticle Heating Efficiency: Implications for Cancer Hyperthermia. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balivada, S.; Rachakatla, R.S.; Wang, H.; Samarakoon, T.N.; Dani, R.K.; Pyle, M.; Kroh, F.O.; Walker, B.; Leaym, X.; Koper, O.B.; et al. A/C Magnetic Hyperthermia of Melanoma Mediated by Iron(0)/Iron Oxide Core/Shell Magnetic Nanoparticles: A Mouse Study. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrião, M.S.; Bakuzis, A.F. Mean-Field and Linear Regime Approach to Magnetic Hyperthermia of Core–Shell Nanoparticles: Can Tiny Nanostructures Fight Cancer? Nanoscale 2016, 8, 8363–8377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, V.R.R.; Vinícius-Araújo, M.; Shrivastava, N.; Sousa, M.H.; Coaquira, J.A.H.; Bakuzis, A.F. Role of the Fraction of Blocked Nanoparticles on the Hyperthermia Efficiency of Mn-Based Ferrites at Clinically Relevant Conditions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 27725–27734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Lim, M.; Goos, J.A.C.M.; Qiao, R.; Ng, Y.Y.; Mansfeld, F.M.; Jackson, M.; Davis, T.P.; Kavallaris, M. Biologically Targeted Magnetic Hyperthermia: Potential and Limitations. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.; Tavares, A.J.; Dai, Q.; Ohta, S.; Audet, J.; Dvorak, H.F.; Chan, W.C.W. Analysis of Nanoparticle Delivery to Tumours. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi-Sohi, R.; Maghari, S.; Raoufi, M.; Jalali, S.A.; Hajipour, M.J.; Ghassempour, A.; Mahmoudi, M. Bypassing Protein Corona Issue on Active Targeting: Zwitterionic Coatings Dictate Specific Interactions of Targeting Moieties and Cell Receptors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 22808–22818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Thanh, N.K.T.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Progress in Applications of Magnetic Nanoparticles in Biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 224001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southern, P.; Pankhurst, Q.A. Commentary on the Clinical and Preclinical Dosage Limits of Interstitially Administered Magnetic Fluids for Therapeutic Hyperthermia Based on Current Practice and Efficacy Models. Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 34, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, A.; Scholz, R.; Wust, P.; Schirra, H.; Schiestel, T.; Schmidt, H.; Felix, R. Endocytosis of Dextran and Silan-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles and the Effect of Intracellular Hyperthermia on Human Mammary Carcinoma Cells in Vitro. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 194, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgill, D.P.; Porter, S.A.; Taylor, H.O. Heat Injury to Cells in Perfused Systems. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1066, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, H.F.; Capistrano, G.; Bakuzis, A.F. In Vivo Magnetic Nanoparticle Hyperthermia: A Review on Preclinical Studies, Low-Field Nano-Heaters, Noninvasive Thermometry and Computer Simulations for Treatment Planning. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 76–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, P.; Ke, X.; Xia, G.; Chen, B. Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles and Chemotherapy Agents Interact Synergistically to Induce Apoptosis in Lymphoma Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, M.-Y.; Liu, H.-L.; Yang, H.-W.; Chen, P.-Y.; Tsai, R.-Y.; Huang, C.-Y.; Tseng, I.-C.; Lyu, L.-A.; Ma, C.-C.; Tang, H.-J.; et al. The Effectiveness of a Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based Delivery System for BCNU in the Treatment of Gliomas. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-W.; Hua, M.-Y.; Liu, H.-L.; Huang, C.-Y.; Tsai, R.-Y.; Lu, Y.-J.; Chen, J.-Y.; Tang, H.-J.; Hsien, H.-Y.; Chang, Y.-S.; et al. Self-Protecting Core-Shell Magnetic Nanoparticles for Targeted, Traceable, Long Half-Life Delivery of BCNU to Gliomas. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6523–6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-W.; Hua, M.-Y.; Liu, H.-L.; Tsai, R.-Y.; Chuang, C.-K.; Chu, P.-C.; Wu, P.-Y.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chuang, H.-C.; Yu, K.-J.; et al. Cooperative Dual-Activity Targeted Nanomedicine for Specific and Effective Prostate Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-W.; Hua, M.-Y.; Liu, H.-L.; Tsai, R.-Y.; Pang, S.-T.; Hsu, P.-H.; Tang, H.-J.; Yen, T.-C.; Chuang, C.-K. An Epirubicin–Conjugated Nanocarrier with MRI Function to Overcome Lethal Multidrug-Resistant Bladder Cancer. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3919–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadollahpour, A.; Rashidi, S. Magnetic Nanoparticles: A Review of Chemical and Physical Characteristics Important in Medical Applications. Orient. J. Chem. 2015, 31, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Long, R.; Wang, S.; Kankala, R.K.; Wang, J.; Jiang, W.; Liu, Y. Bacterial Magnetosomes as an Efficient Gene Delivery Platform for Cancer Theranostics. Microb. Cell Factories 2017, 16, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.; Dai, Q.; Zhou, X.; Cai, D.; Hong, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. Bacterial Magnetosomes-Based Nanocarriers for Co-Delivery of Cancer Therapeutics in Vitro. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 8269–8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Basit, A.; Miao, T.; Liu, W.; Jiang, W. Bacterial Magnetosomes Loaded with Doxorubicin and Transferrin Improve Targeted Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nanotheranostics 2019, 3, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alphandéry, E.; Chebbi, I.; Guyot, F.; Durand-Dubief, M. Use of Bacterial Magnetosomes in the Magnetic Hyperthermia Treatment of Tumours: A Review. Int. J. Hyperth. 2013, 29, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usov, N.A.; Gubanova, E.M. Application of Magnetosomes in Magnetic Hyperthermia. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkwill, D.L.; Maratea, D.; Blakemore, R.P. Ultrastructure of a Magnetotactic Spirillum. J. Bacteriol. 1980, 141, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Tang, T.; Duan, J.; Xu, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Li, Y. Biocompatibility of Bacterial Magnetosomes: Acute Toxicity, Immunotoxicity and Cytotoxicity. Nanotoxicology 2010, 4, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintra, E.R.; Hayasaki, T.G.; Sousa-Junior, A.A.; Silva, A.C.G.; Valadares, M.C.; Bakuzis, A.F.; Mendanha, S.A.; Lima, E.M. Folate-Targeted PEGylated Magnetoliposomes for Hyperthermia-Mediated Controlled Release of Doxorubicin. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 854430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourinho, F.A.; Franck, R.; Massart, R. Aqueous Ferrofluids Based on Manganese and Cobalt Ferrites. J. Mater. Sci. 1990, 25, 3249–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, P. Bestimmung Der Größe Und Der Inneren Struktur von Kolloidteilchen Mittels Röntgenstrahlen. Nachr. Ges. Wiss. Göttingen Math. Kl. 1918, 1918, 98–100. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobi, U.; Kaiser, M.; Toll, R.; Mangelsdorf, S.; Audring, H.; Otberg, N.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Porcine Ear Skin: An in Vitro Model for Human Skin. Ski. Res. Technol. 2007, 13, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpentier, A.; McNichols, R.J.; Stafford, R.J.; Itzcovitz, J.; Guichard, J.P.; Reizine, D.; Delaloge, S.; Vicaut, E.; Payen, D.; Gowda, A.; et al. Real-Time Magnetic Resonance-Guided Laser Thermal Therapy for Focal Metastatic Brain Tumors. Neurosurgery 2008, 63, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, J.; Dorfman, J. Spontaneous and Induced Magnetisation in Ferromagnetic Bodies. Nature 1930, 126, 274–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiles, D.C. Modelling the Effects of Eddy Current Losses on Frequency Dependent Hysteresis in Electrically Conducting Media. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1994, 30, 4326–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zufelato, N.; Aquino, V.R.R.; Shrivastava, N.; Mendanha, S.; Miotto, R.; Bakuzis, A.F. Heat Generation in Magnetic Hyperthermia by Manganese Ferrite-Based Nanoparticles Arises from Néel Collective Magnetic Relaxation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 7521–7539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschi, M.L. Mathematical Models of Drug Release. In Strategies to Modify the Drug Release from Pharmaceutical Systems; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 63–86. ISBN 9780081000922. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, R.R.; Ferreira, F.S.; Cintra, E.R.; Branquinho, L.C.; Bakuzis, A.F.; Lima, E.M. Magnetic Nanoparticles and Rapamycin Encapsulated into Polymeric Nanocarriers. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2012, 8, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz de Escalona, M.; Sáez-Fernández, E.; Prados, J.C.; Melguizo, C.; Arias, J.L. Magnetic Solid Lipid Nanoparticles in Hyperthermia against Colon Cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 504, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, X.; Miao, Y.; Li, J.; Gan, Y. Lipid-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Dual-Modal Imaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, A.A.; Sadat, M.E.; Potter, S.J.; Mast, D.B.; Mohamed, D.F.; Habib, F.S.; Pauletti, G.M. Stability and Magnetically Induced Heating Behavior of Lipid-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Guan, J.; Yoo, J.-W.; Epstein, A.J.; Lee, L.J.; Lee, R.J. Cationic Lipid-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles Associated with Transferrin for Gene Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 358, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, X.-Y.; Du, Y.-Z.; Hong, L.-H.; Yuan, H.; Hu, F.-Q. Magnetic Lipid Nanoparticles Loading Doxorubicin for Intracellular Delivery: Preparation and Characteristics. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Cai, Q.; Tang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, T.; Xu, H.; Wang, S.; Fan, K.; Liu, Z.; et al. PEGylated Lipid Bilayer Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Co-Delivery of Paclitaxel and Curcumin: Design, Characterization and Its Cytotoxic Effect. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 536, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Situ, A.; Wu, B.; Ji, Z.; Chang, C.H.; Nel, A.E. Use of a Lipid-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Platform for Synergistic Gemcitabine and Paclitaxel Delivery to Human Pancreatic Cancer in Mice. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3540–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, K.; Haque, M.; Kumar, A.; Hoq, A.; Hyder, F.; Hoque, S.M. Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticles (MnFe2O4): Size Dependence for Hyperthermia and Negative/Positive Contrast Enhancement in MRI. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Ma, S.; Sun, J.; Xia, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Gao, F.; Gong, Q.; Song, B. Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticle Micellar Nanocomposites as MRI Contrast Agent for Liver Imaging. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2919–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinícius-Araújo, M.; Shrivastava, N.; Sousa-Junior, A.A.; Mendanha, S.A.; de Santana, R.C.; Bakuzis, A.F. ZnxMn1-XFe2O4@SiO2:ZNd+3 Core-Shell Nanoparticles for Low-Field Magnetic Hyperthermia and Enhanced Photothermal Therapy with the Potential for Nanothermometry. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 2190–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regenold, M.; Bannigan, P.; Evans, J.C.; Waspe, A.; Temple, M.J.; Allen, C. Turning down the Heat: The Case for Mild Hyperthermia and Thermosensitive Liposomes. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2022, 40, 102484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray-Schopfer, V.; Wellbrock, C.; Marais, R. Melanoma Biology and New Targeted Therapy. Nature 2007, 445, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, A.; Di Corato, R.; Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Flaud, P.; Pellegrino, T.; Wilhelm, C. Duality of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy: Amplification of Heating Efficiency by Magnetic Hyperthermia and Photothermal Bimodal Treatment. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2436–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, G.; Dewhirst, M.W. Hyperthermia and Liposomes. Int. J. Hyperth. 1999, 15, 345–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, K.; Nakamura, M.; Koumoto, K. Magnetoresponsive Smart Capsules Formed with Polyelectrolytes, Lipid Bilayers and Magnetic Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, M.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Jahangir Alam, S.M.; Gui, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cao, L.; Liang, G.; Hu, G. Preparation of Magadiite-Sodium Alginate Drug Carrier Composite by Pickering-Emulsion-Templated-Encapsulation Method and Its Properties of Sustained Release Mechanism by Baker–Lonsdale and Korsmeyer–Peppas Model. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 3890–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovita, C.; Florea, A.; Scorus, L.; Pall, E.; Dudric, R.; Moldovan, A.I.; Stiufiuc, R.; Tetean, R.; Lucaciu, C.M. Hyperthermia, Cytotoxicity, and Cellular Uptake Properties of Manganese and Zinc Ferrite Magnetic Nanoparticles Synthesized by a Polyol-Mediated Process. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, N.; Shirsath, N.; Singh, A.; Joshi, K.S.; Banerjee, R. Endogenous Lung Surfactant Inspired PH Responsive Nanovesicle Aerosols: Pulmonary Compatible and Site-Specific Drug Delivery in Lung Metastases. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Q.; Qi, T.; Fu, X.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, G.; Zhao, X.; Sun, Q.; et al. Enzyme Responsiveness Enhances the Specificity and Effectiveness of Nanoparticles for the Treatment of B16F10 Melanoma. J. Control. Release 2019, 316, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asín, L.; Ibarra, M.R.; Tres, A.; Goya, G.F. Controlled Cell Death by Magnetic Hyperthermia: Effects of Exposure Time, Field Amplitude, and Nanoparticle Concentration. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hao, J.; Sha, X.; Fang, X. The Potential of Pluronic Polymeric Micelles Encapsulated with Paclitaxel for the Treatment of Melanoma Using Subcutaneous and Pulmonary Metastatic Mice Models. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 5934–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Lugo, M.; Rodriguez, H.L.; Latorre-Esteves, M.; Mendez, J.; Soto, O.; Rodriguez, A.R.; Rinaldi, C. Enhanced Reduction in Cell Viability by Hyperthermia Induced by Magnetic Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toraya-Brown, S.; Fiering, S. Local Tumour Hyperthermia as Immunotherapy for Metastatic Cancer. Int. J. Hyperth. 2014, 30, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toraya-Brown, S.; Sheen, M.R.; Zhang, P.; Chen, L.; Baird, J.R.; Demidenko, E.; Turk, M.J.; Hoopes, P.J.; Conejo-Garcia, J.R.; Fiering, S. Local Hyperthermia Treatment of Tumors Induces CD8+ T Cell-Mediated Resistance against Distal and Secondary Tumors. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2014, 10, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soetaert, F.; Korangath, P.; Serantes, D.; Fiering, S.; Ivkov, R. Cancer Therapy with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Agents of Thermal and Immune Therapies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 163–164, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbet, M.J.; Singh, A.; Mao, C.; Fiering, S.; Ranjan, A. Using Nanoparticles for in Situ Vaccination against Cancer: Mechanisms and Immunotherapy Benefits. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebeke, L.C.; Castillo Gómez, J.D.; Heijman, E.; Rademann, P.; Simon, A.C.; Ekdawi, S.; Vlachakis, S.; Toker, D.; Mink, B.L.; Schubert-Quecke, C.; et al. Hyperthermia-Induced Doxorubicin Delivery from Thermosensitive Liposomes via MR-HIFU in a Pig Model. J. Control. Release 2022, 343, 798–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.A.; Wang, C.; Fiering, S.; Steinmetz, N.F. In Situ Vaccination with Cowpea vs Tobacco Mosaic Virus against Melanoma. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 3700–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoopes, P.J.; Wagner, R.J.; Duval, K.; Kang, K.; Gladstone, D.J.; Moodie, K.L.; Crary-Burney, M.; Ariaspulido, H.; Veliz, F.A.; Steinmetz, N.F.; et al. Treatment of Canine Oral Melanoma with Nanotechnology-Based Immunotherapy and Radiation. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 3717–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
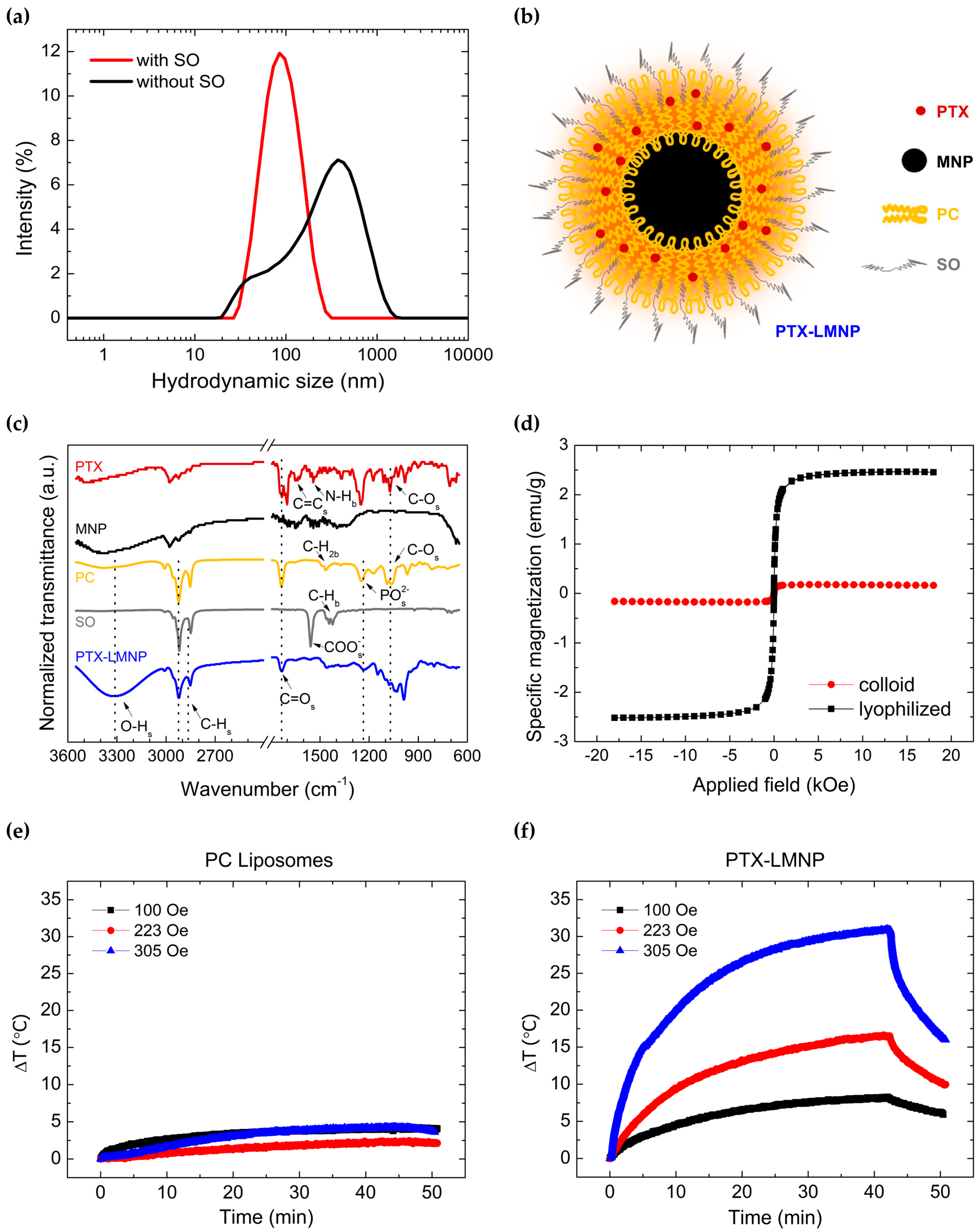

| Sample | DH (nm) | PdI |
|---|---|---|
| without SO | 186 ± 1 | 0.50 ± 0.15 |
| with SO | 90 ± 1 | 0.26 ± 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, R.R.; Cintra, E.R.; Sousa-Junior, A.A.; Moreira, L.C.; da Silva, A.C.G.; de Souza, A.L.R.; Valadares, M.C.; Carrião, M.S.; Bakuzis, A.F.; Lima, E.M. Paclitaxel-Loaded Lipid-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Dual Chemo-Magnetic Hyperthermia Therapy of Melanoma. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030818
Oliveira RR, Cintra ER, Sousa-Junior AA, Moreira LC, da Silva ACG, de Souza ALR, Valadares MC, Carrião MS, Bakuzis AF, Lima EM. Paclitaxel-Loaded Lipid-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Dual Chemo-Magnetic Hyperthermia Therapy of Melanoma. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(3):818. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030818
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Relton R., Emílio R. Cintra, Ailton A. Sousa-Junior, Larissa C. Moreira, Artur C. G. da Silva, Ana Luiza R. de Souza, Marize C. Valadares, Marcus S. Carrião, Andris F. Bakuzis, and Eliana M. Lima. 2023. "Paclitaxel-Loaded Lipid-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Dual Chemo-Magnetic Hyperthermia Therapy of Melanoma" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 3: 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030818
APA StyleOliveira, R. R., Cintra, E. R., Sousa-Junior, A. A., Moreira, L. C., da Silva, A. C. G., de Souza, A. L. R., Valadares, M. C., Carrião, M. S., Bakuzis, A. F., & Lima, E. M. (2023). Paclitaxel-Loaded Lipid-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Dual Chemo-Magnetic Hyperthermia Therapy of Melanoma. Pharmaceutics, 15(3), 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030818







