Current Treatments and New, Tentative Therapies for Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Pathophysiology of the Disease and Possible Therapeutic Targets
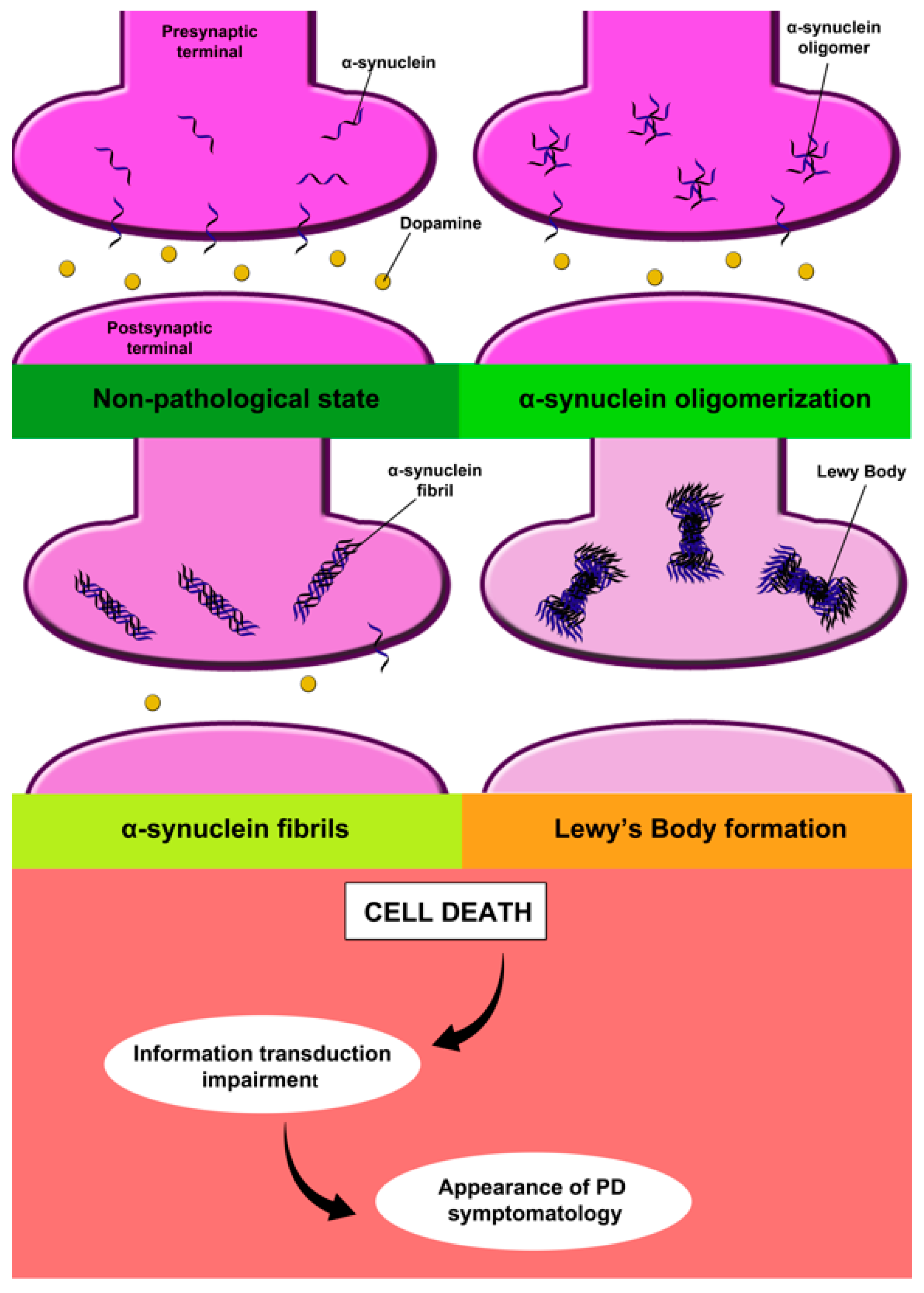
2.1.1. Alpha-Synuclein
2.1.2. Dopamine
2.2. Management of Motor Symptoms
Invasive Treatment Options for Motor Symptoms
2.3. Management of Nonmotor Symptoms
2.3.1. Pharmacological Treatments
2.3.2. Non-Pharmacological Treatments
2.4. Treatments under Investigation
2.4.1. Calcium Homeostasis
2.4.2. Brain Iron Deposits
2.4.3. Peripheral Insulin Resistance
2.4.4. Neuroinflammation
2.4.5. Pathology of α-Synuclein
2.4.6. Faecal Microbiota Transplantation
2.4.7. Neurotrophic Factor Supplementation
2.4.8. Stem Cells Transplantation
2.5. Supplementary Therapies for Treatment and Prevention of PD
2.5.1. Music Therapy
2.5.2. Diet
2.5.3. Phytotherapy
2.6. Main Handicaps in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lew, M. Overview of Parkinson’s Disease. Pharmacotherapy 2007, 27, 155S–160S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driver, J.A.; Logroscino, G.; Gaziano, J.M.; Kurth, T. Incidence and Remaining Lifetime Risk of Parkinson Disease in Advanced Age. Neurology 2009, 72, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.-Y.; Siegel, J.M. Physiological and Anatomical Link Between Parkinson-Like Disease and REM Sleep Behavior Disorder. Mol. Neurobiol. 2003, 27, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tysnes, O.-B.; Storstein, A. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neural Transm. 2017, 124, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Z.; Pan, J.; Tang, S.; Duan, D.; Yu, D.; Nong, H.; Wang, Z. Global Trends in the Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability of Parkinson's Disease in 204 Countries/Territories From 1990 to 2019. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 776847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobson, P.; Meara, J. Mild Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease and Its Progression onto Dementia: A 16-Year Outcome Evaluation of the Denbighshire Cohort. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2015, 30, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmqvist, C.L.; Ariyaratnam, R.; Watters, D.A.; Laing, G.L.; Stupart, D.; Hider, P.; Ng-Kamstra, J.S.; Wilson, L.; Clarke, D.L.; Hagander, L.; et al. Monitoring and Evaluating Surgical Care: Defining Perioperative Mortality Rate and Standardising Data Collection. Lancet 2015, 385, S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wu, I.X.Y. Non-Genetic Risk Factors for Parkinson’s Disease: An Overview of 46 Systematic Reviews. J. Park. Dis. 2021, 11, 919–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerri, S.; Mus, L.; Blandini, F. Parkinson’s Disease in Women and Men: What’s the Difference? J. Park. Dis. 2019, 9, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meles, S.K.; Oertel, W.H.; Leenders, K.L. Circuit Imaging Biomarkers in Preclinical and Prodromal Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.Y.; Ripin, Z.M.; Halim, S.A.; Arifin, W.N.; Yahya, A.S.; Eow, G.B.; Tan, K.; Hor, J.Y.; Wong, C.K. Motion Characteristics of Subclinical Tremors in Parkinson’s Disease and Normal Subjects. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolosa, E.; Garrido, A.; Scholz, S.W.; Poewe, W. Challenges in the Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Inhiesto, E.; Acaiturri-Ayesta, M.T.; Ustarroz-Aguirre, I.; Camahuali, D.; Urtaran-Laresgoiti, M.; Basabe-Aldecoa, M.; Nuño-Solinís, R.; Urizar, E. Direct Cost of Parkinson’s Disease: A Real-World Data Study of Second-Line Therapies. Park. Dis. 2020, 2020, e9106026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Molsberry, S.A.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; Ascherio, A.; Gao, X. Association of Diet and Physical Activity with All-Cause Mortality Among Adults with Parkinson Disease. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2227738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestrino, R.; Schapira, A.h.v. Parkinson Disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehndiratta, M.; Garg, R.K.; Pandey, S. Nonmotor Symptom Complex of Parkinson’s Disease--an under-Recognized Entity. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2011, 59, 302–308, 313. [Google Scholar]
- Inzelberg, R.; Schechtman, E.; Paleacu, D. Onset Age of Parkinson Disease. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2002, 111, 459–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zareparsi, S.; Payami, H. Reply to correspondence from Inzelberg et al.—“onset age of Parkinson disease”. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2002, 111, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Eeden, S.K.; Tanner, C.M.; Bernstein, A.L.; Fross, R.D.; Leimpeter, A.; Bloch, D.A.; Nelson, L.M. Incidence of Parkinson’s Disease: Variation by Age, Gender, and Race/Ethnicity. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 157, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaeffer, E.; Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D. Prodromal PD: A New Nosological Entity. Prog. Brain Res. 2020, 252, 331–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Tanji, K.; Odagiri, S.; Miki, Y.; Mori, F.; Takahashi, H. The Lewy Body in Parkinson’s Disease and Related Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 47, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, G.E.; DeLong, M.R.; Strick, P.L. Parallel Organization of Functionally Segregated Circuits Linking Basal Ganglia and Cortex. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1986, 9, 357–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenewegen, H.J. The Basal Ganglia and Motor Control. Neural Plast. 2003, 10, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, J.; Tan, E.K. Parkinson’s Disease: Etiopathogenesis and Treatment. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordower, J.H.; Chu, Y.; Hauser, R.A.; Freeman, T.B.; Olanow, C.W. Lewy Body-like Pathology in Long-Term Embryonic Nigral Transplants in Parkinson’s Disease. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Kordower, J.H. Lewy Body Pathology in Fetal Grafts. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1184, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeso, J.A.; Rodriguez-Oroz, M.C.; Goetz, C.G.; Marin, C.; Kordower, J.H.; Rodriguez, M.; Hirsch, E.C.; Farrer, M.; Schapira, A.H.V.; Halliday, G. Missing Pieces in the Parkinson’s Disease Puzzle. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, K.R.; Odin, P. The Challenge of Non-Motor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease. Prog. Brain Res. 2010, 184, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davie, C.A. A Review of Parkinson’s Disease. Br. Med. Bull. 2008, 86, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, K.E.; Pahwa, R. The Impact and Management of Nonmotor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease. Am. J. Manag. Care 2011, 17 (Suppl. 12), S308–S314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bidesi, N.S.R.; Vang Andersen, I.; Windhorst, A.D.; Shalgunov, V.; Herth, M.M. The Role of Neuroimaging in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2021, 159, 660–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.-Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in Lewy Bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brundin, P.; Melki, R. Prying into the Prion Hypothesis for Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 9808–9818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchihara, T.; Giasson, B.I. Propagation of Alpha-Synuclein Pathology: Hypotheses, Discoveries, and yet Unresolved Questions from Experimental and Human Brain Studies. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghammer, P. The α-Synuclein Origin and Connectome Model (SOC Model) of Parkinson’s Disease: Explaining Motor Asymmetry, Non-Motor Phenotypes, and Cognitive Decline. J. Park. Dis. 2021, 11, 455–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghammer, P.; Van Den Berge, N. Brain-First versus Gut-First Parkinson’s Disease: A Hypothesis. J. Park. Dis. 2019, 9, S281–S295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsager, J.; Andersen, K.B.; Knudsen, K.; Skjærbæk, C.; Fedorova, T.D.; Okkels, N.; Schaeffer, E.; Bonkat, S.K.; Geday, J.; Otto, M.; et al. Brain-First versus Body-First Parkinson’s Disease: A Multimodal Imaging Case-Control Study. Brain 2020, 143, 3077–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghammer, P.; Horsager, J.; Andersen, K.; Van Den Berge, N.; Raunio, A.; Murayama, S.; Parkkinen, L.; Myllykangas, L. Neuropathological Evidence of Body-First vs. Brain-First Lewy Body Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 161, 105557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesné, J.; Cardoso, V.; Veiga-Fernandes, H. Neuro-Immune Regulation of Mucosal Physiology. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de La Serre, C.B.; de Lartigue, G.; Raybould, H.E. Chronic Exposure to Low Dose Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide Inhibits Leptin Signaling in Vagal Afferent Neurons. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 139, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van IJzendoorn, S.C.D.; Derkinderen, P. The Intestinal Barrier in Parkinson’s Disease: Current State of Knowledge. J. Park. Dis. 2019, 9, S323–S329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obrenovich, M.E.M. Leaky Gut, Leaky Brain? Microorganisms 2018, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajares, M.; Rojo, A.I.; Manda, G.; Boscá, L.; Cuadrado, A. Inflammation in Parkinson’s Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2020, 9, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathnayake, D.; Chang, T.; Udagama, P. Selected Serum Cytokines and Nitric Oxide as Potential Multi-Marker Biosignature Panels for Parkinson Disease of Varying Durations: A Case-Control Study. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietdijk, C.D.; Perez-Pardo, P.; Garssen, J.; van Wezel, R.J.A.; Kraneveld, A.D. Exploring Braak’s Hypothesis of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Rüb, U.; Gai, W.P.; Del Tredici, K. Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease: Possible Routes by Which Vulnerable Neuronal Types May Be Subject to Neuroinvasion by an Unknown Pathogen. J. Neural Transm. 2003, 110, 517–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiser, J.; Weindl, D.; Hiller, K. Complexity of Dopamine Metabolism. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Lim, H.-S.; Masliah, E.; Lee, H.-J. Protein Aggregate Spreading in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Problems and Perspectives. Neurosci. Res. 2011, 70, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nors Perdersen, M.; Foderà, V.; Horvath, I.; van Maarschalkerweerd, A.; Nørgaard Toft, K.; Weise, C.; Almqvist, F.; Wolf-Watz, M.; Wittung-Stafshede, P.; Vestergaard, B. Direct Correlation Between Ligand-Induced α-Synuclein Oligomers and Amyloid-like Fibril Growth. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.L.; Stacy, M.; Simuni, T.; Miyasaki, J.; Oertel, W.H.; Sethi, K.; Fernandez, H.H.; Stocchi, F. The Spectrum of “off” in Parkinson’s Disease: What Have We Learned over 40 Years? Park. Relat. Disord. 2018, 51, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comi, C.; Magistrelli, L.; Oggioni, G.D.; Carecchio, M.; Fleetwood, T.; Cantello, R.; Mancini, F.; Antonini, A. Peripheral Nervous System Involvement in Parkinson’s Disease: Evidence and Controversies. Park. Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, L.; Sobotka, S.; Chen, J.; Su, H.; Sanders, I.; Nyirenda, T.; Adler, C.H.; Shill, H.A.; Caviness, J.N.; Samanta, J.E.; et al. Parkinson Disease Affects Peripheral Sensory Nerves in the Pharynx. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 72, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cersosimo, M.G.; Benarroch, E.E. Pathological Correlates of Gastrointestinal Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 46, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, T.G.; Adler, C.H.; Sue, L.I.; Vedders, L.; Lue, L.; White Iii, C.L.; Akiyama, H.; Caviness, J.N.; Shill, H.A.; Sabbagh, M.N.; et al. Multi-Organ Distribution of Phosphorylated Alpha-Synuclein Histopathology in Subjects with Lewy Body Disorders. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, Y.; Tomiyama, M.; Ueno, T.; Haga, R.; Nishijima, H.; Suzuki, C.; Mori, F.; Kaimori, M.; Baba, M.; Wakabayashi, K. Clinical Availability of Skin Biopsy in the Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 469, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerink, R.H.S. Targeting Exocytosis: Ins and Outs of the Modulation of Quantal Dopamine Release. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2006, 5, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, S.; Jahangeer, M.; Maknoon Razia, D.; Ashiq, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Akram, M.; El Allam, A.; Bouyahya, A.; Garipova, L.; Ali Shariati, M.; et al. Dopamine in Parkinson’s Disease. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2021, 522, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, G. Impact of Dopamine Oxidation on Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.U.; Akram, M.; Daniyal, M.; Zainab, R. Awareness and Current Knowledge of Parkinson’s Disease: A Neurodegenerative Disorder. Int. J. Neurosci. 2019, 129, 55–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Xing, H.; Lin, Q.; Meng, F.; Gong, L. Effectiveness of Therapeutic Massage for Improving Motor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 915232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, A.E.; Siderowf, A.D.; Macklin, E.A.; Poewe, W.; Brooks, D.J.; Fernandez, H.H.; Rascol, O.; Giladi, N.; Stocchi, F.; Tanner, C.M.; et al. Trial of Cinpanemab in Early Parkinson’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeWitt, P.A. Levodopa Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease: Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamiak, U.; Kaldonska, M.; Klodowska-Duda, G.; Wyska, E.; Safranow, K.; Bialecka, M.; Gawronska-Szklarz, B. Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Modeling of Levodopa in Patients with Advanced Parkinson Disease. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 33, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Liang, L.-W.; Shen, Q.; Wang, X.-D.; Ren, S.-M.; Ma, H.-J.; Jiao, S.-J.; Liu, P. Treatment Strategies for Parkinson’s Disease. Neurosci. Bull. 2010, 26, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.-E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonini, A.; Barone, P. Dopamine Agonist-Based Strategies in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 29 (Suppl. 5), S371–S374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oertel, W.; Schulz, J.B. Current and Experimental Treatments of Parkinson Disease: A Guide for Neuroscientists. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139 (Suppl. 1), 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T. Catechol-O-Methyltransferase Inhibitors in Parkinson’s Disease. Drugs 2015, 75, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanawat, M.; Mehta, D.K.; Gupta, S.; Das, R. Understanding the Pathogenesis Involved in Parkinson’s Disease and Potential Therapeutic Treatment Strategies. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binde, C.D.; Tvete, I.F.; Gåsemyr, J.I.; Natvig, B.; Klemp, M. Comparative Effectiveness of Dopamine Agonists and Monoamine Oxidase Type-B Inhibitors for Parkinson’s Disease: A Multiple Treatment Comparison Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 76, 1731–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulisevsky, J.; Pagonabarraga, J. Tolerability and Safety of Ropinirole versus Other Dopamine Agonists and Levodopa in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease: Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Drug Saf. 2010, 33, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, F.; Djamshidian, A.; Seppi, K.; Poewe, W. Apomorphine for Parkinson’s Disease: Efficacy and Safety of Current and New Formulations. CNS Drugs 2019, 33, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okun, M.S. Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson Disease: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhuis, F.A.P.; Esselink, R.; de Bie, R.M.A.; Groenewoud, H.; Bloem, B.R.; Post, B.; Meinders, M.J. Translating Evidence to Advanced Parkinson’s Disease Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 1293–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijk, J.M.; Espay, A.J.; Katzenschlager, R.; de Bie, R.M.A. The Choice Between Advanced Therapies for Parkinson’s Disease Patients: Why, What, and When? J. Park. Dis. 2020, 10, S65–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atchley, T.J.; Elsayed, G.A.; Sowers, B.; Walker, H.C.; Chagoya, G.; Davis, M.C.; Bernstock, J.D.; Omar, N.B.; Patel, D.M.; Guthrie, B.L. Incidence and Risk Factors for Seizures Associated with Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 1–5, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antosik-Wójcińska, A.Z.; Święcicki, Ł. The Use of DBS Stimulation in Mental Disorders-Opportunities and Risks. Psychiatr. Pol. 2015, 49, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krauss, J.K.; Lipsman, N.; Aziz, T.; Boutet, A.; Brown, P.; Chang, J.W.; Davidson, B.; Grill, W.M.; Hariz, M.I.; Horn, A.; et al. Technology of Deep Brain Stimulation: Current Status and Future Directions. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, S.H.; Katzenschlager, R.; Lim, S.-Y.; Barton, B.; de Bie, R.M.A.; Seppi, K.; Coelho, M.; Sampaio, C.; Movement Disorder Society Evidence-Based Medicine Committee. International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society Evidence-Based Medicine Review: Update on Treatments for the Motor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1248–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okun, M.S. Choosing a Parkinson Disease Treatment. JAMA 2020, 323, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afentou, N.; Jarl, J.; Gerdtham, U.-G.; Saha, S. Economic Evaluation of Interventions in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Literature Review. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2019, 6, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, F.C. Treatment Options for Motor and Non-Motor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontone, G.M.; Mills, K.A. Optimal Treatment of Depression and Anxiety in Parkinson’s Disease. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2021, 29, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, S.J.; Laidlaw, K.; Starkstein, S. Cognitive Behaviour Therapy for Depression and Anxiety in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Park. Dis. 2015, 5, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanciulli, A.; Wenning, G.K. Autonomic Failure: A Neglected Presentation of Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 781–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, J.-A.; Kaufmann, H. Treatment of Autonomic Dysfunction in Parkinson Disease and Other Synucleinopathies. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 372–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, G.; Liu, J. Autonomic Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease: Implications for Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 134, 104700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schapira, A.H.V.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Jenner, P. Non-Motor Features of Parkinson Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.; Stacy, M. Non-Motor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurol. 2009, 256 (Suppl. 3), 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, I.H.K.; Walton, C.C.; Hallock, H.; Lewis, S.J.G.; Valenzuela, M.; Lampit, A. Cognitive Training in Parkinson Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurology 2015, 85, 1843–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, B.J.; Gasson, N.; Johnson, A.R.; Booth, L.; Loftus, A.M. Cognitive Training and Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation for Mild Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Park. Dis. 2018, 2018, 4318475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgeta, V.; McDonald, K.R.; Poliakoff, E.; Hindle, J.V.; Clare, L.; Leroi, I. Cognitive Training Interventions for Dementia and Mild Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 2, CD011961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taximaimaiti, R.; Luo, X.; Wang, X.-P. Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Treatments of Sleep Disorders in Parkinson’s Disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 2233–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefani, A.; Högl, B. Sleep in Parkinson’s Disease. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics Consensus Statement on the Scope and Appropriate Use of the Term Probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, M.E.; Merenstein, D.J.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Rastall, R.A. Probiotics and Prebiotics in Intestinal Health and Disease: From Biology to the Clinic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteagudo-Mera, A.; Rastall, R.A.; Gibson, G.R.; Charalampopoulos, D.; Chatzifragkou, A. Adhesion Mechanisms Mediated by Probiotics and Prebiotics and Their Potential Impact on Human Health. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 6463–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.H.; Lim, S.-Y.; Chong, K.K.; Manap, M.A.A.A.; Hor, J.W.; Lim, J.L.; Low, S.C.; Chong, C.W.; Mahadeva, S.; Lang, A.E. Probiotics for Constipation in Parkinson Disease: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study. Neurology 2021, 96, e772–e782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Xie, X.; Liu, R. The Role of α-Synuclein Oligomers in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzabadi, S.; Oryan, S.; Eidi, A.; Aghadavod, E.; Daneshvar Kakhaki, R.; Tamtaji, O.R.; Taghizadeh, M.; Asemi, Z. The Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Gene Expression Related to Inflammation, Insulin and Lipid in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized, Double-Blind, PlaceboControlled Trial. Arch. Iran. Med. 2018, 21, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamtaji, O.R.; Taghizadeh, M.; Daneshvar Kakhaki, R.; Kouchaki, E.; Bahmani, F.; Borzabadi, S.; Oryan, S.; Mafi, A.; Asemi, Z. Clinical and Metabolic Response to Probiotic Administration in People with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2019, 38, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koszła, O.; Stępnicki, P.; Zięba, A.; Grudzińska, A.; Matosiuk, D.; Kaczor, A.A. Current Approaches and Tools Used in Drug Development against Parkinson’s Disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkouzi, A.; Vedam-Mai, V.; Eisinger, R.S.; Okun, M.S. Emerging Therapies in Parkinson Disease-Repurposed Drugs and New Approaches. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 204–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Marini, K.; Mahlknecht, P. New Hopes for Disease Modification in Parkinson’s Disease. Neuropharmacology 2020, 171, 108085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkinson Study Group. STEADY-PD III Investigators Isradipine Versus Placebo in Early Parkinson Disease: A Randomized Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaldan, S.; Bush, A.I.; Devos, D.; Rolland, A.S.; Moreau, C. Striking While the Iron Is Hot: Iron Metabolism and Ferroptosis in Neurodegeneration. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Bastida, A.; Ward, R.J.; Newbould, R.; Piccini, P.; Sharp, D.; Kabba, C.; Patel, M.C.; Spino, M.; Connelly, J.; Tricta, F.; et al. Brain Iron Chelation by Deferiprone in a Phase 2 Randomised Double-Blinded Placebo Controlled Clinical Trial in Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, J.L.Y.; de Pablo-Fernandez, E.; Foltynie, T.; Noyce, A.J. The Association Between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Parkinson’s Disease. J. Park. Dis. 2020, 10, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, F.; Masato, A.; Bubacco, L.; Bisaglia, M. Metformin Repurposing for Parkinson Disease Therapy: Opportunities and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelders, G.; Baekelandt, V.; Van der Perren, A. Linking Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 4784268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caggiu, E.; Arru, G.; Hosseini, S.; Niegowska, M.; Sechi, G.; Zarbo, I.R.; Sechi, L.A. Inflammation, Infectious Triggers, and Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.U.; Yook, T.H.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Yang, G. A Novel Treatment Strategy by Natural Products in NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, R.; Albornoz, E.A.; Christie, D.C.; Langley, M.R.; Kumar, V.; Mantovani, S.; Robertson, A.A.B.; Butler, M.S.; Rowe, D.B.; O’Neill, L.A.; et al. Inflammasome Inhibition Prevents α-Synuclein Pathology and Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in Mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaah4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lashgari, N.-A.; Roudsari, N.M.; Momtaz, S.; Sathyapalan, T.; Abdolghaffari, A.H.; Sahebkar, A. The Involvement of JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neuroimmunol. 2021, 361, 577758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Gibson, S.A.; Buckley, J.A.; Qin, H.; Benveniste, E.N. Role of the JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway in Regulation of Innate Immunity in Neuroinflammatory Diseases. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 189, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, J.; Maaß, S.; Schuberth, M.; Giese, A.; Oertel, W.H.; Poewe, W.; Trenkwalder, C.; Wenning, G.K.; Mansmann, U.; Südmeyer, M.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Epigallocatechin Gallate in Multiple System Atrophy (PROMESA): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 724–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Tan, J.; Qin, L.; Lv, L.; Yan, W.; Zhang, H.; Tang, B.; Wang, C. Molecular Chaperones and Parkinson’s Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 160, 105527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.L.; Koike, M.A.; Khan, A.; Wrasidlo, W.; Rockenstein, E.; Masliah, E.; Bonhaus, D. The Small Molecule Alpha-Synuclein Misfolding Inhibitor, NPT200-11, Produces Multiple Benefits in an Animal Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.S.; Ooi, Y.Y.; Chye, S.M.; Ling, A.P.K.; Koh, R.Y. Immunotherapies for Parkinson’s Disease: Progression of Clinical Development. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2021, 20, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, G.; Taylor, K.I.; Anzures-Cabrera, J.; Marchesi, M.; Simuni, T.; Marek, K.; Postuma, R.B.; Pavese, N.; Stocchi, F.; Azulay, J.-P.; et al. Trial of Prasinezumab in Early-Stage Parkinson’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poewe, W.; Volc, D.; Seppi, K.; Medori, R.; Lührs, P.; Kutzelnigg, A.; Djamshidian, A.; Thun-Hohenstein, C.; Meissner, W.G.; Rascol, O.; et al. Safety and Tolerability of Active Immunotherapy Targeting α-Synuclein with PD03A in Patients with Early Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 1 Study. J. Park. Dis. 2021, 11, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmo, J.T.; Verma, A.; Dodart, J.-C.; Wang, C.Y.; Savistchenko, J.; Melki, R.; Carare, R.O.; Nicoll, J.A.R. Novel Antibodies Detect Additional α-Synuclein Pathology in Synucleinopathies: Potential Development for Immunotherapy. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.; Armstrong, S.; Hamzeh, A.; Visanji, N.P.; Sardi, S.P.; Tandon, A. Alpha-Synuclein Targeting Therapeutics for Parkinson’s Disease and Related Synucleinopathies. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 852003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronich, N.; Abernethy, D.R.; Auriel, E.; Lavi, I.; Rennert, G.; Saliba, W. Β2-Adrenoceptor Agonists and Antagonists and Risk of Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.; Bjørnevik, K.; Im, D.S.; Flierl, A.; Dong, X.; Locascio, J.J.; Abo, K.M.; Long, E.; Jin, M.; Xu, B.; et al. Β2-Adrenoreceptor Is a Regulator of the α-Synuclein Gene Driving Risk of Parkinson’s Disease. Science 2017, 357, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magistrelli, L.; Comi, C. Beta2-Adrenoceptor Agonists in Parkinson’s Disease and Other Synucleinopathies. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020, 15, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koros, C.; Simitsi, A.; Stefanis, L. Genetics of Parkinson’s Disease: Genotype-Phenotype Correlations. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2017, 132, 197–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-L.; Wang, S.-Y.; Chen, T.-C.; Chuang, C.-S. Association between Β2-Adrenoreceptor Medications and Risk of Parkinson’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Medicina 2021, 57, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Carrión, M.D.; Posadas, I.; Solera, J.; Ceña, V. LRRK2 and Proteostasis in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, D.; Huntwork-Rodriguez, S.; Henry, A.G.; Sasaki, J.C.; Meisner, R.; Diaz, D.; Solanoy, H.; Wang, X.; Negrou, E.; Bondar, V.V.; et al. Preclinical and Clinical Evaluation of the LRRK2 Inhibitor DNL201 for Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabj2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senkevich, K.A.; Kopytova, A.E.; Usenko, T.S.; Emelyanov, A.K.; Pchelina, S.N. Parkinson’s Disease Associated with GBA Gene Mutations: Molecular Aspects and Potential Treatment Approaches. Acta Nat. 2021, 13, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Armstrong, M.J. Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease with Cognitive Impairment: Current Approaches and Future Directions. Behav. Sci. 2021, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xu, H.; Luo, Q.; He, J.; Li, M.; Chen, H.; Tang, W.; Nie, Y.; Zhou, Y. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation to Treat Parkinson’s Disease with Constipation. Medicine 2019, 98, e16163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.V.; de Godoy, J.V.P.; Bosque, B.P.; Amorim Neto, D.P.; Tostes, K.; Palameta, S.; Garcia-Rosa, S.; Tonoli, C.C.C.; de Carvalho, H.F.; de Castro Fonseca, M. Transcellular Propagation of Fibrillar α-Synuclein from Enteroendocrine to Neuronal Cells Requires Cell-to-Cell Contact and Is Rab35-Dependent. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuai, X.; Yao, X.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Pei, S.; Zhou, C. Evaluation of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Parkinson’s Disease Patients with Constipation. Microb. Cell Factories 2021, 20, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.-J.; Yu, S.-Y.; Zuo, L.-J.; Lian, T.-H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, R.-D.; Piao, Y.-S.; Guo, P.; Liu, L.; Jin, Z.; et al. Parkinson Disease with Constipation: Clinical Features and Relevant Factors. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, A.; Zlotnik, Y.; Moyal-Atias, K.; Abuhasira, R.; Ifergane, G. Fecal Microbiota Transplant as a Potential Treatment for Parkinson’s Disease–A Case Series. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 207, 106791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Ning, J.; Bao, X.; Shang, M.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, D. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Protects Rotenone-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Mice via Suppressing Inflammation Mediated by the Lipopolysaccharide-TLR4 Signaling Pathway through the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Microbiome 2021, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.-F.; Zhu, Y.-L.; Zhou, Z.-L.; Jia, X.-B.; Xu, Y.-D.; Yang, Q.; Cui, C.; Shen, Y.-Q. Neuroprotective Effects of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation on MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Mice: Gut Microbiota, Glial Reaction and TLR4/TNF-α Signaling Pathway. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2018, 70, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Chen, W.; Gao, H.; Che, N.; Xu, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, M. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Exerts a Protective Role in MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease via the TLR4/PI3K/AKT/NF-ΚB Pathway Stimulated by α-Synuclein. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 3050–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.-J.; Yang, X.-Z.; Tong, Q.; Shen, P.; Ma, S.-J.; Wu, S.-N.; Zheng, J.-L.; Wang, H.-G. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease. Medicine 2020, 99, e22035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Li, Y.; Jiao, Q.; Du, X.; Jiang, H. Cerebral Dopamine Neurotrophic Factor: A Potential Therapeutic Agent for Parkinson’s Disease. Neurosci. Bull. 2017, 33, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.M.; Jerónimo-Santos, A.; Outeiro, T.F.; Sebastião, A.M.; Diógenes, M.J. Challenges and Promises in the Development of Neurotrophic Factor-Based Therapies for Parkinson’s Disease. Drugs Aging 2014, 31, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, W.J.; Howard, D.F.; Federoff, H.J. Gene Therapeutic Strategies for Neuroprotection: Implications for Parkinson’s Disease. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 144, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindholm, P.; Saarma, M. Cerebral Dopamine Neurotrophic Factor Protects and Repairs Dopamine Neurons by Novel Mechanism. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slevin, J.T.; Gash, D.M.; Smith, C.D.; Gerhardt, G.A.; Kryscio, R.; Chebrolu, H.; Walton, A.; Wagner, R.; Young, A.B. Unilateral Intraputamenal Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Patients with Parkinson Disease: Response to 1 Year of Treatment and 1 Year of Withdrawal. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 106, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhang, T.; Gong, X.; Hu, G.; Ding, W.; Wang, X. AAV2-Mediated Striatum Delivery of Human CDNF Prevents the Deterioration of Midbrain Dopamine Neurons in a 6-Hydroxydopamine Induced Parkinsonian Rat Model. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 248, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, N.; Abdollahii, S.; Kouhbanani, M.A.J.; Hassanzadeh, A. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (IPSCs) as Game-Changing Tools in the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disease: Mirage or Reality? J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 9166–9184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morizane, A. [Cell therapy for Parkinson’s disease with induced pluripotent stem cells]. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 2019, 59, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsworth, J.D. Parkinson’s Disease Treatment: Past, Present, and Future. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolagar, T.A.; Farzaneh, M.; Nikkar, N.; Khoshnam, S.E. Human Pluripotent Stem Cells in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Potentials, Advances and Limitations. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 15, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoddard-Bennett, T.; Reijo Pera, R. Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease through Personalized Medicine and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cells 2019, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, D.; Magotani, H.; Kikuchi, T.; Ikeda, M.; Hiramatsu, S.; Yoshida, K.; Amano, N.; Nomura, M.; Umekage, M.; Morizane, A.; et al. Pre-Clinical Study of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Dopaminergic Progenitor Cells for Parkinson’s Disease. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunt, L.; Hoskyns, S.; Swami, S. The Handbook of Music Therapy; Routledge: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Moon, E.; Kim, G.; Kang, S.-U. Perspectives of Circadian-Based Music Therapy for the Pathogenesis and Symptomatic Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 769142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matziorinis, A.M.; Koelsch, S. The Promise of Music Therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2022, 1516, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, R.; Wei, W.; Luan, R.; Li, K. Effects of Music-Based Movement Therapy on Motor Function, Balance, Gait, Mental Health, and Quality of Life for Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2021, 35, 937–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmelat, V.; Duncan, A.; Meltz, S.; Meidinger, R.L.; Hellman, A.M. Fractal Auditory Stimulation Has Greater Benefit for People with Parkinson’s Disease Showing More Random Gait Pattern. Gait Posture 2020, 80, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, D.; Ye, D.; Li, H.; Chen, F. Can Music-Based Movement Therapy Improve Motor Dysfunction in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease? Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 1629–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Véron-Delor, L.; Pinto, S.; Eusebio, A.; Azulay, J.-P.; Witjas, T.; Velay, J.-L.; Danna, J. Musical Sonification Improves Motor Control in Parkinson’s Disease: A Proof of Concept with Handwriting. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1465, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgia, M.; Pili, R.; Corona, F.; Sors, F.; Agostini, T.A.; Bernardis, P.; Casula, C.; Cossu, G.; Guicciardi, M.; Pau, M. The Use of Footstep Sounds as Rhythmic Auditory Stimulation for Gait Rehabilitation in Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado Sotomayor, M.J.; Arufe-Giráldez, V.; Ruíz-Rico, G.; Navarro-Patón, R. Music Therapy and Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review from 2015-2020. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molsberry, S.; Bjornevik, K.; Hughes, K.C.; Healy, B.; Schwarzschild, M.; Ascherio, A. Diet Pattern and Prodromal Features of Parkinson Disease. Neurology 2020, 95, e2095–e2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paknahad, Z.; Sheklabadi, E.; Derakhshan, Y.; Bagherniya, M.; Chitsaz, A. The Effect of the Mediterranean Diet on Cognitive Function in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Clinical Controlled Trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 50, 102366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraki, M.I.; Yannakoulia, M.; Stamelou, M.; Stefanis, L.; Xiromerisiou, G.; Kosmidis, M.H.; Dardiotis, E.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M.; Sakka, P.; Anastasiou, C.A.; et al. Mediterranean Diet Adherence Is Related to Reduced Probability of Prodromal Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe-Roach, A.; Yu, A.C.; Golz, E.; Cirstea, M.; Sundvick, K.; Kliger, D.; Foulger, L.H.; Mackenzie, M.; Finlay, B.B.; Appel-Cresswell, S. MIND and Mediterranean Diets Associated with Later Onset of Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Wang, Y.; Buchman, A.S.; Holland, T.M.; Bennett, D.A.; Morris, M.C. MIND Diet Associated with Reduced Incidence and Delayed Progression of Parkinsonism in Old Age. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 1211–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, A.M.; Kang, J.H.; Feskens, E.J.M.; de Groot, C.P.G.M.; Grodstein, F.; van de Rest, O. Association of Long-Term Adherence to the Mind Diet with Cognitive Function and Cognitive Decline in American Women. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Tripathi, P.; Yadawa, A.K.; Singh, S. Promising Polyphenols in Parkinson’s Disease Therapeutics. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 1731–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Xue, J.; Tan, Y.; Fang, C.; Hu, C.; Yang, Q.; Mei, X.; Qi, D. The Positive Role and Mechanism of Herbal Medicine in Parkinson’s Disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, e9923331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawska, M.; Jodynis-Liebert, J. Polyphenols in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review of In Vivo Studies. Nutrients 2018, 10, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youdim, K.A.; Dobbie, M.S.; Kuhnle, G.; Proteggente, A.R.; Abbott, N.J.; Rice-Evans, C. Interaction between Flavonoids and the Blood-Brain Barrier: In Vitro Studies. J. Neurochem. 2003, 85, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, V.C.J.; Dihal, A.A.; van der Woude, H.; Arts, I.C.W.; Wolffram, S.; Alink, G.M.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Keijer, J.; Hollman, P.C.H. Tissue Distribution of Quercetin in Rats and Pigs. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1718–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jellinger, K.A. Dementia with Lewy Bodies and Parkinson’s Disease-Dementia: Current Concepts and Controversies. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 615–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosp, J.A.; Dressing, A.; Blazhenets, G.; Bormann, T.; Rau, A.; Schwabenland, M.; Thurow, J.; Wagner, D.; Waller, C.; Niesen, W.D.; et al. Cognitive Impairment and Altered Cerebral Glucose Metabolism in the Subacute Stage of COVID-19. Brain J. Neurol. 2021, 144, 1263–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Redondo, R.; García-García, D.; Clavero, P.; Gasca-Salas, C.; García-Eulate, R.; Zubieta, J.L.; Arbizu, J.; Obeso, J.A.; Rodríguez-Oroz, M.C. Grey Matter Hypometabolism and Atrophy in Parkinson’s Disease with Cognitive Impairment: A Two-Step Process. Brain J. Neurol. 2014, 137, 2356–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, F.; Lozupone, M.; Logroscino, G.; Imbimbo, B.P. A Critical Appraisal of Amyloid-β-Targeting Therapies for Alzheimer Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, R.M.; Miller, Z.; Koestler, M.; Rojas, J.C.; Ljubenkov, P.A.; Rosen, H.J.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Fagan, A.M.; Cobigo, Y.; Brown, J.A.; et al. Reactions to Multiple Ascending Doses of the Microtubule Stabilizer TPI-287 in Patients With Alzheimer Disease, Progressive Supranuclear Palsy, and Corticobasal Syndrome: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gan, L.; Ren, L.; Lin, Y.; Ma, C.; Lin, X. Factors Influencing the Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability. Brain Res. 2022, 1788, 147937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasca-Salas, C.; Fernández-Rodríguez, B.; Pineda-Pardo, J.A.; Rodríguez-Rojas, R.; Obeso, I.; Hernández-Fernández, F.; Del Álamo, M.; Mata, D.; Guida, P.; Ordás-Bandera, C.; et al. Blood-Brain Barrier Opening with Focused Ultrasound in Parkinson’s Disease Dementia. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeWitt, P.A.; Lipsman, N.; Kordower, J.H. Focused Ultrasound Opening of the Blood-Brain Barrier for Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 1274–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbagh, A.; Beccaria, K.; Ling, X.; Marisetty, A.; Ott, M.; Caruso, H.; Barton, E.; Kong, L.-Y.; Fang, D.; Latha, K.; et al. Opening of the Blood-Brain Barrier Using Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Enhances Responses to Immunotherapy in Preclinical Glioma Models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4325–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xhima, K.; Nabbouh, F.; Hynynen, K.; Aubert, I.; Tandon, A. Noninvasive Delivery of an α-Synuclein Gene Silencing Vector with Magnetic Resonance-Guided Focused Ultrasound. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1567–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakatsani, M.E.; Wang, S.; Samiotaki, G.; Kugelman, T.; Olumolade, O.O.; Acosta, C.; Sun, T.; Han, Y.; Kamimura, H.A.S.; Jackson-Lewis, V.; et al. Amelioration of the Nigrostriatal Pathway Facilitated by Ultrasound-Mediated Neurotrophic Delivery in Early Parkinson’s Disease. J. Control. Release 2019, 303, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yang, Y.; Rakstys, K.; Mahata, A.; Franckevicius, M.; Mosconi, E.; Skackauskaite, R.; Ding, B.; Brooks, K.G.; Usiobo, O.J.; et al. Tuning Structural Isomers of Phenylenediammonium to Afford Efficient and Stable Perovskite Solar Cells and Modules. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Pople, C.B.; Bethune, A.; Jones, R.M.; Abrahao, A.; Hamani, C.; Kalia, S.K.; Kalia, L.V.; Lipsman, N.; et al. Cavitation Feedback Control of Focused Ultrasound Blood-Brain Barrier Opening for Drug Delivery in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folke, J.; Ferreira, N.; Brudek, T.; Borghammer, P.; Van Den Berge, N. Passive Immunization in Alpha-Synuclein Preclinical Animal Models. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolini Paoletti, F.; Gaetani, L.; Parnetti, L. The Challenge of Disease-Modifying Therapies in Parkinson’s Disease: Role of CSF Biomarkers. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athauda, D.; Foltynie, T. Challenges in Detecting Disease Modification in Parkinson’s Disease Clinical Trials. Park. Relat. Disord. 2016, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pardo-Moreno, T.; García-Morales, V.; Suleiman-Martos, S.; Rivas-Domínguez, A.; Mohamed-Mohamed, H.; Ramos-Rodríguez, J.J.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; González-Acedo, A. Current Treatments and New, Tentative Therapies for Parkinson’s Disease. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030770
Pardo-Moreno T, García-Morales V, Suleiman-Martos S, Rivas-Domínguez A, Mohamed-Mohamed H, Ramos-Rodríguez JJ, Melguizo-Rodríguez L, González-Acedo A. Current Treatments and New, Tentative Therapies for Parkinson’s Disease. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(3):770. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030770
Chicago/Turabian StylePardo-Moreno, Teresa, Victoria García-Morales, Sami Suleiman-Martos, Antonio Rivas-Domínguez, Himan Mohamed-Mohamed, Juan José Ramos-Rodríguez, Lucía Melguizo-Rodríguez, and Anabel González-Acedo. 2023. "Current Treatments and New, Tentative Therapies for Parkinson’s Disease" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 3: 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030770
APA StylePardo-Moreno, T., García-Morales, V., Suleiman-Martos, S., Rivas-Domínguez, A., Mohamed-Mohamed, H., Ramos-Rodríguez, J. J., Melguizo-Rodríguez, L., & González-Acedo, A. (2023). Current Treatments and New, Tentative Therapies for Parkinson’s Disease. Pharmaceutics, 15(3), 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030770







