In Silico Study of Different Thrombolytic Agents for Fibrinolysis in Acute Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
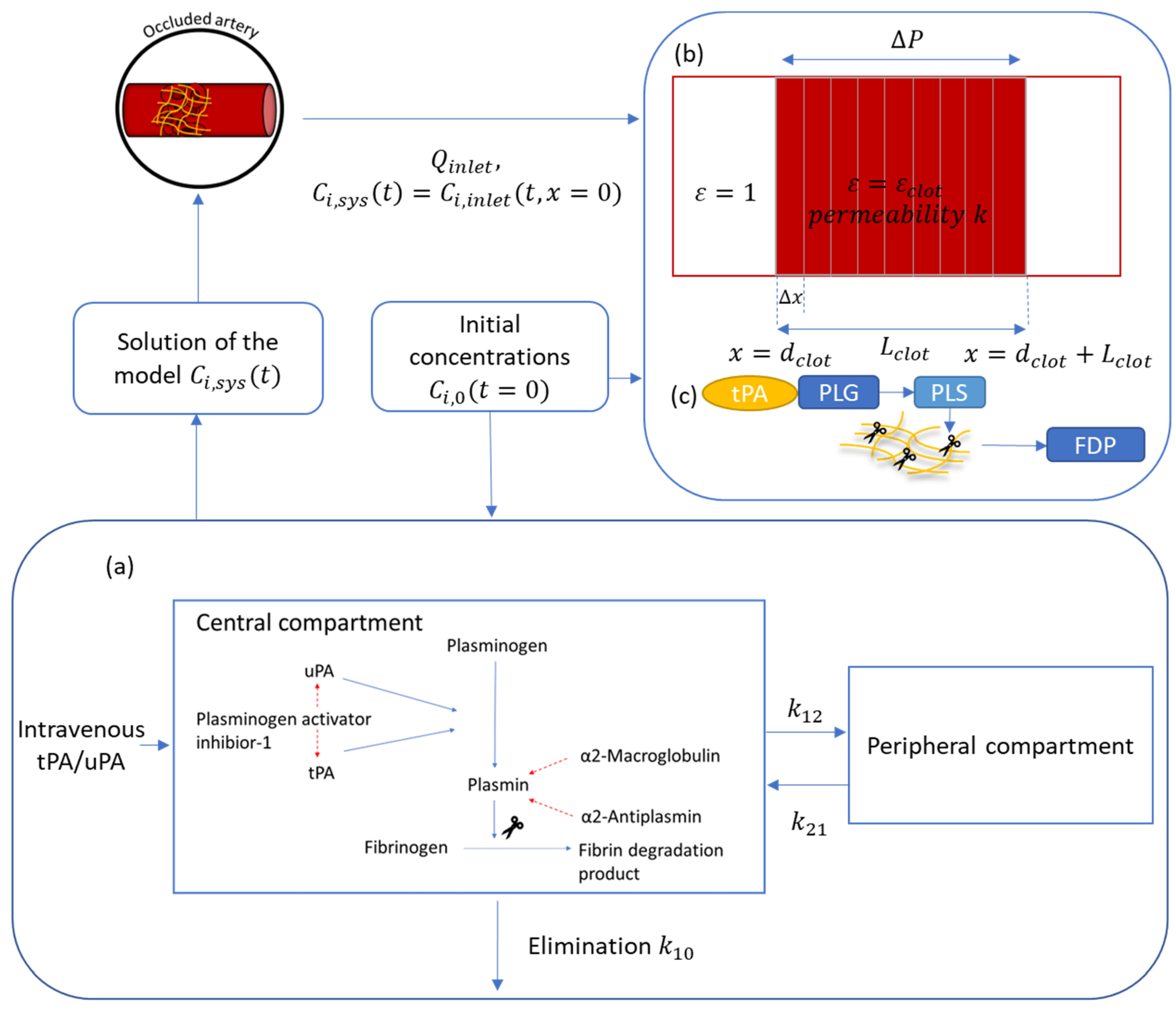
2.1. Drug Properties, Dose Regimen, and Reaction Kinetics
2.2. Mathematical Model
2.3. Additional Kinetic Parameters and Model Validation
3. Results
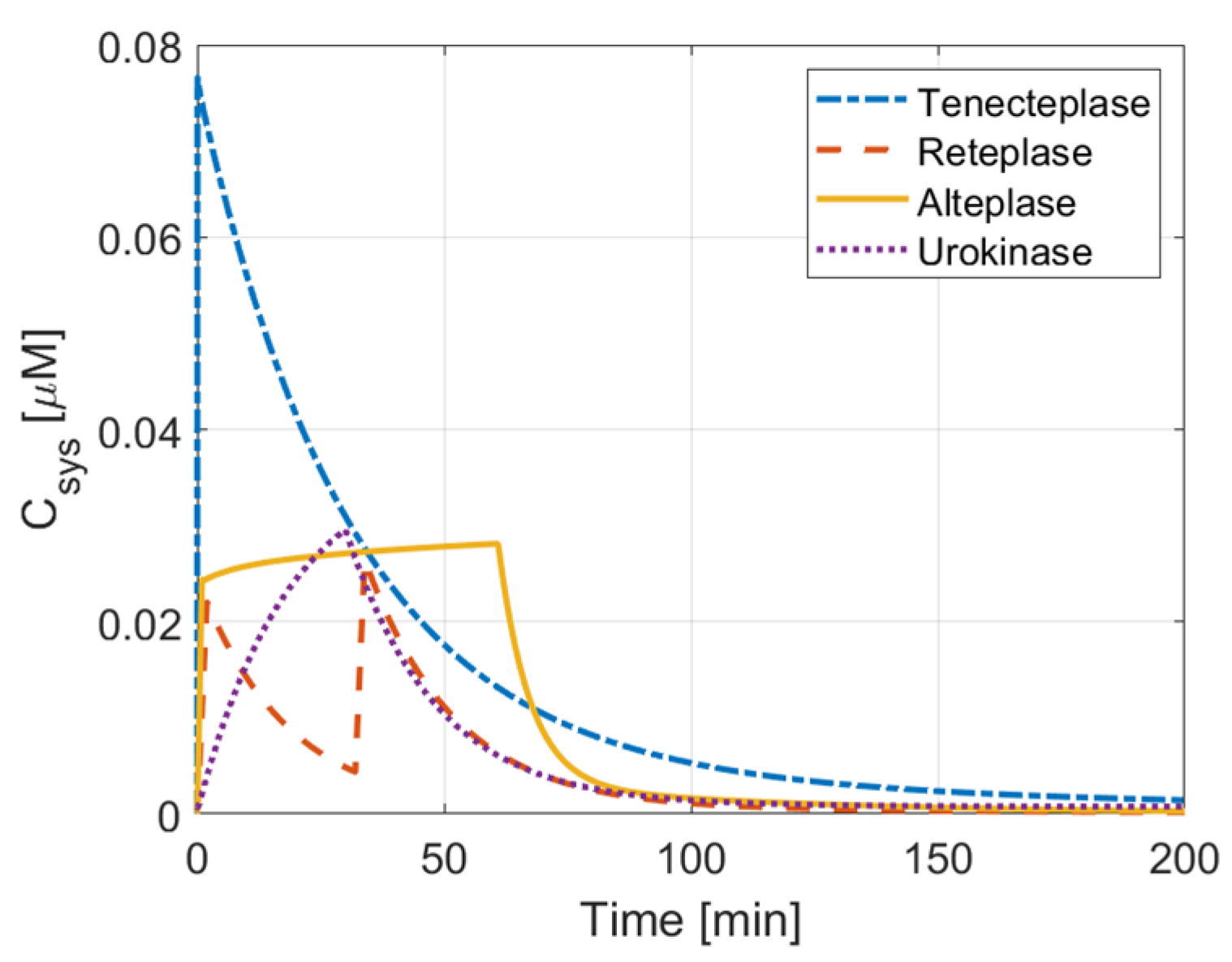
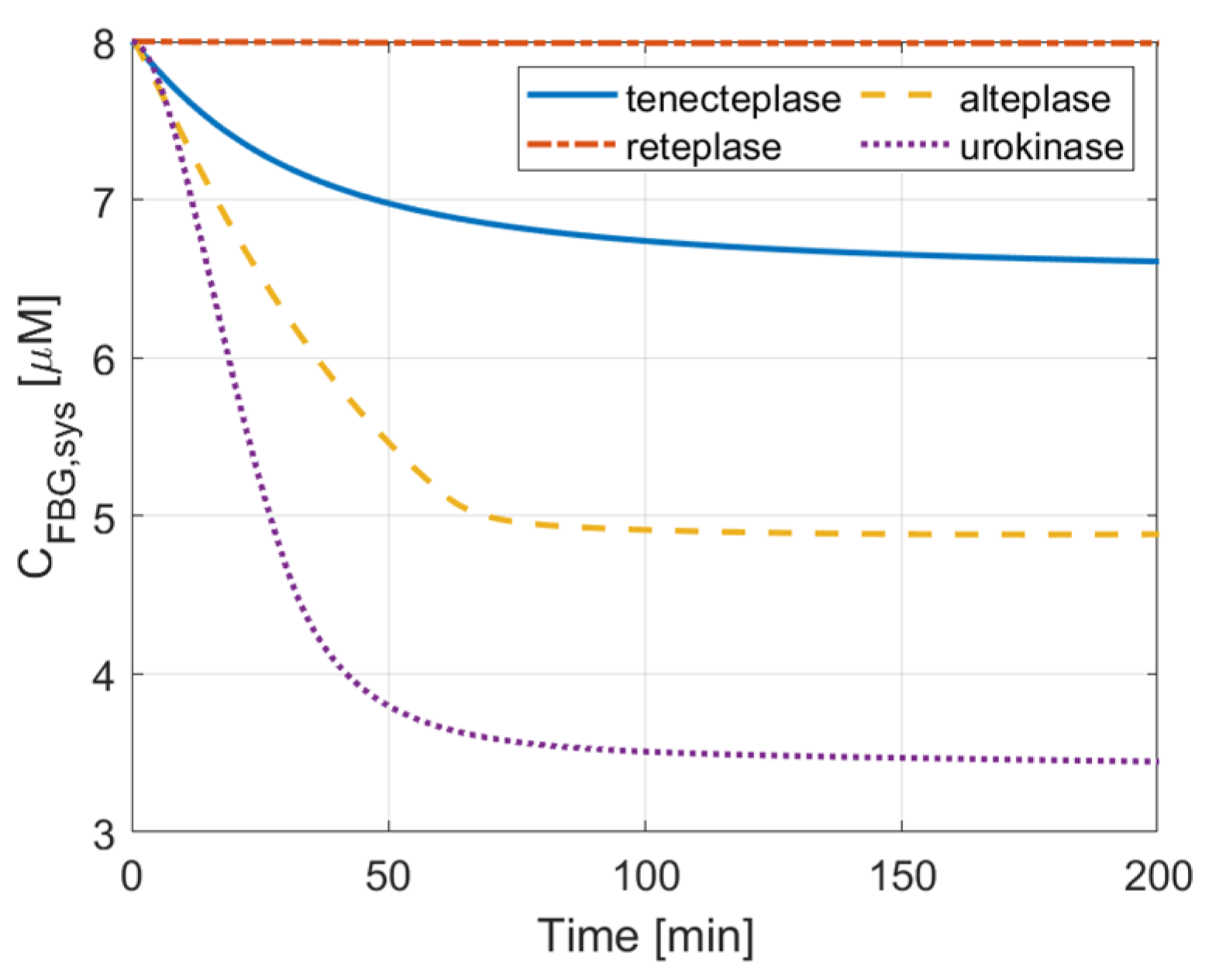
3.1. Comparison of Therapeutic Efficacy
3.2. ICH Risk
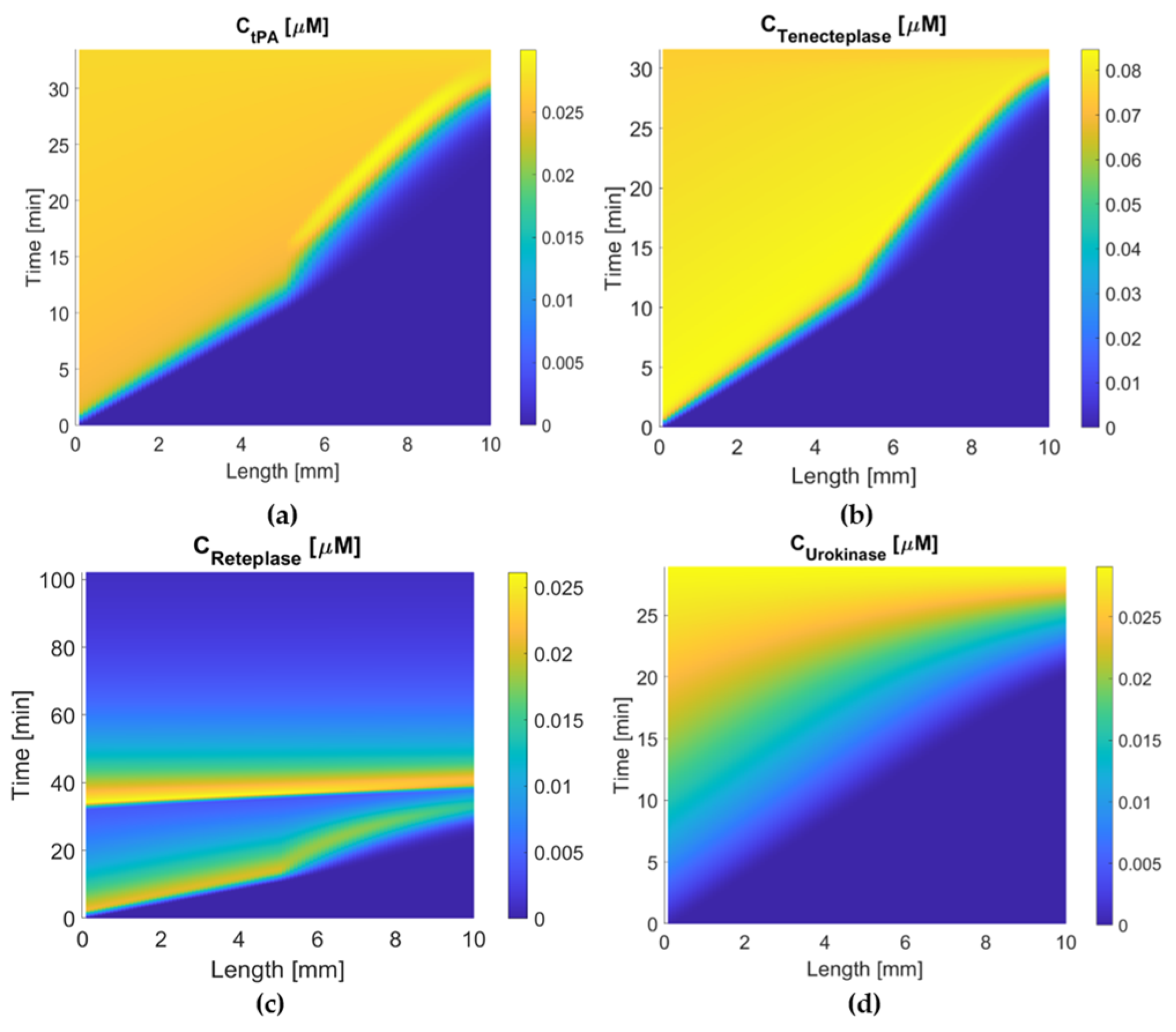
3.3. Activation Time and Extent of Lysis
3.4. PAI-1 Inhibition Effect
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Further Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Comparison with Clinical Data in the Literature
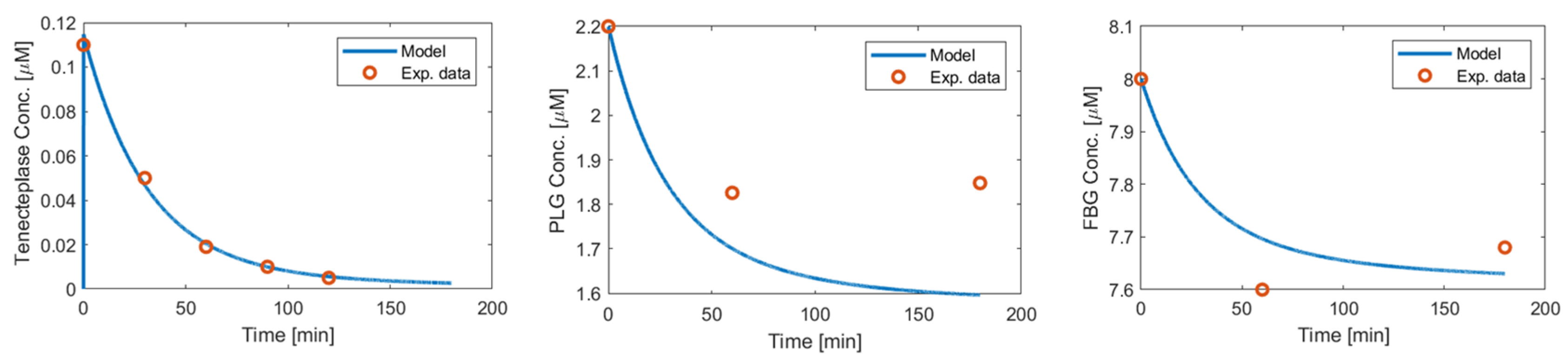
Appendix A.1. Tenecteplase
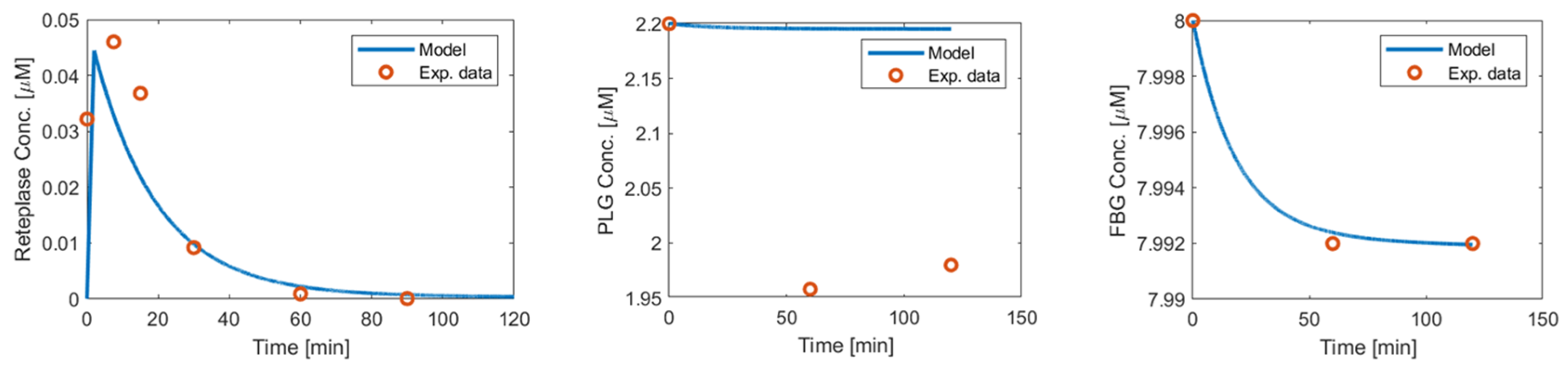
Appendix A.2. Reteplase
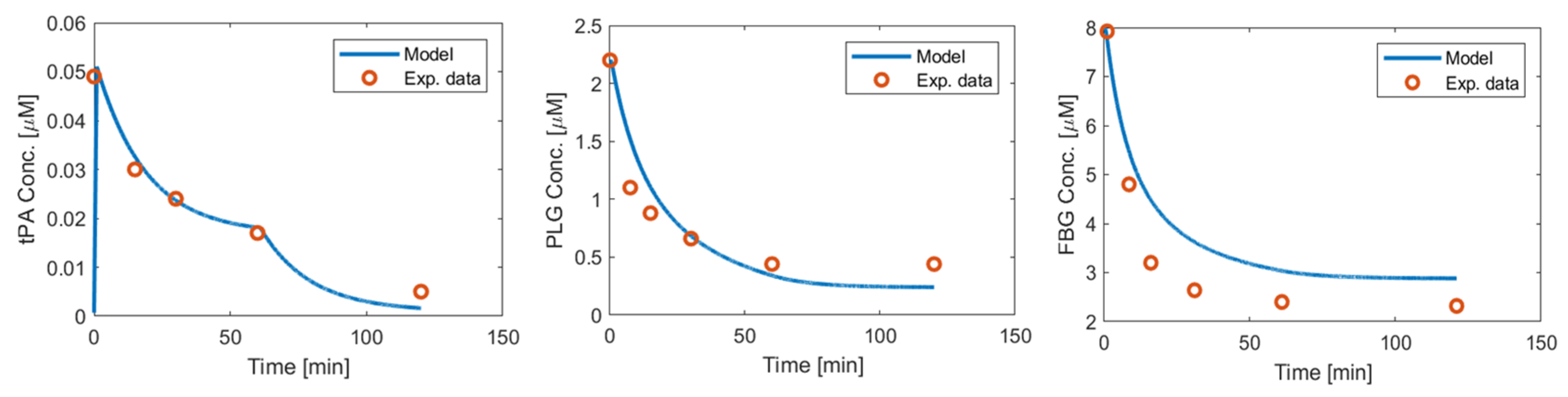
Appendix A.3. Urokinase
References
- Alkarithi, G.; Duval, C.; Shi, Y.; Macrae, F.L.; Ariëns, R.A. Thrombus Structural Composition in Cardiovascular Disease. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 2370–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, E.L.; Kabutey, N.K. Thrombolytic Therapy. In Vascular Surgery: Principles and Practice, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adivitiya; Khasa, Y.P. The evolution of recombinant thrombolytics: Current status and future directions. Bioengineered 2016, 8, 331–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, A.P.; Alkjaersig, N.; Lewis, M.; Tulevski, V.; Davies, A.; Brooks, J.E.; Hardin, W.B.; Landau, W.M.; Raichle, M.E. A pilot study of urokinase therapy in cerebral infarction. Stroke 1976, 7, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnan, G.A.; Davis, S.M.; Chambers, B.R.; Gates, P.C.; Hankey, G.J.; McNeil, J.J.; Rosen, D.; Stewart-Wynne, E.G.; Tuck, R.R. Streptokinase for Acute Ischemic Stroke with Relationship to Time of Administration. JAMA 1996, 276, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahar, E.; Mcgovern, P.G.; Hommel, M.; Boissel, J.P. Letters to the Editor.
- Multicenter Acute Stroke Trial—Europe Study Group. Thrombolytic Therapy with Streptokinase in Acute Ischemic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA; CDER. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Approval Package for Ivermectin; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA; CDER: Beltsville, MD, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghi, H.M.M.; Mohammadi, E.; Seyedhosseini-Ghaheh, H.; Mahnam, K.; Jahanian-Najafabadi, A. Reteplase: Structure, Function, and Production. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2019, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, D.; Choi, S.; Mican, J.; Toul, M.; Ryu, W.-S.; Damborsky, J.; Mikulik, R.; Kim, D.-E. Development and Testing of Thrombolytics in Stroke. J. Stroke 2021, 23, 12–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warach, S.J.; Dula, A.N.; Jr, T.J.M. Tenecteplase Thrombolysis for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2020, 51, 3440–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, D.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Scott, L.J.; Hilleman, D.E. Reteplase: A review of its use in the management of thrombotic occlusive disorders. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2006, 6, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melandri, G. Review of tenecteplase (TNKase) in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2009, 5, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, B.K.; Buck, B.H.; Singh, N.; Deschaintre, Y.; Almekhlafi, M.A.; Coutts, S.B.; Thirunavukkarasu, S.; Khosravani, H.; Appireddy, R.; Moreau, F.; et al. Intravenous tenecteplase compared with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke in Canada (AcT): A pragmatic, multicentre, open-label, registry-linked, randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2022, 400, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.S.; Ok, Y.C.; Lim, J.S.; Lim, B.C.; Cho, K.Y.; Lee, M.C. Outcome Evaluation of Intravenous Infusion of Urokinase for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Chonnam Med. J. 2012, 48, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doh, W.-B.; Lee, B.-C.; Lee, I.-H.; Kim, S.-M.; Kwon, K.-H. Safety and Effect of Continuous Intravenous Urokinase Therapy in Acute Ischemic Stroke (Open Clinical Trial). J. Korean Neurol. Assoc. 1999, 17, 189–194. Available online: https://www.jkna.org/journal/view.php?number=4382 (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Zhang, R.; Wei, H.; Wu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, P.; Wang, T.; Qin, X. Outcomes and Treatment Complications of Intravenous Urokinase Thrombolysis in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Retrospective Cohort Study. SSRN Electron. J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Peng, X. Comparison of Efficacy and Safety of Recombinant Human Prourokinase and Alteplase in the Treatment of STEMI and Analysis of Influencing Factors of Efficacy. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 6702965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taussky, P.; Tawk, R.G.; Daugherty, W.P.; Hanel, R.A. Medical Therapy for Ischemic Stroke: Review of Intravenous and Intra-Arterial Treatment Options. World Neurosurg. 2011, 76, S9–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, R.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, F.; Sheng, B.; Wang, R.; Chen, S.; et al. Effectiveness of intravenous r-tPA versus UK for acute ischaemic stroke: A nationwide prospective Chinese registry study. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2021, 6, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piebalgs, A.; Gu, B.; Roi, D.; Lobotesis, K.; Thom, S.; Xu, X.Y. Computational Simulations of Thrombolytic Therapy in Acute Ischaemic Stroke. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Piebalgs, A.; Huang, Y.; Longstaff, C.; Hughes, A.D.; Chen, R.; Thom, S.A.; Xu, X.Y. Mathematical Modelling of Intravenous Thrombolysis in Acute Ischaemic stroke: Effects of Dose Regimens on Levels of Fibrinolytic Proteins and Clot Lysis Time. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wei, H.; Ren, Y.; Wu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huo, Y.; Feng, J.; Monnier, P.P.; Qin, X. Outcomes and Treatment Complications of Intravenous Urokinase Thrombolysis in Acute Ischemic Stroke in China. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 685454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue Plasminogen Act. Acute Ischemic Stroke 1995, 333, 1581–1588. [CrossRef]
- Thrombolytic Agents—ClinicalKey. Available online: https://www.clinicalkey.com/#!/content/book/3-s2.0-B9780323427913000414 (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Collen, D.; Zamarron, C.; Lijnen, H.R.; Hoylaerts, M. Activation of plasminogen by pro-urokinase. II. Kinetics. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, R.J.; Fredenburgh, J.C.; Leslie, B.A.; Keyt, B.A.; Rischke, J.A.; Weitz, J.I. Identification of the Mechanism Responsible for the Increased Fibrin Specificity of TNK-Tissue Plasminogen Activator Relative to Tissue Plasminogen Activator. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 10112–10120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohnert, U.; Horsch, B.; Fischer, S. A variant of tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) comprised of the Kringle 2 and the protease domain shows a significant difference in the in vitro rate of plasmin formation as compared to the recombinant human t-PA from transformed chinese hamster ovary cells. Fibrinolysis 1993, 7, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekman, C.M.; Loskutoff, D.J. Kinetic analysis of the interactions between plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and both urokinase and tissue plasminogen activator. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1988, 262, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyt, B.A.; Paoni, N.F.; Refino, C.J.; Berleau, L.; Nguyen, H.; Chow, A.; Lai, J.; Peña, L.; Pater, C.; Ogez, J. A faster-acting and more potent form of tissue plasminogen activator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3670–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poeppelmeier, J.; Beier, H.; Carlsson, J.; Guenzler, W.A.; Meierhenrich, R.; Hopkins, G.R.; Tebbe, U. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics and effects on the hemostatic system of saruplase and urokinase in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 1996, 3, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, N.; Fox, N.L.; Clow, F.-W.; Tanswell, P.; Cannon, C.P.; Van De Werf, F.; Braunwald, E. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Tenecteplase: Results from a Phase II Study in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2000, 40, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, U.; Kaufmann, B.; Neugebauer, G. Current Clinical Use of Reteplase for Thrombolysis A Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Perspective. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1999, 36, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanswell, P.; Modi, N.; Combs, D.; Danays, T. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Tenecteplase in Fibrinolytic Therapy of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2002, 41, 1229–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horrevoets, A.; Smilde, A.; de Vries, C.; Pannekoek, H. The specific roles of finger and kringle 2 domains of tissue-type plasminogen activator during in vitro fibrinolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 12639–12644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, M.A.; Straight, D.L.; Fretto, L.J.; McKee, P.A. The effects of fibrinogen and its cleavage products on the kinetics of plasminogen activation by urokinase and subsequent plasmin activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 12171–12177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, U.; Von Möllendorff, E.; Akpan, W.; Kientsch-Engel, R.; Kaufmann, B.; Neugebauer, G. Dose-ranging study of the novel recombinant plasminogen activator BM 06.022 in healthy volunteers. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1991, 50, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, C.P.; Gibson, C.M.; McCabe, C.H.; Adgey, A.A.J.; Schweiger, M.J.; Sequeira, R.F.; Grollier, G.; Giugliano, R.P.; Frey, M.; Mueller, H.S.; et al. TNK–Tissue Plasminogen Activator Compared with Front-Loaded Alteplase in Acute Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 1998, 98, 2805–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keric, N.; Döbel, M.; Krenzlin, H.; Kurz, E.; Tanyildizi, Y.; Heimann, A.; König, J.; Kempski, O.; Ringel, F.; Masomi-Bornwasser, J. Comparative analysis of fibrinolytic properties of Alteplase, Tenecteplase and Urokinase in an in vitro clot model of intracerebral haemorrhage. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 105073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, A.S.; Sheth, K.N. IV tenecteplase: A non-inferior alternative to alteplase? Med 2022, 3, 519–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhadid, K.; Oliveira, L.; Etherton, M.R. Intravenous Thrombolytics in the Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 25, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivard, A.; Huang, X.; Levi, C.R.; Spratt, N.; Campbell, B.C.; Cheripelli, B.K.; Kalladka, D.; Moreton, F.C.; Ford, I.; Bladin, C.F.; et al. Tenecteplase in ischemic stroke offers improved recanalization. Neurology 2017, 89, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Kohnert, U. Major mechanistic differences explain the higher clot lysis potency of reteplase over alteplase: Lack of fibrin binding is an advantage for bolus application of fibrin-specific thrombolytics. Fibrinolysis Proteolysis 1997, 11, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.-J.; Qiu, H.-Y.; Tong, X.-X.; Guo, Y.; Han, M.-F.; Yang, C.-S.; Lin, K.-H.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Yang, Y. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of Reteplase and Alteplase in the treatment of hyper-acute cerebral infarction. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20170730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurewich, V. The sequential, complementary and synergistic activation of fibrin-bound plasminogen by tissue plasminogen activator and pro-urokinase. Fibrinolysis 1989, 3, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Ende, N.A.; Roozenbeek, B.; Smagge, L.E.; Luijten, S.P.; Aerden, L.A.; Kraayeveld, P.; van den Wijngaard, I.R.; Lycklama à Nijeholt, G.J.; den Hertog, H.M.; Flach, H.Z.; et al. Dual thrombolytic therapy with mutant pro-urokinase and small bolus alteplase for ischemic stroke (DUMAS): Study protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled phase II trial. Trials 2022, 23, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guremch, V. Activation of Fibrin-Bound Plasminogen by Pro-Urokinase and Its Complementariness with That by Tissue Plasminogen Activator. Enzyme 1988, 40, 97–108. [Google Scholar]





| Alteplase [19] | Urokinase (uPA) | Tenecteplase (TNK-tPA) | Reteplase | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial concentration C0 | 0.05 nM | 0.7 nM [25] | 0 nM | 0 nM |
| KM | 28 μM | 50 μM [26] | 20 μM [27] | 0.2 μM [28] |
| k1,cat | 0.3 s−1 | 1 s−1 [26] | 0.04 s−1 [27] | 3.3 × 10−4 s−1 [28] |
| k5 | 37 μM−1s−1 | 160 μM−1 [29] | 0.15 μM−1s−1 [30] | 37 μM−1 s−1 [28] |
| kel | 2.27 × 10−3s−1 | 4.06 × 10−4s−1 [31] | 3.89 × 10−4s−1 [32] | 8.33 × 10−4s−1 [33] |
| kcp | 3.1 × 10−4s−1 | 4.39 × 10−4s−1 [31] | 1.1 × 10−4s−1 [32] | 18.2 × 10−5s−1 [33] |
| kpc | 3.34 × 10−4s−1 | 1.28 × 10−4s−1 [31] | 1.37 × 10−4s−1 [32] | 1.53 × 10−4s−1 [33] |
| Vc per body weight | 0.057 L/kg | 0.13 L/kg [31] | 0.0496 L/kg [34] | 0.25 L/kg [33] |
| Alteplase | Tenecteplase | Reteplase | Urokinase | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ka | 0.01 μM−1s−1 [18] | 0.01 μM−1s−1 | 0.01 μM−1s−1 | 0 |
| Dissociation constant kd | 0.58 μM | 0.15 μM [34] | 1.1 μM [35] | 0 |
| kd,tPA | 0.0058 s−1 | 0.0015 s−1 [34] | 0.011 s−1 [35] | 0 |
| KM | 0.16 | 2.8 [27] | 4.6 [28] | 0.81 μM [36] |
| kM,cat | 0.3 | 0.54 [27] | 0.32 [28] | 2.6 s−1 [36] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Gu, B.; Xu, X.Y. In Silico Study of Different Thrombolytic Agents for Fibrinolysis in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030797
Yang Y, Gu B, Xu XY. In Silico Study of Different Thrombolytic Agents for Fibrinolysis in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(3):797. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030797
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yilin, Boram Gu, and Xiao Yun Xu. 2023. "In Silico Study of Different Thrombolytic Agents for Fibrinolysis in Acute Ischemic Stroke" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 3: 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030797
APA StyleYang, Y., Gu, B., & Xu, X. Y. (2023). In Silico Study of Different Thrombolytic Agents for Fibrinolysis in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Pharmaceutics, 15(3), 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030797






